Abstract
A large number of synthetic cannabinoids are included in new psychoactive substances (NPS) and constitute an open research area in analytical pharmaceutical and toxicology when methods are needed to unambiguously identify these substances and their metabolites in biological fluids. A full molecular characterization of five synthetic molecules of the URB series that is able to interact with the endocannabinoid system was achieved with a high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) in positive ion electrospray ionization and collisional experiments on the protonated parent ions, obtaining characteristic fragmentation patterns. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a triple quadrupole (UHPLC-MS/MS) has also been used, which can help develop methods for screening and confirming synthetic cannabinoids in biological fluids.
1. Introduction
Cannabis contains more than 500 compounds, of which at least 100 have pharmacological properties [1] and are therefore classified as phytocannabinoids [2,3]. It is currently the most widely used illicit drug in Europe, with around 22.2 million European adults reporting its use in 2021 [4]. In recent decades, studies on the endocannabinoid system (ECS) have commanded great interest, above all due to the implications deriving from cannabinoid (CB) receptors, which were discovered in the 1990s and are involved in many physiological and pharmacological events [5,6,7,8,9,10]. CB1 receptors are mainly present in some parts of the central nervous system (CNS), (predominantly the cerebellum, basal ganglia, hippocampus, and cerebral cortex), while CB2 are mainly found in the immune system (primarily B cells and natural killers). Despite this, the CB1s are present, albeit scarcely, in districts other than the CNS [8] and the CB2s centrally [11], respectively. For more detail on the CB1 and CB2 receptors, see [9,12]. When CB receptors are activated, there is a decrease in the concentrations of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP), a messenger that is essential for regulating many cellular functions. In fact, following the binding with suitable ligands, they determine an agonist or antagonist activity, depending on whether they are stimulated or blocked. On the other hand, they can also determine a modulating action through the inhibition of the enzymatic proteins responsible for the metabolism of the endogenous molecules that physiologically bind to them [10]. Indeed, the latter, among which the most studied are N-arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide, AEA) [13] and 2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycerol (2-AG) [14,15], plays a very important role in the regulation of many physiological processes after being released on demand from phospholipid membranes [16,17]. The basic concept is that endocannabinoids are produced (and consequently act) when and where it is needed. On the contrary, the administration of non-endogenous molecules that bind to the CB receptors [18,19], in particular when the action is aimed at the CNS, can cause effects of various kinds, such as those exerted by the main psychoactive drug of the cannabis, that is ∆9–tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) [20], or those carried out by non-psychotropic cannabidiol (CBD) [21], which have antipodal pharmacological effects despite their similar structural characteristics. ECS is therefore to be considered as a reference system for the discovery of new drugs.
Evidence of the importance of substances capable of interfering with CB receptors is represented by the presence on the market of medicines containing active pharmaceutical ingredients that are able to bind to CB receptors, such as Cesamet® (nabilone), prescribed for the improvement of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) states in patients who are not responding to conventional antiemetic therapies. Marinol® (dronabinol), administered for CINV and appetite stimulation in patients with AIDS (acquired immune deficiency syndrome), and Sativex® (THC and cannabidiol), used for the symptomatic relief of the pain and/or the management of the neuropathic pain and spasticity in adults with multiple sclerosis and not responsive to other antispasticity therapies or other marketed drugs. More recently, a new drug containing cannabidiol (Epidiolex®) has been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of seizures associated with two rare and severe forms of epilepsy, that is, Lennox–Gastaut syndrome and Dravet syndrome, in patients who are two years of age and older [2,21,22,23].
On the other hand, direct and indiscriminate activation of the ECs receptors, particularly of the central CB1, can cause several side effects, such as dry mouth, muscle weakness, myalgia, palpitations, blurred vision, memory impairment, disorientation, hallucinations, and paranoia [24,25,26,27]. This problem is accentuated in all situations in which there is an uncontrolled intake that leads to abuse and involves substances of both natural and synthetic origin.
In 2008, a synthetic cannabinoid, namely JWH-018 [28], was first identified in Europe as a constituent of the herbal products available on the web, and was advertised as incense, air fragrances, and herbal blends not intended for human consumption [29]. These products were sold under fanciful trade names (Spice, K2), and quickly spread to several countries as they could be consumed alternatively to cannabis because they were not detectable by the classic drug tests in urine. This situation has allowed the marketing of products able to induce similar or more powerful effects than cannabis without incurring penalties because they are not known and are not listed among the prohibited substances [30]. Since then, the number of “spice” products and new synthetic cannabinoids has steadily increased, so much so that, very recently, 280 individual synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists (SCRAs) have been reported to the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) Early Warnings Advisory from 90 different countries up to 2019 [31], and others have been identified in recent years. SCRAs are part of the large family of the so-called new psychoactive substances (NPS), to which, according to UNODC, all substances of abuse belong, either in a pure form or as a preparation, which are not controlled by the 1961 Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs or the 1971 Convention on Psychotropic Substances, but which may pose a public health threat [32]. Among the main classes of NPS, we can include, in addition to SCRAs, synthetic opioids, stimulants, psychedelics, hallucinogens, and so on [33]. Moreover, NPS from 133 countries and territories have been reported [34]. Consequently, the increase in NPS [33,34,35,36] and smart drugs has led to restrictive and monitoring actions by the institutions involved. The continuous emergence of NPS on the market, however, makes legislative restrictions inadequate and the monitoring task of prevention agencies more difficult.
The recent appearance and widespread diffusion of legal hemp-based products (resin, leaves, and inflorescences) with a low THC content but adulterated with highly active synthetic cannabinoids has made the scenario even more complex. In fact, industrial hemp with a low THC concentration is cheaper and the addition of a small amounts of synthetic cannabinoids is enough to mimic the indiscriminate activity aimed at CB targets. This dangerous way of spreading synthetic cannabinoids puts people’s health at risk, not only of those who knowingly buy the drug but also of those who are convinced that they are buying a harmless natural product [4].
At present, most of the cannabimimetic substances identified in seizures of illegal materials in Europe and in other countries derive from commercial products already known, with various abbreviations (e.g., AM, AB, CP, JWH, HU, RCS, UR, URB, and WIN), and belonging to different chemical classes (e.g., adamantoylindoles, aminoalkylindoles, benzoylindoles, cyclohexylphenols, dibenzopyrans, naphthoylindoles, naphthylmethylindoles, naphthylmethylindenes, phenylacylindoles, tetramethylcyclopropylketoindoles, indazole carboxamides, and naphthoylpyrroles) [37]. Recently, an interesting study aiming to explore the steric requirements at CB1 and CB2 receptors and the role of the related amino acid side chain has been developed that uses some SCRAs [38].
The continuous introduction of new analogues of existing CB drugs is certainly a legal problem, but it is also a major cause of analytical and toxicological uncertainty [39]. In fact, the lack of certified reference standards and the inadequacy of knowledge relating to biological activity and metabolism make it difficult to determine and evaluate new compounds, especially biological matrices. Therefore, the increase in knowledge and the characterization of new CB compounds would be important for their identification.
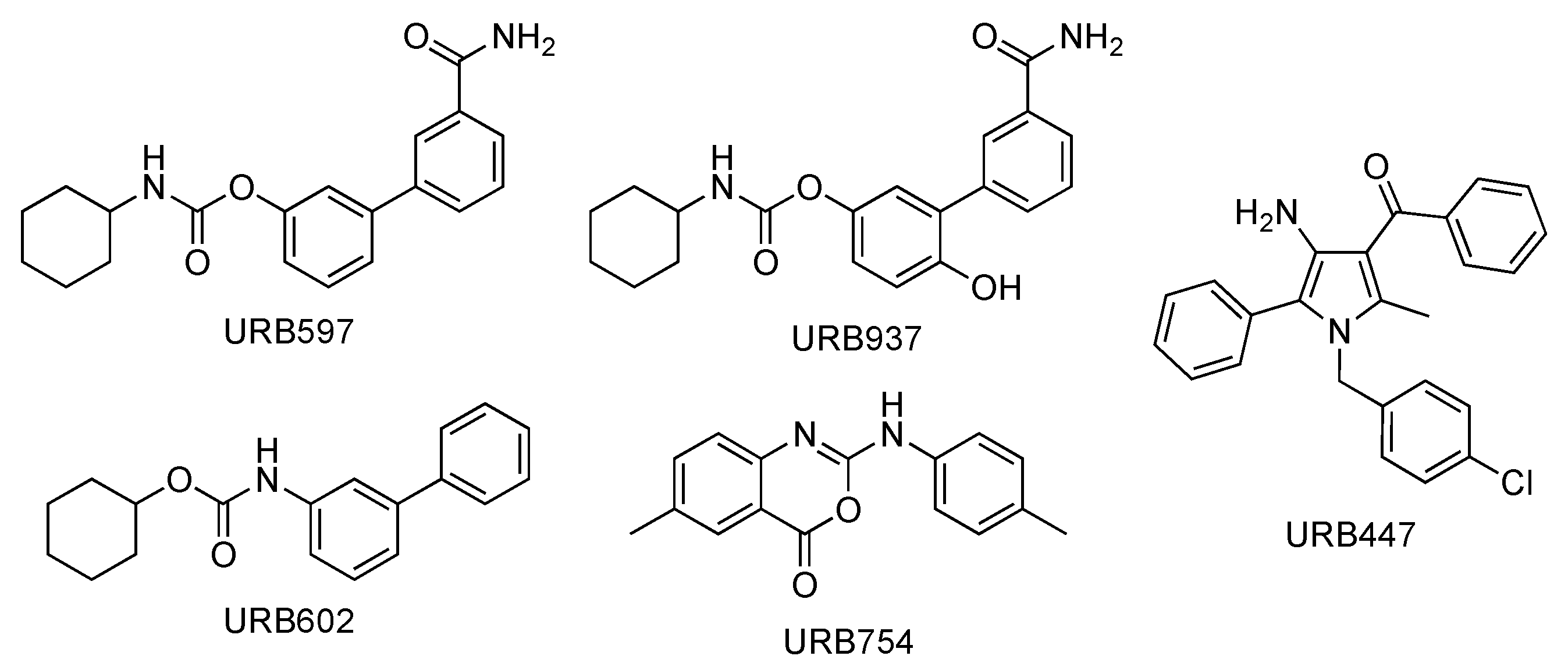
In this work, a full molecular characterization by high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC)–MS/MS of five synthetic molecules of the URB series designed to interact indirectly or directly with ECS (Figure 1) is presented for the first time.
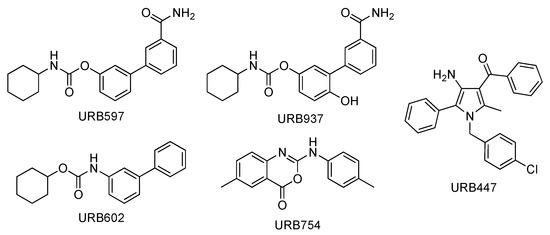
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of URB compounds.
The molecules presented in Figure 1 are defined as synthetic cannabinoids under the broader definition of molecules interfering with the endocannabinoid system without exerting a direct action on the CB receptors (a more classical definition). On the other hand, the EMCDDA (European Monitoring Center for Drugs and Drug Addiction) also includes synthetic cannabinoids molecules that do not bind the receptor.
