Prolonged Alprazolam Treatment Alters Components of Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in the Hippocampus of Male Wistar Rats—The Neuroadaptive Changes following Long-Term Benzodiazepine (Mis)Use
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
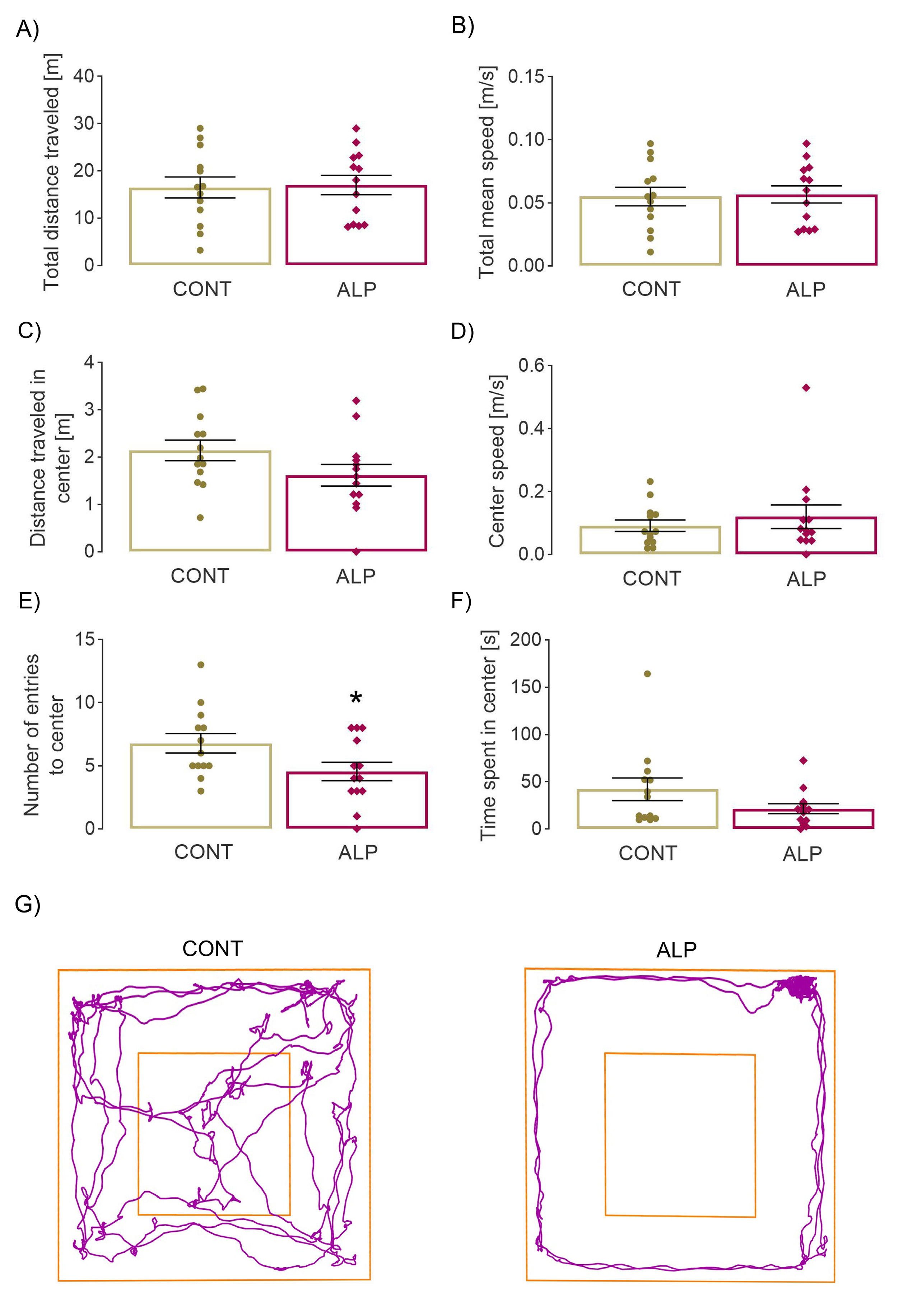
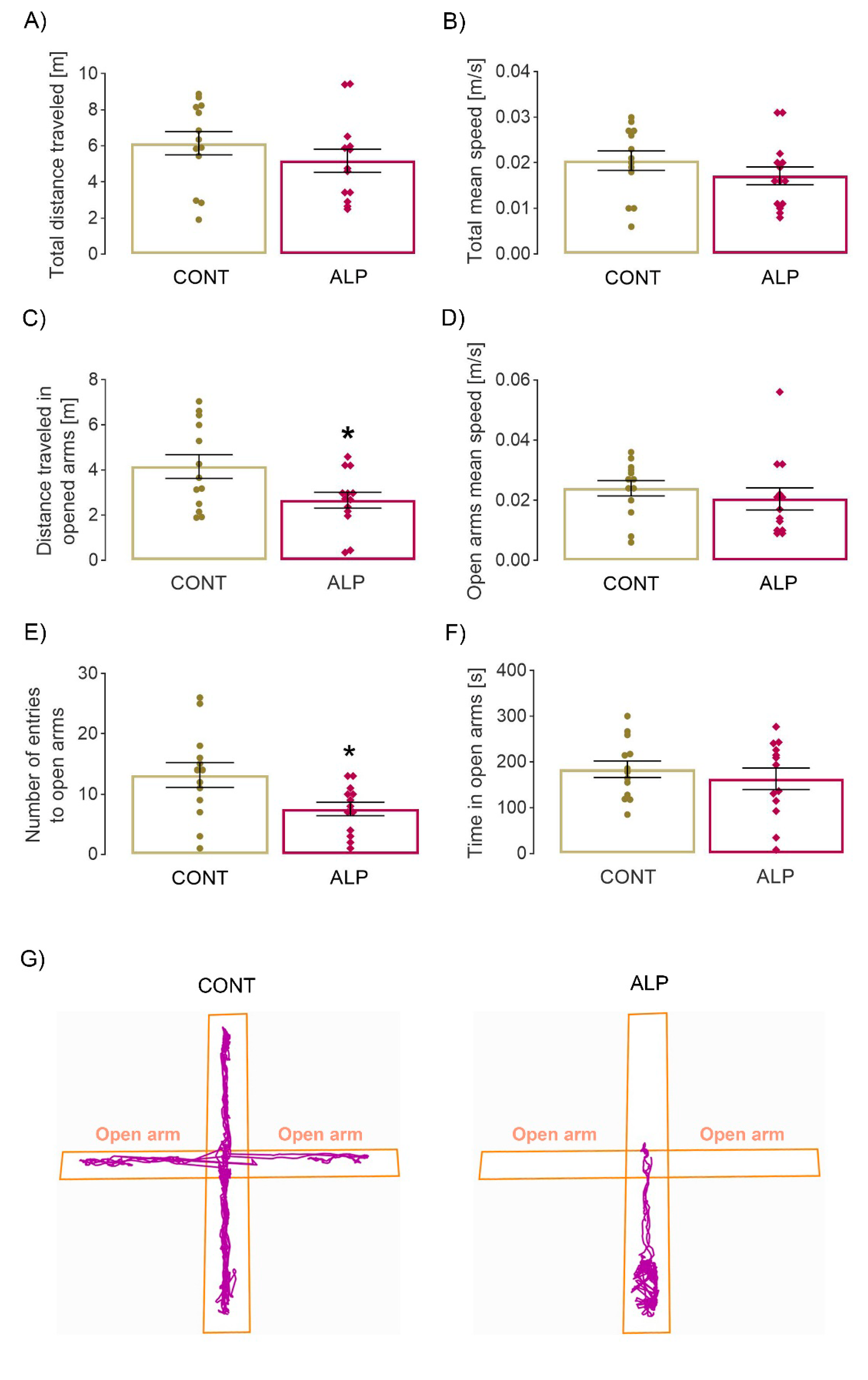
2.1. Effect of Prolonged ALP Treatment on Anxiety—Like Behavior
2.1.1. Open Field Test
2.1.2. Elevated Plus Maze Test
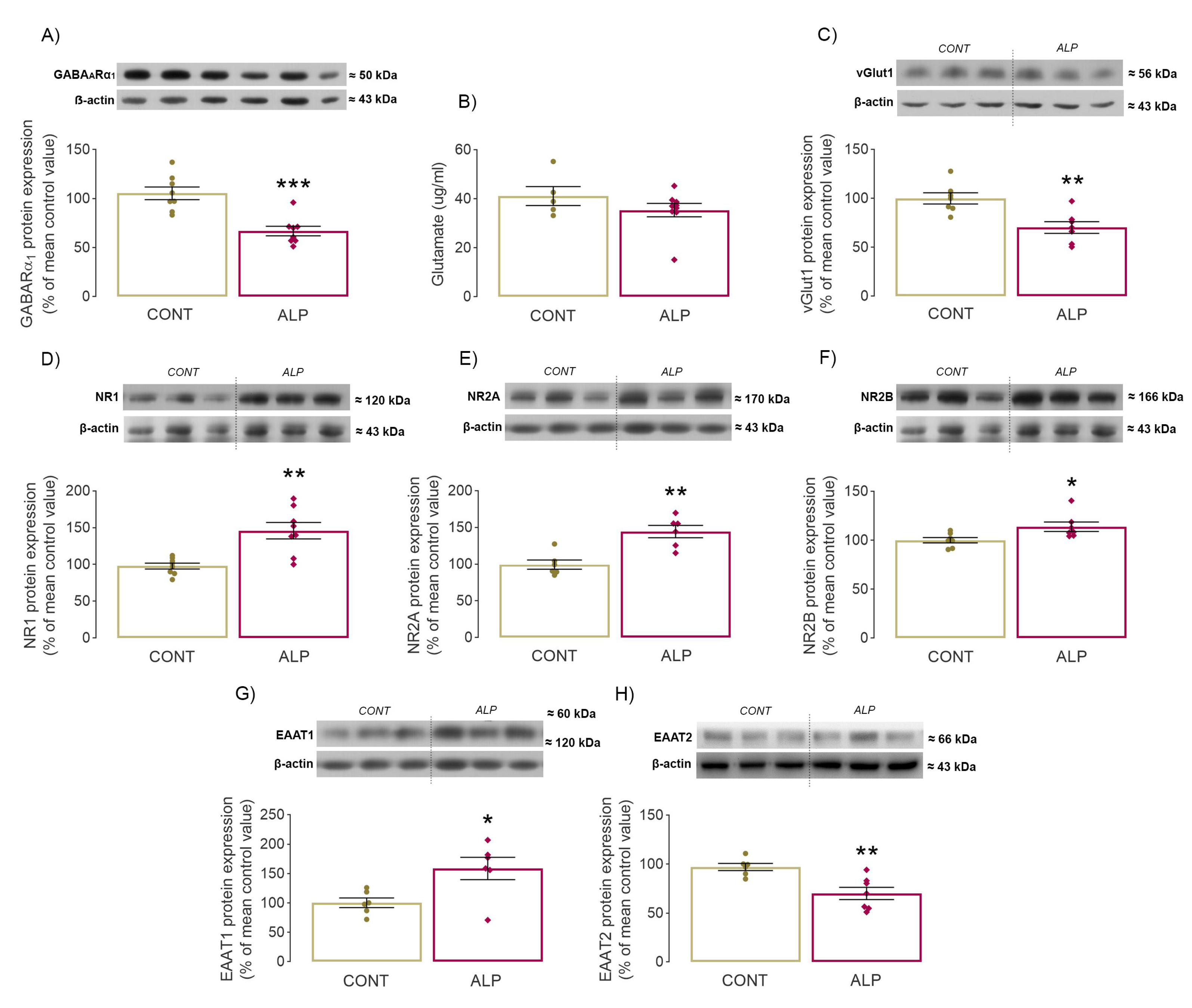
2.2. Effect of Prolonged ALP Treatment on Protein Expression of GARAAR α1 Subunit
2.3. Effect of Prolonged ALP Treatment on Components of Glutamatergic Signaling
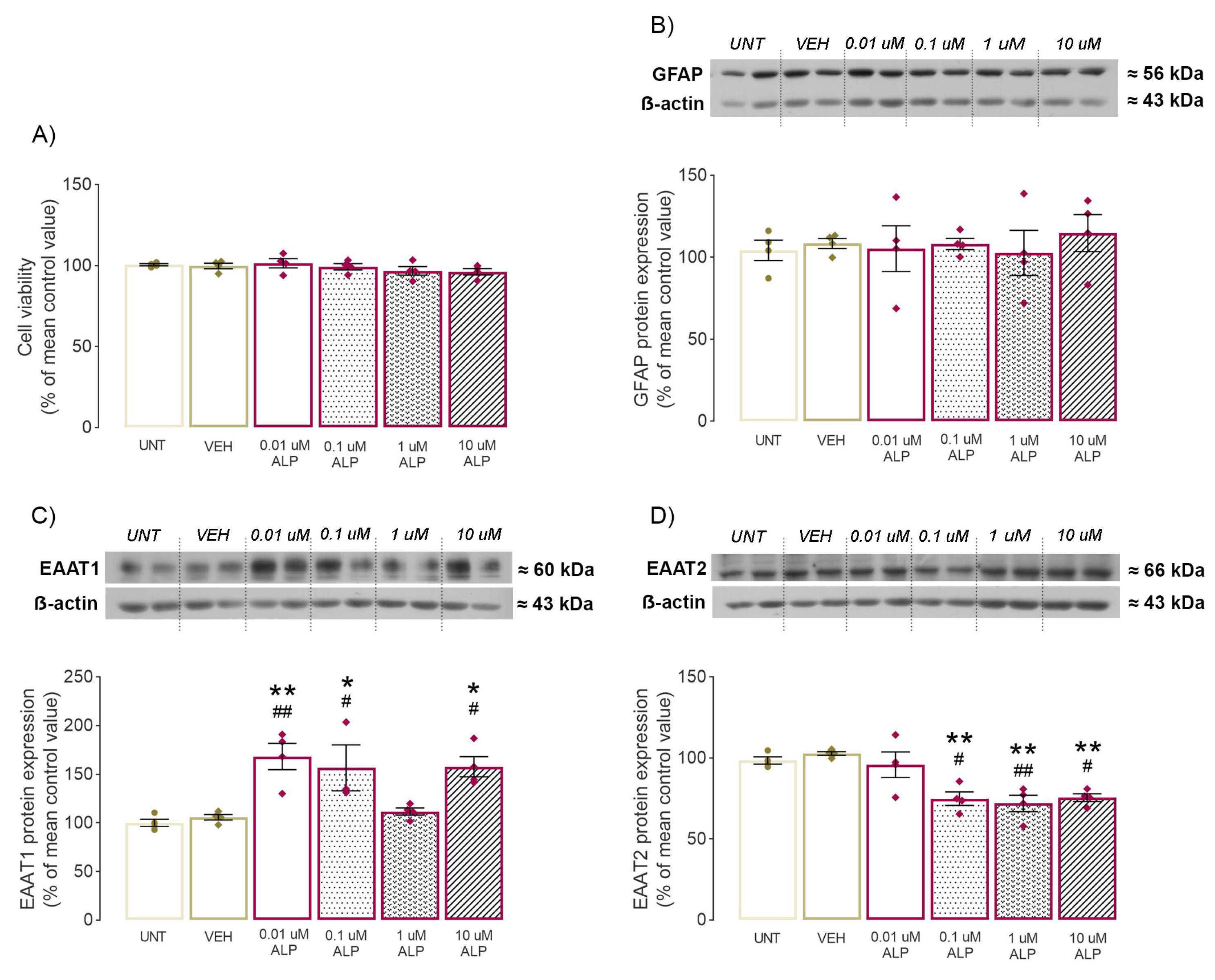
2.4. Effect of 48-h ALP Treatment on Astrocytes’ Viability
2.5. Effect of 48-h ALP Treatment on GFAP Protein Expression In Vitro
2.6. Effect of 48-h ALP Treatment on EAAT1/2 Protein Expression In Vitro
3. Discussion
3.1. “Crosstalk between Behavior and GABAAR”—Changes in Anxiety-Like Behavior Together with Significant GARAARα1 Decrease following Prolonged ALP Treatment
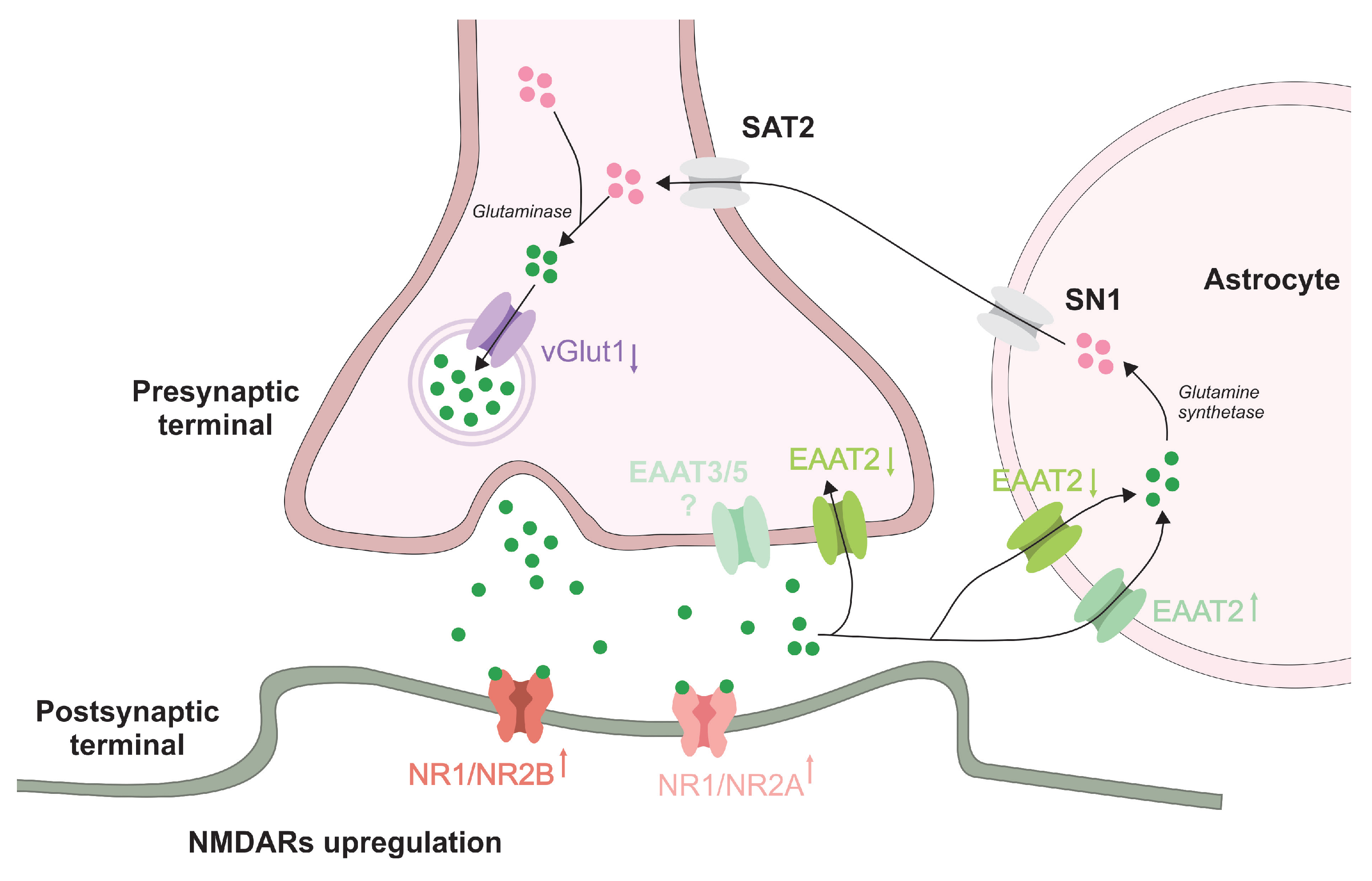
3.2. Changes in Glutamatergic Neurotransmission following Prolonged ALP Treatment—Alterations of NMDAR Subunits, vGlut1 and EAAT1/2 Levels
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Groups and Treatment—In Vivo
4.2. Behavioral Testing
4.3. Open Field Test
4.4. Elevated Plus Maze Test
4.5. Preparation of Crude Synaptosomal P2 fraction In Vivo
4.6. Western Blot Analysis—In Vivo
4.7. Examination of Glutamate Level
4.8. Experimental Groups and Treatment—In Vitro
4.9. Western Blot Analysis—In Vitro
4.10. Microculture Tetrazolium Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALP | alprazolam |
| AMPAR | α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor |
