Multitargeted Virtual Screening and Molecular Simulation of Natural Product-like Compounds against GSK3β, NMDA-Receptor, and BACE-1 for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Virtual Screening of Natural Product-like Compounds
2.2. Drug-Likeness, Pharmacokinetics, and Physicochemical Properties
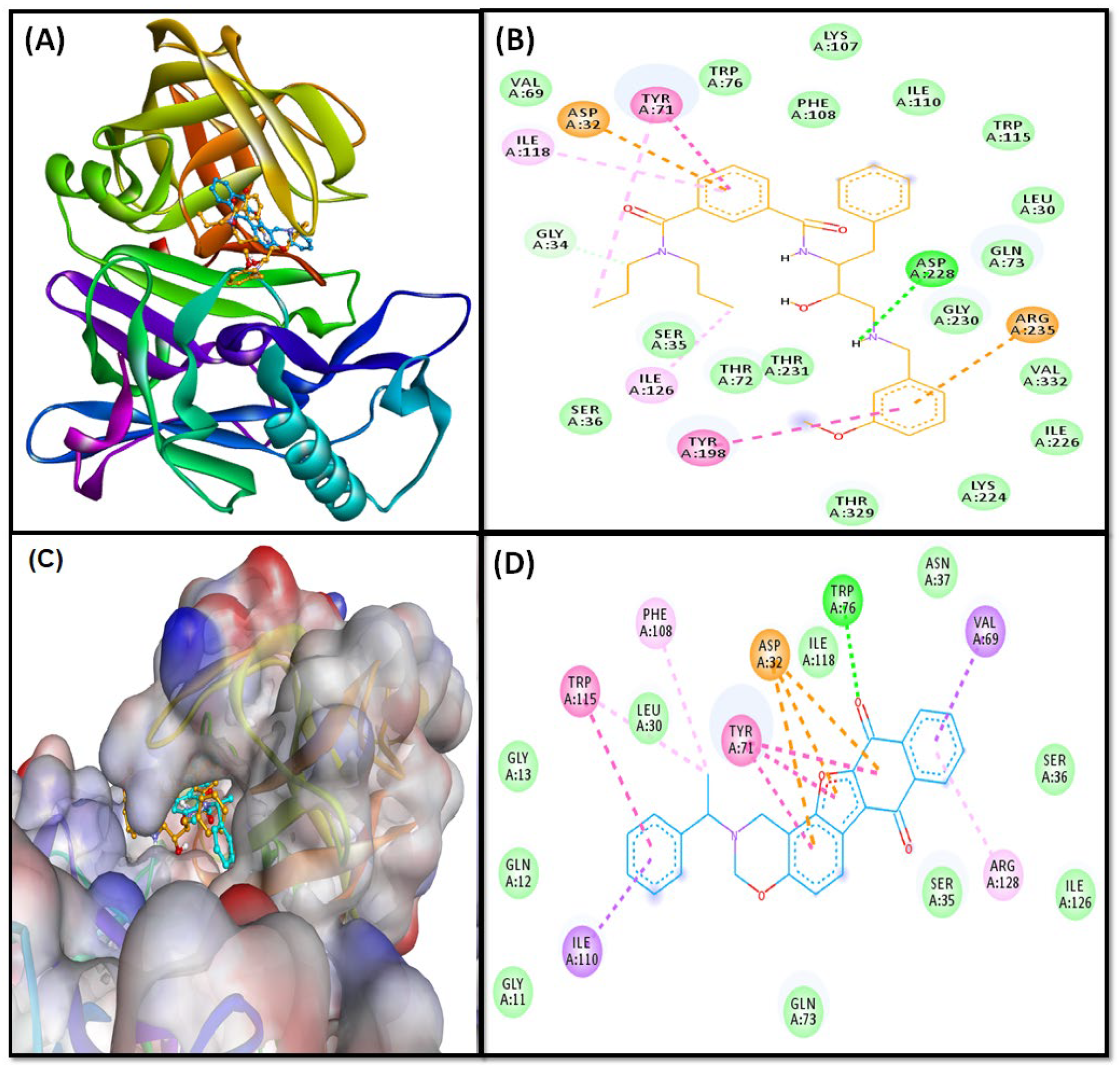
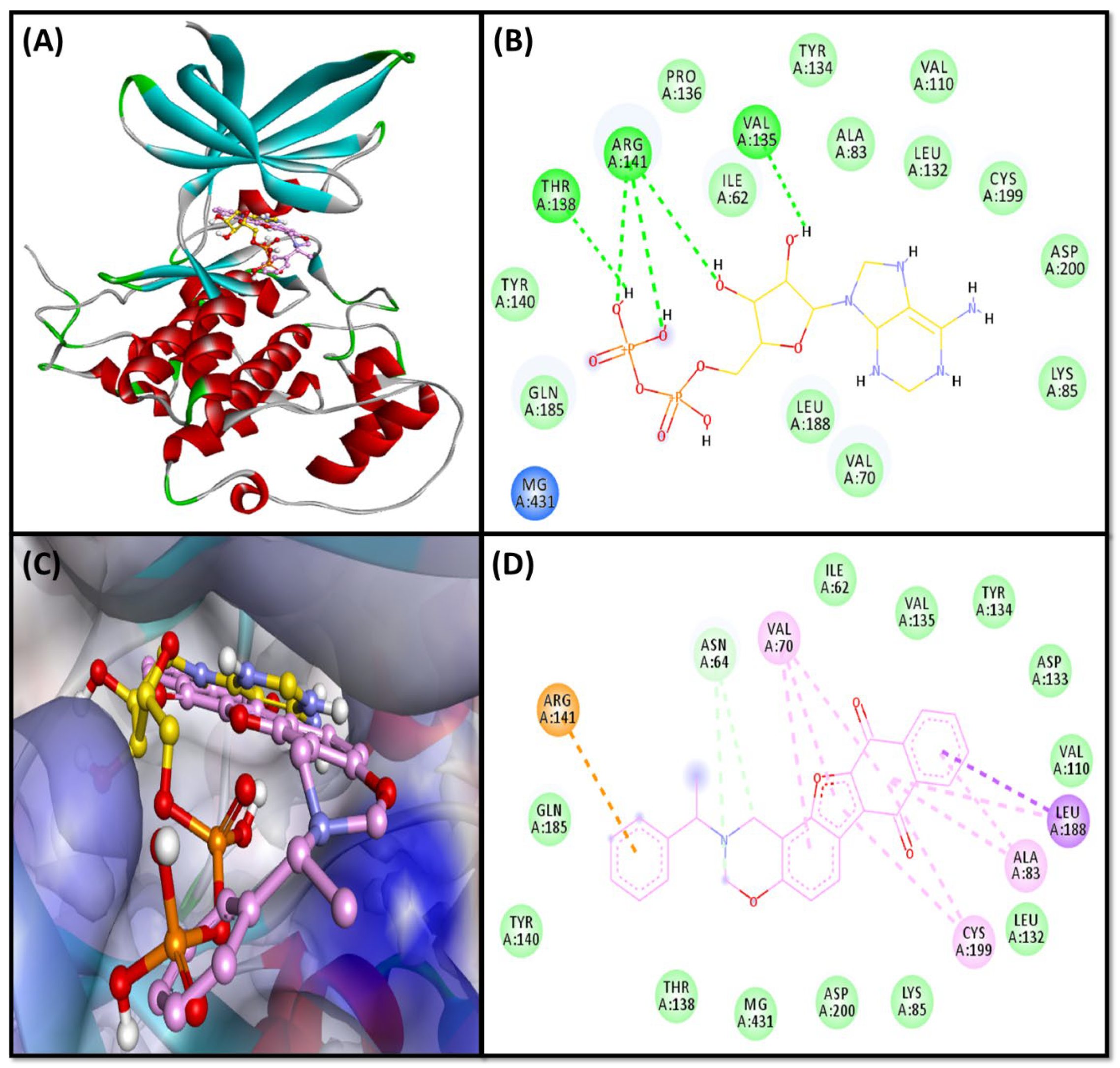
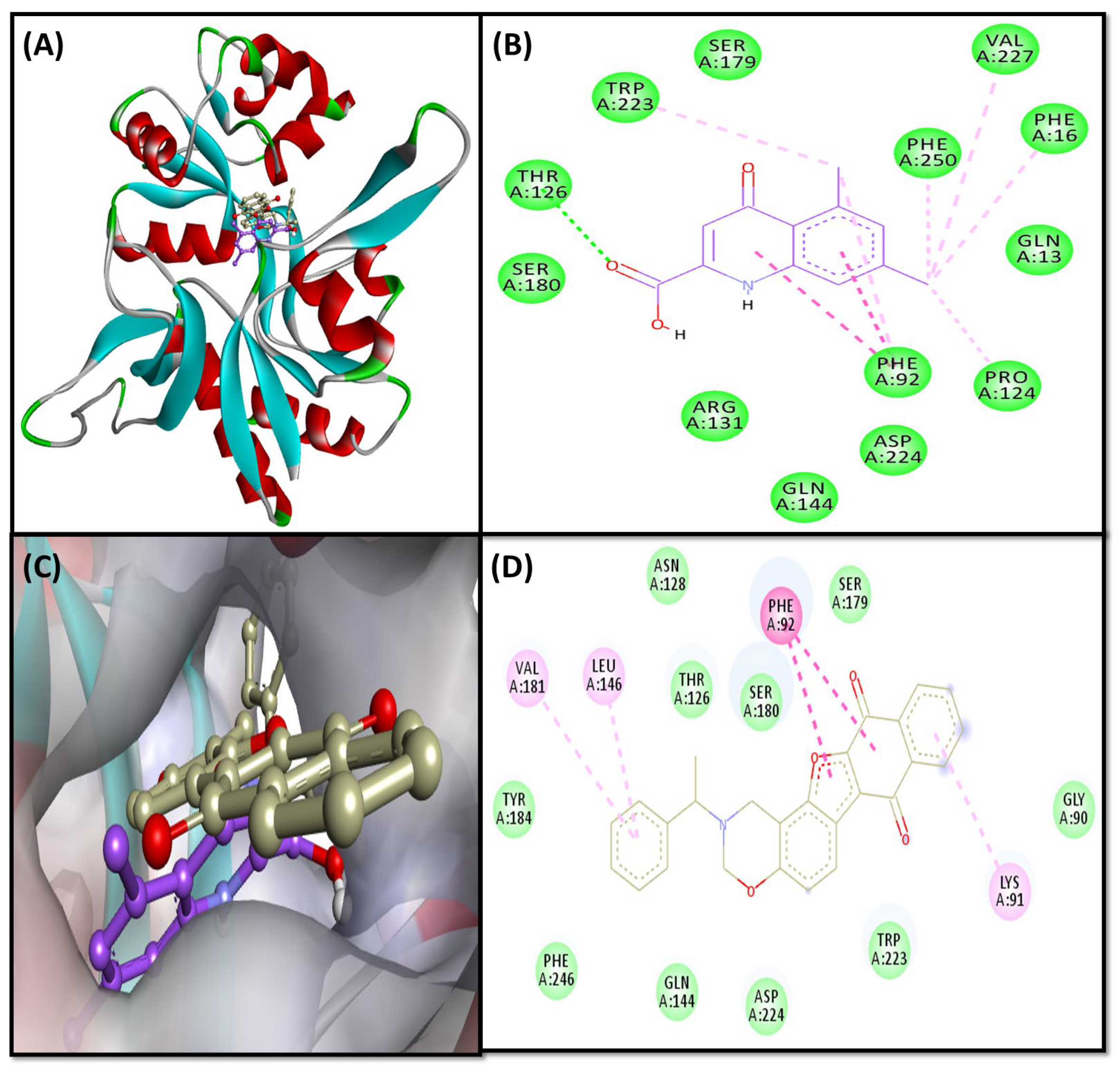
2.3. Molecular Docking Study
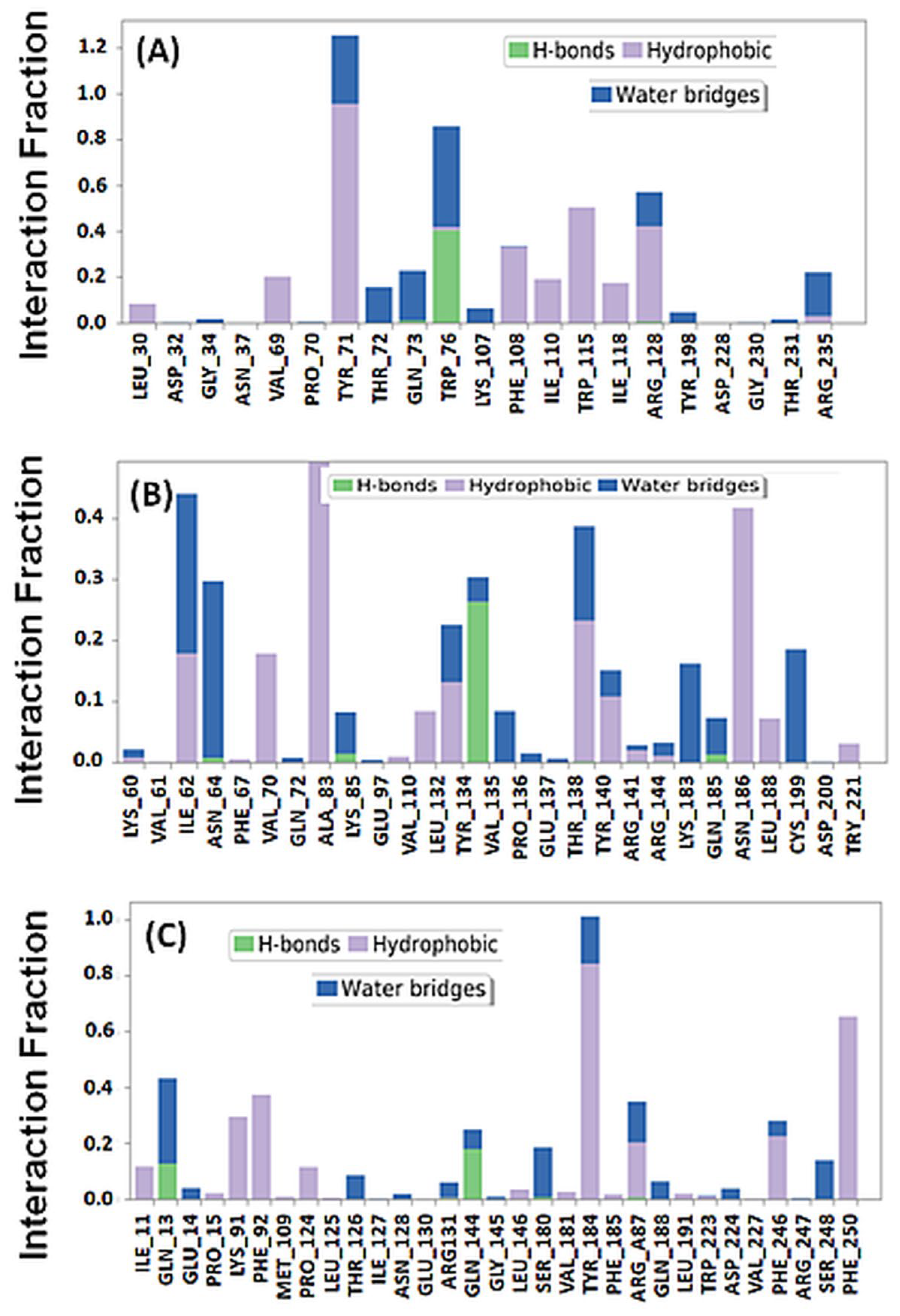
2.3.1. BACE Complex
2.3.2. GSK3β-Complex
2.3.3. NMDA-Complex
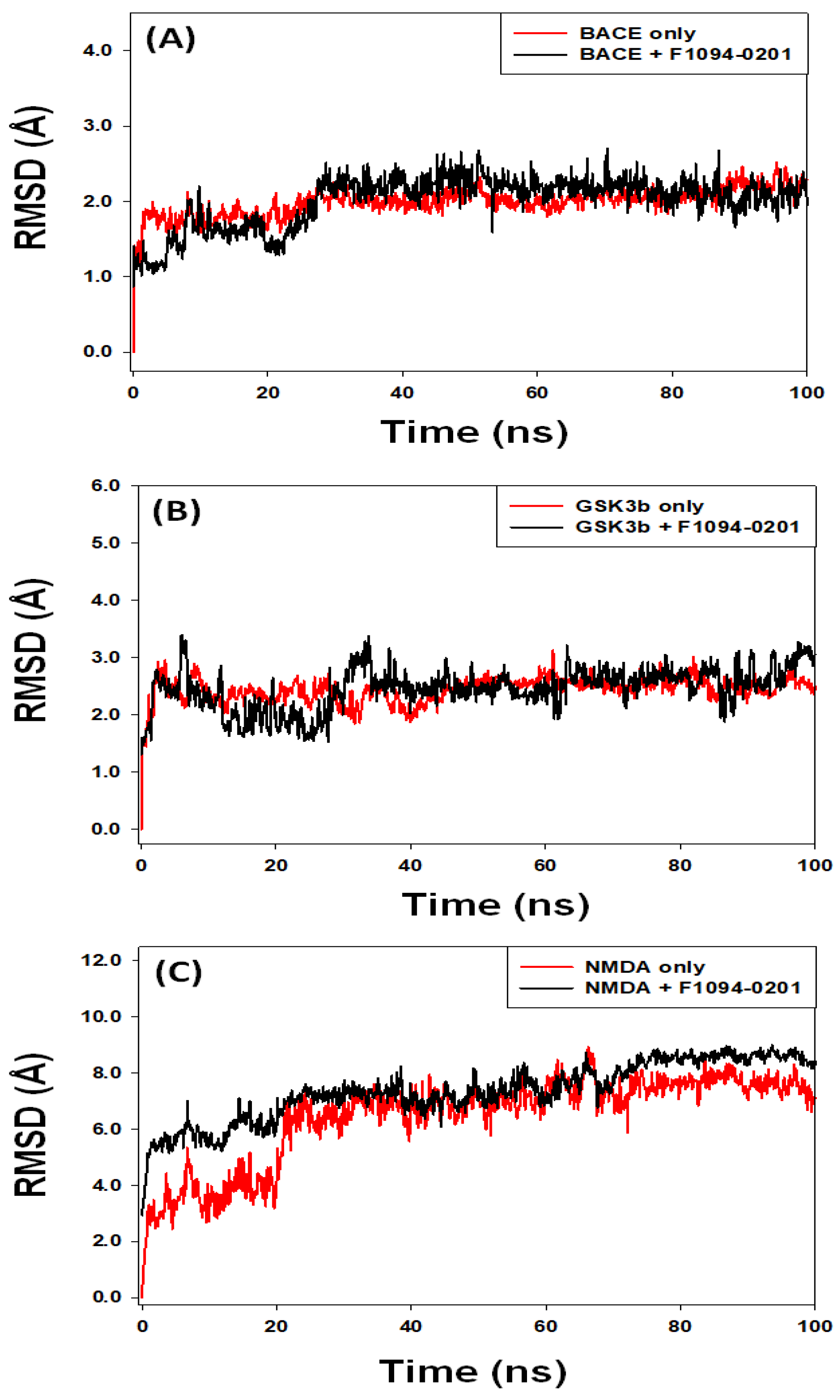
2.4. Analysis of Molecular Dynamics Simulation
2.4.1. Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD)
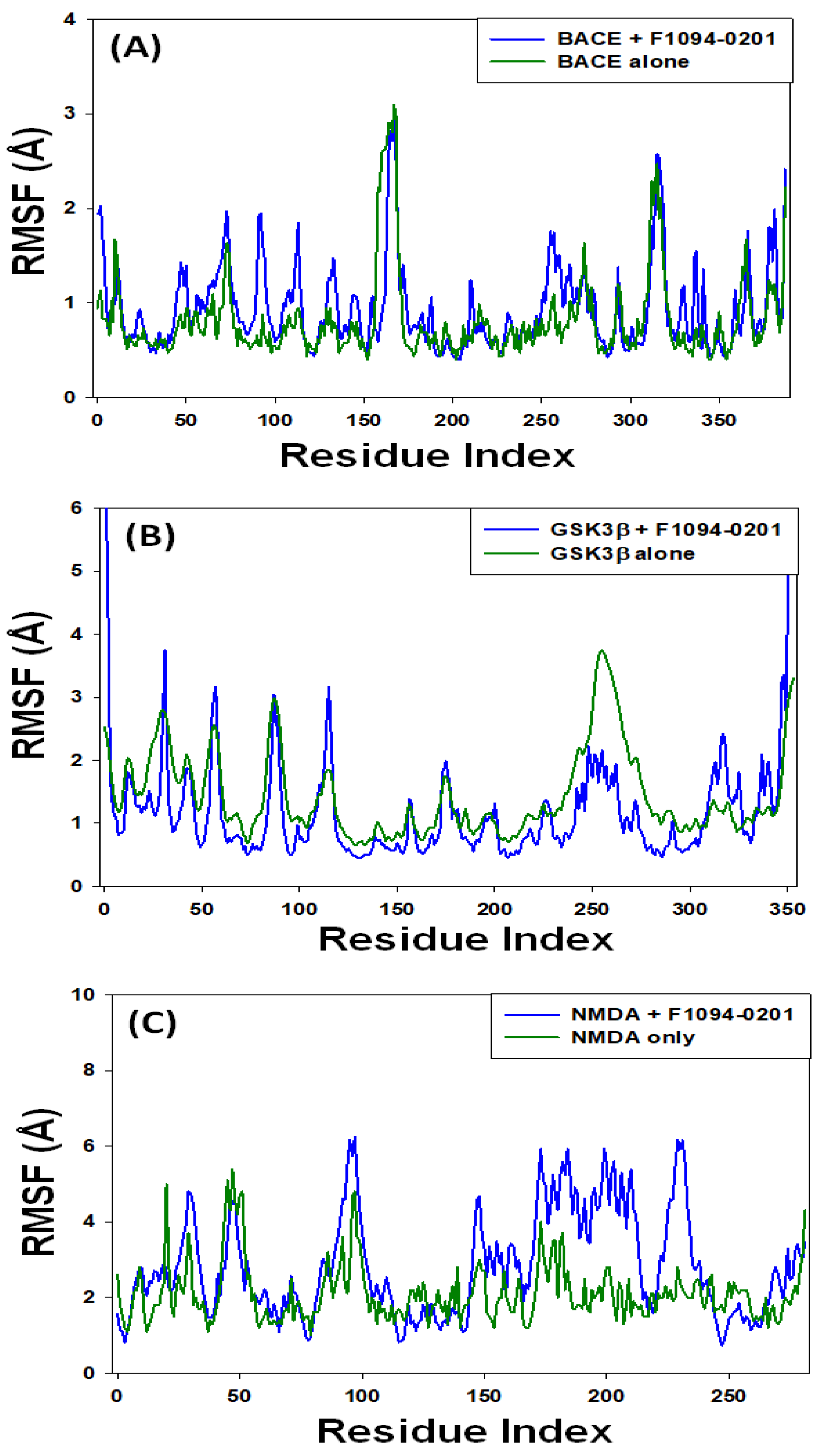
2.4.2. Root Mean Square Fluctuation (RMSF)
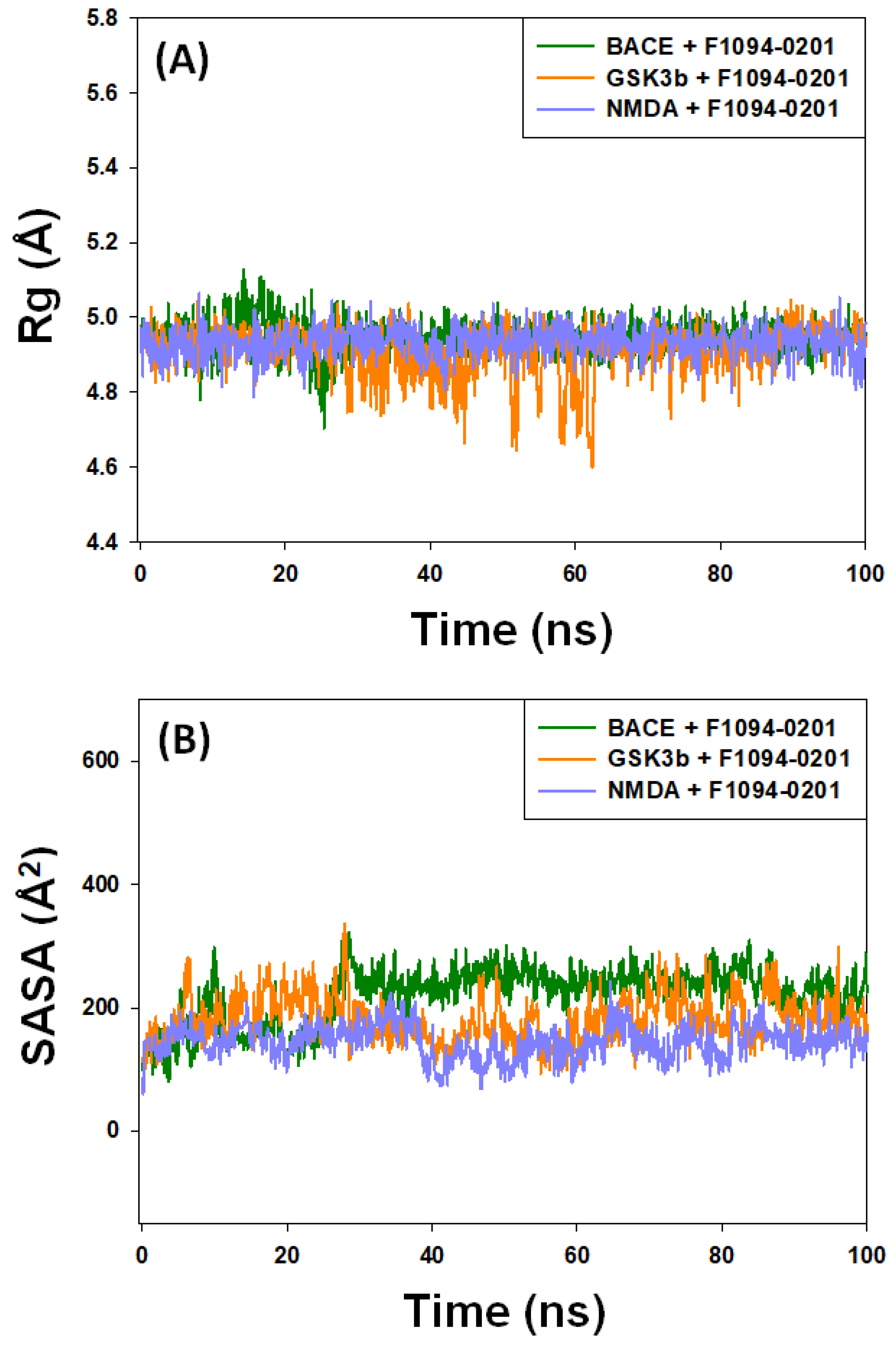
2.4.3. The Radius of Gyration (Rg) and Solvent-Accessible Surface Area (SASA)
2.4.4. Secondary Structure Elements (SSE)
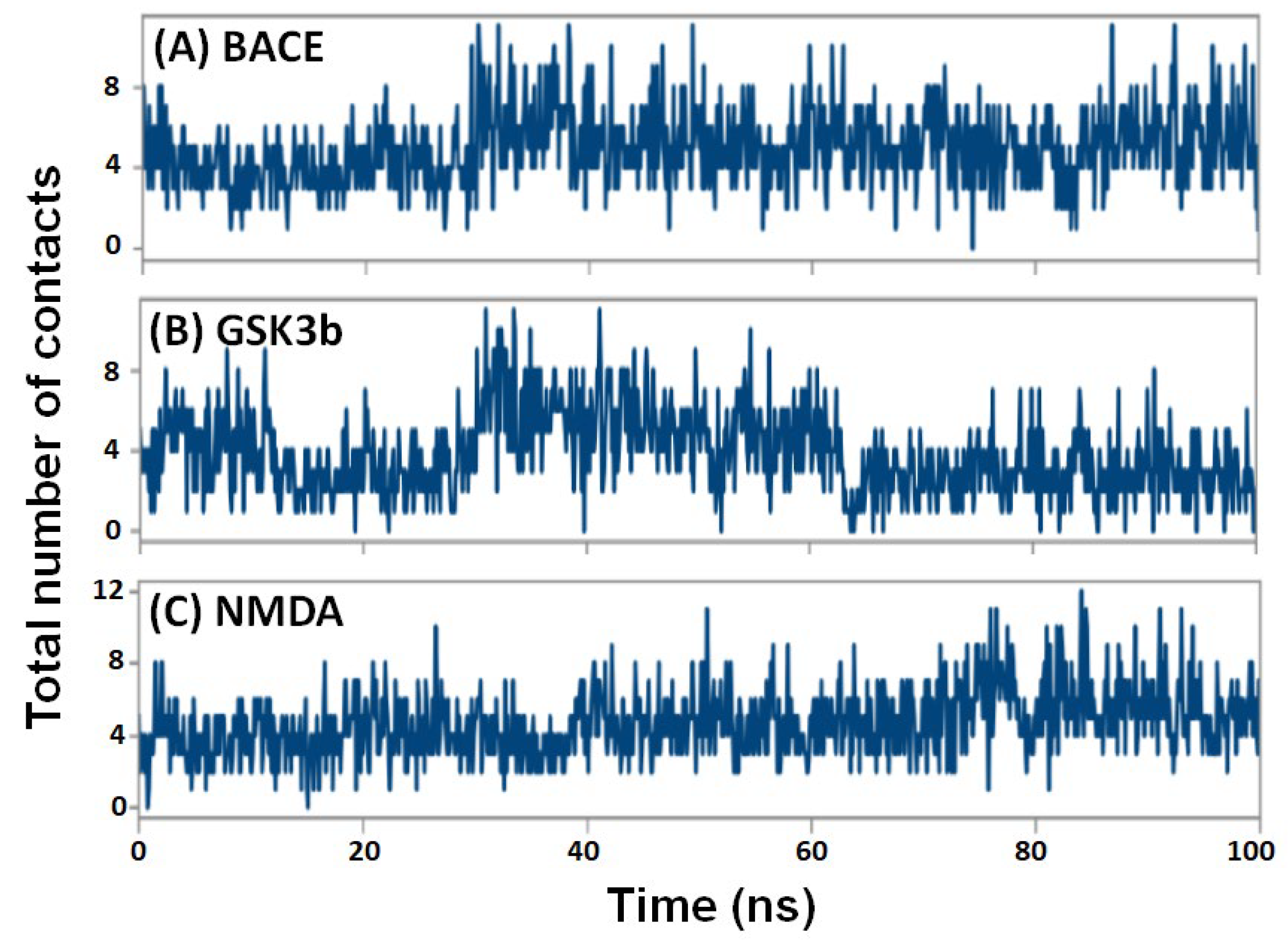
2.4.5. Contacts between Protein and Ligand
2.5. Analysis of Prime/MM-GBSA Free Energy
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Computational Hardware and Software
3.2. Preparation of Ligands and Proteins
3.3. Molecular Docking
3.4. Prediction of Drug-Likeness, Pharmacokinetics, and Physicochemical Properties
3.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.6. Free Energy Calculations Using Prime/MM-GBSA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Dementia. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 31 December 2022).
- Goel, H.; Goyal, K.; Pandey, A.K.; Benjamin, M.; Khan, F.; Pandey, P.; Mittan, S.; Iqbal, D.; Alsaweed, M.; Alturaiki, W.; et al. Elucidations of Molecular Mechanism and Mechanistic Effects of Environmental Toxicants in Neurological Disorders. In CNS & Neurological Disorders-Drug Targets (Formerly Current Drug Targets-CNS & Neurological Disorders); Bentham Science Publishers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2023; Volume 22, pp. 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coman, H.; Nemeş, B. New Therapeutic Targets in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Gerontol. 2017, 11, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Singh, A.; Singh, A.K.; Yadav, Y.; Bajpai, S.; Kumar, P.; Upadhyay, A.D.; Shekhar, S.; Dwivedi, S.; Dey, A.B.; et al. Circulatory GSK-3β: Blood-Based Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 85, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chang, L.; Song, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, Y. The Role of NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinky, P.; Pfitzer, J.; Senfeld, J.; Hong, H.; Bhattacharya, S.; Suppiramaniam, V.; Qureshi, I.; Reed, M. Recent Insights on Glutamatergic Dysfunction in Alzheimer’s Disease and Therapeutic Implications. Neuroscientist 2022, 0, 107385842110698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, D.; Khan, M.S.; Waiz, M.; Rehman, M.T.; Alaidarous, M.; Jamal, A.; Alothaim, A.S.