A Review on Molecular Docking on HDAC Isoforms: Novel Tool for Designing Selective Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Introduction to HDACs
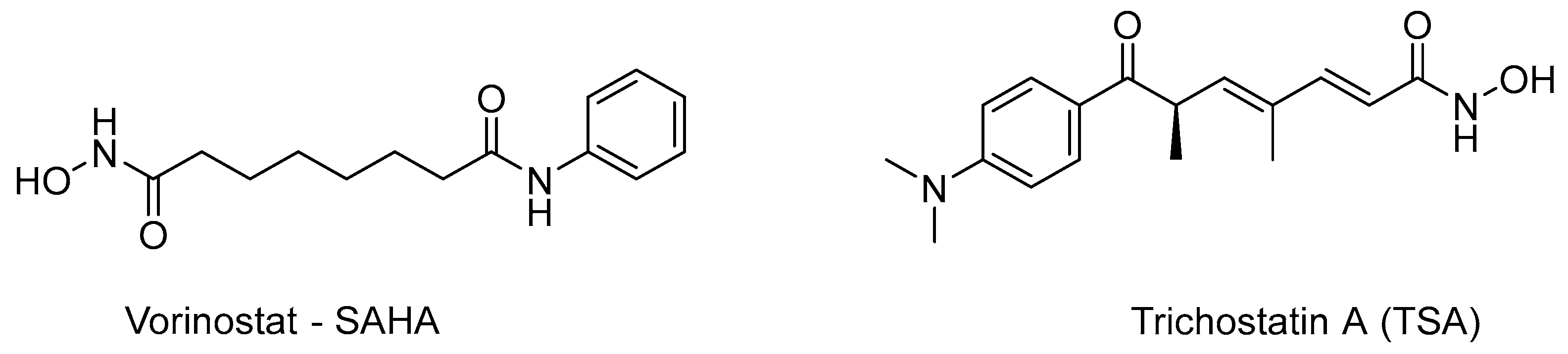
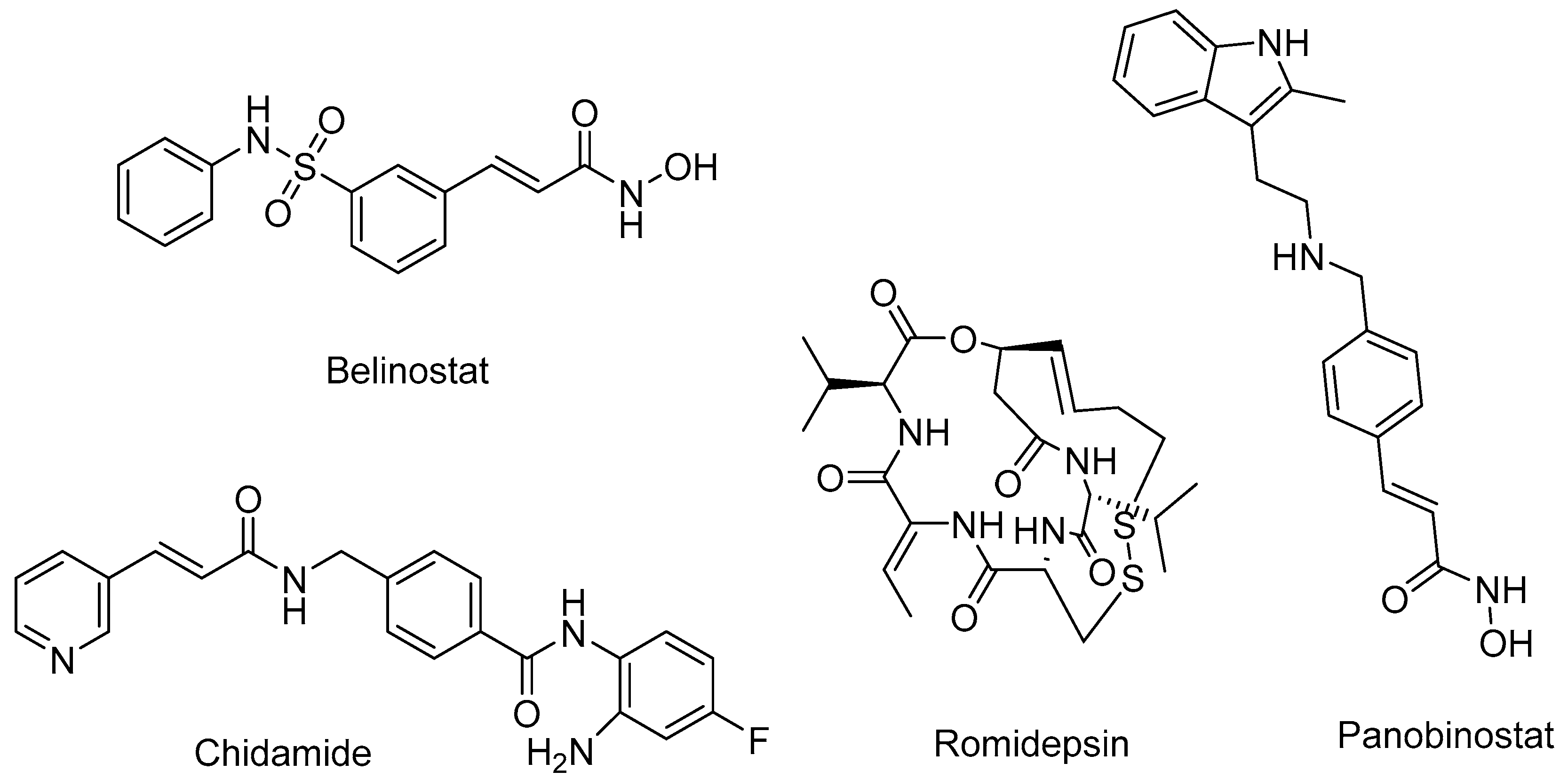
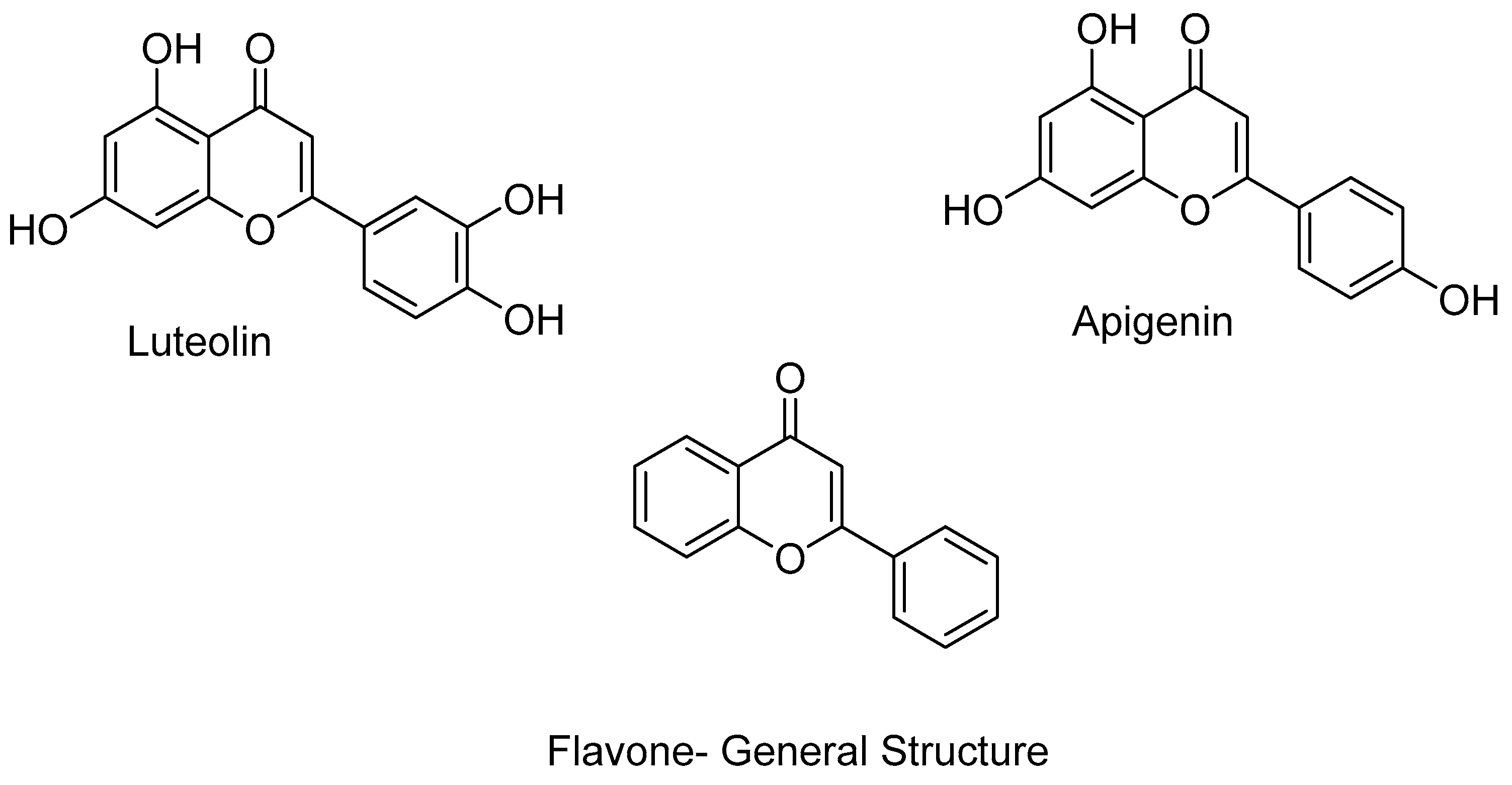
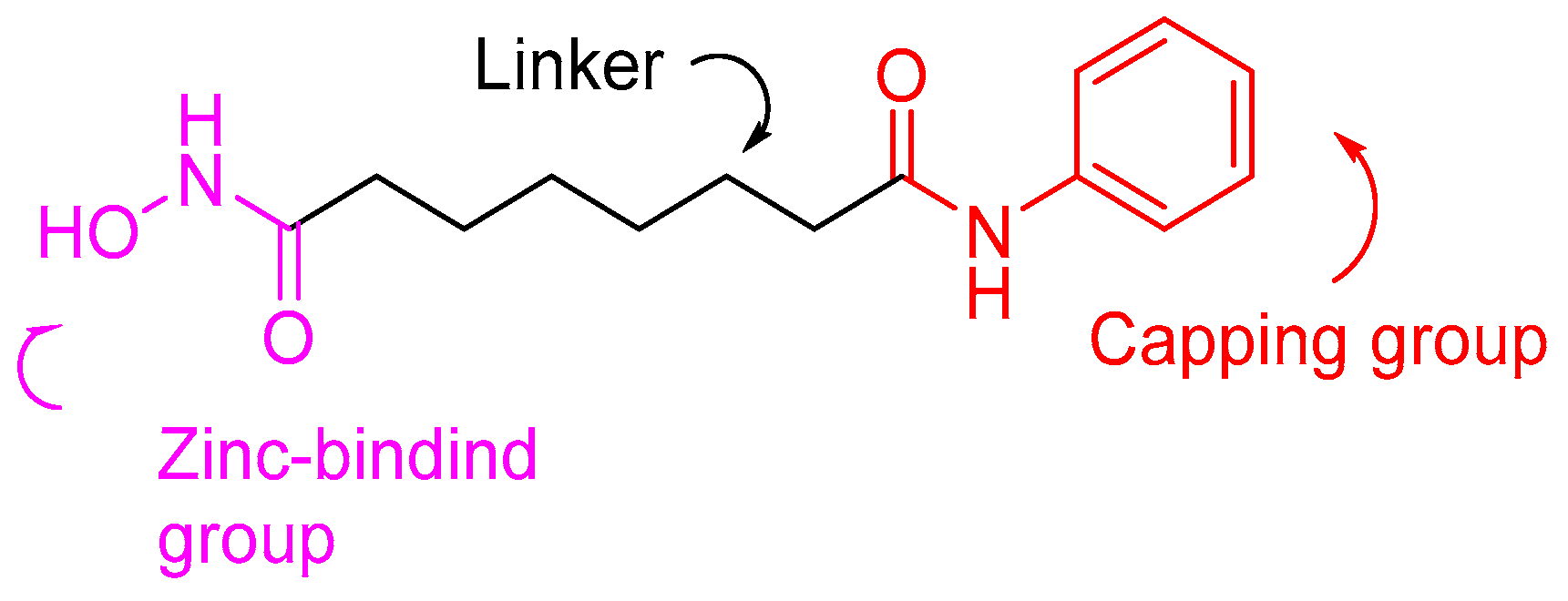
1.2. HDAC Inhibition and Inhibitors
2. Molecular Docking Studies on HDACs
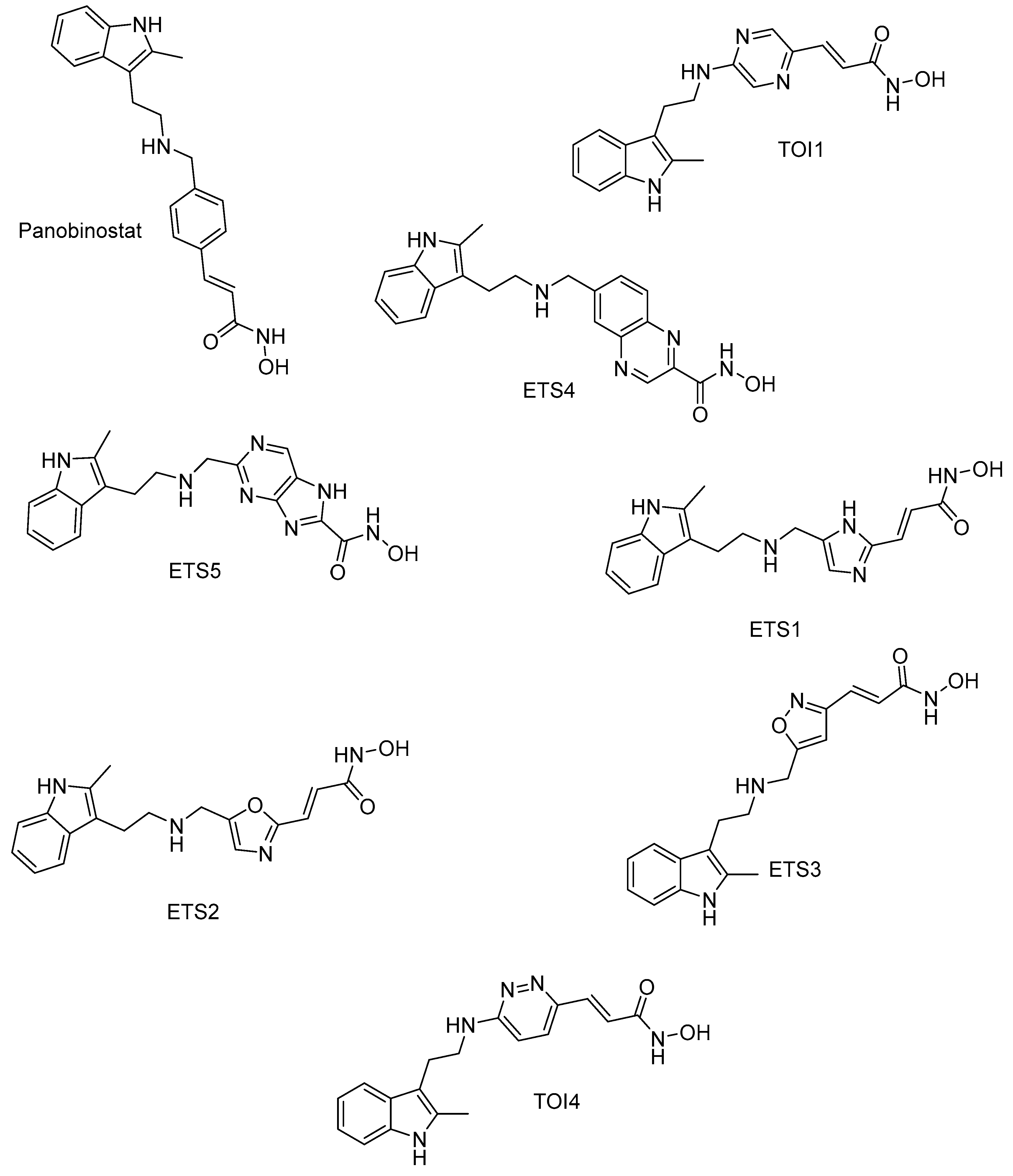
2.1. HDAC 1
2.2. HDAC 2
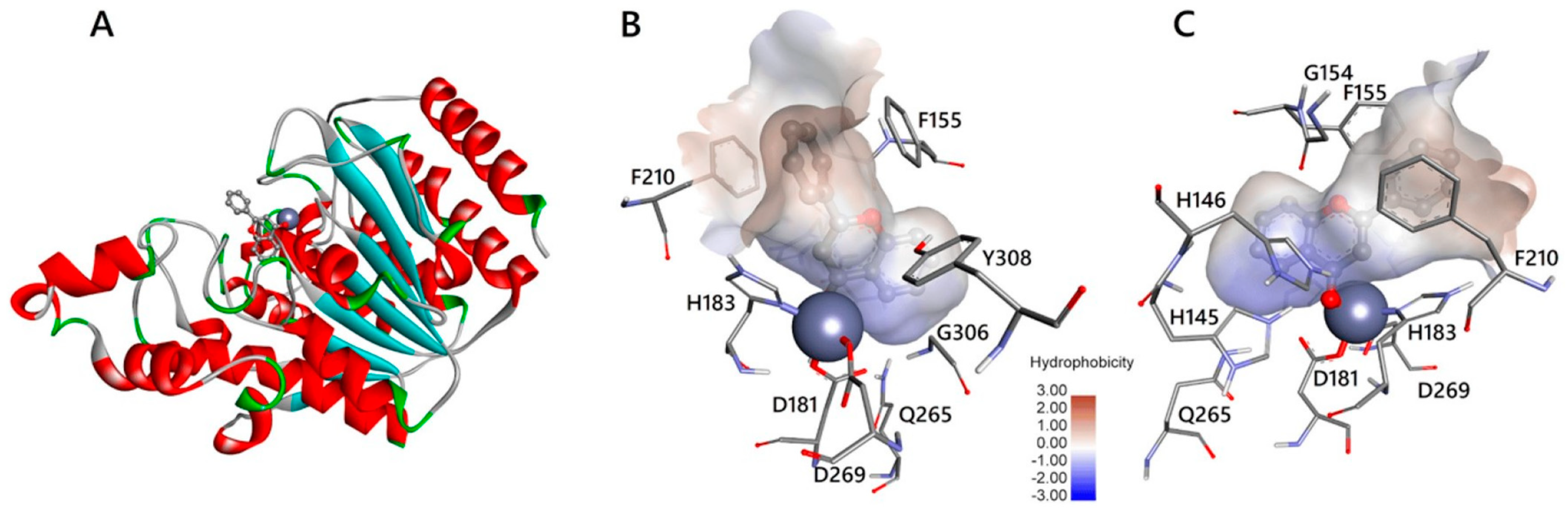
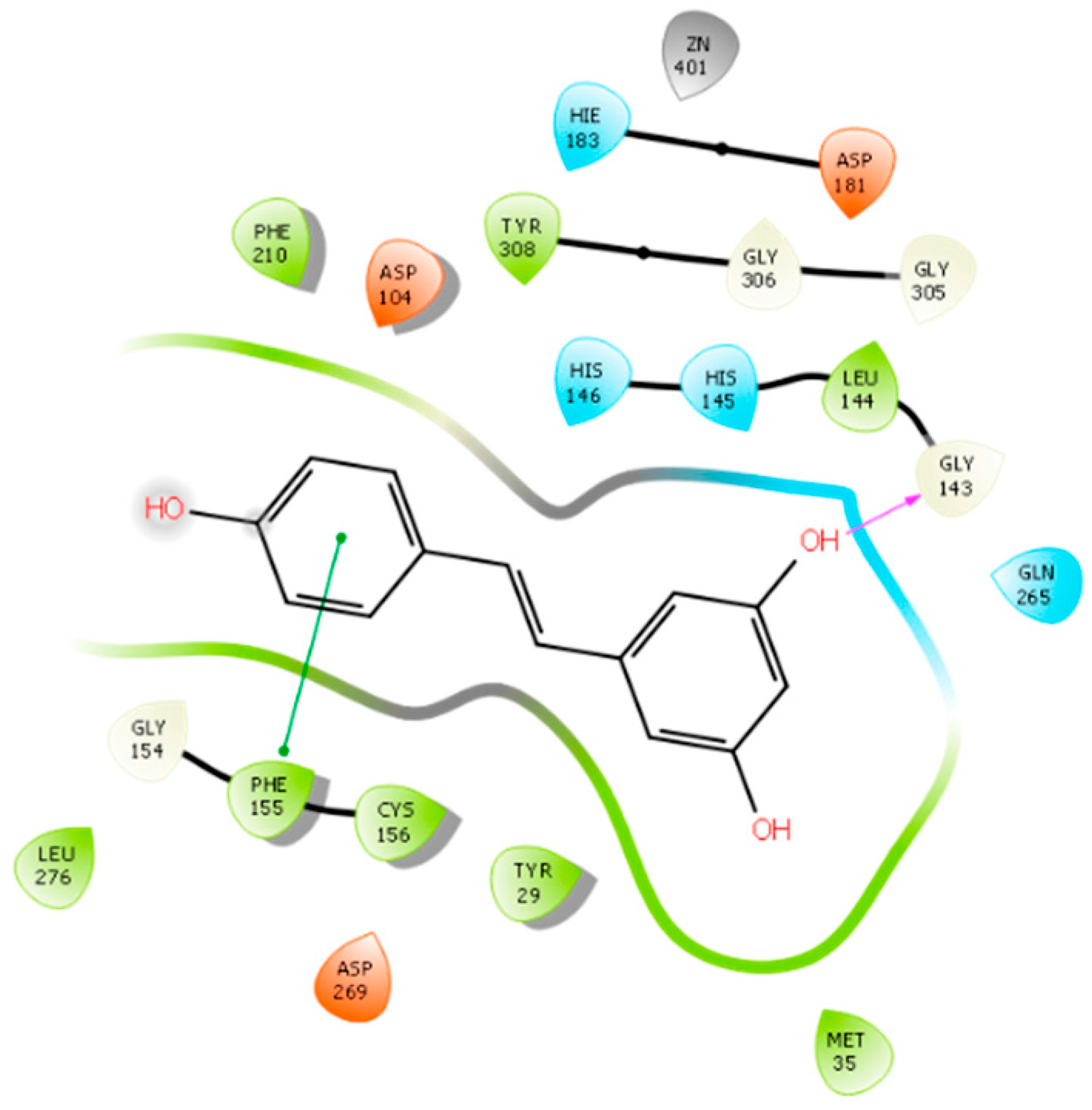
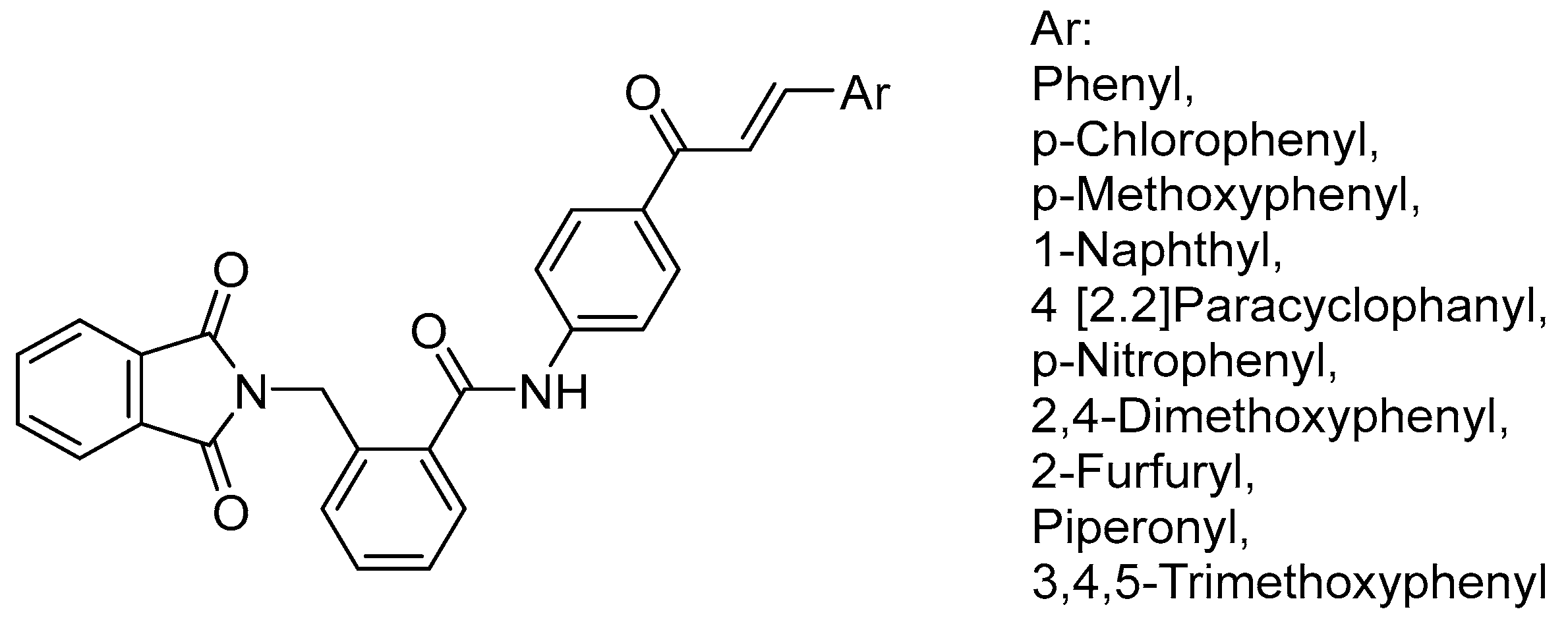
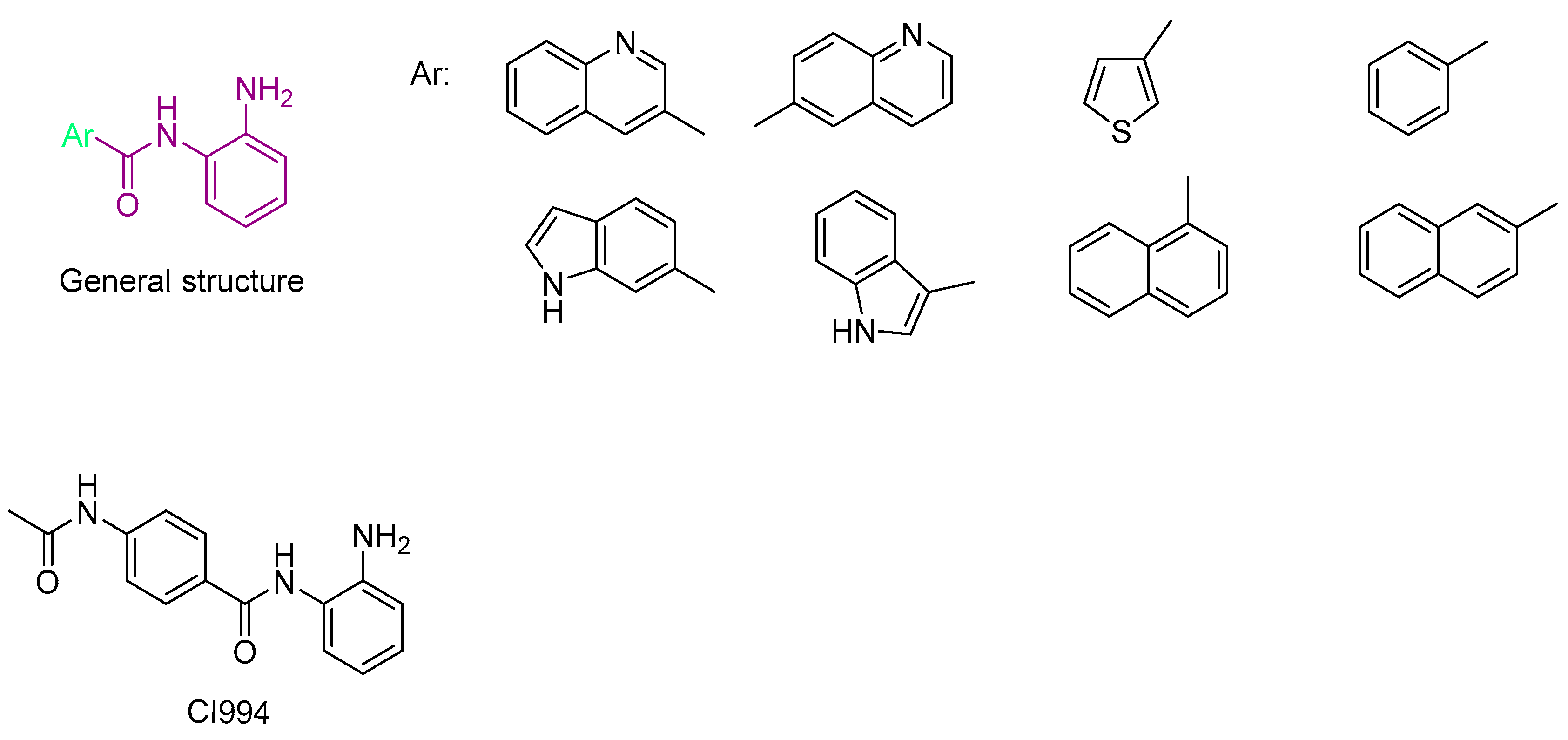
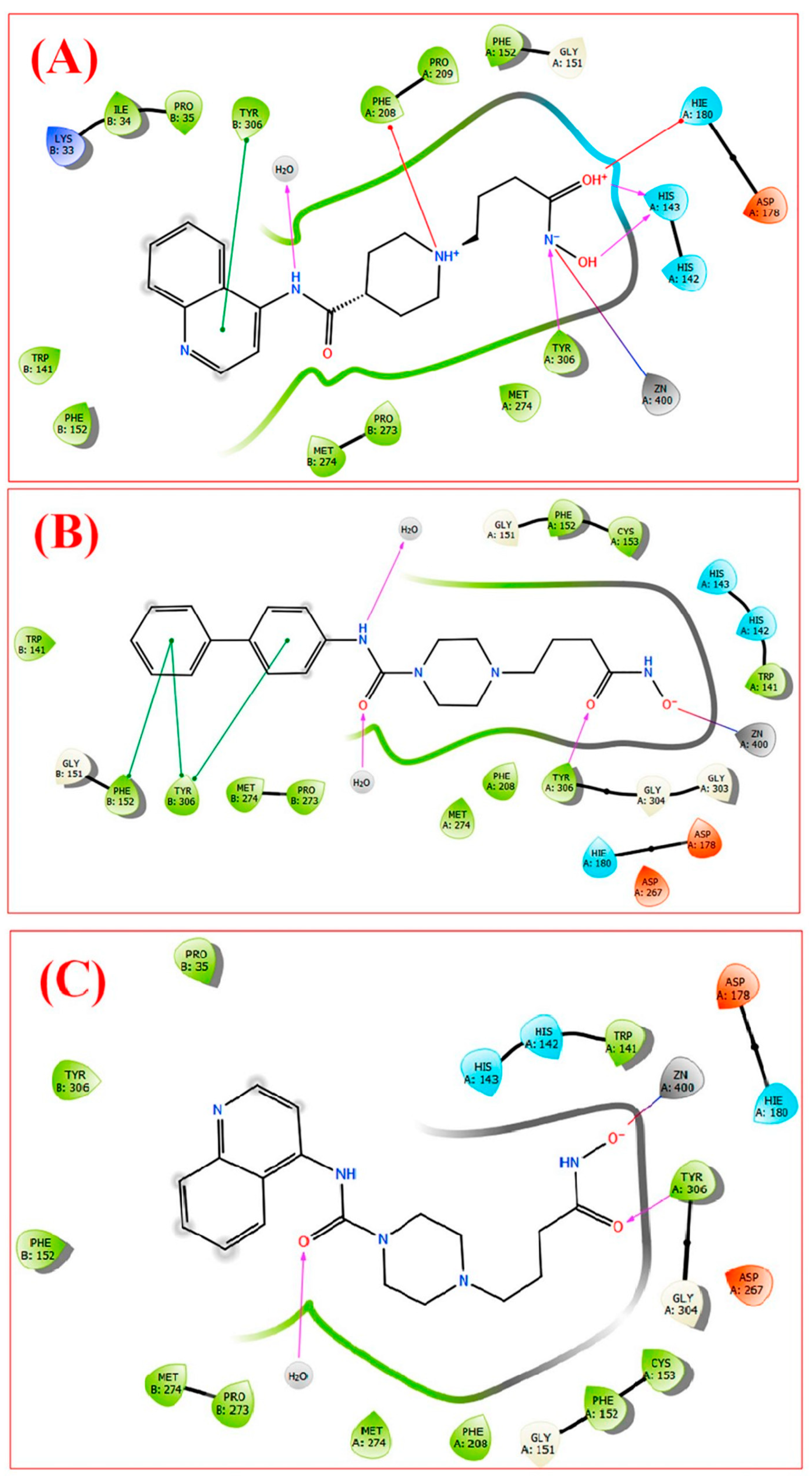
2.3. HDAC 3
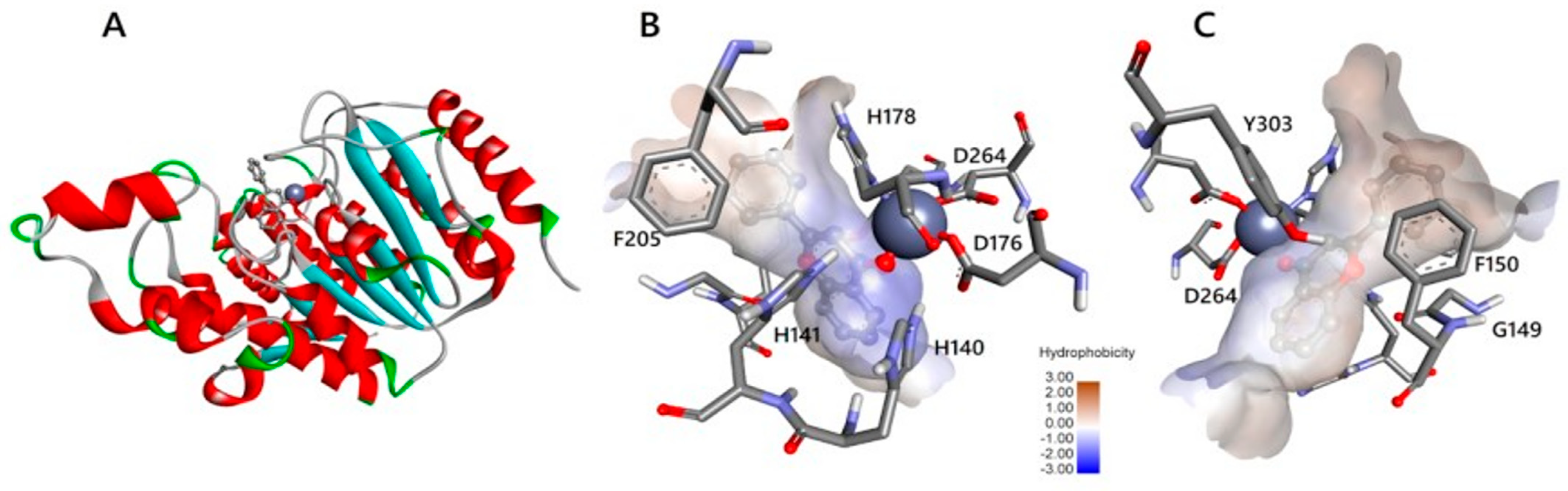
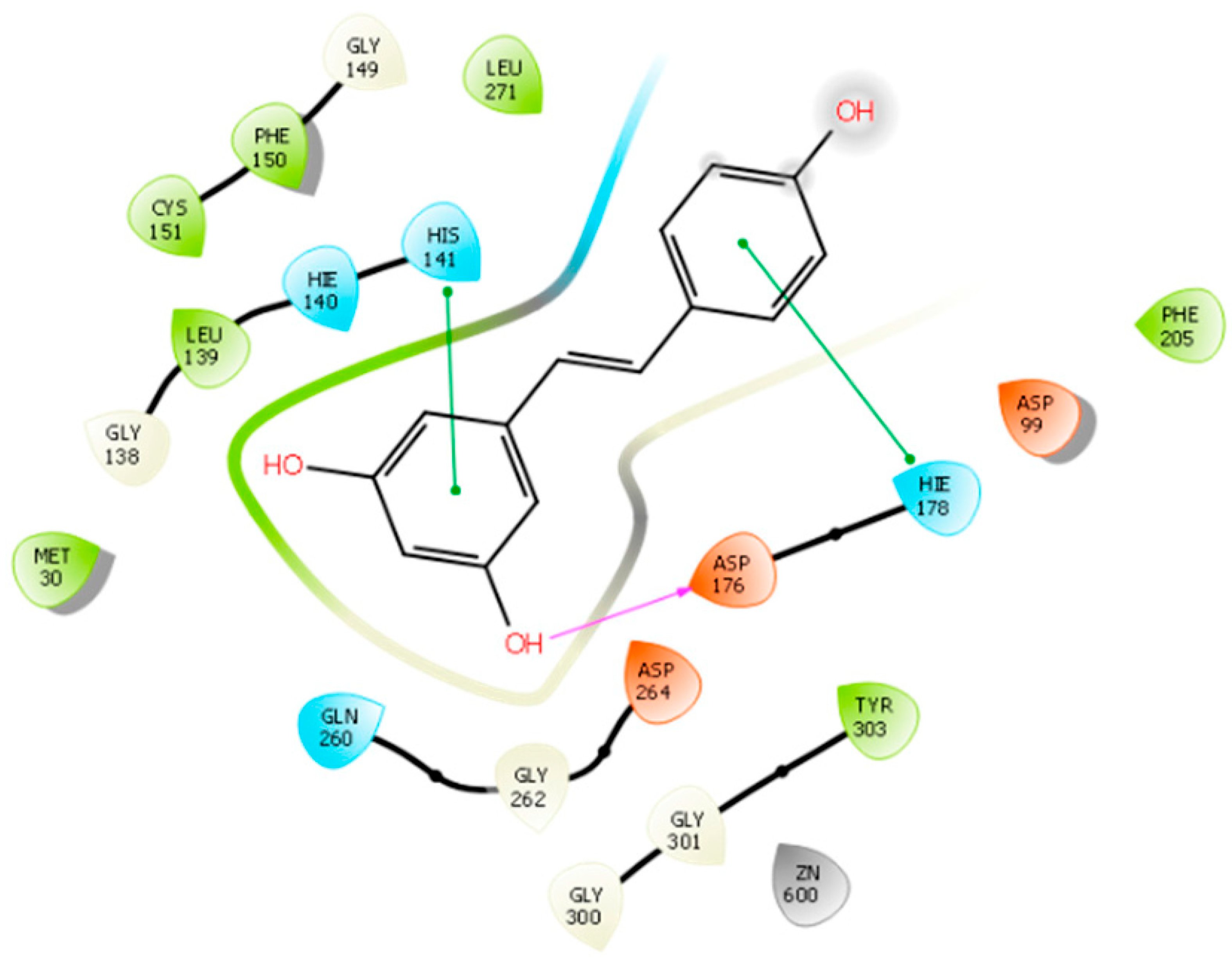
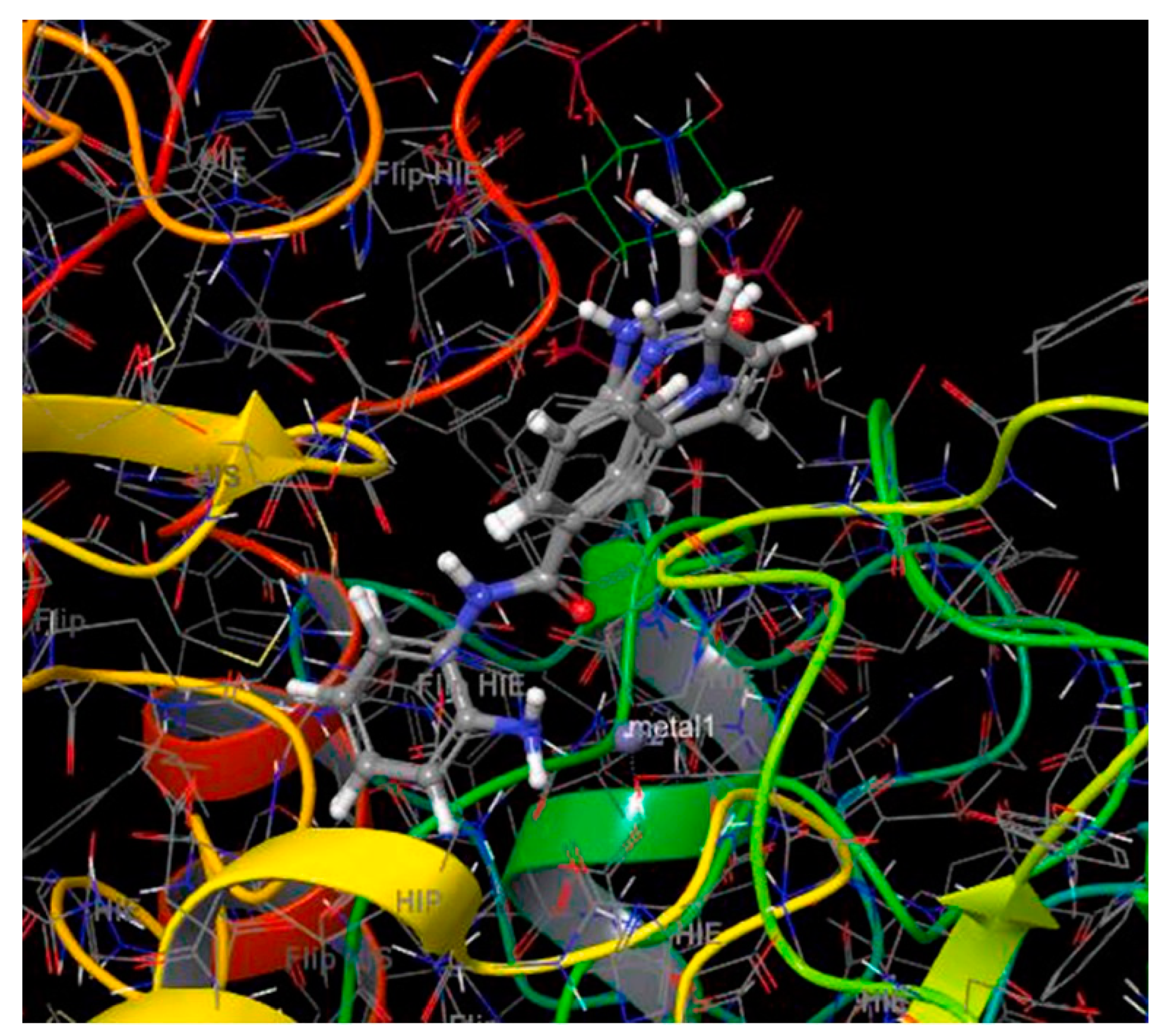
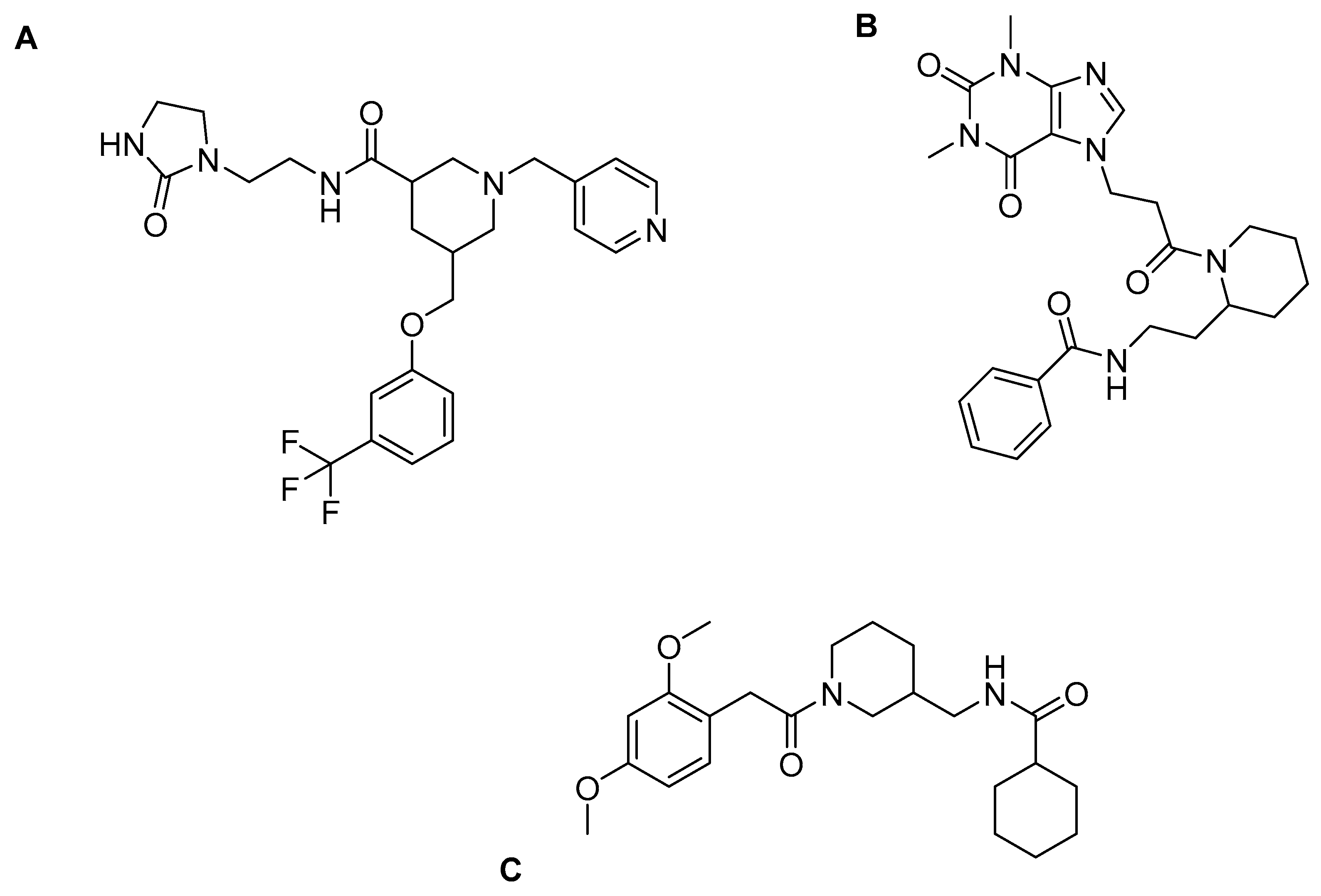
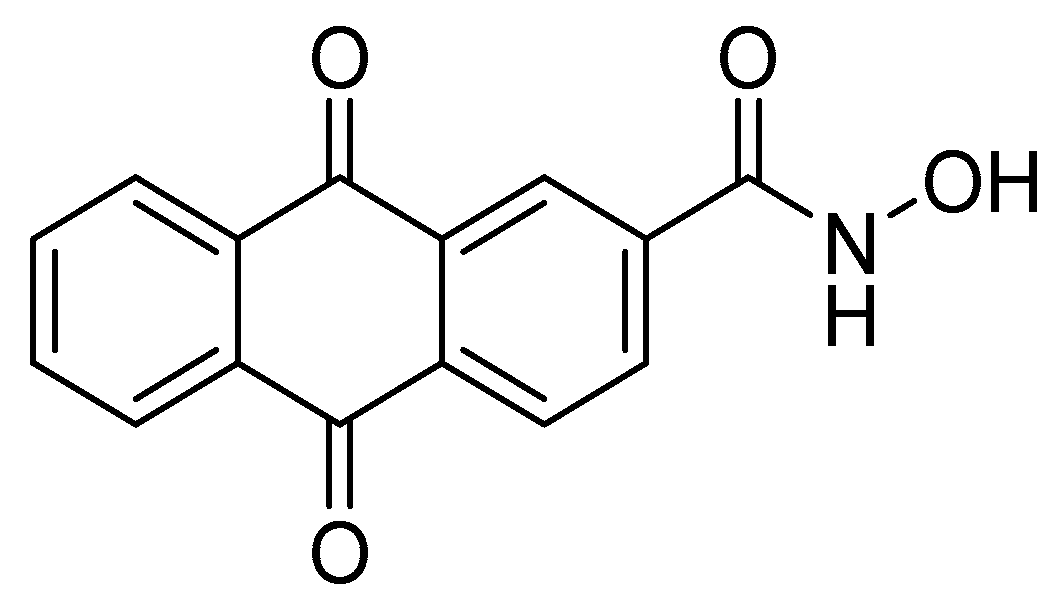
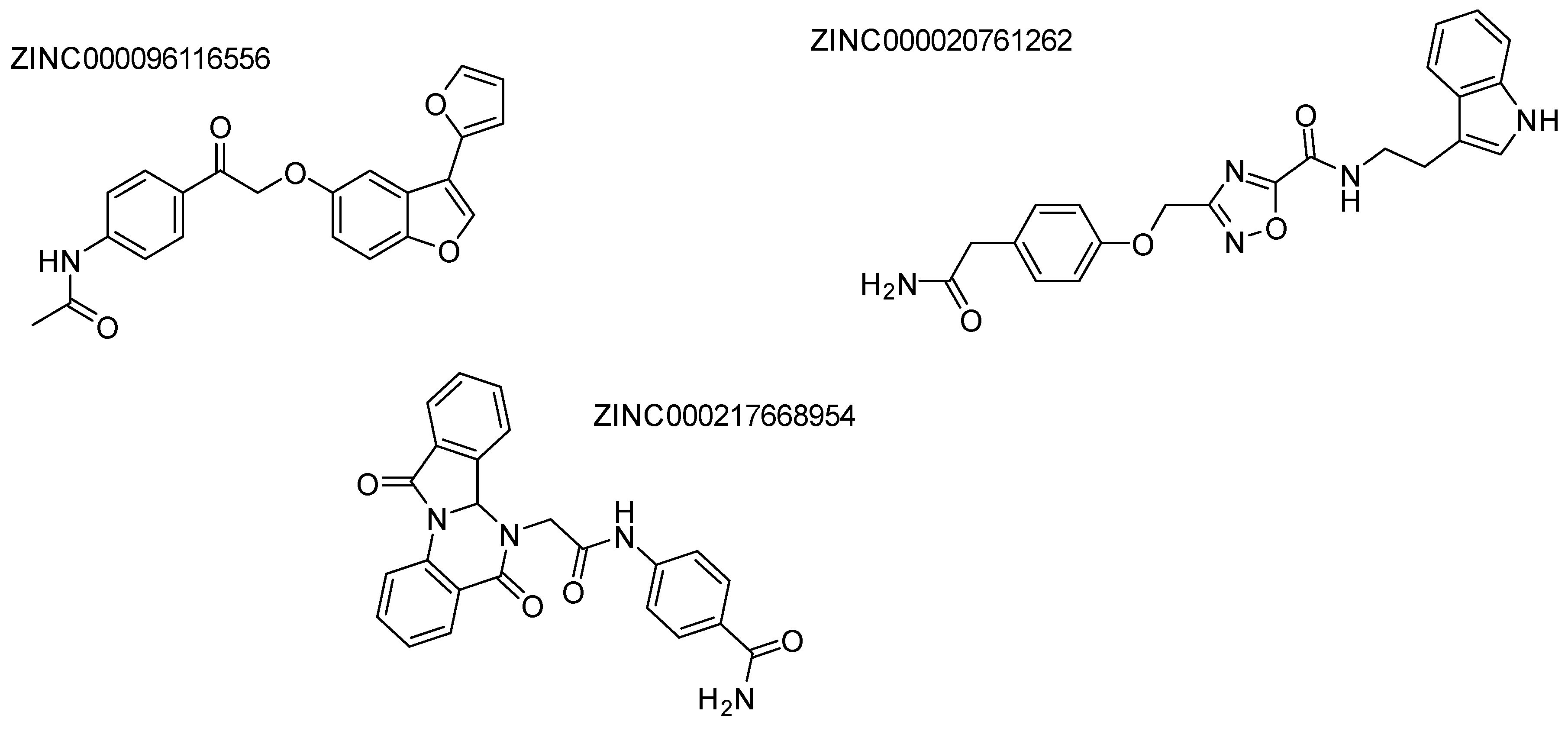
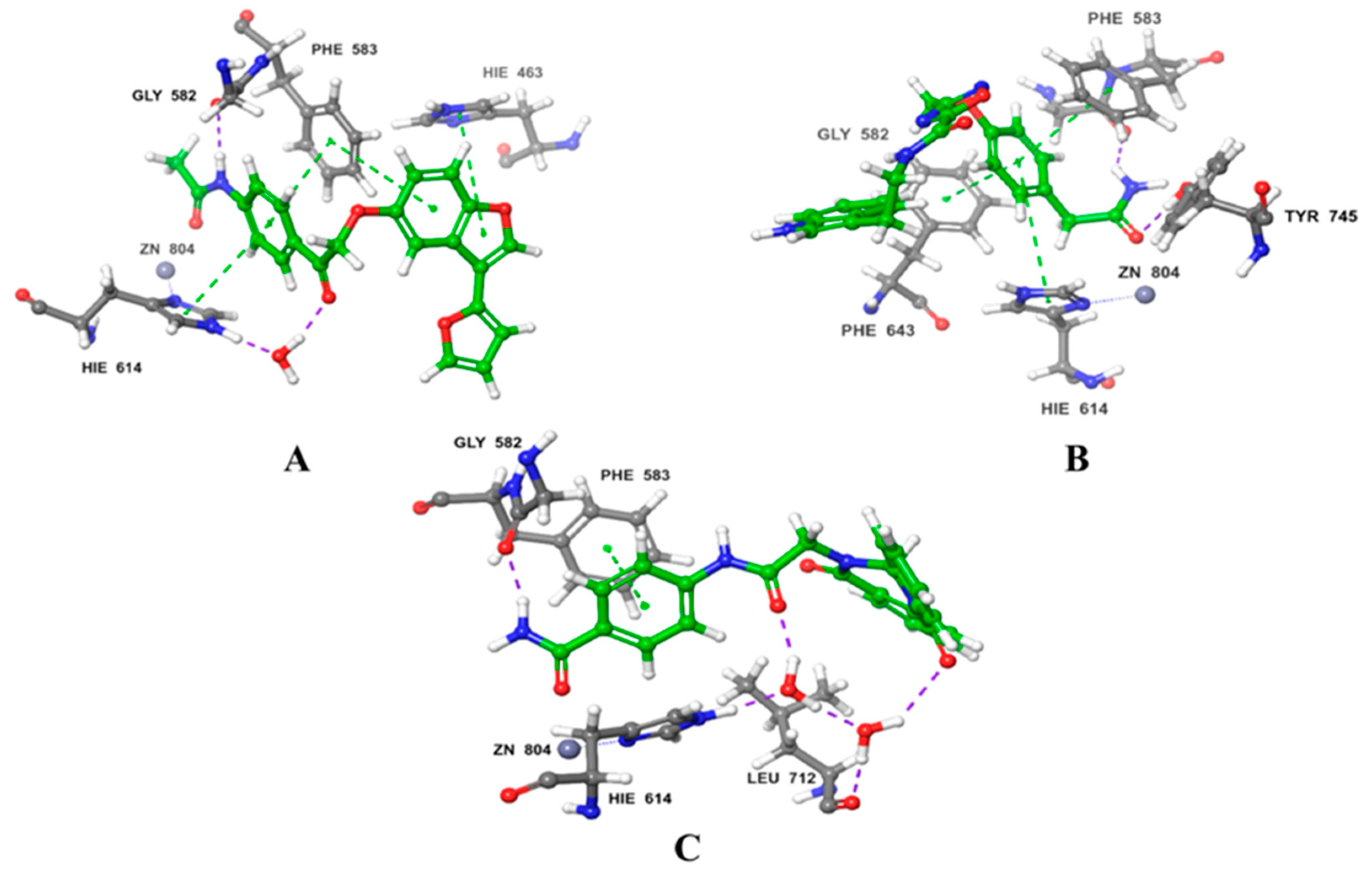
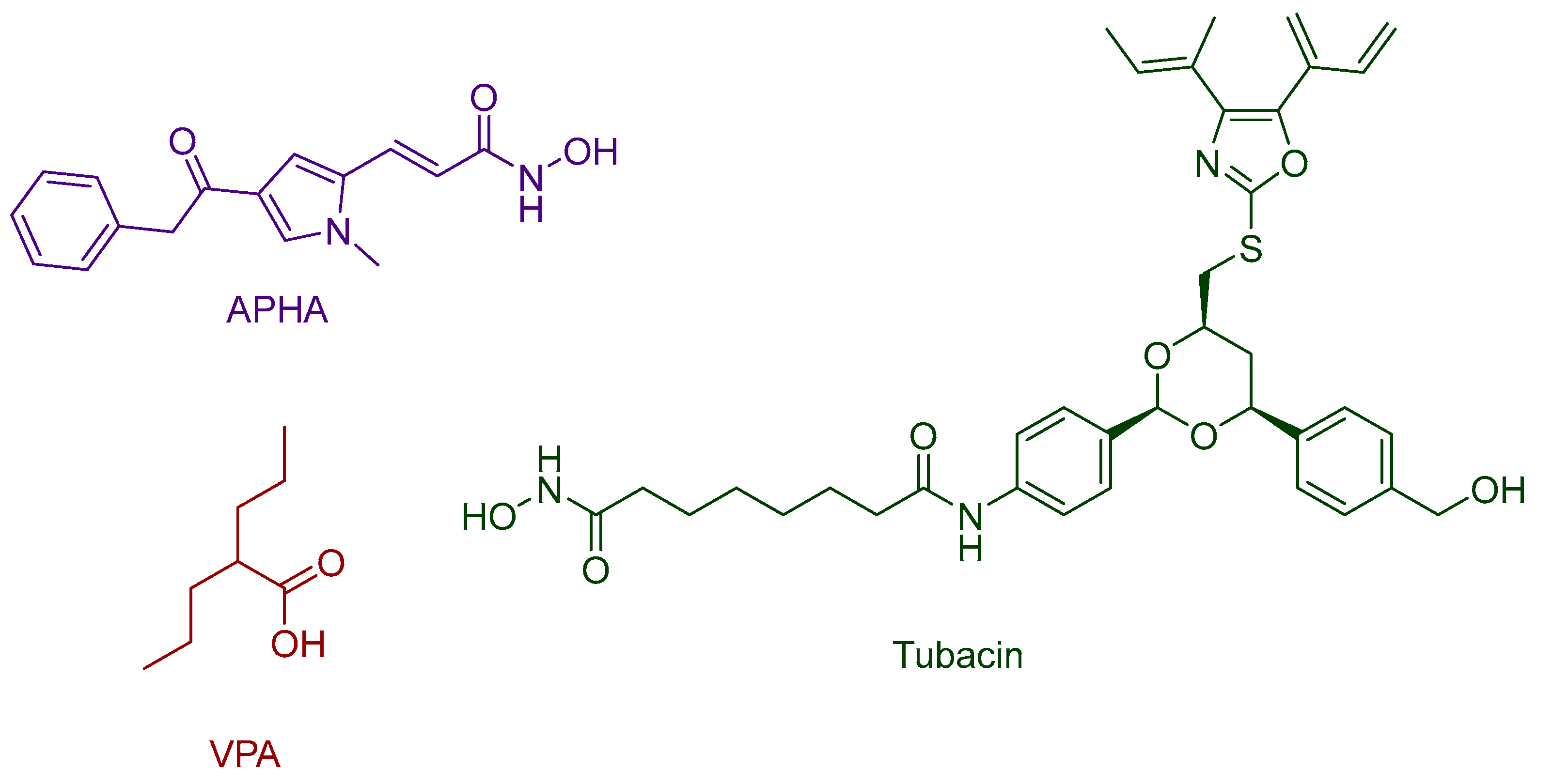
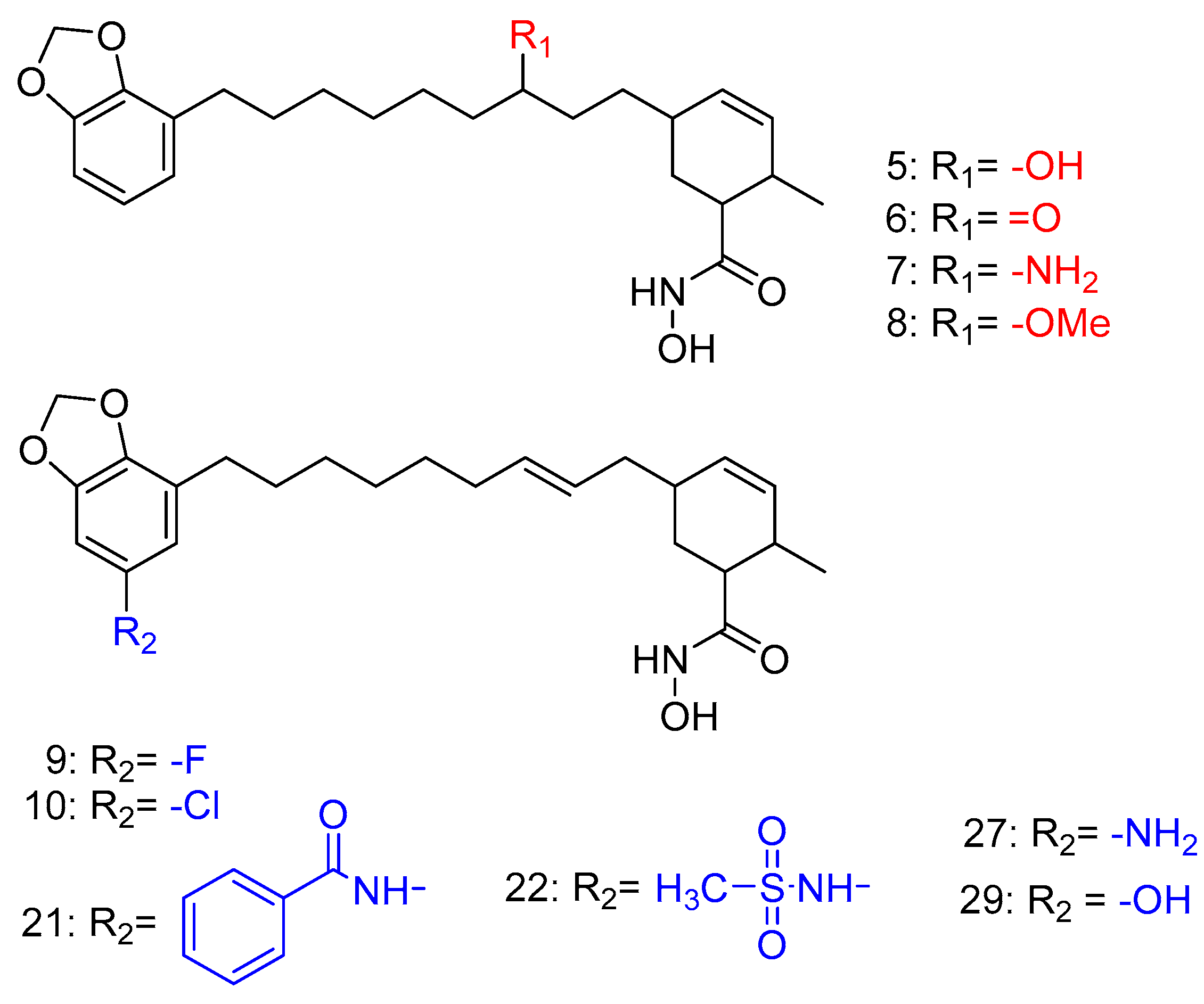
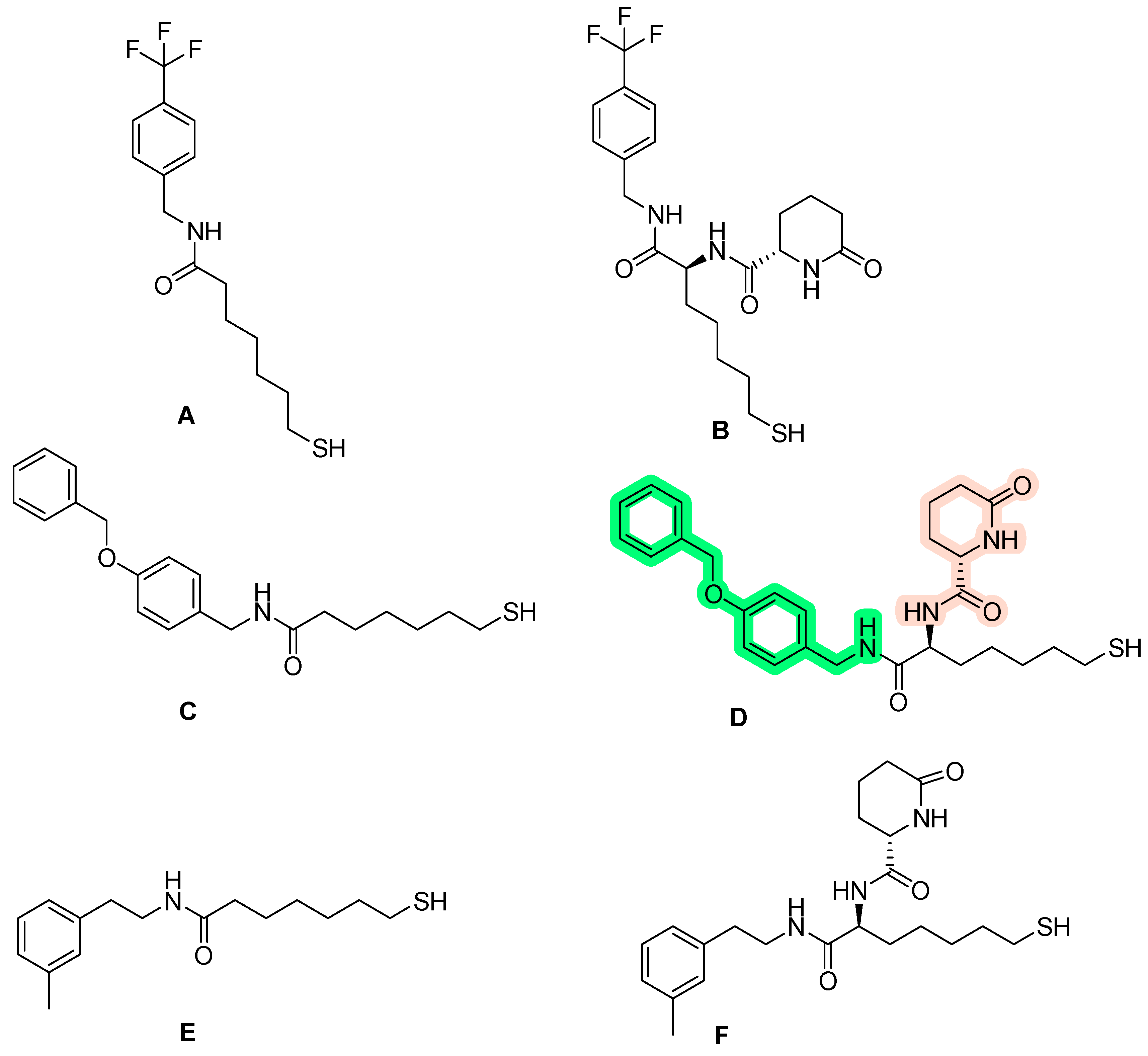
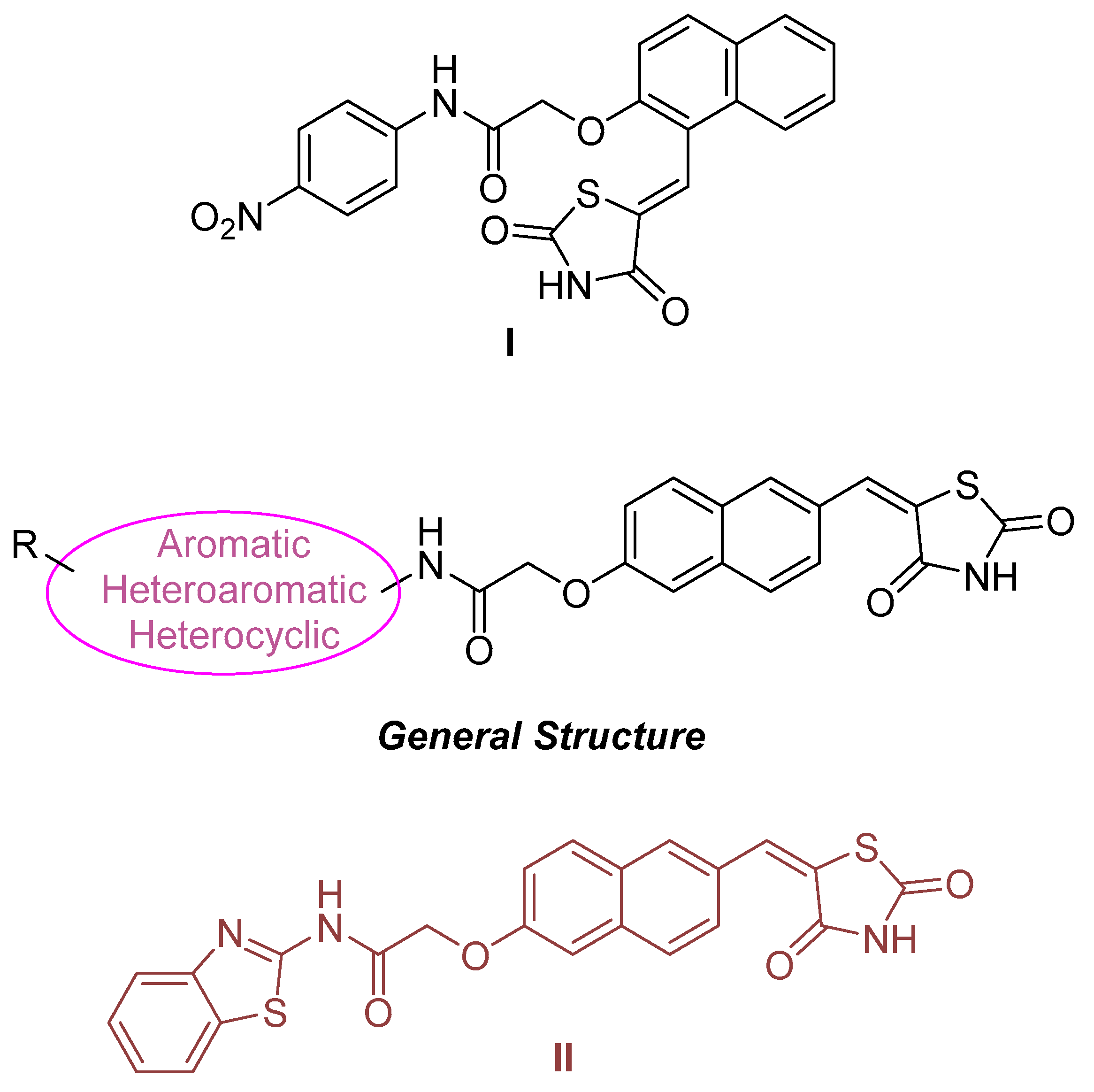
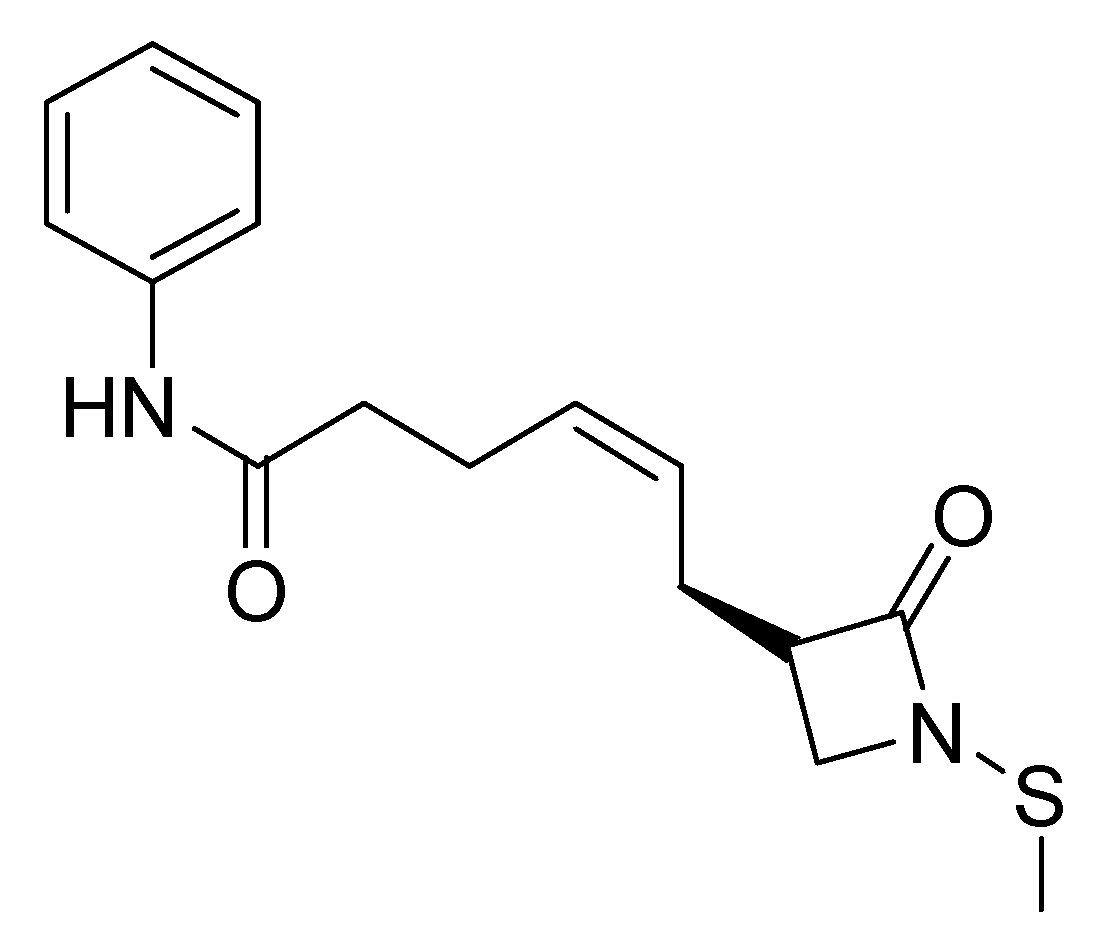
2.4. HDAC 6
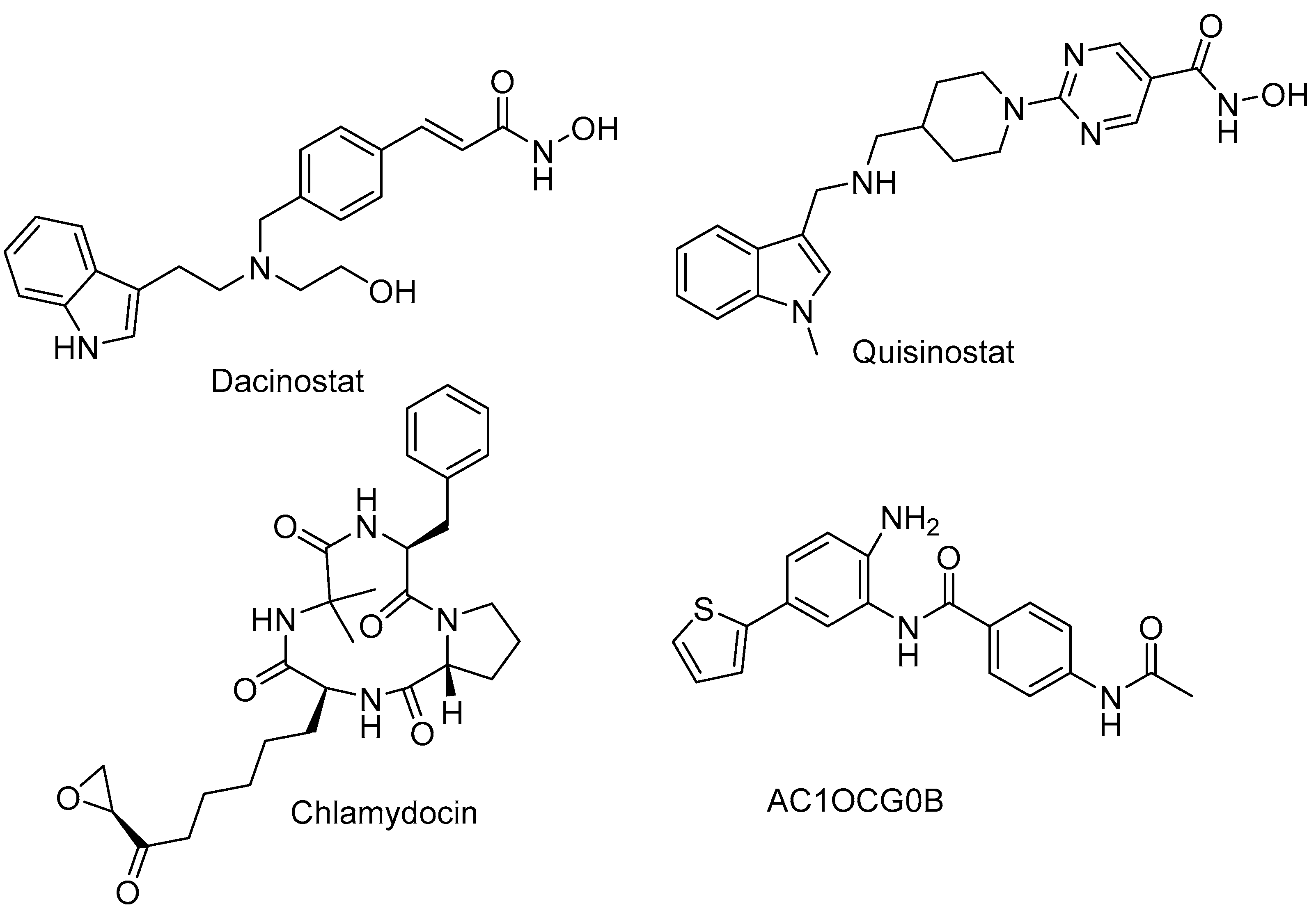
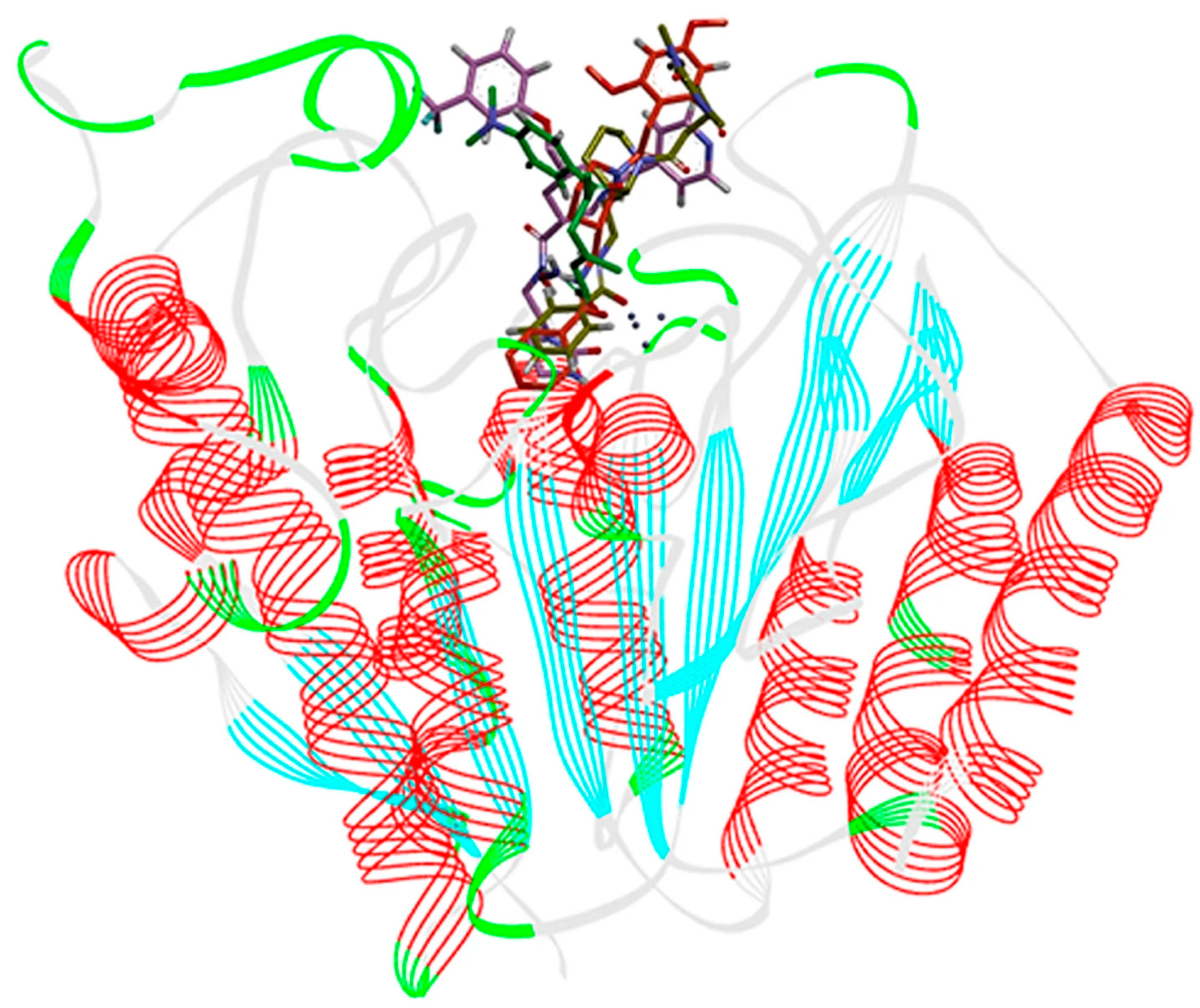
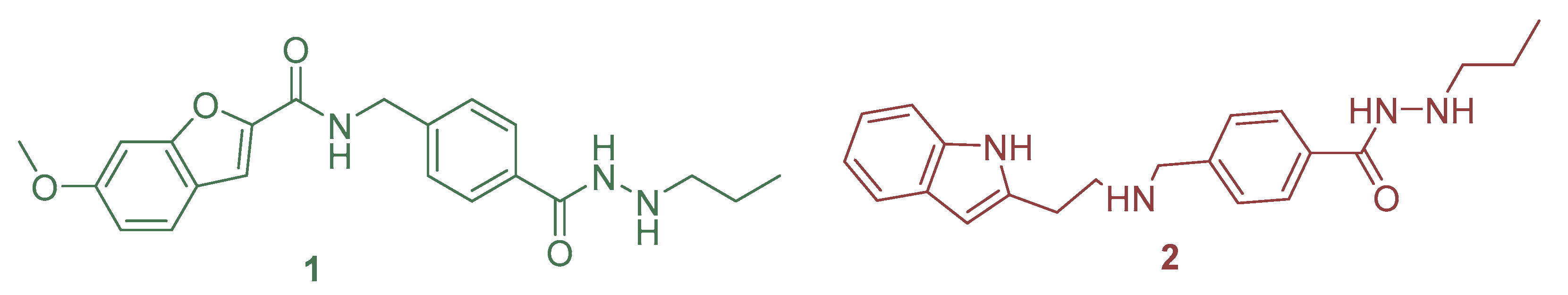
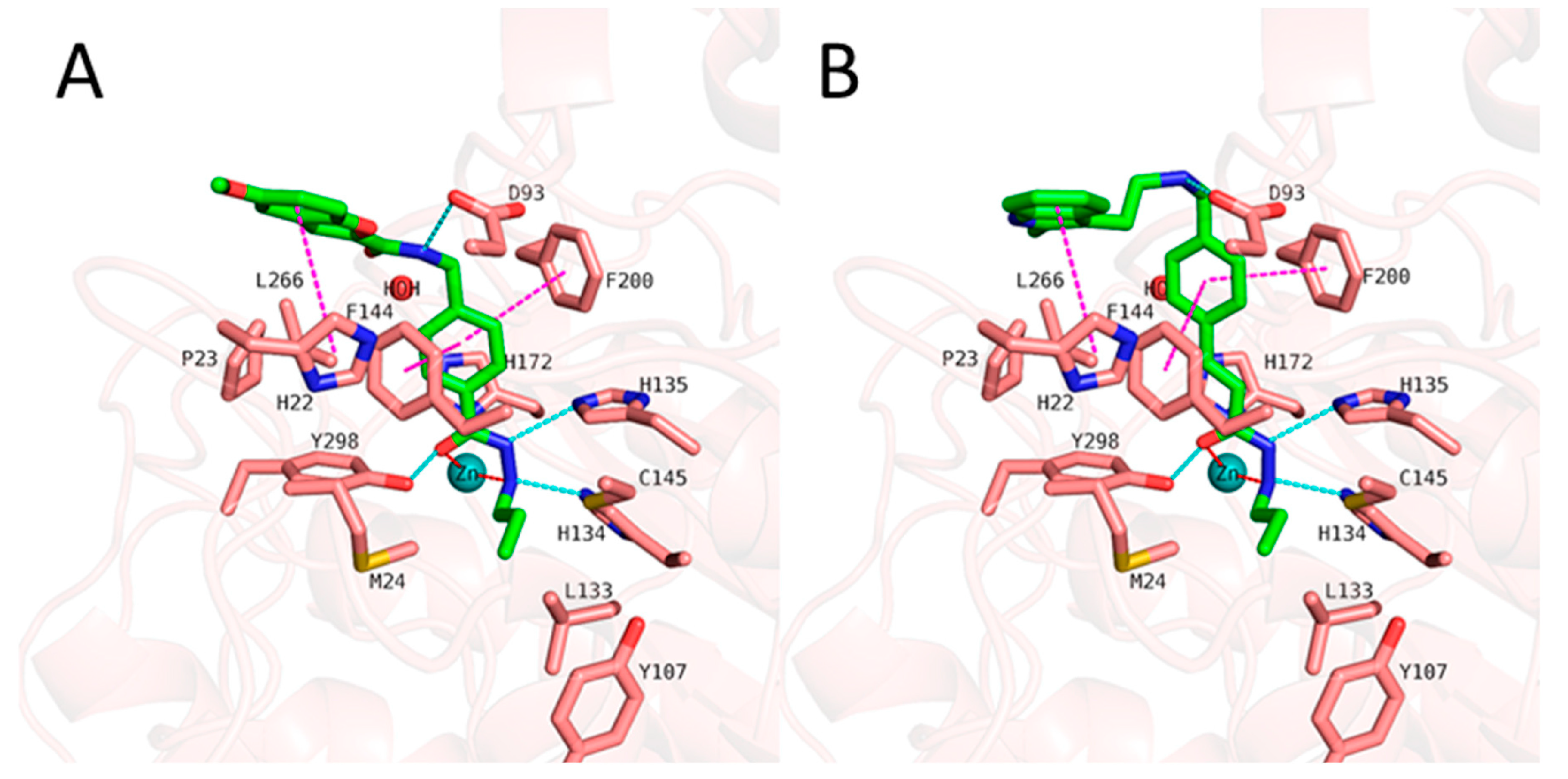
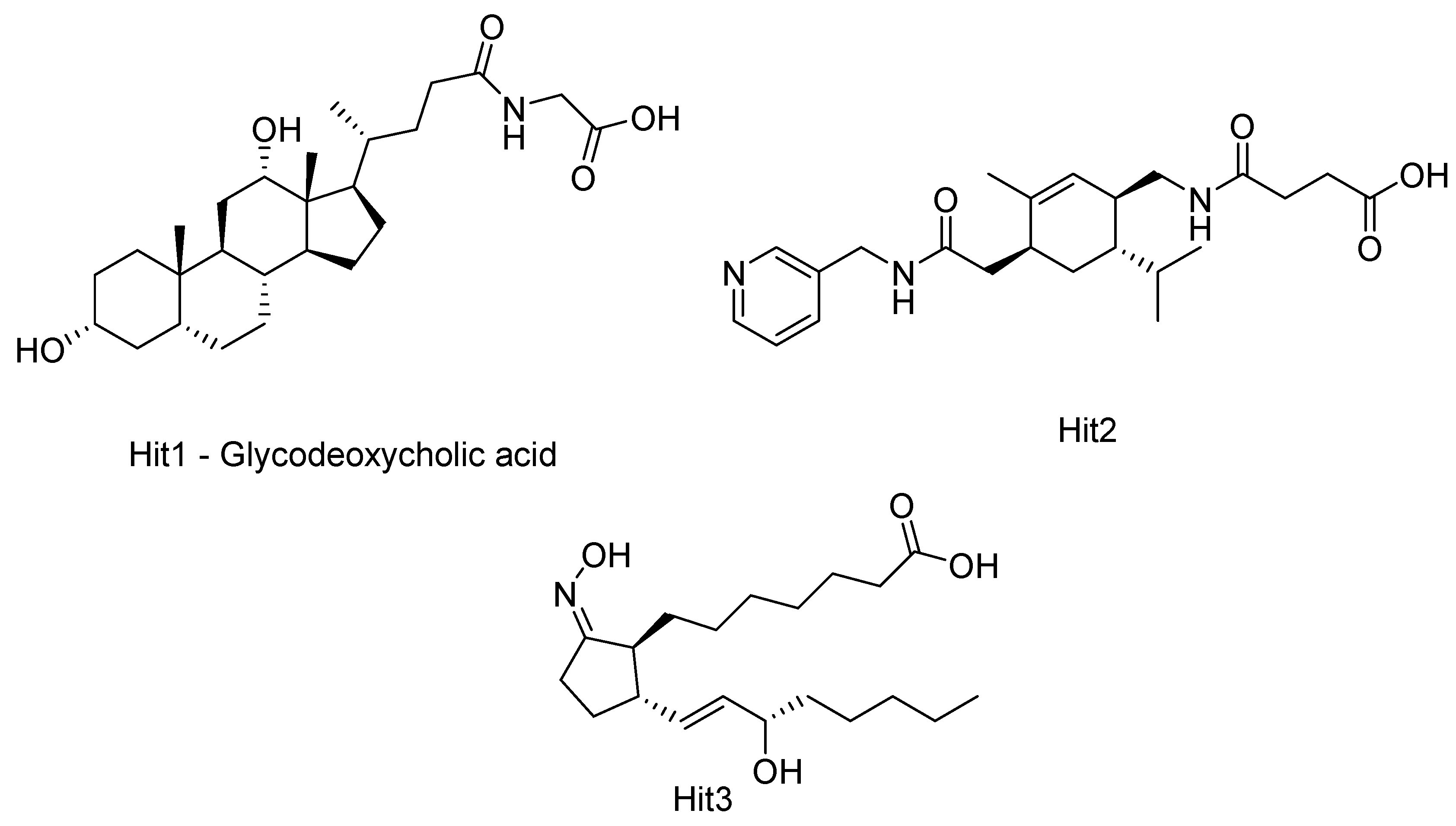
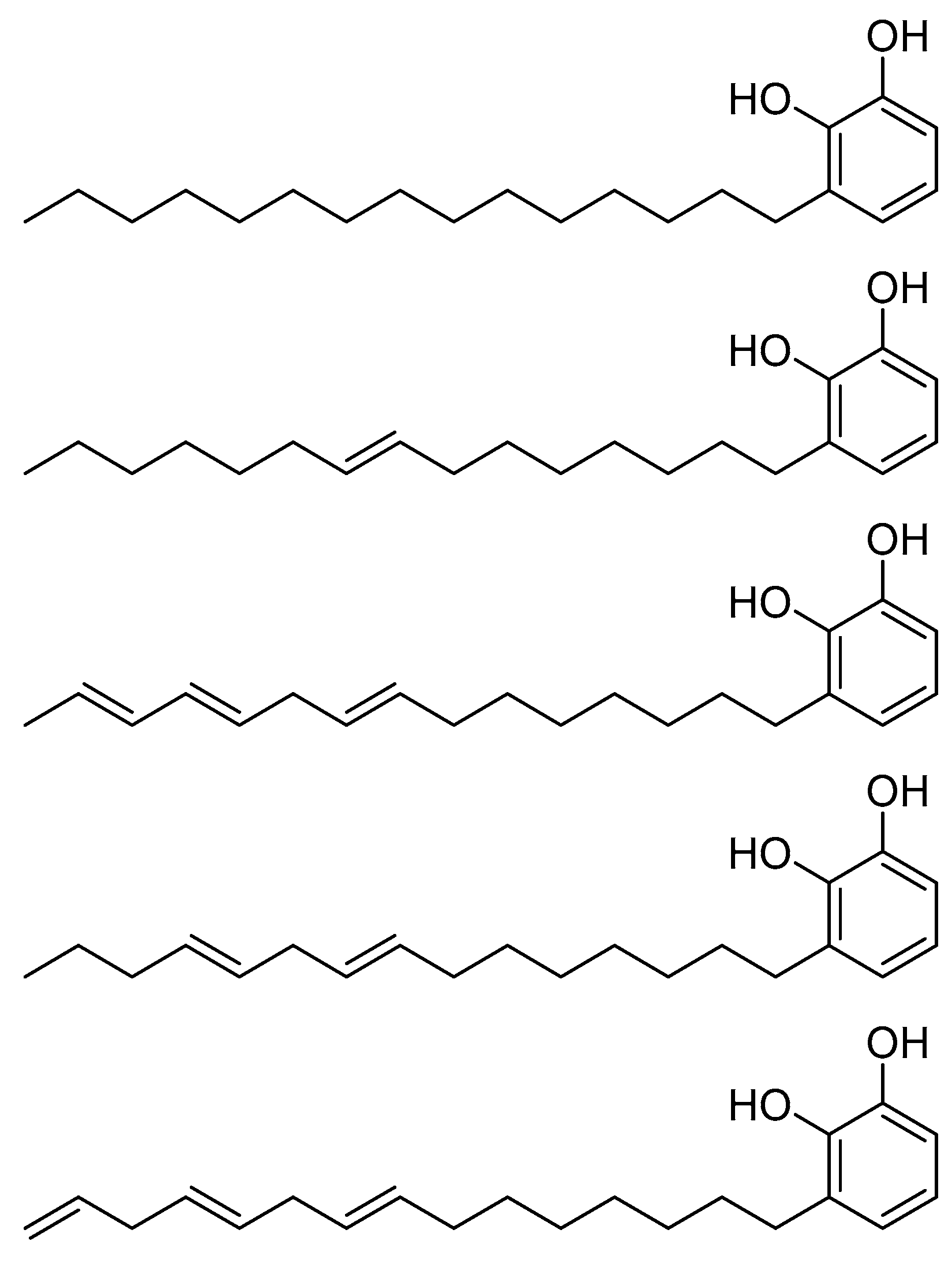
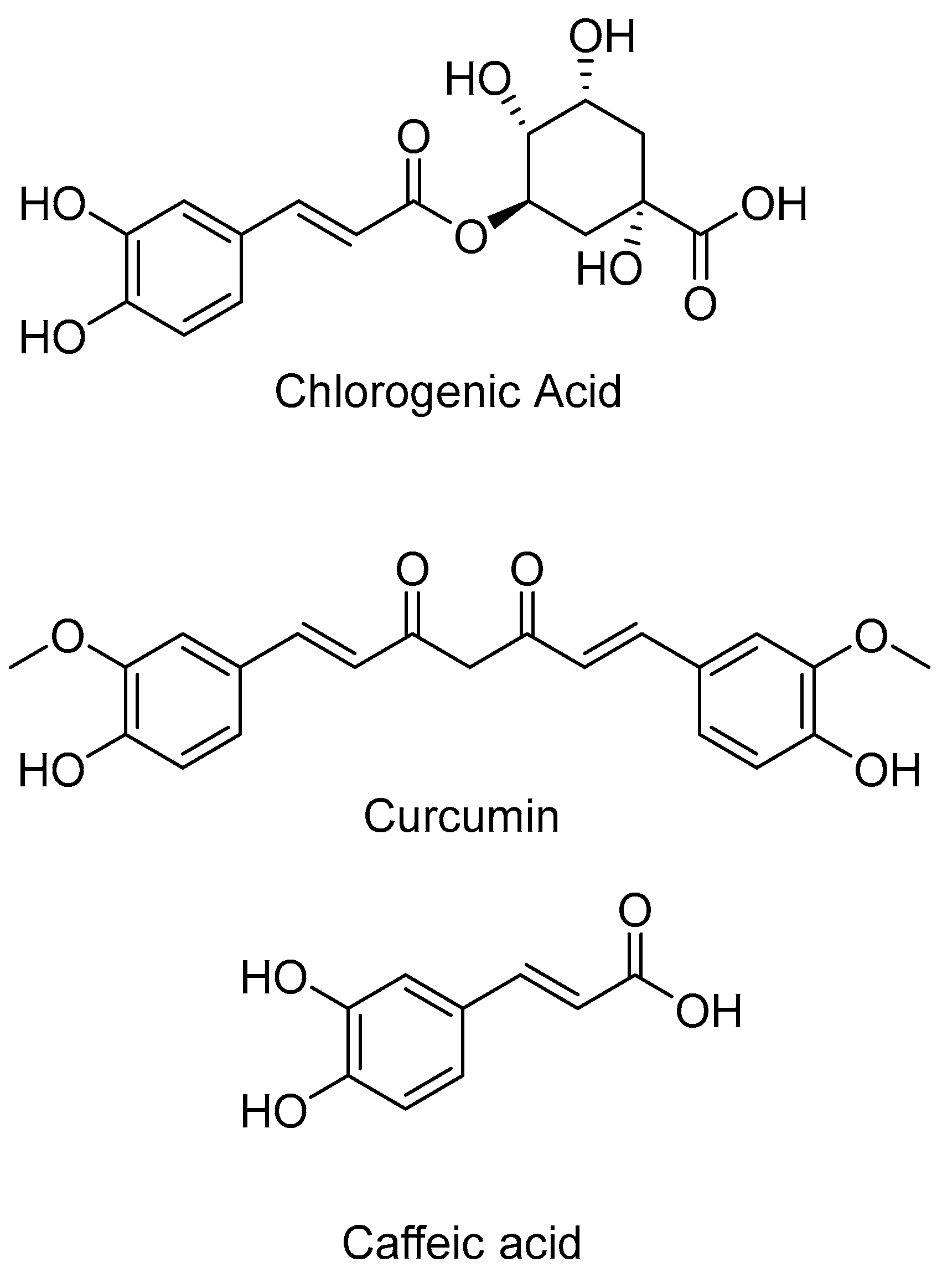
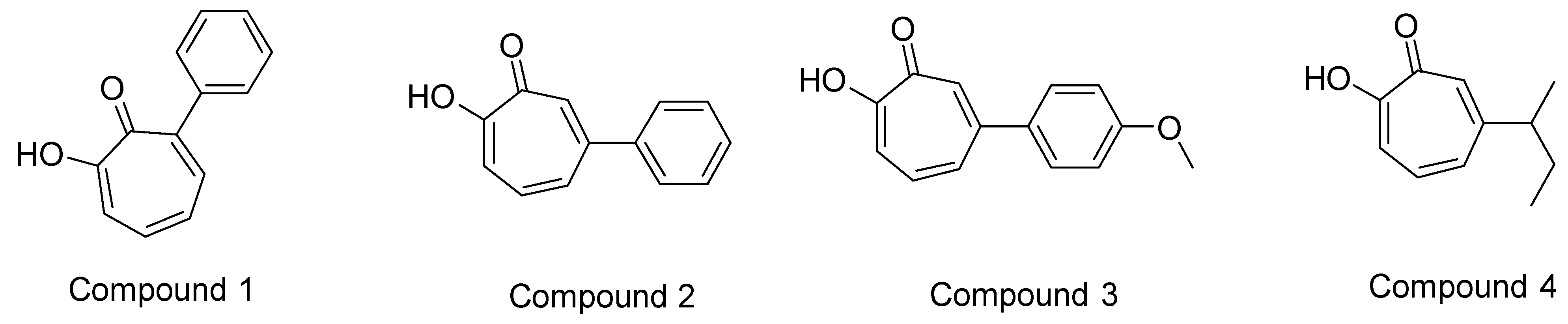
2.5. HDAC 8
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, C.; Croteau, S.; Hardy, P. Histone deacetylase (HDAC) 9: Versatile biological functions and emerging roles in human cancer. Cell. Oncol. 2021, 44, 997–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milazzo, G.; Mercatelli, D.; Di Muzio, G.; Triboli, L.; De Rosa, P.; Perini, G.; Giorgi, F.M. Histone Deacetylases (HDACs): Evolution, Specificity, Role in Transcriptional Complexes, and Pharmacological Actionability. Genes 2020, 11, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.P.; Zhao, Y.T.; Zhao, T.C. Histone Deacetylases and Mechanisms of Regulation of Gene Expression. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2015, 20, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauffer, B.E.L.; Mintzer, R.; Fong, R.; Mukund, S.; Tam, C.; Zilberleyb, I.; Flicke, B.; Ritscher, A.; Fedorowicz, G.; Vallero, R.; et al. Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitor Kinetic Rate Constants Correlate with Cellular Histone Acetylation but Not Transcription and Cell Viability. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 26926–26943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miceli, M.; Bontempo, P.; Nebbioso, A.; Altucci, L. Natural compounds in epigenetics: A current view. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 73, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.S.; Wu, X.; Golub, V.M.; Dashwood, W.M.; Dashwood, R.H. Measuring Histone Deacetylase Inhibition in the Brain. Curr. Protoc. Pharmacol. 2018, 81, e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barneda-Zahonero, B.; Parra, M. Histone deacetylases and cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokmanovic, M.; Clarke, C.; Marks, P.A. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: Overview and Perspectives. Mol. Cancer Res. 2007, 5, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glozak, M.A.; Sengupta, N.; Zhang, X.; Seto, E. Acetylation and deacetylation of non-histone proteins. Gene 2005, 363, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.N.; Zhang, G.; Hwa, Y.L.; Li, J.; Dowdy, S.C.; Jiang, S.-W. Nonhistone protein acetylation as cancer therapy targets. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2010, 10, 935–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, E.; Yoshida, M. Erasers of Histone Acetylation: The Histone Deacetylase Enzymes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a018713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Kang, G.; Eom, G.H. HDAC Inhibitors: Therapeutic Potential in Fibrosis-Associated Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Eom, G.H. HDAC and HDAC Inhibitor: From Cancer to Cardiovascular Diseases. Chonnam. Med. J. 2016, 52, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkenberg, K.J.; Johnstone, R.W. Histone deacetylases and their inhibitors in cancer, neurological diseases and immune disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 673–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villagra, A.; Cheng, F.; Wang, H.