Sorafenib Alleviates Inflammatory Signaling of Tumor Microenvironment in Precancerous Lung Injuries
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
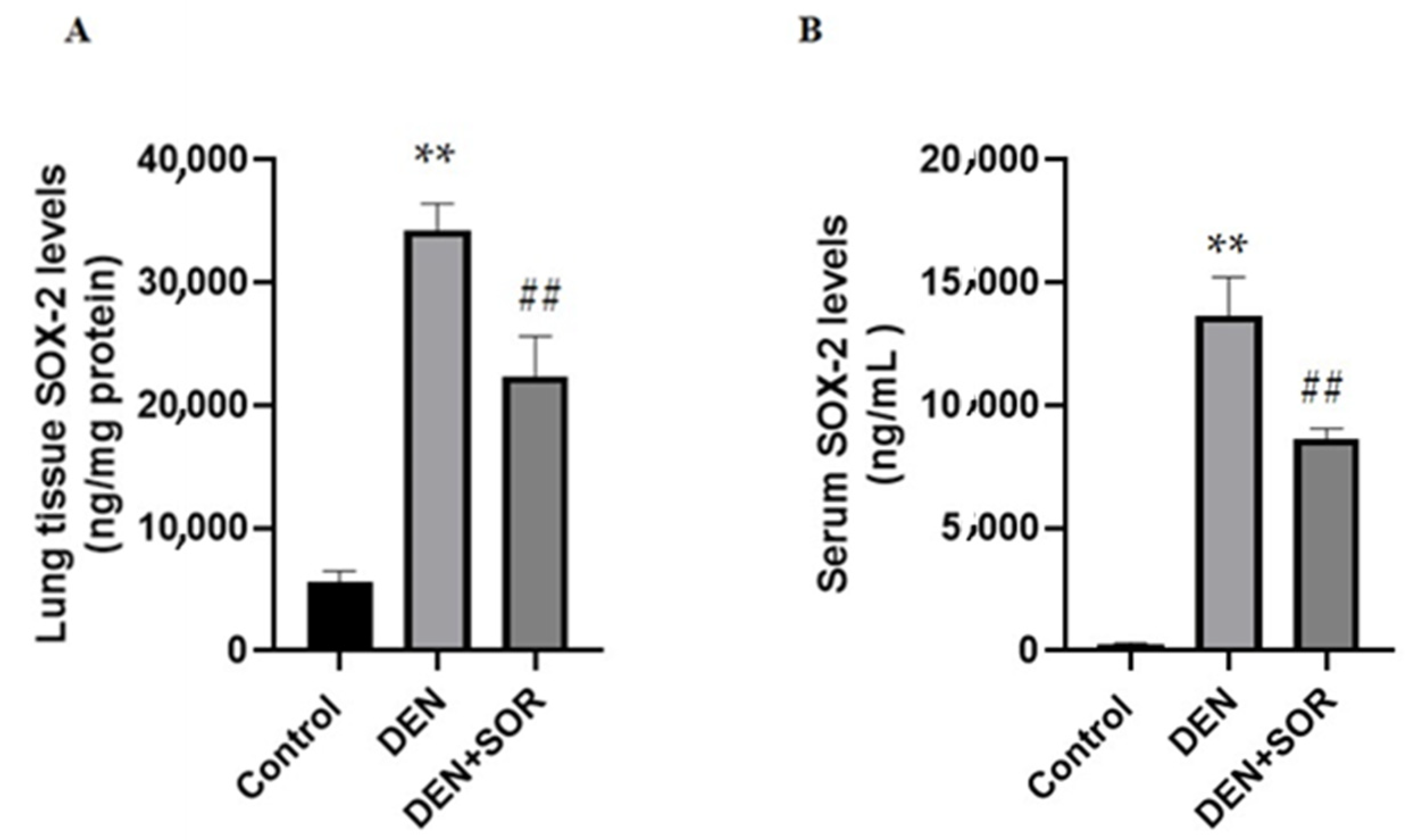
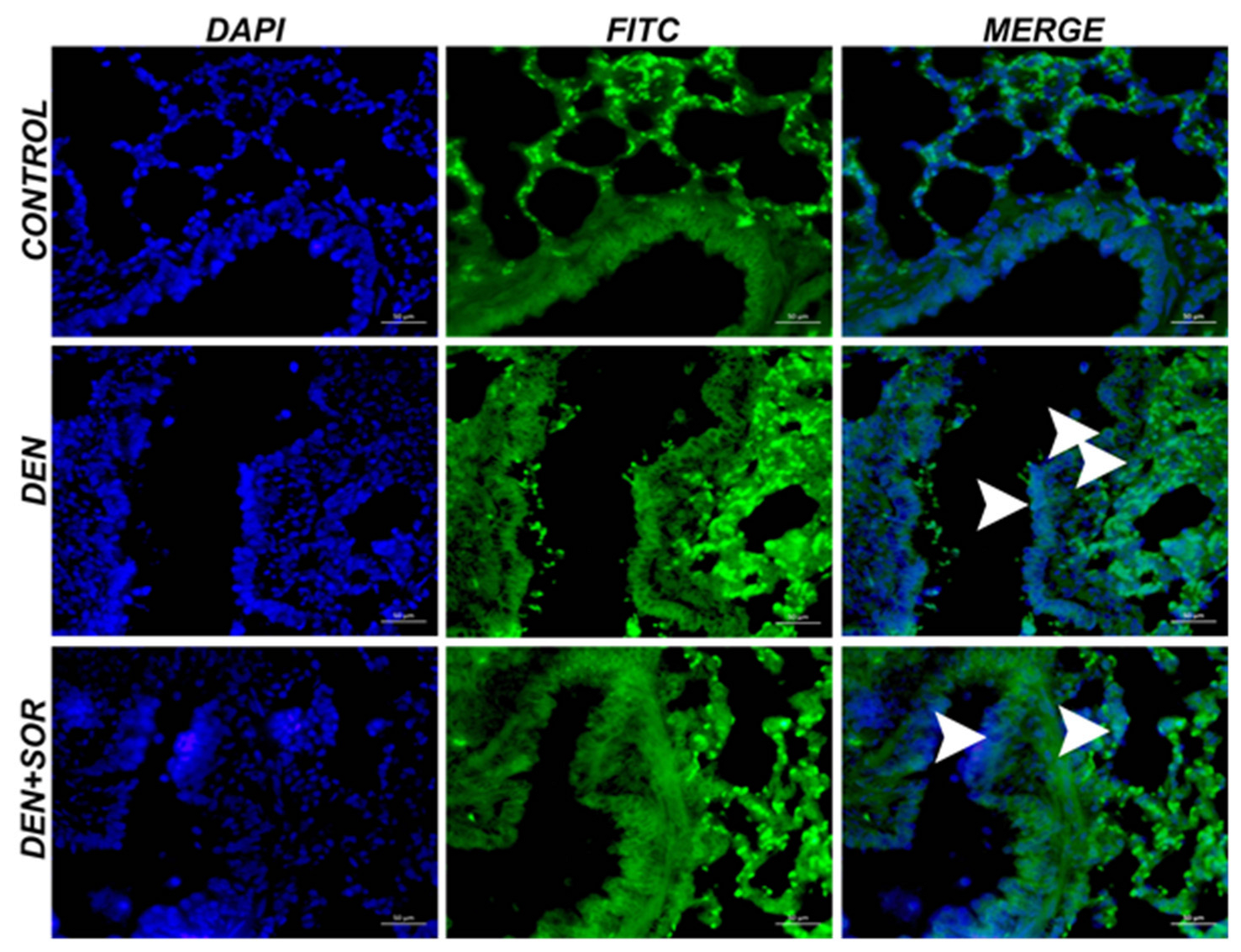
2.1. Effects of SOR on Lung and Serum SOX-2 Levels in DEN-Induced Lung Carcinogenesis in Rats
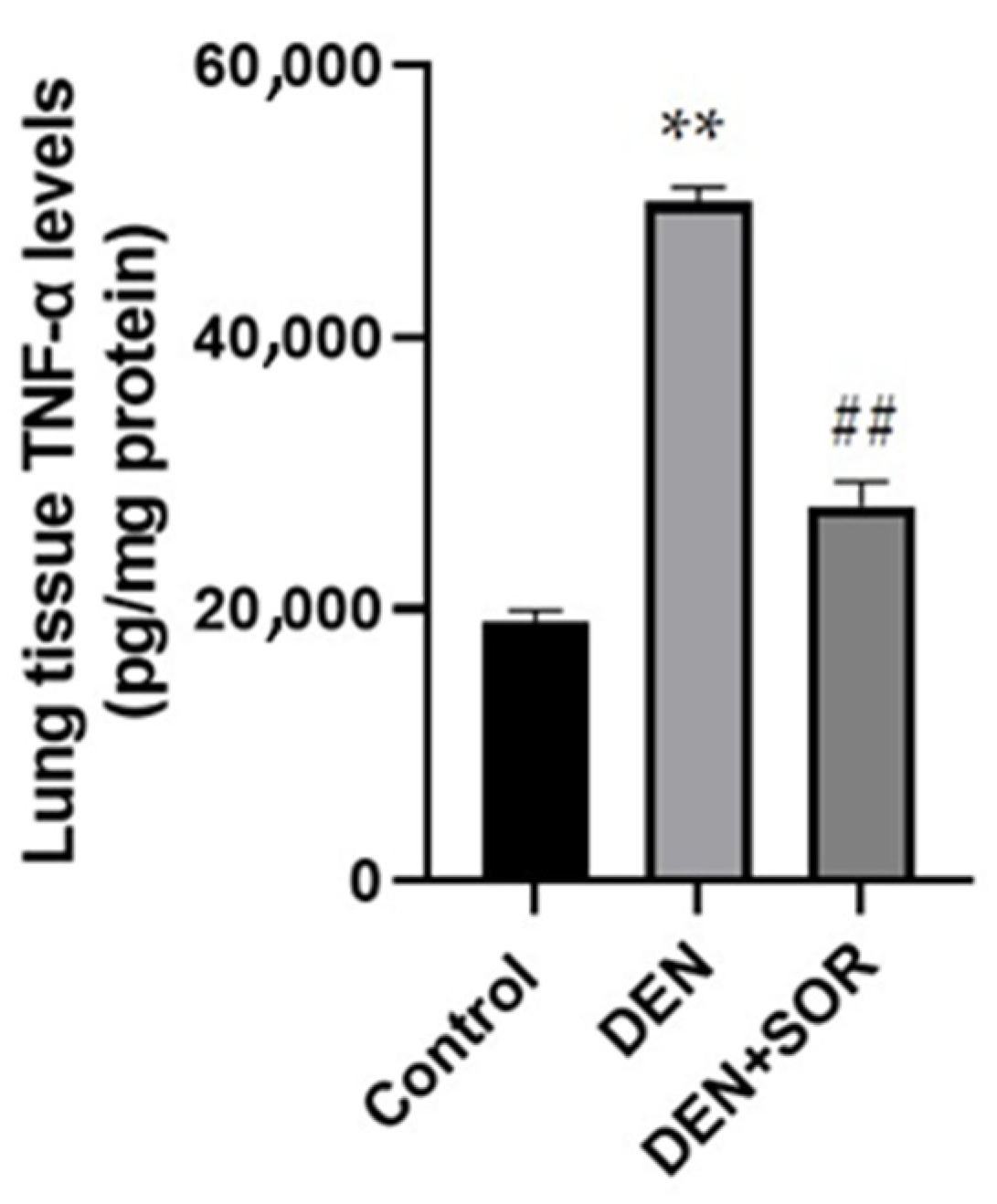
2.2. Effect of SOR Treatment on Lung TNF-α Levels in DEN-Induced Lung Carcinogenesis in Rats
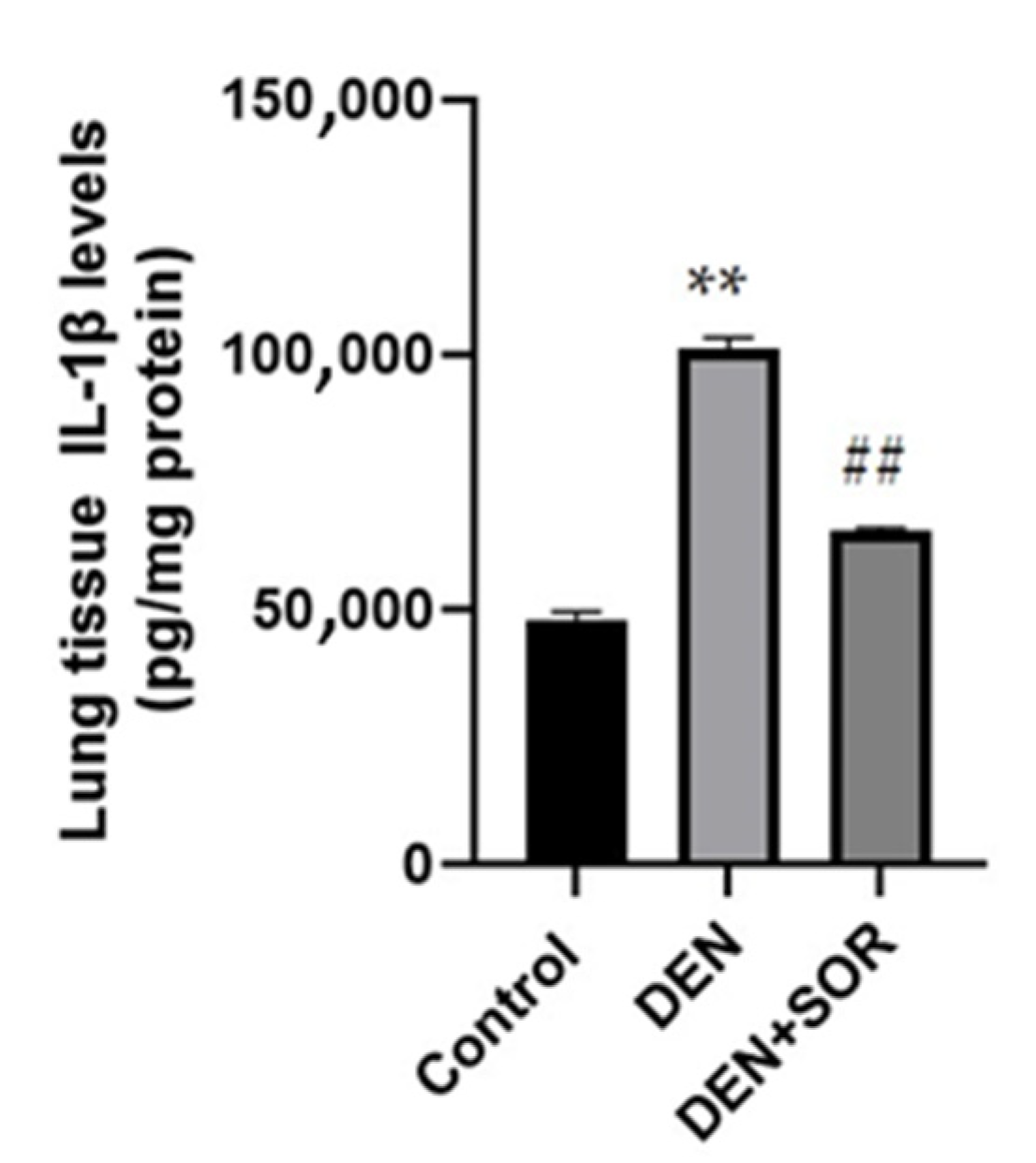
2.3. Effect of SOR Treatment on Lung IL-1β Levels in DEN-Induced Lung Carcinogenesis in Rats
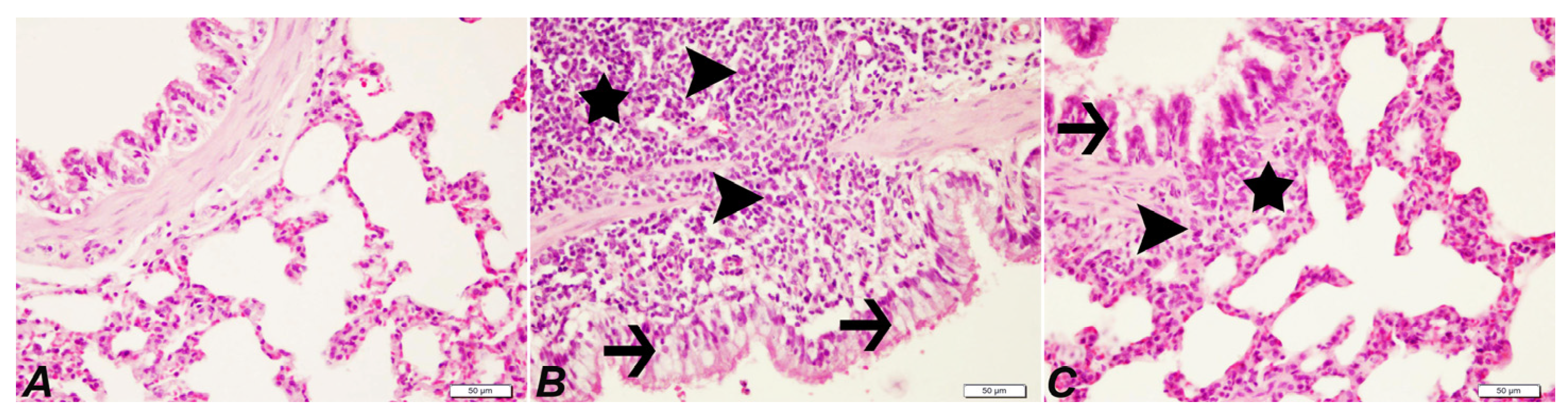
2.4. Histopathological Examination of Lung
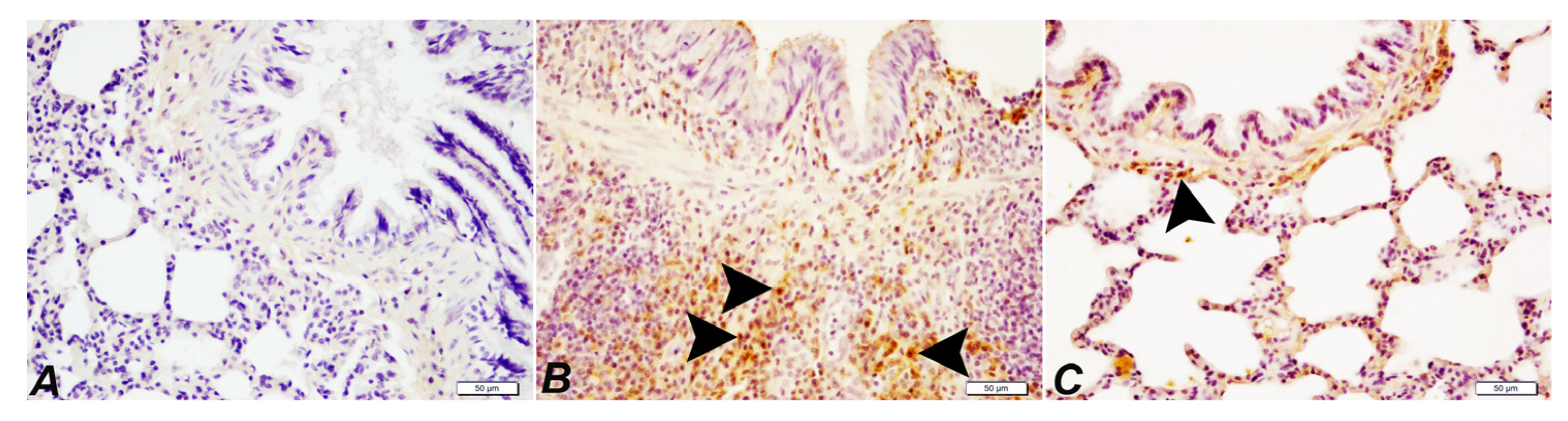
2.5. Effects of SOR on the COX-2 Levels in Lung Tissue
2.6. Effects of SOR on the JNK Levels in Lung Tissue
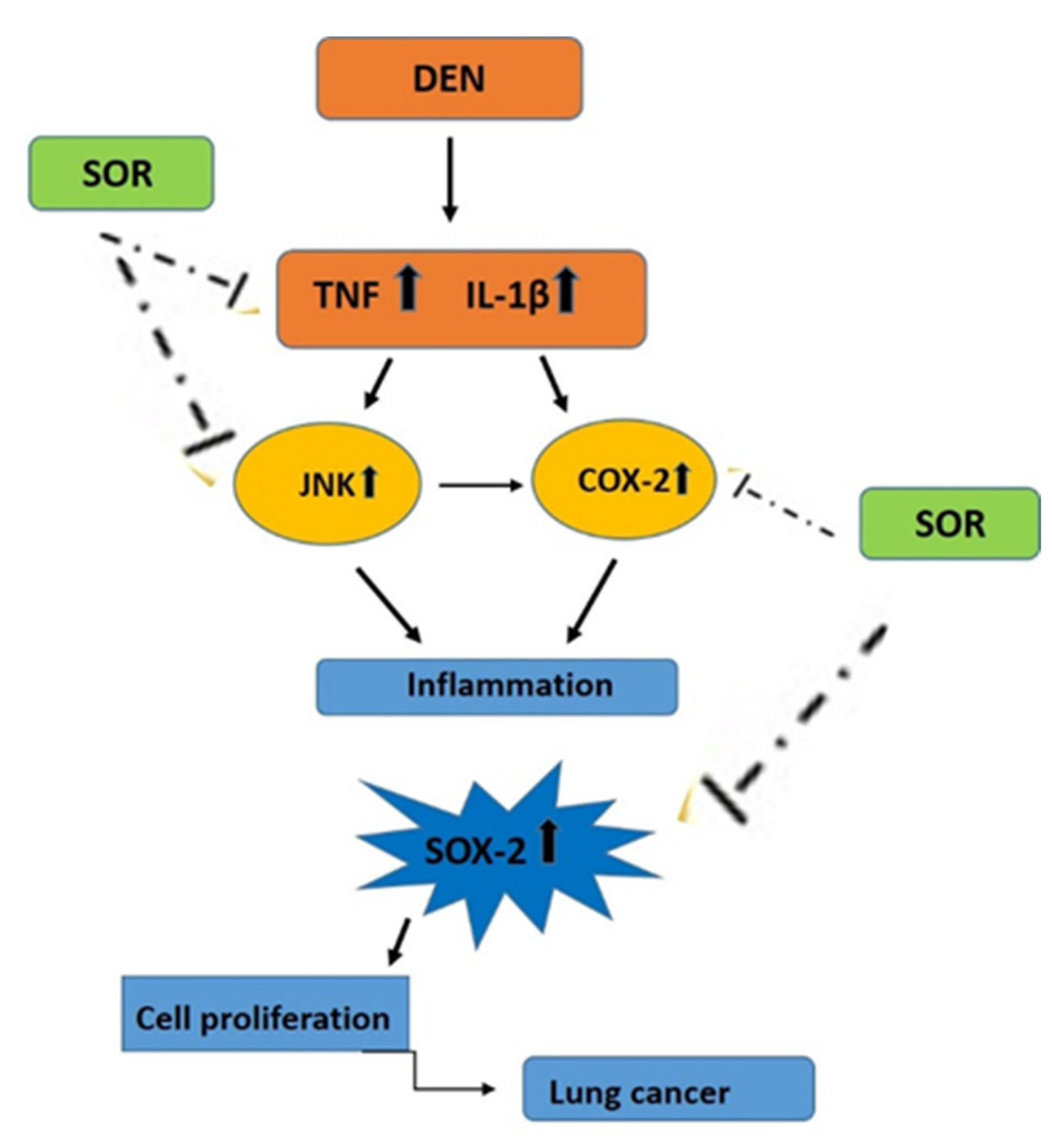
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Drugs and Reagents
4.2. Experimental Animals
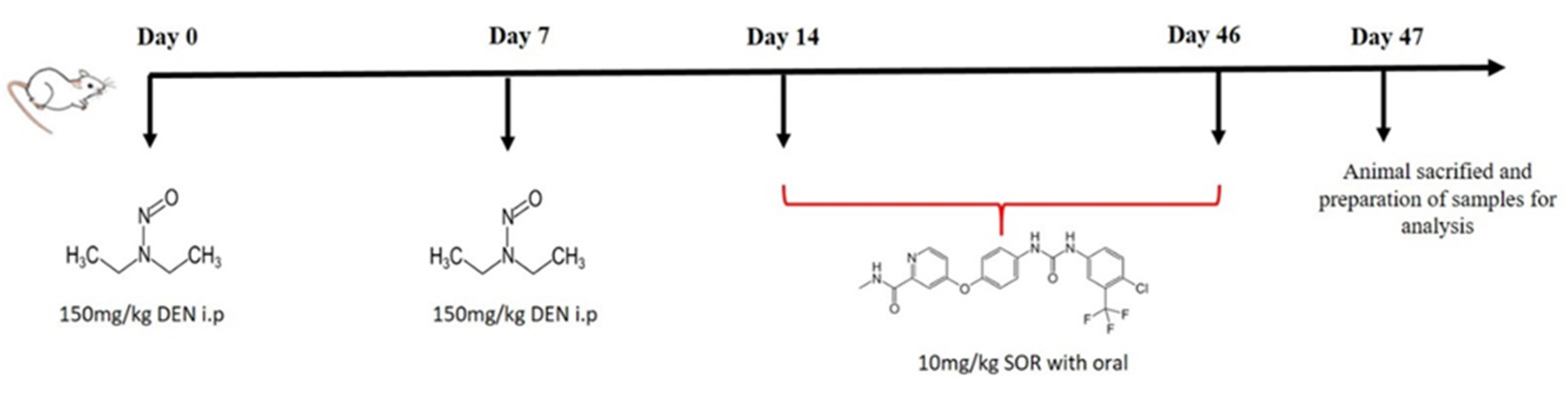
4.3. Induction of Lung Carcinogenesis and SOR Treatment Schedule
4.4. Experimental Design
4.5. Biochemical Analysis
4.6. Histopathological Analysis
4.7. Immunohistochemical and Immunofluorescence Examination
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; He, X.; Le, Y.; Guo, X.; Bryant, M.S.; Atrakchi, A.H.; McGovern, T.J.; Davis-Bruno, K.L.; Keire, D.A.; Heflich, R.H.; et al. Genotoxicity evaluation of nitrosamine impurities using human TK6 cells transduced with cytochrome P450s. Arch. Toxicol. 2022, 96, 3077–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciemniak, A. A comparison of N-nitrosodimethylamine contents in selected meat products. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2006, 57, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramos, A.C.; Araujo, M.R.; Lopes, L.R.; Andreollo, N.A. Role of the vitamin C in diethylnitrosamine-induced esophageal cancer in Wistar rats. Acta Cir. Bras. 2009, 24, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulien, I.; Hasselblatt, P. Diethylnitrosamine-induced liver tumorigenesis in mice. Methods Cell Biol. 2021, 163, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mervai, Z.; Egedi, K.; Kovalszky, I.; Baghy, K. Diethylnitrosamine induces lung adenocarcinoma in FVB/N mouse. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jainu, M.; Priya, V.V.; Mohan, S.K. Biochemical evidence for the antitumor potential of Garcinia mangostana Linn. On diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic carcinoma. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2018, 14, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivalingam, K.; Amirthalingam, V.; Ganasan, K.; Huang, C.-Y.; Viswanadha, V.P. Neferine suppresses diethylnitrosamine-induced lung carcinogenesis in Wistar rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 123, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draškovič, T.; Zidar, N.; Hauptman, N. Circulating Tumor DNA Methylation Biomarkers for Characterization and Determination of the Cancer Origin in Malignant Liver Tumors. Cancers 2023, 15, 859. [Google Scholar]