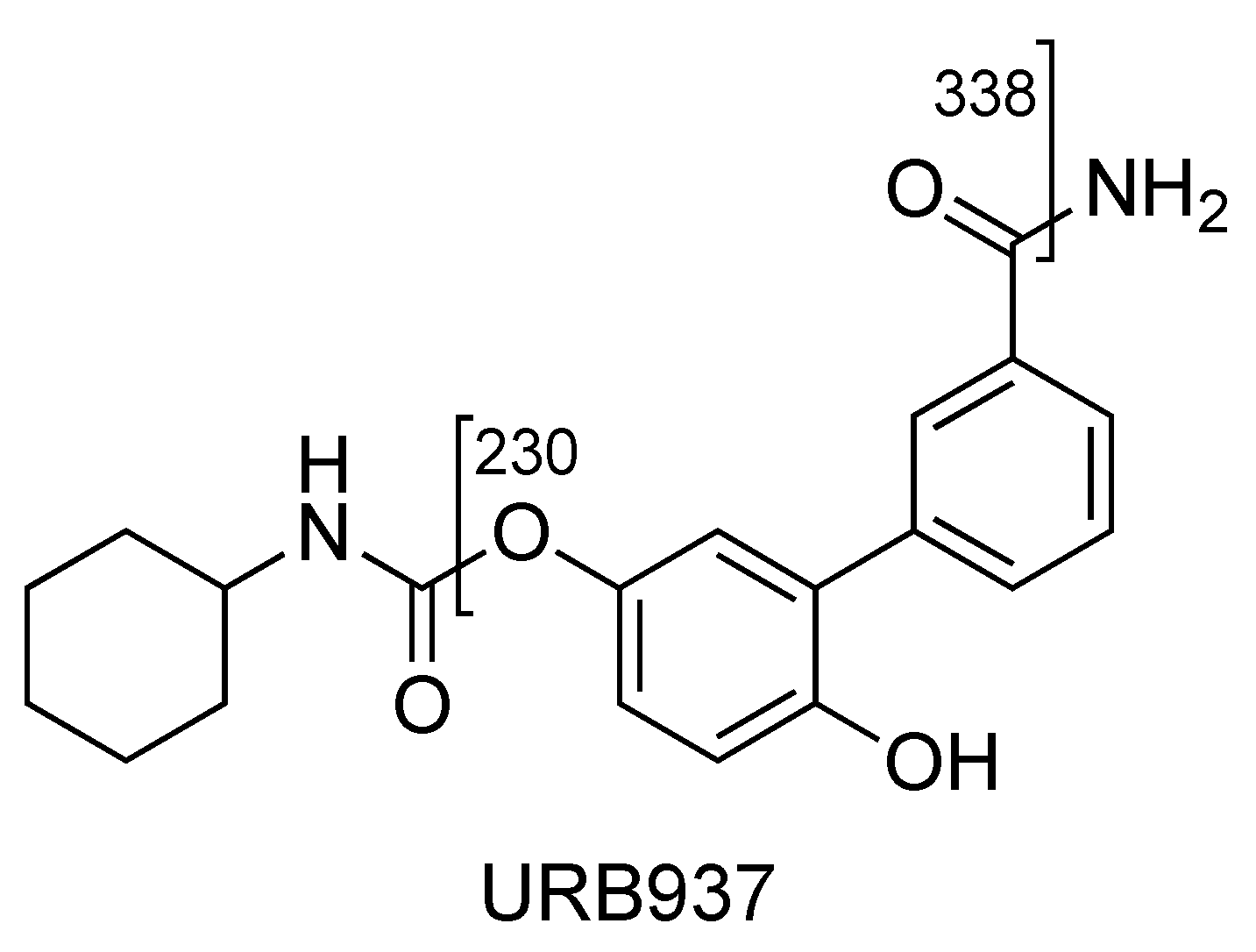
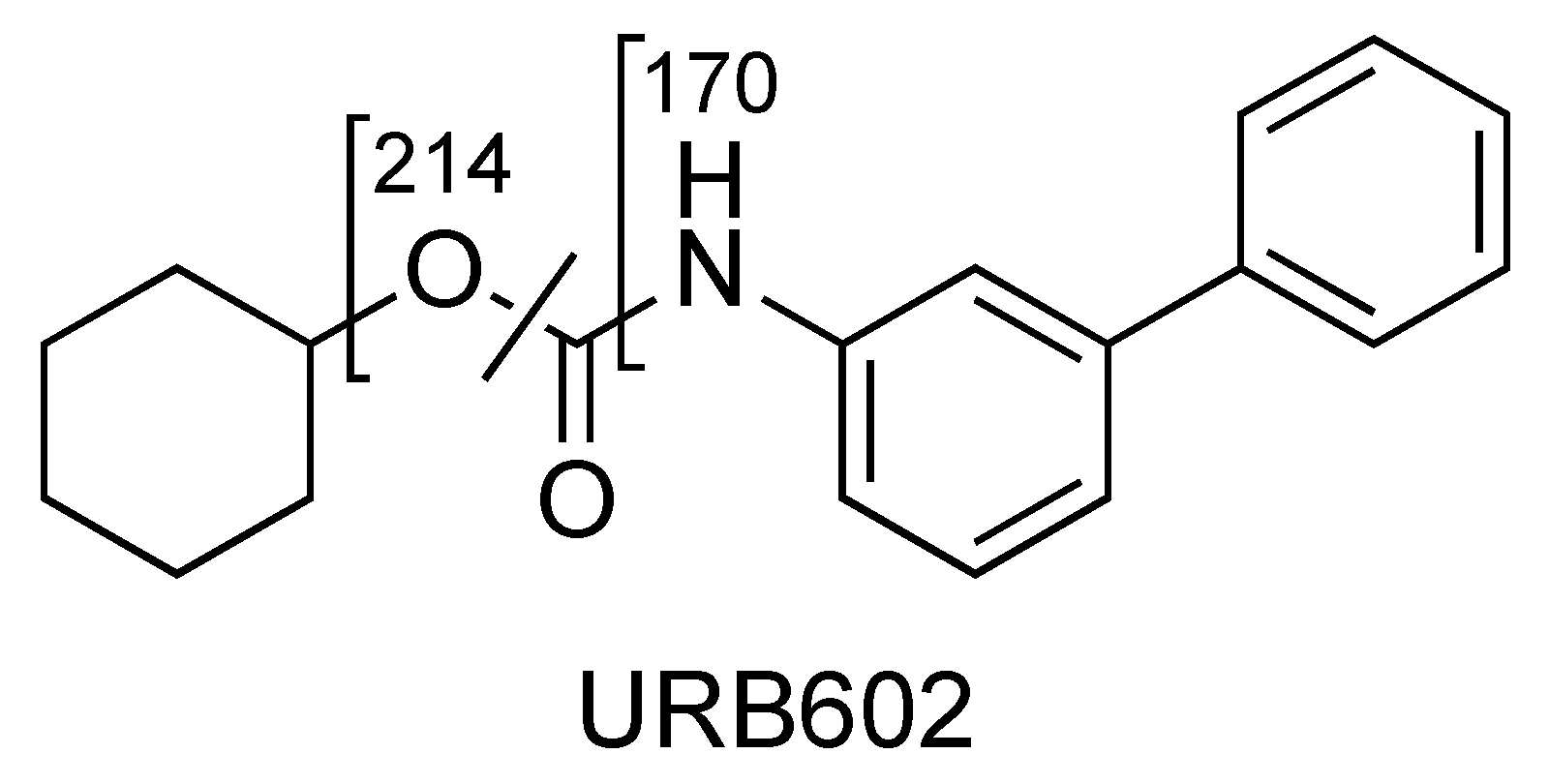
The compounds of the URB series studied here are representative of molecules able to interfere indirectly (enzyme inhibitors) or directly (ligands) with the biological targets of the endocannabinoid system. These include the following molecules: (A) Two carbamates that inhibit fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), which catalyze the intracellular hydrolysis of the endocannabinoid AEA, and are able to exert anxiolytic and analgesic properties (cyclohexylcarbamic acid 3′-carbamoylbiphenyl-3-yl ester, URB597) [40] or restricted peripheral analgesic effects (cyclohexylcarbamic acid 3′-carbamoyl-6-hydroxybiphenyl-3-yl ester, URB937) [41]. They play a very important role in the panorama of FAAH inhibitors because they were the first ever with a good overall profile. Still today, they constitute reference molecules in the specific research oriented toward the study of molecules that are able to interfere with the endocannabinoid system. So much of this is true that URB597 is the most widely used pharmacological tool in the field, the use of which serves to further understand pharmacological applications. Both are covalent and irreversible inhibitors. (B) A reverse carbamic analogue of FAAH inhibitors that inactivates the enzyme degrading 2-AG, which is a monoglyceride lipase (MGL), and is able to relieve the stress-induced pain and induce neuroprotection (biphenyl-3-yl carbamic acid cyclohexyl ester, URB602 [42]). It is a covalent and partially reversible inhibitor. (C) A benzoxazinone derivative initially studied as an MGL inhibitor (6-methyl-2-p-tolylaminobenzo[d]oxazin-4-one, URB754) [43,44]. (D) Finally, a peripherally restricted mixed CB1 antagonist/CB2 agonist pyrrolic drug endowed with anti-obesity, neuroprotective, and antitumor properties [45,46], and an interesting anti-inflammatory profile (data not available) {[4-amino-1-(4-chlorobenzyl)-2-methyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-3-yl] (phenyl)methanone, URB447. These compounds were included among the monitored commercial substances. Notably, URB597 was found in herbal products in both Japan [47] and the United States of America [48], which was notified by the European Union Early Warning System in 2013 (found in Poland) [49], while URB754 has been reported in the literature as a new designer drug [50].
Although, at the moment, the phenomena of abuse and fatality have not been correlated with the considered drugs, the molecular characterization and MS fragmentation behavior of the protonated molecules reported here are important for the unambiguous identification of the substances. They also play a key role in the future development of LC–MS/MS or LC–HRMS screening methods that are useful for their research on seized samples.
In fact, the substances studied in this work are potentially dangerous because they are active at very low concentrations (lower than most direct cannabinoids). Furthermore, they are emerging drugs and sufficient epidemiological data to describe their consumption have not yet been acquired (on the other hand, if no one includes them in the screening of real intoxication cases, no one can estimate their prevalence).
2. Results and Discussion
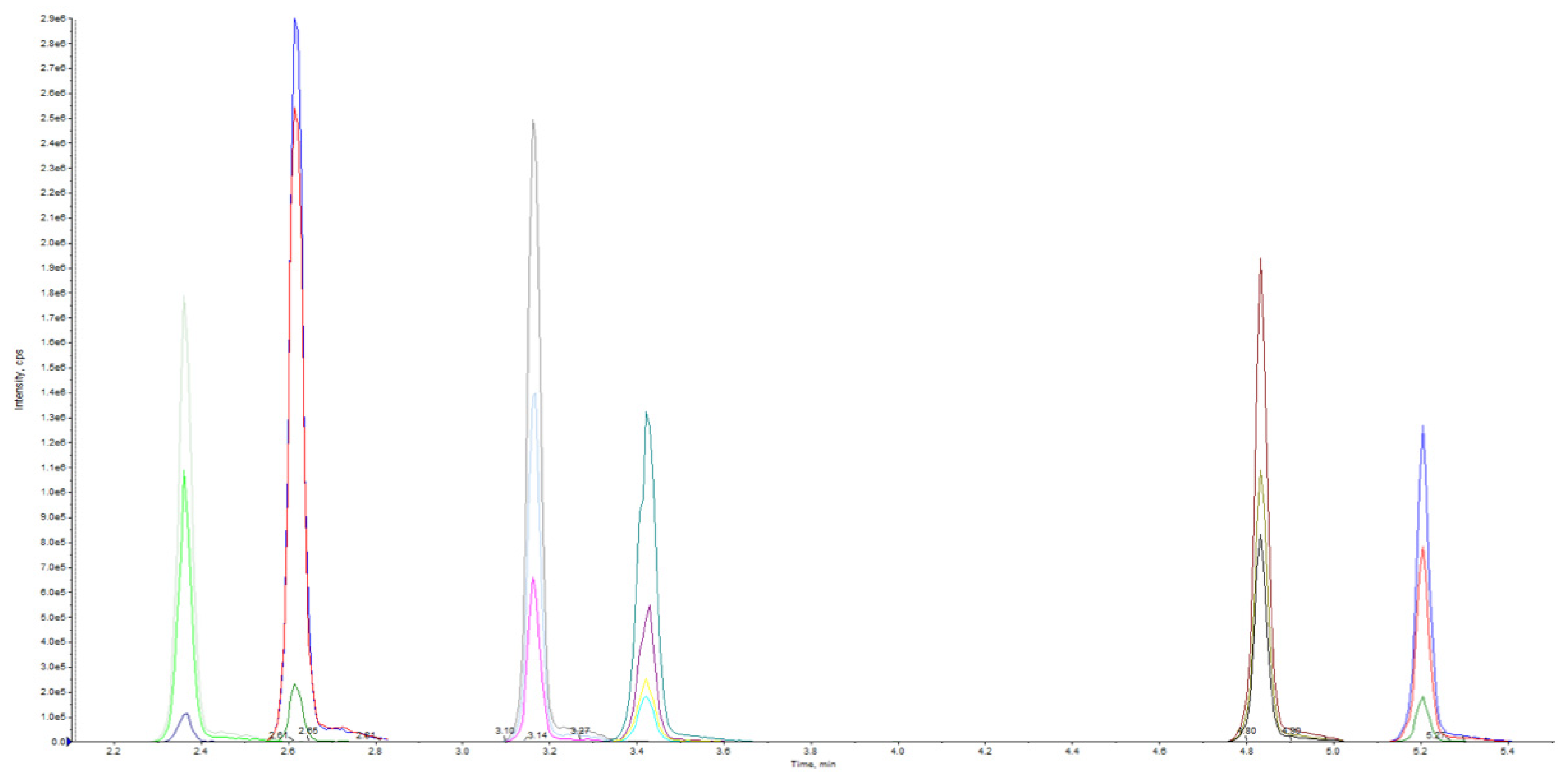
The tuning parameters optimized in UHPLC-MS/MS to obtain fragment ions of high abundance for use in the multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) method are reported in Table 1 and Figure 2.

Table 1.
Compound-dependent parameters for optimal monitoring of multiple reactions.
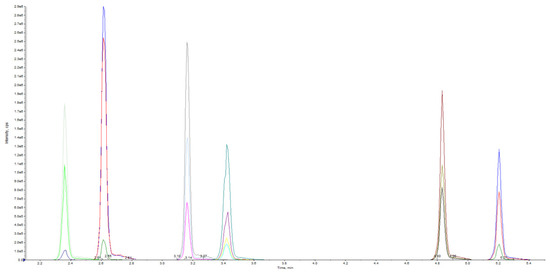
Figure 2.
MRM extracted ion chromatogram of methanol standard solution.
The identity of the observed fragment ions was confirmed by HRMS and collision-induced dissociation (CID) measurements in an Orbitrap comparing the theoretical to the experimental accurate masses, as reported in Table 2 (fragments of data are partially shown). The characteristic fragmentation patterns of URB compounds were subsequently interpreted as follows.

Table 2.
HRMS of protonated molecules and CID-induced fragment ions.
2.1. URB597
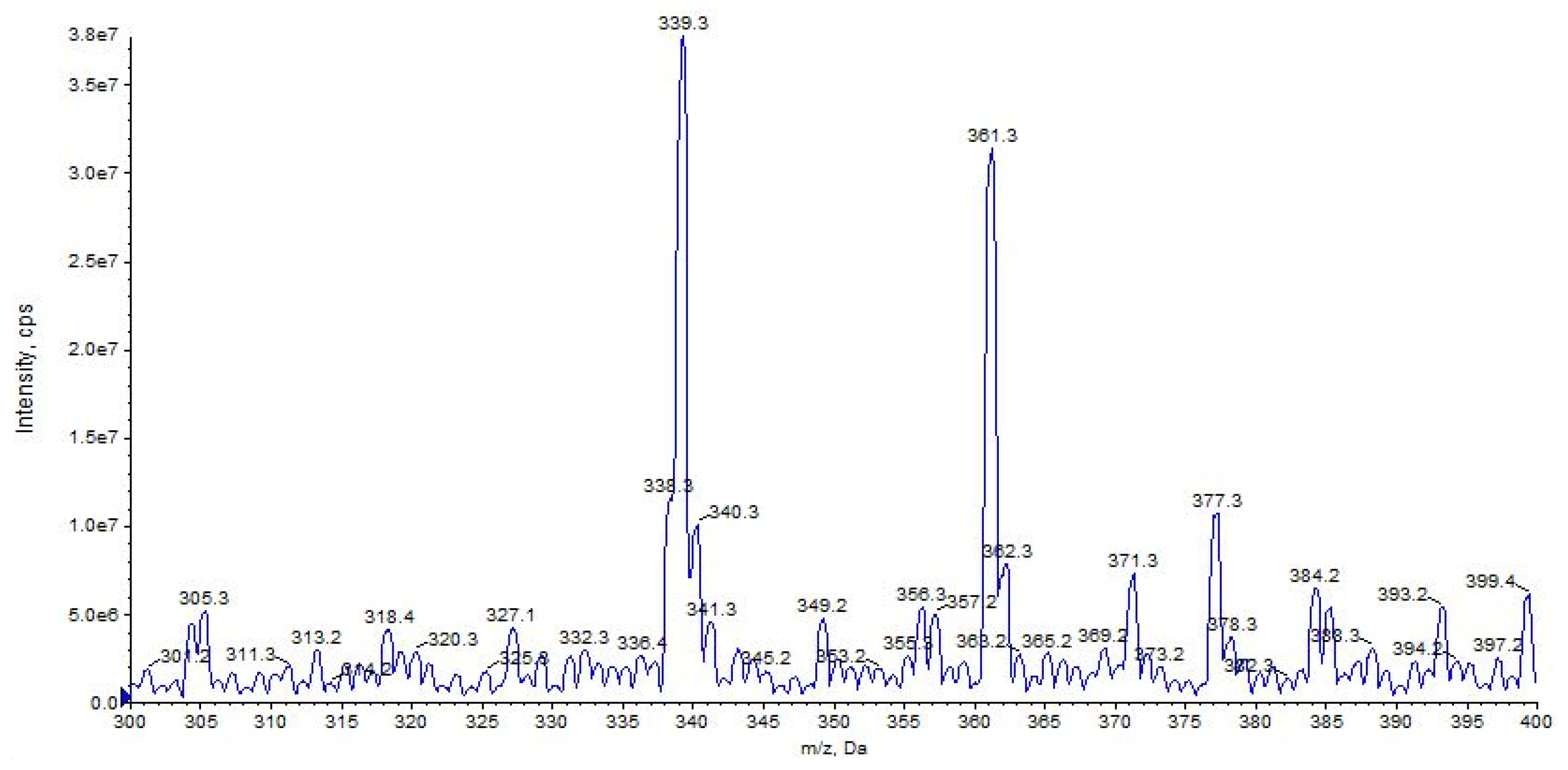
URB597 ([M + H]+ at m/z 339) shows a high affinity for the alkali metal with a high abundance of the sodium adduct [M + Na]+ at m/z 361, while a small amount of potassium adducts [M + K]+ at m/z 377 was detected (Figure 3).
