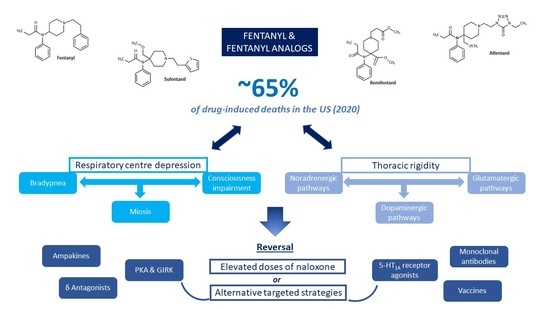
Mechanisms of Neurorespiratory Toxicity Induced by Fentanyl Analogs—Lessons from Animal Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
3. Neurorespiratory Effects of Fentanyl and Analogs
3.1. Depression of the Ventilation Command
3.2. Chest Wall Rigidity
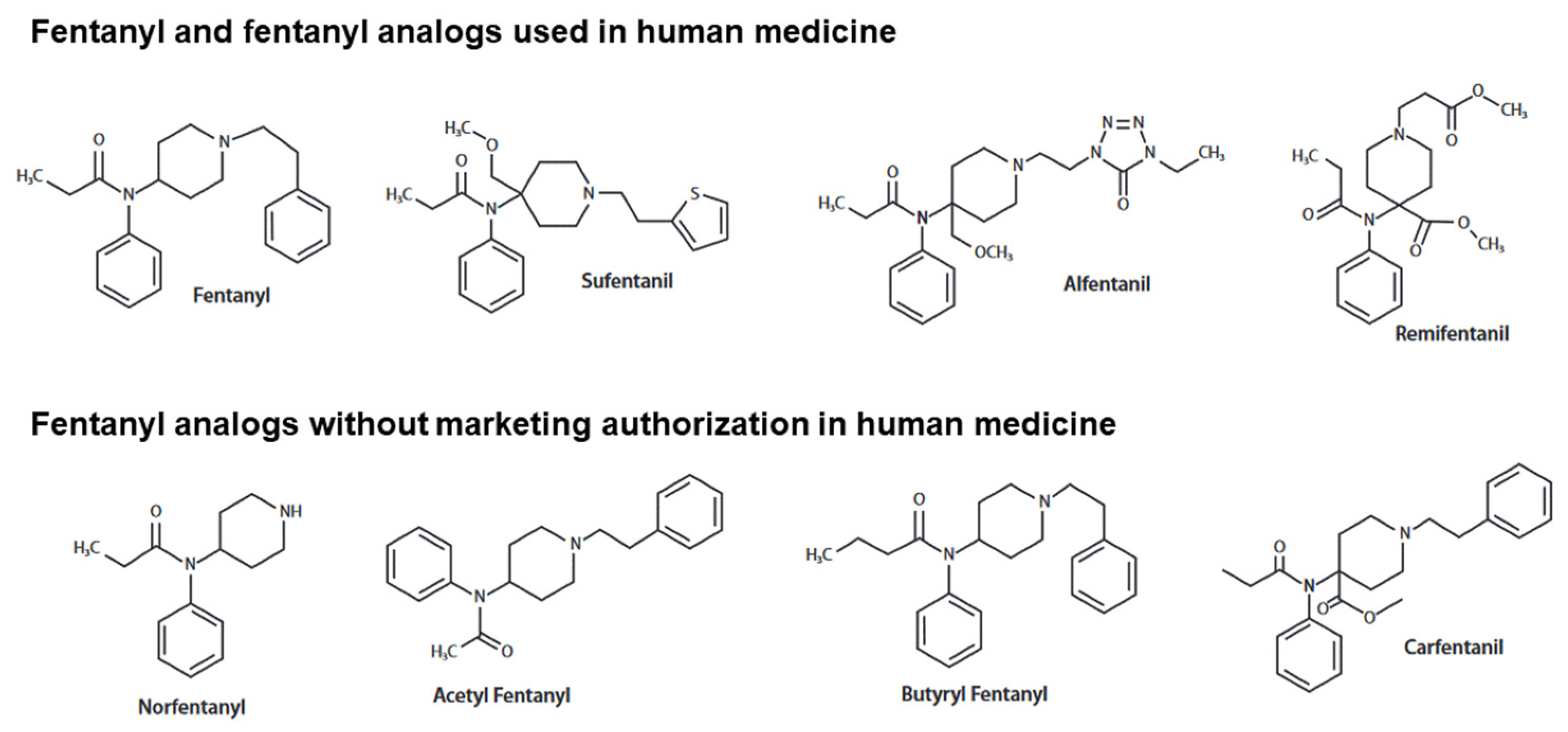
4. Specificities of the Main Fentanyl Analogs
4.1. Carfentanil
4.2. Alfentanil
4.3. Sufentanil
5. Reversal of the Neurorespiratory Toxicity Induced by Fentanyl and Analogs
5.1. Effects of Naloxone
5.2. Alternative Targeted Strategies
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). Overdose Death Rates. National Institute on Drug Abuse. 2023. Available online: https://www.drugabuse.gov/drug-topics/trends-statistics/overdose-death-rates (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- Jannetto, P.J.; Helander, A.; Garg, U.; Janis, G.C.; Goldberger, B.; Ketha, H. The Fentanyl Epidemic and Evolution of Fentanyl Analogs in the United States and the European Union. Clin. Chem. 2019, 65, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardanyan, R.S.; Hruby, V.J. Fentanyl-Related Compounds and Derivatives: Current Status and Future Prospects for Pharmaceutical Applications. Future Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 385–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichini, S.; Solimini, R.; Berretta, P.; Pacifici, R.; Busardò, F.P. Acute Intoxications and Fatalities From Illicit Fentanyl and Analogues: An Update. Ther. Drug Monit. 2018, 40, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoff, E.N.; Zaney, M.E.; Kahl, J.H.; Hime, G.W.; Boland, D.M. Qualitative Identification of Fentanyl Analogs and Other Opioids in Postmortem Cases by UHPLC-Ion Trap-MSn. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2017, 41, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Expert Committee on Drug Dependence, World Health Organization (Ed.) WHO Expert Committee on Drug Dependence: Thirty-Eighth Report; WHO Technical Report Series; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-92-4-121014-0. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Schrier, R.; Dahan, J.D.C.; Boon, M.; Sarton, E.; van Velzen, M.; Niesters, M.; Dahan, A. Advances in Reversal Strategies of Opioid-Induced Respiratory Toxicity. Anesthesiology 2022, 136, 618–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, R.B.; Pryor, M.M.; Baillie, R.; Kudrycki, K.; Friedrich, C.; Reed, M.; Carlo, D.J. Higher naloxone dosing in a quantitative systems pharmacology model that predicts naloxone-fentanyl competition at the opioid mu receptor level. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, J.; Godwin, J.; Purssell, R.; O’Sullivan, F.; Hau, J.P.; Purssell, E.; Curran, J.; Doyle-Waters, M.M.; Brasher, P.M.A.; Buxton, J.A.; et al. Naloxone dosing in the era of ultra-potent opioid overdoses: A systematic review. Can. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 22, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manral, L.; Muniappan, N.; Gupta, P.K.; Ganesan, K.; Malhotra, R.C.; Vijayaraghavan, R. Effect of Exposure to Fentanyl Aerosol in Mice on Breathing Pattern and Respiratory Variables. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 32, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevillard, L.; Mégarbane, B.; Risède, P.; Baud, F.J. Characteristics and Comparative Severity of Respiratory Response to Toxic Doses of Fentanyl, Methadone, Morphine, and Buprenorphine in Rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 191, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.; Santhakumar, R.; Dewey, W.; Kelly, E.; Henderson, G. Fentanyl Depression of Respiration: Comparison with Heroin and Morphine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshneya, N.B.; Hassanien, S.H.; Holt, M.C.; Stevens, D.L.; Layle, N.K.; Bassman, J.R.; Iula, D.M.; Beardsley, P.M. Respiratory Depressant Effects of Fentanyl Analogs Are Opioid Receptor-Mediated. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 195, 114805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, F.; May, W.J.; Gruber, R.B.; Discala, J.F.; Puscovic, V.; Young, A.P.; Baby, S.M.; Lewis, S.J. Role of Central and Peripheral Opiate Receptors in the Effects of Fentanyl on Analgesia, Ventilation and Arterial Blood-Gas Chemistry in Conscious Rats. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2014, 191, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhuang, J.; Xu, F. Contribution of Central μ-Receptors to Switching Pulmonary C-Fibers-Mediated Rapid Shallow Breathing into an Apnea by Fentanyl in Anesthetized Rats. Brain Res. 2012, 1469, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, S.E.; Baekey, D.M.; Levitt, E.S. Fentanyl effects on respiratory neuron activity in the dorsolateral pons. J. Neurophysiol. 2022, 128, 1117–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haouzi, P.; Mellen, N.; McCann, M.; Sternick, M.; Guck, D.; Tubbs, N. Evidence for the Emergence of an Opioid-Resistant Respiratory Rhythm Following Fentanyl Overdose. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2020, 277, 103428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Yuan, M.; Yang, H.; Zhuang, X.; Li, H. P-Glycoprotein on Blood-Brain Barrier Plays a Vital Role in Fentanyl Brain Exposure and Respiratory Toxicity in Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 164, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, C.M.; Waller, J.L.; Moldenhauer, C.C. Postoperative Rigidity Following Fentanyl Anesthesia. Anesthesiology 1983, 58, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, J.A.; Abrams, J.T.; Van Riper, D.F.; Horrow, J.C. Difficult or Impossible Ventilation after Sufentanil-Induced Anesthesia Is Caused Primarily by Vocal Cord Closure. Anesthesiology 1997, 87, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larach, D.B.; Hah, J.M.; Brummett, C.M. Perioperative Opioids, the Opioid Crisis, and the Anesthesiologist. Anesthesiology 2022, 136, 594–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haouzi, P.; Tubbs, N. Effects of Fentanyl Overdose-Induced Muscle Rigidity and Dexmedetomidine on Respiratory Mechanics and Pulmonary Gas Exchange in Sedated Rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 132, 1407–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.W.; Tsou, M.Y.; Lee, T.Y.; Chan, S.H.; Lui, P.W. Antagonization of Fentanyl-Induced Muscular Rigidity by Neurotensin at the Locus Coeruleus of the Rat. Regul. Pept. 1994, 51, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergh, M.S.-S.; Bogen, I.L.; Garibay, N.; Baumann, M.H. Evidence for Nonlinear Accumulation of the Ultrapotent Fentanyl Analog, Carfentanil, after Systemic Administration to Male Rats. Neuropharmacology 2019, 158, 107596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitriou, V.; Zogogiannis, I.; Liotiri, D.; Wambi, F.; Tawfeeq, N.; Koumi, A.; Geldhof, G. Impossible Mask Ventilation after an Unusually Low Dose Fentanyl-Induced Muscle Rigidity in a Patient with Essential Tremor: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Middle East J. Anaesthesiol. 