Exploring the Association between Citrus Nutraceutical Eriocitrin and Metformin for Improving Pre-Diabetes in a Dynamic Microbiome Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
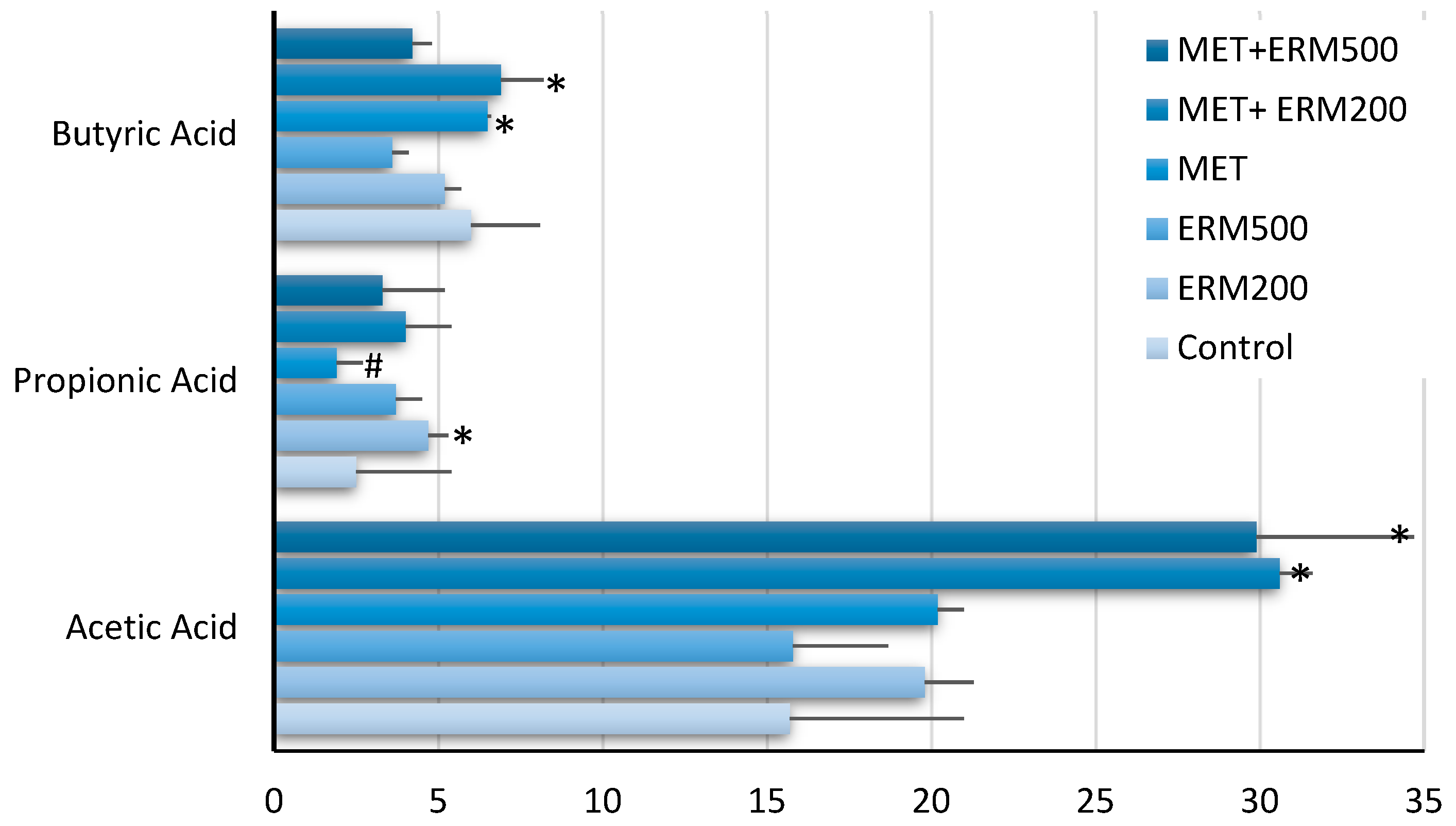
2.1. Effect of Eriomin® Combined with Metformin