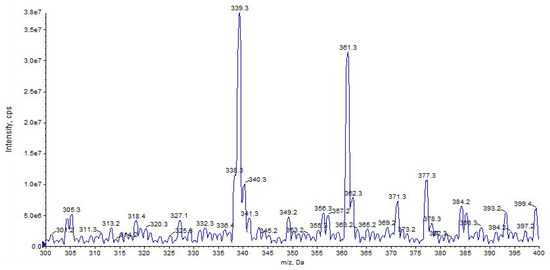
Figure 3.
Representation of alkali metal peaks of URB597 compound. Exponential scale to base 10.
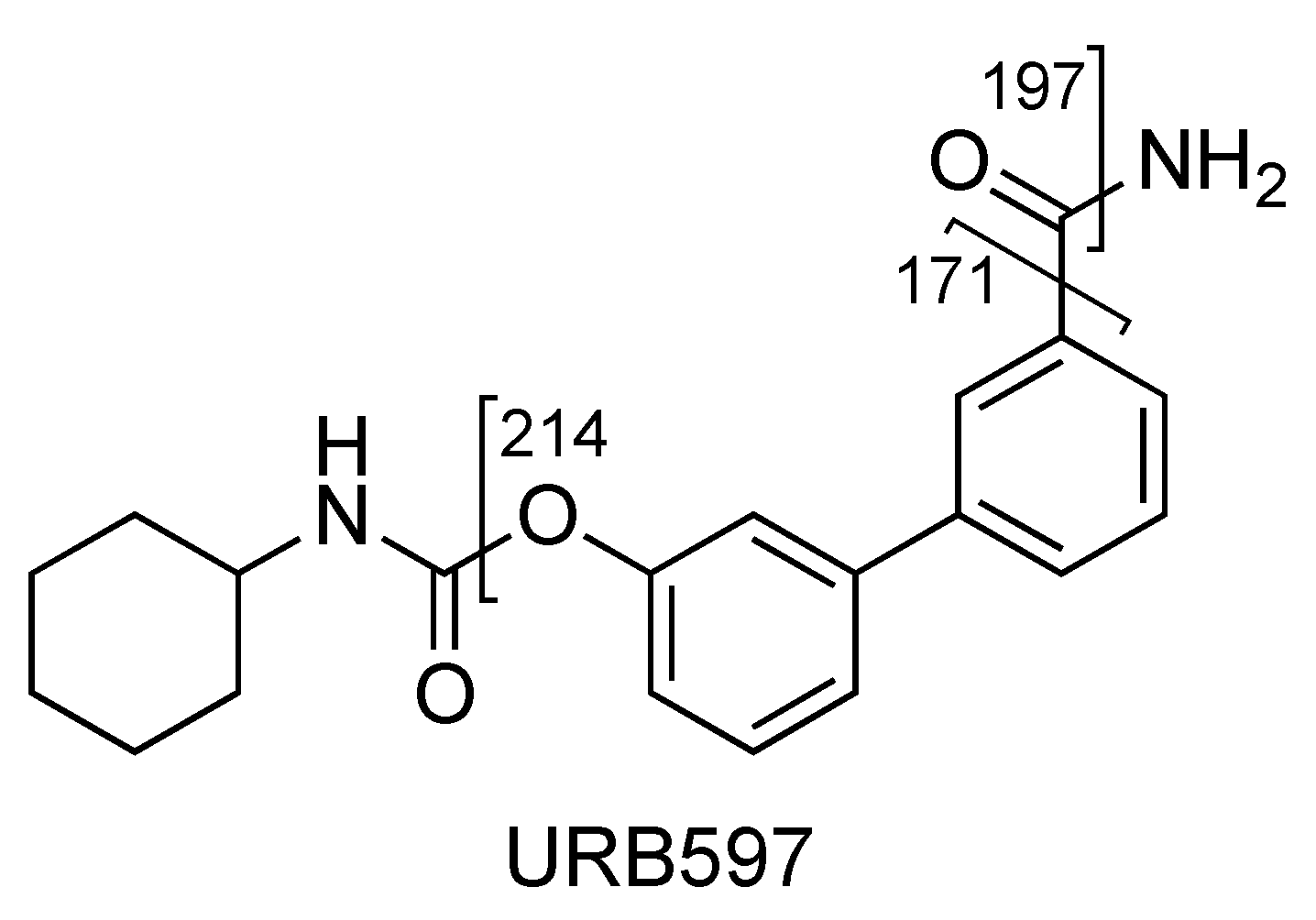
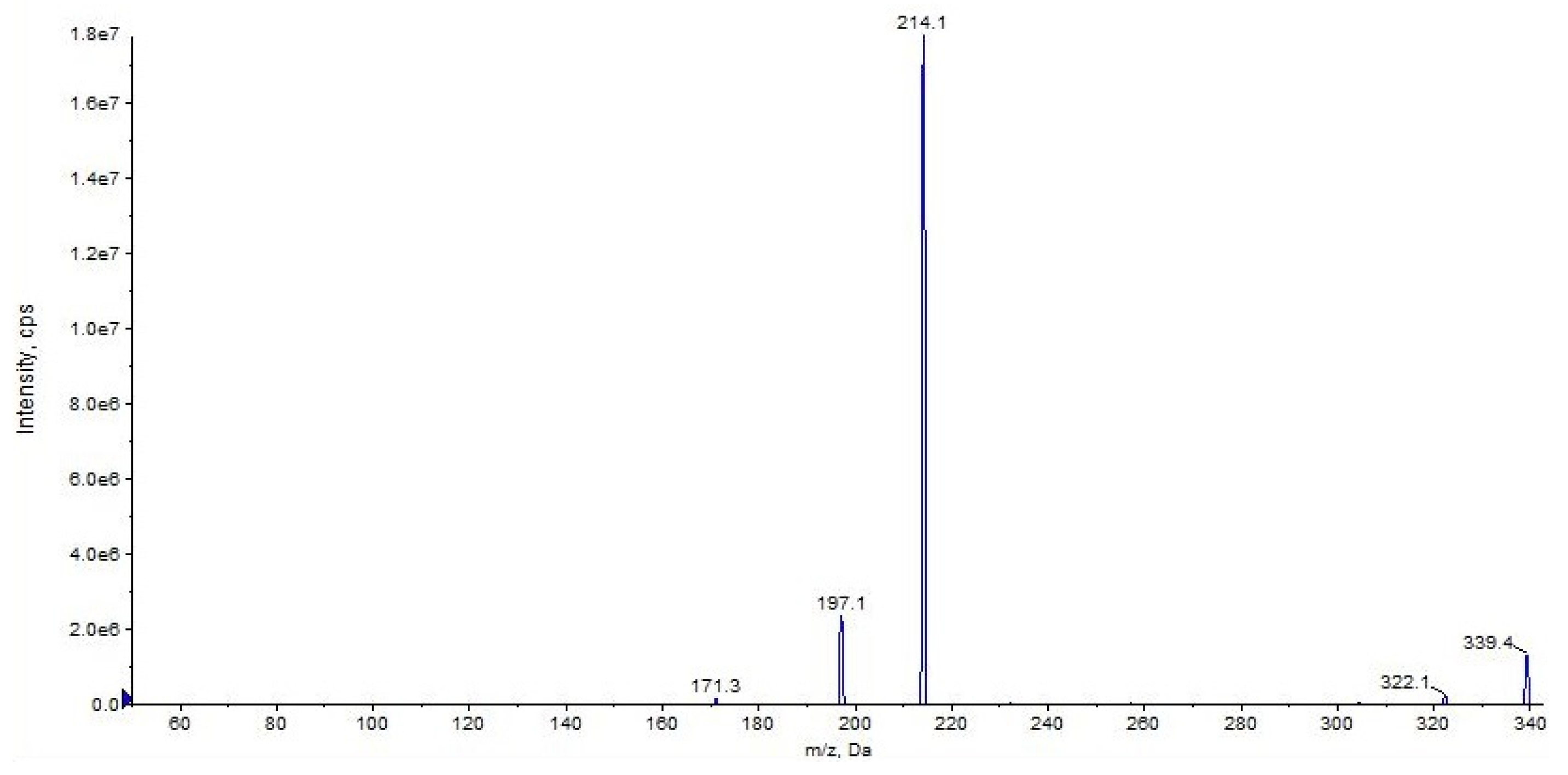
The fragment ion at m/z 214 is due to the loss of cyclohexyl isocyanate and that at m/z 197 is due to the loss of cyclohexyl isocyanate and ammonia (Figure 4 and Figure 5, CE 20 V). Other fragment ions are those at m/z 322 due to the loss of ammonia from 339 and at m/z 171, which differs from the fragment at m/z 214 due to the loss of the carbamoyl group (Figure 4 and Figure 5).
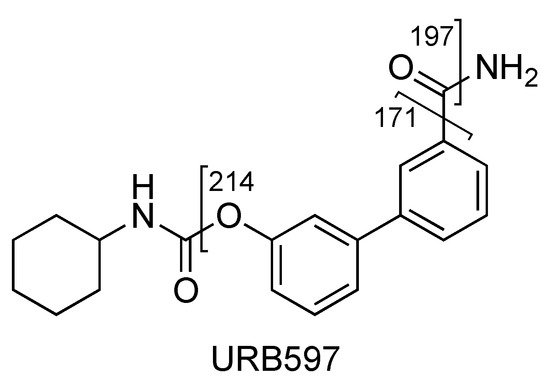
Figure 4.
Representation of the collisional-induced fragment ions of URB597 compound.
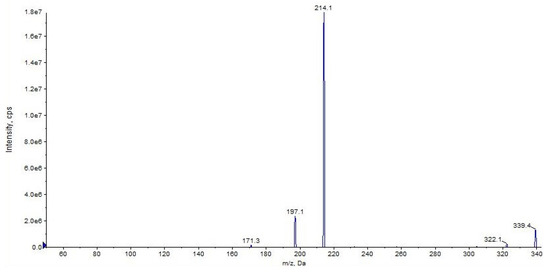
Figure 5.
Product ion scan of URB597 compound obtained by QqQ. Exponential scale to base 10.
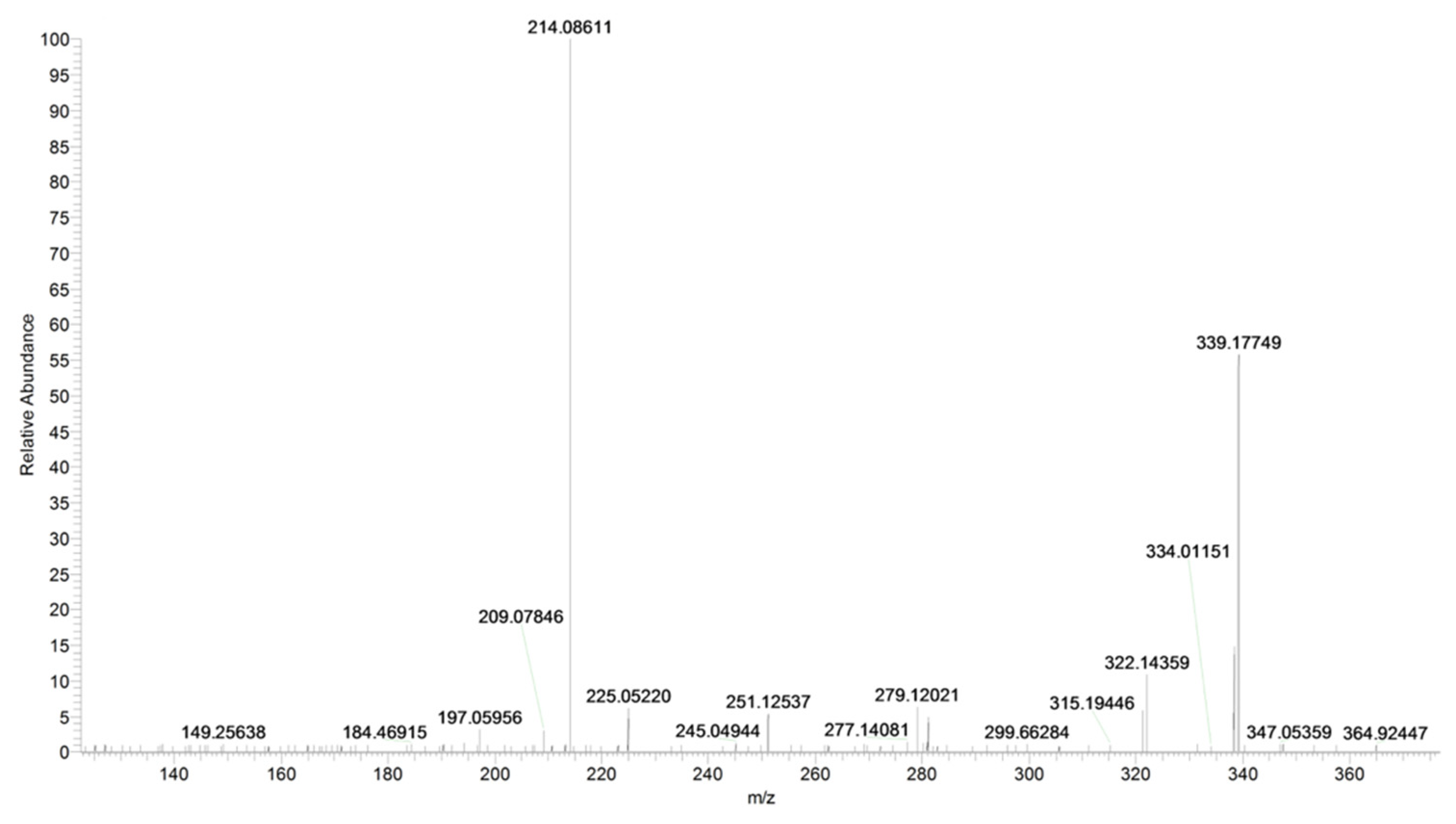
The main fragmentation pathways are driven by α-cleavages to the carbonyl moieties (Table 2, Figure 6).
