In Vitro Analyses of the Multifocal Effects of Natural Alkaloids Berberine, Matrine, and Tabersonine against the O’nyong-nyong Arthritogenic Alphavirus Infection and Inflammation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
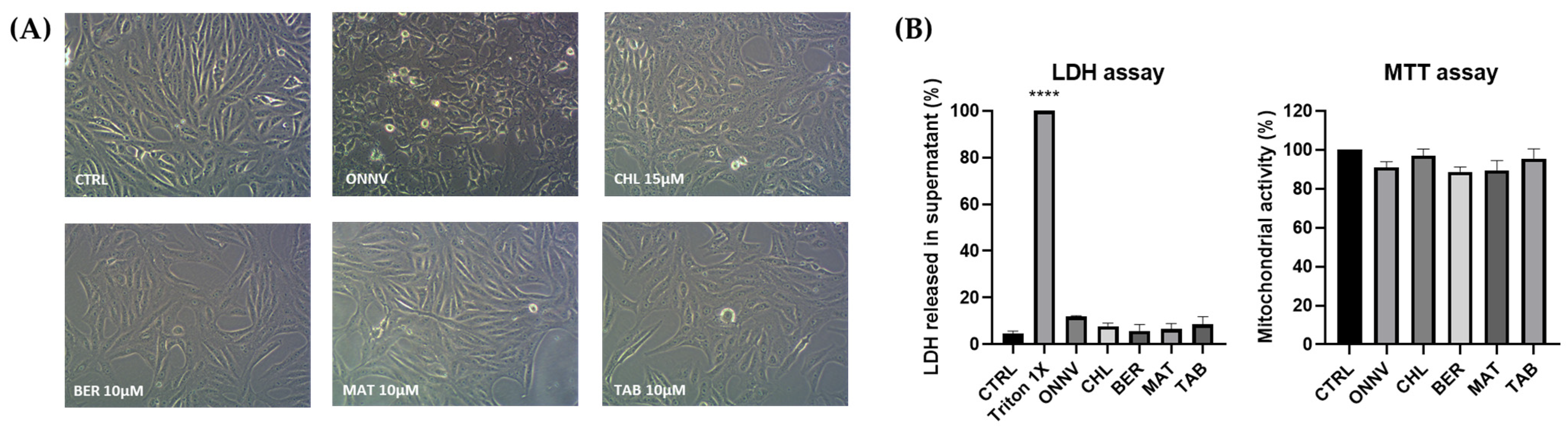
2.1. Cytotoxicity
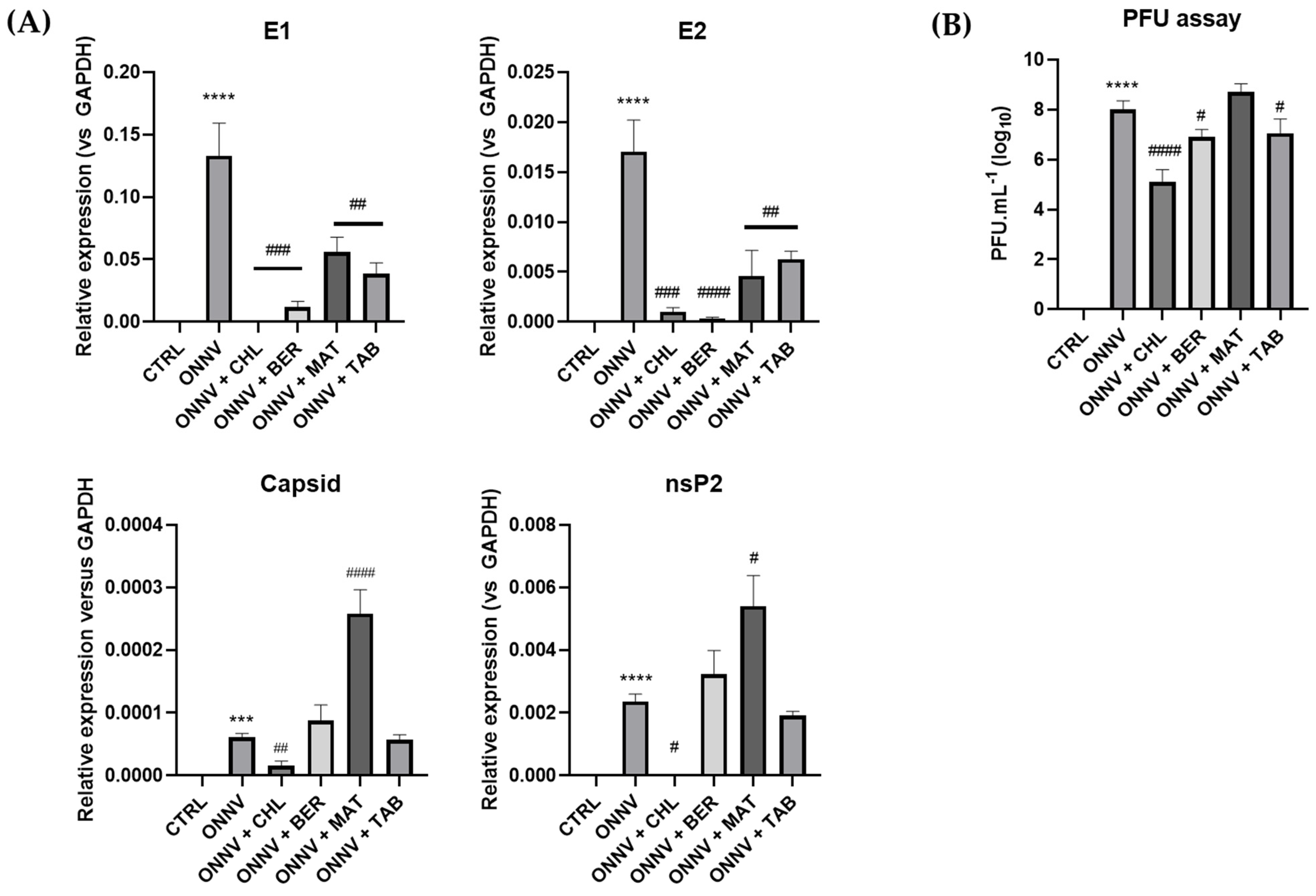
2.2. Effects of Three Alkaloids on the Viral Replication
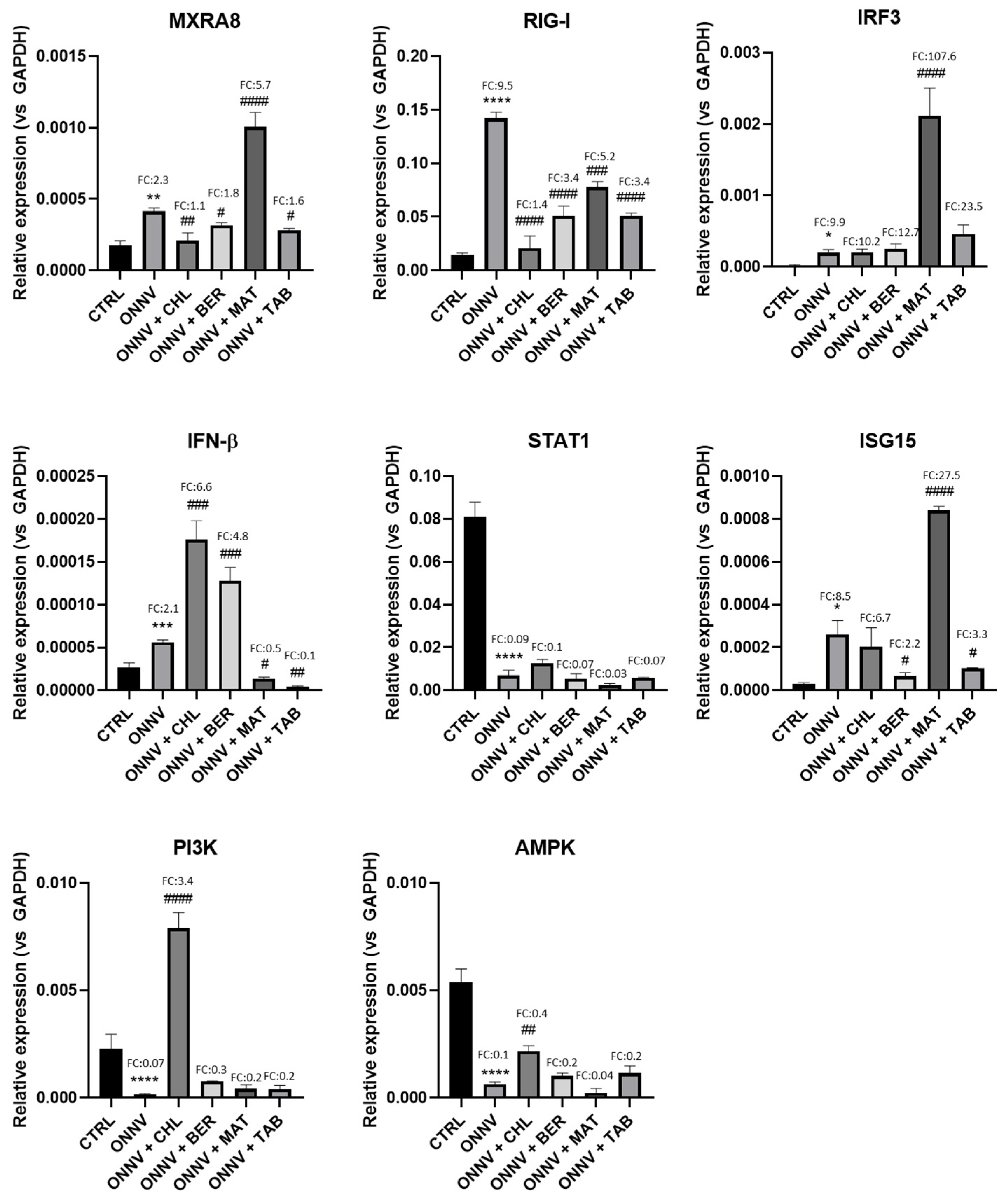
2.3. Effects of Infection and Three Alkaloids on the Antiviral Type-I Interferon Signaling Pathway
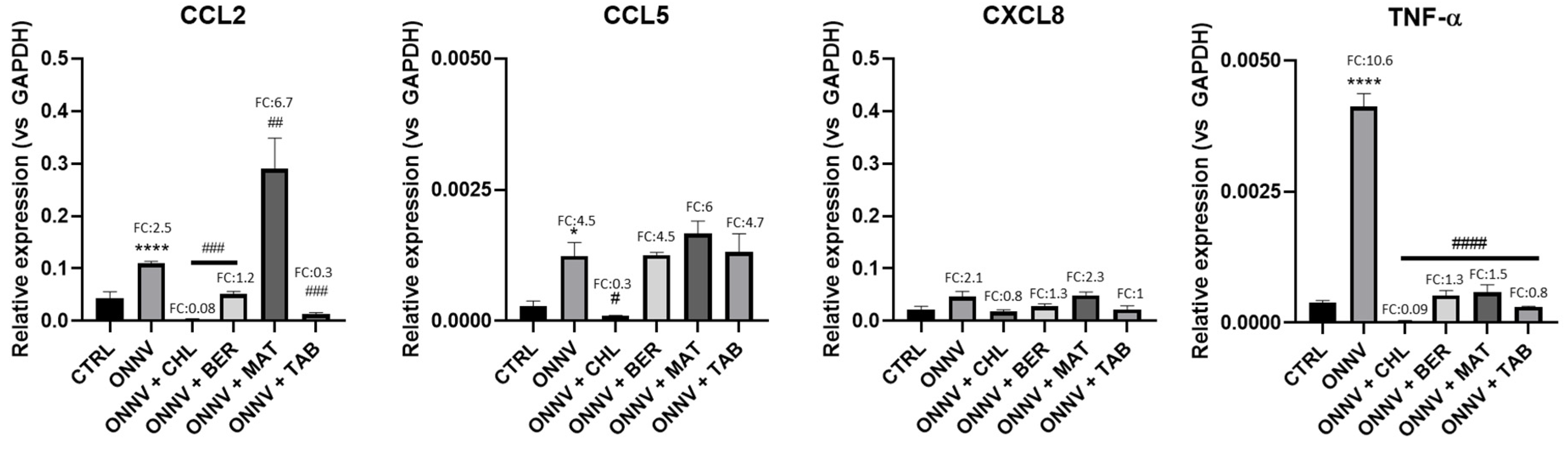
2.4. Effects of Infection and Three Alkaloids on Inflammatory Mediators and Signaling Pathways
2.5. Effects of Infection and Three Alkaloids on Inflammatory Signaling Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Virus
4.2. Cell Infection and/or Treatment
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olivia, L.W.; Obanda, V.; Bucht, G.; Mosomtai, G.; Otieno, V.; Ahlm, C.; Evander, M. Global emergence of Alphaviruses that cause arthritis in humans. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2015, 5, 29853. [Google Scholar]
- Zaid, A.; Burt, F.J.; Liu, X.; Poo, Y.S.; Zandi, K.; Suhrbier, A.; Weaver, S.C.; Texeira, M.M.; Mahalingam, S. Arthritogenic alphaviruses: Epidemiological and clinical perspective on emerging arboviruses. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, e123–e133. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1473309920304916 (accessed on 18 October 2021). [CrossRef]