| BDZ | benzodiazepine |
| EAAT1 | excitatory amino acid transporter 1 |
| EAAT2 | excitatory amino acid transporter 2 |
| GABA | gammaaminobutyric acid |
| GABAAR | gammaaminobutyric acid receptor type A |
| GABAARα1 | α1 subunit of gammaaminobutyric acid receptor type A |
| HIP | hippocampus |
| MTT assay | microculture tetrazolium assay |
| NMDAR | N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor |
| NR1 | type 1 subunit of N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor |
| NR2A | type 2A subunit of N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor |
| NR2B | type 2B subunit of N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor |
| vGluT1 | vesicular glutamate transporter 1 |
References
- Ait-Daoud, N.; Hamby, A.S.; Sharma, S.; Blevins, D. A Review of Alprazolam Use, Misuse, and Withdrawal. J. Addict. Med. 2018, 12, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, I.A.; Gorgels, W.J.; Oude Voshaar, R.C.; Mulder, J.; Lucassen, P.L. Tolerance to benzodiazepines among long-term users in primary care. Fam. Pract. 2013, 30, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edinoff, A.N.; Nix, C.A.; Hollier, J.; Sagrera, C.E.; Delacroix, B.M.; Abubakar, T.; Cornett, E.M.; Kaye, A.M.; Kaye, A.D. Benzodiazepines: Uses, Dangers, and Clinical Considerations. Neurol. Int. 2021, 13, 594–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedegaard, H.; Bastian, B.A.; Trinidad, J.P.; Spencer, M.; Warner, M. Drugs Most Frequently Involved in Drug Overdose Deaths: United States, 2011–2016. Natl. Vital Stat. Rep. 2018, 67, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- George, T.T.; Tripp, J. Alprazolam. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- McKernan, R.M.; Rosahl, T.W.; Reynolds, D.S.; Sur, C.; Wafford, K.A.; Atack, J.R.; Farrar, S.; Myers, J.; Cook, G.; Ferris, P.; et al. Sedative but not anxiolytic properties of benzodiazepines are mediated by the GABA(A) receptor alpha1 subtype. Nat. Neurosci. 2000, 3, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinkers, C.H.; Olivier, B. Mechanisms Underlying Tolerance after Long-Term Benzodiazepine Use: A Future for Subtype-Selective GABA(A) Receptor Modulators? Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 2012, 416864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izzo, E.; Auta, J.; Impagnatiello, F.; Pesold, C.; Guidotti, A.; Costa, E. Glutamic acid decarboxylase and glutamate receptor changes during tolerance and dependence to benzodiazepines. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3483–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steppuhn, K.G.; Turski, L. Diazepam dependence prevented by glutamate antagonists. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 6889–6893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sickle, B.J.; Cox, A.S.; Schak, K.; Greenfield, L.J., Jr.; Tietz, E.I. Chronic benzodiazepine administration alters hippocampal CA1 neuron excitability: NMDA receptor function and expression. Neuropharmacology 2002, 43, 595–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, C.; Pratt, J.A. Neuroadaptive processes in GABAergic and glutamatergic systems in benzodiazepine dependence. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 98, 171–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Campuzano, A.G.; Ortega, A. Glutamate transporters: Critical components of glutamatergic transmission. Neuropharmacology 2021, 192, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braestrup, C.; Albrechtsen, R.; Squires, R.F. High densities of benzodiazepine