-W.; Suarez, I.; Glozak, M.; Maurin, M.; Nguyen, D.; Wright, K.L.; Atadja, P.W.; Bhalla, K.; et al. The histone deacetylase HDAC11 regulates the expression of interleukin 10 and immune tolerance. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gräff, J.; Rei, D.; Guan, J.-S.; Wang, W.-Y.; Seo, J.; Hennig, K.M.; Nieland, T.J.F.; Fass, D.M.; Kao, P.F.; Kahn, M.; et al. An epigenetic blockade of cognitive functions in the neurodegenerating brain. Nature 2012, 483, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.-J.; Seto, E. HATs and HDACs: From structure, function and regulation to novel strategies for therapy and prevention. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5310–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckschlager, T.; Plch, J.; Stiborova, M.; Hrabeta, J. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Anticancer Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ropero, S.; Esteller, M. The role of histone deacetylases (HDACs) in human cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2007, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadikovic, B.; Al-Romaih, K.; Squire, J.A.; Zielenska, M. Cause and Consequences of Genetic and Epigenetic Alterations in Human Cancer. Curr. Genom. 2008, 9, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulya, S.; Amin, S.A.; Adhikari, N.; Biswas, S.; Jha, T.; Ghosh, B. HDAC6 as privileged target in drug discovery: A perspective. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 163, 105274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruijter, A.J.D.; Gennip, A.H.V.; Caron, H.N.; Kemp, S.; Kuilenburg, A.B.V. Histone deacetylases (HDACs): Characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem. J. 2003, 370, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradner, J.E.; West, N.; Grachan, M.L.; Greenberg, E.F.; Haggarty, S.J.; Warnow, T.; Mazitschek, R. Chemical phylogenetics of histone deacetylases. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregoretti, I.; Lee, Y.-M.; Goodson, H.V. Molecular Evolution of the Histone Deacetylase Family: Functional Implications of Phylogenetic Analysis. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 338, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witt, O.; Deubzer, H.E.; Milde, T.; Oehme, I. HDAC family: What are the cancer relevant targets? Cancer Lett. 2009, 277, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, S.-I.; Armstrong, C.M.; Kaeberlein, M.; Guarente, L. Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature 2000, 403, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frye, R.A. Phylogenetic Classification of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Sir2-like Proteins. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 273, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richon, V.M. Cancer biology: Mechanism of antitumour action of vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid), a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Tomar, R.S.; Rath, S.K. Anticancer potential of the histone deacetylase inhibitor-like effects of flavones, a subclass of polyphenolic compounds: A review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 42, 1515–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, U.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Pandey, A.K. Medicinal attributes of major phenylpropanoids present in cinnamon. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Ahmad, M.K.; Waseem, M.; Pandey, A.K. Drug Targets for Cancer Treatment: An Overview. Med. Chem. 2015, 5, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.C.; Johnstone, R.W. New and emerging HDAC inhibitors for cancer treatment. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y. Chidamide tablets: HDAC inhibition to treat lymphoma. Drugs Today 2017, 53, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchu, S.N.; Brijmohan, A.S.; Advani, A. The therapeutic hope for HDAC6 inhibitors in malignancy and chronic disease. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 987–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Won, A.J.; Lee, J.; Jung, J.H.; Yoon, S.; Lee, B.M.; Kim, H.S. Molecular Mechanism of SAHA on Regulation of Autophagic Cell Death in Tamoxifen-Resistant MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Med Sci. 2012, 9, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, P.M.; Cole, K.E.; Dowling, D.P.; Christianson, D.W. Structure, mechanism, and inhibition of histone deacetylases and related metalloenzymes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2011, 21, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganai, S.A.; Farooq, Z.; Banday, S.; Altaf, M. In silico approaches for investigating the binding propensity of apigenin and luteolin against class I HDAC isoforms. Futur. Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 1925–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Marks, P.; Dokmanovic, M. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Discovery and development as anticancer agents. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2005, 14, 1497–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.X.; Dean, D.C. Chromatin Remodeling and Transcriptional Regulation. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999, 91, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolden, J.E.; Peart, M.J.; Johnstone, R.W. Anticancer activities of histone deacetylase inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bürli, R.W.; Luckhurst, C.A.; Aziz, O.; Matthews, K.L.; Yates, D.; Lyons, K.A.; Beconi, M.; McAllister, G.; Breccia, P.; Stott, A.J.; et al. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Potent and Selective Class IIa Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors as a Potential Therapy for Huntington’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 9934–9954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielcarek, M.; Landles, C.; Weiss, A.; Bradaia, A.; Seredenina, T.; Inuabasi, L.; Osborne, G.F.; Wadel, K.; Touller, C.; Butler, R.; et al. HDAC4 Reduction: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy to Target Cytoplasmic Huntingtin and Ameliorate Neurodegeneration. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebzehnrübl, F.A.; Raber, K.A.; Urbach, Y.K.; Schulze-Krebs, A.; Canneva, F.; Moceri, S.; Habermeyer, J.; Achoui, D.; Gupta, B.; Steindler, D.A.; et al. Early postnatal behavioral, cellular, and molecular changes in models of Huntington disease are reversible by HDAC inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8765–E8774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, K.T.; Haque, A.; Jones, M.K. HDAC inhibitors in parasitic diseases. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2012, 90, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontempo, P.; Mita, L.; Miceli, M.; Doto, A.; Nebbioso, A.; De Bellis, F.; Conte, M.; Minichiello, A.; Manzo, F.; Carafa, V.; et al. Feijoa sellowiana derived natural Flavone exerts anti-cancer action displaying HDAC inhibitory activities. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 1902–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bontempo, P.; Rigano, D.; Doto, A.; Formisano, C.; Conte, M.; Nebbioso, A.; Carafa, V.; Caserta, G.; Sica, V.; Molinari, A.M.; et al. Genista sessilifolia DC. extracts induce apoptosis across a range of cancer cell lines. Cell Prolif. 2013, 46, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magri, A.; Adiletta, G.; Petriccione, M. Evaluation of Antioxidant Systems and Ascorbate-Glutathione Cycle in Feijoa Edible Flowers at Different Flowering Stages. Foods 2020, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F. Chemical and biological properties of feijoa (Acca sellowiana). Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 81, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, J.; Bertrand, P. Inside HDACs with more selective HDAC inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 121, 451–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attoub, S.; Hassan, A.H.; Vanhoecke, B.; Iratni, R.; Takahashi, T.; Gaben, A.-M.; Bracke, M.; Awad, S.; John, A.; Kamalboor, H.A.; et al. Inhibition of cell survival, invasion, tumor growth and histone deacetylase activity by the dietary flavonoid luteolin in human epithelioid cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 651, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Kaur, P.; Shukla, S.; Abbas, A.; Fu, P.; Gupta, S. Plant flavone apigenin inhibits HDAC and remodels chromatin to induce growth arrest and apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells: In vitro and in vivo study. Mol. Carcinog. 