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Alshehri, B.M.; Banawas, S.; et al. Exploring the Binding Pattern of Geraniol with Acetylcholinesterase through In Silico Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and In Vitro Enzyme Inhibition Kinetics Studies. Cells 2021, 10, 3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, D.; Rehman, M.T.; Bin Dukhyil, A.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Al Ajmi, M.F.; Alshehri, B.M.; Banawas, S.; Khan, M.S.; Alturaiki, W.; Alsaweed, M. High-Throughput Screening and Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Natural Product-like Compounds against Alzheimer’s Disease through Multitarget Approach. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, S.; Redhu, N.S.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Iqbal, D.; Khan, J.; Banawas, S.; Alaidarous, M.; Alshehri, B.; Mir, S.A.; Adnan, M.; et al. Nobiletin as a Neuroprotectant against NMDA Receptors: An In Silico Approach. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, N.; Maheshwari, S.K.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Albadrani, H.M.; Alsagaby, S.A.; Alturaiki, W.; Iqbal, D.; Zia, Q.; Villa, C.; Jha, S.K.; et al. Homology Modelling, Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies of CALMH1 against Secondary Metabolites of Bauhinia Variegata to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.; Jindal, D.; Chopra, H.; Jha, S.K.; Singh, S.K.; Ashraf, G.M.; Kamal, M.; Iqbal, D.; Chellappan, D.K.; Dey, A.; et al. ROCK2 Inhibition: A Futuristic Approach for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 142, 104871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, K.-X.; Tan, M.-S.; Tan, C.-C.; Cao, X.-P.; Hou, X.-H.; Guo, Q.-H.; Tan, L.; Mok, V.; Yu, J.-T. Comparative Safety and Effectiveness of Cholinesterase Inhibitors and Memantine for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis of 41 Randomized Controlled Trials. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Tam, K.Y. Pathological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatulian, S.A. Challenges and Hopes for Alzheimer’s Disease. Drug Discov. Today 2022, 27, 1027–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Habib, A.H.; Rafeeq, M.M.; Alafnan, A.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Iqbal, D.; Jamal, Q.M.S.; Unissa, R.; Sharma, D.C.; Moin, A.; et al. Oleuropein as a Potent Compound against Neurological Complications Linked with COVID-19: A Computational Biology Approach. Entropy 2022, 24, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Gabr, M.T. Multitarget Therapeutic Strategies for Alzheimer’s Disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, D.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Rehman, M.T.; Khan, M.S.; Bin Dukhyil, A.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Alshehri, B.M.; Banawas, S.; Zia, Q.; Alsaweed, M.; et al. Soyasapogenol-B as a Potential Multitarget Therapeutic Agent for Neurodegenerative Disorders: Molecular Docking and Dynamics Study. Entropy 2022, 24, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maramai, S.; Benchekroun, M.; Gabr, M.T.; Yahiaoui, S. Multitarget Therapeutic Strategies for Alzheimer’s Disease: Review on Emerging Target Combinations. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, e5120230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moin, A.; Huwaimel, B.; Alobaida, A.; Break, M.K.B.; Iqbal, D.; Unissa, R.; Jamal, Q.M.S.; Hussain, T.; Sharma, D.C.; Rizvi, S.M.D. Dithymoquinone Analogues as Potential Candidate(s) for Neurological Manifestation Associated with COVID-19: A Therapeutic Strategy for Neuro-COVID. Life 2022, 12, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J. Evaluation of Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Ficus Carica Leaves: An In Vitro Approach. J. Plant Pathol. Microb. 2012, 4, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Bhatnagar, S.; Saxena, R.; Iqbal, D.; Ghosh, A.K.; Dutta, R. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Gold Nanoparticles: Kinetics, in Vitro and in Vivo Study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2017, 78, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, F.; Hashim, A.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, S.; Iqbal, D.; Srivastava, A.K.; Siddiqui, M.H. Antioxidant, α-Amylase Inhibitory and Oxidative DNA Damage Protective Property of Boerhaavia Diffusa (Linn.) Root. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2013, 88, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, F.; Alvi, S.S.; Ahmad, P.; Iqbal, D.; Alshehri, B.M.; Khan, M.S. Therapeutic Efficacy of Boerhaavia Diffusa (Linn.) Root Methanolic Extract in Attenuating Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes, Diabetes-Linked Hyperlipidemia and Oxidative-Stress in Rats. Biomed. Res. Ther. 2019, 6, 3293–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsagaby, S.A.; Iqbal, D.; Ahmad, I.; Patel, H.; Mir, S.A.; Madkhali, Y.A.; Oyouni, A.A.A.; Hawsawi, Y.M.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Alshehri, B.; et al. In Silico Investigations Identified Butyl Xanalterate to Competently Target CK2α (CSNK2A1) for Therapy of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvi, S.; Ahmad, P.; Ishrat, M.; Iqbal, D.; Khan, S. Secondary Metabolites from Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.): Structure, Biochemistry and Therapeutic Implications Against Neurodegenerative Diseases. In Natural Bio-Active Compounds: Volume 2: Chemistry, Pharmacology and Health Care Practices; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–24. ISBN 9789811372049. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, R.; Das, S.S.; Biswal, S.S.; Nath, A.; Das, D.; Basu, A.; Malik, S.; Kumar, L.; Kar, S.; Singh, S.K.; et al. Mechanistic Role of HPV-Associated Early Proteins in Cervical Cancer: Molecular Pathways and Targeted Therapeutic Strategies. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2022, 174, 103675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bijani, S.; Iqbal, D.; Mirza, S.; Jain, V.; Jahan, S.; Alsaweed, M.; Madkhali, Y.; Alsagaby, S.A.; Banawas, S.; Algarni, A.; et al. Green Synthesis and Anticancer Potential of 1,4-Dihydropyridines-Based Triazole Derivatives: In Silico and In Vitro Study. Life 2022, 12, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, D.; Pawar, R.K.; Sharma, R.K. Physico-Chemical Standardization of Butea Monosperma (Lam.) Kuntze (Palasha): An Ayurvedic Drug. Int. J. Pharm. Qual. Assur. 