Anti-Cancer Effect of Neural Stem Cells Transfected with Carboxylesterase and sTRAIL Genes in Animals with Brain Lesions of Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
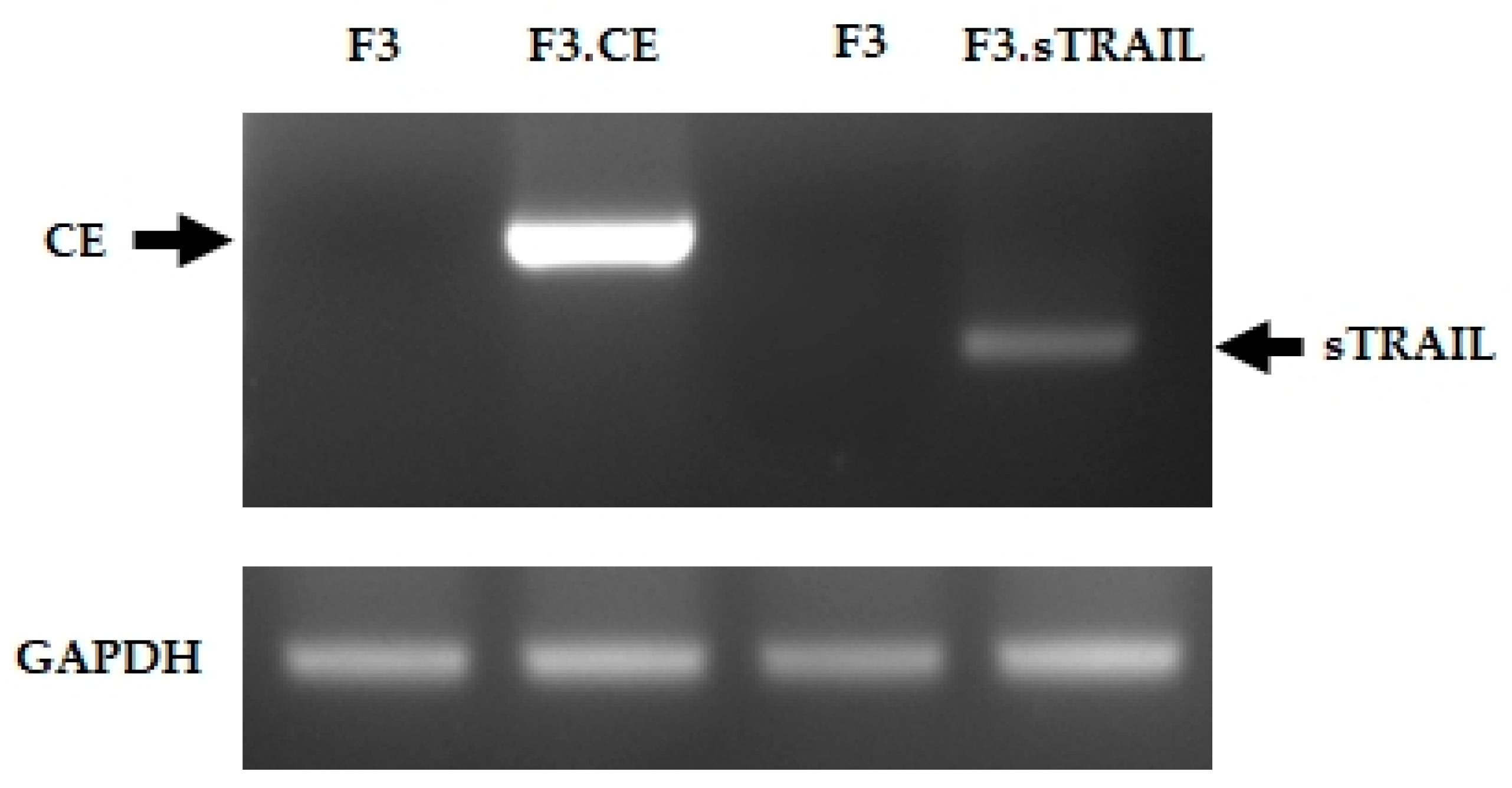
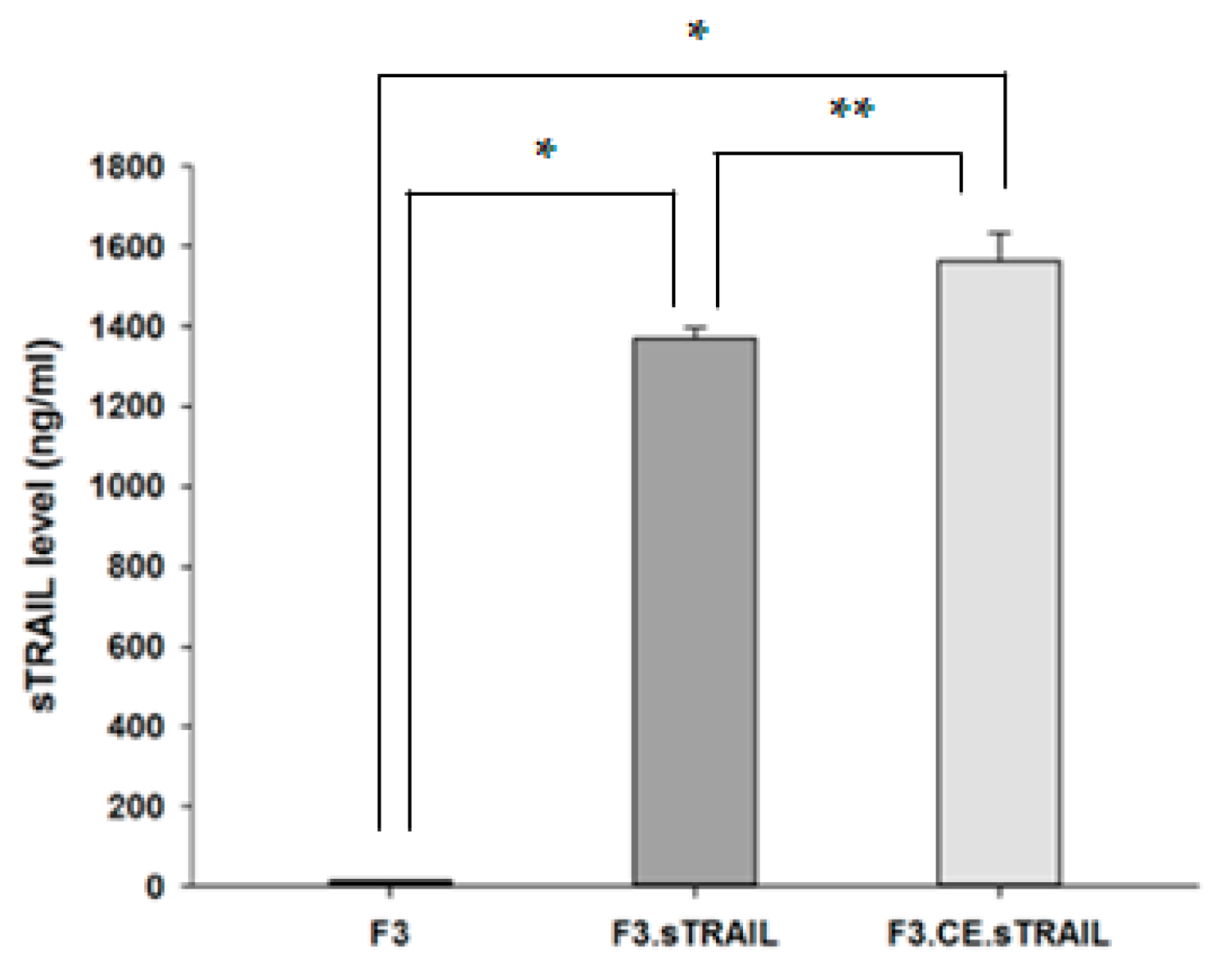
2.1. Establish Human NSCs Expressing rCE and sTRAIL
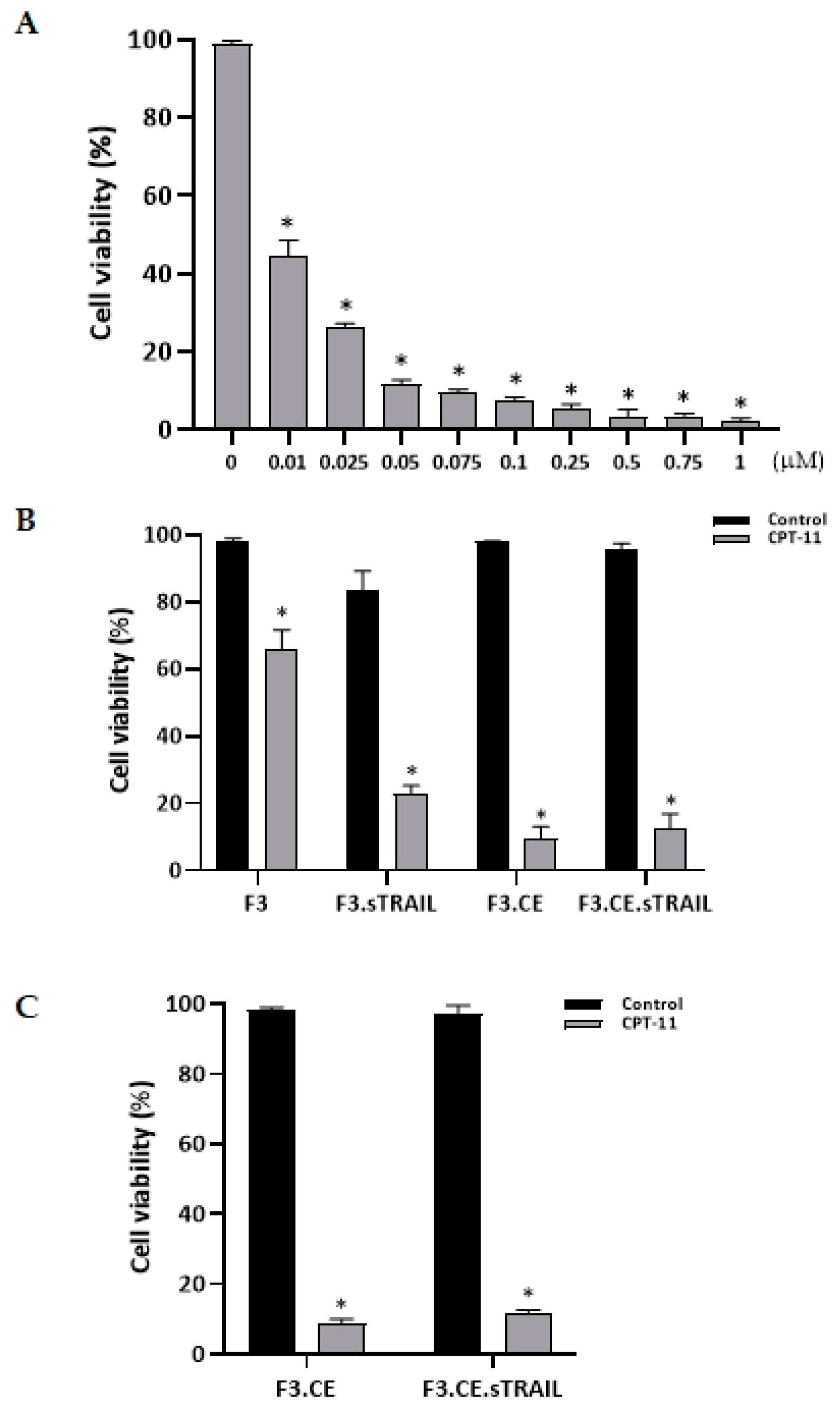
2.2. Differential Cytotoxic Effects of CPT-11 on NSCs Expressing CE and sTRAIL
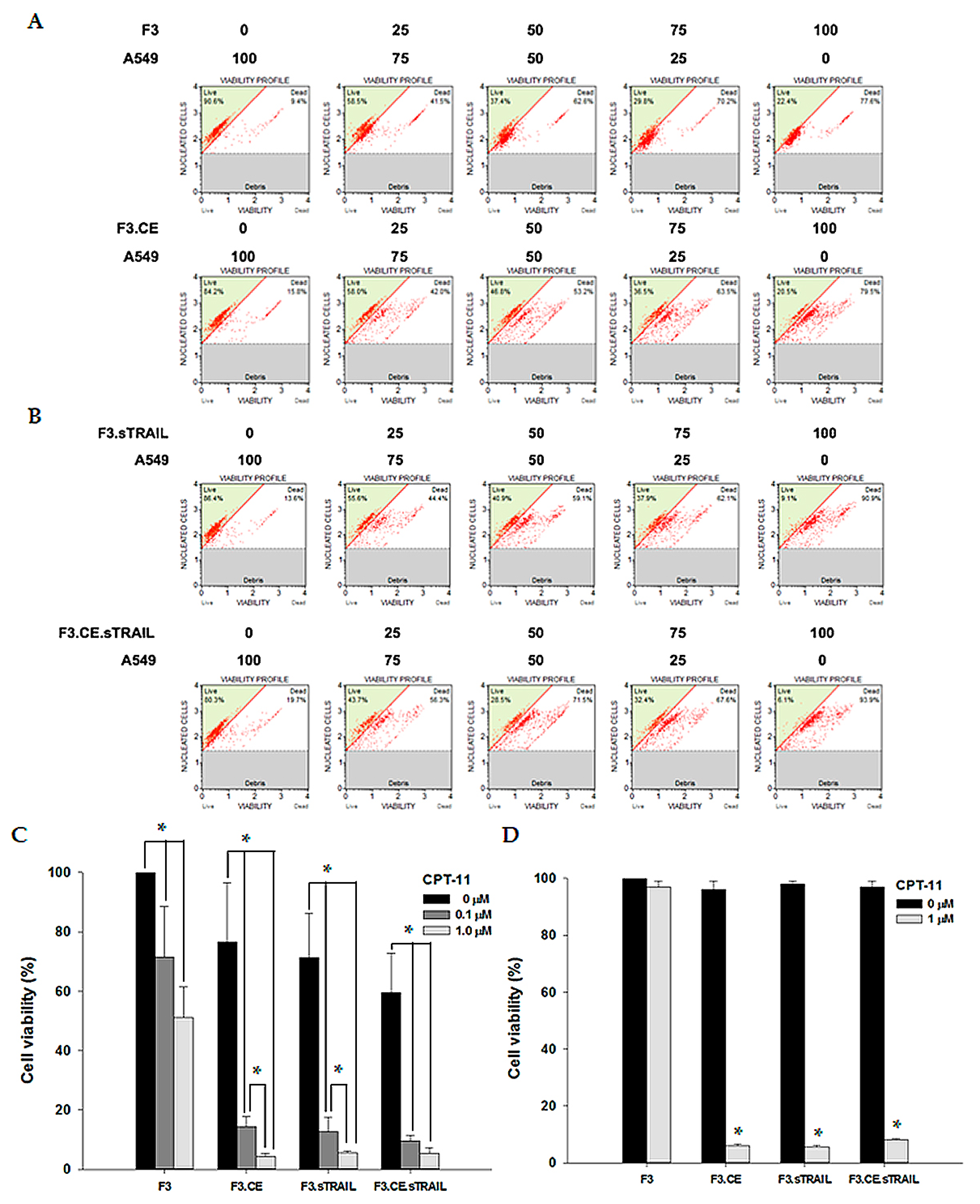
2.3. In Vitro Bystander Effects on Lung Cancer Cells
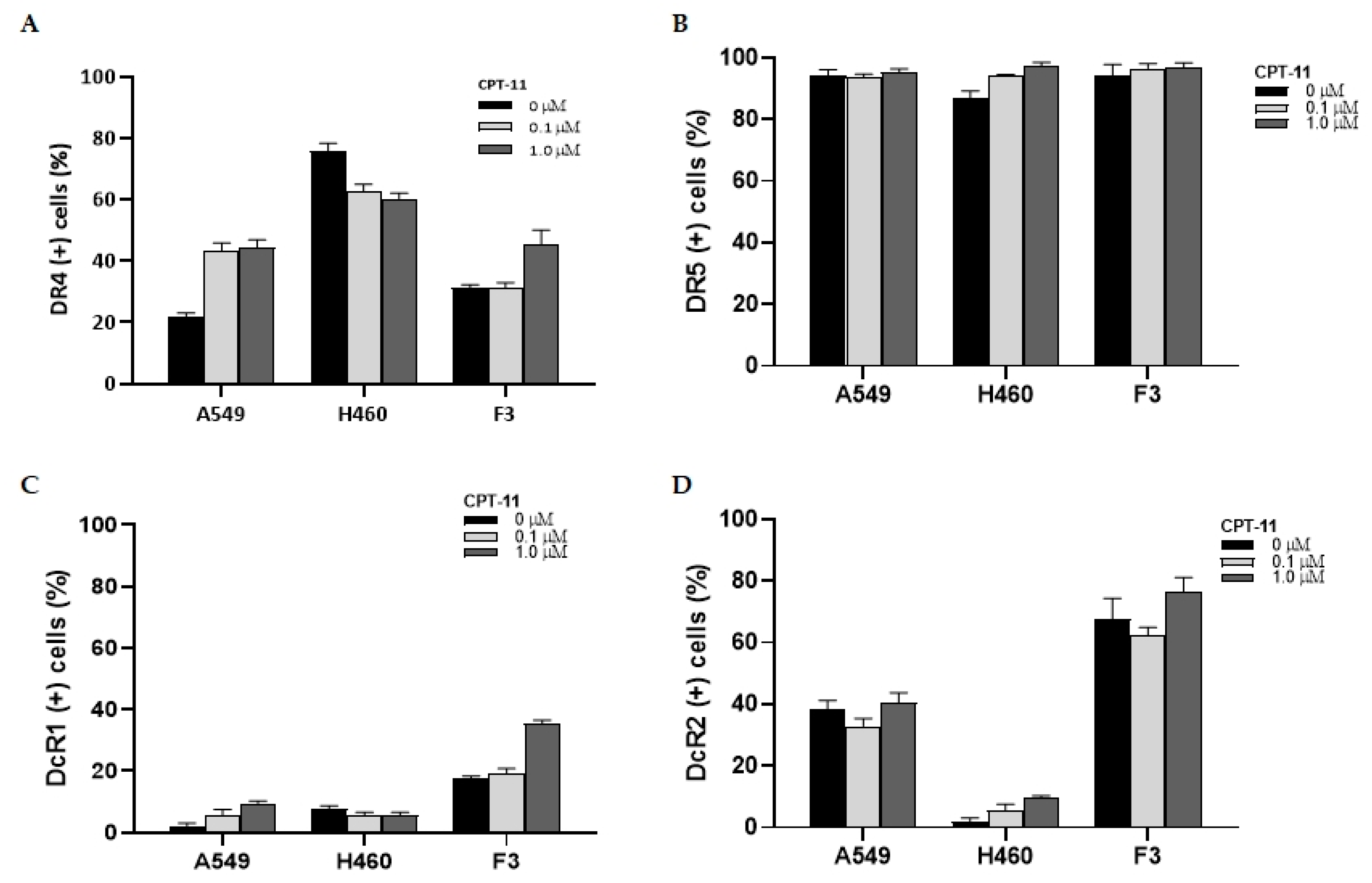
2.4. Changes in the Expression of TRAIL Receptors
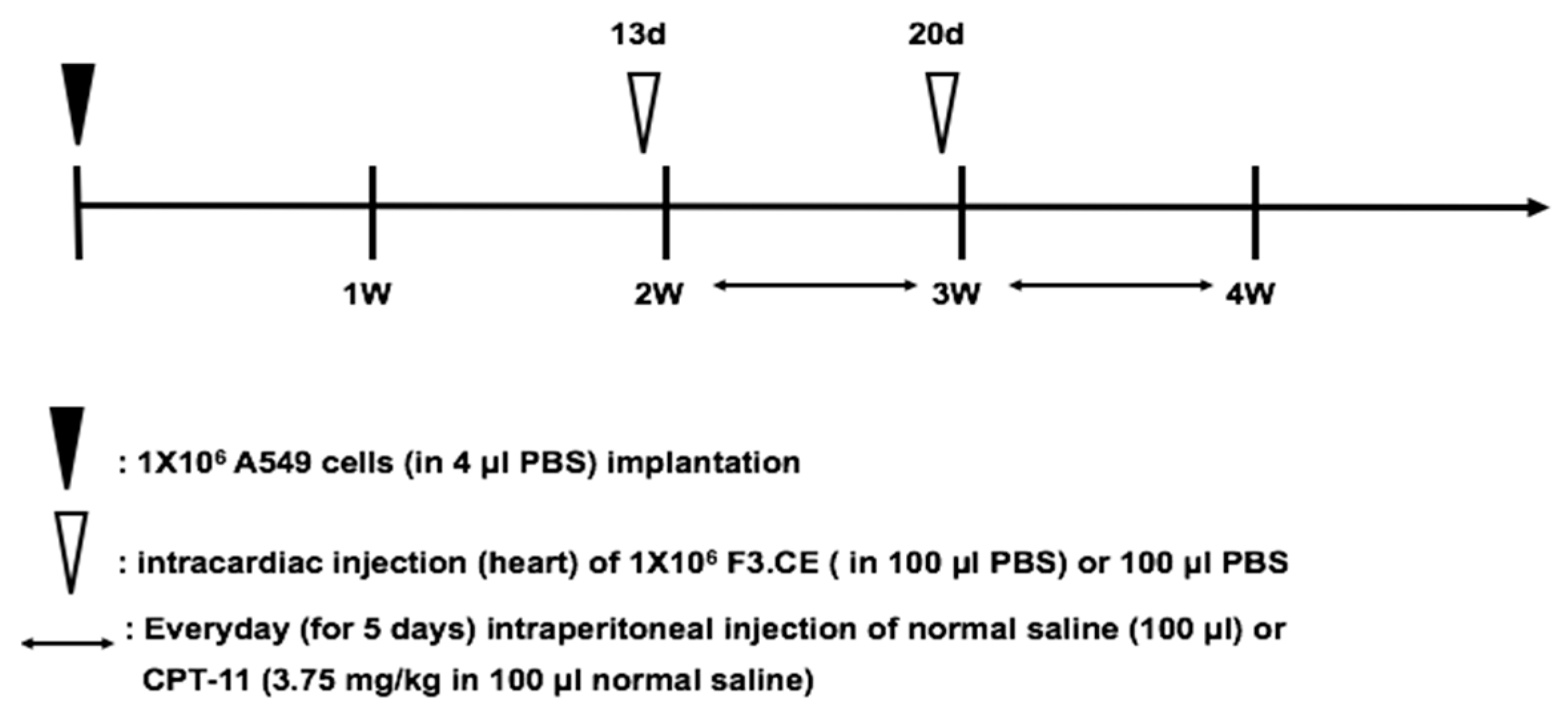
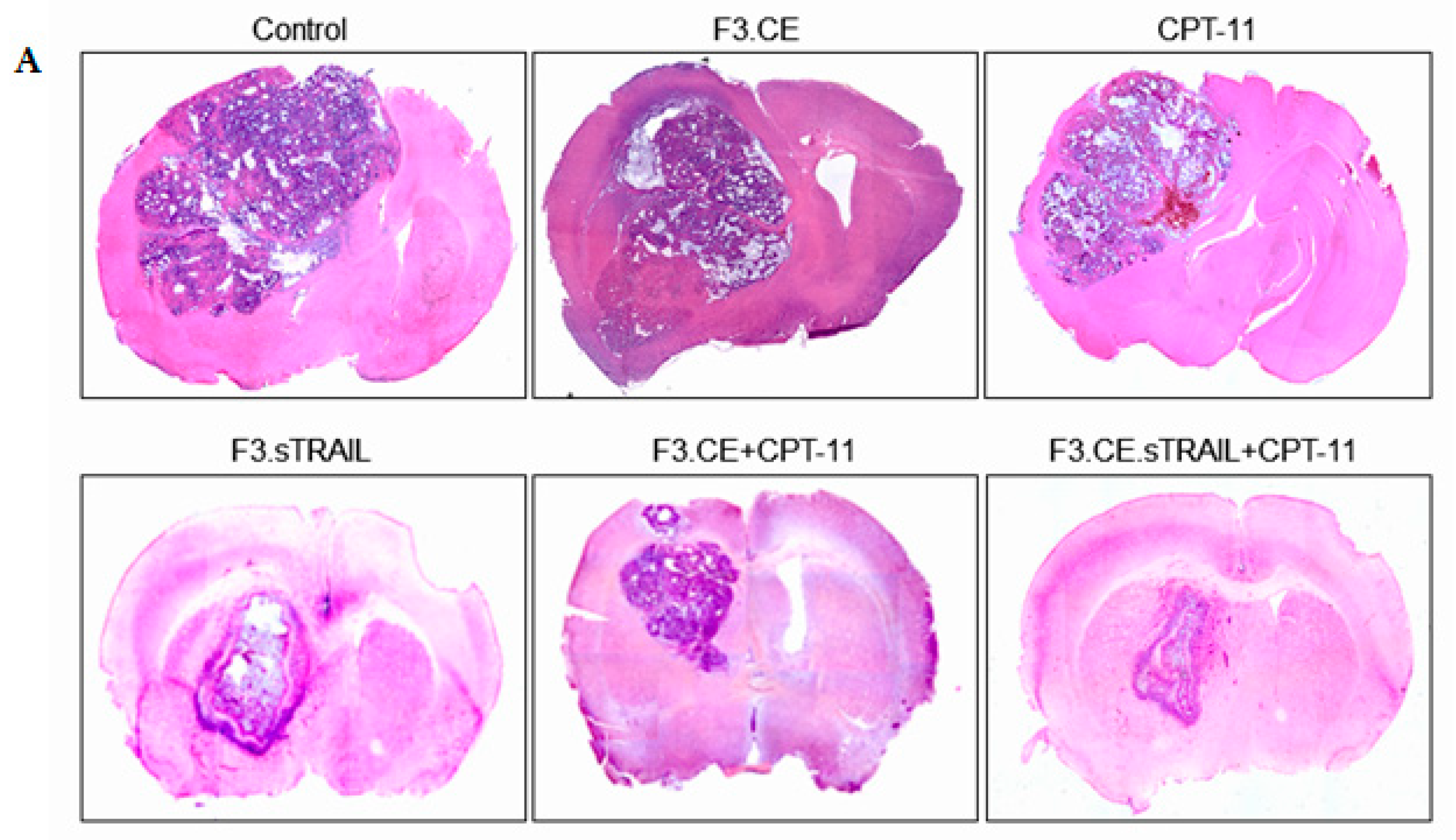
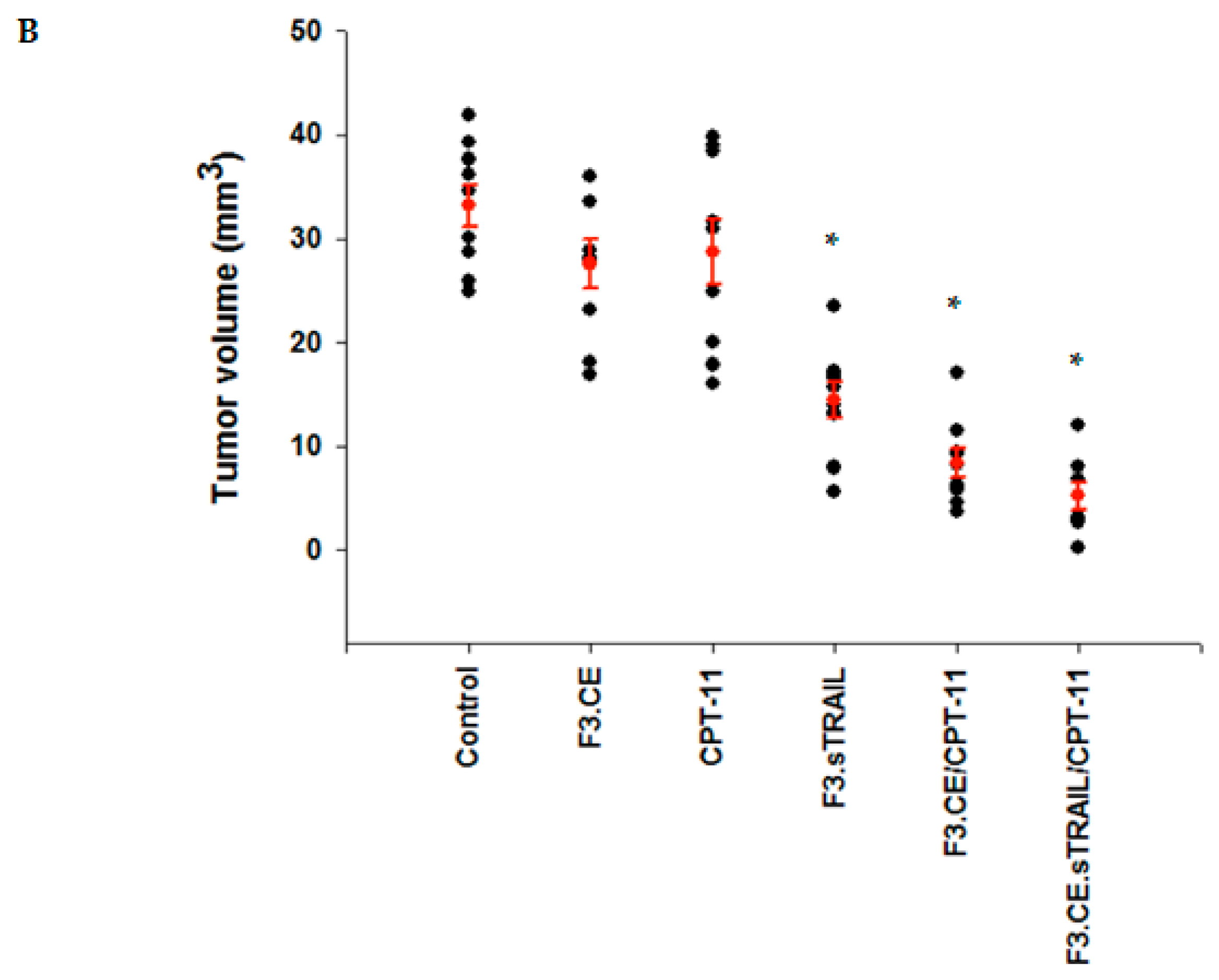
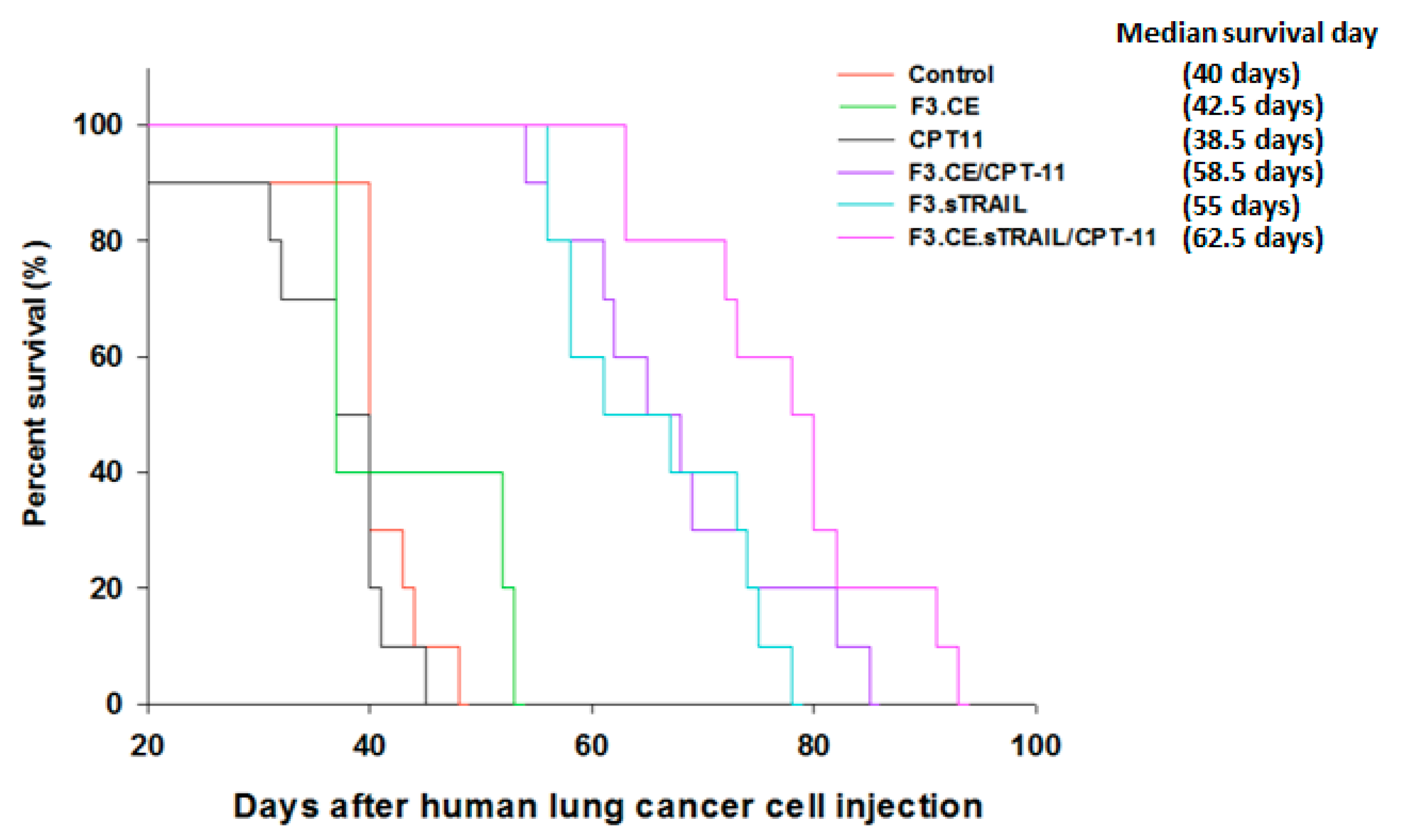
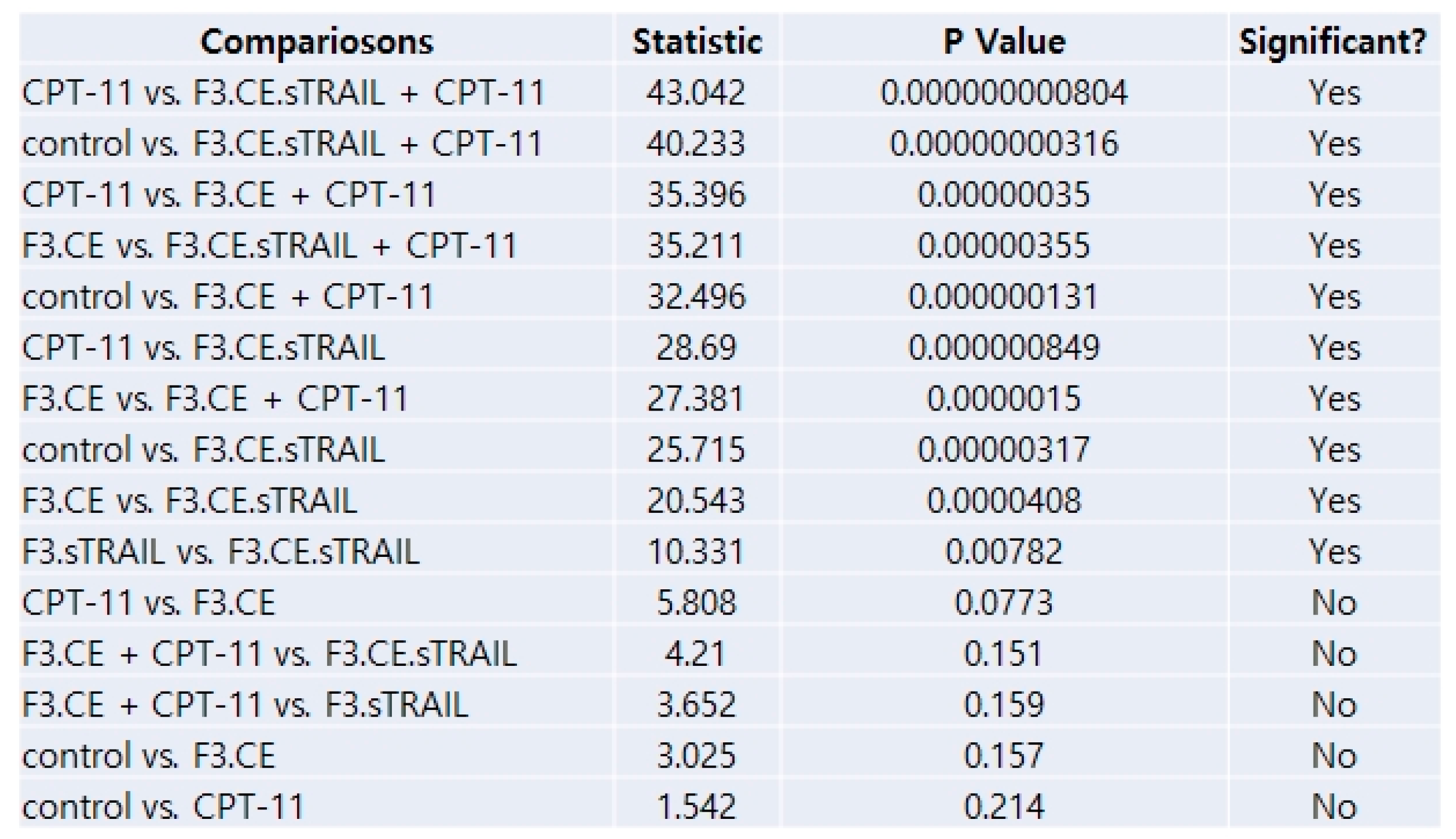
2.5. In Vivo Therapeutic Efficacy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Genetic Engineering of Therapeutic Cells
4.3. Reverse Transcription–Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. In Vitro Bystander Effect Experiments
4.7. FACS Analysis of TRAIL Receptors
4.8. Animal Model of Lung Cancer Brain Metastasis
4.9. In Vivo Therapeutic Efficacy
4.10. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, S.D.; Adler, J.R. Current treatment of patients with multiple brain metastases. Neurosurg. Focus 2000, 9, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilovic, I.T.; Posner, J.B. Brain metastases: Epidemiology and pathophysiology. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2005, 75, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuette, W. Treatment of brain metastases from lung cancer: Chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 2004, 45, S253–S257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achrol, A.S.; Rennert, R.C.; Anders, C.; Soffietti, R.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Nayak, L.; Peters, S.; Arvold, N.D.; Harsh, G.R.; Steeg, P.S. Brain metastases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboody, K.S.; Najbauer, J.; Schmidt, N.O.; Yang, W.; Wu, J.K.; Zhuge, Y.; Przylecki, W.; Carroll, R.; Black, P.M.; Perides, G. Targeting of melanoma brain metastases using