- Wongvaranon, P.; Pongrakhananon, V.; Chunhacha, P.; Chanvorachote, P. Acquired resistance to chemotherapy in lung cancer cells mediated by prolonged nitric oxide exposure. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 5433–5444. [Google Scholar]
- Sosa Iglesias, V.; Giuranno, L.; Dubois, L.J.; Theys, J.; Vooijs, M. Drug Resistance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Potential for NOTCH Targeting? Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Salah-Eldin, A.E.; Omoteyama, K. Apoptosis and anticancer drug resistance. Hum. Cell 2001, 14, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xu, T.; Yan, K.; Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Chang, F.; Guo, X.; Peng, J.; Li, M.; et al. RNF8-mediated regulation of Akt promotes lung cancer cell survival and resistance to DNA damage. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 109854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, M.; Antunes, L.; Redondo, P.; Borges, M.; Hermans, R.; Patel, D.; Grimson, F.; Munro, R.; Chaib, C.; Lacoin, L.; et al. Real-world treatment patterns and survival outcomes for advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the pre-immunotherapy era in Portugal: A retrospective analysis from the I-O Optimise initiative. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicek, B.; Genc, S.; Yeni, Y.; Kuzucu, M.; Cetin, A.; Yildirim, S.; Bolat, I.; Kantarci, M.; Hacimuftuoglu, A.; Lazopoulos, G.; et al. Artichoke (Cynara Scolymus) Methanolic Leaf Extract Alleviates Diethylnitrosamine-Induced Toxicity in BALB/c Mouse Brain: Involvement of Oxidative Stress and Apoptotically Related Klotho/PPARγ Signaling. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Yan, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y. Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaylock, R.L. Cancer microenvironment, inflammation and cancer stem cells: A hypothesis for a paradigm change and new targets in cancer control. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2015, 6, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammouda, M.B.; Ford, A.E.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.Y. The JNK Signaling Pathway in Inflammatory Skin Disorders and Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tournier, C. The 2 Faces of JNK Signaling in Cancer. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genc, S.; Pennisi, M.; Yeni, Y.; Yildirim, S.; Gattuso, G.; Altinoz, M.A.; Taghizadehghalehjoughi, A.; Bolat, I.; Tsatsakis, A.; Hacımüftüoğlu, A.; et al. Potential Neurotoxic Effects of Glioblastoma-Derived Exosomes in Primary Cultures of Cerebellar Neurons via Oxidant Stress and Glutathione Depletion. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wu, W.; Fu, B.; Shi, L.; Wang, X.; Kuca, K. JNK signaling in cancer cell survival. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 2082–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukas, S.G.; Vageli, D.P.; Doukas, P.G.; Nikitovic, D.; Tsatsakis, A.; Judson, B.L. The Effect of Tobacco Smoke N-Nitrosamines, NNK and NDEA, and Nicotine, on DNA Mismatch Repair Mechanism and miRNA Markers, in Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: An In Vivo Model and Clinical Evidence. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vageli, D.P.; Doukas, P.G.; Doukas, S.G.; Tsatsakis, A.; Judson, B.L. Noxious Combination of Tobacco Smoke Nitrosamines with Bile, Deoxycholic Acid, Promotes Hypopharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma, via NFκB, In Vivo. Cancer Prev. Res. 2022, 15, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doukas, S.G.; Vageli, D.P.; Lazopoulos, G.; Spandidos, D.A.; Sasaki, C.T.; Tsatsakis, A. The Effect of NNK, A Tobacco Smoke Carcinogen, on the miRNA and Mismatch DNA Repair Expression Profiles in Lung and Head and Neck Squamous Cancer Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, C.T.; Doukas, S.G.; Costa, J.; Vageli, D.P. Biliary reflux as a causal factor in hypopharyngeal carcinoma: New clinical evidence and implications. Cancer 2019, 125, 3554–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vageli, D.P.; Doukas, S.G.; Doukas, P.G.; Judson, B.L. Bile reflux and hypopharyngeal cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2021, 46, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vageli, D.P.; Doukas, S.G.; Sasaki, C.T. Inhibition of NF-κB prevents the acidic bile-induced oncogenic mRNA phenotype, in human hypopharyngeal cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 5876–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolawole, O.R.; Kashfi, K. NSAIDs and Cancer Resolution: New Paradigms beyond Cyclooxygenase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yue, W.; Wang, H.; Lai, B.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Gu, M. Cyclooxygenase-2 is associated with malignant phenotypes in human lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 3836–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Valenzuela, F.; Escobar, E.; Pérez-Tomás, R.; Montecinos, V.P. The Inflammatory Profile of the Tumor Microenvironment, Orchestrated by Cyclooxygenase-2, Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 686792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.Y.; Hurst, E.A.; Argyle, D.J. Cyclooxygenase-2: A Role in Cancer Stem Cell Survival and Repopulation of Cancer Cells during Therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 2048731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shi, P.; Zhao, G.; Xu, J.