2010, 2, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, D.; Khan, M.S.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, S.; Srivastava, A.K. An in Vitro and Molecular Informatics Study to Evaluate the Antioxidative and β-Hydroxy-β-Methylglutaryl-CoA Reductase Inhibitory Property of Ficus Virens Ait. Phytother. Res. 2014, 28, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, D.; Khan, M.S.; Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, S.; Hussain, M.S.; Ali, M. Bioactivity Guided Fractionation and Hypolipidemic Property of a Novel HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor from Ficus Virens Ait. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, D.; Khan, M.S.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, S. Extenuating the Role of Ficus Virens Ait and Its Novel Bioactive Compound on Antioxidant Defense System and Oxidative Damage in Cigarette Smoke Exposed Rats. Biomed. Res. Ther. 2016, 3, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, D.; Khan, A.; Ansari, I.A.; Khan, M.S. Investigating The Role of Novel Bioactive Compound from Ficus Virens Ait on Cigarette Smoke Induced Oxidative Stress and Hyperlipidemia in Rats. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 16, 1089–1103. [Google Scholar]
- Jahan, S.; Ansari, U.A.; Siddiqui, A.J.; Iqbal, D.; Khan, J.; Banawas, S.; Alshehri, B.; Alshahrani, M.M.; Alsagaby, S.A.; Redhu, N.S.; et al. Nobiletin Ameliorates Cellular Damage and Stress Response and Restores Neuronal Identity Altered by Sodium Arsenate Exposure in Human IPSCs-Derived HNPCs. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, A.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Das, S.S.; Srivastava, A.; Choudhury, A.; Bhattacharjee, R.; De, S.; Perveen, A.; Iqbal, D.; Gupta, P.K.; et al. Molecular Insights into Therapeutic Potentials of Hybrid Compounds Targeting Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 3512–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, A.; Khan, F.; Ahmad, N.; Shaikh, S.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Shakil, S.; Al-Qahtani, M.H.; Abuzenadah, A.M.; Tabrez, S.; Ahmed, A.B.F.; et al. Silver Nanoparticles from Leaf Extract of Mentha Piperita: Eco-Friendly Synthesis and Effect on Acetylcholinesterase Activity. Life Sci. 2018, 209, 430–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khushtar, M.; Siddiqui, H.H.; Dixit, R.K.; Khan, M.S.; Iqbal, D.; Rahman, M.A. Amelioration of Gastric Ulcers Using a Hydro-Alcoholic Extract of Triphala in Indomethacin-Induced Wistar Rats. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2016, 8, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, N.; Iqbal, D.; Al Othaim, A.; Kamal, M.; Albadrani, H.M.; Algehainy, N.A.; Alyenbaawi, H.; Alghofaili, F.; Amir, M. Roohi Antibacterial Efficacy of Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles of Microbacterium Proteolyticum LA2(R) and Streptomyces Rochei LA2(O) against Biofilm Forming Meningitis Causing Microbes. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhoqail, W.A.; Alothaim, A.S.; Suhail, M.; Iqbal, D.; Kamal, M.; Asmari, M.M.; Jamal, A. Husk-like Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Induce Apoptosis through ROS Generation in Epidermoid Carcinoma Cells: Effect of Incubation Period on Sol-Gel Synthesis and Anti-Cancerous Properties. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciantini, M.; Leri, M.; Scuto, M.; Ontario, M.; Trovato Salinaro, A.; Calabrese, E.J.; Calabrese, V.; Stefani, M. Xenohormesis Underlyes the Anti-Aging and Healthy Properties of Olive Polyphenols. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2022, 202, 111620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leri, M.; Bertolini, A.; Stefani, M.; Bucciantini, M. EVOO Polyphenols Relieve Synergistically Autophagy Dysregulation in a Cellular Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciantini, M.; Leri, M.; Nardiello, P.; Casamenti, F.; Stefani, M. Olive Polyphenols: Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripodi, F.; Falletta, E.; Leri, M.; Angeloni, C.; Beghelli, D.; Giusti, L.; Milanesi, R.; Sampaio-Marques, B.; Ludovico, P.; Goppa, L.; et al. Anti-Aging and Neuroprotective Properties of Grifola Frondosa and Hericium Erinaceus Extracts. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvi, S.; Iqbal, D.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, S. Molecular Rationale Delineating the Role of Lycopene as a Potent HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor: In Vitro and in Silico Study. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 2111–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, P.; Alvi, S.S.; Iqbal, D.; Khan, M.S. Insights into Pharmacological Mechanisms of Polydatin in Targeting Risk Factors-Mediated Atherosclerosis. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; Supuran, C.T. Natural Products in Drug Discovery: Advances and Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blahova, J.; Martiniakova, M.; Babikova, M.; Kovacova, V.; Mondockova, V.; Omelka, R. Pharmaceutical Drugs and Natural Therapeutic Products for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Li, X.; Lin, X. A Review on Applications of Computational Methods in Drug Screening and Design. Molecules 2020, 25, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabe, V.T.; Ntombela, T.; Jhamba, L.A.; Maguire, G.E.M.; Govender, T.; Naicker, T.; Kruger, H.G. Current Trends in Computer Aided Drug Design and a Highlight of Drugs Discovered via Computational Techniques: A Review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, W.P.; Stahl, M.T.; Murcko, M.A. Virtual Screening—An Overview. Drug Discov. Today 1998, 3, 160–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMasi, J.A.; Hansen, R.W.; Grabowski, H.G. The Price of Innovation: New Estimates of Drug Development Costs. J. Health Econ. 2003, 22, 151–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A. Lead- and Drug-like Compounds: The Rule-of-Five Revolution. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2004, 1, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Estimate Solubility and Permeability in Drug Discovery and Development Settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veber, D.F.; Johnson, S.R.