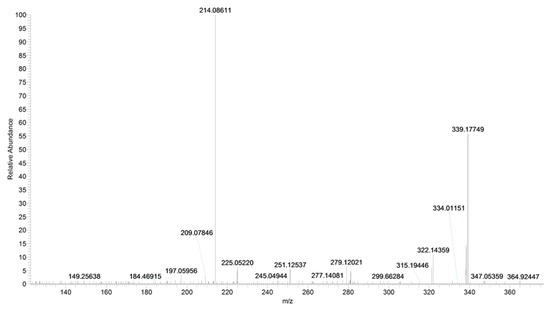
Figure 6.
Product ion scan of URB597 compound obtained by HRMS.
2.2. URB937
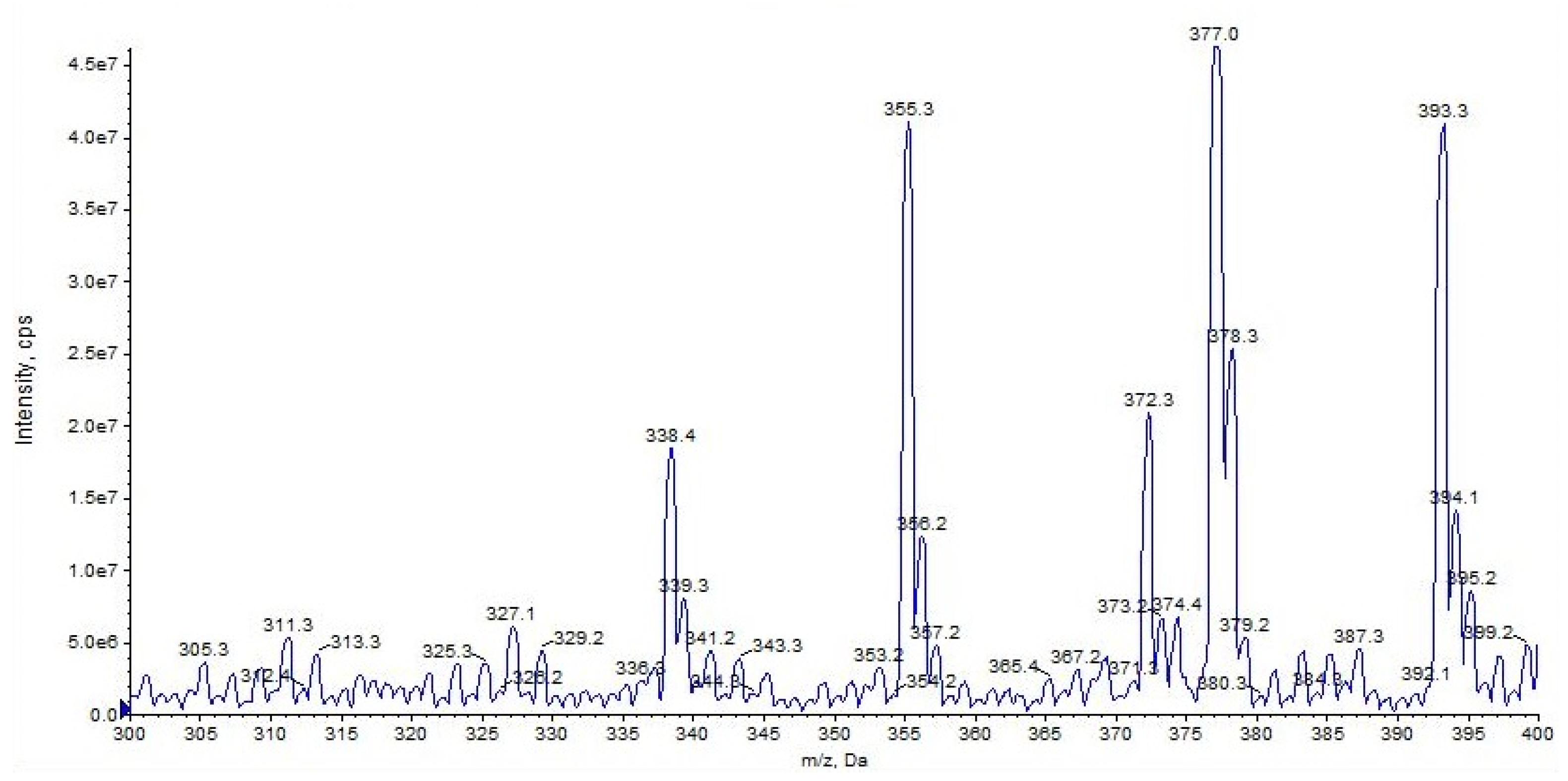
URB937 differs from URB597 by the presence of a 6–hydroxy group on the proximal phenyl ring. URB937 ([M + H]+ m/z 355) shows the same fragmentation pattern as URB597, displaying fragment ions at m/z 377 [M + Na]+ and m/z 393 [M + K]+ but more affinity with alkali metal (Figure 7).
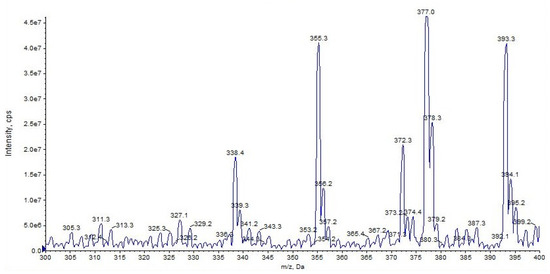
Figure 7.
Representation of alkali metal peaks of URB937 compound.
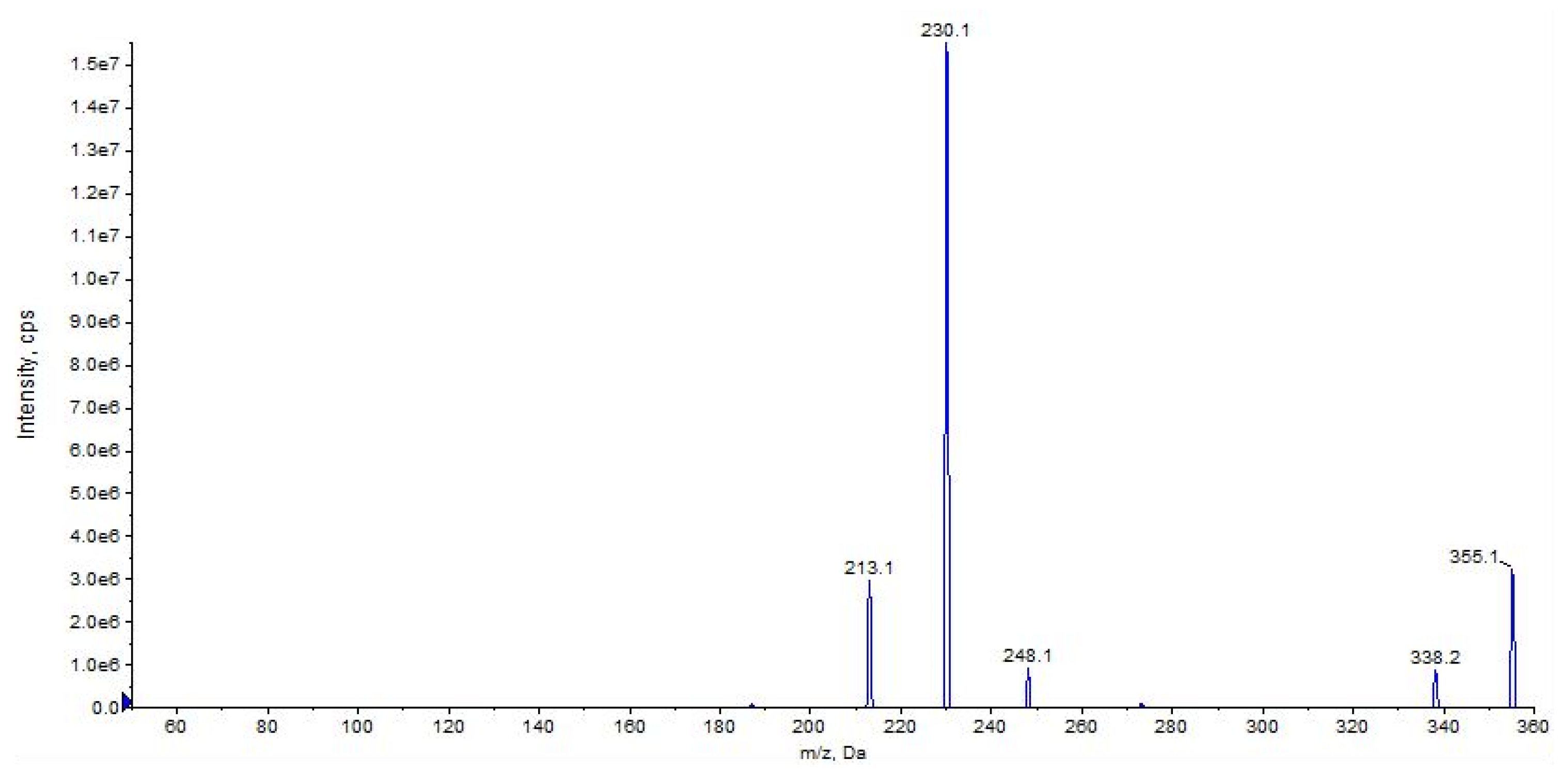
The most abundant ion at m/z 230 results from the loss of cyclohexyl isocyanate (Figure 8, CE 20 V).
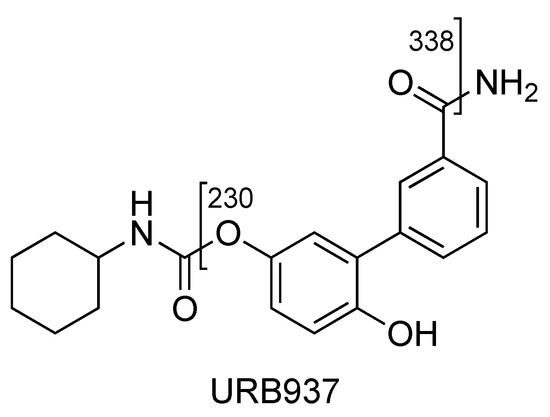
Figure 8.
Representation of the collisional-induced fragment ions of URB937 compound.
Other main characteristic fragments are observed at m/z 213 due to the loss of cyclohexyl isocyanate and ammonia, and m/z 338 due to the loss of ammonia only (Figure 8 and Figure 9).
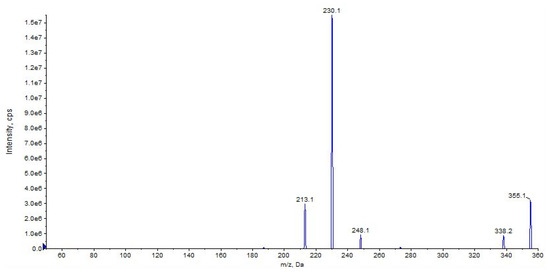
Figure 9.
Product ion scan of URB937 compound obtained by QqQ. Exponential scale to base 10.
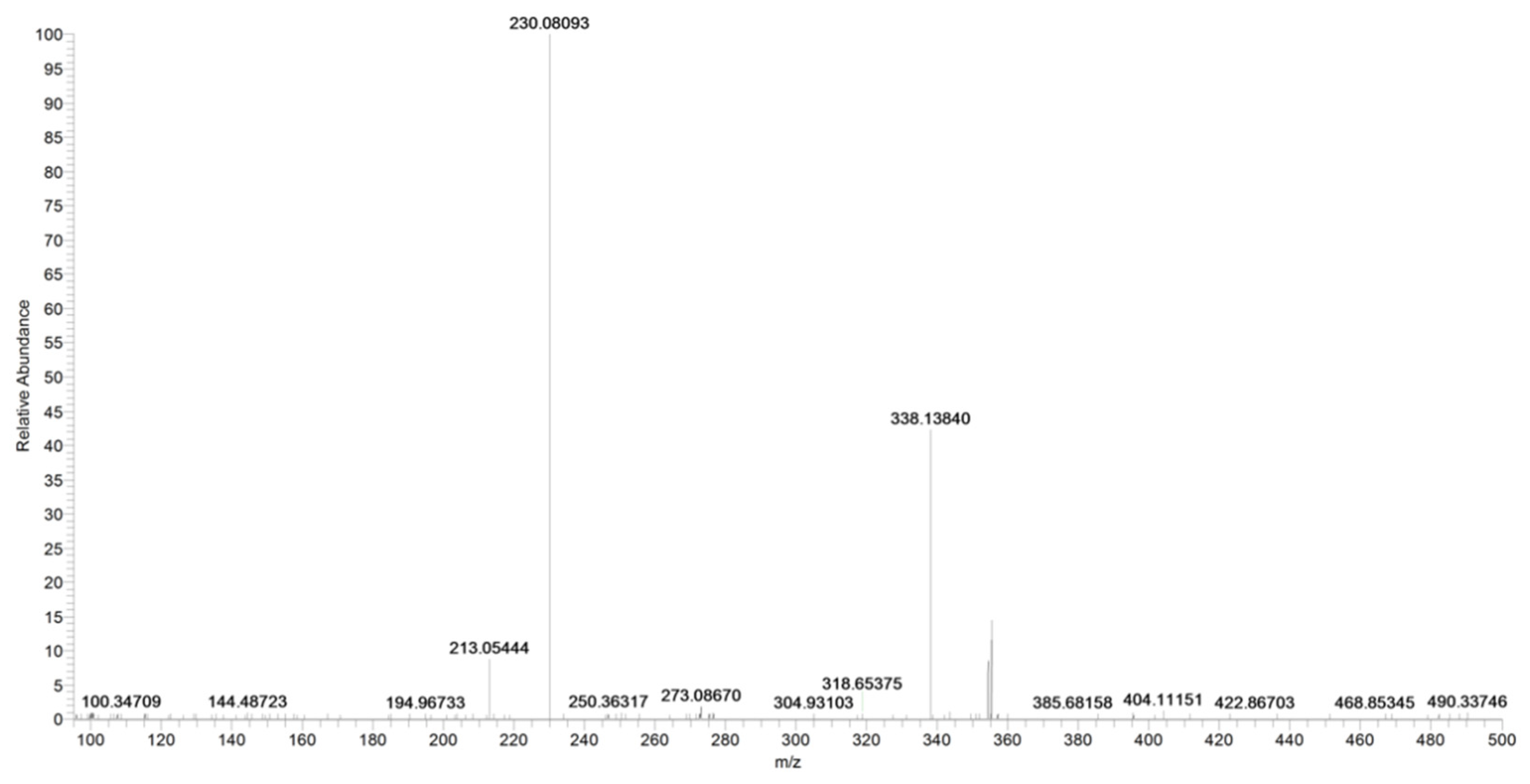
The ion at m/z 187, due to the loss of the carbamoyl group, is observed only at higher collision energies (figure not shown). In the case of URB937, the presence of [M2 + Na] and [M3 + Na] at m/z 731.3057 and 1085.4636, respectively, was observed by accurate mass (Figure 10).