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Dong, Z.; Chen, F.; et al. Targeting Cancer Stem Cell Pathways for Cancer Therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabavathy, D.; Swarnalatha, Y.; Ramadoss, N. Lung cancer stem cells—Origin, characteristics and therapy. Stem Cell Investig. 2018, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xiong, X.; Sun, Y. Functional characterization of SOX2 as an anticancer target. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karachaliou, N.; Rosell, R.; Viteri, S. The role of SOX2 in small cell lung cancer, lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2013, 2, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Ozawa, H.; Imanishi, Y.; Sekimizu, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Ito, F.; Ikari, Y.; Nakahara, N.; Kameyama, K.; Ogawa, K. Cyclooxygenase-2 expression is associated with chemoresistance through cancer stemness property in hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Shan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cai, Z.; Tong, X.; et al. Stem Cell Factor SOX2 Confers Ferroptosis Resistance in Lung Cancer via Upregulation of SLC7A11. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 5217–5229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.H.; Tan, A.M.; Shi, Y. New and Emerging Targeted Therapies for Advanced Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laface, C.; Fedele, P.; Maselli, F.M.; Ambrogio, F.; Foti, C.; Molinari, P.; Ammendola, M.; Lioce, M.; Ranieri, G. Targeted Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Old and New Opportunities. Cancers 2022, 14, 4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, M.A.; Mandour, Y.M.; El-Aziz, M.K.A.; Stein, U.; El Tayebi, H.M. Small Molecule Inhibitors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Advances and Challenges. Molecules 2022, 27, 5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, R.C.; Farrell, A.T.; Saber, H.; Tang, S.; Williams, G.; Jee, J.M.; Liang, C.; Booth, B.; Chidambaram, N.; Morse, D.; et al. Sorafenib for the Treatment of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 7271–7278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Kulkarni, N.S.; Farrales, P.; Kanabar, D.D.; Parvathaneni, V.; Kunda, N.K.; Muth, A.; Gupta, V. Sorafenib Loaded Inhalable Polymeric Nanocarriers against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenschein, G., Jr. Sorafenib in lung cancer: Clinical developments and future directions. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, S124–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.Q.; Wang, Y.L.; Li, Z.Y.; Lin, T.Y. Therapeutic effects of sorafenib on the A549/DDP human lung adenocarcinoma cell line in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raoul, J.