In Vivo Imaging and Kinetic Modeling of Novel Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Radiotracers [11C]OCM-44 and [18F]OCM-50 in Non-Human Primates
Abstract
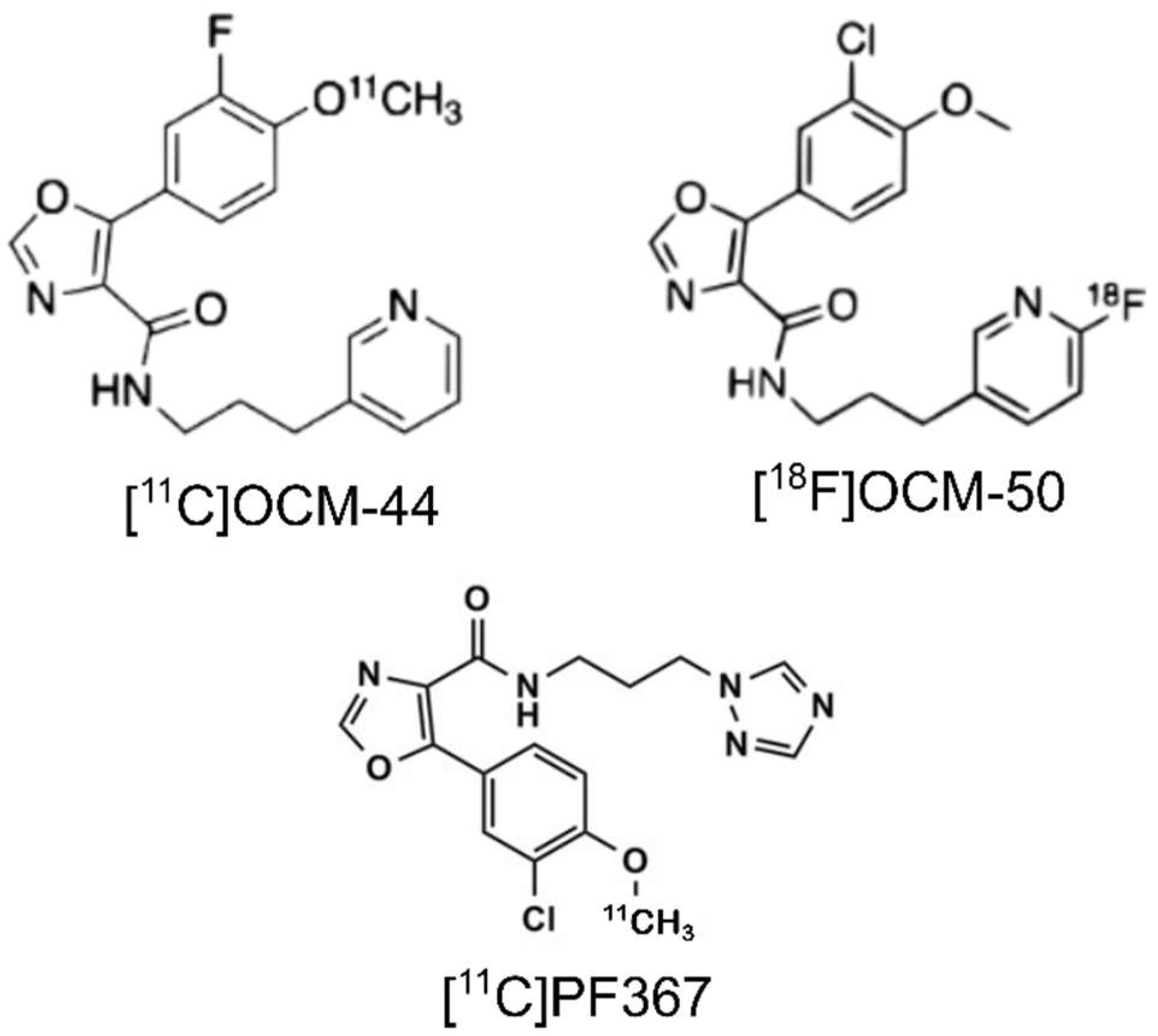
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Radiochemistry and Injection Parameters
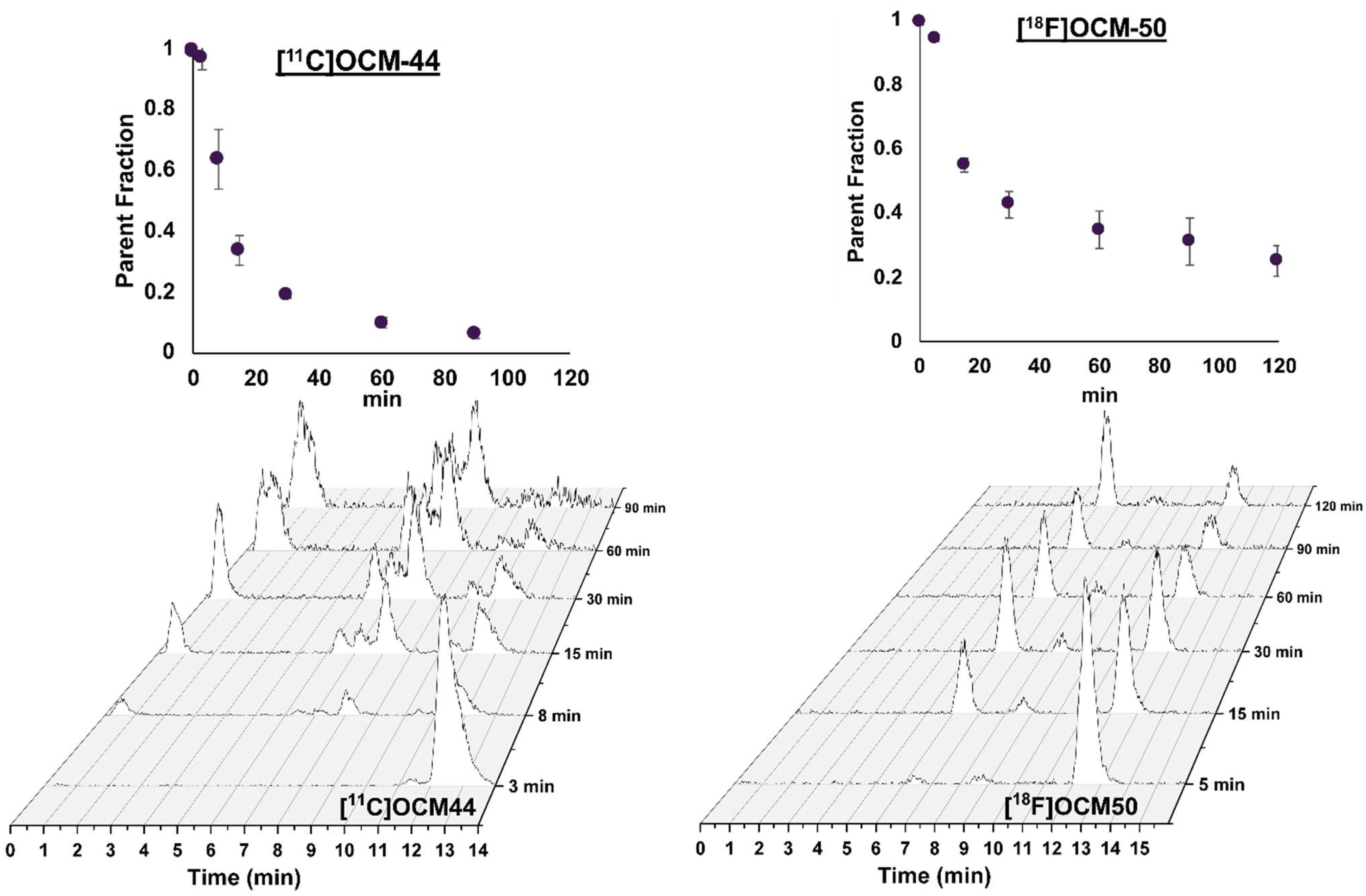
2.2. Blood Measurements
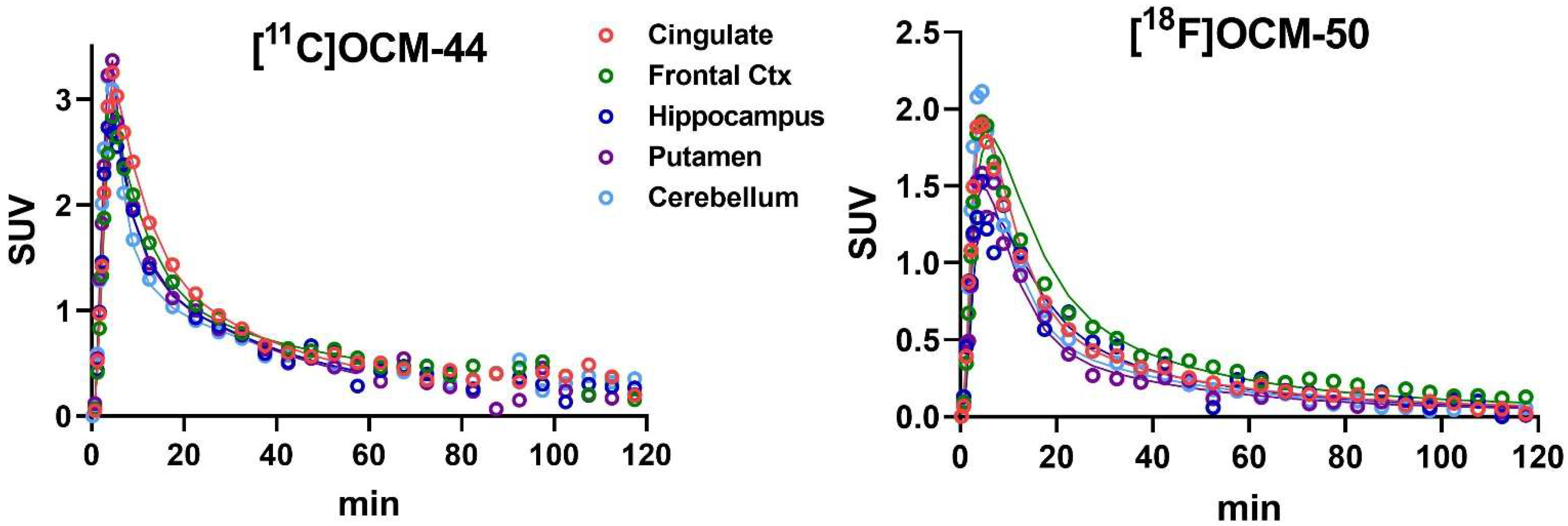
2.3. Brain Distribution and Kinetics
2.4. Kinetic Modeling
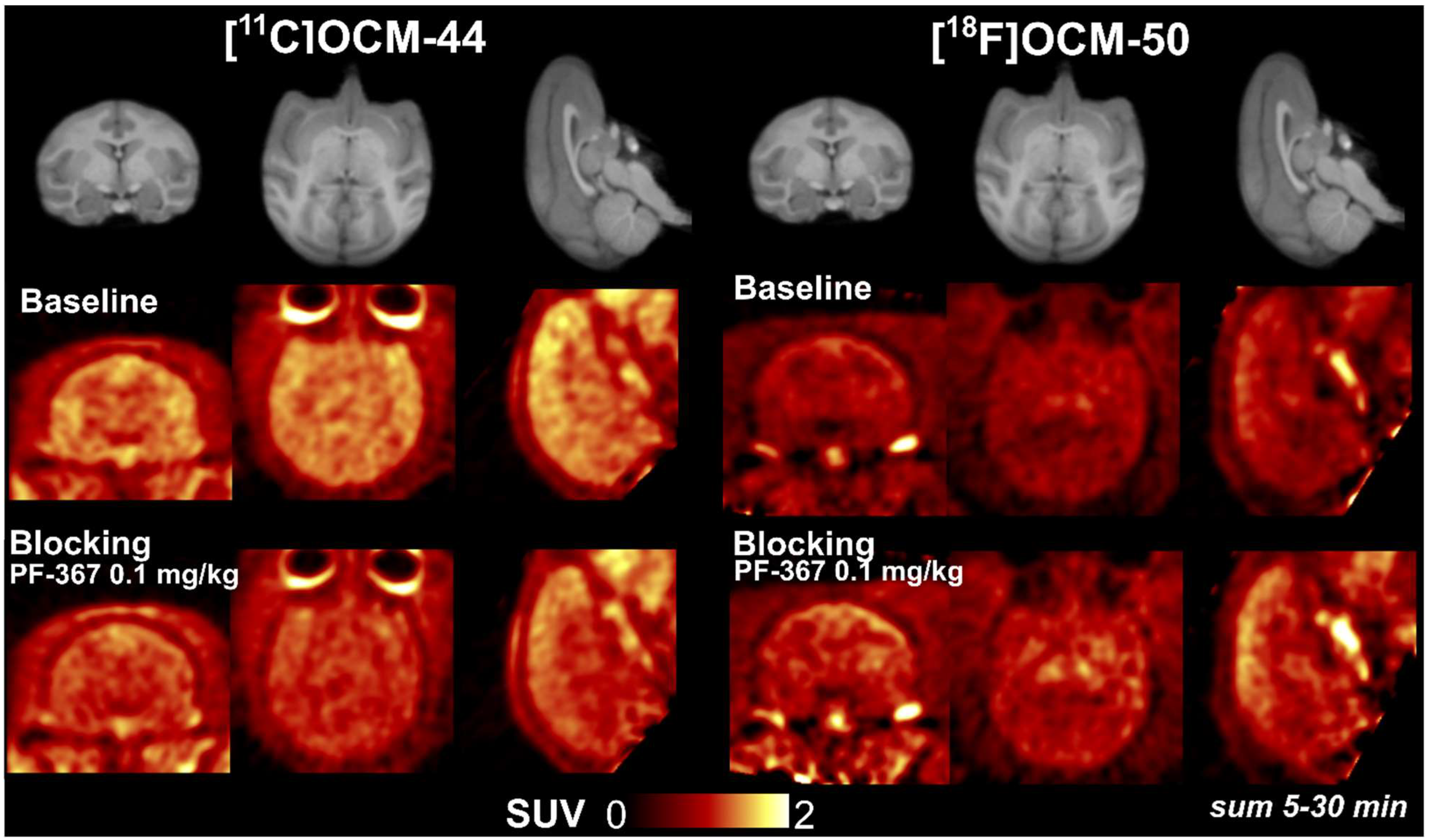
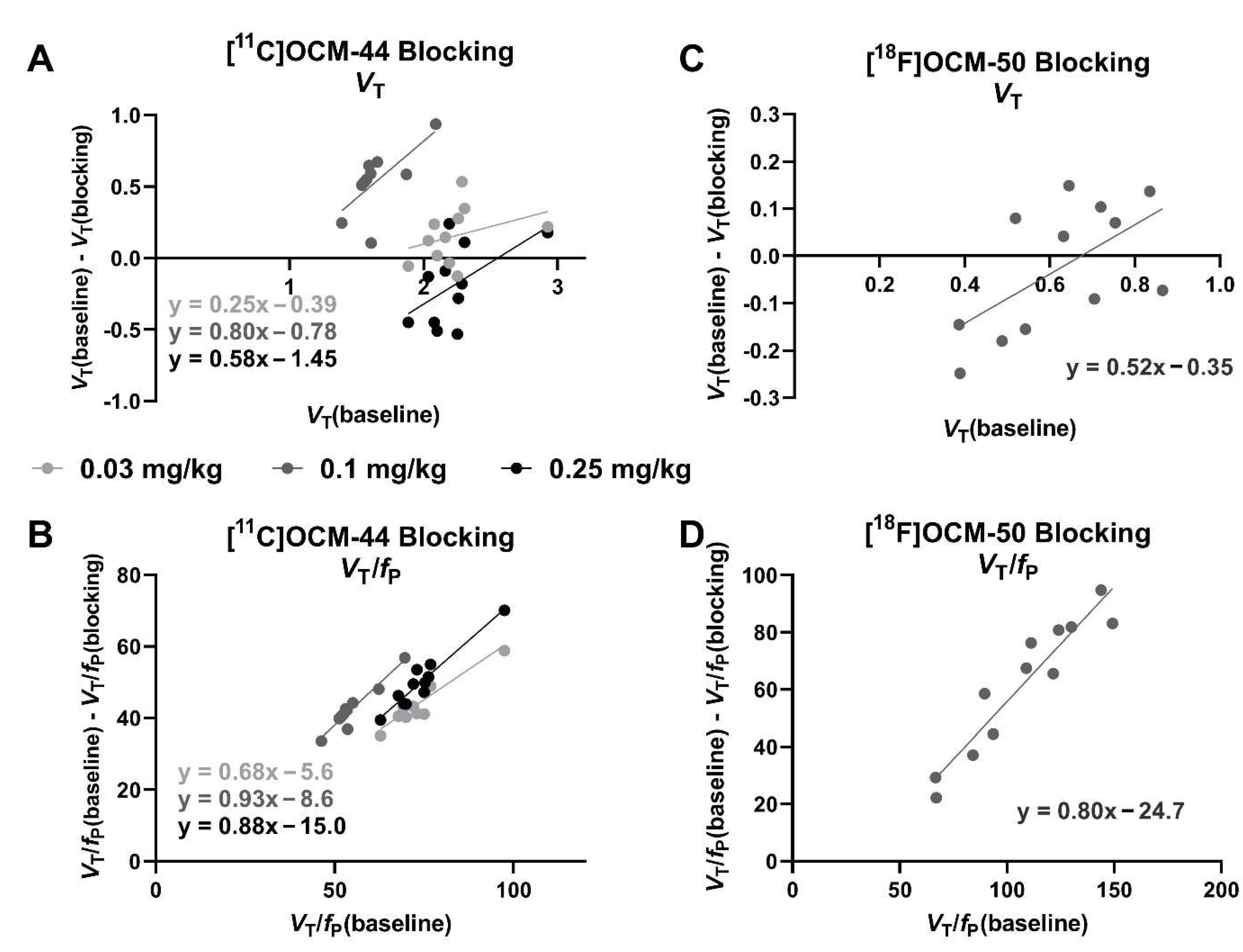
2.5. Blocking Studies
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Radiochemistry
4.3. PET Imaging
4.4. Plasma Radiometabolite Analysis and Input Function Measurement
4.5. Image Processing
4.6. Kinetic Modeling and Blocking Study Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beurel, E.; Grieco, S.F.; Jope, R.S. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): Regulation, actions, and diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 148, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworski, T.; Banach-Kasper, E.; Gralec, K. GSK-3β at the Intersection of Neuronal Plasticity and Neurodegeneration. Neural Plast. 2019, 2019, 4209475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, O.; Nolan, Y. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 as a therapeutic target for cognitive dysfunction in neuropsychiatric disorders. CNS Drugs 2015, 29, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manduca, J.D.; Theriault, R.K.; Perreault, M.L. Glycogen synthase kinase-3: The missing link to aberrant circuit function in disorders of cognitive dysfunction? Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 157, 104819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, C.; Killick, R.; Lovestone, S. The GSK3 hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2008, 104, 1433–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippin, I.; Eldar-Finkelman, H. Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications of GSK-3 in Treating Neurodegeneration. Cells 2021, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Ayton, S.; Bush, A.I.; Adlard, P.A. GSK-3 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 2011, 189246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciniegas Ruiz, S.M.; Eldar-Finkelman, H. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Inhibitors: Preclinical and Clinical Focus on CNS-A Decade Onward. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 792364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, P.; Wisniewski, J.; Wojtowicz, T.; Wójcicka, O.; Jaśkiewicz, M.; Drulis-Fajdasz, D.; Rakus, D.; McCubrey, J.A.; Gizak, A. Targeting GSK3 signaling as a potential therapy of neurodegenerative diseases and aging. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.K.; DeGrado, T.R. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK-3)-Targeted Therapy and Imaging. Theranostics 2016, 6, 571–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasdev, N.; Garcia, A.; Stableford, W.T.; Young, A.B.; Meyer, J.H.; Houle, S.; Wilson, A.A. Synthesis and ex vivo evaluation of carbon-11 labelled N-(4-methoxybenzyl)-N′-(5-nitro-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)urea ([11C]AR-A014418): A radiolabelled glycogen synthase kinase-3β specific inhibitor for PET studies. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 5270–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Patnaik, D.; Collier, T.L.; Lee, K.N.; Gao, H.; Swoyer, M.R.; Rotstein, B.H.; Krishnan, H.S.; Liang, S.H.; Wang, J.; et al. Development of [18F]Maleimide-Based Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β Ligands for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.H.; Chen, J.M.; Normandin, M.D.; Chang, J.S.; Chang, G.C.; Taylor, C.K.; Trapa, P.; Plummer, M.S.; Para, K.S.; Conn, E.L.; et al. Discovery of a Highly Selective Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Inhibitor (PF-04802367) That Modulates Tau Phosphorylation in the Brain: Translation for PET Neuroimaging. Angew. Chem. 2016, 55, 9601–9605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, J.; Zanderigo, F.; Sai, K.K.S.; Rubin-Falkone, H.; Jorgensen, M.J.; Kaplan, J.R.; Mintz, A.; Mann, J.J.; Kumar, M.J. Radiosynthesis and in Vivo Evaluation of [11C]A1070722, a High Affinity GSK-3 PET Tracer in Primate Brain. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2017, 8, 1697–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shao, X.; Cole, E.L.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Ferrari, V.; Hong, Y.T.; Williamson, D.J.; Fryer, T.D.; Quesada, C.A.; Sherman, P.; et al. Synthesis and Initial in Vivo Studies with [11C]SB-216763: The First Radiolabeled Brain Penetrative Inhibitor of GSK-3. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yang, S.; Cui, J.