on Short-Chain Fatty Acid (SCFAs) Production by the Gut Microbiome
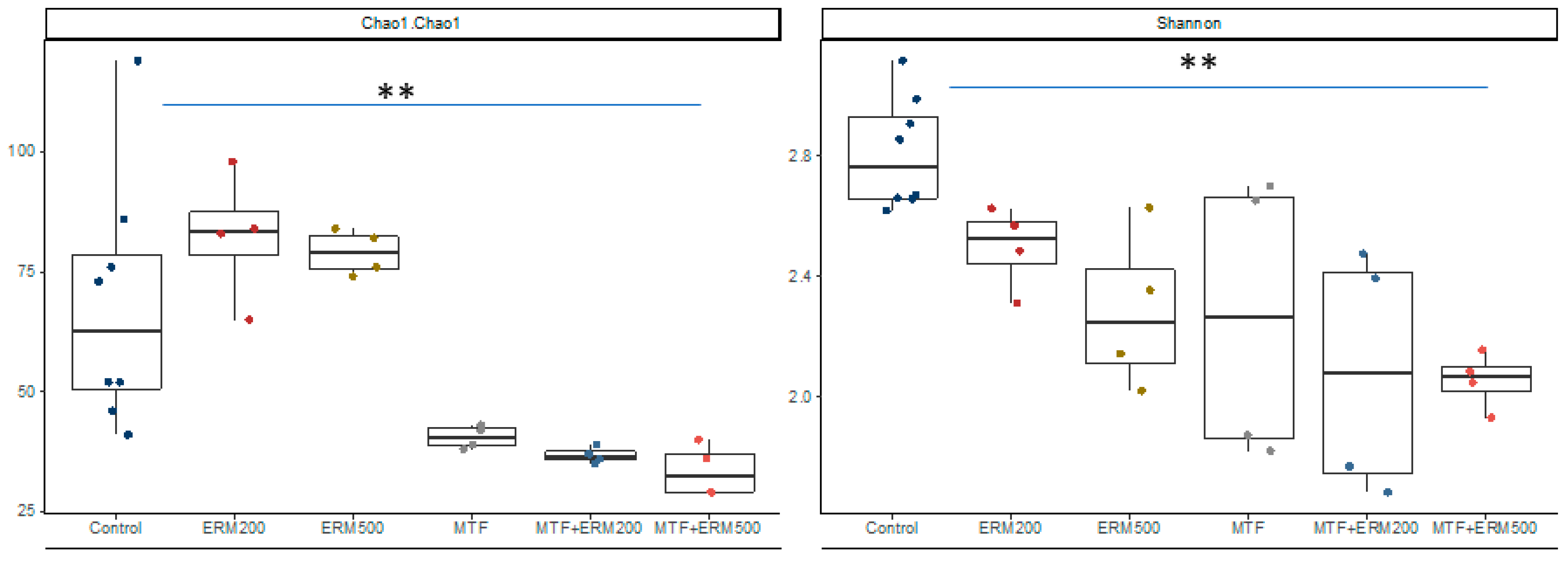
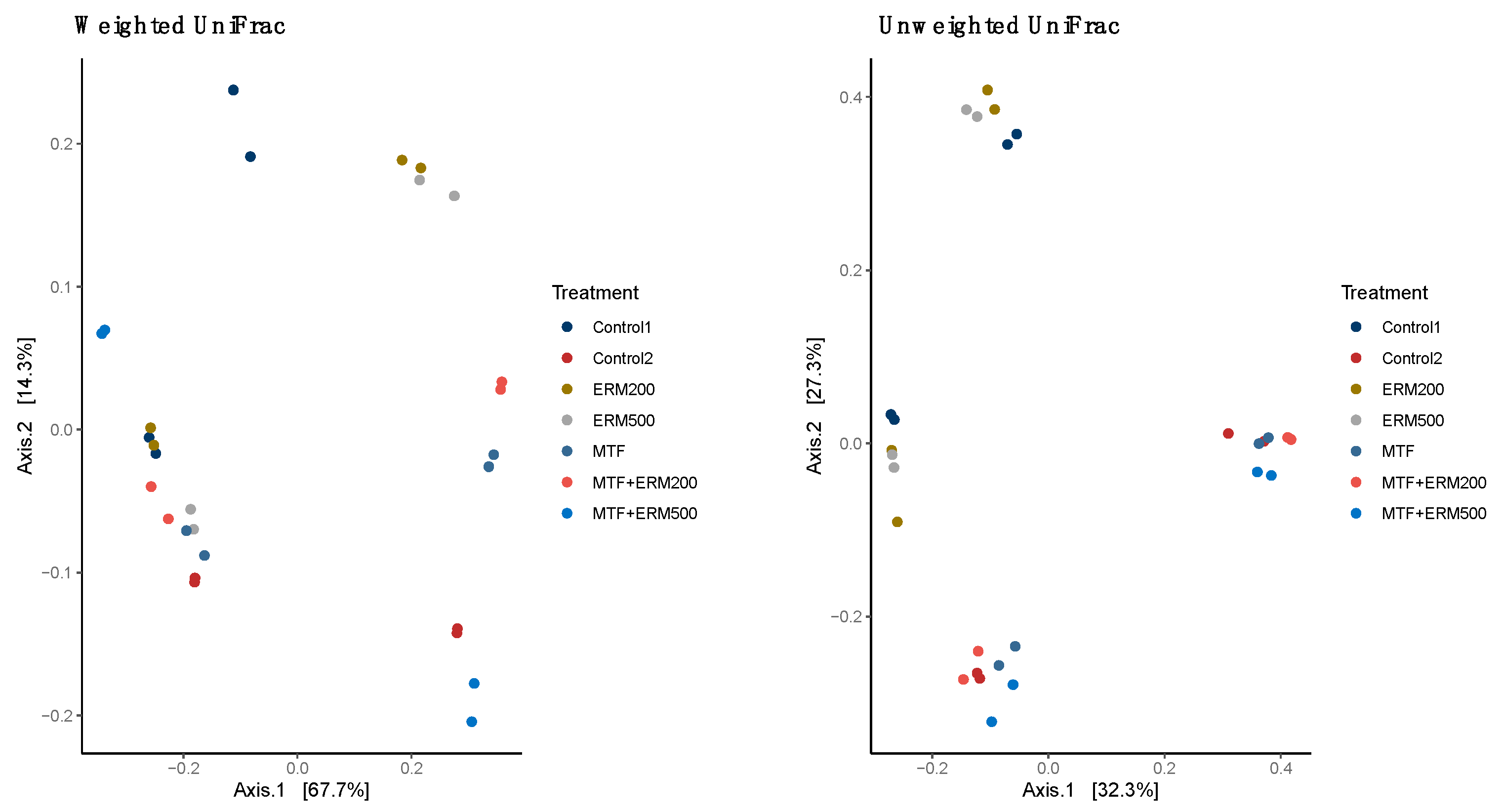
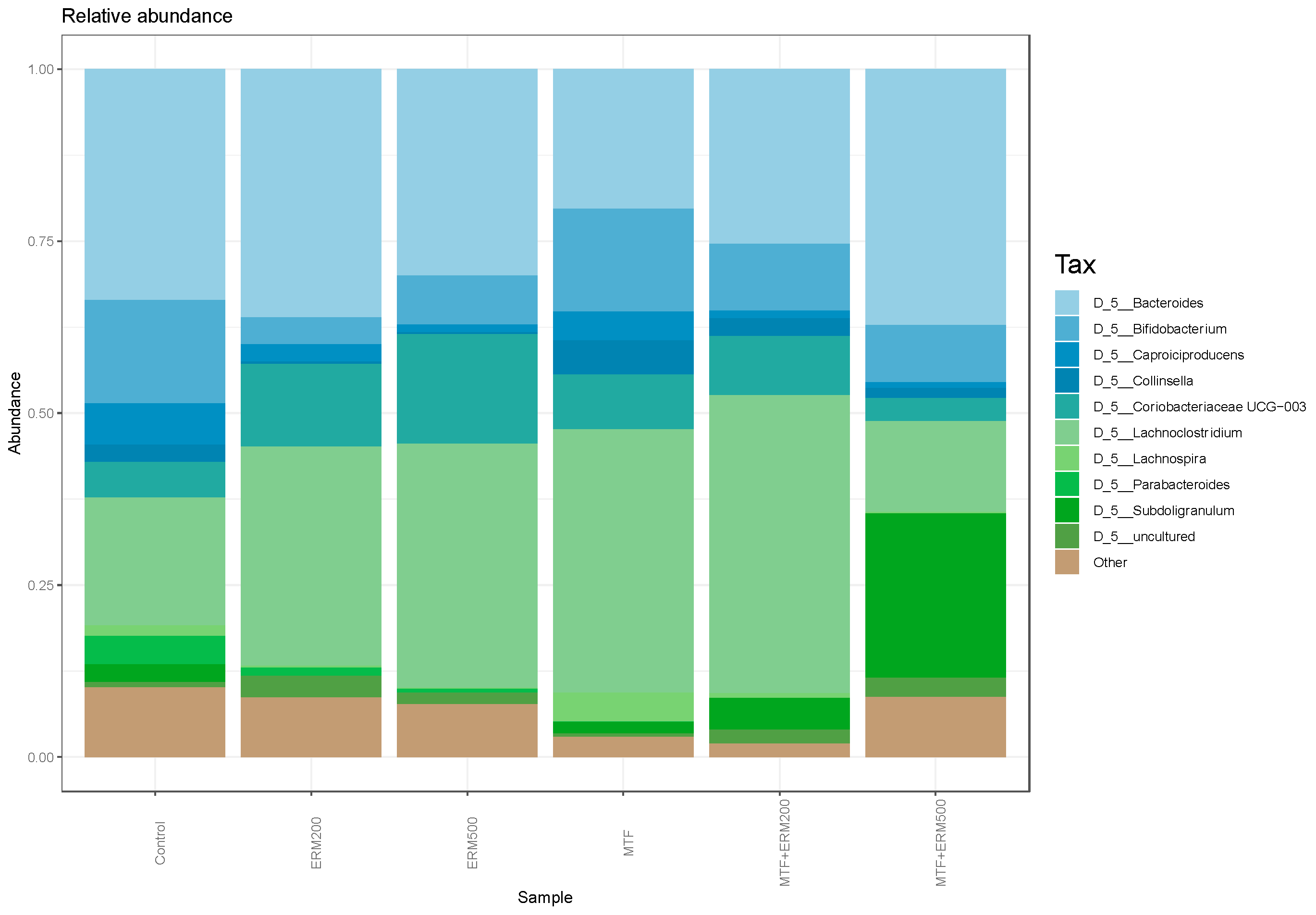
2.2. Effects of Eriomin® Combined with Metformin on the Gut Microbial Composition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Simulated Digestion in the Dynamic Microbiome Model
4.2. Experimental Protocol
- ERM200: Microbiota treated with Eriomin® (200 mg/d) for seven days;
- ERM500: Microbiota treated with Eriomin® (500 mg/d) for seven days;
- MTF: Microbiota treated with metformin (500 mg/d) for seven days;
- MTF + ERM200: Microbiota treated with metformin (500 mg/d) + Eriomin® (200 mg/d) for seven days;
- MTF + ERM500: Microbiota treated with metformin (500 mg/d) + Eriomin® (500 mg/d) for seven days.