-L.; Adhoute, X.; Penaranda, G.; Perrier, H.; Castellani, P.; Oules, V.; Bourlière, M. Sorafenib: Experience and Better Management of Side Effects Improve Overall Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients: A Real-Life Retrospective Analysis. Liver Cancer 2019, 8, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajighasemlou, S.; Nikbakht, M.; Pakzad, S.; Muhammadnejad, S.; Gharibzadeh, S.; Mirmoghtadaei, M.; Zafari, F.; Seyhoun, I.; Ai, J.; Verdi, J. Sorafenib and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy: A Promising Approach for Treatment of HCC. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 9602728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyhoun, I.; Hajighasemlou, S.; Muhammadnejad, S.; Ai, J.; Nikbakht, M.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Hosseinzadeh, F.; Mirmoghtadaei, M.; Seyhoun, S.M.; Verdi, J. Combination therapy of sorafenib with mesenchymal stem cells as a novel cancer treatment regimen in xenograft models of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 9495–9503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-L.; Ibrahim, N.; Yu, Y.; Walsh, W.R. Molecular targeted therapies for cancer: Sorafenib mono�therapy and its combination with other therapies (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Wang, Y.; Lineen, A.M.; Gunning, W.T.; Stoner, G.D.; Anderson, M.W. Mutagenesis of the K-ras protooncogene in mouse lung tumors induced by N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea or N-nitrosodiethylamine. Carcinogenesis 1992, 13, 1583–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Moneim, A.; Ahmed, O.M.; El-Twab, S.M.A.; Zaky, M.Y.; Bakry, L.N. Prophylactic effects of Cynara scolymus L. leaf and flower hydroethanolic extracts against diethylnitrosamine/acetylaminoflourene-induced lung cancer in Wistar rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 43515–43527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Liu, X.; Qi, X.; Liu, X.; Peng, F.; Li, H.; Fu, H.; Pei, S.; Chen, L.; Chi, X.; et al. PDIA6 modulates apoptosis and autophagy of non-small cell lung cancer cells via the MAP4K1/JNK signaling pathway. Ebiomedicine 2019, 42, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, S.; Law, H. JNK in Tumor Microenvironment: Present Findings and Challenges in Clinical Translation. Cancers 2021, 13, 2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwandner, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Cao, Z. Requirement of Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor–Associated Factor (Traf)6 in Interleukin 17 Signal Transduction. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1233–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Veeramachaneni, N. Targeting interleukin-1β and inflammation in lung cancer. Biomark. Res. 2022, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukas, S.G.; Doukas, P.G.; Sasaki, C.T.; Vageli, D. The in vivo preventive and therapeutic properties of curcumin in bile reflux-related oncogenesis of the hypopharynx. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 10311–10321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vageli, D.P.; Doukas, P.G.; Siametis, A.; Judson, B.L. Targeting STAT3 prevents bile reflux-induced oncogenic molecular events linked to hypopharyngeal carcinogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doukas, P.; Vageli, D.; Sasaki, C.; Judson, B. Pepsin Promotes Activation of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Downstream Oncogenic Pathways, at Slightly Acidic and Neutral pH, in Exposed Hypopharyngeal Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, K.; Guo, G.; Beckley, N.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Sharma, M.; Habib, A.A. Tumor necrosis factor in lung cancer: Complex roles in biology and resistance to treatment. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.R.; Pelly, V.S.; Moeini, A.; Chiang, S.-C.; Flanagan, E.; Bromley, C.P.; Clark, C.; Earnshaw, C.H.; Koufaki, M.A.; Bonavita, E.; et al. Chemotherapy-induced COX-2 upregulation by cancer cells defines their inflammatory properties and limits the efficacy of chemoimmunotherapy combinations. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Falcone, D.J.; Subbaramaiah, K.; Dannenberg, A.J. Macrophages induce COX-2 expression in breast cancer cells: Role of IL-1β autoamplification. Carcinog. 2011, 32, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, P.-S.; Mak, O.-T.; Huang, H.-J. Induction of COX-2 protein expression by vanadate in A549 human lung carcinoma cell line through EGF receptor and p38 MAPK-mediated pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 339, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.; Li, J.; Qiu, P.; Liu, Z.; Ma, L.; Gao, W. Inhibition of lung cancer in diethylnitrosamine-induced mice by Rhizoma paridis saponins. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, E.E.; Ahmed, O.M.; Abdel-Moneim, A.; Zoheir, K.M.A.; Elesawy, B.H.; Al Askary, A.; Hassaballa, A.; El-Shahawy, A.A.G. Protective Effects of Naringin–Dextrin Nanoformula against Chemically Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Wistar Rats: Roles of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Cell Apoptosis, and Proliferation. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdu, S.; Juaid, N.; Amin, A.; Moulay, M.; Miled, N. Therapeutic Effects of Crocin Alone or in Combination with Sorafenib against Hepatocellular Carcinoma: In Vivo & In Vitro Insights. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Guo, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, X.; Cui, H. Synergistic antitumor activity of low-dose c-Met tyrosine kinase inhibitor and sorafenib on human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 5081–5086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Tang, B.; Miao, H.; Xu, Q.; Chen, X. Combination of sorafenib and gadolinium chloride (GdCl3) attenuates dimethylnitrosamine(DMN)-induced liver fibrosis in rats. BMC Gastroenterol. 