Gas6/Axl Axis Activation Dampens the Inflammatory Response in Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes and Synovial Explants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
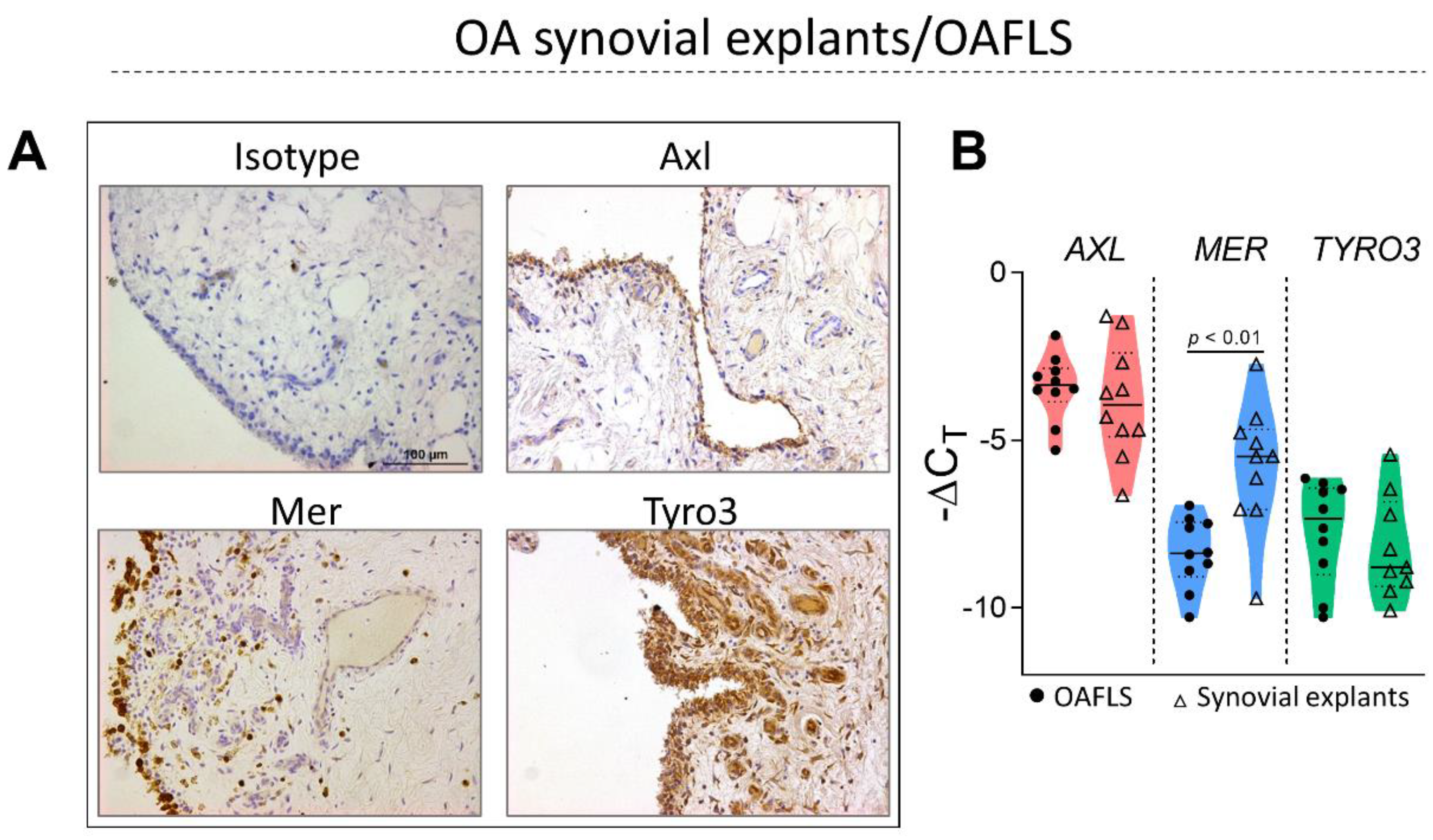
2.1. TAM Receptors Are Distinctively Expressed in OA Synovial Tissue
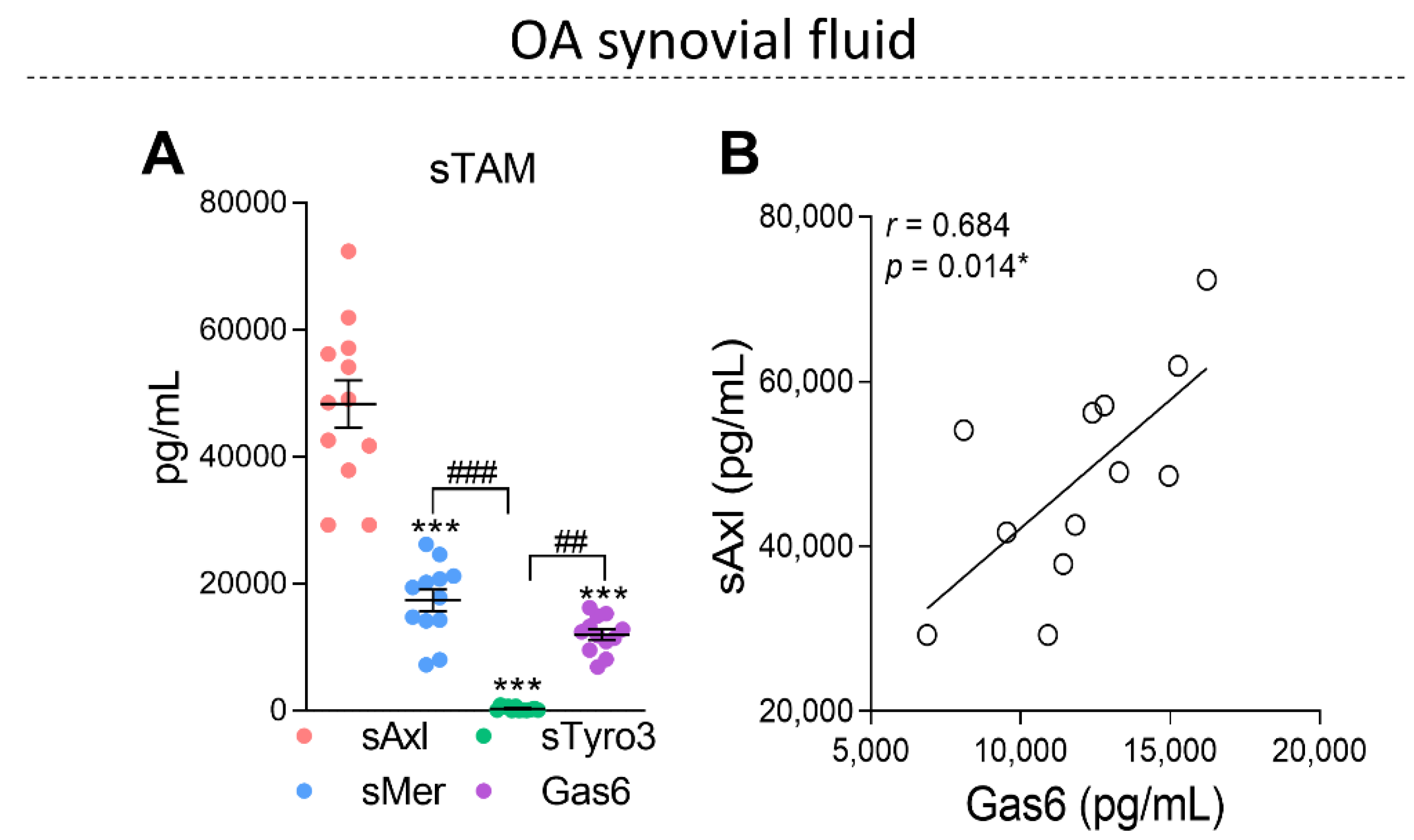
2.2. The Soluble Forms of TAM Receptors Are Present in OA Synovial Fluid with Higher Levels of sAxl
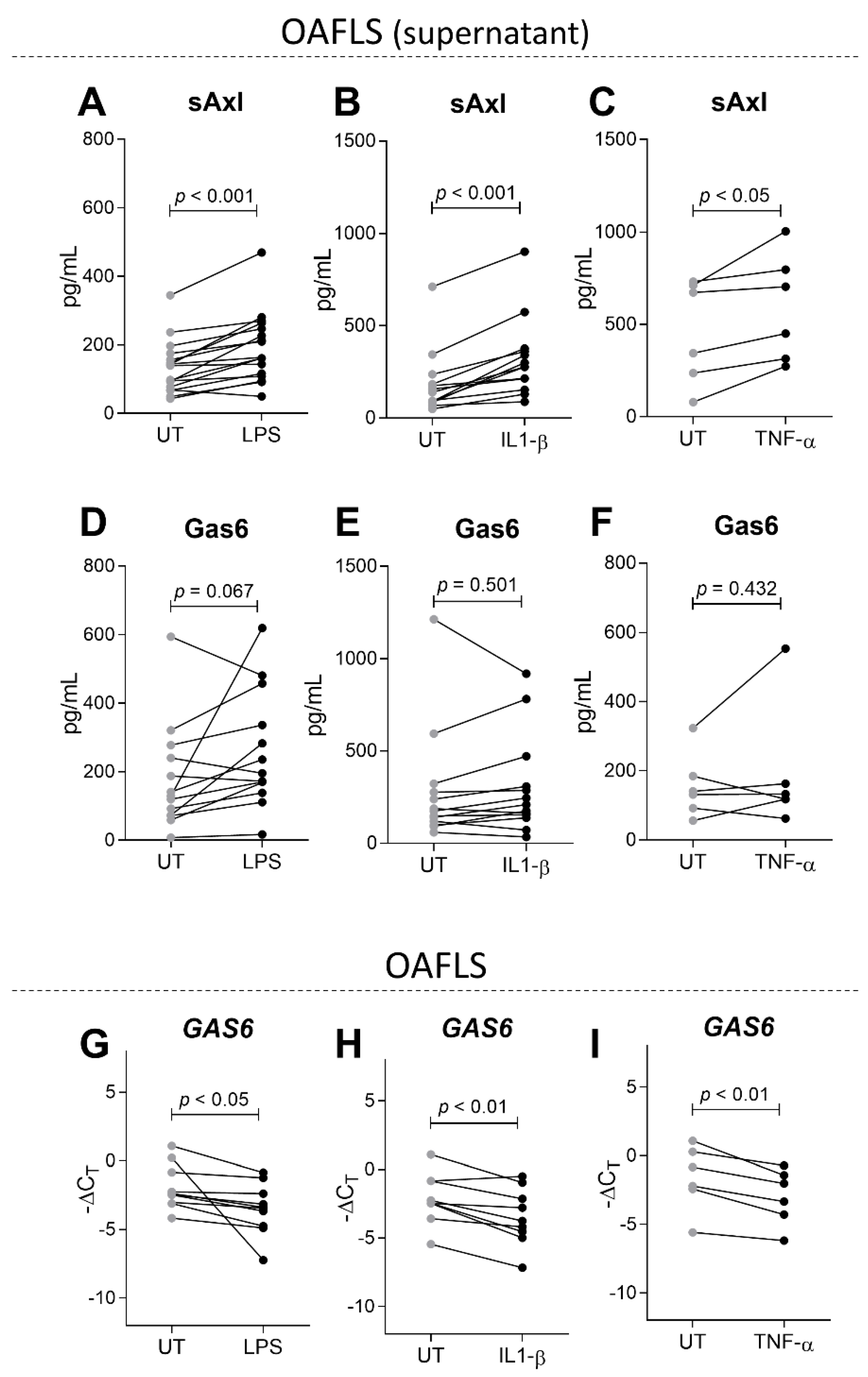
2.3. sAxl Is Increased in OAFLS Supernatants under Inflammatory Stimuli
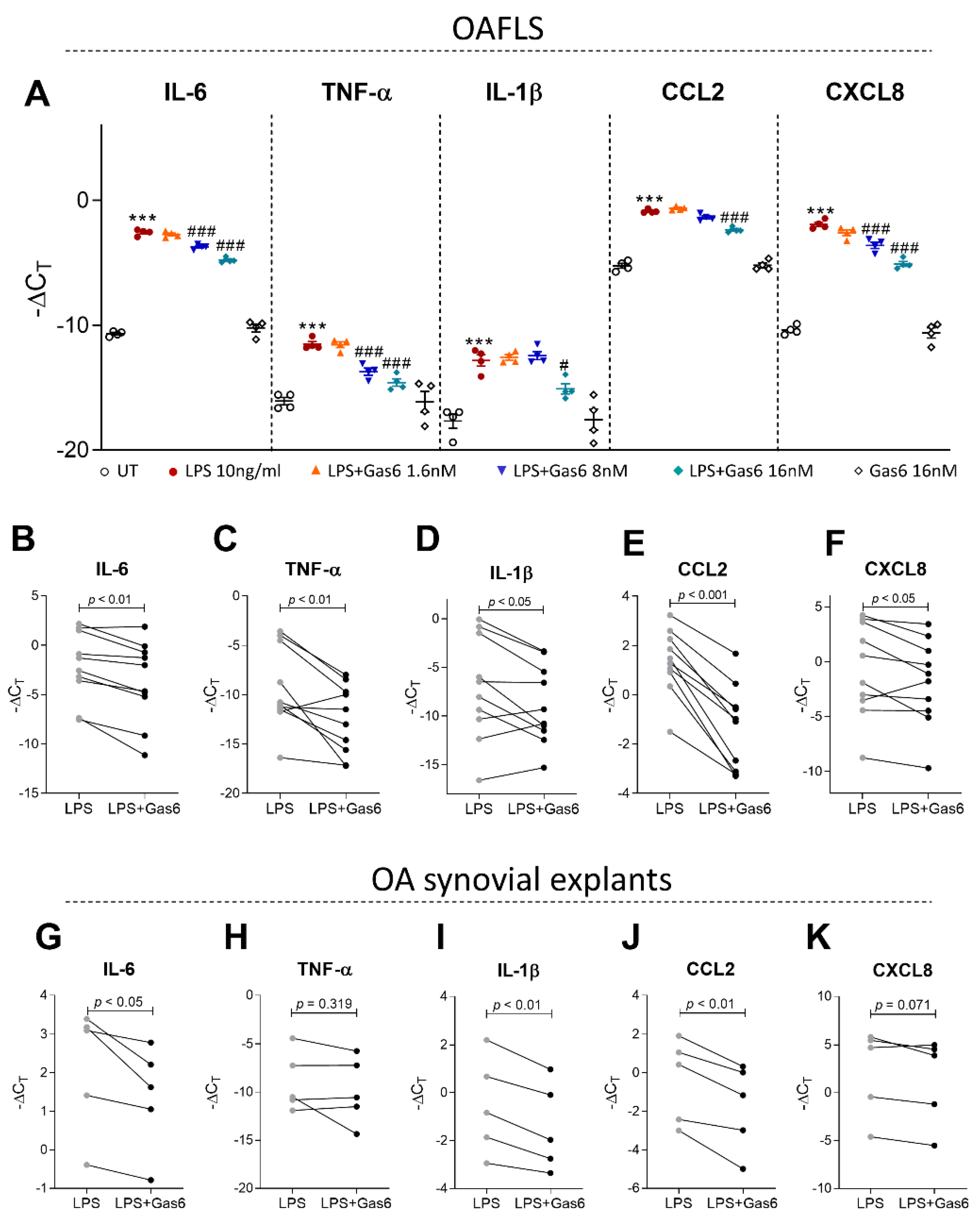
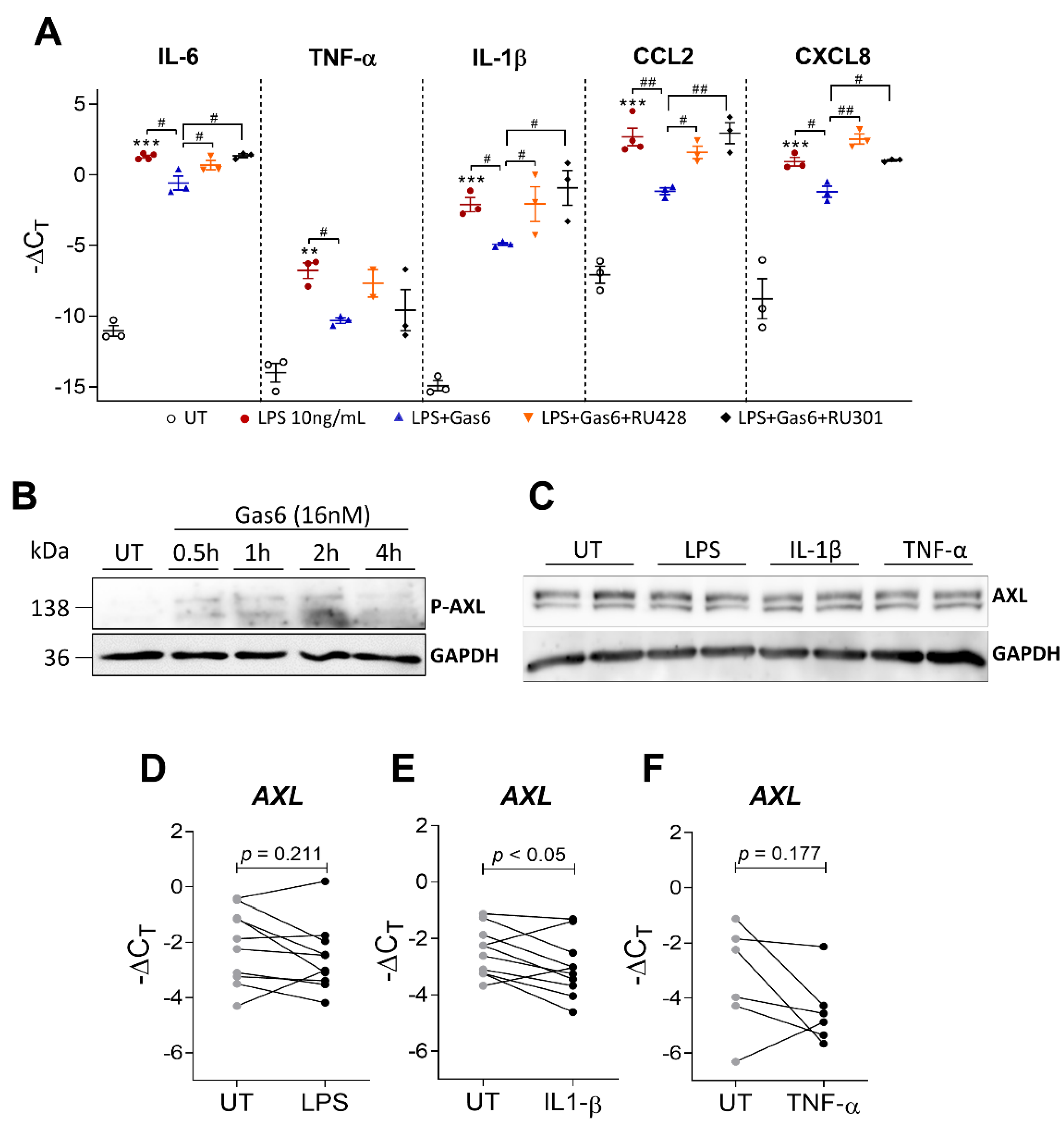
2.4. Activation of TAM Receptors by Gas6 Downregulates Pro-Inflammatory Markers in OAFLS and OA Synovial Explants
2.5. Gas6 Anti-Inflammatory Effects Are Dependent on Axl Receptor
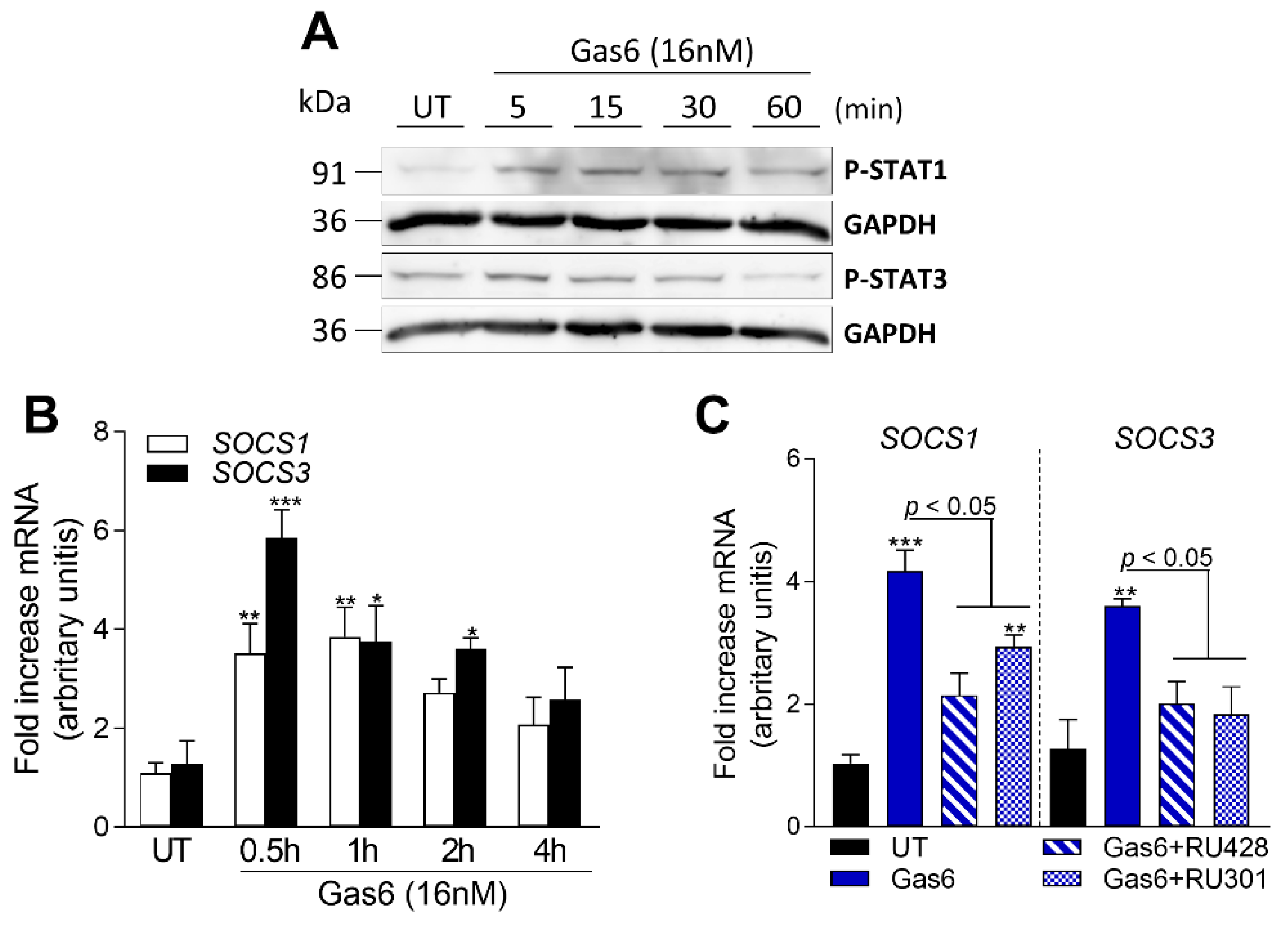
2.6. Gas6 Induces STAT-SOCS Signaling in OAFLS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Material
4.2. OA Fibroblast-like Synoviocyte and Synovial Explant Isolation
4.3. Synovial Fluid Preparation
4.4. Cloning and Lentivirus Production for Gas6 Overexpression
4.5. Gas6-Conditioned Medium
4.6. OAFLS and Synovial Explant Stimulation and Treatments
4.7. qPCR Analysis
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. ELISA
4.10. Measurement of Cytokines by Multiplex ELISA
4.11. Immunohistochemistry
4.12. Efferocytosis Assay
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loeser, R.F.; Goldring, S.R.; Scanzello, C.R.; Goldring, M.B. Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Bryan, R.; Terkeltaub, R. Emerging regulators of the inflammatory process in osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellam, J.; Berenbaum, F. The role of synovitis in pathophysiology and clinical symptoms of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanzello, C.R.; Goldring, S.R. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone 2012, 51, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanzello, C.R.; Plaas, A.; Crow, M.K. Innate immune system activation in osteoarthritis: Is osteoarthritis a chronic wound? Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2008, 20, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanzello, C.R. Chemokines and inflammation in osteoarthritis: Insights from patients and animal models. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 35, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bosch, M.H.J.; van Lent, P.; van der Kraan, P.M. Identifying effector molecules, cells, and cytokines of innate immunity in OA. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2020, 28, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, M.; Nam, J. The role of changes in extracellular matrix of cartilage in the presence of inflammation on the pathology of osteoarthritis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 284873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, G. Biology of the TAM receptors. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a009076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, E.D.; Oh, J.; Burrola, P.G.; Lax, I.; Zagorska, A.; Traves, P.G.; Schlessinger, J.; Lemke, G. Differential TAM receptor-ligand-phospholipid interactions delimit differential TAM bioactivities. eLife 2014, 3, e03385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Yan, K.; Han, D. Toll-like receptor-mediated inhibition of Gas6 and ProS expression facilitates inflammatory cytokine production in mouse macrophages. Immunology 2012, 135, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothlin, C.V.; Ghosh, S.; Zuniga, E.I.; Oldstone, M.B.; Lemke, G. TAM receptors are pleiotropic inhibitors of the innate immune response. Cell 2007, 131, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.; Hedl, M.; Abraham, C. TAM receptor-dependent regulation of SOCS3 and MAPKs contributes to proinflammatory cytokine downregulation following chronic NOD2 stimulation of human macrophages. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1928–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vago, J.P.; Amaral, F.A.; van de Loo, F.A.J. Resolving inflammation by TAM receptor activation. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 227, 107893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, S.; Bellan, M.; Mauro, D.; Castello, L.M.; Avanzi, G.C.; Lewis, M.J.