4.3. Microbial Metabolites Analysis
4.4. Microbiological Analysis Employing 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46 (Suppl. 1), S19–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garber, A.J.; Duncan, T.G.; Goodman, A.M.; Mills, D.J.; Rohlf, J.L. Efficacy of metformin in type II diabetes: Results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response trial. Am. J. Med. 1997, 103, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H. Metformin: Current clinical applications in nondiabetic patients with cancer. Aging 2020, 12, 3993–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flory, J.; Lipska, K. Metformin in 2019. JAMA 2019, 321, 1926–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, C.B.; Ramos, F.M.; Manthey, J.A.; Cesar, T.B. Effectiveness of Eriomin® in managing hyperglycemia and reversal of prediabetes condition: A double-blind, randomized, controlled study. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 1921–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesar, T.B.; Ramos, F.M.M.; Ribeiro, C.B. Nutraceutical Eriocitrin (Eriomin) Reduces Hyperglycemia by Increasing Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 and Downregulates Systemic Inflammation: A Crossover-Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Med. Food 2022, 25, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baky, M.H.; Elshahed, M.; Wessjohann, L.; Farag, M.A. Interactions between dietary flavonoids and the gut microbiome: A comprehensive review. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 128, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, M.N.; Kim, M.; Bennett, B.J. Modulating the Microbiota as a Therapeutic Intervention for Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 632335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, M.; Li, Z.; You, H.; Rodrigues, R.; Jump, D.B.; Morgun, A.; Shulzhenko, N. Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. EBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenman, L.K.; Waget, A.; Garret, C.; Briand, F.; Burcelin, R.; Sulpice, T.; Lahtinen, S. Probiotic B420 and prebiotic polydextrose improve efficacy of antidiabetic drugs in mice. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2015, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 2021, 44 (Suppl. 1), S15–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, X.; Wu, H.; Xiong, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Gu, Q.; Li, P. Metabolism of eriocitrin in the gut and its regulation on gut microbiota in mice. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1111200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanna, S.; van Zuydam, N.R.; Mahajan, A.; Kurilshikov, A.; Vich Vila, A.; Võsa, U.; Mujagic, Z.; Masclee, A.A.M.; Jonkers, D.M.A.E.; Oosting, M.; et al. Causal relationships among the gut microbiome, short-chain fatty acids and metabolic diseases. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, M.A.G.; Canfora, E.E.; Jocken, J.W.E.; Blaak, E.E. The Short-Chain Fatty Acid Acetate in Body Weight Control and Insulin Sensitivity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikalidis, A.K.; Maykish, A. The Gut Microbiome and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Discussing a Complex Relationship. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniar, K.; Moideen, A.; Mittal, A.; Patil, A.; Chakrabarti, A.; Banerjee, D. A story of metformin-butyrate synergism to control various pathological conditions as a consequence of gut microbiome modification: Genesis of a wonder drug? Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 117, 103–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buse, J.B.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Rosenstock, J.; Kim, T.; Burns, C.; Skare, S.; Baron, A.; Fineman, M. The Primary Glucose-Lowering Effect of Metformin Resides in the Gut, Not the Circulation: Results From Short-term Pharmacokinetic and 12-Week Dose-Ranging Studies. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chu, J.; Hao, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Yang, C.; Yang, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, H. Gut Microbiota and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Association, Mechanism, and Translational Applications. Mediators Inflamm. 2021, 2021, 5110276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.R.; Zhao, L.Y.; Zhu, F.R.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, J.Y.; Chen, Z.C.; Lv, X.C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, B. Anti-Diabetic Effects of Ethanol Extract from Sanghuangporous vaninii in High-Fat/Sucrose Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice by Modulating Gut Microbiota. Foods 2022, 11, 974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, E.; DeLong, E.F.; Lory, S.; Stackebrandt, E.; Thompson, F. (Eds.) The Prokaryotes: Actinobacteria; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez, I.; Perdicaro, D.J.; Brown, A.W.; Hammons, S.; Carden, T.J.; Carr, T.P.; Eskridge, K.M.; Walter, J. Diet-induced alterations of host cholesterol metabolism are likely to affect the gut microbiota composition in hamsters. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Mao, B.; Gu, J.; Wu, J.; Cui, S.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Blautia—A new functional genus with potential probiotic properties? Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.Y.; Lu, H.C.; Chou, Y.H.; Liu, P.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Huang, M.C.; Lin, C.H.; Tsai, C.N. Gut Microbial Signatures for Glycemic Responses of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetic Patients: A Pilot Study. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 814770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, H.; Saier, M.H., Jr. Gut Bacteroides species in health and disease. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Ryu, S.; Fukuda, S.; Hase, K.; Yang, C.S.; Lim, H.S.; Kim, M.S.; et al. Gut commensal Bacteroides acidifaciens prevents obesity and improves insulin sensitivity in mice. Mucosal Immunol. 2017, 10, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, P.G.; Santacruz, A.; Moya, Á.; Sanz, Y. Bacteroides uniformis CECT 7771 ameliorates metabolic and immunological dysfunction in mice with high-fat-diet induced obesity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41079. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, J.; Kubota, T.; Takada, E.; Takai, K.; Fujiwara, N.; Arimitsu, N.; Murayama, M.A.; Ueda, Y.; Wakisaka, S.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Propionate-producing bacteria in the intestine may associate with skewed responses of IL10-producing regulatory T cells in patients with relapsing polychondritis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaakoush, N.O.; Day, A.S.; Huinao, K.D.; Leach, S.T.; Lemberg, D.A.; Dowd, S.E.; Mitchell, H.M. Microbial dysbiosis in pediatric patients with Crohn’s disease. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3258–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hul, M.; Le Roy, T.; Prifti, E.; Dao, M.C.; Paquot, A.; Zucker, J.D.; Delzenne, N.M.; Muccioli, G.; Clément, K.; Cani, P.D. From correlation to causality: The case of Subdoligranulum. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1849998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, N.T.; Differding, M.K.; Zhang, M.; Maruthur, N.M.; Juraschek, S.P.; Miller, E.R.; Appel, L.J., 3rd; Yeh, H.C. Metformin Affects Gut Microbiome Composition and Function and Circulating Short-Chain Fatty Acids: A Randomized Trial. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, J.H.; Yu, T.; Chen, Q.K. Effects of berberine and metformin on intestinal inflammation and gut microbiome composition in db/db mice. Biomed. Pharmacother 2019, 118, 109131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, S.; Razazan, A.; Nagpal, R.; Jain, S.; Wang, B.; Mishra, S.P.; Wang, S.; Justice, J.; Ding, J.; McClain, D.A.; et al. Metformin Reduces Aging-Related Leaky Gut and Improves Cognitive Function by Beneficially Modulating Gut Microbiome/Goblet Cell/Mucin Axis. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. J 2020, 75, e9–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.S.; Manthey, J.A.; Nery, M.S.; Spolidorio, L.C.; Cesar, T.B. Low doses of eriocitrin attenuate metabolic impairment of glucose and lipids in ongoing obesogenic diet in mice. J. Nutr. Sci. 2020, 9, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, T.R.; Salgaço, M.K.; Adorno, M.A.T.; Silva, M.A.; Piazza, R.M.F.; Sivieri, K.; Moreira, C.G. Human microbiota modulation via QseC sensor kinase mediated in the Escherichia coli O104:H4 outbreak strain infection in microbiome model. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgaço, M.K.; Perina, N.P.; Tomé, T.M.; Mosquera, E.M.B.; Lazarini, T.; Sartoratto, A.; Sivieri, K. Probiotic infant cereal improves children’s gut microbiota: Insights using the Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME®). Food Res. Int. 2021, 143, 110292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possemiers, S.; Verthé, K.; Uyttendale, S.; Verstraete, W. PCR-DGGE-based quantification of stability of the microbial community in a simulator of the human intestinal microbial ecosystem. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 49, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molly, K.; Woestyne, M.V.; Smet, I.; Verstraete, W. Validation of the Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME) Reactor Using Microorganism-associated Activities. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 1994, 7, 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, N.M.; Oliveira, D.L.; Saleh, M.A.D.; Pintado, M.; Madureira, A.R. Preservation of human gut microbial inoculums for in vitro fermentation studies. Fermentation 2021, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.; Larsen, N.; Tieghi, T.M.; Adorno, M.A.T.; Kot, W.; Saad, S.M.I.; Jespersen, L.; Sivieri, K. Modulation of gut microbiota from obese individuals by in vitro fermentation of citrus pectin in combination with Bifidobacterium longum BB-46. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 8827–8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostal, A.; Baumgartner, J.; Riesen, N.; Chassard, C.; Smuts, C.M.