engineered neural stem/progenitor cells. Neuro-Oncology 2006, 8, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, N.O.; Przylecki, W.; Yang, W.; Ziu, M.; Teng, Y.D.; Kim, S.U.; Black, P.M.; Aboody, K.S.; Carroll, R.S. Brain tumor tropism of transplanted human neural stem cells is induced by vascular endothelial growth factor. Neoplasia 2005, 7, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.U. Neural stem cell-based gene therapy for brain tumors. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2011, 7, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Choi, S.; Lee, J.; Wang, K.; Phi, J.; Lee, D.; Song, S.; Song, J.; Jin, X.; Kim, H. Therapeutic targeting of subdural medulloblastomas using human neural stem cells expressing carboxylesterase. Cancer Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seol, H.J.; Jin, J.; Seong, D.-H.; Joo, K.M.; Kang, W.; Yang, H.; Kim, J.; Shin, C.S.; Kim, Y.; Kim, K.H. Genetically engineered human neural stem cells with rabbit carboxyl esterase can target brain metastasis from breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2011, 311, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Najbauer, J.; Annala, A.J.; Garcia, E.; Metz, M.Z.; Gutova, M.; Polewski, M.D.; Gilchrist, M.; Glackin, C.A.; Kim, S.U. Human neural stem cell tropism to metastatic breast cancer. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboody, K.S.; Bush, R.A.; Garcia, E.; Metz, M.Z.; Najbauer, J.; Justus, K.A.; Phelps, D.A.; Remack, J.S.; Yoon, K.J.; Gillespie, S. Development of a tumor-selective approach to treat metastatic cancer. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.-R.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, Y.-B.; Lee, H.J.; Cho, M.-H.; Choi, K.-C. Antitumor effects of genetically engineered stem cells expressing yeast cytosine deaminase in lung cancer brain metastases via their tumor-tropic properties. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1823–1828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aboody, K.; Najbauer, J.; Danks, M. Stem and progenitor cell-mediated tumor selective gene therapy. Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Natsume, A.; Lee, H.; Motomura, K.; Nishimira, Y.; Ohno, M.; Ito, M.; Kinjo, S.; Momota, H.; Iwami, K. Neural stem cell-based dual suicide gene delivery for metastatic brain tumors. Cancer Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutova, M.; Shackleford, G.M.; Khankaldyyan, V.; Herrmann, K.A.; Shi, X.-H.; Mittelholtz, K.; Abramyants, Y.; Blanchard, M.S.; Kim, S.U.; Annala, A.J. Neural stem cell-mediated CE/CPT-11 enzyme/prodrug therapy in transgenic mouse model of intracerebellar medulloblastoma. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.Y.; Kim, S.U.; Leung, P.C.; Jeung, E.B.; Choi, K.C. Influence of the prodrugs 5-fluorocytosine and CPT-11 on ovarian cancer cells using genetically engineered stem cells: Tumor-tropic potential and inhibition of ovarian cancer cell growth. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibarra, L.E.; Beaugé, L.; Arias-Ramos, N.; Rivarola, V.A.; Chesta, C.A.; Lopez-Larrubia, P.; Palacios, R.E. Trojan horse monocyte-mediated delivery of conjugated polymer nanoparticles for improved photodynamic therapy of glioblastoma. Nanomedicine 2020, 15, 1687–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanathan, A.; Lorimer, I.A. Engineered cells as glioblastoma therapeutics. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaettler, M.O.; Desai, R.; Wang, A.Z.; Livingstone, A.J.; Kobayashi, D.K.; Coxon, A.T.; Bowman-Kirigin, J.A.; Liu, C.J.; Li, M.; Bender, D.E. TCR-engineered adoptive cell therapy effectively treats intracranial murine glioblastoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashkenazi, A.; Pai, R.C.; Fong, S.; Leung, S.; Lawrence, D.A.; Marsters, S.A.; Blackie, C.; Chang, L.; McMurtrey, A.E.; Hebert, A. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczak, H.; Miller, R.E.; Ariail, K.; Gliniak, B.; Griffith, T.S.; Kubin, M.; Chin, W.; Jones, J.; Woodward, A.; Le, T. Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis–inducing ligand in vivo. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, S.R.; Schooley, K.; Smolak, P.J.; Din, W.S.; Huang, C.-P.; Nicholl, J.K.; Sutherland, G.R.; Smith, T.D.; Rauch, C.; Smith, C.A. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 1995, 3, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitti, R.M.; Marsters, S.A.; Ruppert, S.; Donahue, C.J.; Moore, A.; Ashkenazi, A. Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 12687–12690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kischkel, F.C.; Lawrence, D.A.; Chuntharapai, A.; Schow, P.; Kim, K.J.; Ashkenazi, A. Apo2L/TRAIL-dependent recruitment of endogenous FADD and caspase-8 to death receptors 4 and 5. Immunity 2000, 12, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, P.; Tschopp, J. Apoptosis induced by death receptors. Pharmacochem. Libr. 2000, 31, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Mellier, G.; Huang, S.; Shenoy, K.; Pervaiz, S. TRAILing death in cancer. Mol. Asp. Med. 2010, 31, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegehuis, J.H.; de Wilt, L.H.; de Vries, E.G.; Groen, H.J.; de Jong, S.; Kruyt, F.A. TRAIL receptor targeting therapies for non-small cell lung cancer: Current status and perspectives. Drug Resist. Updates 2010, 13, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimberg, L.Y.; Anderson, C.K.; Camidge, R.; Behbakht, K.; Thorburn, A.; Ford, H.L. On the TRAIL to successful cancer therapy? Predicting and counteracting resistance against TRAIL-based therapeutics. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frese, S.; Brunner, T.; Gugger, M.; Uduehi, A.; Schmid, R.A. Enhancement of Apo2L/TRAIL (tumor necrosis factor–related apoptosis-inducing ligand)–induced apoptosis in non–small cell lung cancer cell lines by chemotherapeutic agents without correlation to the expression level of cellular protease caspase-8 inhibitory protein. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2002, 123, 168–174. [Google Scholar]
- Odoux, C.; Albers, A.; Amoscato, A.A.; Lotze, M.T.; Wong, M.K. TRAIL, Fasl and a blocking anti-DR5 antibody augment paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in human non-small-cell lung cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 97, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliniak, B.; Le, T. Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand’s antitumor activity in vivo is enhanced by the chemotherapeutic agent CPT-11. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 6153–6158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pore, M.M.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Kruyt, F.A. Targeting apoptosis pathways in lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 332, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugamura, K.; Gibbs, J.F.; Belicha-Villanueva, A.; Andrews, C.; Repasky, E.A.; Hylander, B.L. Synergism of CPT-11 and Apo2L/TRAIL against two differentially sensitive human colon tumor xenografts. Oncology 2008, 74, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frese, S.; Schüller, A.; Frese-Schaper, M.; Gugger, M.; Schmid, R.A. Cytotoxic effects of camptothecin and cisplatin combined with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (Apo2L/TRAIL) in a model of primary culture of non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 2905–2911. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashkenazi, A. Targeting death and decoy receptors of the tumour-necrosis factor superfamily. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Lee, D.-H.; Kim, H.A.; Choi, S.-A.; Lee, H.J.; Park, C.-K.; Phi, J.H.; Wang, K.-C.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, S.-K. Double suicide gene therapy using human neural stem cells against glioblastoma: Double safety measures. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2014, 116, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaner, C. Prodrug cancer gene therapy. Cancer Lett. 2008, 270, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danks, M.K.; Yoon, K.J.; Bush, R.A.; Remack, J.S.; Wierdl, M.; Tsurkan, L.; Kim, S.U.; Garcia, E.; Metz, M.Z.; Najbauer, J. Tumor-targeted enzyme/prodrug therapy mediates long-term disease-free survival of mice bearing disseminated neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-K.; Kim, S.U.; Park, I.H.; Bang, J.H.; Aboody, K.S.; Wang, K.-C.; Cho, B.-K.; Kim, M.; Menon, L.G.; Black, P.M. Human neural stem cells target experimental intracranial medulloblastoma and deliver a therapeutic gene leading to tumor regression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5550–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimato, S.; Natsume, A.; Takeuchi, H.; Wakabayashi, T.; Fujii, M.; Ito, M.; Ito, S.; Park, I.; Bang, J.; Kim, S. Human neural stem cells target and deliver therapeutic gene to experimental leptomeningeal medulloblastoma. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kendall, S.E.; Najbauer, J.; Johnston, H.F.; Metz, M.Z.; Li, S.; Bowers, M.; Garcia, E.; Kim, S.U.; Barish, M.E.; Aboody, K.S. Neural stem cell targeting of glioma is dependent on phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, K.M.; Park, I.H.; Shin, J.Y.; Jin, J.; Kang, B.G.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, S.J.; Jo, M.-Y.; Kim, S.U.; Nam, D.-H. Human neural stem cells can target and deliver therapeutic genes to breast cancer brain metastases. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Lee, J.-E.; Kim, S.U.; Cho, K.-G. Stereological analysis on migration of human neural stem cells in the brain of rats bearing glioma. Neurosurgery 2010, 66, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierdl, M.; Morton, C.L.; Weeks, J.K.; Danks, M.K.; Harris, L.C.; Potter, P.M. Sensitization of human tumor cells to CPT-11 via adenoviral-mediated delivery of a rabbit liver carboxylesterase. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5078–5082. [Google Scholar]
- Prados, M.D.; Lamborn, K.; Yung, W.; Jaeckle, K.; Robins, H.I.; Mehta, M.; Fine, H.A.; Wen, P.Y.; Cloughesy, T.; Chang, S. A phase 2 trial of irinotecan (CPT-11) in patients with recurrent malignant glioma: A North American Brain Tumor Consortium study. Neuro-Oncology 2006, 8, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.A.; Jiang, S.X.; Reardon, D.A.; Desjardins, A.; Vredenburgh, J.J.; Friedman, A.H.; Sampson, J.H.; McLendon, R.E.; Herndon, J.E.; Friedman, H.S. Phase II trial of temozolomide (TMZ) plus irinotecan (CPT-11) in adults with newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme before radiotherapy. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2009, 95, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, J.F.; Yung, W.K.A. Bevacizumab and irinotecan in the treatment of recurrent malignant gliomas. Cancer J. 2008, 14, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, H.S.; Grunnet, K.; Sorensen, M.; Olsen, P.; Hasselbalch, B.; Nelausen, K.; Kosteljanetz, M.; Lassen, U. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan in the treatment patients with progressive recurrent malignant brain tumours. Acta Oncol. 2009, 48, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, E.J.; Choi, H.B.; Lee, K.H.; Park, I.H.; Ko, Y.; Jeong, S.W.; Kim, S.U. Brain transplantation of immortalized human neural stem cells promotes functional recovery in mouse intracerebral hemorrhage stroke model. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.U.; Nagai, A.; Nakagawa, E.; Choi, H.B.; Bang, J.H.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, M.A.; Lee, Y.B.; Park, I.H. Production and characterization of immortal human neural stem cell line with multipotent differentiation property. Neural Stem Cells Methods Protoc. 2008, 438, 103–121. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.U.; De Vellis, J. Stem cell-based cell therapy in neurological diseases: A review. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 2183–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.U. Human neural stem cells genetically modified for brain repair in neurological disorders. Neuropathology 2004, 24, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, P.M.; Pawlik, C.A.; Morton, C.L.; Naeve, C.W.; Danks, M.K. Isolation and partial characterization of a cDNA encoding a rabbit liver carboxylesterase that activates the prodrug irinotecan (CPT-11). Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 2646–2651. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishii, M.; Iwai, M.; Harada, Y.; Kishida, T.; Asada, H.; Shin-Ya, M.; Itoh, Y.; Imanishi, J.; Okanoue, T.; Mazda, O. Soluble TRAIL gene and actinomycin D synergistically suppressed multiple metastasis of TRAIL-resistant colon cancer in the liver. Cancer Lett. 2007, 245, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, F.; Kishida, T.; Ohashi, S.; Asada, H.; Yasutomi, K.; Satoh, E.; Kubo, T.; Fushiki, S.; Imanishi, J.; Mazda, O. Highly efficient gene transfer into murine liver achieved by intravenous administration of naked Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-based plasmid vectors. Gene Ther. 2001, 8, 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| Gene | Sense | Antisense |