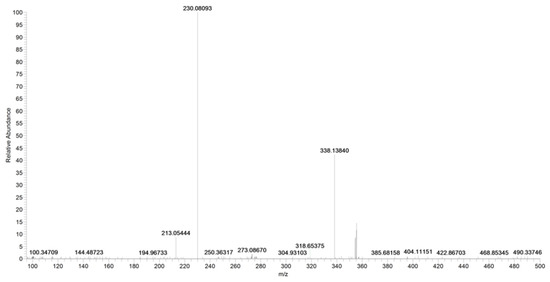
Figure 10.
Product ion scan of URB937 compound obtained by HRMS.
2.3. URB602
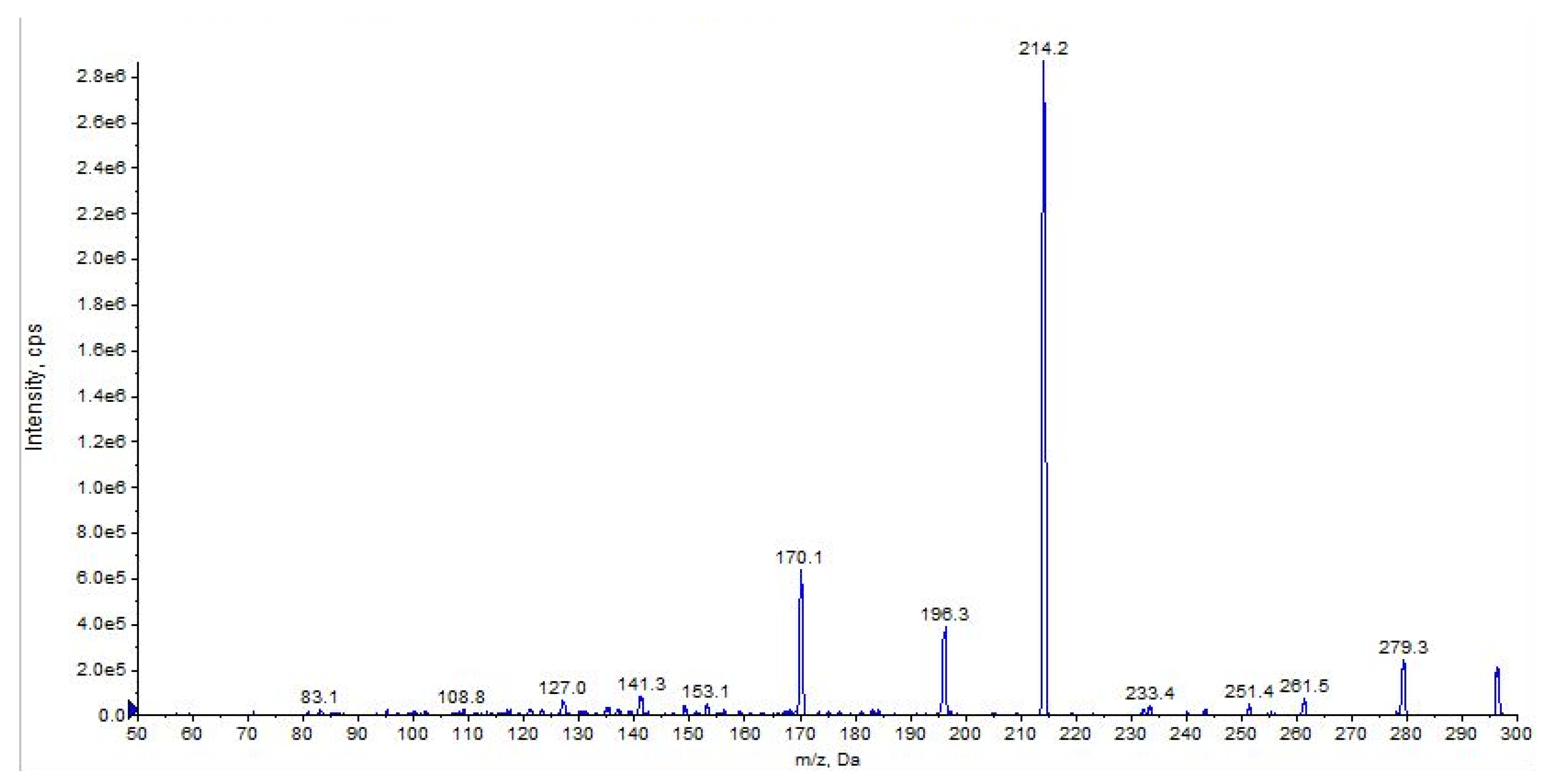
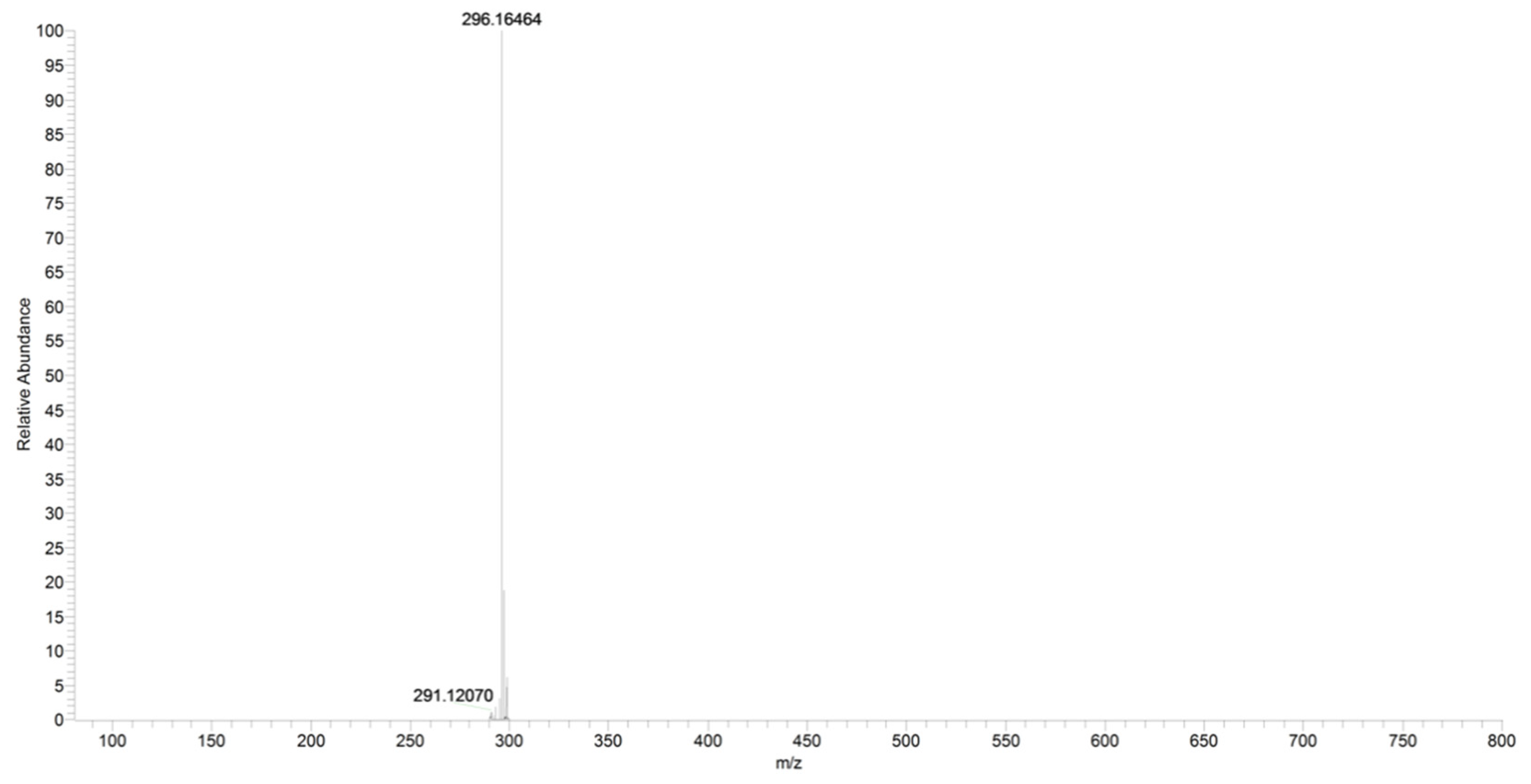
The main fragment ions of URB602 ([M + H]+ m/z 296) are those at m/z 214, due to the loss of cyclohexyl, at m/z 196 and m/z 170, depending on the losses of water and carbon anhydride, respectively (Figure 11 and Figure 12, CE 20 V).
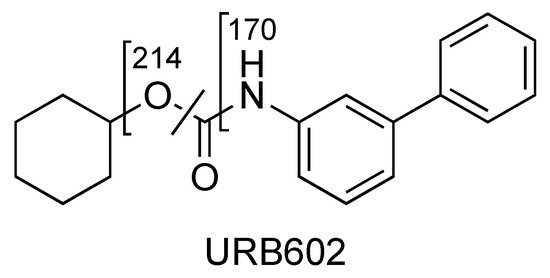
Figure 11.
Representation of the collisional-induced fragment ions of URB602 compound.
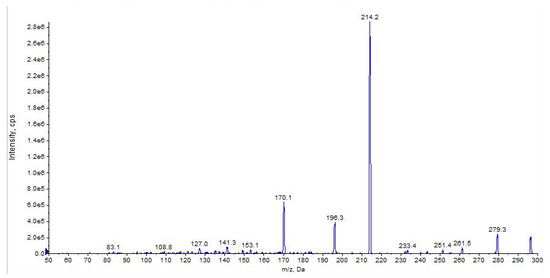
Figure 12.
Product ion scan of URB602 compound obtained by QqQ. Exponential scale to base 10.
For URB602, a significant in-source fragmentation occurred after the direct injection of the URB602 solution (1 ppm). In fact, only a small amount of this protonated ion was observed in the scan mode in both QqQ and in HRMS (Figure 13). The poor ionization and different collisional conditions in the linear trap of Orbitrap did not permit an HRMS fragment ions characterization.
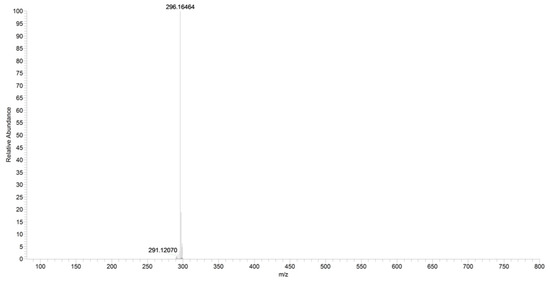
Figure 13.
Scan of URB602 compound obtained by HRMS.
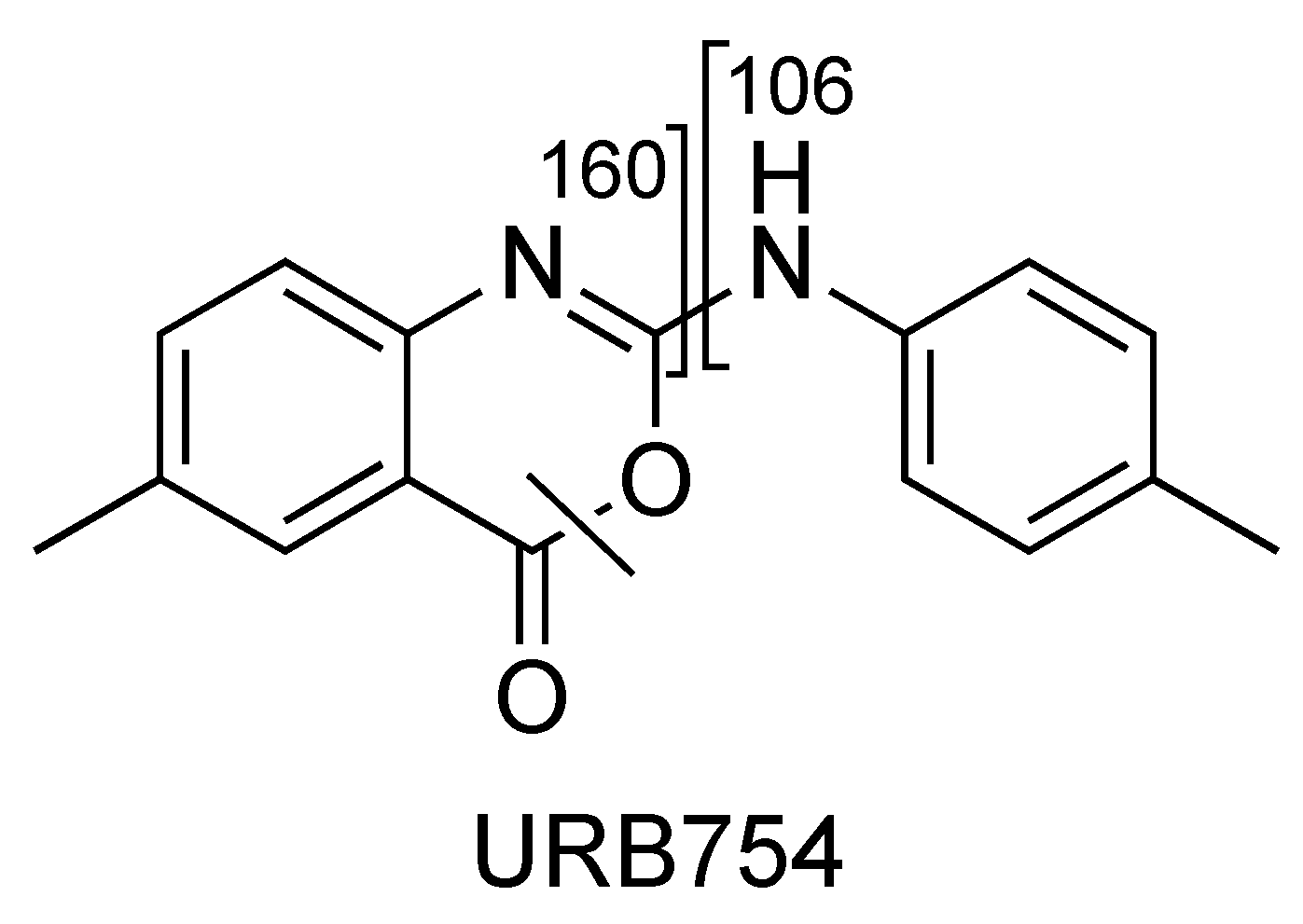
2.4. URB754
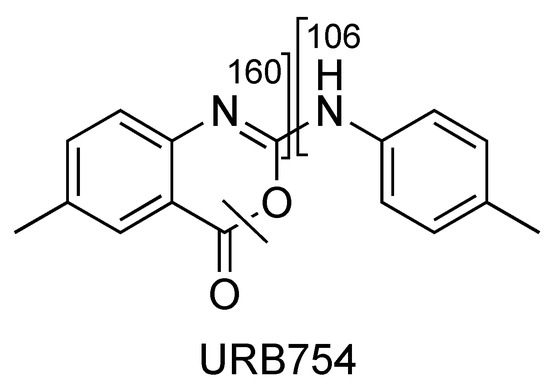
Figure 14.