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Feng, P.; Huang, S.; Li, H.; et al. Novel 18F-Labeled Isonicotinamide-Based Radioligands for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, J.; Sai, K.K.S.; Sattiraju, A.; Mintz, A.; Mann, J.J.; Kumar, J.S.D. Radiosynthesis and evaluation of [11C]CMP, a high affinity GSK3 ligand. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 778–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard-Gauthier, V.; Mossine, A.V.; Knight, A.; Patnaik, D.; Zhao, W.-N.; Cheng, C.; Krishnan, H.S.; Xuan, L.L.; Chindavong, P.S.; Reis, S.A.; et al. Structural Basis for Achieving GSK-3beta Inhibition with High Potency, Selectivity, and Brain Exposure for Positron Emission Tomography Imaging and Drug Discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 9600–9617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlow, C.; Mossine, A.V.; Bernard-Gauthier, V.; Scott, P.J.H.; Vasdev, N. Radiofluorination of oxazole-carboxamides for preclinical PET neuroimaging of GSK-3. J. Fluor. Chem. 2021, 245, 109760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, A.C.; Varlow, C.; Tong, J.; Vasdev, N. In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of GSK-3 Radioligands in Alzheimer’s Disease: Preliminary Evidence of Sex Differences. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2021, 4, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giglio, J.; Fernandez, S.; Martinez, A.; Zeni, M.; Reyes, L.; Rey, A.; Cerecetto, H. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Maleimide Inhibitors As Potential PET-Tracers for Imaging Alzheimer’s Disease: 11C-Synthesis and In Vivo Proof of Concept. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.N.; Dwivedi, Y.; Rizavi, H.S.; Teppen, T.; Gaszner, G.L.; Roberts, R.C.; Conley, R.R. GSK-3β gene expression in human postmortem brain: Regional distribution, effects of age and suicide. Neurochem. Res. 2009, 34, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, A.J.; Narvaez, A.; Chasse, M.; Vasdev, N. PET imaging of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in pancreatic cancer xenograft mouse models. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2022, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nabulsi, N.; Huang, Y.; Weinzimmer, D.; Ropchan, J.; Frost, J.J.; McCarthy, T.; Carson, R.E.; Ding, Y.-S. High-resolution imaging of brain 5-HT1B receptors in the rhesus monkey using [11C]P943. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2010, 37, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilton, J.; Yokoi, F.; Dannals, R.F.; Ravert, H.T.; Szabo, Z.; Wong, D.F. Column-switching HPLC for the analysis of plasma in PET imaging studies. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2000, 27, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Owen, D.R.; Rabiner, E.A.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Gunn, R.N. A graphical method to compare the in vivo binding potential of PET radioligands in the absence of a reference region: Application to [11C]PBR28 and [18F]PBR111 for TSPO imaging. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2014, 34, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| [11C]OCM-44 | [18F]OCM-50 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline n = 2 | Blocking n = 3 | Baseline n = 2 | Blocking n = 2 | |