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Pitzalis, C.; Nerviani, A. New Insights into the Role of Tyro3, Axl, and Mer Receptors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Dis. Markers 2020, 2020, 1614627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vullings, J.; Vago, J.P.; Waterborg, C.E.J.; Thurlings, R.M.; Koenders, M.I.; van Lent, P.; van der Kraan, P.M.; Amaral, F.A.; van de Loo, F.A.J. Selective Increment of Synovial Soluble TYRO3 Correlates with Disease Severity and Joint Inflammation in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 9690832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, K.; Harkes, I.C.; Dougherty, L.; Wicks, I.P. Expression of receptor tyrosine kinase Axl and its ligand Gas6 in rheumatoid arthritis: Evidence for a novel endothelial cell survival pathway. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassyouni, I.H.; El-Wakd, M.M.; Azab, N.A.; Bassyouni, R.H. Diminished soluble levels of growth arrest specific protein 6 and tyrosine kinase receptor Axl in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 20, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Bryan, J.P.; Fridell, Y.W.; Koski, R.; Varnum, B.; Liu, E.T. The transforming receptor tyrosine kinase, Axl, is post-translationally regulated by proteolytic cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekman, C.; Stenhoff, J.; Dahlback, B. Gas6 is complexed to the soluble tyrosine kinase receptor Axl in human blood. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhenghai, S. Increased serum AXL is associated with radiographic knee osteoarthritis severity. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 25, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, M.; Balakrishnan, L.; Renuse, S.; Advani, J.; Goel, R.; Sathe, G.; Keshava Prasad, T.S.; Nair, B.; Jois, R.; Shankar, S.; et al. Synovial fluid proteome in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Proteom. 2016, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Brand, B.T.; Abdollahi-Roodsaz, S.; Vermeij, E.A.; Bennink, M.B.; Arntz, O.J.; Rothlin, C.V.; van den Berg, W.B.; van de Loo, F.A. Therapeutic efficacy of Tyro3, Axl, and Mer tyrosine kinase agonists in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterborg, C.E.J.; Broeren, M.G.A.; Blaney Davidson, E.N.; Koenders, M.I.; van Lent, P.; van den Berg, W.B.; van der Kraan, P.M.; van de Loo, F.A.J. The level of synovial AXL expression determines the outcome of inflammatory arthritis, possibly depending on the upstream role of TGF-beta1. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterborg, C.E.J.; Koenders, M.I.; van Lent, P.; van der Kraan, P.M.; van de Loo, F.A.J. Tyro3/Axl/Mertk-deficient mice develop bone marrow edema which is an early pathological marker in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterborg, C.E.J.; Beermann, S.; Broeren, M.G.A.; Bennink, M.B.; Koenders, M.I.; van Lent, P.; van den Berg, W.B.; van der Kraan, P.M.; van de Loo, F.A.J. Protective Role of the MER Tyrosine Kinase via Efferocytosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis Models. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorp, E.; Vaisar, T.; Subramanian, M.; Mautner, L.; Blobel, C.; Tabas, I. Shedding of the Mer tyrosine kinase receptor is mediated by ADAM17 protein through a pathway involving reactive oxygen species, protein kinase Cdelta, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 33335–33344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothlin, C.V.; Carrera-Silva, E.A.; Bosurgi, L.; Ghosh, S. TAM receptor signaling in immune homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 355–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Deng, T.; Zhang, Y.; Su, S.; Wei, C.; Han, D. Lipopolysaccharide inhibits macrophage phagocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils by regulating the production of tumour necrosis factor alpha and growth arrest-specific gene 6. Immunology 2011, 132, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Happonen, K.E.; Tran, S.; Morgelin, M.; Prince, R.; Calzavarini, S.; Angelillo-Scherrer, A.; Dahlback, B. The Gas6-Axl Protein Interaction Mediates Endothelial Uptake of Platelet Microparticles. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 10586–10601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, K.; Kumar, S.; Kimani, S.G.; Kholodovych, V.; Kasikara, C.; Mizuno, K.; Sandiford, O.; Rameshwar, P.; Kotenko, S.V.; Birge, R.B. Requirement of Gamma-Carboxyglutamic Acid Modification and Phosphatidylserine Binding for the Activation of Tyro3, Axl, and Mertk Receptors by Growth Arrest-Specific 6. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsou, W.I.; Nguyen, K.Q.; Calarese, D.A.; Garforth, S.J.; Antes, A.L.; Smirnov, S.V.; Almo, S.C.; Birge, R.B.; Kotenko, S.V. Receptor tyrosine kinases, TYRO3, AXL, and MER, demonstrate distinct patterns and complex regulation of ligand-induced activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 25750–25763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, S.G.; Kumar, S.; Bansal, N.; Singh, K.; Kholodovych, V.; Comollo, T.; Peng, Y.; Kotenko, S.V.