Characterization of Anticancer Effects of the Analogs of DJ4, a Novel Selective Inhibitor of ROCK and MRCK Kinases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. DJ4 Decreases Survival in Various NSCLC and Breast Cancer Cell Lines
2.2. DJ4 Inhibits Colony Forming Ability of Cancer Cells
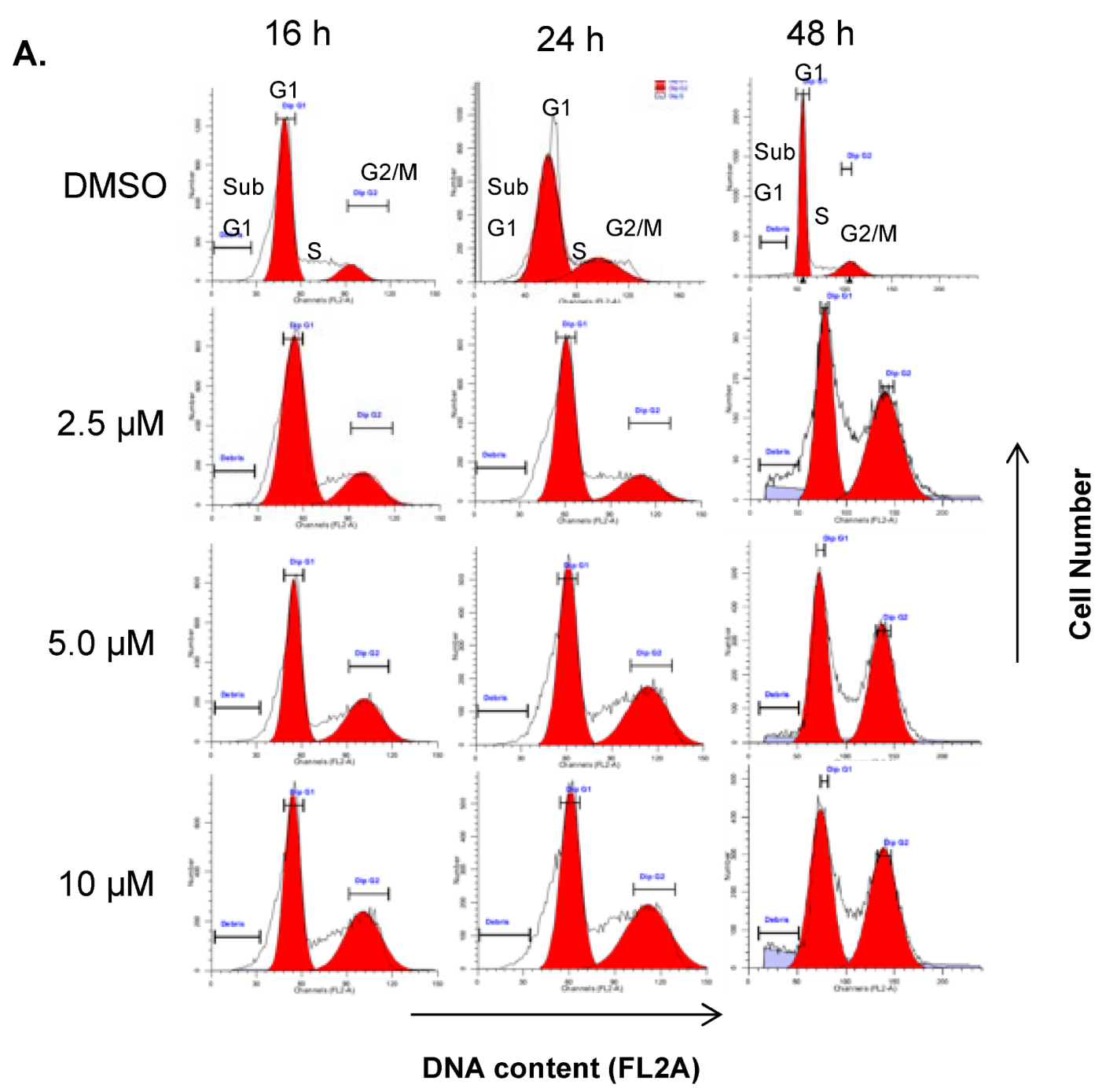
2.3. DJ4 Treatment Arrests Cancer Cells in G2/M Phase
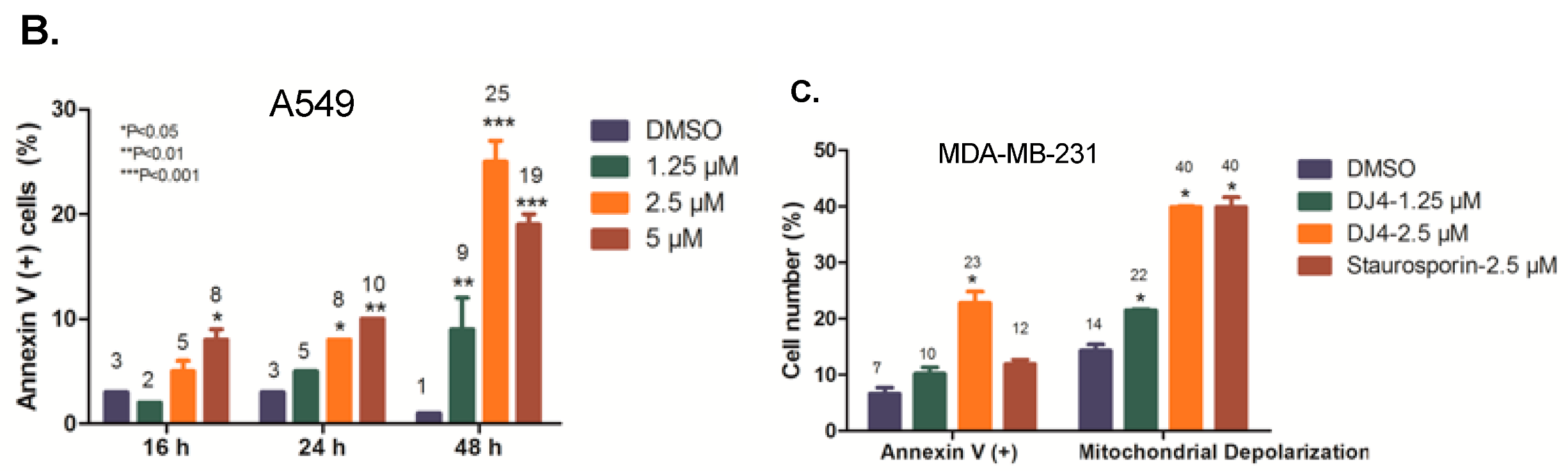
2.4. DJ4 Induces Intrinsic Apoptotic Signaling Pathway
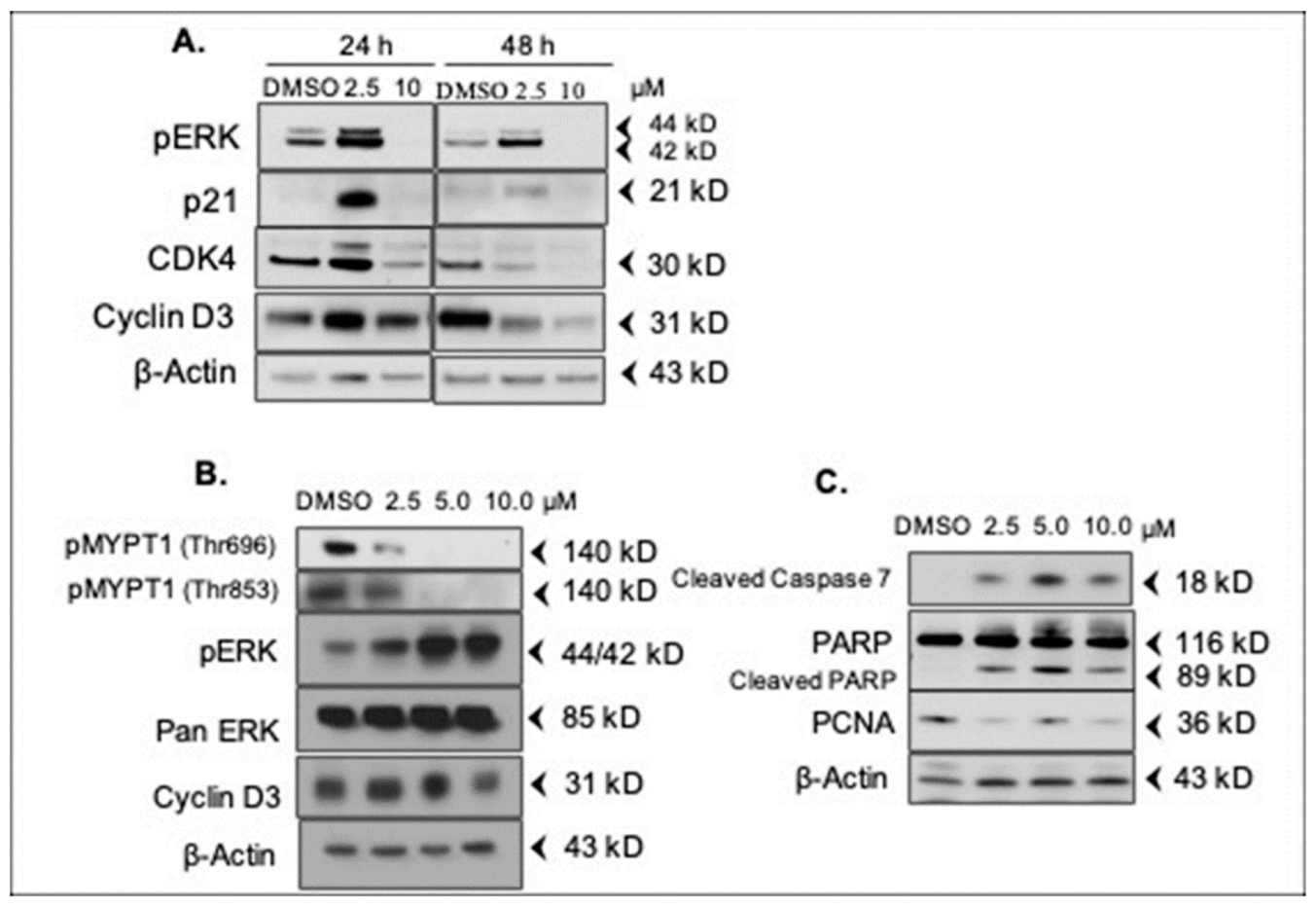
2.5. DJ4 Modulates Expression of Cell Cycle- and Apoptosis-Regulatory Proteins
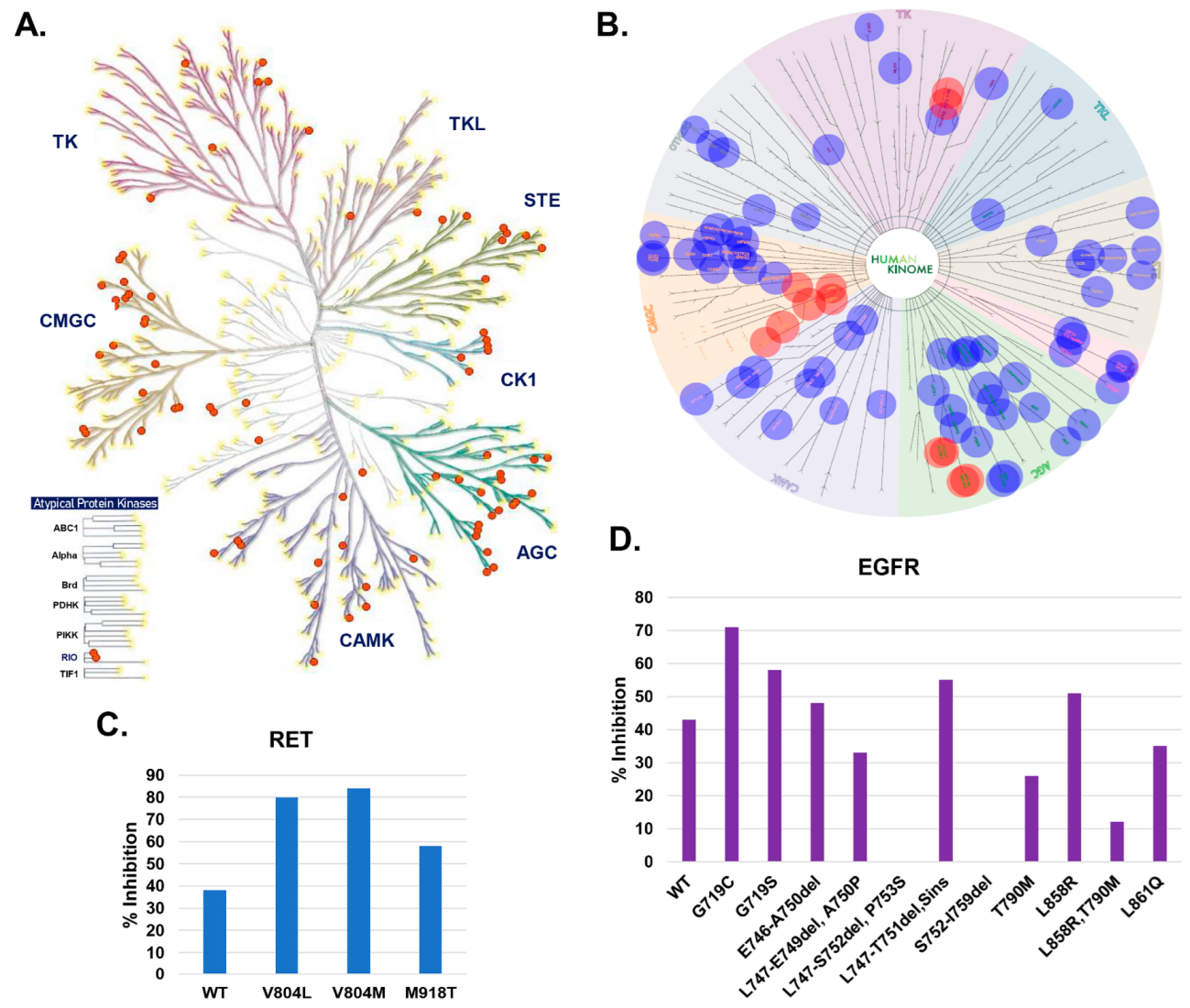
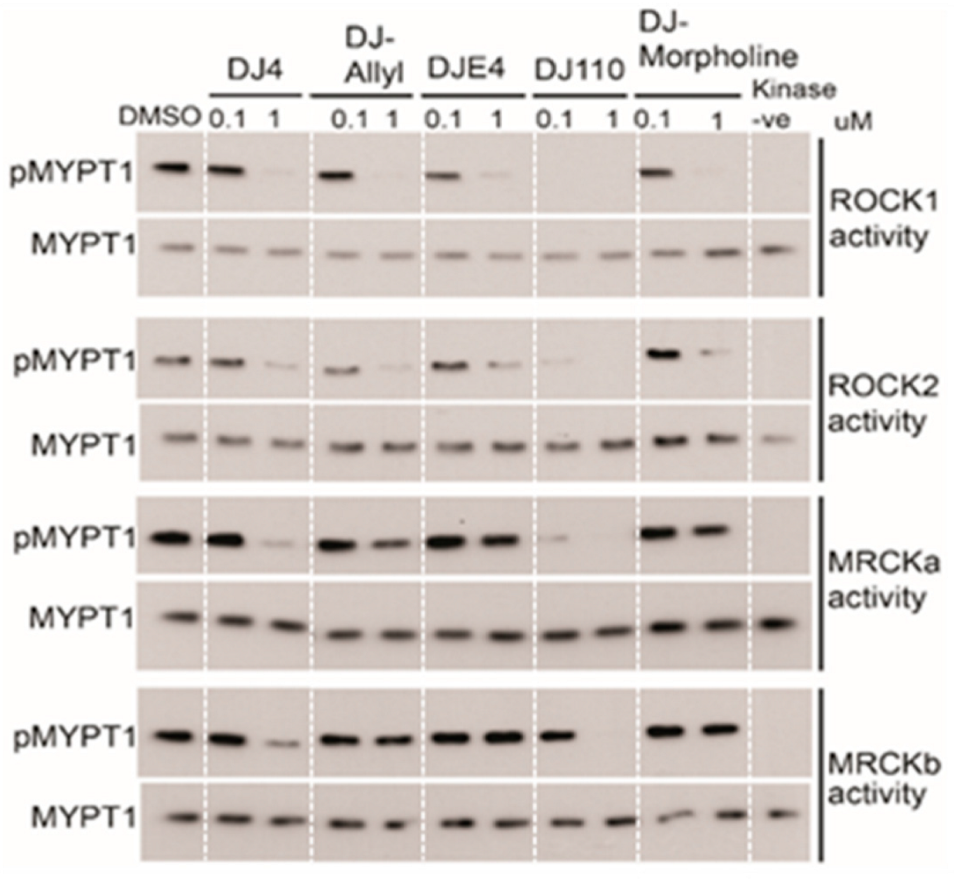
2.6. Assessment of the Kinase Specificity of DJ4
2.7. Optimization of ROCK and MRCK Kinase Inhibitory Potential through Development of DJ4 Analogs
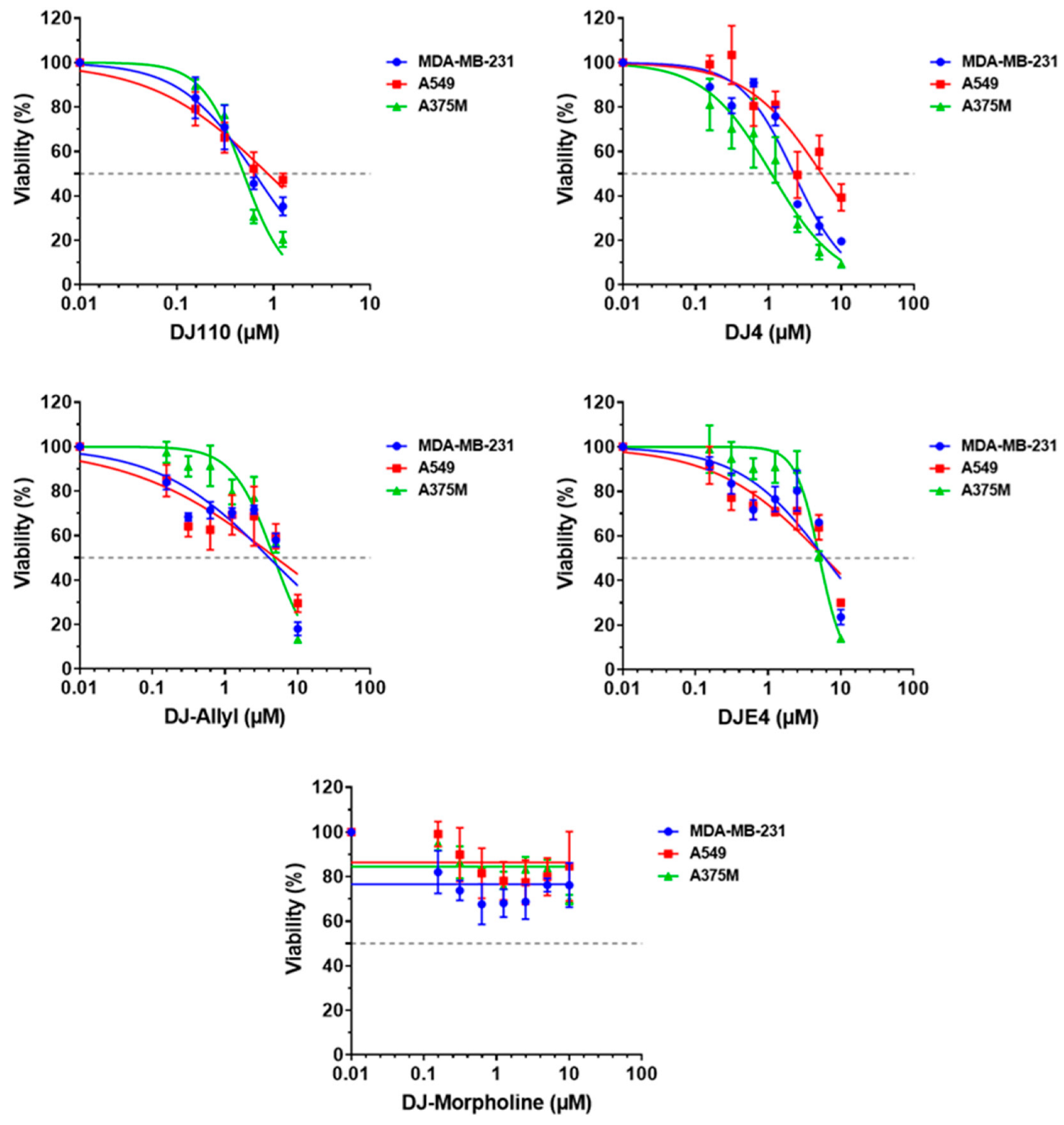
2.8. DJ4 Analogs Effectively Inhibit Cancer Cell Growth
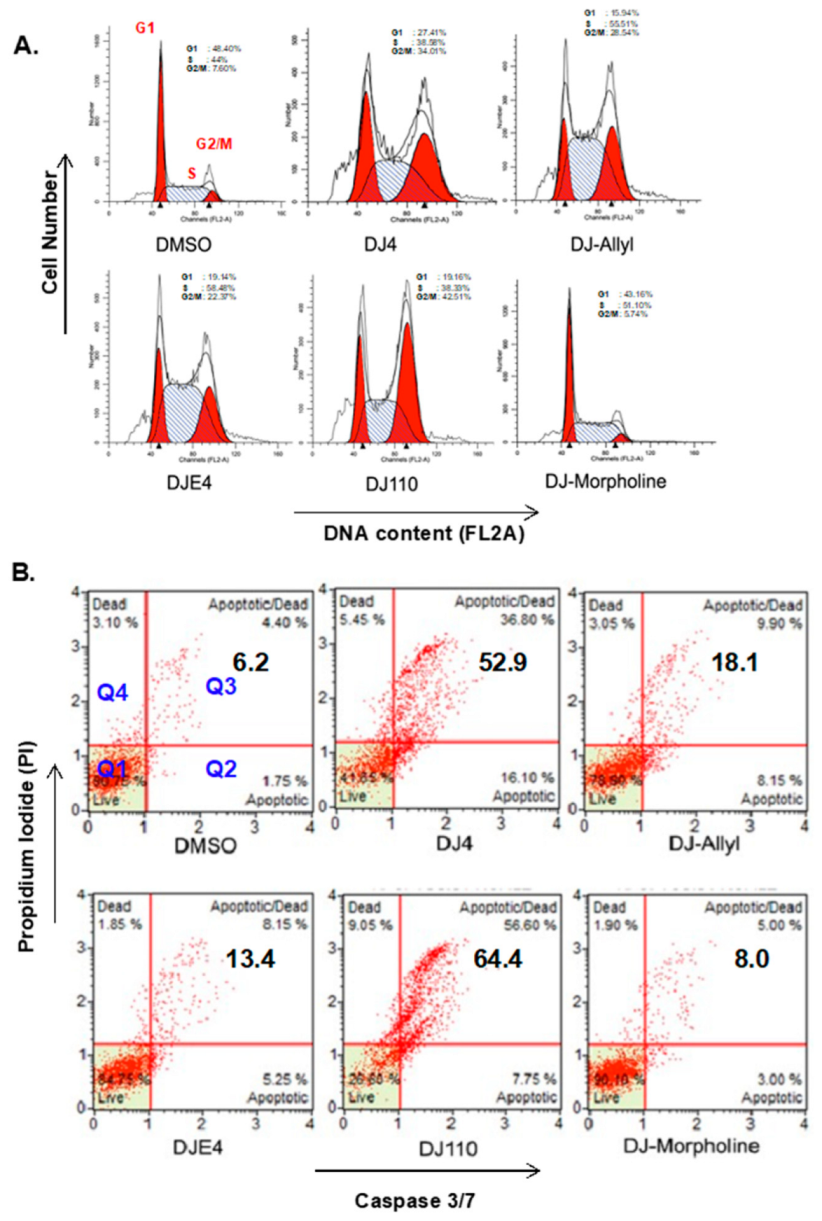
2.9. DJ4 Analogs Induce Cell Cycle Arrest
2.10. DJ4 Analogs Induce Apoptotic Cell Death
2.11. NCI-60 Human Cancer Cell Line Screening
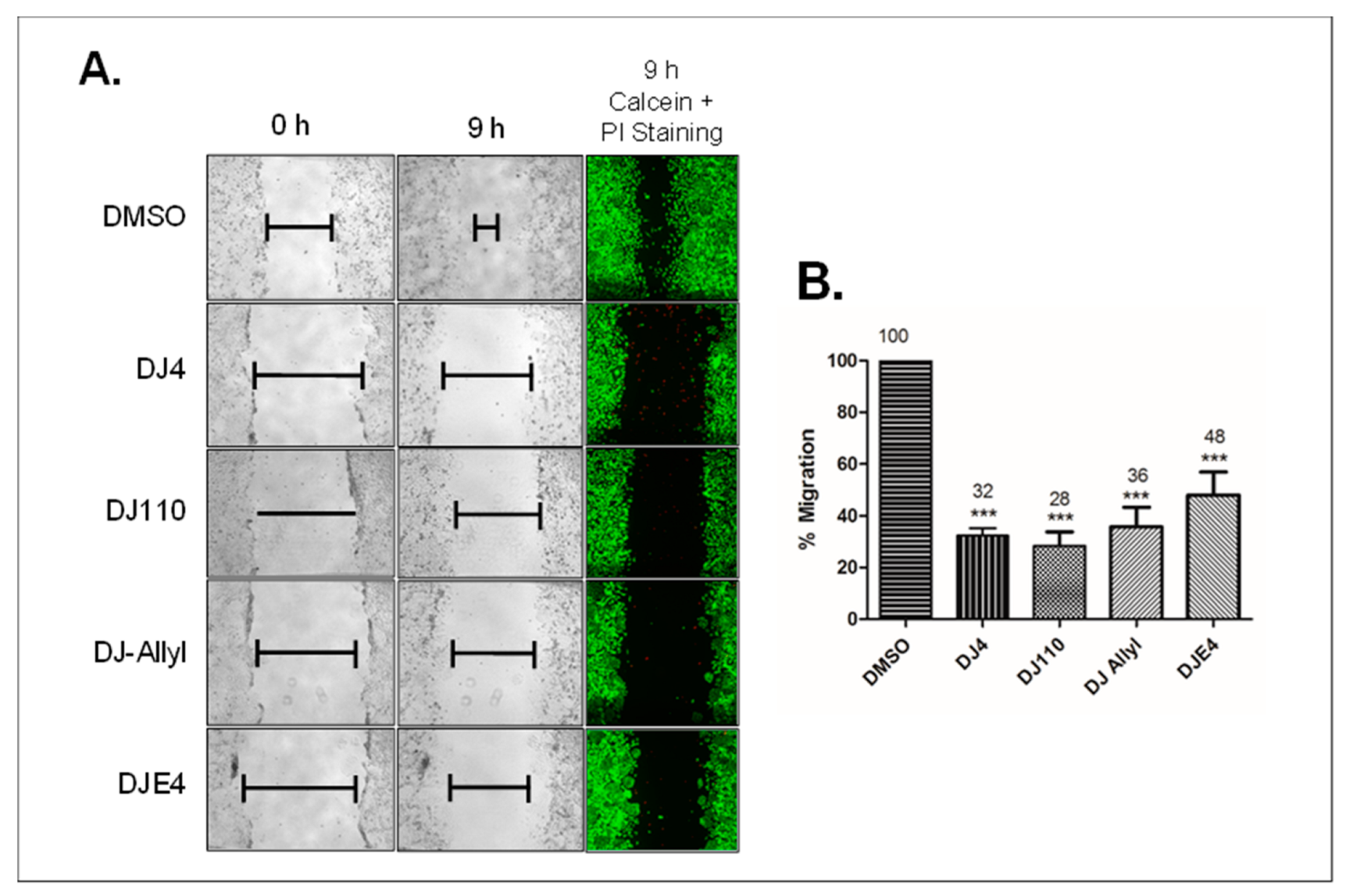
2.12. DJ4 Analogs Potently Inhibit Migration of Cancer Cells
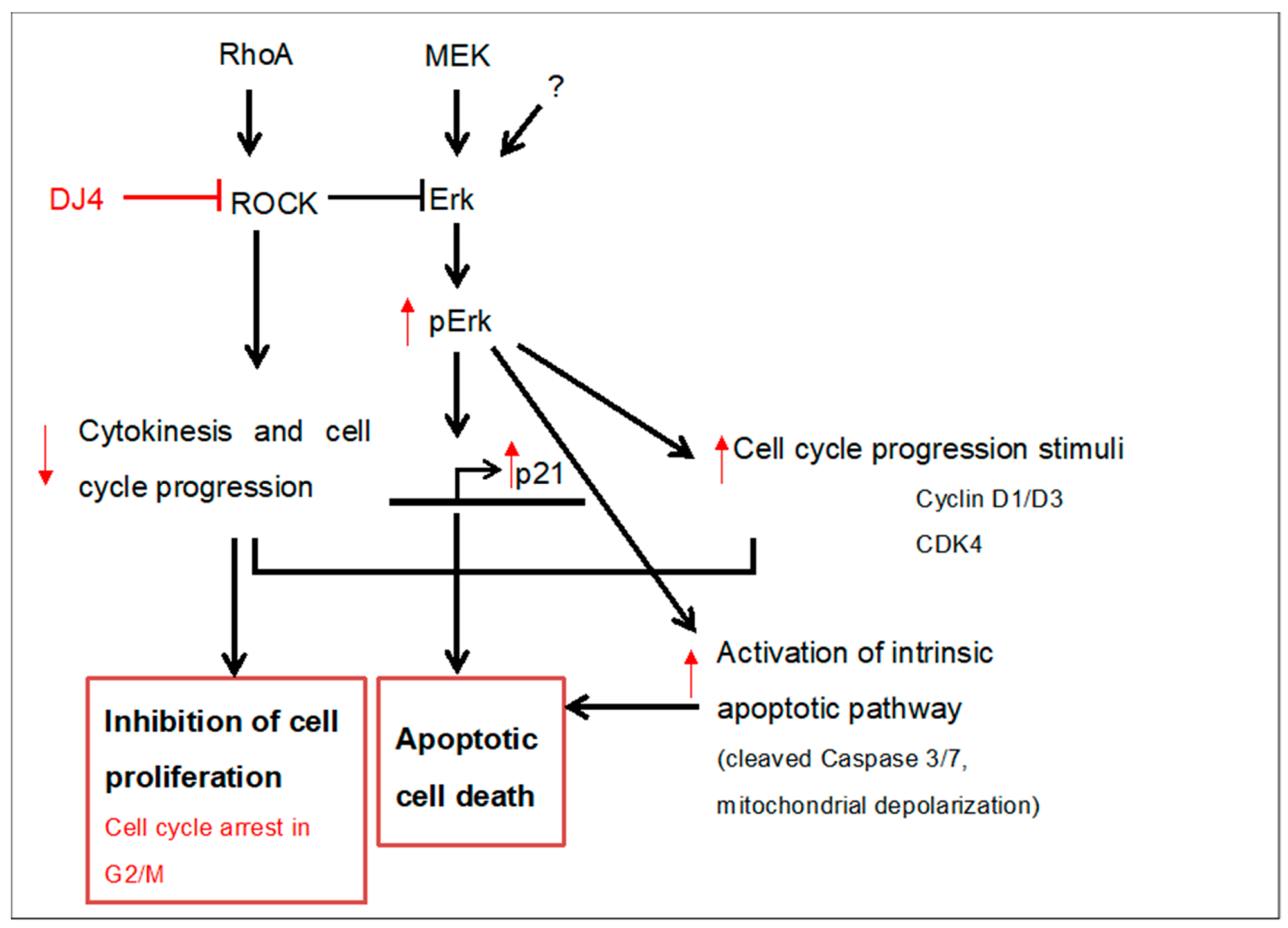
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell-Free (Biochemical) Kinase Activity Assays
4.2. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.4. Caspase 3/7 Assay
4.5. Live/Dead Cell Count
4.6. Annexin V Analysis
4.7. Mitochondrial Membrane Depolarization
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Cell Migration Assay
4.10. MTT Assay
4.11. Kinase Inhibition Assay
4.12. NCI-60 Human Cancer Cell Line Screen
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, H.I.; Watson, C.T.; Badal, S.; Toyang, N.J.; Bryant, J. Cycloartane-3,24,25-triol inhibits MRCKalpha kinase and demonstrates promising anti prostate cancer activity in vitro. Cancer Cell Int. 2012, 12, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotulainen, P.; Lappalainen, P. Stress fibers are generated by two distinct actin assembly mechanisms in motile cells. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 173, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, L.; Olson, M.F. Rho-associated coiled-coil containing kinases (ROCK): Structure, regulation, and functions. Small GTPases 2014, 5, e29846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, T.; Chen, X.