receptors in human cortical areas. Nature 1977, 269, 702–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Blas, A.L.; Vitorica, J.; Friedrich, P. Localization of the GABAA receptor in the rat brain with a monoclonal antibody to the 57,000 Mr peptide of the GABAA receptor/benzodiazepine receptor/Cl- channel complex. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 602–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squires, R.F.; Brastrup, C. Benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain. Nature 1977, 266, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkus, C.; McHugh, S.B.; Sprengel, R.; Seeburg, P.H.; Rawlins, J.N.; Bannerman, D.M. Hippocampal NMDA receptors and anxiety: At the interface between cognition and emotion. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 626, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.C.; Su, K.; Goldberg, A.R.; Luna, V.M.; Biane, J.S.; Ordek, G.; Zhou, P.; Ong, S.K.; Wright, M.A.; Zweifel, L.; et al. Anxiety Cells in a Hippocampal-Hypothalamic Circuit. Neuron 2018, 97, 670–683.e676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanselow, M.S.; Dong, H.W. Are the dorsal and ventral hippocampus functionally distinct structures? Neuron 2010, 65, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelmsson, U.; Bushong, E.A.; Price, D.L.; Smarr, B.L.; Phung, V.; Terada, M.; Ellisman, M.H.; Pekny, M. Redefining the concept of reactive astrocytes as cells that remain within their unique domains upon reaction to injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17513–17518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, A.R.; Willnow, T.E. Excitatory Amino Acid Transporters in Physiology and Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- File, S.E. Tolerance to the behavioral actions of benzodiazepines. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1985, 9, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haigh, J.R.; Feely, M. Tolerance to the anticonvulsant effect of benzodiazepines. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1988, 9, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, U.; Luddens, H.; Hiemke, C. Behavioral analysis indicates benzodiazepine-tolerance mediated by the benzodiazepine binding-site at the GABA(A)-receptor. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 25, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravielle, M.C. Activation-induced regulation of GABAA receptors: Is there a link with the molecular basis of benzodiazepine tolerance? Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 109, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duke, A.N.; Tiruveedhula, V.; Sharmin, D.; Knutson, D.E.; Cook, J.M.; Platt, D.M.; Rowlett, J.K. Tolerance and dependence following chronic alprazolam treatment in rhesus monkeys: Role of GABA(A) receptor subtypes. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2021, 228, 108985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, J.S.; Hines, R.M. Regulation of GABAA Receptor Subunit Expression in Substance Use Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.E.; Jensen, J.E.; Licata, S.C.; Ravichandran, C.; Butman, M.L.; Shanahan, M.; Lauriat, T.L.; Renshaw, P.F. The acute and late CNS glutamine response to benzodiazepine challenge: A pilot pharmacokinetic study using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Psychiatry Res. 2010, 184, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonavita, C.; Ferrero, A.; Cereseto, M.; Velardez, M.; Rubio, M.; Wikinski, S. Adaptive changes in the rat hippocampal