Representation of the collisional-induced fragment ions of URB754 compound.
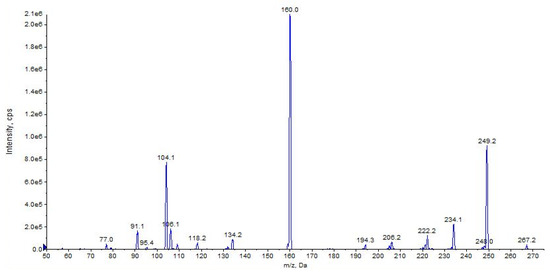
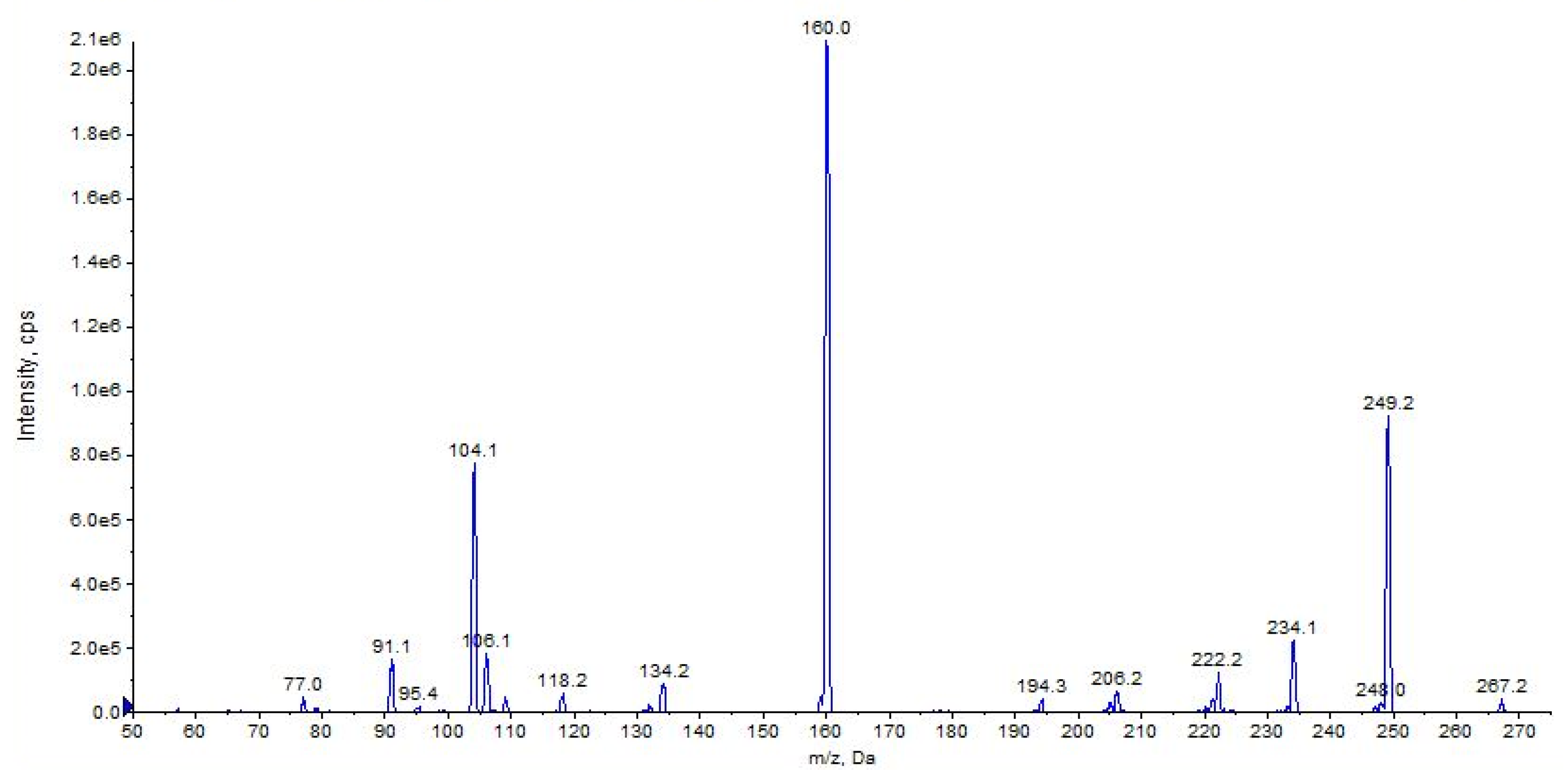
Figure 15.
Product ion scan of URB754 compound obtained by QqQ. Exponential scale to base 10.
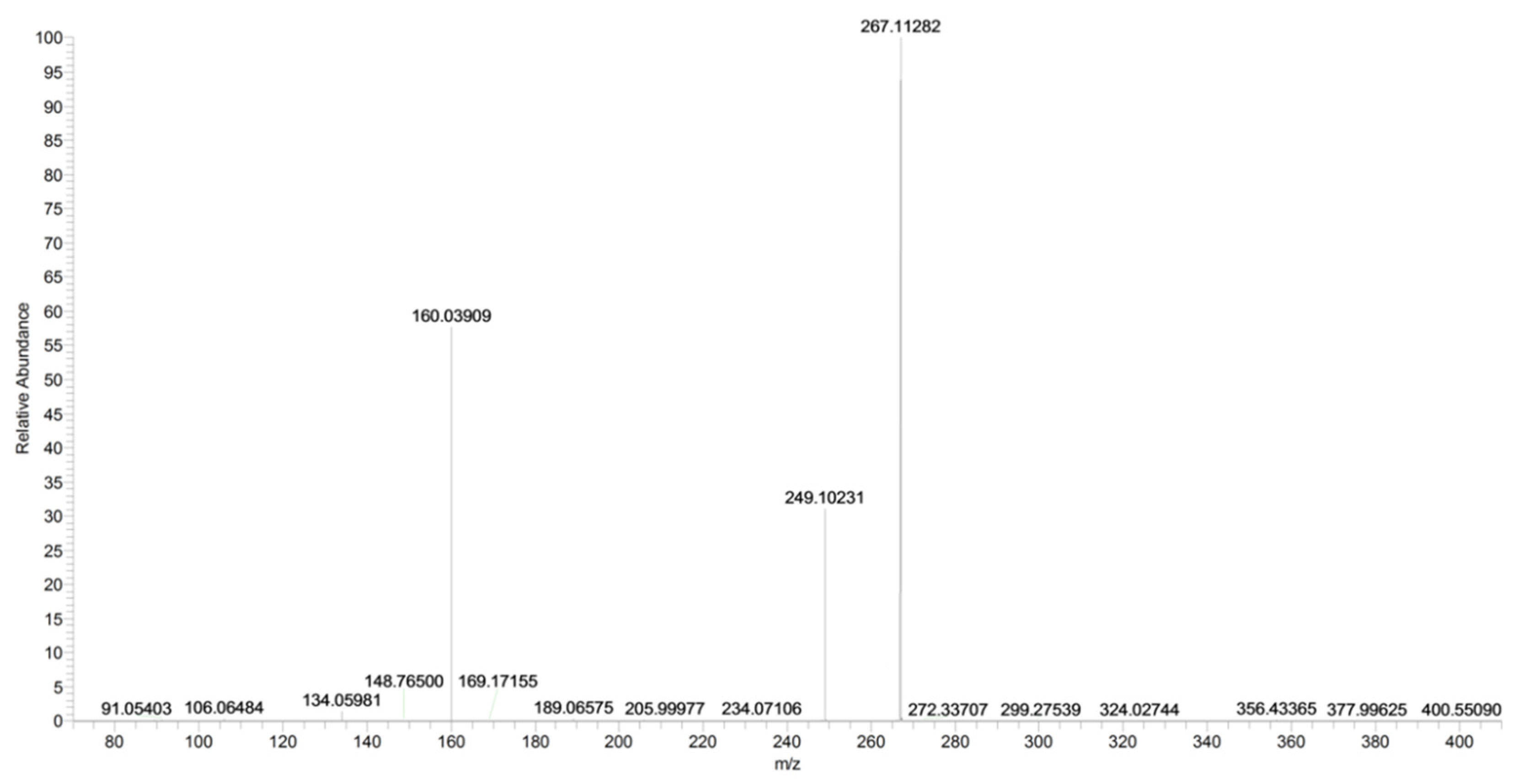
The main fragment ions of URB754 ([M + H]+ at m/z 267) are 6-methyl-4-oxo-4H-3,1-benzoxazin-2-ylium at m/z 160, due to the loss of 4-methylaniline, and the ion at m/z 249, due to the loss of water caused by the opening of the 1,3-oxazin-6-one ring. A fragment ion at m/z 106 was also observed, caused by the formation of the toluidine derivative ion. The description of the accurate mass is shown in Figure 16.
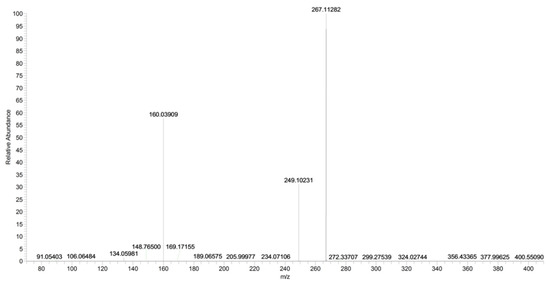
Figure 16.
Product ion scan of URB754 compound obtained by HRMS.
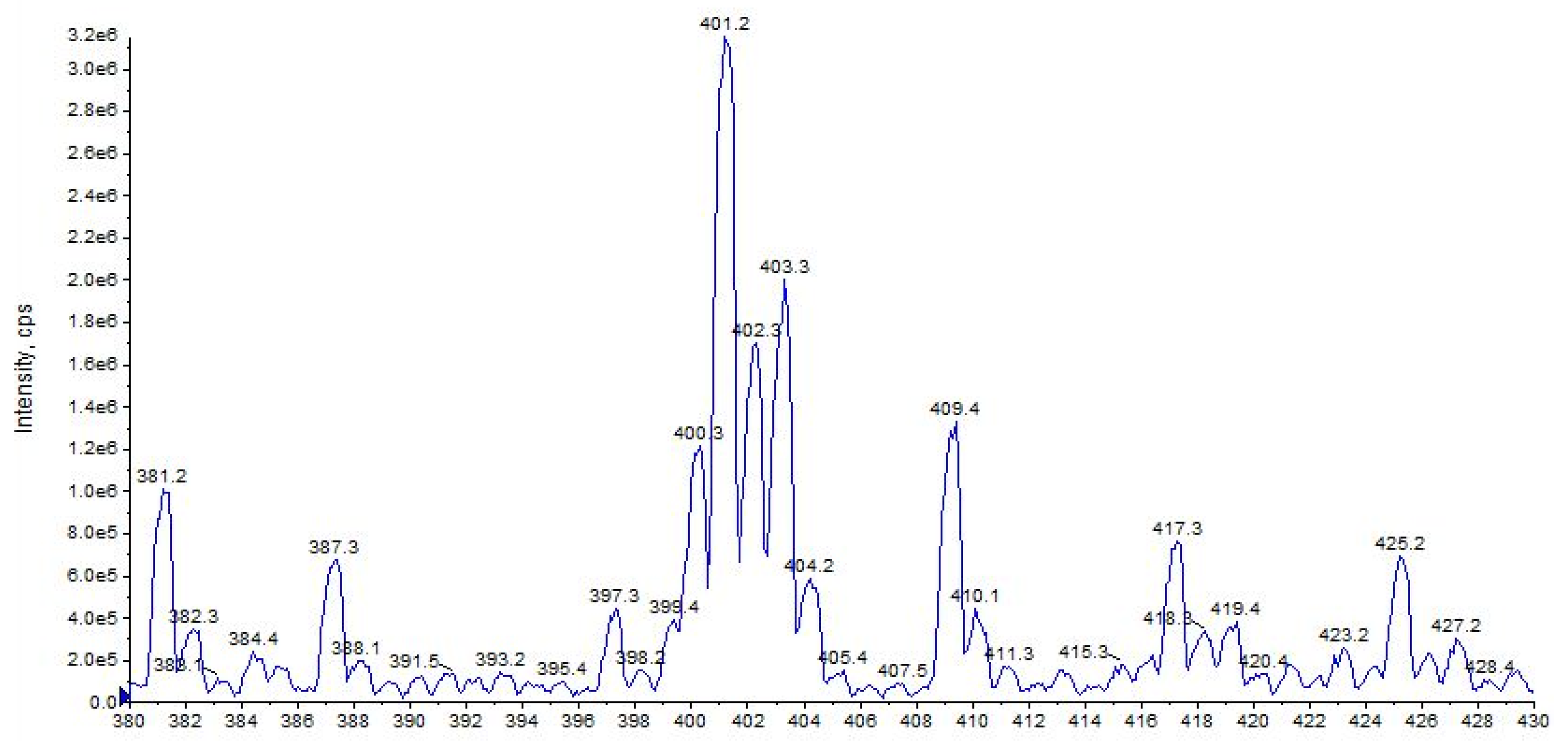
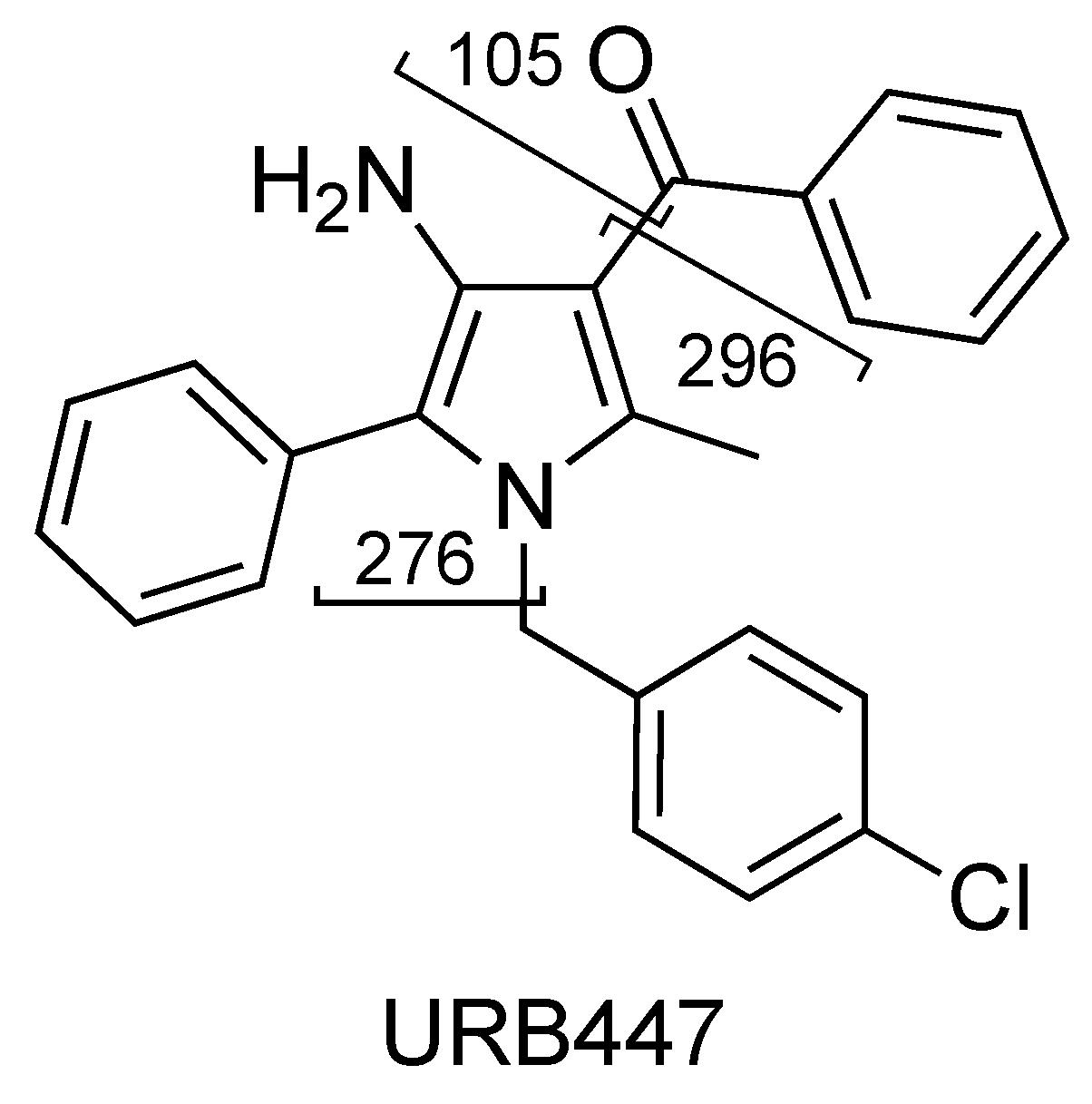
2.5. URB447
URB447 shows a quasi-molecular ion [M + H]+ at m/z 401 and 403, due to the presence of the characteristic isotopic pattern of chlorine 35Cl and 37Cl (Figure 17).