-Q.; Tan, I.; Manser, E.; Lim, L. Myotonic Dystrophy Kinase-Related Cdc42-Binding Kinase Acts as a Cdc42 Effector in Promoting Cytoskeletal Reorganization. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amano, M.; Ito, M.; Kimura, K.; Fukata, Y.; Chihara, K.; Nakano, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Kaibuchi, K. Phosphorylation and Activation of Myosin by Rho-associated Kinase (Rho-kinase). J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 20246–20249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Manzanares, M.; Ma, X.; Adelstein, R.S.; Horwitz, A.R. Non-muscle myosin II takes centre stage in cell adhesion and migration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.; Paterson, H.F.; Marshall, C.J. Cdc42–MRCK and Rho–ROCK signalling cooperate in myosin phosphorylation and cell invasion. Nature 2005, 7, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckoff, J.B.; Pinner, S.E.; Gschmeissner, S.; Condeelis, J.S.; Sahai, E. ROCK- and Myosin-Dependent Matrix Deformation Enables Protease-Independent Tumor-Cell Invasion In Vivo. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, V.P.; Hengst, J.A.; Desai, D.H.; Amin, S.G.; Yun, J.K. The regulatory roles of ROCK and MRCK kinases in the plasticity of cancer cell migration. Cancer Lett. 2015, 361, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golla, U.; Ehudin, M.A.; Annageldiyev, C.; Zeng, Z.; Tukaramrao, D.B.; Tarren, A.; Date, A.A.; Elcheva, I.; Berg, A.; Amin, S.; et al. DJ4 Targets the Rho-Associated Protein Kinase Pathway and Attenuates Disease Progression in Preclinical Murine Models of Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiskanen, K.M.; Bhat, M.B.; Wang, H.-W.; Ma, J.; Nieminen, A.-L. Mitochondrial Depolarization Accompanies Cytochrome cRelease During Apoptosis in PC6 Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 5654–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, E.; Armour, S.M.; Harris, M.H.; Thompson, C.B. Mitochondrial membrane potential regulates matrix configuration and cytochrome c release during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccarelli, C.; Marampon, F.; Scoglio, A.; Mauro, A.; Giacinti, C.; De