2015, 15, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, K. Combining sorafenib with celecoxib synergistically inhibits tumor growth of non-small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Shibuya, K.; Sato, A.; Seino, S.; Watanabe, E.; Suzuki, S.; Seino, M.; Kitanaka, C. Specific role of JNK in the maintenance of the tumor-initiating capacity of A549 human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 1957–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, S.; Paskeh, M.D.A.; Entezari, M.; Mirmazloomi, S.R.; Hassanpoor, A.; Aboutalebi, M.; Rezaei, S.; Hejazi, E.S.; Kakavand, A.; Heidari, H.; et al. SOX2 function in cancers: Association with growth, invasion, stemness and therapy response. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 156, 113860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wang, D.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Wo, L.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhan, M.; He, M.; et al. TGFB2-AS1 inhibits triple-negative breast cancer progression via interaction with SMARCA4 and regulating its targets TGFB2 and SOX2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2117988119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.-H.; Lee, A.-C.; Hsiao, S.-H.; Lin, S.-E.; Chiu, Y.-F.; Yang, L.-H.; Yu, C.-C.; Chiou, S.-H.; Huang, H.-N.; Ko, J.-C. Cross-talk between SOX2 and TGFβ Signaling Regulates EGFR–TKI Tolerance and Lung Cancer DisseminationInterplay of SOX2 and TGFβ on EGFR–TKI Tolerance. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 4426–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Beggs, K.; Borude, P.; Edwards, G.; Bhushan, B.; Walesky, C.; Roy, N.; Manley, M.W., Jr.; Gunewardena, S.; O’Neil, M.; et al. Bile acids promote diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma via increased inflammatory signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2016, 311, G91–G104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surapaneni, S.K.; Nottingham, E.; Mondal, A.; Patel, N.; Arthur, P.; Gebeyehu, A.; Kalvala, A.K.; Rishi, A.K.; Singh, M. Telmisartan Facilitates the Anticancer Effects of CARP-1 Functional Mimetic and Sorafenib in Rociletinib Resistant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2021, 41, 4215–4228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jilkova, Z.M.; Kuyucu, A.Z.; Kurma, K.; Pour, S.T.A.; Roth, G.S.; Abbadessa, G.; Yu, Y.; Schwartz, B.; Sturm, N.; Marche, P.N.; et al. Combination of AKT inhibitor ARQ 092 and sorafenib potentiates inhibition of tumor progression in cirrhotic rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 11145–11158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.S.; Macek Jilkova, Z.; Zeybek Kuyucu, A.; Kurma, K.; Ahmad Pour, S.T.; Abbadessa, G.; Yu, Y.; Busser, B.; Marche, P.N.; Leroy, V. Efficacy of AKT Inhibitor ARQ 092 Compared with Sorafenib in a