Therapeutic Drug Monitoring for Sirolimus in Children with Vascular Anomalies: What Can We Learn from a Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of Patients
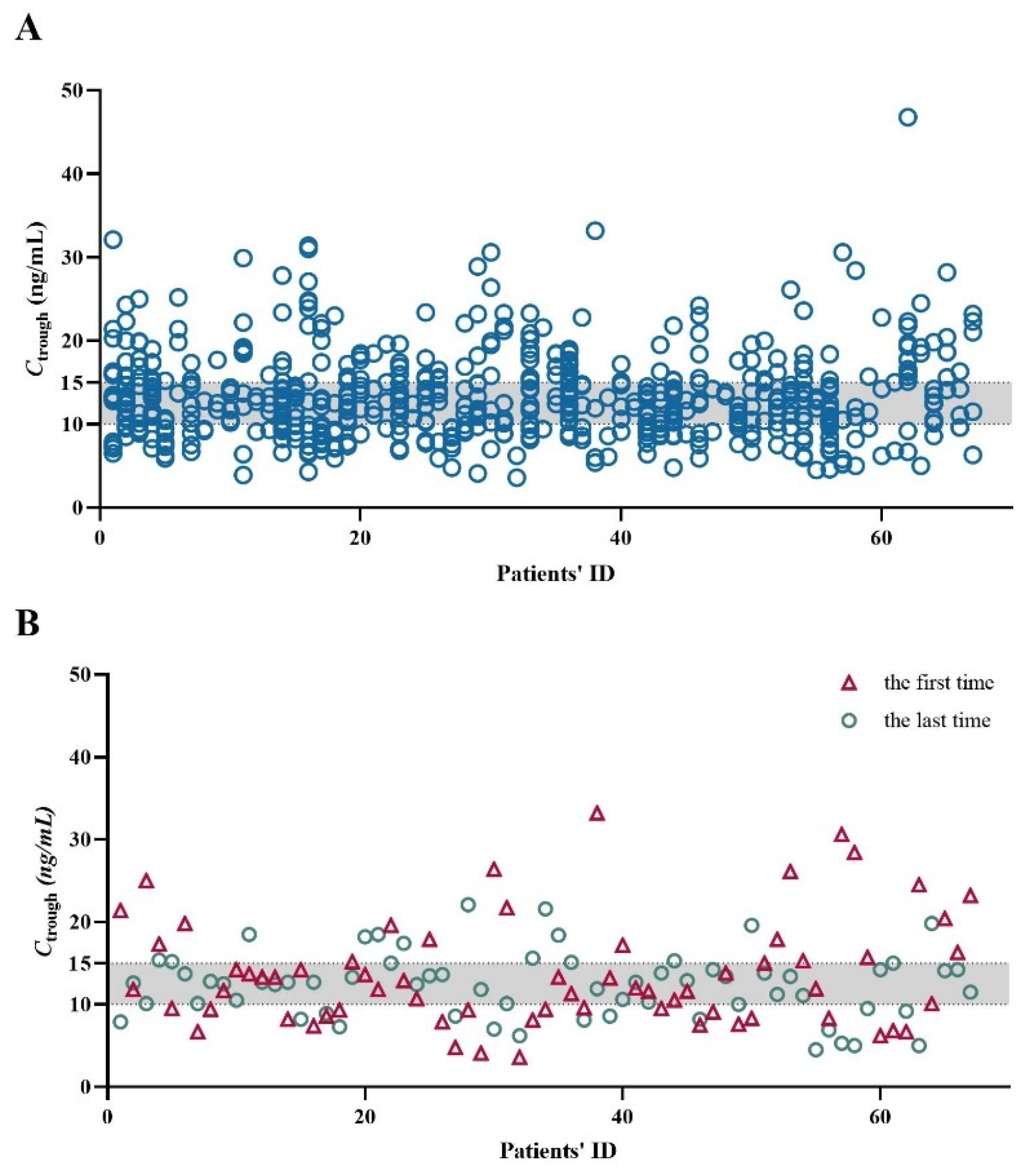
2.2. Whole Blood Ctrough of SRL
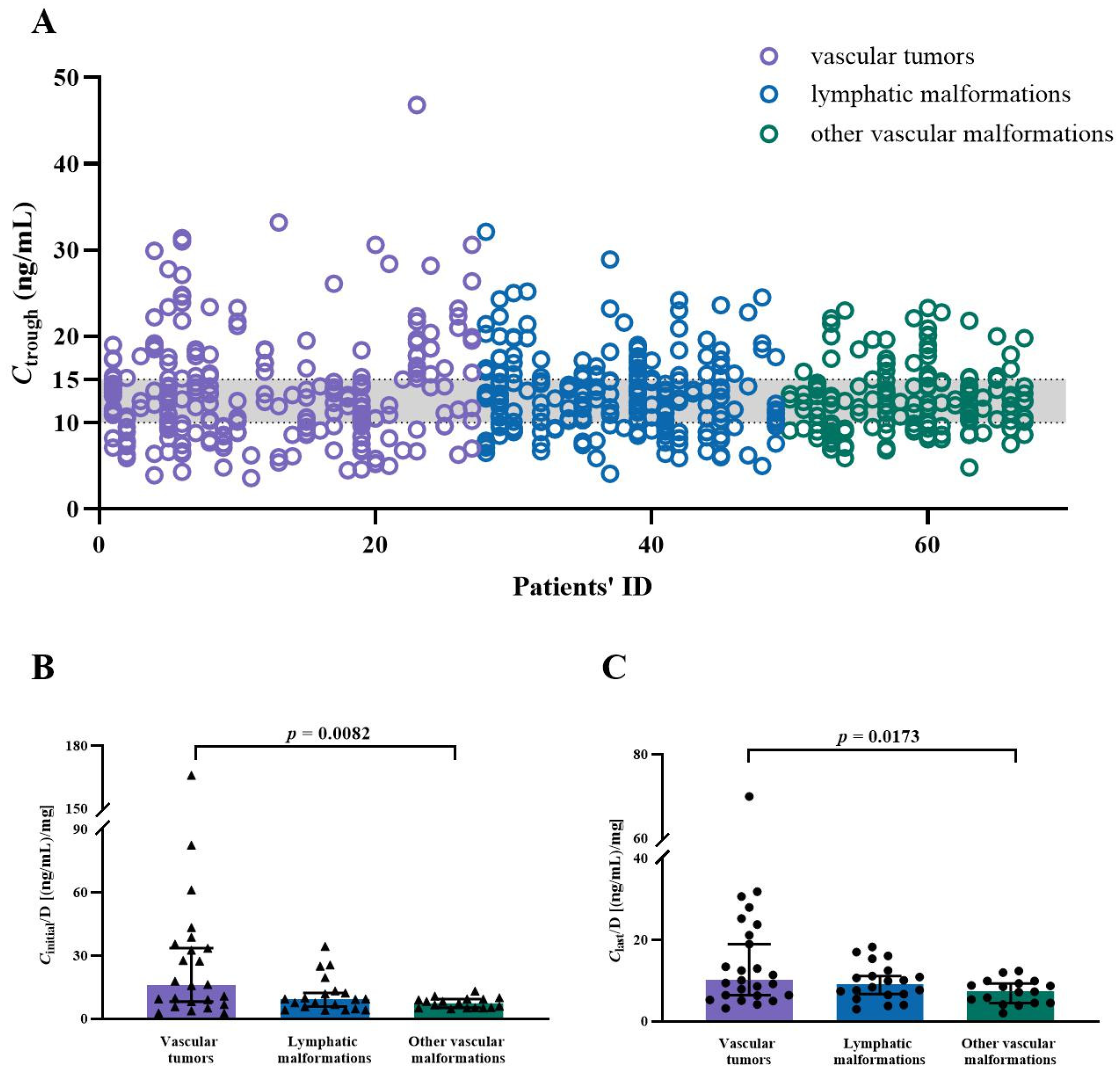
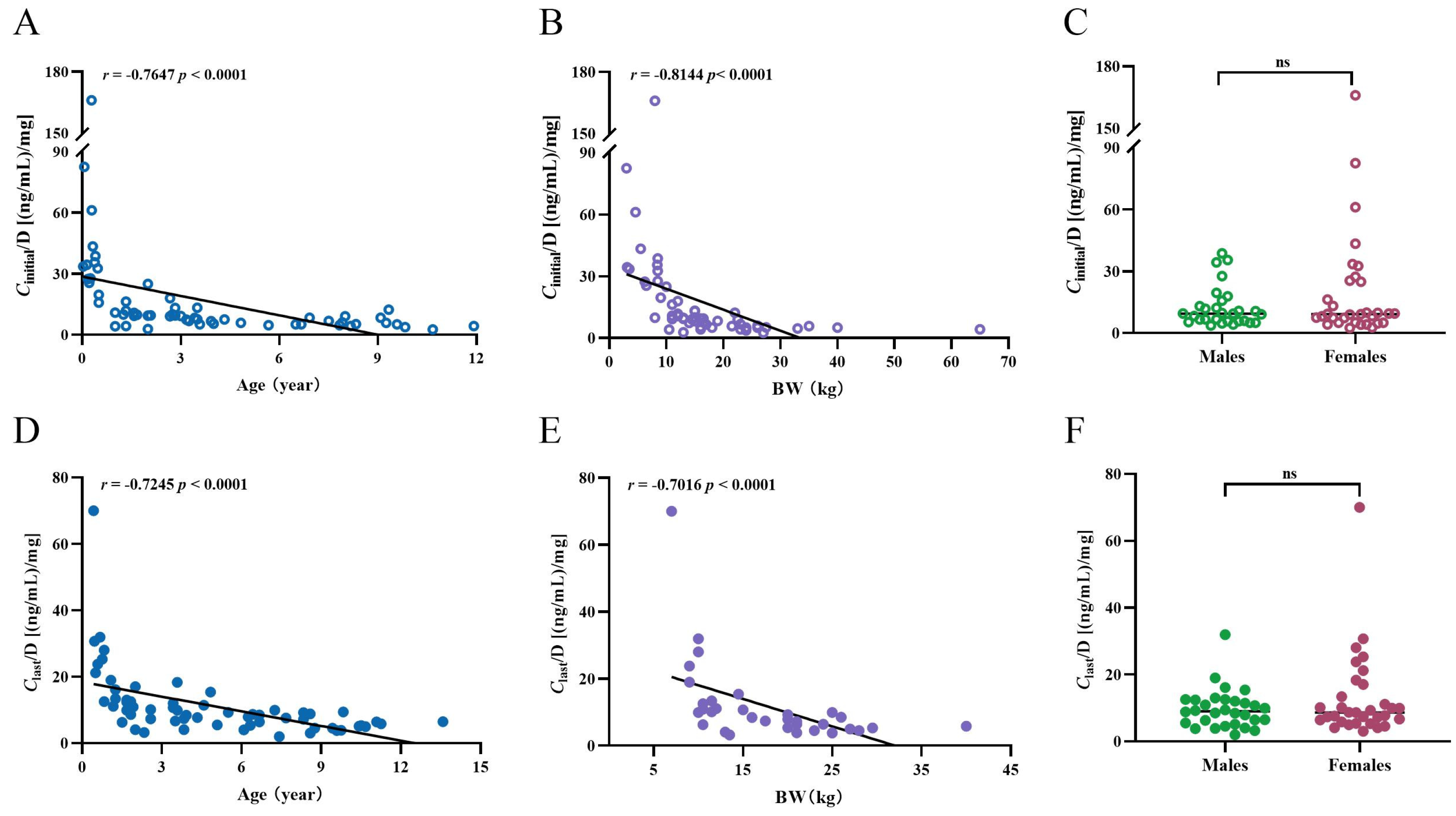
2.3. Age, BW, Sex, BMI, and the Ctrough-to-Daily Dose (Ctrough/Dose) Ratio of SRL
2.4. Concomitant Medications and the Ctrough/Dose Ratio of SRL
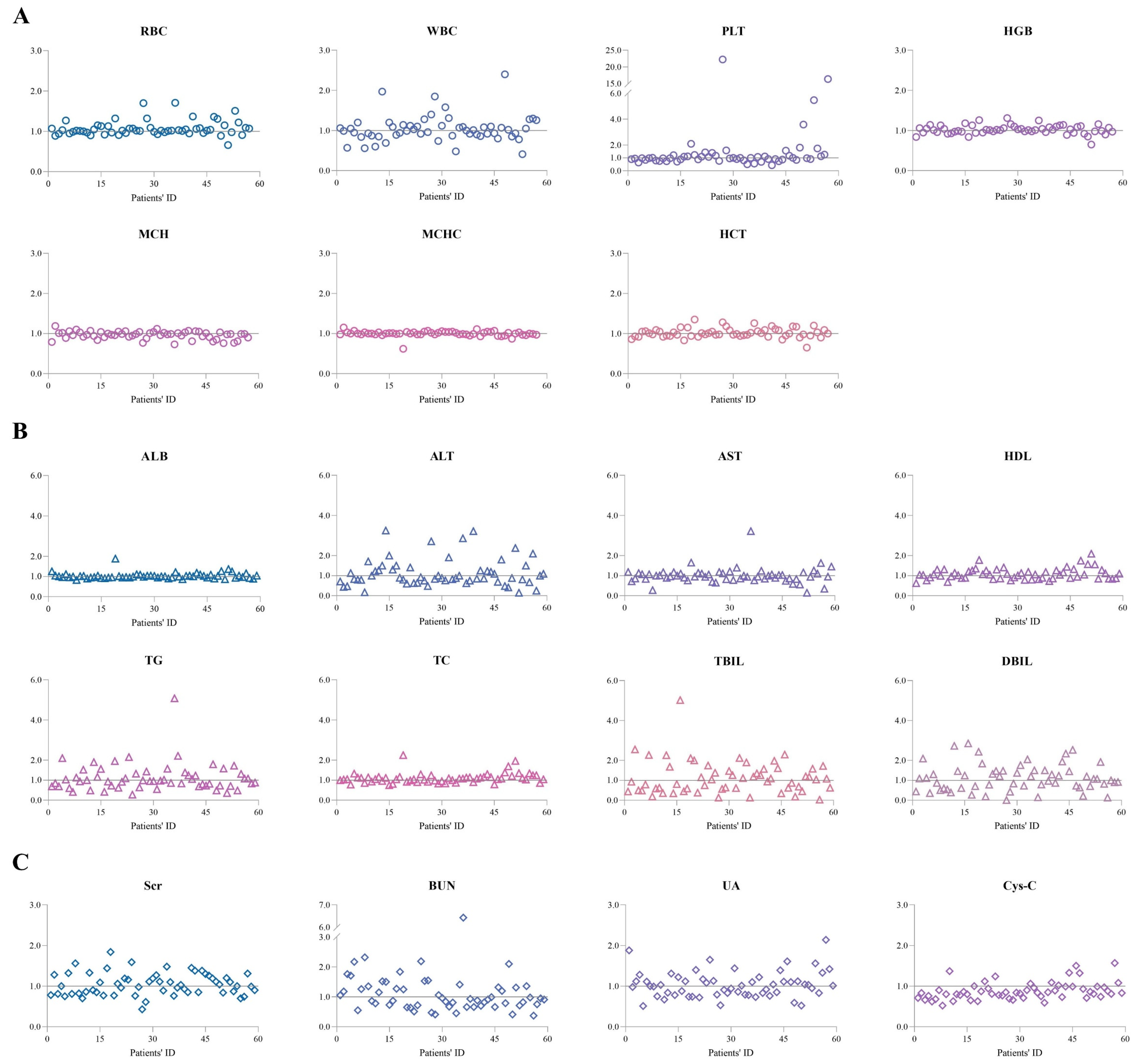
2.5. Laboratory Test Results
2.6. The Incidence and Severity of Adverse Events
2.7. Clinical Outcome
3. Discussion
4. Patients and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Data Collection
4.3. Routine Therapeutic Monitoring of SRL
4.4. Outcome Measures and Definitions
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sadick, M.; Müller-Wille, R.; Wildgruber, M.; Wohlgemuth, W.A. Vascular Anomalies (Part I): Classification and Diagnostics of Vascular Anomalies. Rofo 2018, 190, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISSVA. Classification of Vascular Anomalies. 2018. Available online: https://www.issva.org/classification (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Kunimoto, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Jinnin, M. ISSVA Classification of Vascular Anomalies and Molecular Biology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.M.; Trenor, C.C.; Hammill, A.M.; Vinks, A.A.; Patel, M.N.; Chaudry, G.; Wentzel, M.S.; Mobberley-Schuman, P.S.; Campbell, L.M.; Brookbank, c.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Sirolimus in the Treatment of Complicated Vascular Anomalies. Pediatrics 2016, 137, e20153257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignot, S.; Faivre, S.; Aguirre, D.; Raymond, E. mTOR-targeted therapy of cancer with rapamycin derivatives. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.Y.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR at the nexus of nutrition, growth, ageing and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 183–203. [Google Scholar]