2012, 51, 952–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soflaei, S.S.; Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A.; Majeed, M.; Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P.; Sahebkar, A. Curcumin: A Natural Pan-HDAC Inhibitor in Cancer. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D. Computational Studies on the Histone Deacetylases and the Design of Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2009, 9, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-F.; Helquist, P.; Wiech, N.L.; Wiest, O. Toward Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Design: Homology Modeling, Docking Studies, and Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Human Class I Histone Deacetylases. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 6936–6947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furumai, R.; Komatsu, Y.; Nishino, N.; Khochbin, S.; Yoshida, M.; Horinouchi, S. Potent histone deacetylase inhibitors built from trichostatin A and cyclic tetrapeptide antibiotics including trapoxin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yu, L.; Nebbioso, A.; Carafa, V.; Chen, Y.; Altucci, L.; You, Q. Novel N-hydroxybenzamide-based HDAC inhibitors with branched CAP group. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6284–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, P. Inside HDAC with HDAC inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 2095–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zou, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; He, B. Nε-acetyl lysine derivatives with zinc binding groups as novel HDAC inhibitors. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahnen, E.; Hauke, J.; Tränkle, C.; Eyüpoglu, I.Y.; Wirth, B.; Blümcke, I. Mba Histone deacetylase inhibitors: Possible implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2008, 17, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, M.; Tibes, U. 5 Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: A Novel Class of Anti-Cancer Agents on its Way to the Market. Prog. Med. Chem. 2008, 46, 205–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sixto-López, Y.; Gómez-Vidal, J.A.; de Pedro, N.; Bello, M.; Rosales-Hernández, M.C.; Correa-Basurto, J. Hydroxamic acid derivatives as HDAC1, HDAC6 and HDAC8 inhibitors with antiproliferative activity in cancer cell lines. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-F.; Wiest, O.; Helquist, P.; Lan-Hargest, H.-Y.; Wiech, N.L. On the Function of the 14 Å Long Internal Cavity of Histone Deacetylase-Like Protein: Implications for the Design of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 3409–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biel, M.; Wascholowski, V.; Giannis, A. Epigenetics—An Epicenter of Gene Regulation: Histones and Histone-Modifying Enzymes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3186–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannini, A.; Volpari, C.; Filocamo, G.; Casavola, E.C.; Brunetti, M.; Renzoni, D.; Chakravarty, P.; Paolini, C.; De Francesco, R.; Gallinari, P.; et al. Crystal structure of a eukaryotic zinc-dependent histone deacetylase, human HDAC8, complexed with a hydroxamic acid inhibitor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15064–15069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knegtel, R.M.; Kuntz, I.D.; Oshiro, C. Molecular docking to ensembles of protein structures. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 266, 424–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Zhang, K.Y.J. Investigation on the Effect of Key Water Molecules on Docking Performance in CSARdock Exercise. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 1880–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, G.; Meiler, J. Towards Ligand Docking Including Explicit Interface Water Molecules. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.; Davis, E.; Jones, G.; Sage, C.R. Molecular Docking—A Solved Problem? In Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry III; Chackalamannil, S., Rotella, D., Ward, S.E., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 297–318. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, L.H.S.; Ferreira, R.S.; Caffarena, E.R. Integrating Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2053, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. Docking Screens for Novel Ligands Conferring New Biology. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 4103–4120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, P.H.M.; Sodero, A.C.R.; Jofily, P.; Silva, F.P., Jr. Key Topics in Molecular Docking for Drug Design. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzi, L.; Rastelli, G. Molecular Docking: Shifting Paradigms in Drug Discovery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senese, S.; Zaragoza, K.; Minardi, S.; Muradore, I.; Ronzoni, S.; Passafaro, A.; Bernard, L.; Draetta, G.F.; Alcalay, M.; Seiser, C.; et al. Role for Histone Deacetylase 1 in Human Tumor Cell Proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 4784–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Kwon, H.J.; Yoon, B.-I.; Kim, J.-H.; Han, S.U.; Joo, H.J.; Kim, D.-Y. Expression Profile of Histone Deacetylase 1 in Gastric Cancer Tissues. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2001, 92, 1300–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krusche, C.A.; Wuïfing, P.; Kersting, C.; Vloet, A.; Böcker, W.B.; Kiesel, L.; Beier, H.M.; Alfer, J. Histone deacetylase-1 and-3 protein expression in human breast cancer: A tissue microarray analysis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2005, 90, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkidou, K.; Gaughan, L.; Cook, S.; Leung, H.Y.; Neal, D.E.; Robson, C.N. Upregulation and Nuclear Recruitment of HDAC1 in Hormone Refractory Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2004, 59, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wambua, M.K.; Nalawansha, D.A.; Negmeldin, A.T.; Pflum, M.K.H. Mutagenesis Studies of the 14 Å Internal Cavity of Histone Deacetylase 1: Insights toward the Acetate-Escape Hypothesis and Selective Inhibitor Design. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalakshmi, R.; Husayn Ahmed, P.; Mahadevan, V. HDAC inhibitors show differential epigenetic regulation and cell survival strategies on p53 mutant colon cancer cells. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 36, 938–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wang, C.; Deng, T.; Tao, R.; Li, W. Novel urushiol derivatives as HDAC8 inhibitors: Rational design, virtual screening, molecular docking and molecular dynamics studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 36, 1966–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methot, J.L.; Chakravarty, P.K.; Chenard, M.; Close, J.; Cruz, J.C.; Dahlberg, W.K.; Fleming, J.; Hamblett, C.L.; Hamill, J.E.; Harrington, P.; et al. Exploration of the internal cavity of histone deacetylase (HDAC) with selective HDAC1/HDAC2 inhibitors (SHI-1:2). Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.A.; Chabner, B.A. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5459–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scafuri, B.; Bontempo, P.; Altucci, L.; De Masi, L.; Facchiano, A. Molecular Docking Simulations on Histone Deacetylases (HDAC)-1 and -2 to Investigate the Flavone Binding. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Lu, Z.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Y. Zinc Chelation with Hydroxamate in Histone Deacetylases Modulated by Water Access to the Linker Binding Channel. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 6110–6113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sixto-López, Y.; Bello, M.; Correa-Basurto, J. Insights into structural features of HDAC1 and its selectivity inhibition elucidated by Molecular dynamic simulation and Molecular Docking. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 37, 584–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arts, J.; King, P.; Mariën, A.; Floren, W.; Beliën, A.; Janssen, L.; Pilatte, I.; Roux, B.; Decrane, L.; Gilissen, R.; et al. JNJ-26481585, a Novel Second-Generation Oral Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Shows Broad-Spectrum Preclinical Antitumoral Activity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6841–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atadja, P.; Gao, L.; Kwon, P.; Trogani, N.; Walker, H.; Hsu, M.; Yeleswarapu, L.; Chandramouli, N.; Perez, L.; Versace, R.; et al. Selective Growth Inhibition of Tumor Cells by a Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, NVP-LAQ824. Cancer Res 2004, 64, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuiyan, M.P.; Kato, T.; Okauchi, T.; Nishino, N.; Maeda, S.; Nishino, T.G.; Yoshida, M. Chlamydocin analogs bearing carbonyl group as possible ligand toward zinc atom in histone deacetylases. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 3438–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Martins, D.; Forli, S.; Ramos, M.J.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4Zn: An Improved AutoDock Force Field for Small-Molecule Docking to Zinc Metalloproteins. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 2371–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urias, B.S.; Pavan, A.R.; Albuquerque, G.R.; Prokopczyk, I.M.; Alves, T.M.F.; de Melo, T.R.F.; Sartori, G.R.; da Silva, J.H.M.; Chin, C.M.; Dos Santos, J.L. Optimization of Resveratrol Used as a Scaffold to Design Histone Deacetylase (HDAC-1 and HDAC-2) Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingólfsson, H.I.; Thakur, P.; Herold, K.F.; Hobart, E.A.; Ramsey, N.B.; Periole, X.; de Jong, D.H.; Zwama, M.; Yilmaz, D.; Hall, K.; et al. Phytochemicals Perturb Membranes and Promiscuously Alter Protein Function. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1788–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosquesi, P.L.; Melchior, A.C.B.; Pavan, A.R.; Lanaro, C.; de Souza, C.M.; Rusinova, R.; Chelucci, R.C.; Barbieri, K.P.; dos Santos Fernandes, G.F.; Carlos, I.Z.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of resveratrol derivatives as fetal hemoglobin inducers. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 100, 103948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturelli, S.; Berger, A.; Böcker, A.; Busch, C.; Weiland, T.; Noor, S.; Leischner, C.; Schleicher, S.; Mayer, M.; Weiss, T.S.; et al. Resveratrol as a Pan-HDAC Inhibitor Alters the Acetylation Status of Jistone Proteins in Human-Derived Hepatoblastoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Noh, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Eun, J.W.; Ahn, Y.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Park, W.S.; Yoo, N.J.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. Increased expression of histone deacetylase 2 is found in human gastric cancer. APMIS 2005, 113, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichert, W.; Röske, A.; Niesporek, S.; Noske, A.; Buckendahl, A.-C.; Dietel, M.; Gekeler, V.; Boehm, M.; Beckers, T.; Denkert, C. Class I Histone Deacetylase Expression Has Independent Prognostic Impact in Human Colorectal Cancer: Specific Role of Class I Histone Deacetylases In vitro and In vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1669–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weichert, W.; Denkert, C.; Schmidt, M.; Gekeler, V.; Wolf, G.; Köbel, M.; Dietel, M.; Hauptmann, S. Polo-like kinase isoform expression is a prognostic factor in ovarian carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddard, S.V.; May, X.A.; Rivas, F.; Dodson, K.; Vijayan, S.; Adhika, S.; Parker, K.; Watkins, D.L. Design of Potent Panobinostat Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Derivatives: Molecular Considerations for Enhanced Isozyme Selectivity between HDAC2 and HDAC8. Mol. Inform. 2019, 38, e1800080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atadja, P. Development of the pan-DAC inhibitor panobinostat (LBH589): Successes and challenges. Cancer Lett. 2009, 280, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Micco, S.; Chini, M.G.; Terracciano, S.; Bruno, I.; Riccio, R.; Bifulco, G. Structural basis for the design and synthesis of selective HDAC inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 3795–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourad, A.A.; Mourad, M.A.; Jones, P.G. Novel HDAC/Tubulin Dual Inhibitor: Design, Synthesis and Docking Studies of α-Phthalimido-Chalcone Hybrids as Potential Anticancer Agents with Apoptosis-Inducing Activity. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 3111–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, N.; Amin, S.A.; Trivedi, P.; Jha, T.; Ghosh, B. HDAC3 is a potential validated target for cancer: An overview on the benzamide-based selective HDAC3 inhibitors through comparative SAR/QSAR/QAAR approaches. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 1127–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, P.J.; Fairall, L.; Santos, G.M.; Schwabe, J.W.R. Structure of HDAC3 bound to co-repressor and inositol tetraphosphate. Nature 2012, 481, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guenther, M.G.; Barak, O.; Lazar, M.A. The SMRT and N-CoR Corepressors Are Activating Cofactors for Histone Deacetylase 3. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 6091–6101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagianni, P.; Wong, J. HDAC3: Taking the SMRT-N-CoRrect road to repression. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5439–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuown, S.C.; Barrett, R.M.; Matheos, D.P.; Post, R.J.; Rogge, G.A.; Alenghat, T.; Mullican, S.E.; Jones, S.; Rusche, J.R.; Lazar, M.A.; et al. HDAC3 Is a Critical Negative Regulator of Long-Term Memory Formation. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardai, F.H.; D’Mello, S.R. Selective Toxicity by HDAC3 in Neurons: Regulation by Akt and GSK3β. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, R.; Banerjee, S.; Amin, S.A.; Adhikari, N.; Jha, T. Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) inhibitors as anticancer agents: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 192, 112171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.A.; Adhikari, N.; Kotagiri, S.; Jha, T.; Ghosh, B. Histone deacetylase 3 inhibitors in learning and memory processes with special emphasis on benzamides. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 166, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Tong, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Qian, L.B.; Chen, S.Y.; Sun, J.; Cai, L. Inhibition of HDAC3 prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy in OVE26 mice via epigenetic regulation of DUSP5-ERK1/2 pathway. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1841–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvaez, M.; McQuown, S.C.; Rogge, G.A.; Astarabadi, M.; Jacques, V.; Carreiro, S.; Rusche, J.R.; Wood, M.A. HDAC3-selective inhibitor enhances extinction of cocaine-seeking behavior in a persistent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2647–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogge, G.A.; Singh, H.; Dang, R.; Wood, M.A. HDAC3 Is a Negative Regulator of Cocaine-Context-Associated Memory Formation. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 6623–6632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Zhang, P.; Liu, W.; Zeng, X.; Ma, X.; Shi, L.; Wang, T.; Yin, Y.; Chang, W.; Zhang, P.; et al. HDAC is indispensable for IFN-γ-induced B7-H1 expression in gastric cancer. Clin. Epigenetics 2018, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlknecht, U.; Will, J.; Varin, A.; Hoelzer, D.; Herbein, G. Histone Deacetylase 3, a Class I Histone Deacetylase, Suppresses MAPK11-Mediated Activating Transcription Factor-2 Activation and Represses TNF Gene Expression. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3979–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendinelli, P.; Matteucci, E.; Maroni, P.; Desiderio, M.A. NF-κB Activation, Dependent on Acetylation/Deacetylation, Contributes to HIF-1 Activity and Migration of Bone Metastatic Breast Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2009, 7, 1328–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.-J.; Huang, F.-X.; Sun, Z.-T.; Zhang, R.-X.; Huang, S.-F.; Wang, J. Stat3 inhibits Beclin 1 expression through recruitment of HDAC3 in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 7097–7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-C.; Choi, K.-C.; Choi, H.-K.; Kang, H.-B.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lee, O.-H.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Jun, W.; et al. HDAC3 selectively represses CREB3-mediated transcription and migration of metastatic breast cancer cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 3499–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bülbül, E.F.; Melesina, J.; Ibrahim, H.S.; Abdelsalam, M.; Vecchio, A.; Robaa, D.; Zessin, M.; Schutkowski, M.; Sippl, W. Docking, Binding Free Energy Calculations and In Vitro Characterization of Pyrazine Linked 2-Aminobenzamides as Novel Class I Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors. Molecules 2022, 27, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Routholla, G.; Pulya, S.; Patel, T.; Amin, S.A.; Adhikari, N.; Biswas, S.; Jha, T.; Ghosh, B. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and molecular docking analysis of novel linker-less benzamide based potent and selective HDAC3 inhibitors. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 114, 105050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrçdinger Suite, Schrçdinger, LLC, New York, USA. Available online: http://www.Schrödinger.com/glide (accessed on 2 November 2023).