Cirrhotic Rat Model with Hepatocellular CarcinomaARQ 092 in DEN-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 2157–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omaklı, S.; Sevim, Ç.; Kontadakis, G.; Doğan, E.; Taghizadehghalehjoughi, A.; Özkaraca, M.; Aschner, M.; Nikolouzakis, T.K.; Tsatsakis, A. Acute glufosinate-based herbicide treatment in rats leads to increased ocular interleukin-1β and c-Fos protein levels, as well as intraocular pressure. Toxicol. Rep. 2019, 6, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varmazyari, A.; Taghizadehghalehjoughi, A.; Sevim, C.; Baris, O.; Eser, G.; Yildirim, S.; Hacimuftuoglu, A.; Buha, A.; Wallace, D.R.; Tsatsakis, A.; et al. Cadmium sulfide-induced toxicity in the cortex and cerebellum: In vitro and in vivo studies. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Control Group | DEN Group | DEN + SOR Group | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peribronchiolar cell infiltrations | − | +++ | + |
| Macrophage in alveolar lumens | − | +++ | − |
| Proliferation and degeneration in the bronchial-bronchiole epithelium | − | +++ | + |
| Hyperemia | − | +++ | ++ |
| Control Group | DEN Group | DEN + SOR Group | |
|---|---|---|---|
| COX-2 | 18.26 ± 2.48 a | 59.65 ± 1.94 b | 32.16 ± 2.71 c |
| Control Group | DEN Group | DEN + SOR Group | |
|---|---|---|---|
| JNK | 23.18 ± 3.44 a | 63.18 ± 2.67 b | 37.86 ± 3.4 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cicek, B.; Hacimuftuoglu, A.; Kuzucu, M.; Cetin, A.; Yeni, Y.; Genc, S.; Yildirim, S.; Bolat, I.; Kantarci, M.; Gul, M.; et al. Sorafenib Alleviates Inflammatory Signaling of Tumor Microenvironment in Precancerous Lung Injuries. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020221
Cicek B, Hacimuftuoglu A, Kuzucu M, Cetin A, Yeni Y, Genc S, Yildirim S, Bolat I, Kantarci M, Gul M, et al. Sorafenib Alleviates Inflammatory Signaling of Tumor Microenvironment in Precancerous Lung Injuries. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(2):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020221
Chicago/Turabian StyleCicek, Betul, Ahmet Hacimuftuoglu, Mehmet Kuzucu, Ahmet Cetin, Yesim Yeni, Sidika Genc, Serkan Yildirim, Ismail Bolat, Mecit Kantarci, Mustafa Gul, and et al. 2023. "Sorafenib Alleviates Inflammatory Signaling of Tumor Microenvironment in Precancerous Lung Injuries" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 2: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020221
APA StyleCicek, B., Hacimuftuoglu, A., Kuzucu, M., Cetin, A., Yeni, Y., Genc, S., Yildirim, S., Bolat, I., Kantarci, M., Gul, M., Hayme, S., Matthaios, D., Vageli, D. P., Doukas, S. G., Tsatsakis, A., & Taghizadehghalehjoughi, A. (2023). Sorafenib Alleviates Inflammatory Signaling of Tumor Microenvironment in Precancerous Lung Injuries. Pharmaceuticals, 16(2), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020221