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Smith, B.R.; Ward, K.W.; Kopple, K.D. Molecular Properties That Influence the Oral Bioavailability of Drug Candidates. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 2615–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and Computational Approaches to Estimate Solubility and Permeability in Drug Discovery and Development Settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajouhesh, H.; Lenz, G.R. Medicinal Chemical Properties of Successful Central Nervous System Drugs. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 541–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahar Doan, K.M.; Humphreys, J.E.; Webster, L.O.; Wring, S.A.; Shampine, L.J.; Serabjit-Singh, C.J.; Adkison, K.K.; Polli, J.W. Passive Permeability and P-Glycoprotein-Mediated Efflux Differentiate Central Nervous System (CNS) and Non-CNS Marketed Drugs. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 303, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampel, H.; Vassar, R.; Strooper, B.D.; Hardy, J.; Willem, M.; Singh, N.; Zhou, J.; Yan, R.; Vanmechelen, E.; Vos, A.D.; et al. The β-Secretase BACE1 in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 89, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Anderson, J.P.; Barbour, R.; Basi, G.S.; Caccavello, R.; Davis, D.; Doan, M.; Dovey, H.F.; Frigon, N.; Hong, J.; et al. Purification and Cloning of Amyloid Precursor Protein β-Secretase from Human Brain. Nature 1999, 402, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Vuillard, L.; Cleasby, A.; Murray, C.W.; Yon, J. Apo and Inhibitor Complex Structures of BACE (β-Secretase). J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 343, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeniji, A.O.; Adams, P.W.; Mody, V.V. Chapter 7—Amyloid β Hypothesis in the Development of Therapeutic Agents for Alzheimer’s Disease. In Drug Discovery Approaches for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disorders; Adejare, A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 109–143. ISBN 978-0-12-802810-0. [Google Scholar]
- Venugopal, C.; Demos, C.M.; Rao, K.S.J.; Pappolla, M.A.; Sambamurti, K. Beta-Secretase: Structure, Function, and Evolution. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2008, 7, 278–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.A.; Johora, F.T.; Sarkar, B.; Araf, Y.; Ahmed, N.; Nahar, A.N.; Akter, T. Computer-Assisted Evaluation of Plant-Derived β-Secretase Inhibitors in Alzheimer’s Disease. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2021, 22, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorens-Marítin, M.; Jurado, J.; Hernández, F.; Ávila, J. GSK-3β, a Pivotal Kinase in Alzheimer Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 7, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Elangovan, N.D.; Dhanabalan, A.K.; Gunasekaran, K.; Kandimalla, R.; Sankarganesh, D. Screening of Potential Drug for Alzheimer’s Disease: A Computational Study with GSK-3 β Inhibition through Virtual Screening, Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 