- Kumbhar, N.; Nimal, S.; Barale, S.; Kamble, S.; Bavi, R.; Sonawane, K.; Gacche, R. Identification of novel leads as potent inhibitors of HDAC3 using ligand-based pharmacophore modeling and MD simulation. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bülbül, E.F.; Robaa, D.; Sun, P.; Mahmoudi, F.; Melesina, J.; Zessin, M.; Schutkowski, M.; Sippl, W. Application of Ligand- and Structure-Based Prediction Models for the Design of Alkylhydrazide-Based HDAC3 Inhibitors as Novel Anti-Cancer Compounds. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger LLC. Release 2019-1: Maestro, Protein Preparation Wizard, Prime, Epik, Ligprep, Confgen, Glide; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sixto-López, Y.; Bello, M.; Rodríguez-Fonseca, R.A.; Rosales-Hernández, M.C.; Martínez-Archundia, M.; Gómez-Vidal, J.A.; Correa-Basurto, J. Searching the conformational complexity and binding properties of HDAC6 through docking and molecular dynamic simulations. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 35, 2794–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Caron, C.; Matthias, G.; Hess, D.; Khochbin, S.; Matthias, P. HDAC-6 interacts with and deacetylates tubulin and microtubules in vivo. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1168–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khochbin, S.; Verdel, A.; Lemercier, C.; Seigneurin-Berny, D. Functional significance of histone deacetylase diversity. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2001, 11, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gilquin, B.; Khochbin, S.; Matthias, P. Two Catalytic Domains Are Required for Protein Deacetylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 2401–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grozinger, C.M.; Hassig, C.A.; Schreiber, S.L. Three proteins define a class of human histone deacetylases related to yeast Hda1p. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4868–4873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, N.; Ping, L.; Feng, L.; Zheng, X.; Song, Y.; Zhu, J. Histone deacetylase 6 activity is critical for the metastasis of Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2014, 14, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolden, J.E.; Shi, W.; Jankowski, K.; Kan, C.-Y.; Cluse, L.; Martin, B.P.; MacKenzie, K.L.; Smyth, G.K.; Johnstone, R.W. HDAC inhibitors induce tumor-cell-selective pro-apoptotic transcriptional responses. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yong, S.; Salas-Burgos, A.; Koomen, J.; Olashaw, N.; Parsons, J.T.; Yang, X.-J.; Dent, S.R.; et al. HDAC6 Modulates Cell Motility by Altering the Acetylation Level of Cortactin. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracy, T.E.; Sohn, P.D.; Minami, S.S.; Wang, C.; Min, S.-W.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Le, D.; Lo, I.; Ponnusamy, R.; et al. Acetylated Tau Obstructs KIBRA-Mediated Signaling in Synaptic Plasticity and Promotes Tauopathy-Related Memory Loss. Neuron 2016, 90, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.-W.; Chen, X.; Tracy, T.E.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Shirakawa, K.; Minami, S.S.; Defensor, E.; Mok, S.-A.; et al. Critical role of acetylation in tau-mediated neurodegeneration and cognitive deficits. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, T.J.; Guo, J.L.; Hurtado, D.E.; Kwong, L.K.; Mills, I.P.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.Y. The acetylation of tau inhibits its function and promotes pathological tau aggregation. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, C.; Carlomagno, Y.; Gendron, T.F.; Dunmore, J.; Scheffel, K.; Stetler, C.; Davis, M.; Dickson, D.; Jarpe, M.; DeTure, M.; et al. Acetylation of the KXGS motifs in tau is a critical determinant in modulation of tau aggregation and clearance. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnapp, E.; Breithaupt, H. The A-T gene hunt. Embo Rep. 2019, 20, e48947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, C.; Schnekenburger, M.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Histone deacetylase 6 in health and disease. Epigenomics 2015, 7, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalin, J.H.; Bergman, J.A. Development and Therapeutic Implications of Selective Histone Deacetylase 6 Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 6297–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A.; Park, C.; Rampogu, S.; Son, M.; Lee, G.; Lee, K.W. Structure-Based Drug Designing Recommends HDAC6 Inhibitors to Attenuate Microtubule-Associated Tau-Pathogenesis. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 1326–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Lim, J.; Seo, Y.H. A novel class of anthraquinone-based HDAC6 inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 164, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Song, W. Zinc binding groups for histone deacetylase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbdElmoniem, N.; Abdallah, M.H.; Mukhtar, R.M.; Moutasim, F.; Ahmed, A.R.; Edris, A.; Ibraheem, W.; Makki, A.A.; Elshamly, E.M.; Elhag, R.; et al. Identification of Novel Natural Dual HDAC and Hsp90 Inhibitors for Metastatic TNBC Using e-Pharmacophore Modeling, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Studies. Molecules 2023, 28, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, F.J.; Ansari, M.; Braunholz, D.; Decroos, C.; Wilde, J.J.; Fincher, C.T.; Kaur, M.; Bando, M.; Amor, D.J.; Atwal, P.S.; et al. Loss-of-function HDAC8 mutations cause a phenotypic spectrum of Cornelia de Lange syndrome-like features, ocular hypertelorism, large fontanelle and X-linked inheritance. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 2888–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decroos, C.; Bowman, C.M.; Moser, J.-A.S.; Christianson, K.E.; Deardorff, M.A.; Christianson, D.W. Compromised Structure and Function of HDAC8 Mutants Identified in Cornelia de Lange Syndrome Spectrum Disorders. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 2157–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Nian, H.; Rajendran, P.; Kim, E.; Dashwood, W.M.; Pinto, J.T.; A Boardman, L.; Thibodeau, S.N.; Limburg, P.J.; Löhr, C.V.; et al. HDAC8 and STAT3 repress BMF gene activity in colon cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimburg, T.; Kolbinger, F.R.; Zeyen, P.; Ghazy, E.; Herp, D.; Schmidtkunz, K.; Melesina, J.; Shaik, T.B.; Erdmann, F.; Schmidt, M.; et al. Structure-Based Design and Biological Characterization of Selective Histone Deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) Inhibitors with Anti-Neuroblastoma Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 10188–10204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehme, I.; Deubzer, H.E.; Wegener, D.; Pickert, D.; Linke, J.-P.; Hero, B.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Westermann, F.; Ulrich, S.M.; von Deimling, A.; et al. Histone Deacetylase 8 in Neuroblastoma Tumorigenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulandaivelu, U.; Chilakamari, L.M.; Jadav, S.S.; Rao, T.R.; Jayaveera, K.; Shireesha, B.; Hauser, A.-T.; Senger, J.; Marek, M.; Romier, C.; et al. Hydroxamates of para-aminobenzoic acid as selective inhibitors of HDAC8. Bioorganic Chem. 2014, 57, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingham, O.J.; Paranal, R.M.; Smith, W.B.; Escobar, R.A.; Yueh, H.; Snyder, T.; Porco, J.A.; Bradner, J.E.; Beeler, A.B. Development of a Potent and Selective HDAC8 Inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 929–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Jeffers, M.; Kumar, S.; Hackett, C.; Boldog, F.; Khramtsov, N.; Qian, X.; Mills, E.; Berghs, S.C.; Carey, N.; et al. Determination of the class and isoform selectivity of small-molecule histone deacetylase inhibitors. Biochem. J. 2008, 409, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somoza, J.R.; Skene, R.; Katz, B.A.; Mol, C.; Ho, J.D.; Jennings, A.J.; Luong, C.; Arvai, A.; Buggy, J.J.; Chi, E.; et al. Structural Snapshots of Human HDAC8 Provide Insights into the Class I Histone Deacetylases. Structure 2004, 12, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.A.; Witter, D.J.; Belvedere, S. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 5097–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, A.; Massa, S.; Rotili, D.; Cerbara, I.; Valente, S.; Pezzi, R.; Simeoni, S.; Ragno, R. Histone deacetylation in epigenetics: An attractive target for anticancer therapy. Med. Res. Rev. 2005, 25, 261–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradei, O.M.; Mallais, T.C.; Frechette, S.; Paquin, I.; Tessier, P.E.; Leit, S.M.; Fournel, M.; Bonfils, C.; Trachy-Bourget, M.-C.; Liu, J.; et al. Novel Aminophenyl Benzamide-Type Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors with Enhanced Potency and Selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5543–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez-Lugo, J.A.; Perez-Gonzalez, O.; Rosales-Hernández, M.C.; Ilizaliturri-Flores, I.; Trujillo-Ferrara, J.; Correa-Basurto, J. Exploration of the valproic acid binding site on histone deacetylase 8 using docking and molecular dynamic simulations. J. Mol. Model. 2012, 18, 2301–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sixto-López, Y.; Gómez-Vidal, J.A.; Correa-Basurto, J. Exploring the Potential binding Sites of Some Known HDAC Inhibitors on Some HDAC8 Conformers by Docking Studies. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 173, 1907–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, T.; Lu, R.; Sakai, R.; Ishimura, T.; Miyakoshi, T. Characterization and comparison of Asian lacquer saps. Prog. Org. Coat. 2008, 61, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradei, O.; Maroun, C.R.; Paquin, I.; Vaisburg, A. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: Latest Developments, Trends and Prospects. Curr. Med. Chem. Agents 2005, 5, 529–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Miyata, N. Non-hydroxamate Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 2867–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora-Tatar, G.; Dayangaç-Erden, D.; Demir, A.S.; Dalkara, S.; Yelekçi, K.; Erdem-Yurter, H. Molecular modifications on carboxylic acid derivatives as potent histone deacetylase inhibitors: Activity and docking studies. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5219–5228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huey, R.; Morris, G.M.; Olson, A.J.; Goodsell, D.S. A semiempirical free energy force field with charge-based desolvation. J. Comput. Chem. 2007, 28, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Goodsell, D.S.; Halliday, R.S.; Huey, R.; Hart, W.E.; Belew, R.K.; Olson, A.J. Automated Docking Using a Lamarckian Genetic Algorithm and an Empirical Binding Free Energy Function. J. Comput. Chem. 1998, 19, 1639–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, K.; Kakkar, R. An insight into selective and potent inhibition of histone deacetylase 8 through induced-fit docking, pharmacophore modeling and QSAR studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 38, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Adhikari, N.; Amin, S.A.; Bobde, Y.; Ganesh, R.; Jha, T.; Ghosh, B. Design, synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking study of arylcarboxamido piperidine and piperazine-based hydroxamates as potential HDAC8 inhibitors with promising anticancer activity. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 138, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, G.; Vesci, L.; Battistuzzi, G.; Vignola, D.; Milazzo, F.M.; Guglielmi, M.B.; Barbarino, M.; Santaniello, M.; Fantò, N.; Mor, M.; et al. ST7612AA1, a Thioacetate-ω(γ-lactam carboxamide) Derivative Selected from a Novel Generation of Oral HDAC Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 8358–8377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassadonia, A.; Cioffi, P.; Simiele, F.; Iezzi, L.; Zilli, M.; Natoli, C. Role of Hydroxamate-Based Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (Hb-HDACIs) in the Treatment of Solid Malignancies. Cancers 2013, 5, 919–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddei, M.; Cini, E.; Giannotti, L.; Giannini, G.; Battistuzzi, G.; Vignola, D.; Vesci, L.; Cabri, W. Lactam based 7-amino suberoylamide hydroxamic acids as potent HDAC inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger, LLC. Maestro, version 9.6; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2013.
- Schrödinger, LLC. LigPrep, version 2.8; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2013.
- Schrödinger Suite 2013 Protein Preparation Wizard, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2013; (b) Epik version 2.6; Schrödinger, LLC, New York, NY, USA, 2013; (c) Impact, version 6.1; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2013; (d) Prime, version 3.3; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2013.
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 1. Method and Assessment of Docking Accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrödinger, LLC. Glide, version 6.1; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2013.
- Tilekar, K.; Hess, J.D.; Upadhyay, N.; Bianco, A.L.; Schweipert, M.; Laghezza, A.; Loiodice, F.; Meyer-Almes, F.-J.; Aguilera, R.J.; Lavecchia, A.; et al. Thiazolidinedione “Magic Bullets” Simultaneously Targeting PPARγ and HDACs: Design, Synthesis, and Investigations of their In Vitro and In Vivo Antitumor Effects. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 6949–6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilekar, K.; Upadhyay, N.; Jänsch, N.; Schweipert, M.; Mrowka, P.; Meyer-Almes, F.; Ramaa, C. Discovery of 5-naphthylidene-2,4-thiazolidinedione derivatives as selective HDAC8 inhibitors and evaluation of their cytotoxic effects in leukemic cell lines. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 95, 103522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Du, J.; Liu, R.; Zhou, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, W.; Fang, H. Enhancing the Sensitivity of Pharmacophore-Based Virtual Screening by Incorporating Customized ZBG Features: A Case Study Using Histone Deacetylase 8. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KrennHrubec, K.; Marshall, B.L.; Hedglin, M.; Verdin, E.; Ulrich, S.M. Design and evaluation of ‘Linkerless’ hydroxamic acids as selective HDAC8 inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 2874–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Chao, S.; Yang, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Hou, W.; Chen, M.; Lee, T.; Yang, P.; et al. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of ortho-Aryl N-Hydroxycinnamides as Potent Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) 8 Isoform-Selective Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 1815–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthyala, R.; Shin, W.S.; Xie, J.; Sham, Y.Y. Discovery of 1-hydroxypyridine-2-thiones as selective histone deacetylase inhibitors and their potential application for treating leukemia. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 4320–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.S.; Bergstrom, A.; Bonomo, R.A.; Crowder, M.W.; Muthyala, R.; Sham, Y.Y. Discovery of 1-Hydroxypyridine-2(1H)-thione-6-carboxylic Acid as a First-in-Class Low-Cytotoxic Nanomolar Metallo β-Lactamase Inhibitor. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galletti, P.; Quintavalla, A.; Ventrici, C.; Giannini, G.; Cabri, W.; Penco, S.; Gallo, G.; Vincenti, S.; Giacomini, D. Azetidinones as Zinc-Binding Groups to Design Selective HDAC8 Inhibitors. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 1991–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Jung, J.-C.; Avery, M.A. Synthesis of New β-Lactam Analogs and Evaluation of Their Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Activity. Z. Für Naturforschung B 2007, 62, 1459–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ononye, S.N.; VanHeyst, M.D.; Oblak, E.Z.; Zhou, W.; Ammar, M.; Anderson, A.C.; Wright, D.L. Tropolones as Lead-Like Natural Products: The Development of Potent and Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 4, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Słoczyńska, K.; Gunia-Krzyżak, A.; Koczurkiewicz, P.; Wójcik-Pszczoła, K.; Żelaszczyk, D.; Popiół, J.; Pękala, E. Metabolic stability and its role in the discovery of new chemical entities. Acta Pharm. 2019, 69, 345–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flipo, M.; Charton, J.; Hocine, A.; Dassonneville, S.; Deprez, B.; Deprez-Poulain, R. Hydroxamates: Relationships between Structure and Plasma Stability. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6790–6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yamauchi, H. Hinokitiol, a metal chelator derived from natural plants, suppresses cell growth and disrupts androgen receptor signaling in prostate carcinoma cell lines. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunsteiner, M.; Petukhov, P.A. Insights from comprehensive multiple receptor docking to HDAC8. J. Mol. Model. 2012, 18, 3927–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drakontaeidi, A.; Pontiki, E. A Review on Molecular Docking on HDAC Isoforms: Novel Tool for Designing Selective Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16121639
Drakontaeidi A, Pontiki E. A Review on Molecular Docking on HDAC Isoforms: Novel Tool for Designing Selective Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(12):1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16121639
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrakontaeidi, Aliki, and Eleni Pontiki. 2023. "A Review on Molecular Docking on HDAC Isoforms: Novel Tool for Designing Selective Inhibitors" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 12: 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16121639
APA StyleDrakontaeidi, A., & Pontiki, E. (2023). A Review on Molecular Docking on HDAC Isoforms: Novel Tool for Designing Selective Inhibitors. Pharmaceuticals, 16(12), 1639. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16121639