|---|---|---|
| DR4 | GCGGGGAGGATTGAACCAC | CGACGACAAACTTGAAGGTCTT |
| DR5 | ATGGAACAACGGGGACAGAAC | CTGCTGGGGAGCTAGGTCT |
| DcR1 | ACCAACGCTTCCAACAATGAA | CTAGGGCACCTGCTACACTTC |
| DcR2 | GTTGGCTTTTCATGTCGGAAGA | CCCAGGAACTCGTGAAGGAC |
| Top1 | CCAGACGGAAGCTCGGAAAC | GTCCAGGAGGCTCTATCTTGAA |
| Top2a | ACCATTGCAGCCTGTAAATGA | GGGCGGAGCAAAATATGTTCC |
| Top2b | GGTTCGTGTAGAGGGGTCAAG | GCCGTCCACCTTTTGTAGTTG |
| Top3a | CCCGAAGACCGTGCCTTTT | CTCATGCGACCGTTTGACAG |
| Top3b | TGGCGAGAAGACCGTGTTC | AATCACCGTATTTCCCCTGGA |
| Topbp1 | TGAGTGTGCCAAGAGATGGAA | TGCTTCTGGTCTAGGTTCTGT |
| Top1mt | ACGAAGACGGGGTGAAGTG | CCGGAAAACCTCCTTTGTTGTG |
| rCE | ATGATGGCCTGGCTCTTTCT | TCTCGGAAAATTGCTCGATG |
| sTRAIL | GGAATCATCAAGGAGTGGGC | TGGACCATTTGTTTGTCGTT |
| GADPH | CATGACCACAGTCCATGCCATCACT | TGAGGTCCACCACCCTGTTGCTGTA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Lee, D.-S.; Hong, S.H.; Lee, H.J. Anti-Cancer Effect of Neural Stem Cells Transfected with Carboxylesterase and sTRAIL Genes in Animals with Brain Lesions of Lung Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081156
Kim JH, Ahn JS, Lee D-S, Hong SH, Lee HJ. Anti-Cancer Effect of Neural Stem Cells Transfected with Carboxylesterase and sTRAIL Genes in Animals with Brain Lesions of Lung Cancer. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(8):1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081156
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jung Hak, Jae Sung Ahn, Dong-Seok Lee, Seok Ho Hong, and Hong J. Lee. 2023. "Anti-Cancer Effect of Neural Stem Cells Transfected with Carboxylesterase and sTRAIL Genes in Animals with Brain Lesions of Lung Cancer" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 8: 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081156
APA StyleKim, J. H., Ahn, J. S., Lee, D.-S., Hong, S. H., & Lee, H. J. (2023). Anti-Cancer Effect of Neural Stem Cells Transfected with Carboxylesterase and sTRAIL Genes in Animals with Brain Lesions of Lung Cancer. Pharmaceuticals, 16(8), 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081156