- Karar, J.; Maity, A. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway in Angiogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Huber, S.; Bruns, C.J.; Schmid, G.; Hermann, P.C.; Conrad, C.; Niess, H.; Huss, R.; Graeb, C.; Jauch, K.-W.; Heeschen, C.; et al. Inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin impedes lymphangiogenesis. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.F.; Hung, M.C. All roads lead to mTOR: Integrating inflammation and tumor angiogenesis. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 3011–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.B. Sirolimus in the treatment of vascular anomalies. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 71, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triana, P.; Dore, M.; Cerezo, V.N.; Cervantes, M.; Sánchez, A.V.; Ferrero, M.M.; González, M.D.; Lopez-Gutierrez, J.C. Sirolimus in the Treatment of Vascular Anomalies. Eur. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 27, 86–90. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhou, J.; Yang, K.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, B.; Qiu, T.; Gong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lan, Y. Sirolimus plus prednisolone vs sirolimus monotherapy for kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: A randomized clinical trial. Blood. 2022, 139, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, J.A.; Zhang, X.; Bobbala, S.; Frey, M.A.; Fuentes, C.B.; Haddad, H.F.; Allen, S.D.; Richardson, R.A.K.; Ameer, G.A. Subcutaneous nanotherapy repurposes the immunosuppressive mechanism of rapamycin to enhance allogeneic islet graft viability. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2022, 17, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahan, B.D.; Napoli, K.L.; Kelly, P.A.; Podbielski, J.; Hussein, I.; Urbauer, D.L.; Katz, S.H.; Van Buren, C.T. Therapeutic drug monitoring of sirolimus: Correlations with efficacy and toxicity. Clin. Transplant. 