Cesaris, P.; Zani, B.M. p21WAF1 expression induced by MEK/ERK pathway activation or inhibition correlates with growth arrest, myogenic differentiation and onco-phenotype reversal in rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Mol. Cancer 2005, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Ito, M.; Ichikawa, K.; Isaka, N.; Nishikawa, M.; Hartshorne, D.J.; Nakano, T. Inhibitory Phosphorylation Site for Rho-associated Kinase on Smooth Muscle Myosin Phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 37385–37390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurki, P.; Vanderlaan, M.; Dolbeare, F.; Gray, J.; Tan, E.M. Expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)/cyclin during the cell cycle. Exp. Cell Res. 1986, 166, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, V.P.; Hengst, J.A.; Desai, D.H.; Dick, T.E.; Choe, K.N.; Colledge, A.L.; Takahashi, Y.; Sung, S.-S.; Amin, S.G.; Yun, J.K. A novel selective multikinase inhibitor of ROCK and MRCK effectively blocks cancer cell migration and invasion. Cancer Lett. 2014, 354, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, M.A.; Biggs, W.H., III; Treiber, D.K.; Atteridge, C.E.; Azimioara, M.D.; Benedetti, M.G.; Carter, T.A.; Ciceri, P.; Edeen, P.T.; Floyd, M.; et al. A small molecule–kinase interaction map for clinical kinase inhibitors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K.; Mazo, I.; Leung, H.; Engelke, K.; Von Andrian, U.H.; Deryugina, E.I.; Strongin, A.Y.; Bröcker, E.B.; Friedl, P. Compensation mechanism in tumor cell migration: Mesenchymal-amoeboid transition after blocking of pericellular proteolysis. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkila, T.; Wheatley, E.; Crighton, D.; Schroder, E.; Boakes, A.; Kaye, S.J.; Mezna, M.; Pang, L.; Rushbrooke, M.; Turnbull, A.; et al. Co-crystal structures of inhibitors with MRCKbeta, a key regulator of tumor cell invasion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uehara, R.; Goshima, G.; Mabuchi, I.; Vale, R.D.; Spudich, J.A.; Griffis, E.R. Determinants of Myosin II Cortical Localization during Cytokinesis. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Goto, H.; Izawa, I.; Mizutani, H.; Inagaki, M. Aurora-B and Rho-kinase/ROCK, the two cleavage furrow kinases, independently regulate the progression of cytokinesis: Possible existence of a novel cleavage furrow kinase phosphorylates ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM). Genes Cells 2005, 10, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, H.; Kosako, H.; Tanabe, K.; Yanagida, M.; Sakurai, M.; Amano, M.; Kaibuchi, K.; Inagaki, M. Phosphorylation of Vimentin by Rho-associated Kinase at a Unique Amino-terminal Site That Is Specifically Phosphorylated during Cytokinesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 11728–11736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, Y.; Amano, M.; Nagata, K.-I.; Inagaki, N.; Nakamura, H.; Saya, H.; Kaibuchi, K.; Inagaki, M. Roles of Rho-associated Kinase in Cytokinesis; Mutations in Rho-associated Kinase Phosphorylation Sites Impair Cytokinetic Segregation of Glial Filaments. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickson, G.R.; Echard, A.; O’Farrell, P.H. Rho-kinase Controls Cell Shape Changes during Cytokinesis. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizaki, T.; Uehata, M.; Tamechika, I.; Keel, J.; Nonomura, K.; Maekawa, M.; Narumiya, S. Pharmacological properties of Y-27632, a specific inhibitor of rho-associated kinases. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 976–983. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.; Hannon, G.J. Suppression of p160ROCK bypasses cell cycle arrest after Aurora-A/STK15 depletion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8975–8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, M.; Fu, P.; Xie, M.; Wang, W.; Luo, X. ROCK inhibition with Y27632 promotes the proliferation and cell cycle progression of cultured astrocyte from spinal cord. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Jiang, Q.; Shi, K.J.; Luo, H.; Yang, Y.; Xu, C.M. RhoA modulates functional and physical interaction between ROCK1 and Erk1/2 in selenite-induced apoptosis of leukaemia cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Martindale, J.L.; Gorospe, M.; Holbrook, N.J. Regulation of p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression through mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olson, M.F.; Paterson, H.F.; Marshall, C.J. Signals from Ras and Rho GTPases interact to regulate expression of p21Waf1/Cip1. Nature 1998, 394, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, G.; Clifton, G.L.; Godwin, M.L.; Bakajsova, D. Activation of ERK1/2 pathway mediates oxidant-induced decreases in mitochondrial function in renal cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2006, 291, F840–F855. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, S.; Yan, Y.; Daubert, R.A.; Han, J.; Schnellmann, R.G.; Kurosaki, Y.; Imoto, A.; Kawakami, F.; Yokoba, M.; Takenaka, T.; et al. ERK promotes hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis through caspase-3 activation and inhibition of Akt in renal epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2007, 292, F440–F447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.S.; Hong, J.S.; Kim, S.W.; Koh, J.M.; An, C.S.; Choi, J.Y.; Cheng, S.L. Leptin induces apoptosis via ERK/cPLA2/cytochrome C pathway in human bone marrow stromal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 21920–21929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-L.; Wu, L.-J.; Zuo, H.-J.; Tashiro, S.-I.; Onodera, S.; Ikejima, T. Cytochrome c Release From Oridonin-Treated Apoptotic A375-S2 Cells Is Dependent on p53 and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase Activation. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 96, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Martindale, J.L.; Holbrook, N.J. Requirement for ERK Activation in Cisplatin-induced Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39435–39443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Kim, H.J.; Kwon, C.H.; Kim, J.H.; Woo, J.S.; Jung, J.S.; Kim, J.M. Role of ERK activation in cisplatin-induced apoptosis in OK renal epithelial cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2005, 25, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.G.; Yoo, C.I.; Kim, H.T.; Kwon, C.H.; Kim, Y.K. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in osteoblastic cells. Toxicology 2005, 215, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez–Sarosi, L.A.; Strasberg–Rieber, M.; Rieber, M. ERK activation increases nitroprusside induced apoptosis in human melanoma cells irrespective of p53 status: Role of superoxide dismutases. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffer, C.L.; Weinberg, R.A. A Perspective on Cancer Cell Metastasis. Science 2011, 331, 1559–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, R.H. The NCI60 human tumour cell line anticancer drug screen. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, W.; Yu, P.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Guo, C.; Zhou, L.; Li, C.; Li, K. MCF-7/ADR cells (re-designated NCI/ADR-RES) are not derived from MCF-7 breast cancer cells: A loss for breast cancer multidrug-resistant research. Med. Oncol. 2011, 28 (Suppl. 1), S135–S141. [Google Scholar]
- Karaman, M.W.; Herrgard, S.; Treiber, D.K.; Gallant, P.; Atteridge, C.E.; Campbell, B.T.; Chan, K.W.; Ciceri, P.; Davis, M.I.; Edeen, P.T.; et al. A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, S.; Turk, S.; Volkamer, A.; Rippmann, F.; Fulle, S. KinMap: A web-based tool for interactive navigation through human kinome data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCI. Leading Causes of Death in US, 1975 vs. 2011; NCI: Bethesda, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Street, C.A.; Bryan, B.A. Rho kinase proteins--pleiotropic modulators of cell survival and apoptosis. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 3645–3657. [Google Scholar]
- Paull, K.D.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Hodes, L.; Monks, A.; Scudiero, D.A.; Rubinstein, L.; Plowman, J.; Boyd, M.R. Display and Analysis of Patterns of Differential Activity of Drugs Against Human Tumor Cell Lines: Development of Mean Graph and COMPARE Algorithm. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1989, 81, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, A.K.; Viswanadhan, V.N.; Wendoloski, J.J. A Knowledge-Based Approach in Designing Combinatorial or Medicinal Chemistry Libraries for Drug Discovery. 1. A Qualitative and Quantitative Characterization of Known Drug Databases. J. Comb. Chem. 1999, 1, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cell Lines | IC50 (µM) |
|---|---|
| H1299 | 0.44 ± 0.04 |
| H226 | 0.67 ± 0.38 |
| A549 | 0.98 ± 0.21 |
| H522 | 1.69 ± 0.48 |
| H23 | 2.91 ± 0.71 |
| H460 | 9.53 ± ND |
| Compound | MDA-MB-231 | A549 | A375M |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJ110 | 0.65 ± 0.07 | 0.88 ± 0.16 | 0.49 ± 0.03 |
| DJ4 | 2.3 ± 0.23 | 5.4 ± 1.19 | 1.1 ± 0.15 |
| DJ-Allyl | 4.1 ± 1.23 | 5.0 ± 2.20 | 4.7 ± 0.52 |
| DJE4 | 5.9 ± 1.63 | 6.1 ± 1.69 | 5.1 ± 0.32 |
