Characterization of Lemon Pepper and Black Ginger Extracts and Macroemulsions as Natural Pain Relievers for Spice Stick Balsam Formulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Yield and Active Compounds Profiling of Lemon Pepper and Black Ginger Extracts
2.2. Characteristics of Lemon Pepper and Black Ginger Macroemulsions
2.3. Antioxidant Activity of Lemon Pepper and Black Ginger Extracts and Macroemulsions
2.4. Characteristics and Stability of Lemon Pepper and Black Ginger Stick Balsams
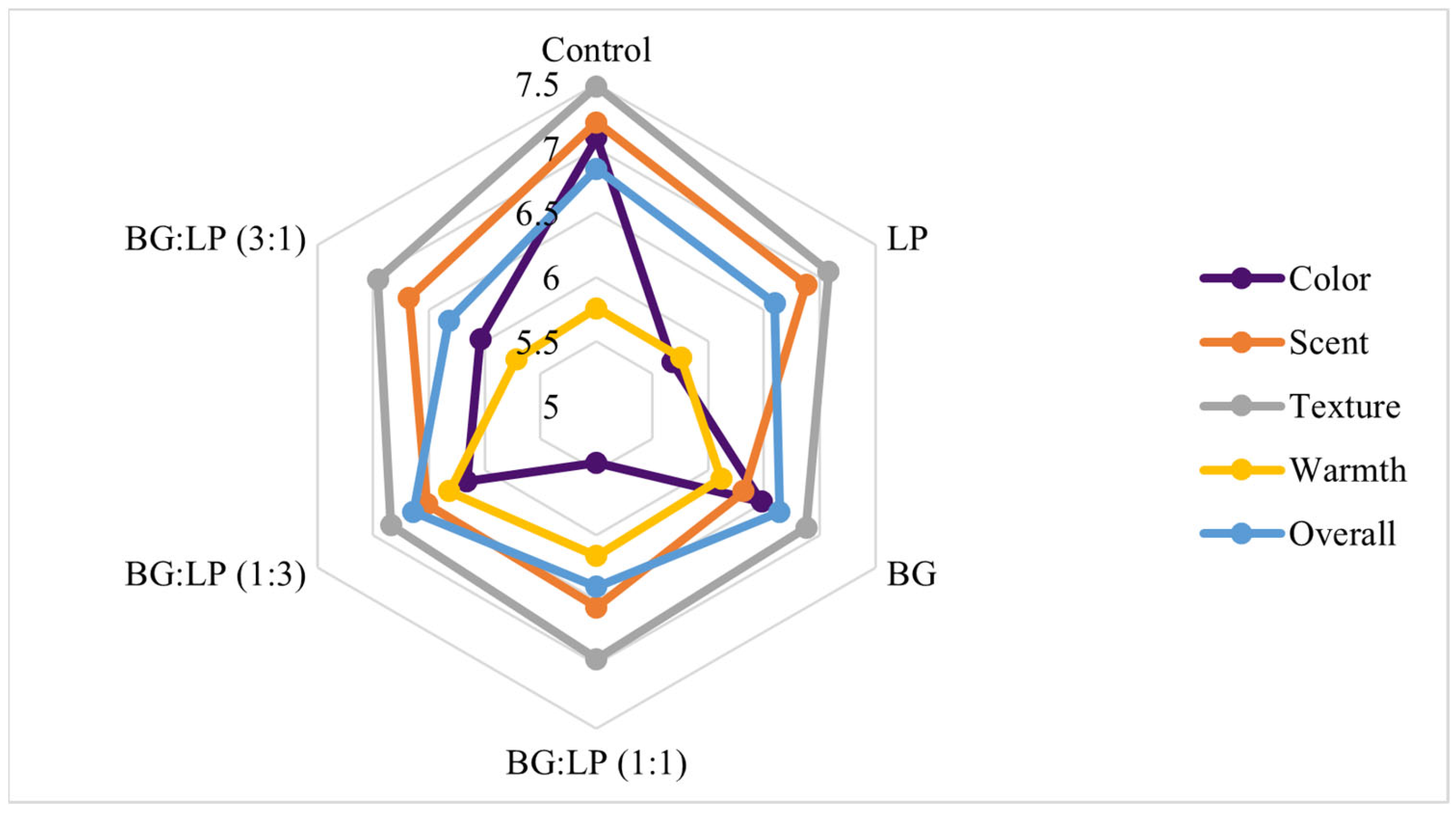
2.5. Organoleptic Results of Lemon Pepper and Black Ginger Stick Balsams
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Spices Preparation and Extraction
4.2. Active Compounds Profiling
4.3. Macroemulsion Formulation
4.4. Antioxidant Activity Assay
4.5. Spice Balsam Formulation
4.6. Characteristic Tests
4.7. Stability Test
4.8. Organoleptic Test
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Indonesian Agency for Drug and Food Control. Regulation of Safety and Quality of Traditional Drugs; Indonesian Agency for Drug and Food Control: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, Y.H.; Sun, C.C.; Tseng, Y.H.; Chu, C.Y. Contact dermatitis to topical medicaments: A retrospective study from a medical center from Taiwan. Dermatol. Sin. 2015, 33, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmania, A.N.; Ersalin, C.N.A.; Pratiwi, R.; Ula, C.L.; Murti, B.H.; Jikson, N.A.; Amirah, N.F.; Wijayanti, P.; Addin, M.A.; Rianti, M.C.; et al. Society knowledge on the use of transdermal patch for pain relief as the external analgesic drug. JFK 2015, 2, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wijaya, C.H.; Napitupulu, F.I.; Karnady, V.; Indariani, S. A review of the bioactivity and flavor properties of the exotic spice “andaliman” (Zanthoxylum acanthopodium DC.). Foods Rev. Int. 2019, 35, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanti, T.E.P.; Nuriasari, N.; Juliana, K. Lemon pepper fruit extract (Zanthoxylum acanthopodium DC.) suppresses the expression of inflammatory mediators in lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophages in vitro. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechol. 2011, 7, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Setiadi, A.Y.L.A.; Karmawan, L.U.; Yanti. Anti-arthritic and anti-inflammatory effects of andaliman extract and nanoandaliman in inflammatory arthritic mice. Foods 2022, 11, 3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.L.; Li, H.L.; Li, W.; Feng, S.; Deng, D.S. Kaempferia parviflora and its methoxyflavones: Chemistry and biological activities. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 4057456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, R.C.S.; Andrade, L.N.; Sousa, D.P. A review on anti-inflammatory activity of monoterpenes. Molecules 2013, 18, 1227–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Asamenew, G.; Kim, H.W.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Cha, Y.S.; Yoo, S.M.; Kim, J.B. Characterization of phenolic compounds from normal ginger (Zingiber officinale Rosc.) and black ginger (Kaempferia parviflora Wall.) using UPLC–DAD–QToF–MS. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q.Q.; Xu, X.Y.; Cao, S.Y.; Gan, R.Y.; Corke, H.; Beta, T.; Li, H.B. Bioactive compounds and bioactivities of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe). Foods 2019, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaranjani, M.; Leskinen, K.; Aravindraja, C.; Saavalainen, P.; Pandian, S.K.; Skurnik, M.; Ravi, A.V. Deciphering the antibacterial mode of action of alpha-mangostin on Staphylococcus epidermidis RP62A through an integrated transcriptomic and proteomic approach. Front Microbiol. 2019, 10, 150–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizawa, Y.; Miyagawa, Y.; Yoshida9, M.; Adachi, S. Effect of crystallization of oil phase on the destabilization of O/W emulsions containing vegetable oils with low melting points. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 582, 123824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, D.K.; Lestari, R.S.D. Effect of time and stirring speed on emulsion of sunflower oil (Helianthus annuus L.) and water. J. Integr. Pros. 2015, 5, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Kedare, S.B.; Singh, R.P. Genesis and development of DPPH method of antioxidant assay. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatimah, F.; Fardiaz, D.; Apriyantono, A.; Andarwulan, N. Effect of oil content on antioxidant activity in oil-in-water emulsion. J. Teknol. Indus. Pangan. 2005, 16, 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Indonesian Agency for Drug and Food Control. Regulation for Total Plate Count Number in Food and Drug Products in Indonesia. Available online: https://peraturanpedia.id/peraturan-badan-pengawas-obat-dan-makanan-nomor-1-tahun-2019/ (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Tarwendah, I.P. Journal review: Comparison study on sensory attributes and awareness for food brands. J. Pangan. Agroindus. 2017, 5, 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- Panggabean, L.; Nurhamidah; Handayani, D. Phytochemical profile and toxicity test of ethanolic extract of Zanthoxylum acanthopodium DC (andaliman) using BSLT method. J. Pend. Ilmu. Kim. 2020, 4, 59–68. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, Z.A.; Shukor, S.A.; Abbas, H.; Machap, C.A.L.; Alias, M.S.B.; Mirad, R.; Sofiyanand, S.; Othman, A.N. Optimization of extraction conditions for total phenolics and total flavonoids from Kaempferia parviflora rhizomes. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2018, 9, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, O.Z.; Rao, K.S.; Bidalia, A.; Wangkheirakpam, R.; Singh, O.M. GC-MS analysis of phytocomponents and antifungal activities of Zanthoxylum acanthopodium DC. collected from Manipur, India. Eur. J. Med. Plants 2015, 10, EJMP.19353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitakpawasutthi, Y.; Palanuvej, C.; Ruangrungsi, N. Quality evaluation of Kaempferia parviflora rhizome with reference to 5,7-dimethoxyflavone. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2018, 9, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hayati, R.; Balqis, C.P. Formulation of garlic topical emulsion (Allium sativum L.) as a natural insecticidal agent against hair lice. Pharm. J. Indones. 2020, 17, 30–316. [Google Scholar]
- Ghimeray, A.K.; Jung, U.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Ryu, E.K.; Chang, M.S. In vitro antioxidant, collagenase inhibition, and in vivo anti-wrinkle effects of combined formulation containing Punica granatum, Ginkgo biloba, Ficus carica, and Morus alba fruits extracts. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 8, 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athaillah, A.; Lianda, S.O. Formulation and evaluation of stick balsam made from red ginger oleoresin (Zingiber officinale Rosc) as a pain relief for muscle and joint. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 4, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Abna, I.M.; Amir, M.; Puspitalena, A.; Hurit, H.E. Determination of bacterial total viable count in several unbranded pasteurized milk products at Cengkareng region, West Jakarta. Arch. Pharm. 2021, 3, 49–57. [Google Scholar]




| Extract | Group | Compound | RT | SI | Area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lemon pepper | Monoterpenes | D-limonene | 11.02 | 635 | 0.26 |
| Verbenol | 7.72 | 671 | 0.06 | ||
| Geraniol | 15.72 | 882 | 17.26 | ||
| Citronellal | 13.33 | 789 | 1.01 | ||
| Geranyl formate | 16.67 | 848 | 5.63 | ||
| Black ginger | Phenolics | 6-Shogaol | 40.36 | 899 | 5.73 |
| 6-Iso-shogaol | 59.32 | 634 | 10.05 | ||
| Polyphenols | Gingerol | 41.88 | 686 | 2.28 | |
| Methylated flavonoids | 2-hydroxy-7,3′,4′,5′ tetramethoxyflavone | 33.93 | 586 | 0.07 | |
| Xanthones | Mangostine | 57.19 | 950 | 0.33 |
| Stick Balsam | Homogeneity | Spread Ability (cm) | Adhesion (s) | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Yes | 4.90 ± 0.10 | 70.00 ± 9.54 | 6.00 ± 0.00 |
| LP | Yes | 4.83 ± 0.12 | 37.67 ± 7.37 | 5.00 ± 0.00 |
| BG | Yes | 4.70 ± 0.10 | 43.67 ± 1.15 | 5.00 ± 0.00 |
| BG:LP (1:1) | Yes | 4.53 ± 0.06 | 34.67 ± 3.51 | 5.00 ± 0.00 |