2000, 14, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.R.; Courter, J.D.; Saldaña, S.N.; Widemann, B.C.; Fisher, M.; Weiss, B.; Perentesis, J.; Vinks, A.A. Population pharmacokinetics of sirolimus in pediatric patients with neurofibromatosis type 1. Ther. Drug Monit. 2013, 35, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenor, C.C., 3rd. Sirolimus for refractory vascular anomalies. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2011, 57, 904–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-T.; Dai, H.-R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Guo, H.-L.; Ding, X.-S.; Hu, Y.-H.; Chen, F. Comparison of LC-MS/MS and EMIT methods for the precise determination of blood sirolimus in children with vascular anomalies. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 925018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moes, D.J.; Guchelaar, H.J.; de Fijter, J.W. Sirolimus and everolimus in kidney transplantation. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 1243–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieri, M.; Miraglia, N.; Polichetti, G.; Tarantino, G.; Acampora, A.; Capone, D. Analytical and pharmacological aspects of therapeutic drug monitoring of mTOR inhibitors. Curr. Drug Metab. 2011, 12, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triana, P.; Miguel, M.; Díaz, M.; López-Gutierrez, J.C. Clinical Monitoring Challenges in the Pharmacological Treatment and Management of Lymphatic Anomalies With Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibition. Ther. Drug Monit. 2019, 41, 547–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queisser, A.; Seront, E.; Boon, L.M.; Vikkula, M. Genetic Basis and Therapies for Vascular Anomalies. Circ. Res. 2021, 129, 155–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, T.; Boon, L.M.; Vikkula, M.; Alitalo, K. Lymphatic Malformations: Genetics, Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Circ. Res. 2021, 129, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freixo, C.; Ferreira, V.; Martins, J.; Almeida, R.; Caldeira, D.; Rosa, M.; Costa, J.; Ferreira, J. Efficacy and safety of sirolimus in the treatment of vascular anomalies: A systematic review. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 71, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.; Vincent, L.; Chenel, M.; Ogungbenro, K.; Galetin, A. Impact of Hepatic CYP3A4 Ontogeny Functions on Drug-Drug Interaction Risk in Pediatric Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Modeling: Critical Literature Review and Ivabradine Case Study. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 109, 1618–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, G.L.; Abdel-Rahman, S.M.; Alander, S.W.; Blowey, D.L.; Leeder, J.S.; Kauffman, R.E. Developmental pharmacology—drug disposition, action, and therapy in infants and children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Chen, X.; Li, Z. Population pharmacokinetics of sirolimus in pediatric patients with kaposiform hemangioendothelioma: A retrospective study. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 2412–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, T.; Fukuda, T.; Emoto, C.; Mobberley-Schuman, P.S.; Hammill, A.M.; Adams, D.M.; Vinks, A.A. Developmental pharmacokinetics of sirolimus: Implications for precision dosing in neonates and infants with complicated vascular anomalies. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, H.; Zhao, L.; Zang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wu, R. The first study in pediatric: Population pharmacokinetics of sirolimus and its application in Chinese children with immune cytopenia. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2020, 34, 2058738420934936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel, G.A.; Ariceta, G. Growth failure associated with sirolimus: Case report. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2009, 24, 2047–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, D.; García, C.D.; Azócar, M.; Waller, S.; Alonso, A.; Ariceta, G.; Mejía, N.; Santos, F. Growth of kidney-transplanted pediatric patients treated with sirolimus. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2011, 26, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Zou, L.-P.; Xu, K.-F.; Xu, W.-S.; Zhang, M.-N.; Lu, Q.; Tian, X.-L.; Pang, L.-Y.; He, W.; Wang, Q.-H.; et al. Long-term safety and influence on growth in patients receiving sirolimus: A pooled analysis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2024, 19, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lempers, V.J.; Martial, L.C.; Schreuder, M.F.; Blijlevens, N.M.; Burger, D.M.; Aarnoutse, R.E.; Brüggemann, R.J. Drug-interactions of azole antifungals with selected immunosuppressants in transplant patients: Strategies for optimal management in clinical practice. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 24, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, J.J. Exposure-response relationships and drug interactions of sirolimus. AAPS J. 2004, 6, e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, J.J.; Harper, D.; Getsy, J.; Jusko, W.J. Pharmacokinetic interactions between sirolimus and microemulsion cyclosporine when orally administered jointly and 4 hours apart in healthy volunteers. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 43, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, K.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, X.; Xu, X.; Lu, G.; Qiu, L.; Kong, F.; et al. Prospective multicenter study of sirolimus for complicated vascular anomalies. J. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 74, 1673–1681 e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadal, M.; Giraudeau, B.; Tavernier, E.; Jonville-Bera, A.P.; Lorette, G.; Maruani, A. Efficacy and Safety of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Inhibitors in Vascular Anomalies: A Systematic Review. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2016, 96, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandbank, S.; Molho-Pessach, V.; Farkas, A.; Barzilai, A.; Greenberger, S. Oral and Topical Sirolimus for Vascular Anomalies: A Multicentre Study and Review. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2019, 99, 990–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruani, A.; Boccara, O.; Tavernier, E.; Mazereeuw-Hautier, J.; Leducq, S.; Bessis, D.; Guibaud, L.; Vabres, P.; Carmignac, V.; Mallet, S.; et al. Sirolimus (Rapamycin) for Slow-Flow Malformations in Children: The Observational-Phase Randomized Clinical PERFORMUS Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2021, 157, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yang, K.; Qiu, T.; Zhou, J.; Gong, X.; Ji, Y. Safety Evaluation of Oral Sirolimus in the Treatment of Childhood Diseases: A Systematic Review. Children 2022, 9, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dai, Y.; Lee, Y.; Yuan, E.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Su, Y. Pediatric reference intervals of liver and renal function tests from birth to adolescence in Chinese children as performed on the Olympus AU5400. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 490, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohn, M.K.; Horn, P.; League, D.; Steele, P.; Hall, A.; Adeli, K. Pediatric reference intervals for 32 routine biochemical markers using the siemens healthineers atellica(R) CH assays in healthy children and adolescents. Clin. Biochem. 2022, 99, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | Value |
|---|---|
| Age (year) | |
| Median [IQR] | 3.4 [6.0] |
| Range | 0.0–13.6 |
| Sex | |
| Females | 35 |
| Males | 32 |
| Body weight (kg) | |
| Median [IQR] | 15.0 [12.4] |
| Range | 3.0–65.0 |
| Body mass index (kg/m²) | |
| Median [IQR] | 16.2 [3.4] |
| Range | 13.0–26.3 |
| Type of vascular anomalies, n (%) | |
| Vascular tumors | 21 (31.3%) |
| Vascular malformations | 46 (68.7%) |
| Type of VAs | The Initial Measurements | The Last Measurements | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age and Ctrough/D | BW and Ctrough/D | Sex and Ctrough/D | Age and Ctrough/D | BW and Ctrough/D | Sex and Ctrough/D | |
| Vascular tumors | Correlation: | Correlation: | No difference | Correlation: | Correlation: | No difference |