- Suhrbier, A. Rheumatic manifestations of chikungunya: Emerging concepts and interventions. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, J.Y.-S.; Ng, M.M.-L.; Chu, J.J.H. Replication of Alphaviruses: A Review on the Entry Process of Alphaviruses into Cells. Adv. Virol. 2011, 2011, 249640. Available online: http://www.hindawi.com/journals/av/2011/249640/ (accessed on 1 October 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezza, G.; Chen, R.; Weaver, S.C. O’nyong-nyong fever: A neglected mosquito-borne viral disease. Pathog. Glob. Health 2017, 111, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.C.; Winegar, R.; Manger, I.D.; Forrester, N.L. Alphaviruses: Population genetics and determinants of emergence. Antivir. Res. 2012, 94, 242–257. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S016635421200085X (accessed on 18 October 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinson, R.S.; Strauss, J.H.; Strauss, E.G. Complete sequence of the genomic RNA of O’Nyong-Nyong virus and its use in the construction of alphavirus phylogenetic trees. Virology 1990, 175, 110–123. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/004268229090191S (accessed on 1 October 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assunção-Miranda, I.; Cruz-Oliveira, C.; Da Poian, A.T. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in the Pathogenesis of Alphavirus-Induced Arthritis. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 973516. Available online: http://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2013/973516/ (accessed on 28 October 2019). [CrossRef]