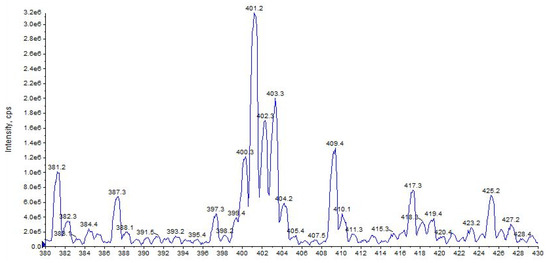
Figure 17.
Representation of alkali metal peaks of URB447 compound. Exponential scale to base 10.
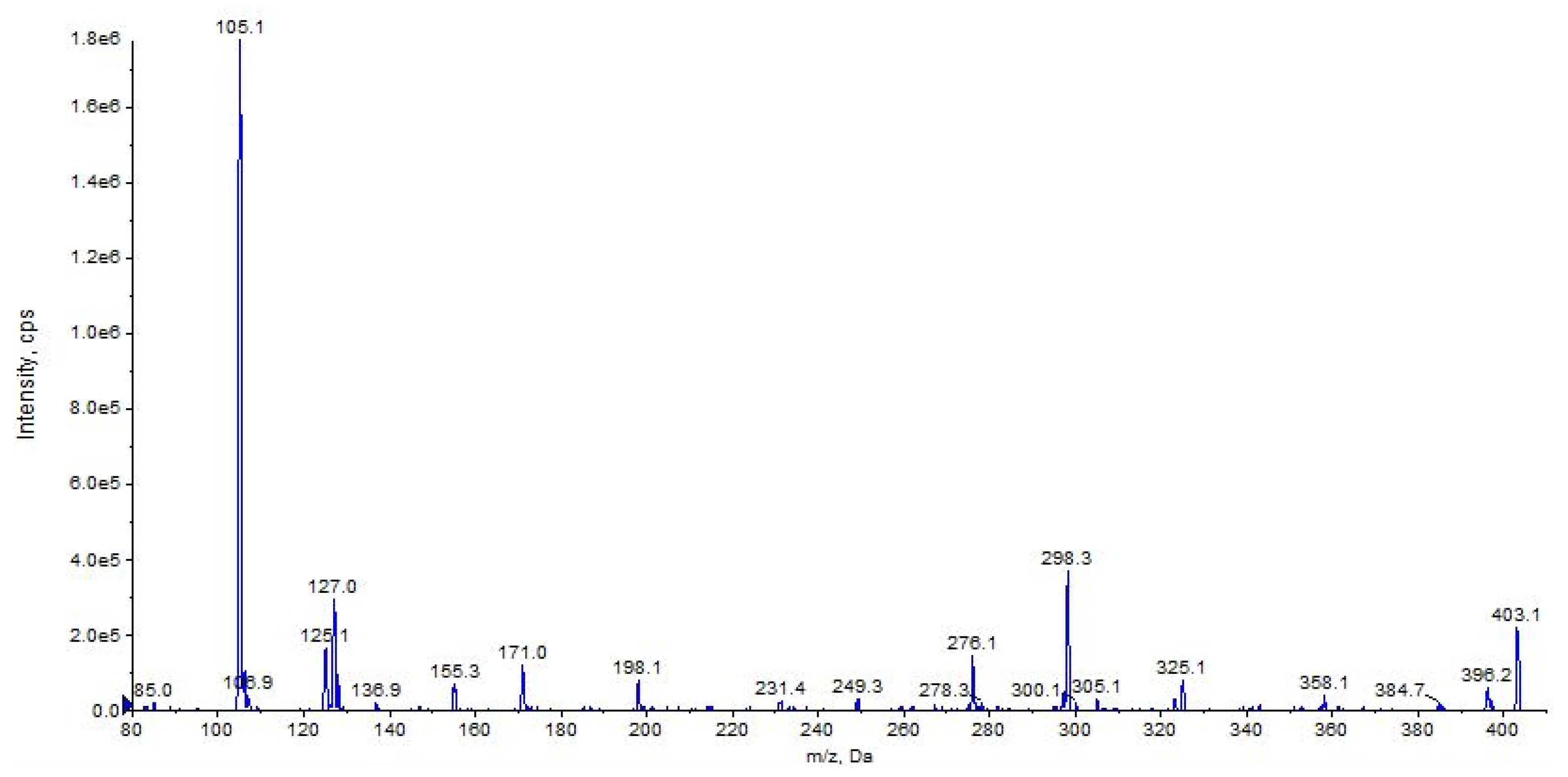
The fragment ions observed for URB447 are due to the cleavages of the carbon–carbon bond between the carbonyl and 3-pyrrolyl groups resulting in a benzoyl ion at m/z 105 or a 4-amino-1-[(4-chlorophenyl)methyl]-2-methyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-3-ylium ion at m/z 296 (Figure 18 and Figure 19, CE 35 V).
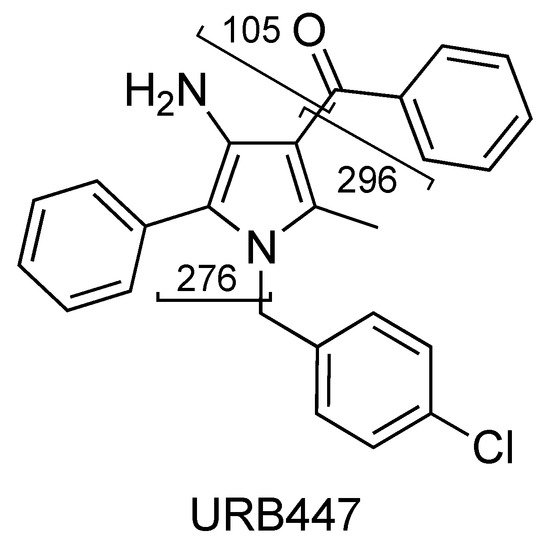
Figure 18.
Representation of the collisional-induced fragment ions of URB447 compound.
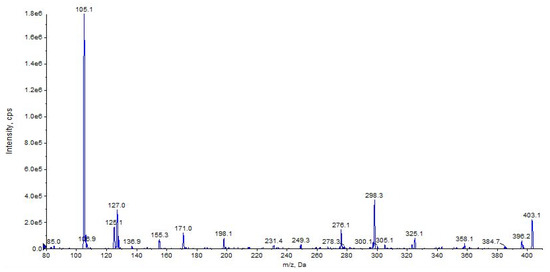
Figure 19.
Product ion scan of URB447 compound obtained by QqQ. Exponential scale to base 10.
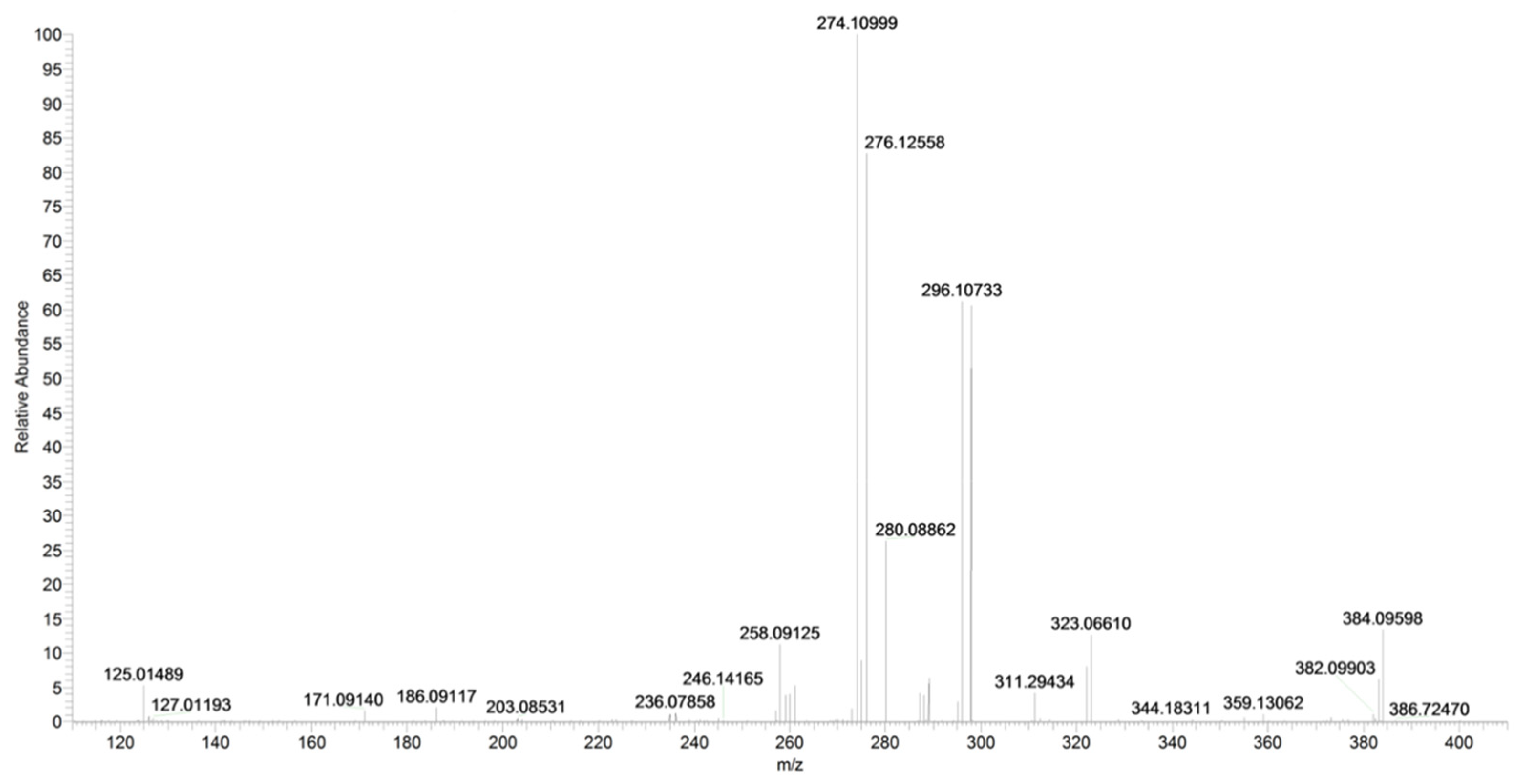
A direct cleavage of the C–N bond between the 4-chlorobenzyl group and the N-pyrrolyl group results in a 4-chlorobenzylium ion at m/z 125 or 4-amino-3-benzoyl-2-methyl-5-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-1-ylium ion at m/z 276 (C18H16N2O) (Figure 18 and Figure 19). Analogue fragment ions at m/z 127 and at m/z 298 were observed starting from a similar precursor ion at m/z 403 (figure not shown). The description of the accurate mass is shown in Figure 20.
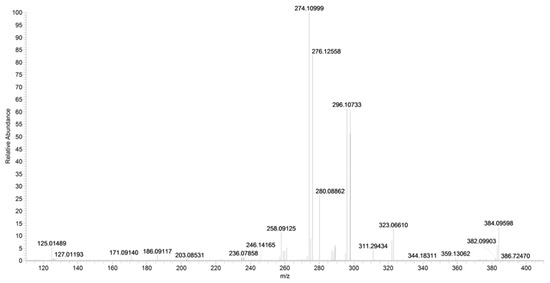
Figure 20.