7065–7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.; Yokota, T.; Sugiura, I.; Sasaki, C.; Hasegawa, T.; Okumura, C.; Ishiguro, K.; Kohno, T.; Sugio, S.; Matsuzaki, T. Structural Insight into Nucleotide Recognition in Tau-Protein Kinase I/Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabir, N.R.; Shakil, S.; Tabrez, S.; Khan, M.S.; Rehman, M.T.; Ahmed, B.A. In Silico Screening of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Targeted Ligands against Acetylcholinesterase and Its Probable Relevance to Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 39, 5083–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Reddy, P.H. Role of Glutamate and NMDA Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2017, 57, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leeson, P.D.; Iversen, L.L. The Glycine Site on the NMDA Receptor: Structure-Activity Relationships and Therapeutic Potential. J. Med. Chem. 1994, 37, 4053–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Gouaux, E. Mechanisms of Activation, Inhibition and Specificity: Crystal Structures of the NMDA Receptor NR1 Ligand-Binding Core. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2873–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.; Kumar, S. In Silico Analysis of Binding Interaction of Phytoconstituents with N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor for Potential Therapeutic Use in Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2018, 14, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugale, V.G.; Bari, S.B. Identification of Potential Gly/NMDA Receptor Antagonists by Cheminformatics Approach: A Combination of Pharmacophore Modelling, Virtual Screening and Molecular Docking Studies. SAR QSAR Environ. Res. 2016, 27, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, T.I.; Omotuyi, O.I.; Agboola, O.D.; Okonkwo, D.C.; Adelakun, N.S. Identification of Gly/NMDA Receptor Antagonist from Chromolaena Odorata’s Derived Compounds Using Induced Fit Docking and ADME Study. J. Biol. Eng. Res. Rev. 2019, 6, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Adelusi, T.I.; Oyedele, A.-Q.K.; Boyenle, I.D.; Ogunlana, A.T.; Adeyemi, R.O.; Ukachi, C.D.; Idris, M.O.; Olaoba, O.T.; Adedotun, I.O.; Kolawole, O.E.; et al. Molecular Modeling in Drug Discovery. Inform. Med. Unlocked 2022, 29, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karplus, M.; Petsko, G.A. Molecular Dynamics Simulations in Biology. Nature 1990, 347, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genheden, S.; Ryde, U. The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA Methods to Estimate Ligand-Binding Affinities. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallakyan, S.; Olson, A.J. Small-Molecule Library Screening by Docking with PyRx. In Chemical Biology: Methods and Protocols; Methods in Molecular, Biology; Hempel, J.E., Williams, C.H., Hong, C.C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 243–250. ISBN 978-1-4939-2269-7. [Google Scholar]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BIOVIA. BIOVIA Discovery Studio. Available online: https://www.3ds.com/products-services/biovia/products/molecular-modeling-simulation/biovia-discovery-studio/ (accessed on 1 October 2021).