- Suchowiecki, K.; Reid, S.P.; Simon, G.L.; Firestein, G.S.; Chang, A. Persistent Joint Pain Following Arthropod Virus Infections. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2021, 23, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawman, D.W.; Burrack, K.S.; E Morrison, T. Mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of arthritogenic alphaviruses: Host immune responses and virus persistence. Future Virol. 2014, 9, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomeeusen, K.; Daniel, M.; LaBeaud, D.A.; Gasque, P.; Peeling, R.W.; Stephenson, K.E.; Ng, L.F.P.; Ariën, K.K. Chikungunya fever. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2023, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couderc, T.; Chrétien, F.; Schilte, C.; Disson, O.; Brigitte, M.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Touret, Y.; Barau, G.; Cayet, N.; Schuffenecker, I.; et al. A Mouse Model for Chikungunya: Young Age and Inefficient Type-I Interferon Signaling Are Risk Factors for Severe Disease. PLoS Pathog. 2008, 4, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourisseau, M.; Schilte, C.; Casartelli, N.; Trouillet, C.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Rudnicka, D.; Sol-Foulon, N.; Roux, K.L.; Prevost, M.-C.; Fsihi, H.; et al. Characterization of Reemerging Chikungunya Virus. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, e89. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1904475/ (accessed on 21 December 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thon-Hon, V.G.; Denizot, M.; Li-Pat-Yuen, G.; Giry, C.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.-C.; Gasque, P. Deciphering the differential response of two human fibroblast cell lines following Chikungunya virus infection. Virol. J. 2012, 9, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, S.; Coles, M.; Thomas, T.; Kollias, G.; Ludewig, B.; Turley, S.; Brenner, M.; Buckley, C.D. Fibroblasts as immune regulators in infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 704–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafavi, H.; Abeyratne, E.; Zaid, A.; Taylor, A. Arthritogenic Alphavirus-Induced Immunopathology and Targeting Host Inflammation as A Therapeutic Strategy for Alphaviral Disease. Viruses 2019, 11, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Kim, A.S.; Fox, J.M.; Nair, S.; Basore, K.; Klimstra, W.B.; Rimkunas, R.; Fong, R.H.; Lin, H.; Poddar, S.; et al. Mxra8 is a receptor for multiple arthritogenic alphaviruses. Nature 2018, 557, 570–574. Available online: http://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0121-3 (accessed on 2 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.C.H.; Ng, W.H.; Liu, X. Host Immune Responses to Arthritogenic Alphavirus Infection, with Emphasis on Type I IFN Responses. Zoonoses 2022, 2. Available online: https://scienceopen.com/hosted-document?doi=10.15212/ZOONOSES-2022-0028 (accessed on 28 October 2019).