2014, 22, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lui, P.W.; Lee, T.Y.; Chan, S.H. Involvement of Coerulospinal Noradrenergic Pathway in Fentanyl-Induced Muscular Rigidity in Rats. Neurosci. Lett. 1990, 108, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.J.; Tsen, L.Y.; Lee, T.Y.; Lui, P.W.; Chan, S.H. Involvement of cerulospinal glutamatergic neurotransmission in fentanyl-induced muscular rigidity in the rat. Anesthesiology 1997, 87, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freye, E.; Kuschinsky, K. Effects of Fentanyl and Droperidol on the Dopamine Metabolism of the Rat Striatum. Pharmacology 1976, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Gelais, F.; Jomphe, C.; Trudeau, L.-É. The Role of Neurotensin in Central Nervous System Pathophysiology: What Is the Evidence? J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2006, 31, 229–245. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, S.; Lui, P. Inhibition by Neuropeptide Y of Fentanyl-Induced Muscular Rigidity at the Locus Coeruleus in Rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 280, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaros, T.; Kolasiewicz, W. Attenuation of the Fentanyl-Induced Muscle Rigidity by the Selective 5HT1A Agonist 8-OH-DPAT. Pol. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 47, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, M.J.; Lin, T.C.; Lui, P.W.; Lee, T.Y.; Chan, S.H. Involvement of G(o) Alpha Subtype of Guanine Nucleotide-Binding Regulatory Protein at the Locus Coeruleus in Fentanyl-Induced Muscular Rigidity in the Rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1994, 165, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.Y.; Fu, M.J.; Lui, P.W.; Chan, S.H. Involvement of Potassium and Calcium Channels at the Locus Coeruleus in Fentanyl-Induced Muscular Rigidity in the Rat. Neurosci. Lett. 1995, 199, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuet, W.Y.; Pierce, S.A.; Racine, M.C.; Tressler, J.; McCranor, B.J.; Sciuto, A.M.; Wong, B. Changes in Murine Respiratory Dynamics Induced by Aerosolized Carfentanil Inhalation: Efficacy of Naloxone and Naltrexone. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 316, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, B.; Perkins, M.W.; Tressler, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Devorak, J.; Sciuto, A.M. Effects of Inhaled Aerosolized Carfentanil on Real-Time Physiological Responses in Mice: A Preliminary Evaluation of Naloxone. Inhal. Toxicol. 2017, 29, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Port, J.D.; Stanley, T.H.; Steffey, E.P.; Pace, N.L.; Henrickson, R.; McJames, S.W. Intravenous Carfentanyl in the dog and Rhesus monkey. Anesthesiol. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 1984, 61, A378. [Google Scholar]
- Langston, J.L.; Moffett, M.C.; Makar, J.R.; Burgan, B.M.; Myers, T.M. Carfentanil Toxicity in the African Green Monkey: Therapeutic Efficacy of Naloxone. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 325, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moresco, A.; Larsen, R.S.; Sleeman, J.M.; Wild, M.A.; Gaynor, J.S. Use of Naloxone to Reverse Carfentanil Citrate-Induced Hypoxemia and Cardiopulmonary Depression in Rocky Mountain Wapiti (Cervus Elaphus Nelsoni). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2001, 32, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewson, G.; Bradley, P.B. The Effects of Anilidopiperidine Analgesics on Single Respiratory and Non-Respiratory Neurones in the Brain Stem of the Rat. Life Sci. 1982, 31, 2335–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.; Weinger, M.B.; Quinn, M. Alterations in Diaphragm EMG Activity during Opiate-Induced Respiratory Depression. Respir. Physiol. 1995, 100, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butelman, E.R.; France, C.P.; Woods, J.H. Apparent PA2 Analysis on the Respiratory Depressant Effects of Alfentanil, Etonitazene, Ethylketocyclazocine (EKC) and Mr2033 in Rhesus Monkeys. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1993, 264, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Freye, E.; Segeth, M.; Hartung, E. Somatosensory evoked potentials under alfentanyl. Anaesthesist 1984, 33, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Furst, S.R.; Weinger, M.B. Dexmedetomidine, a selective alpha 2-agonist, does not potentiate the cardiorespiratory depression of alfentanil in the rat. Anesthesiology 1990, 72, 882–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeger, K.; Scheinichen, D.; Heine, J.; André, M.; Bund, M.; Piepenbrock, S.; Leuwer, M. Remifentanil, Fentanyl, and Alfentanil Have No Influence on the Respiratory Burst of Human Neutrophils in Vitro. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1998, 42, 1110–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björkman, S.; Redke, F. Influence of Escherichia Coli Endotoxin on the Pharmacokinetics and Respiratory Depressant Effect of Alfentanil in Rabbits. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 85, 680–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latasch, L.; Freye, E. Sufentanil-Related Respiratory Depression and Antinociception in the Dog. Mediation by Different Receptor Types. Arzneimittelforschung 2002, 52, 870–876. [Google Scholar]
- Verborgh, C.M.; Camu, F.; Meert, T.F. Interaction between Sufentanil and U-50488H with Respect to Antinociception and Respiratory Depression in Rats. Acta Anaesthesiol. Scand. 1997, 41, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hoogen, R.H.W.M.; Bervoets, K.J.W.; Colpaert, F.C. Respiratory effects of epidural morphine and sufentanil in the absence and presence of chlordiazepoxide. Pain 1989, 37, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hoogen, R.H.; Bervoets, K.J.; Colpaert, F.C. Respiratory effects of epidural and subcutaneous morphine, meperidine, fentanyl and sufentanil in the rat. Anesth. Analg. 1988, 67, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meert, T.F.; Lu, H.R.; van Craenndonck, H.; Janssen, P.A. Comparison between Epidural Fentanyl, Sufentanil, Carfentanil, Lofentanil and Alfentanil in the Rat: Analgesia and Other in Vivo Effects. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 1988, 5, 313–321. [Google Scholar]
- Hedenqvist, P.; Roughan, J.V.; Flecknell, P.A. Sufentanil and Medetomidine Anaesthesia in the Rat and Its Reversal with Atipamezole and Butorphanol. Lab. Anim. 2000, 34, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, F.; Dierssen, M.; Flórez, J.; Hurlé, M.A. Potentiation of Acute Opioid-Induced Respiratory Depression and Reversal of Tolerance by the Calcium Antagonist Nimodipine in Awake Rats. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1993, 348, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierssen, M.; Flórez, J.; Hurlé, M.A. Calcium Channel Modulation by Dihydropyridines Modifies Sufentanil-Induced Antinociception in Acute and Tolerant Conditions. Naunyn. Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1990, 342, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuczyńska, K.; Grzonkowski, P.; Kacprzak, Ł.; Zawilska, J.B. Abuse of Fentanyl: An Emerging Problem to Face. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 289, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquardt, K.A.; Tharratt, R.S. Inhalation Abuse of Fentanyl Patch. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1994, 32, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poklis, A. Fentanyl: A Review for Clinical and Analytical Toxicologists. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1995, 33, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, P.J.H.; Koeppe, R.A.; Shao, X.; Rodnick, M.E.; Sowa, A.R.; Henderson, B.D.; Stauff, J.; Sherman, P.S.; Arteaga, J.; Carlo, D.J.; et al. The Effects of Intramuscular Naloxone Dose on Mu Receptor Displacement of Carfentanil in Rhesus Monkeys. Mol. Basel Switz. 2020, 25, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralva, R.; Janowsky, A. Noradrenergic Mechanisms in Fentanyl-Mediated Rapid Death Explain Failure of Naloxone in the Opioid Crisis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 371, 453–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.H.; Pleuvry, B.J. Antagonism of the Respiratory Effects of Alfentanil and Fentanyl by Naloxone in the Conscious Rabbit. Br. J. Anaesth. 1981, 53, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhasmana, K.M.; Prakash, O.; Saxena, P.R. Effects of Fentanyl, and the Antagonism by Naloxone, on Regional Blood Flow and Biochemical Variables in Conscious Rabbits. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1982, 260, 115–129. [Google Scholar]
- Voronkov, M.; Nikonov, G.; Ataiants, J.; Isakulyan, L.; Stefanut, C.; Cernea, M.; Abernethy, J. Modifying Naloxone to Reverse Fentanyl-Induced Overdose. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 611, 121326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Ding, X.; Funk, G.D.; Greer, J.J. Ampakine CX717 Protects against Fentanyl-Induced Respiratory Depression and Lethal Apnea in Rats. Anesthesiol. J. Am. Soc. Anesthesiol. 2009, 110, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freye, E.; Latasch, L.; Portoghese, P.S. The Delta Receptor Is Involved in Sufentanil-Induced Respiratory Depression--Opioid Subreceptors Mediate Different Effects. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 1992, 9, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, V.M.; Castaneda, G.; France, C.P. Methocinnamox Reverses and Prevents Fentanyl-Induced Ventilatory Depression in Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2021, 377, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavala, C.A.; Thomaz, A.C.; Iyer, V.; Mackie, K.; Hohmann, A.G. Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Activation Attenuates Fentanyl-Induced Respiratory Depression. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021, 6, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Ding, X.; Greer, J.J. Activating A4β2 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors Alleviates Fentanyl-Induced Respiratory Depression in Rats. Anesthesiology 2019, 130, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutschmann, M.; Waki, H.; Manzke, T.; Simms, A.E.; Pickering, A.E.; Richter, D.W.; Paton, J.F.R. The Potency of Different Serotonergic Agonists in Counteracting Opioid Evoked Cardiorespiratory Disturbances. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2611–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahibzada, N.; Ferreira, M.; Wasserman, A.M.; Taveira-DaSilva, A.M.; Gillis, R.A. Reversal of Morphine-Induced Apnea in the Anesthetized Rat by Drugs That Activate 5-Hydroxytryptamine(1A) Receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292, 704–713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manzke, T.; Dutschmann, M.; Schlaf, G.; Mörschel, M.; Koch, U.R.; Ponimaskin, E.; Bidon, O.; Lalley, P.M.; Richter, D.W. Serotonin Targets Inhibitory Synapses to Induce Modulation of Network Functions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Ding, X.; Greer, J.J. 5-HT1A Receptor Agonist Befiradol Reduces Fentanyl-Induced Respiratory Depression, Analgesia, and Sedation in Rats. Anesthesiology 2015, 122, 424–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Yong, Z.; Su, R. Inhibition of Protein Kinase A and GIRK Channel Reverses Fentanyl-Induced Respiratory Depression. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 677, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, R.R.; Furuya, W.I.; Bautista, T.G.; Dick, T.E.; Galán, R.F.; Dutschmann, M. Increasing Local Excitability of Brainstem Respiratory Nuclei Reveals a Distributed Network Underlying Respiratory Motor Pattern Formation. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasceno, R.S.; Takakura, A.C.; Moreira, T.S. Regulation of the Chemosensory Control of Breathing by Kölliker-Fuse Neurons. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 307, R57–R67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautista, T.G.; Dutschmann, M. Inhibition of the Pontine Kölliker-Fuse Nucleus Abolishes Eupneic Inspiratory Hypoglossal Motor Discharge in Rat. Neuroscience 2014, 267, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, S.E.; Levitt, E.S. Kölliker-Fuse/Parabrachial Complex Mu Opioid Receptors Contribute to Fentanyl-Induced Apnea and Respiratory Rate Depression. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2020, 275, 103388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yong, Z.; Gao, X.; Ma, W.; Dong, H.; Gong, Z.; Su, R. Nalmefene Reverses Carfentanil-Induced Loss of Righting Reflex and Respiratory Depression in Rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 738, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.F.; McNutt, R.W.; Chang, K.J. Delta-Opioid Ligands Reverse Alfentanil-Induced Respiratory Depression but Not Antinociception. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 287, 815–823. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.C.; Bremer, P.T.; Hwang, C.S.; Zhou, B.; Ellis, B.; Hixon, M.S.; Janda, K.D. Monoclonal Antibodies for Combating Synthetic Opioid Intoxication. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 10489–10503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baehr, C.A.; Wu, M.M.; Pandit, S.G.; Arias-Umana, J.; AuCoin, D.; Pravetoni, M. Pharmacological Profiling of Antifentanyl Monoclonal Antibodies in Combination with Naloxone in Pre- and Postexposure Models of Fentanyl Toxicity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2022, 381, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, D.; Baehr, C.; Silva-Ortiz, P.; Khaimraj, A.; Luengas, D.; Hamid, F.A.; Pravetoni, M. Advancing Humanized Monoclonal Antibody for Counteracting Fentanyl Toxicity towards Clinical Development. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 18, 2122507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raleigh, M.D.; Baruffaldi, F.; Peterson, S.J.; Le Naour, M.; Harmon, T.M.; Vigliaturo, J.R.; Pentel, P.R.; Pravetoni, M. A Fentanyl Vaccine Alters Fentanyl Distribution and Protects against Fentanyl-Induced Effects in Mice and Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 368, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haile, C.N.; Baker, M.D.; Sanchez, S.A.; Lopez Arteaga, C.A.; Duddupudi, A.L.; Cuny, G.D.; Norton, E.B.; Kosten, T.R.; Kosten, T.A. An Immunconjugate Vaccine Alters Distribution and Reduces the Antinociceptive, Behavioral and Physiological Effects of Fentanyl in Male and Female Rats. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baehr, C.; Robinson, C.; Kassick, A.; Jahan, R.; Gradinati, V.; Averick, S.E.; Runyon, S.P.; Pravetoni, M. Preclinical Efficacy and Selectivity of Vaccines Targeting Fentanyl, Alfentanil, Sufentanil, and Acetylfentanyl in Rats. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 16584–16592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, C.; Gradinati, V.; Hamid, F.; Baehr, C.; Crouse, B.; Averick, S.; Kovaliov, M.; Harris, D.; Runyon, S.; Baruffaldi, F.; et al. Therapeutic and Prophylactic Vaccines to Counteract Fentanyl Use Disorders and Toxicity. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 14647–14667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Combination | Pharmacological Class | Animal Model | Observed Effects | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sufentanil | U-50488H (co-administration) | selective κ-opioid agonist | Rat | Mild increase in PaCO2 at the highest tested dose, suggesting that μ- and κ-opioid receptor agonists are more beneficial if combined than if administered alone [46] |
| Sufentanil | Chlordiazepoxide (pretreatment) | Benzodiazepine | Rat | More profoundly depressed ventilation [47] |
| Sufentanil | Medetomidine (co-administration) | α2-adrenergic agonist | Rat | Noticeable respiratory depression 30 min post-administration: <50% of resting RR and SaO2 reduced to half [50] |
| Sufentanil | Nimodipine (pretreatment) | Dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker | Rat Cat | Potentiating effects (respiratory rate and tidal volume) [51] |
| Sufentanil | Nimodipine (co-administration) | Dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker | Rat | No additional potentiating effects but counteraction of tolerance to respiratory depression [51] |
| Sufentanil | Bay K 8644 (co-administration) | L-type calcium channel agonist | Cat | Partial antagonization [52] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chamoun, K.; Chevillard, L.; Hajj, A.; Callebert, J.; Mégarbane, B. Mechanisms of Neurorespiratory Toxicity Induced by Fentanyl Analogs—Lessons from Animal Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030382
Chamoun K, Chevillard L, Hajj A, Callebert J, Mégarbane B. Mechanisms of Neurorespiratory Toxicity Induced by Fentanyl Analogs—Lessons from Animal Studies. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(3):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030382
Chicago/Turabian StyleChamoun, Karam, Lucie Chevillard, Aline Hajj, Jacques Callebert, and Bruno Mégarbane. 2023. "Mechanisms of Neurorespiratory Toxicity Induced by Fentanyl Analogs—Lessons from Animal Studies" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 3: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030382
APA StyleChamoun, K., Chevillard, L., Hajj, A., Callebert, J., & Mégarbane, B. (2023). Mechanisms of Neurorespiratory Toxicity Induced by Fentanyl Analogs—Lessons from Animal Studies. Pharmaceuticals, 16(3), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030382