| BG:LP (1:3) | Yes | 4.73 ± 0.15 | 38.67 ± 5.51 | 5.00 ± 0.00 |
| BG:LP (3:1) | Yes | 4.73 ± 0.06 | 51.00 ± 3.61 | 5.00 ± 0.00 |
| Commercial stick balsam (GELIGA®) | Yes | 4.77 ± 0.06 | 51.33 ± 4.04 | 6.00 ± 0.00 |
| Stick Balsam | Color | Scent | Texture | Warmth | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 7.08 ± 1.32 b | 7.2 ± 1.41 a | 7.48 ± 1.23 a | 5.76 ± 1.71 a | 6.84 ± 1.07 a |
| LP | 5.68 ± 1.44 a | 6.88 ± 1.45 a | 7.08 ± 1.04 a | 5.76 ± 1.54 a | 6.6 ± 1.22 a |
| BG | 6.48 ± 1.58 ab | 6.32 ± 1.60 a | 6.88 ± 1.51 a | 6.12 ± 1.36 a | 6.64 ± 1.29 a |
| BG:LP (1:1) | 5.44 ± 1.87 a | 6.56 ± 1.76 a | 6.96 ± 1.46 a | 6.16 ± 1.80 a | 6.4 ± 1.44 a |
| BG:LP (1:3) | 6.16 ± 1.25 ab | 6.52 ± 1.61 a | 6.84 ± 1.18 a | 6.32 ± 1.38 a | 6.64 ± 1.41 a |
| BG:LP (3:1) | 6.04 ± 2.24 ab | 6.68 ± 1.38 a | 6.96 ± 1.49 a | 5.72 ± 1.62 a | 6.32 ± 1.46 a |
| Composition | Amount (%) |
|---|---|
| Spice extract * | 10 |
| Soy oil | 10 |
| Propylene glycol | 20 |
| Tween 80 | 20 |
| Ethanol 96% food grade | 15 |
| Aquadest | 25 |
| Formulation (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Composition | Control (a) | LP (b) | BG (c) | BG:LP (1:1) (d) | BG:LP (1:3) (e) | BG:LP (3:1) (f) |
| LP * | - | 15.00 | - | 7.50 | 11.25 | 3.75 |
| BG * | - | - | 15.00 | 7.50 | 3.75 | 11.25 |
| Paraffin | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 |
| Cera alba | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 | 8.00 |
| Vaseline | 65.00 | 65.00 | 65.00 | 65.00 | 65.00 | 65.00 |
| Menthol | 3.50 | 3.50 | 3.50 | 3.50 | 3.50 | 3.50 |
| BHT | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yanti; Harijono, C.; Lay, B.W. Characterization of Lemon Pepper and Black Ginger Extracts and Macroemulsions as Natural Pain Relievers for Spice Stick Balsam Formulation. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030371
Yanti, Harijono C, Lay BW. Characterization of Lemon Pepper and Black Ginger Extracts and Macroemulsions as Natural Pain Relievers for Spice Stick Balsam Formulation. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(3):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030371
Chicago/Turabian StyleYanti, Celinia Harijono, and Bibiana Widiyati Lay. 2023. "Characterization of Lemon Pepper and Black Ginger Extracts and Macroemulsions as Natural Pain Relievers for Spice Stick Balsam Formulation" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 3: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030371
APA StyleYanti, Harijono, C., & Lay, B. W. (2023). Characterization of Lemon Pepper and Black Ginger Extracts and Macroemulsions as Natural Pain Relievers for Spice Stick Balsam Formulation. Pharmaceuticals, 16(3), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030371