| Drug (dose) | n/a | PF-367 (0.03, 0.1, or 0.25 mg/kg) | n/a | PF-367 (0.1 mg/kg) |
| Injected dose (MBq) | 180, 174 | 177 ± 2.3 | 163, 171 | 155, 167 |
| Injected mass (ng/kg) | 29.6, 44.7 | 51.9 ± 28 | 5.1, 6.1 | 4.2, 14.3 |
| [11C]OCM-44 VT (mL/cm3) | [18F]OCM-50 VT (mL/cm3) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Blocking (PF-367) | Baseline | Blocking (PF-367) | |||||
| Animal 1 | Animal 2 | 0.03 mg/kg (Animal 1) | 0.1 mg/kg (Animal 2) | 0.25 mg/kg (Animal 1) | Animal 3 | 0.1 mg/kg (Animal 3) | 0.1 mg/kg (Animal 4) | |
| Frontal cortex | 2.60 | 2.09 | 2.34 | 1.15 | 4.43 | 0.87 | 0.94 | 0.96 |
| Temporal cortex | 2.10 | 1.68 | 2.08 | 7.33 | 2.61 | 0.72 | 0.44 | 0.62 |
| Occipital cortex | 2.26 | 1.57 | 1.98 | 1.02 | 2.54 | 0.84 | 0.70 | 0.79 |
| Cingulate | 2.92 | 1.87 | 2.71 | 1.29 | 2.74 | 0.71 | 0.80 | 1.01 |
| Insula | 2.25 | 1.65 | 2.38 | 0.98 | 2.78 | 0.39 | 0.53 | 0.68 |
| Caudate | 2.31 | 1.54 | 1.96 | 1.03 | 2.19 | 0.39 | 0.64 | 0.76 |
| Putamen | 2.16 | 1.61 | 2.01 | 1.01 | 2.25 | 0.54 | 0.70 | 0.84 |
| Pallidum | 2.19 | 1.39 | 2.23 | 1.14 | 1.95 | 0.49 | 0.67 | 0.78 |
| Hippocampus | 2.29 | 1.61 | 1.75 | 1.50 | 2.47 | 0.65 | 0.50 | 0.58 |
| Amygdala | 1.87 | 1.71 | 1.71 | n.d. | 3.40 | 0.45 | 0.19 | 0.37 |
| Thalamus | 2.03 | 1.56 | 1.91 | 1.03 | 2.16 | 0.52 | 0.44 | 0.71 |
| Pons | 1.88 | 1.48 | 1.94 | 2.31 | 2.34 | 0.75 | 0.68 | 0.76 |