glutamatergic neurotransmission are observed during long-term treatment with lorazepam. Psychopharmacology 2003, 166, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.F.; Salmiron, R.; Ramirez, O.A. NMDA-NR1 and -NR2B subunits mRNA expression in the hippocampus of rats tolerant to Diazepam. Behav. Brain Res. 2003, 144, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Shimizu, N.; Yajima, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Misawa, M. Hypersusceptibility to DMCM-induced seizures during diazepam withdrawal in mice: Evidence for upregulation of NMDA receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’Pharmacol. 1998, 357, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- File, S.E.; Fernandes, C. Dizocilpine prevents the development of tolerance to the sedative effects of diazepam in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1994, 47, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, D.N.; Turski, L. Kindling to the benzodiazepine receptor inverse agonist, FG 7142: Evidence for involvement of NMDA, but not non-NMDA, glutamatergic receptors. Neuropharmacology 1993, 32, 1011–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, D.N.; Andrews, J.S.; Turski, L.; Schneider, H.H. Excitatory Amino Acids and Anxiety. In New Concepts in Anxiety; Briley, M., File, S.E., Eds.; Macmillan Education: London, UK, 1991; pp. 366–381. [Google Scholar]
- Palmada, M.; Kinne-Saffran, E.; Centelles, J.J.; Kinne, R.K. Benzodiazepines differently modulate EAAT1/GLAST and EAAT2/GLT1 glutamate transporters expressed in CHO cells. Neurochem. Int. 2002, 40, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, P. The Laboratory Rat: Relating Its Age With Human’s. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mitrovic, N.; Gusevac, I.; Drakulic, D.; Stanojlovic, M.; Zlatkovic, J.; Sevigny, J.; Horvat, A.; Nedeljkovic, N.; Grkovic, I. Regional and sex-related differences in modulating effects of female sex steroids on ecto-5′-nucleotidase expression in the rat cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2016, 235, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwell, M.A.; Haas, S.M.; Bieber, L.L.; Tolbert, N.E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal. Biochem. 1978, 87, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragic, M.; Milicevic, K.; Adzic, M.; Stevanovic, I.; Ninkovic, M.; Grkovic, I.; Andjus, P.; Nedeljkovic, N. Trimethyltin Increases Intracellular Ca(2+) Via L-Type Voltage-Gated Calcium Channels and Promotes Inflammatory Phenotype in Rat Astrocytes In Vitro. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 1792–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Antigen | Manufacturer and Catalog No | Species and Dilution |
|---|---|---|
| NR1 | Cell Signaling Techonology, USA, #5704 RRID: AB_1904067 | rabbit monoclonal; 1:1000 |
| NR2A | Merck Millipore, USA, #07-632 RRID: AB_310837 | rabbit monoclonal; 1:1000 |
| NR2B | Abcam, UK, 93610 RRID: AB_10561972 | mouse monoclonal, 1:4000 |
| vGluT1 | Abcam, UK, 134283 RRID: AB_2923539 | mouse monoclonal, 1:4000 |
| EAAT1 | Cell Signaling Techonology, USA; # 5684T RRID: AB_10671594 | rabbit monoclonal; 1:1000 |
| EAAT2 | Abcam, UK; ab69098 RRID: AB_2190732 | rabbit monoclonal; 1:1000 |
| GABAAR α1 | Sigma Aldrich, USA, G4416 RRID: AB_477016 | rabbit monoclonal; 1:5000 |
| β-actin | Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA; PA1-21167 RRID: AB_557422 | rabbit polyclonal; 1:5000 |
| mouse IgG | R&D systems, bio-techne, USA; HAF007 RRID: AB_357234 | goat polyclonal; 10,000 |