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Lacroix, C. Effects of iron supplementation on dominant bacterial groups on the gut, faecal SCFA and gut inflammation: Arandomised, placebo-controlled intervention trial in South African children. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iturbe-Espinoza, P.; Brandt, B.W.; Braster, M.; Bonte, M.; Brown, D.M.; van Spanning, R.J.M. Effects of DNA preservation solution and DNA extraction methods on microbial community profiling of soil. Folia Microbiol. 2021, 66, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Walters, W.A.; González, A.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R. Using QIIME to analyze 16S rRNA gene sequences from microbial communities. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2011, 36, 10.7.1–10.7.20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagerty, S.L.; Hutchison, K.E.; Lowry, C.A.; Bryan, A.D. An empirically derived method for measuring human gut microbiome alpha diversity: Demonstrated utility in predicting health-related outcomes among a human clinical sample. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Compunting: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.r-project.org (accessed on 17 January 2023).
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S.; Watson, M. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fierer, N.; Lauber, C.L.; Zhou, N.; McDonald, D.; Costello, E.K.; Knight, R. Forensic identification using skin bacterial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6477–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Drai, D.; Elmer, G.; Kafkafi, N.; Golani, I. Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior genetics research. Behav. Brain Res. 2001, 125, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO/WHO. Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics in Food; Report of a Joint FAO/WHO Working Group on Drafting Guidelines for the Evaluation of Probiotics on Food; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: London, ON, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
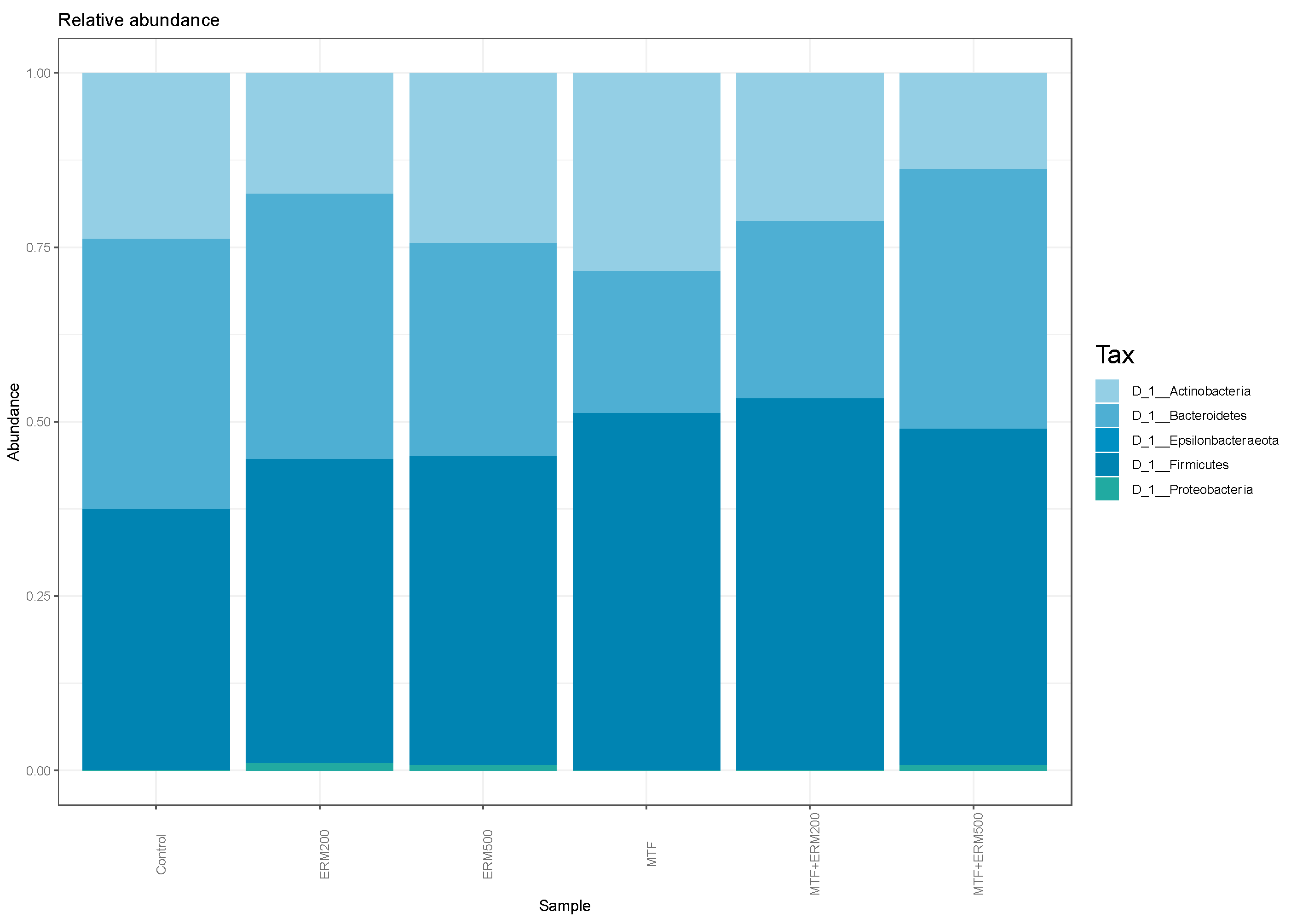
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cesar, T.; Salgaço, M.K.; Mesa, V.; Sartoratto, A.; Sivieri, K. Exploring the Association between Citrus Nutraceutical Eriocitrin and Metformin for Improving Pre-Diabetes in a Dynamic Microbiome Model. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050650
Cesar T, Salgaço MK, Mesa V, Sartoratto A, Sivieri K. Exploring the Association between Citrus Nutraceutical Eriocitrin and Metformin for Improving Pre-Diabetes in a Dynamic Microbiome Model. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(5):650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050650
Chicago/Turabian StyleCesar, Thais, Mateus Kawata Salgaço, Victoria Mesa, Adilson Sartoratto, and Katia Sivieri. 2023. "Exploring the Association between Citrus Nutraceutical Eriocitrin and Metformin for Improving Pre-Diabetes in a Dynamic Microbiome Model" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 5: 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050650
APA StyleCesar, T., Salgaço, M. K., Mesa, V., Sartoratto, A., & Sivieri, K. (2023). Exploring the Association between Citrus Nutraceutical Eriocitrin and Metformin for Improving Pre-Diabetes in a Dynamic Microbiome Model. Pharmaceuticals, 16(5), 650. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16050650