| r = −0.8741 | r = −0.9126 | r = −0.8205 | r = −0.7634 | |||
| p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p < 0.0001 | p = 0.0014 | |||
| A difference between age ≤ 6 years and age > 6 years (p = 0.0006). | A difference between BW ≤ 10 kg and BW between 10 to ≤20 kg (p = 0.0031), and a difference between BW ≤ 10 kg and BW ≥ 20 kg (p < 0.0001). | A difference between age ≤ 6 years and age > 6 years (p = 0.0071). | A difference between BW ≤ 10 kg and BW between 10 to ≤20 kg (p = 0.0081), and a difference between BW ≤ 10 kg and BW ≥ 20 kg (p < 0.0076). | |||
| Lymphatic malformations (LMs) | Correlation: | Correlation: | No difference | Correlation: | Correlation: | No difference |
| r = −0.4802 | r = −0.6705 | r = −0.5962 | r = −0.7311 | |||
| p = 0.0321 | p = 0.0023 | p = 0.0055 | p = 0.0252 | |||
| No difference between age ≤ 6 years and age > 6 years. | A difference between BW ≤ 10 kg and BW between 10 to ≤20 kg (p = 0.0148), and a difference between BW ≤ 10 kg and BW ≥ 20 kg (p = 0.0053). | A difference between age ≤ 6 years and age > 6 years (p = 0.0037). | Analysis could not be performed because the majority of patients weighed in 10 ≤ 20 kg. | |||
| Other vascular malformations | Correlation: | Correlation: | No difference | Correlation: | No correlation | No difference |
| r = −0.5022 | r = −0.6575 | r = −0.5515 | ||||
| p = 0.0399 | p = 0.0056 | p = 0.0217 | ||||
| No difference between age ≤ 6 years and age > 6 years. | A difference between BW > 20 kg and BW between 10 to ≤20 kg (p = 0.0221). This population could just be divided into these two groups. | No difference between age ≤ 6 years and age > 6 years. | Analysis could not be performed because all of the patients weighed > 20 kg. | |||
| Diagnosis | Patients | SRL Duration (Months) | Ctrough (ng/mL) | Outcome | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GR | PR | SD | PD | |||||
| vascular tumors | KHE | 13 (24.1) | 11.2 (6.9–16.0) | 12.5 (9.6–17.7) | 4 (30.8) | 4 (30.8) | 3 (23.1) | 2 (15.4) |