| Cerebellum | 2.08 | 1.59 | 1.84 | 0.94 | 2.53 | 0.63 | 0.59 | 0.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smart, K.; Zheng, M.-Q.; Holden, D.; Felchner, Z.; Zhang, L.; Han, Y.; Ropchan, J.; Carson, R.E.; Vasdev, N.; Huang, Y. In Vivo Imaging and Kinetic Modeling of Novel Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Radiotracers [11C]OCM-44 and [18F]OCM-50 in Non-Human Primates. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020194
Smart K, Zheng M-Q, Holden D, Felchner Z, Zhang L, Han Y, Ropchan J, Carson RE, Vasdev N, Huang Y. In Vivo Imaging and Kinetic Modeling of Novel Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Radiotracers [11C]OCM-44 and [18F]OCM-50 in Non-Human Primates. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(2):194. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020194
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmart, Kelly, Ming-Qiang Zheng, Daniel Holden, Zachary Felchner, Li Zhang, Yanjiang Han, Jim Ropchan, Richard E. Carson, Neil Vasdev, and Yiyun Huang. 2023. "In Vivo Imaging and Kinetic Modeling of Novel Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Radiotracers [11C]OCM-44 and [18F]OCM-50 in Non-Human Primates" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 2: 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020194
APA StyleSmart, K., Zheng, M.-Q., Holden, D., Felchner, Z., Zhang, L., Han, Y., Ropchan, J., Carson, R. E., Vasdev, N., & Huang, Y. (2023). In Vivo Imaging and Kinetic Modeling of Novel Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Radiotracers [11C]OCM-44 and [18F]OCM-50 in Non-Human Primates. Pharmaceuticals, 16(2), 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020194