| DJ-Morpholine | >10 ± NA | >10 ± NA | >10 ± NA |
| Panel Name | Cell Line | DJ4 | DJ4-HCl | DJ-Allyl | DJE4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leukemia | CCRF-CEM | 9.9 | 5.5 | 7.1 | 3.0 |
| HL-60(TB) | 6.8 | −6.6 | −14.5 | −22.4 | |
| K-562 | 29.9 | 28.5 | 42.1 | 26.3 | |
| MOLT-4 | 11.4 | 8.6 | 5.8 | −6.0 | |
| RPMI-8226 | 39.2 | 38.7 | 42.7 | 29.1 | |
| SR | 5.6 | −1.5 | −9.5 | 0.4 | |
| Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | A549/ATCC | 19.1 | 8.1 | 13.2 | 11.1 |
| EKVX | 46.0 | 40.9 | 30.5 | 14.1 | |
| HOP-62 | 19.9 | −3.0 | −10.8 | −26.5 | |
| HOP-92 | −9.7 | 11.8 | −1.9 | 4.4 | |
| NCI-H226 | 3.3 | 22.4 | 10.7 | 10.8 | |
| NCI-H23 | 9.1 | 3.0 | 6.8 | −7.9 | |
| NCI-H322M | 5.2 | 19.6 | 10.2 | 5.8 | |
| NCI-H460 | 14.1 | 15.1 | 2.2 | 2.4 | |
| NCI-H522 | 26.6 | 4.3 | −5.3 | −28.6 | |
| Colon Cancer | COLO 205 | 4.8 | −6.8 | −20.1 | −33.3 |
| HCC-2998 | 53.9 | 66.2 | 44.6 | 10.2 | |
| HCT-116 | 9.7 | 5.8 | 6.3 | 4.0 | |
| HCT-15 | 36.5 | 33.5 | 24.7 | 16.0 | |
| HT29 | 30.6 | 27.8 | 26.4 | 4.3 | |
| KM12 | 13.1 | 9.3 | 7.9 | 6.2 | |
| SW-620 | 9.9 | 7.8 | 7.4 | 6.5 | |
| CNS Cancer | SF-268 | 10.4 | 8.9 | −3.3 | −5.8 |
| SF-295 | 22.6 | 18.7 | 13.0 | 5.0 | |
| SF-539 | 0.4 | −37.2 | −66.2 | −64.2 | |
| SNB-75 | −10.9 | −13.3 | −67.3 | −71.8 | |
| U251 | 15.8 | 7.6 | 0.8 | −9.5 | |
| Melanoma | LOX IMVI | 16.3 | 8.3 | 0.6 | 1.8 |
| MALME-3M | 30.6 | 44.8 | 40.2 | −6.2 | |
| M14 | 29.9 | 31.7 | 24.5 | 0.7 | |
| MDA-MB-435 | 21.0 | 18.5 | 21.1 | −0.8 | |
| SK-MEL-2 | 28.8 | −4.6 | −8.4 | −48.7 | |
| SK-MEL-28 | 16.0 | 0.8 | −2.4 | −17.2 | |
| SK-MEL-5 | 14.5 | −0.2 | 2.0 | 9.2 | |
| UACC-257 | 14.6 | −1.7 | 9.6 | −15.9 | |
| UACC-62 | −1.4 | −1.3 | 9.8 | −16.0 | |
| Ovarian Cancer | IGROV1 | 14.0 | 25.6 | 17.0 | 21.7 |
| OVCAR-3 | 5.6 | 3.4 | −7.0 | −2.1 | |
| OVCAR-4 | 23.8 | 32.3 | 34.7 | 19.5 | |
| OVCAR-5 | 37.8 | 18.1 | 5.3 | 8.7 | |
| OVCAR-8 | 14.0 | 9.7 | 10.7 | 6.3 | |
| NCI/ADR-RES | 72.9 | 58.4 | 42.1 | 29.7 | |
| SK-OV-3 | 27.0 | 2.1 | −7.0 | −10.3 | |
| Renal Cancer | 786-0 | 9.0 | 19.7 | 4.4 | 3.0 |
| A498 | −7.6 | −21.3 | −34.5 | −54.2 | |
| ACHN | 16.0 | −12.0 | −1.2 | 0.7 | |
| CAKI-1 | 37.4 | 54.8 | 30.2 | 20.6 | |
| RXF 393 | −20.2 | −30.1 | −41.3 | −39.3 | |
| SN12C | 15.9 | 33.5 | 24.0 | 12.6 | |