| rabbit IgG | Invitrogen, USA; # 31460 RRID: AB_228341 | goat polyclonal; 1:10,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zaric Kontic, M.; Dragic, M.; Martinovic, J.; Mihajlovic, K.; Brkic, Z.; Mitrovic, N.; Grkovic, I. Prolonged Alprazolam Treatment Alters Components of Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in the Hippocampus of Male Wistar Rats—The Neuroadaptive Changes following Long-Term Benzodiazepine (Mis)Use. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030331
Zaric Kontic M, Dragic M, Martinovic J, Mihajlovic K, Brkic Z, Mitrovic N, Grkovic I. Prolonged Alprazolam Treatment Alters Components of Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in the Hippocampus of Male Wistar Rats—The Neuroadaptive Changes following Long-Term Benzodiazepine (Mis)Use. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(3):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030331
Chicago/Turabian StyleZaric Kontic, Marina, Milorad Dragic, Jelena Martinovic, Katarina Mihajlovic, Zeljka Brkic, Natasa Mitrovic, and Ivana Grkovic. 2023. "Prolonged Alprazolam Treatment Alters Components of Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in the Hippocampus of Male Wistar Rats—The Neuroadaptive Changes following Long-Term Benzodiazepine (Mis)Use" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 3: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030331
APA StyleZaric Kontic, M., Dragic, M., Martinovic, J., Mihajlovic, K., Brkic, Z., Mitrovic, N., & Grkovic, I. (2023). Prolonged Alprazolam Treatment Alters Components of Glutamatergic Neurotransmission in the Hippocampus of Male Wistar Rats—The Neuroadaptive Changes following Long-Term Benzodiazepine (Mis)Use. Pharmaceuticals, 16(3), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16030331