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brańka, A. Nosé-Hoover Chain Method for Nonequilibrium Molecular Dynamics Simulation. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 61, 4769–4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyna, G.J.; Tobias, D.J.; Klein, M.L. Constant Pressure Molecular Dynamics Algorithms. J. Chem. Phys. 1994, 101, 4177–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Binding Energy (ΔG) kcal mol−1 | Binding Affinity (Kd) M−1 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targets | BACE (1w51) | GSK3β (1j1c) | NMDAr (1pbq) | BACE (1w51) | GSK3β (1j1c) | NMDAr (1pbq) | |
| ID number | |||||||
| C1 | F0870-0001 | −12.0 | −11.2 | −12.3 | 6.25 × 108 | 1.62 × 108 | 1.04 × 109 |
| C2 | F1094-0201 | −12.0 | −10.6 | −11.7 | 6.25 × 108 | 5.89 × 107 | 3.77 × 108 |
| C3 | F0882-0397 | −11.0 | −10.4 | −12.3 | 1.16 × 108 | 4.20 × 107 | 1.04 × 109 |
| C4 | F1217-0041 | −11.0 | −9.8 | −11.6 | 1.16 × 108 | 1.53 × 107 | 3.18 × 108 |
| C5 | F1094-0199 | −11.1 | −9.7 | −10.9 | 1.37 × 108 | 1.29 × 107 | 9.77 × 107 |
| C6 | F1094-0205 | −11.2 | −9.9 | −10.9 | 1.62 × 108 | 1.81 × 107 | 9.77 × 107 |
| C7 | F1094-0196 | −11.1 | −9.9 | −10.8 | 1.37 × 108 | 1.81 × 107 | 8.25 × 107 |
| C8 | F1094-0198 | −11.4 | −9.8 | −10.5 | 2.27 × 108 | 1.53 × 107 | 4.97 × 107 |
| C9 | F1094-0206 | −10.9 | −9.9 | −10.5 | 9.77 × 107 | 1.81 × 107 | 4.97 × 107 |
| C10 | F3161-0307 | −11.5 | −9.3 | −10.1 | 2.69 × 108 | 6.56 × 106 | 2.53 × 107 |
| RL1 | Non-peptidic inhibitor | −10.6 | ND | ND | 5.89 × 107 | ND | ND |
| RL2 | Adenosine-5′-Diphosphate | ND | −7.7 | ND | ND | 4.41 × 105 | ND |
| RL3 | 5,7-Dichlorokynurenic acid | ND | ND | −7.2 | ND | ND | 1.90 × 105 |
| Physicochemical Properties | Pharmacokinetics | Drug-Likeness | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formula | MW | RB | HBA | HBD | MR | TPSA | XLOGP3 | GIA | BBB+ | Pgp-S | Fcsp3 | LV | |
| C1 | C24H15NO6 | 413.38 | 3 | 7 | 2 | 114.31 | 113.77 | 2.12 | High | No | Yes | 0.04 | 0 |
| C2 | C26H19NO4 | 409.43 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 119.78 | 59.75 | 5.18 | High | Yes | No | 0.15 | 0 |
| C3 | C24H13NO5 | 395.36 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 110.01 | 93.45 | 4.09 | High | No | No | 0 | 0 |
| C4 | C26H19NO4 | 409.43 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 119.78 | 59.75 | 5.24 | High | Yes | Yes | 0.15 | 0 |
| C5 | C22H17NO6S | 423.44 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 111.75 | 102.27 | 2.85 | High | No | No | 0.27 | 0 |
| C6 | C26H23NO4 | 413.47 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 121.54 | 59.75 | 5.33 | High | Yes | Yes | 0.31 | 0 |
| C7 | C24H21NO4 | 387.43 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 112.4 | 59.75 | 5.09 | High | Yes | Yes | 0.33 | 0 |
| C8 | C23H19NO4 | 373.4 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 107.6 | 59.75 | 4.55 | High | Yes | No | 0.300 | 0 |
| C9 | C28H23NO6 | 469.49 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 132.76 | 78.21 | 5.18 | High | No | Yes | 0.21 | 0 |
| C10 | C26H32Cl2O2 | 447.44 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 125.46 | 37.3 | 7.19 | Low | No | No | 0.65 | 1 |
| Target Proteins | ΔEMM | ΔGSolv or ΔGSolGB | ΔGSelf contact | ΔGH-bond | ΔGSA or ΔGSol_Lipo | ΔGPacking | ΔG or ΔGBind | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔGCoulomb | ΔGvdW | ΔGCovalent | |||||||
| BACE | −8.66 ± 0.73 | −48.86 ± 3.13 | 0.70 ± 0.06 | 15.30 ± 0.81 | 0 | −0.26 ± 0.03 | −26.48 ± 1.97 | −5.52 ± 0.45 | −73.78 ± 4.31 |
| GSK3β | −4.39 ± 0.56 | −36.71 ± 2.42 | 0.71 ± 0.03 | 18.78 ± 1.04 | 0 | −0.14 ± 0.02 | −26.45 ± 2.02 | −4.32 ± 0.32 | −52.51 ± 2.85 |
| NMDA | −5.04 ± 0.91 | −44.92 ± 3.48 | 1.34 ± 0.10 | 11.67 ± 0.87 | 0 | −0.02 ± 0.02 | −31.23 ± 2.29 | −4.57 ± 0.28 | −72.77 ± 3.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iqbal, D.; Rehman, M.T.; Alajmi, M.F.; Alsaweed, M.; Jamal, Q.M.S.; Alasiry, S.M.; Albaker, A.B.; Hamed, M.; Kamal, M.; Albadrani, H.M. Multitargeted Virtual Screening and Molecular Simulation of Natural Product-like Compounds against GSK3β, NMDA-Receptor, and BACE-1 for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040622
Iqbal D, Rehman MT, Alajmi MF, Alsaweed M, Jamal QMS, Alasiry SM, Albaker AB, Hamed M, Kamal M, Albadrani HM. Multitargeted Virtual Screening and Molecular Simulation of Natural Product-like Compounds against GSK3β, NMDA-Receptor, and BACE-1 for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(4):622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040622
Chicago/Turabian StyleIqbal, Danish, Md Tabish Rehman, Mohamed F. Alajmi, Mohammed Alsaweed, Qazi Mohammad Sajid Jamal, Sharifa M. Alasiry, Awatif B. Albaker, Munerah Hamed, Mehnaz Kamal, and Hind Muteb Albadrani. 2023. "Multitargeted Virtual Screening and Molecular Simulation of Natural Product-like Compounds against GSK3β, NMDA-Receptor, and BACE-1 for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 4: 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040622
APA StyleIqbal, D., Rehman, M. T., Alajmi, M. F., Alsaweed, M., Jamal, Q. M. S., Alasiry, S. M., Albaker, A. B., Hamed, M., Kamal, M., & Albadrani, H. M. (2023). Multitargeted Virtual Screening and Molecular Simulation of Natural Product-like Compounds against GSK3β, NMDA-Receptor, and BACE-1 for the Management of Alzheimer’s Disease. Pharmaceuticals, 16(4), 622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16040622