Product ion scan of URB447 compound obtained by HRMS.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Standard and Solvents
JWH–018 (Internal Standard, IS) was supplied by Lipomed AG (Arlesheim, CH). Water, acetonitrile, isopropyl alcohol, and methanol LC-MS grade were furnished from PanReac AppliChem (Nova Chimica; Cinisello Balsamo, Italy). Formic acid LC-MS grade was provided by Sigma-Aldrich (Milan, Italy).
3.2. Chemicals
URB compounds were synthesized in the laboratories of the Department of Biomolecular Sciences of the University of Urbino Carlo Bo as described [41,42,43,44,45]. Information about the core assays is reported in [40,41,43,45,50]. Data regarding mp, NMR, and IR are present in [41,44,45,51,52]. Results on pharmacological tests are published in [40,41,42,43,45].
3.3. UHPLC-MS/MS
The characterization of compounds by UHPLC-MS/MS was carried out with a UHPLC system (Nexera X2, Shimazdu, Kyoto, Japan) coupled with a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (Hybrid System 4000 Qtrap, AB Sciex, Framingham, MA, USA). Chromatographic separation was performed on a 50 × 2.1 mm KINETEX EVO 1.9 μm C18 column (Phenomenex, Bologna, Italy). The mobile phase was composed of solvent “A” (0.1% formic acid) and “B” (0.1% formic acid in acetonitrile with 5% water). The initial chromatographic conditions were 20% “B”, and the gradient was programmed as follows: 0–0.1 min hold 20% “B”, 0.1–6.0 min to 80% “B”, and 6.0–6.1 min to 100% “B”, and it was kept for 3 min. Finally, the initial condition was restored and kept for 2 min to equilibrate the system. Total run time was 11 min at the constant flow rate (0.5 mL/min); the column temperature was set at 40 °C; the autosampler was maintained at 10 °C. The mass spectrometer operated in positive ion mode using ESI TurboIonSpray® under the following conditions: curtain gas (CUR) 30.0 psi, ion spray voltage (IS) 4000 V, temperature (TEM) 500 °C, ion source gas 1 (GS1) 40.0 psi, and ion GS2 55.0 psi. Identification was performed using MRM mode. MRM transitions were experimentally established. At least three MRM transitions were monitored for each compound. A total of 19 transition were monitored with an MRM pause time of 5 ms and a dwell time of 20 ms for each transition; the total scan time was 0.47 s.
3.4. HRMS Compound Characterization
The methanolic solutions of the individual standards (URB597, URB937, URB602, URB754, and URB447) were prepared separately in 10 mL volumetric flasks at an approximate concentration of 100 or 1000 μg/mL. Each drug was diluted to a concentration from 0.1 to 1 ppm in methanol. The determination of the exact mass of ionic species in the URB compounds was performed on HRMS experiments using a Linear Trap Quadrupole (LTQ) Orbitrap XL hybrid mass spectrometry (Thermo ScientificTM, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) equipped with an electrospray ion source operated in positive ion mode. Direct infusion of compounds into the MS ion source was performed using a syringe pump at a flow rate of 10 µL/min. The protonated molecules of each compound were isolated in the linear ion trap and fragmented at varying collision energies in order to identify the most abundant and characteristic product ions.
4. Conclusions
The present study integrates and extends the mass spectrometry characterization of synthetic drugs that are able to interact with the cannabinoid system. It provides the first description of URB937, URB602, URB754, and URB447 compounds by CID in tandem with the quadrupole mass spectrometry and hybrid ion trap-orbitrap mass spectrometry. It should also be considered that, so far, the analyses and characterizations have been carried out in MS (EI) [44,45,51,52] or MS (ESI) [41] only. The methods used here have made it possible to unequivocally characterize the molecules under examination with the aim to determine the operating conditions for their accurate identification and, therefore, laying the foundations for the future development of analytical methods aimed at the early screening of NPS in seizures or biological samples. However, these substances have long been monitored as potential alerts [48,53]. In this respect, studies on the metabolism of the URB compounds are necessary, and the work is in progress.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A., D.F., and A.D.; methodology, M.A., and D.F.; formal analysis, M.A., C.R., and S.V.; investigation, C.R., and S.V.; resources, D.F., and A.D.; data curation, M.A., and D.F.; writing—original draft preparation, M.A., D.F., and A.D.; writing—review and editing, M.A., D.F., and A.D.; supervision, M.A., D.F., and A.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dario Melita for his support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Kumar, P.; Mahato, D.K.; Kamle, M.; Borah, R.; Sharma, B.; Pandhi, S.; Tripathi, V.; Yadav, H.S.; Devi, S.; Patil, U.; et al. Pharmacological properties, therapeutic potential, and legal status of Cannabis sativa L.: An overview. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 6010–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, C.; Navarra, G.; Coppola, L.; Avilia, G.; Bifulco, M.; Laezza, C. Cannabinoids: Therapeutic use in clinical practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gülck, T.; Møller, B.L. Phytocannabinoids: Origins and biosynthesis. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 985–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. European Drug Reports. Trends and Developments. 2022. Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/system/files/publications/14644/TDAT22001ENN.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Devane, W.A.; Dysarz, F.A.; Johnson, M.R.; Melvin, L.S.; Howlett, A.C. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988, 34, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, L.A.; Lolait, S.J.; Brownstein, M.J.; Young, A.C.; Bonner, T.I. Structure of a cannabinoid receptor and functional ex-pression of the cloned cDNA. Nature 1990, 346, 561–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Abu-Shaar, M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature 1993, 365, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, B. Neurobiology of cannabinoid receptor signaling. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 22, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, F.; Grandi, V.; Banerjee, A.; Trant, J.F. Cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors: The story so far. iScience 2020, 23, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, N. Potential application of endocannabinoid system agents in neuropsychiatric and neuro-degenerative diseases—Focusing on FAAH/MAGL inhibitors. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sickle, M.D.; Duncan, M.; Kingsley, P.J.; Mouihate, A.; Urbani, P.; Mackie, K.; Stella, N.; Makriyannis, A.; Piomelli, D.; Davison, J.S.; et al. Identification and functional characterization of brainstem cannabinoid CB2 receptors. Science 2005, 310, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Li, L. Cannabinoid receptors in myocardial injury: A brother born to rival. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devane, W.A.; Hanus, L.; Breuer, A.; Pertwee, R.G.; Stevenson, L.A.; Griffin, G.; Gibson, D.; Mandelbaum, A.; Etinger, A.; Mech-oulam, R. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science 1992, 258, 1946–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R.; Ben-Shabat, S.; Hanus, L.; Ligumsky, M.; Kaminski, N.E.; Schatz, A.R.; Gopher, A.; Almog, S.; Martin, B.R.; Compton, D.R. Identification of an endogenous 2-monoglyceride, present in canine gut, that binds to cannabinoid receptors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1995, 50, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Kondo, S.; Sukagawa, A.; Nakane, S.; Shinoda, A.; Itoh, K.; Yamashita, A.; Waku, K. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol: A possible endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand in brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1995, 215, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piomelli, D. The molecular logic of endocannabinoid signalling. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 873–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustin, S.M.; Lovinger, D.M. Functional Relevance of endocannabinoid-dependent synaptic plasticity in the central nervous system. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 2146–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, H.; Toyang, N.; Steele, B.; Bryant, J.; Ngwa, W. The endocannabinoid system: A potential target for the treatment of various diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piomelli, D.; Mabou Tagne, A. Endocannabinoid-based therapies. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 62, 17.1–17.25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaoni, Y.; Mechoulam, R. Isolation, structure, and partial synthesis of an active constituent of hashish. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 1646–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Fan, M.; An, C.; Ni, F.; Huang, W.; Luo, J. A narrative review of molecular mechanism and therapeutic effect of cannabidiol (CBD). Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 130, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manera, C.; Bertini, S. Cannabinoid-Based Medicines and Multiple Sclerosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1264, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazz Pharmaceutics Website. Available online: https://www.jazzpharma.com/medicines/our-medicines/ (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Pertwee, R.G. Targeting the endocannabinoid system with cannabinoid receptor agonists: Pharmacological strategies and therapeutic possibilities. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2012, 367, 3353–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, M.A.; Fattore, L. Therapeutic use of synthetic cannabinoids: Still an open issue? Clin. Ther. 2018, 40, 1457–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, D.; Peigneur, S.; Hendrickx, L.A.; Tytgat, J. Targeting cannabinoid receptors: Current status and prospects of natural prod-ucts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada, J.A.; Contreras, I. Endocannabinoid receptors in the CNS: Potential drug targets for the prevention and treatment of neurologic and psychiatric disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 769–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, J.L.; Compton, D.R.; Dai, D.; Lainton, J.A.H.; Phillips, M.; Huffman, J.W.; Martin, B.R. Structure-activity relationships of indole- and pyrrole-derived cannabinoids. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1998, 285, 995–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Auwärter, V.; Dresen, S.; Weinmann, W.; Müller, M.; Pütz, M.; Ferreirós, N. ‘Spice’ and other herbal blends: Harmless incense or cannabinoid designer drugs? J. Mass Spectrom. 2009, 44, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, B.K.; Huffman, J.; Straiker, A.; Mackie, K. JWH018, a common constituent of ‘Spice’ herbal blends, is a potent and efficacious cannabinoid CB receptor agonist. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNODC Early Warning Advisory Toxicology Highlights. Current NPS Threats, Volume II, January 2020. Available online: https://www.unodc.org/documents/scientific/Current_NPS_Threats_Volume_II_Web.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Shafi, A.; Berry, A.J.; Sumnall, H.; Wood, D.M.; Tracy, D.K. New psychoactive substances: A review and updates. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2020, 10, 2045125320967197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgetti, A.; Pascali, J.P.; Fai, P.; Pelletti, G.; Gabbin, A.; Franchetti, G.; Cecchetto, G.; Viel, G. Molecular mechanisms of action of novel psychoactive substances (NPS). A new threat for young drug users with forensic-toxicological implications. Life 2021, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNODC Early Warning Advisory Toxicology Highlights. Current NPS Threats, Volume IV. November 2021. Available online: https://www.unodc.org/documents/scientific/NPS_threats-IV.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Chung, E.Y.; Cha, H.J.; Min, H.K.; Yun, J. Pharmacology and adverse effects of new psychoactive substances: Synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2021, 44, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UNODC Early Warning Advisory on New Psychoactive Substances. What Are NPS? December 2021. Available online: https://www.unodc.org/LSS/Page/NPS (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. Synthetic Cannabinoids in Europe—A Review. 2021. Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/system/files/publications/14035/Synthetic-cannabinoids-in-Europe-EMCDDA-technical-report.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Markham, J.; Sparkes, E.; Boyd, R.; Chen, S.; Manning, J.J.; Finlay, D.; Lai, F.; McGregor, E.; Maloney, C.J.; Gerona, R.R.; et al. Defining steric requirements at CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors using synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists 5F-AB-PINACA, 5F-ADB-PINACA, PX-1, PX-2, NNL-1, and their analogues. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, V.L.; Gonçalves, J.L.; Aguiar, J.; Teixeira, H.M.; Câmara, J.S. The synthetic cannabinoids phenomenon: From structure to toxicological properties. A review. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathuria, S.; Gaetani, S.; Fegley, D.; Valiño, F.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Mor, M.; Tarzia, G.; La Rana, G.; Calignano, A.; et al. Modulation of anxiety through blockade of anandamide hydrolysis. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clapper, J.R.; Moreno-Sanz, G.; Russo, R.; Guijarro, A.; Vacondio, F.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Sanchini, S.; Sciolino, N.R.; Spradley, J.M.; et al. Anandamide suppresses pain initiation through a peripheral endocannabinoid mechanism. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohmann, A.G.; Suplita, R.L.; Bolton, N.M.; Neely, M.H.; Fegley, D.; Mangieri, R.; Krey, J.F.; Walker, J.M.; Holmes, P.V.; Crystal, J.D.; et al. An endocannabinoid mechanism for stress-induced analgesia. Nature 2005, 435, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makara, J.K.; Mor, M.; Fegley, D.; Szabó, S.I.; Kathuria, S.; Astarita, G.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Tarzia, G.; Rivara, S.; et al. Selective inhibition of 2-AG hydrolysis enhances endocannabinoid signaling in hippocampus. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1139–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarzia, G.; Antonietti, F.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Mor, M.; Rivara, S.; Traldi, P.; Astarita, G.; King, A.; Clapper, J.R.; et al. Identification of a bioactive impurity in a commercial sample of 6-methyl-2-p-tolylaminobenzo[d][1,3]oxazin-4-one (URB754). Ann. Chim. 2007, 97, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoVerme, J.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Spadoni, G.; Mor, M.; Rivara, S.; Stella, N.; Xu, C.; Tarzia, G.; Piomelli, D. Synthesis and characterization of a peripherally restricted CB1 cannabinoid antagonist, URB447, that reduces feeding and body-weight gain in mice. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedicto, A.; Arteta, B.; Duranti, A.; Alonso-Alconada, D. The synthetic cannabinoid URB447 exerts antitumor and antimetastatic effect in melanoma and colon cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, J.; Takahashi, M.; Seto, T.; Kanai, C.; Suzuki, J.; Yoshida, M.; Uemura, N.; Hamano, T. Analysis of azepane isomers of AM-2233 and AM-1220, and detection of an inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase [3′-(aminocarbonyl)(1,1′-biphenyl)-3-yl]-cyclohexylcarbamate (URB597) obtained as designer drugs in the Tokyo area. Forensic Toxicol. 2013, 31, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, K.G.; Behonick, G.S.; Dahn, T.; Terrell, A. Identification of novel third-generation synthetic cannabinoids in products by ultra-performance liquid chromatography and time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2013, 37, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/attachements.cfm/att_229598_EN_TDAN14001ENN.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2022).
- Uchiyama, N.; Kawamura, M.; Kikura-Hanajiri, R.; Goda, Y. URB-754: A new class of designer drug and 12 synthetic cannabinoids detected in illegal products. Forensic Sci. Int. 2013, 227, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarzia, G.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Piersanti, G.; Mor, M.; Rivara, S.; Plazzi, P.V.; Park, C.; Kathuria, S.; Piomelli, D. Design, synthesis, and structure–activity relationships of alkylcarbamic acid aryl esters, a new class of fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mor, M.; Rivara, S.; Lodola, A.; Plazzi, P.V.; Tarzia, G.; Duranti, A.; Tontini, A.; Piersanti, G.; Kathuria, S.; Piomelli, D. Cyclohexylcarbamic Acid 3′- or 4′-substituted biphenyl-3-yl esters as fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors: Synthesis, quantitative structure-activity relationships, and molecular modelling studies. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 4998–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://namsdl.org/wp-content/uploads/Summary-of-Synthetic-Drugs-Bills-and-Proposed-Regulations.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).