| other | 7 (13.0) | 10.8 (4.9–21.3) | 10.5 (9.1–15.1) | 2 (28.6) | 4 (57.1) | 1 (14.3) | 0 (0) | |
| vascular malformations | LMs | 23 (42.6) | 21.9 (12.3–34.0) | 12.7 (10.0–15.6) | 4 (17.4) | 11 (47.8) | 2 (8.7) | 6 (26.1) |
| BRBNS | 1 (2.0) | 15.7 | 13.4 (10.5–16.4) | 0 (0) | 1 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| CVM | 1 (2.0) | 10.4 | 13.0 (11.3–17.4) | 1 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| other | 9 (16.7) | 14.7 (8.7–19.0) | 11.8 (9.5–14.6) | 1 (11.1) | 6 (66.7) | 2 (22.2) | 0 (0) | |
| Total | 54 (100) | 13.8 (10.3–22.3) | 13.2 (6.9–16.0) | 12 (22.2) | 26 (48.1) | 8 (14.8) | 8 (14.8) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.-H.; Zhao, Y.-T.; Guo, H.-L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wang, J.; Ding, X.-S.; Zou, J.-J.; Chen, F. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring for Sirolimus in Children with Vascular Anomalies: What Can We Learn from a Retrospective Study. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101255
Hu Y-H, Zhao Y-T, Guo H-L, Li Y, Zhang Y-Y, Wang J, Ding X-S, Zou J-J, Chen F. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring for Sirolimus in Children with Vascular Anomalies: What Can We Learn from a Retrospective Study. Pharmaceuticals. 2024; 17(10):1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101255
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Ya-Hui, Yue-Tao Zhao, Hong-Li Guo, Yue Li, Yuan-Yuan Zhang, Jie Wang, Xuan-Sheng Ding, Ji-Jun Zou, and Feng Chen. 2024. "Therapeutic Drug Monitoring for Sirolimus in Children with Vascular Anomalies: What Can We Learn from a Retrospective Study" Pharmaceuticals 17, no. 10: 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101255
APA StyleHu, Y.-H., Zhao, Y.-T., Guo, H.-L., Li, Y., Zhang, Y.-Y., Wang, J., Ding, X.-S., Zou, J.-J., & Chen, F. (2024). Therapeutic Drug Monitoring for Sirolimus in Children with Vascular Anomalies: What Can We Learn from a Retrospective Study. Pharmaceuticals, 17(10), 1255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17101255