- Rulli, N.E.; Rolph, M.S.; Srikiatkhachorn, A.; Anantapreecha, S.; Guglielmotti, A.; Mahalingam, S. Protection From Arthritis and Myositis in a Mouse Model of Acute Chikungunya Virus Disease by Bindarit, an Inhibitor of Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1 Synthesis. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, 1026–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninla-Aesong, P.; Mitarnun, W.; Noipha, K. Proinflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines as Biomarkers of Persistent Arthralgia and Severe Disease after Chikungunya Virus Infection: A 5-Year Follow-Up Study in Southern Thailand. Viral Immunol. 2019, 32, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pott, F.; Postmus, D.; Brown, R.J.P.; Wyler, E.; Neumann, E.; Landthaler, M.; Goffinet, C. Single-cell analysis of arthritogenic alphavirus-infected human synovial fibroblasts links low abundance of viral RNA to induction of innate immunity and arthralgia-associated gene expression. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 2151–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedoui, Y.; Septembre-Malaterre, A.; Giry, C.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.-C.; Selambarom, J.; Guiraud, P.; Gasque, P. Robust COX-2-mediated prostaglandin response may drive arthralgia and bone destruction in patients with chronic inflammation post-chikungunya. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peinado, R.d.S.; Eberle, R.J.; Arni, R.K.; Coronado, M.A. A Review of Omics Studies on Arboviruses: Alphavirus, Orthobunyavirus and Phlebovirus. Viruses 2022, 14, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Huizen, E.; McInerney, G.M. Activation of the PI3K-AKT Pathway by Old World Alphaviruses. Cells 2020, 9, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Foo, S.S.; Zaid, A.; Teng, T.S.; Herrero, L.J.; Wolf, S.; Tharmarajah, K.; Vu, L.D.; Van Vreden, C.; Taylor, A.; et al. Specific inhibition of NLRP3 in chikungunya disease reveals a role for inflammasomes in alphavirus-induced inflammation. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 1435–1445. Available online: http://www.nature.com/articles/s41564-017-0015-4 (accessed on 16 November 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Castro-Jorge, L.A.; de Carvalho, R.; Klein, T.M.; Hiroki, C.H.; Lopes, A.H.; Guimarães, R.M.; Fumagalli, M.J.; Floriano, V.G.; Agostinho, M.R.; Slhessarenko, R.D.; et al. The NLRP3 inflammasome is involved with the pathogenesis of Mayaro virus. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007934. Available online: https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1007934 (accessed on 11 November 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejía, C.R.; López-Vélez, R. Tropical Arthritogenic Alphaviruses. Reumatol. Clínica 2018, 14, 97–105. Available online: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2173574318300236 (accessed on 8 January 2019). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedoui, Y.; Guillot, X.; Sélambarom, J.; Guiraud, P.; Giry, C.; Jaffar-Bandjee, M.C.; Ralandison, S.; Gasque, P. Methotrexate an Old Drug with New Tricks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelnabi, R.; Jacobs, S.; Delang, L.; Neyts, J. Antiviral drug discovery against arthritogenic alphaviruses: Tools and molecular targets. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 174, 113777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi, L.I.; Vignuzzi, M. Arthritogenic Alphaviruses: A Worldwide Emerging Threat? Microorganisms 2019, 7, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, B.; Singh, W.S.; Das, M.; Goswami, S.; Singh, M.K.; Maiti, D.; Manna, K. Role of plant alkaloids on human health: A review of biological activities. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 9, 56–72. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2468519418300685 (accessed on 15 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Byler, K.G.; Collins, J.T.; Ogungbe, I.V.; Setzer, W.N. Alphavirus protease inhibitors from natural sources: A homology modeling and molecular docking investigation. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2016, 64, 163–184. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1476927116300901 (accessed on 15 November 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Thiruchelvan, M.; Lee, R.C.H.; Chen, H.; Chen, K.C.; Ng, M.L.; Chu, J.J.H. Inhibition of Chikungunya Virus Replication by Harringtonine, a Novel Antiviral That Suppresses Viral Protein Expression. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.J.; Brown, R.S.; Kielian, M. Berberine Chloride is an Alphavirus Inhibitor That Targets Nucleocapsid Assembly. mBio 2020, 11, e01382-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.-R.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Deng, C.-L.; Zhang, B.; Shang, L.-Q.; Ye, H.-Q. In Vitro Inhibition of Alphaviruses by Lycorine. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 1465–1474. Available online: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s12250-021-00438-z (accessed on 15 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Troost, B.; Mulder, L.M.; Diosa-Toro, M.; Van De Pol, D.; Rodenhuis-Zybert, I.A.; Smit, J.M. Tomatidine, a natural steroidal alkaloid shows antiviral activity towards chikungunya virus in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6364. Available online: http://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-63397-7 (accessed on 8 July 2022). [CrossRef]
- Abdelnabi, R.; Delang, L. Antiviral Strategies against Arthritogenic Alphaviruses. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, V.; Urban, E.; Langer, T. Antivirals against the Chikungunya Virus. Viruses 2021, 13, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobi, A.; Gasque, P.; Guiraud, P.; Selambarom, J. Irinotecan (CPT-11) Canonical Anti-Cancer Drug Can also Modulate Antiviral and Pro-Inflammatory Responses of Primary Human Synovial Fibroblasts. Cells 2021, 10, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seteyen, A.-L.S.; Girard-Valenciennes, E.; Septembre-Malaterre, A.; Gasque, P.; Guiraud, P.; Sélambarom, J. Anti-Alphaviral Alkaloids: Focus on Some Isoquinolines, Indoles and Quinolizidines. Molecules 2022, 27, 5080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Santhosh, S.R.; Tiwari, M.; Rao, P.V.L.; Parida, M. Assessment of in vitro prophylactic and therapeutic efficacy of chloroquine against Chikungunya virus in vero cells. J. Med. Virol. 2010, 82, 817–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neag, M.A.; Mocan, A.; Echeverría, J.; Pop, R.M.; Bocsan, C.I.; Crişan, G.; Buzoianu, A.D. Berberine: Botanical Occurrence, Traditional Uses, Extraction Methods, and Relevance in Cardiovascular, Metabolic, Hepatic, and Renal Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 557. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2018.00557/full (accessed on 7 April 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Och, A.; Podgórski, R.; Nowak, R. Biological Activity of Berberine—A Summary Update. Toxins 2020, 12, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varghese, F.S.; Kaukinen, P.; Gläsker, S.; Bespalov, M.; Hanski, L.; Wennerberg, K.; Kümmerer, B.M.; Ahola, T. Discovery of berberine, abamectin and ivermectin as antivirals against chikungunya and other alphaviruses. Antivir. Res. 2016, 126, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, F.S.; Thaa, B.; Amrun, S.N.; Simarmata, D.; Rausalu, K.; Nyman, T.A.; Merits, A.; McInerney, G.M.; Ng, L.F.P.; Ahola, T. The Antiviral Alkaloid Berberine Reduces Chikungunya Virus-Induced Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 9743–9757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-Y.; Jia, L.-Y.; Rong, Z.; Zhou, X.; Cao, L.-Q.; Li, A.-H.; Guo, M.; Jin, J.; Wang, Y.-D.; Huang, L.; et al. Research Advances on Matrine. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 867318. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2022.867318 (accessed on 2 October 2022). [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Wu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yu, K.; He, H.; Xu, J.; Sun, L.; et al. Tabersonine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via suppressing TRAF6 ubiquitination. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 154, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, A.C.; Basore, K.; Fremont, D.H.; Diamond, M.S. A molecular understanding of alphavirus entry. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupp, J.C.; Sokoloski, K.J.; Gebhart, N.N.; Hardy, R.W. Alphavirus RNA synthesis and non-structural protein functions. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 2483–2500. Available online: https://www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/journal/jgv/10.1099/jgv.0.000249 (accessed on 11 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.; Taylor, A. Arthritogenic Alphavirus Capsid Protein. Life 2021, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhrymuk, I.; Frolov, I.; Frolova, E.I. Both RIG-I and MDA5 detect alphavirus replication in concentration-dependent mode. Virology 2016, 487, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frolova, E.I.; Fayzulin, R.Z.; Cook, S.H.; Griffin, D.E.; Rice, C.M.; Frolov, I. Roles of Nonstructural Protein nsP2 and Alpha/Beta Interferons in Determining the Outcome of Sindbis Virus Infection. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 11254–11264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fros, J.J.; Liu, W.J.; Prow, N.A.; Geertsema, C.; Ligtenberg, M.; Vanlandingham, D.L.; Schnettler, E.; Vlak, J.M.; Suhrbier, A.; Khromykh, A.A.; et al. Chikungunya Virus Nonstructural Protein 2 Inhibits Type I/II Interferon-Stimulated JAK-STAT Signaling. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 10877–10887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fros, J.J.; Pijlman, G.P. Alphavirus Infection: Host Cell Shut-Off and Inhibition of Antiviral Responses. Viruses 2016, 8, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Echavarria-Consuegra, L.; Smit, J.M.; Reggiori, F. Role of autophagy during the replication and pathogenesis of common mosquito-borne flavi- and alphaviruses. Open Biol. 2019, 9, 190009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Bowman, J.W.; Jung, J.U. Autophagy during viral infection—A double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 341–354. Available online: http://www.nature.com/articles/s41579-018-0003-6 (accessed on 11 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.R.; van der Ende-Metselaar, H.; Mulder, H.L.; Smit, J.M.; Rodenhuis-Zybert, I.A. Mechanism and role of MCP-1 upregulation upon chikungunya virus infection in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32288. Available online: http://www.nature.com/articles/srep32288 (accessed on 11 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.F.P.; Chow, A.; Sun, Y.-J.; Kwek, D.J.C.; Lim, P.-L.; Dimatatac, F.; Ng, L.-C.; Ooi, E.-E.; Choo, K.-H.; Her, Z.; et al. IL-1β, IL-6, and RANTES as Biomarkers of Chikungunya Severity. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob-Nascimento, L.C.; Carvalho, C.X.; Silva, M.M.O.; Kikuti, M.; Anjos, R.O.; Fradico, J.R.B.; Campi-Azevedo, A.C.; Tauro, L.B.; Campos, G.S.; Moreira, P.S.d.S.; et al. Acute-Phase Levels of CXCL8 as Risk Factor for Chronic Arthralgia Following Chikungunya Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 744183. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.744183/full (accessed on 11 November 2022). [CrossRef]
- Moreira, T.P.; de Sousa, C.D.F.; Costa, V.R.D.M.; Queiroz-Junior, C.M.; Santos, F.M.; Bonilha, C.S.; Ésper, L.M.; Nogueira, M.L.; Cunha, T.M.; Teixeira, M.M.; et al. Tumour necrosis factor plays a deleterious role in the pathogenesis of chikungunya virus infection. Immunology 2022, 168, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.X.; Park, E.; Schultz, K.L.W.; Griffin, D.E. NF-κB Activation Promotes Alphavirus Replication in Mature Neurons. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01071-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, L.M. The Role of Nuclear Factor κB in the Interferon Response. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, D.K. MAP Kinase Pathways. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2012, 4, a011254. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3536342/ (accessed on 10 March 2020). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Nash, R.J.; Frey, T.K. Cellular responses to Sindbis virus infection of neural progenitors derived from human embryonic stem cells. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 757. Available online: https://bmcresnotes.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1756-0500-7-757 (accessed on 11 November 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Groslambert, M.; Py, B.F. Spotlight on the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. J. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 11, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Name | Sequence | Supplier |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | F: CCA TGC GGA AGG TGA AGG TC | Eurogentec |
| R: ACA TGT AAA CCA TGT AGT TGA GGT | ||
| E1 | F: CAC CGT CCC CGT ACG TAA AA | Eurofins |
| R: GGC TCT GTA GGC TGA TGC AA | ||
| E2 | F: CCC CTG ACT ACA CGC TGA TG | Eurogentec |
| R: CCT TCA TTG GAG CCG TCA CA | ||
| nsP2 | F: GCG GAG CAG GTA AAA ACG TG | Eurogentec |
| R: TAG AAC ACG CCC GTC GTA TG | ||
| Capsid | F: CGC AGC TTA CGG GTT TCA TA | Genecust |
| R: GCA ACG CCT TCA GAA ACG C | ||
| ISG15 | F: TTT GCC AGT ACA GGA GCT TGT G | Sigma |
| R: GGG TGA TCT GCG CCT TCA | ||
| IFN-β | F: GTC ACT GTG CCT GGA CCA TA | Eurogentec |
| R: ACA GCA TCT GCT GGT TGA AGA | ||
| MXRA8 | F: TTA CTG TGG CCT GCA CGA AC | Eurogentec |
| R: CTC TCG GGG ACG ATG ACA TT | ||
| RIG–I | F: CCA TAT CTC AGC TGG GTG ACA A | Sigma |
| R: GCT ATC GGG TCA ACA ACA GCT T | ||
| IRF3 | F: CCT CAC GAC CCA CAT AAA ATC | Sigma |
| R: GTA GAA GGC TGT CAC CTC GAA | ||
| CCL2 | F: CTG CTC ATA GCA GCC ACC TT | Eurogentec |
| R: CTT GAA GAT CAC AGC TTC TTT GGG | ||
| IL-1β | F: ACAGATGAAGTGCTCCTTCCA | Eurogentec |
| R: GTCGGAGATTCGTAGCTGGAT | ||
| STAT-1 | F: TGG TGA AAT TGC AAG AGC TG | Sigma |
| R: AGA GGT CGT CTC GAG GTC AA | ||
| MAPK | F: AGCAAGGGAGAGATGGTGTAA | Genecust |
| R: CAGTGTCTAAGGGCTGCCAC | ||
| AMPK | F: GGGAAAGTGAAGGTGGGCAA | Genecust |
| R: GATGTGAGGGTGCCTGAACA | ||
| NF-κB | CCGGCCCGCCTGAATCATTCTC | Eurogentec |
| CAGGTGGCGACCGTGATACCT | ||
| Pi3K | F: ACCATGGAGGAGAACCCTTATG | Genecust |
| R: ACGGACAGTGCTCCTCCTTA | ||
| Caspase 1 | F: GCTTTCTGCTCTTCCACACC | Genecust |
| R: AAATGAAAATCGAACCTTGC | ||
| STAT-3 | F: CCGAGCCAATTGTGATGCTT | Genecust |
| R: GCATGTTGTACCACAGGATG | ||
| CCL5 | F: TCC TCA TTG CTA CTG CCC TC | Eurogentec |
| R: TCG GGT GAC AAA GAC GAC TG | ||
| CXCL8 | F: CAG AGA CAG CAG AGC ACA CA | Genecust |
| R: GGC AAA ACT GCA CCT TCA CA | ||
| TNF-α | F: GCT GCA CTT TGG AGT GAT CG | Sigma |
| R: GAG GGG TTT GCT ACA ACA TGG G |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sandenon Seteyen, A.-L.; Guiraud, P.; Gasque, P.; Girard-Valenciennes, E.; Sélambarom, J. In Vitro Analyses of the Multifocal Effects of Natural Alkaloids Berberine, Matrine, and Tabersonine against the O’nyong-nyong Arthritogenic Alphavirus Infection and Inflammation. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081125
Sandenon Seteyen A-L, Guiraud P, Gasque P, Girard-Valenciennes E, Sélambarom J. In Vitro Analyses of the Multifocal Effects of Natural Alkaloids Berberine, Matrine, and Tabersonine against the O’nyong-nyong Arthritogenic Alphavirus Infection and Inflammation. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(8):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081125
Chicago/Turabian StyleSandenon Seteyen, Anne-Laure, Pascale Guiraud, Philippe Gasque, Emmanuelle Girard-Valenciennes, and Jimmy Sélambarom. 2023. "In Vitro Analyses of the Multifocal Effects of Natural Alkaloids Berberine, Matrine, and Tabersonine against the O’nyong-nyong Arthritogenic Alphavirus Infection and Inflammation" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 8: 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081125
APA StyleSandenon Seteyen, A.-L., Guiraud, P., Gasque, P., Girard-Valenciennes, E., & Sélambarom, J. (2023). In Vitro Analyses of the Multifocal Effects of Natural Alkaloids Berberine, Matrine, and Tabersonine against the O’nyong-nyong Arthritogenic Alphavirus Infection and Inflammation. Pharmaceuticals, 16(8), 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081125