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Bertino, J.R.; et al. Small molecule inhibitors block Gas6-inducible TAM activation and tumorigenicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Chen, X.Q.; Gao, M.J.; Lee, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, Y.F.; Wang, G.D. The Pros1/Tyro3 axis protects against periodontitis by modulating STAT/SOCS signalling. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 2769–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.K.; Wu, C.P.; Lin, J.Y.; Peng, S.C.; Lee, C.H.; Huang, K.L.; Shen, C.H. Gas6/Axl signaling attenuates alveolar inflammation in ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute lung injury by up-regulating SOCS3-mediated pathway. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, D.L.; Hilton, D.J. SOCS proteins: Negative regulators of cytokine signaling. Stem Cells 2001, 19, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culemann, S.; Gruneboom, A.; Nicolas-Avila, J.A.; Weidner, D.; Lammle, K.F.; Rothe, T.; Quintana, J.A.; Kirchner, P.; Krljanac, B.; Eberhardt, M.; et al. Locally renewing resident synovial macrophages provide a protective barrier for the joint. Nature 2019, 572, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wei, K.; Slowikowski, K.; Fonseka, C.Y.; Rao, D.A.; Kelly, S.; Goodman, S.M.; Tabechian, D.; Hughes, L.B.; Salomon-Escoto, K.; et al. Defining inflammatory cell states in rheumatoid arthritis joint synovial tissues by integrating single-cell transcriptomics and mass cytometry. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alivernini, S.; MacDonald, L.; Elmesmari, A.; Finlay, S.; Tolusso, B.; Gigante, M.R.; Petricca, L.; Di Mario, C.; Bui, L.; Perniola, S.; et al. Distinct synovial tissue macrophage subsets regulate inflammation and remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sather, S.; Kenyon, K.D.; Lefkowitz, J.B.; Liang, X.; Varnum, B.C.; Henson, P.M.; Graham, D.K. A soluble form of the Mer receptor tyrosine kinase inhibits macrophage clearance of apoptotic cells and platelet aggregation. Blood 2007, 109, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Eisenman, J.R.; Mahimkar, R.M.; Peschon, J.J.; Paxton, R.J.; Black, R.A.; Johnson, R.S. A proteomic approach for the identification of cell-surface proteins shed by metalloproteases. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2002, 1, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekman, C.; Gottsater, A.; Lindblad, B.; Dahlback, B. Plasma concentrations of Gas6 and soluble Axl correlate with disease and predict mortality in patients with critical limb ischemia. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 43, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flem-Karlsen, K.; Nyakas, M.; Farstad, I.N.; McFadden, E.; Wernhoff, P.; Jacobsen, K.D.; Florenes, V.A.; Maelandsmo, G.M. Soluble AXL as a marker of disease progression and survival in melanoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staufer, K.; Dengler, M.; Huber, H.; Marculescu, R.; Stauber, R.; Lackner, C.; Dienes, H.P.; Kivaranovic, D.; Schachner, C.; Zeitlinger, M.; et al. The non-invasive serum biomarker soluble Axl accurately detects advanced liver fibrosis and cirrhosis. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengler, M.; Staufer, K.; Huber, H.; Stauber, R.; Bantel, H.; Weiss, K.H.; Starlinger, P.; Pock, H.; Kloters-Plachky, P.; Gotthardt, D.N.; et al. Soluble Axl is an accurate biomarker of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma development: Results from a large scale multicenter analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 46234–46248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, S.; Zhou, S.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, L.; Wang, T.; Zhou, R. Elevated Levels of Soluble Axl (sAxl) Regulates Key Angiogenic Molecules to Induce Placental Endothelial Dysfunction and a Preeclampsia-Like Phenotype. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 619137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinger, J.G.; Omari, K.M.; Marsden, K.; Raine, C.S.; Shafit-Zagardo, B. Up-regulation of soluble Axl and Mer receptor tyrosine kinases negatively correlates with Gas6 in established multiple sclerosis lesions. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Heiland, G.; Zhao, Y.; Derer, A.; Braun, T.; Engelke, K.; Neumann, E.; Mueller-Ladner, U.; Liu, Y.; Zwerina, J.; Schett, G. Deletion of the receptor tyrosine kinase Tyro3 inhibits synovial hyperplasia and bone damage in arthritis. Ann. Rheum Dis 2014, 73, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Lajeunesse, D.; Pelletier, J.P.; Fahmi, H. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldring, M.B.; Otero, M.; Tsuchimochi, K.; Ijiri, K.; Li, Y. Defining the roles of inflammatory and anabolic cytokines in cartilage metabolism. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67 (Suppl. 3), iii75–iii82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, V.B.; McDaniel, G.; Huebner, J.L.; Stabler, T.V.; Pieper, C.F.; Shipes, S.W.; Petry, N.A.; Low, P.S.; Shen, J.; McNearney, T.A.; et al. Direct in vivo evidence of activated macrophages in human osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Guo, S.; Cong, H.; Liu, L. Analysis on the expression and value of CCL2 and CCL3 in patients with osteoarthritis. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2021, 118, 104576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, R.M.; Bliddal, H.; Blanco, F.J.; Schnitzer, T.J.; Peterfy, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Feng, S.; Conaghan, P.G.; Berenbaum, F.; et al. A Phase II Trial of Lutikizumab, an Anti-Interleukin-1alpha/beta Dual Variable Domain Immunoglobulin, in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients with Synovitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksymowych, W.P.; Russell, A.S.; Chiu, P.; Yan, A.; Jones, N.; Clare, T.; Lambert, R.G. Targeting tumour necrosis factor alleviates signs and symptoms of inflammatory osteoarthritis of the knee. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, X.; Goupille, P.; Beaulieu, A.D.; Burch, F.X.; Bensen, W.G.; Conrozier, T.; Loeuille, D.; Kivitz, A.J.; Silver, D.; Appleton, B.E. Intraarticular injection of anakinra in osteoarthritis of the knee: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, S.J.; Pan, A.; Franci, C.; Hu, Y.; Chang, B.; Li, W.; Duan, M.; Torneros, A.; Yu, J.; Heckrodt, T.J.; et al. R428, a selective small molecule inhibitor of Axl kinase, blocks tumor spread and prolongs survival in models of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1544–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| IL-6 | CCL2 | TNF-α | IL-1β | CXCL8 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | |
| Gas6 | −0.401 | 0.250 | 0.359 | 0.252 | 0.444 | 0.199 | 0.093 | 0.826 | −0.314 | 0.378 |
| sAxl | −0.241 | 0.503 | 0.266 | 0.404 | 0.616 | 0.058 | −0.026 | 0.952 | −0.114 | 0.753 |
| sMer | −0.440 | 0.204 | 0.115 | 0.772 | −0.110 | 0.762 | −0.267 | 0.523 | −0.470 | 0.170 |
| sTyro3 | −0.245 | 0.500 | −0.485 | 0.110 | −0.369 | 0.294 | −0.613 | 0.106 | −0.007 | 0.984 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vago, J.P.; Valdrighi, N.; Blaney-Davidson, E.N.; Hornikx, D.L.A.H.; Neefjes, M.; Barba-Sarasua, M.E.; Thielen, N.G.M.; van den Bosch, M.H.J.; van der Kraan, P.M.; Koenders, M.I.; et al. Gas6/Axl Axis Activation Dampens the Inflammatory Response in Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes and Synovial Explants. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050703
Vago JP, Valdrighi N, Blaney-Davidson EN, Hornikx DLAH, Neefjes M, Barba-Sarasua ME, Thielen NGM, van den Bosch MHJ, van der Kraan PM, Koenders MI, et al. Gas6/Axl Axis Activation Dampens the Inflammatory Response in Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes and Synovial Explants. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(5):703. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050703
Chicago/Turabian StyleVago, Juliana P., Natália Valdrighi, Esmeralda N. Blaney-Davidson, Daniel L. A. H. Hornikx, Margot Neefjes, María E. Barba-Sarasua, Nathalie G. M. Thielen, Martijn H. J. van den Bosch, Peter M. van der Kraan, Marije I. Koenders, and et al. 2023. "Gas6/Axl Axis Activation Dampens the Inflammatory Response in Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes and Synovial Explants" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 5: 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050703
APA StyleVago, J. P., Valdrighi, N., Blaney-Davidson, E. N., Hornikx, D. L. A. H., Neefjes, M., Barba-Sarasua, M. E., Thielen, N. G. M., van den Bosch, M. H. J., van der Kraan, P. M., Koenders, M. I., Amaral, F. A., & van de Loo, F. A. J. (2023). Gas6/Axl Axis Activation Dampens the Inflammatory Response in Osteoarthritic Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes and Synovial Explants. Pharmaceuticals, 16(5), 703. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050703