| TK-10 | 34.2 | 18.8 | 1.7 | −3.8 | |
| UO-31 | 25.2 | 36.6 | 3.1 | 7.5 | |
| Prostate Cancer | PC-3 | 25.9 | 19.2 | 12.6 | 2.3 |
| DU-145 | 20.7 | 15.3 | 12.7 | 9.9 | |
| Breast Cancer | MCF7 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 |
| MDA-MB-231 | 25.5 | 25.9 | 19.8 | 10.7 | |
| HS 578T | 8.8 | 8.8 | −15.0 | −15.1 | |
| BT-549 | −7.9 | 5.3 | −29.5 | −50.4 | |
| T-47D | 2.6 | −1.3 | −8.7 | −9.7 | |
| MDA-MB-468 | −14.5 | −2.1 | 1.0 | −34.7 |
 Positive values indicate percent cell growth and value zero (0) indicate no growth compared to concurrent DMSO treated control at 48 h, while negative values indicate cell death compared to time zero; Cell growth and cell line sensitivity scale.
Positive values indicate percent cell growth and value zero (0) indicate no growth compared to concurrent DMSO treated control at 48 h, while negative values indicate cell death compared to time zero; Cell growth and cell line sensitivity scale.Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kale, V.P.; Hengst, J.A.; Sharma, A.K.; Golla, U.; Dovat, S.; Amin, S.G.; Yun, J.K.; Desai, D.H. Characterization of Anticancer Effects of the Analogs of DJ4, a Novel Selective Inhibitor of ROCK and MRCK Kinases. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081060
Kale VP, Hengst JA, Sharma AK, Golla U, Dovat S, Amin SG, Yun JK, Desai DH. Characterization of Anticancer Effects of the Analogs of DJ4, a Novel Selective Inhibitor of ROCK and MRCK Kinases. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(8):1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081060
Chicago/Turabian StyleKale, Vijay Pralhad, Jeremy A. Hengst, Arati K. Sharma, Upendarrao Golla, Sinisa Dovat, Shantu G. Amin, Jong K. Yun, and Dhimant H. Desai. 2023. "Characterization of Anticancer Effects of the Analogs of DJ4, a Novel Selective Inhibitor of ROCK and MRCK Kinases" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 8: 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081060
APA StyleKale, V. P., Hengst, J. A., Sharma, A. K., Golla, U., Dovat, S., Amin, S. G., Yun, J. K., & Desai, D. H. (2023). Characterization of Anticancer Effects of the Analogs of DJ4, a Novel Selective Inhibitor of ROCK and MRCK Kinases. Pharmaceuticals, 16(8), 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16081060










