Jietacin Derivative Inhibits TNF-α-Mediated Inflammatory Cytokines Production via Suppression of the NF-κB Pathway in Synovial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of JD on TNF-α-Stimulated Inflammatory Reaction in Synovial Cells
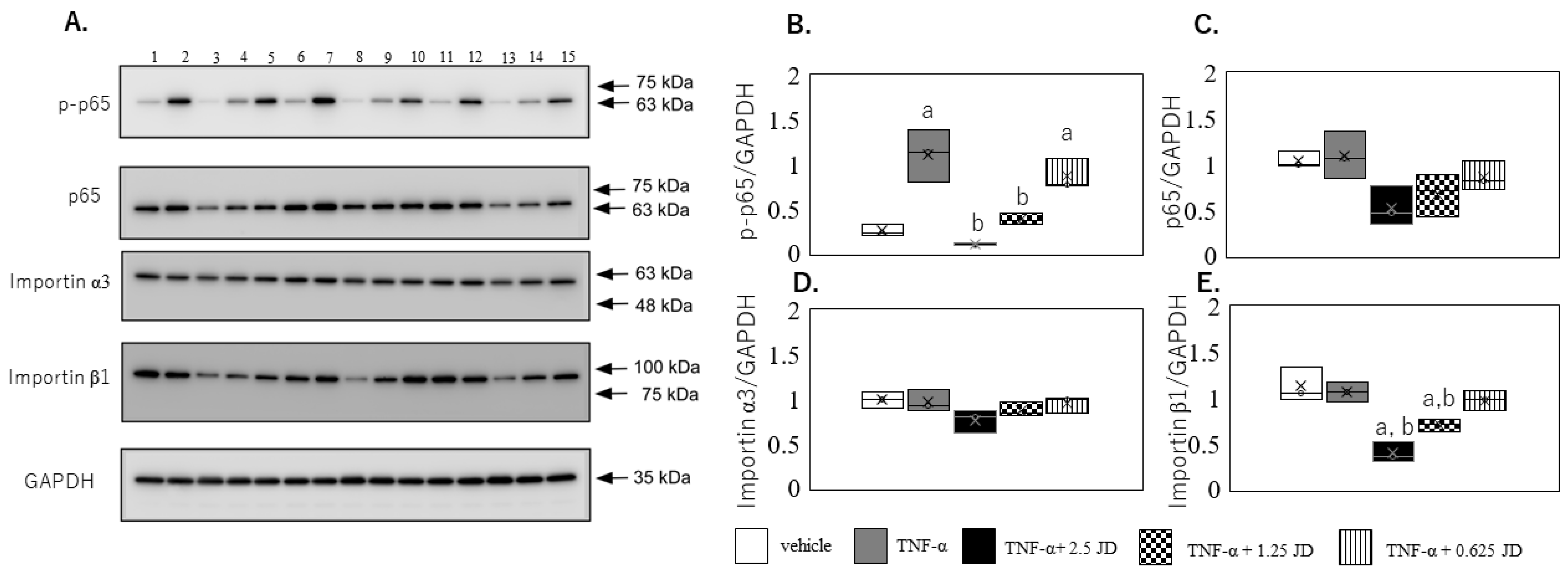
2.2. Effect of JD on NF-κB Pathway
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of JD
3.2. Cell Culture
3.3. RNA-Seq
3.4. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
3.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
3.6. Western Blot
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunter, D.J.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet 2019, 393, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruyere, O.; Cooper, C.; Pelletier, J.P.; Branco, J.; Brandi, M.L.; Guillemin, F.; Hochberg, M.C.; Kanis, J.A.; Kvien, T.K.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; et al. An algorithm recommendation for the management of knee osteoarthritis in Europe and internationally: A report from a task force of the European Society for Clinical and Economic Aspects of Osteoporosis and Osteoarthritis (ESCEO). Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 44, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochberg, M.C.; Altman, R.D.; April, K.T.; Benkhalti, M.; Guyatt, G.; McGowan, J.; Towheed, T.; Welch, V.; Wells, G.; Tugwell, P.; et al. American College of Rheumatology 2012 recommendations for the use of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies in osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, K.M.; Arden, N.K.; Doherty, M.; Bannwarth, B.; Bijlsma, J.W.; Dieppe, P.; Gunther, K.; Hauselmann, H.; Herrero-Beaumont, G.; Kaklamanis, P.; et al. EULAR Recommendations 2003: An evidence based approach to the management of knee osteoarthritis: Report of a Task Force of the Standing Committee for International Clinical Studies Including Therapeutic Trials (ESCISIT). Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlindon, T.E.; Bannuru, R.R.; Sullivan, M.C.; Arden, N.K.; Berenbaum, F.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.; Hawker, G.A.; Henrotin, Y.; Hunter, D.J.; Kawaguchi, H.; et al. OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2014, 22, 363–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, M.J.; Veale, D.J.; FitzGerald, O.; van den Berg, W.B.; Bresnihan, B. Synovial tissue inflammation in early and late osteoarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Hung, M.C. Beyond NF-kappaB activation: Nuclear functions of IkappaB kinase alpha. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabey, T.; Taleongpong, P.; Udomsinprasert, W.; Jirathanathornnukul, N.; Honsawek, S. Plasma and synovial fluid autotaxin correlate with severity in knee osteoarthritis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 444, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdasiewicz, P.; Poniatowski, L.A.; Szukiewicz, D. The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 561459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, Y.Y.; Huebner, J.L.; Haaland, B.; Wong, S.B.S.; Kraus, V.B. Synovial fluid pro-inflammatory profile differs according to the characteristics of knee pain. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2017, 25, 1420–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radojcic, M.R.; Thudium, C.S.; Henriksen, K.; Tan, K.; Karlsten, R.; Dudley, A.; Chessell, I.; Karsdal, M.A.; Bay-Jensen, A.C.; Crema, M.D.; et al. Biomarker of extracellular matrix remodelling C1M and proinflammatory cytokine interleukin 6 are related to synovitis and pain in end-stage knee osteoarthritis patients. Pain 2017, 158, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pein, M.; Insua-Rodriguez, J.; Hongu, T.; Riedel, A.; Meier, J.; Wiedmann, L.; Decker, K.; Essers, M.A.G.; Sinn, H.P.; Spaich, S.; et al. Metastasis-initiating cells induce and exploit a fibroblast niche to fuel malignant colonization of the lungs. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarnaz, J.D.; Ren, H.; Torres, A.A.; Shmeleva, E.V.; Melo, C.A.; Bannister, A.J.; Brember, M.P.; Chung, B.Y.; Smith, G.L. Molecular mimicry of NF-kappaB by vaccinia virus protein enables selective inhibition of antiviral responses. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 154–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deligiannidou, G.E.; Papadopoulos, R.E.; Kontogiorgis, C.; Detsi, A.; Bezirtzoglou, E.; Constantinides, T. Unraveling Natural Products’ Role in Osteoarthritis Management-An Overview. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Xie, W.; Huang, D.; Cui, Y.; Yue, J.; He, Q.; Jiang, L.; Xiong, J.; Sun, W.; Yi, Q. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester attenuates osteoarthritis progression by activating NRF2/HO1 and inhibiting the NFkappaB signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 50, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imamura, N.; Kuga, H.; Otoguro, K.; Tanaka, H.; Omura, S. Structures of jietacines: Unique alpha,beta-unsaturated azoxy antibiotics. J. Antibiot. 1989, 42, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, S.; Otoguro, K.; Imamura, N.; Kuga, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Masuma, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Su, X.H.; You, E.T. Jietacins A and B, new nematocidal antibiotics from a Streptomyces sp. Taxonomy, isolation, and physico-chemical and biological properties. J. Antibiot. 1987, 40, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Sugawara, A.; Noguchi, Y.; Hirose, T.; Omura, S.; Sunazuka, T.; Horie, R. Jietacins, azoxy natural products, as novel NF-kappaB inhibitors: Discovery, synthesis, biological activity, and mode of action. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 178, 636–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansai, M.; Phitak, T.; Klangjorhor, J.; Udomrak, S.; Fanhchaksai, K.; Pothacharoen, P.; Kongtawelert, P. Effects of sesamin on primary human synovial fibroblasts and SW982 cell line induced by tumor necrosis factor-alpha as a synovitis-like model. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stannus, O.; Jones, G.; Cicuttini, F.; Parameswaran, V.; Quinn, S.; Burgess, J.; Ding, C. Circulating levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha are associated with knee radiographic osteoarthritis and knee cartilage loss in older adults. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2010, 18, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Manrique, M.; Calvet, J.; Orellana, C.; Berenguer-Llergo, A.; Garcia-Cirera, S.; Llop, M.; Albinana-Gimenez, N.; Galisteo-Lencastre, C.; Gratacos, J. Synovial fluid but not plasma interleukin-8 is associated with clinical severity and inflammatory markers in knee osteoarthritis women with joint effusion. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Guo, S.; Cong, H.; Liu, L. Analysis on the expression and value of CCL2 and CCL3 in patients with osteoarthritis. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2021, 118, 104576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Tan, J.; Yuan, Z.; Meng, G.; Bi, L.; Liu, J. Expression profile of cytokines and chemokines in osteoarthritis patients: Proinflammatory roles for CXCL8 and CXCL11 to chondrocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 40, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Li, Y.; Ding, L.B.; Liu, G.Y.; Zheng, X.F.; Xue, W.; Wang, H.J. Relationship between serum and synovial fluid CCL20 concentrations with disease severity in primary knee osteoarthritis. J. Musculoskelet. Neuronal Interact. 2019, 19, 326–332. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, M.D.; Triantafillou, S.; Parker, A.; Youssef, P.P.; Coleman, M. Synovial membrane inflammation and cytokine production in patients with early osteoarthritis. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 24, 365–371. [Google Scholar]
- Doss, F.; Menard, J.; Hauschild, M.; Kreutzer, H.J.; Mittlmeier, T.; Muller-Steinhardt, M.; Muller, B. Elevated IL-6 levels in the synovial fluid of osteoarthritis patients stem from plasma cells. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2007, 36, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, A.S., Jr. The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996, 14, 649–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumann, M.; Scheidereit, C. Activation of NF-kappa B in vivo is regulated by multiple phosphorylations. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 4597–4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, P.; Ye, Z.S.; Baltimore, D. RAG-1 interacts with the repeated amino acid motif of the human homologue of the yeast protein SRP1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 7633–7637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, C.A.; Kirch, S.A.; Gyuris, J.; Brent, R.; Oettinger, M.A. Rch1, a protein that specifically interacts with the RAG-1 recombination-activating protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 6156–6160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, M.; Ansieau, S.; Prehn, S.; Leutz, A.; Haller, H.; Hartmann, E. Cloning of two novel human importin-alpha subunits and analysis of the expression pattern of the importin-alpha protein family. FEBS Lett. 1997, 417, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, M.; Speck, C.; Christiansen, M.; Bischoff, F.R.; Prehn, S.; Haller, H.; Gorlich, D.; Hartmann, E. Evidence for distinct substrate specificities of importin alpha family members in nuclear protein import. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 7782–7791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, T.; Tada, S.; Katada, T.; Enomoto, T. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a novel importin-alpha homologue, Qip1: Discrimination of Qip1 and Rch1 from hSrp1 by their ability to interact with DNA helicase Q1/RecQL. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 234, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejomurtula, J.; Lee, K.B.; Tripurani, S.K.; Smith, G.W.; Yao, J. Role of importin alpha8, a new member of the importin alpha family of nuclear transport proteins, in early embryonic development in cattle. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 81, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlich, D.; Kutay, U. Transport between the cell nucleus and the cytoplasm. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1999, 15, 607–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harel, A.; Forbes, D.J. Importin beta: Conducting a much larger cellular symphony. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokin, A.V.; Kim, E.R.; Ovchinnikov, L.P. Nucleocytoplasmic transport of proteins. Biochemistry 2007, 72, 1439–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, T.J.; Lokareddy, R.K.; Yeggoni, D.P.; Sankhala, R.S.; Ott, C.A.; Gillilan, R.E.; Cingolani, G. Differential recognition of canonical NF-kappaB dimers by Importin alpha3. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Li, S.; Cong, S.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, B. KPNB1, XPO7 and IPO8 mediate the translocation ofNF-kappaB/p65 into the nucleus. Traffic 2013, 14, 1132–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, U.; Aggarwal, B.B. Regulation of proliferation, survival and apoptosis by members of the TNF superfamily. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 66, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, S.; Ye, J.; Bai, S.; Huang, F.; Guo, Y.L. NF-kappaB, but not p38 MAP kinase, is required for TNF-alpha-induced expression of cell adhesion molecules in endothelial cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2008, 105, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Tetsuka, T.; Yoshida, S.; Watanabe, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Matsui, N.; Okamoto, T. The role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in IL-6 and IL-8 production from the TNF-alpha- or IL-1beta-stimulated rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 2000, 465, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
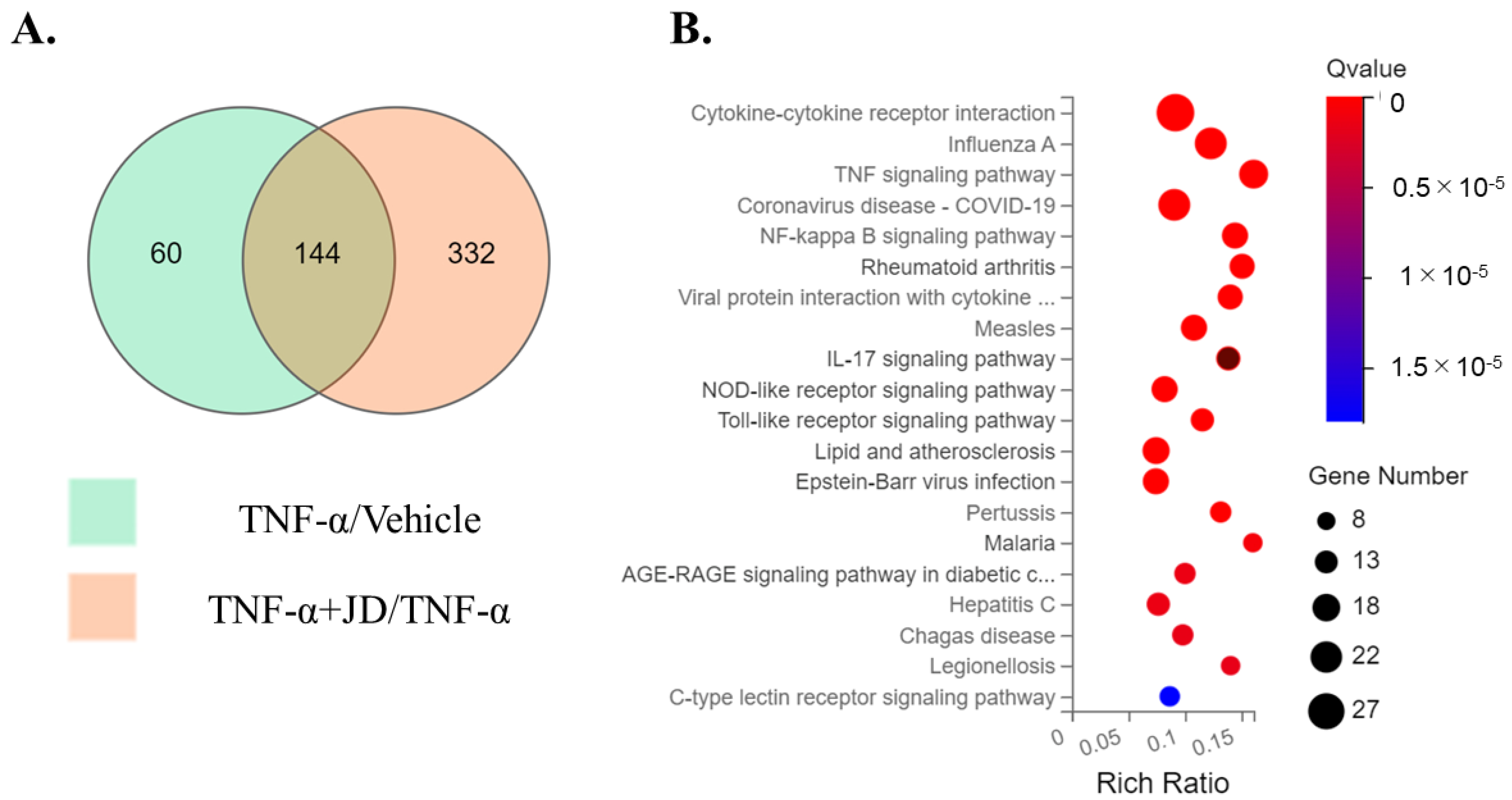





| KEGG Pathway | Gene Symbol | TNF/Vehicle | TNF + JD/TNF | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Log2 FC | Q-Value | Log2 FC | Q-Value | ||
| C | ACKR4 | 2.12 | 9.25 × 10−6 | −2.61 | 1.12 × 10−6 |
| N | BCL2A1 | 5.13 | 3.58 × 10−5 | −4.61 | 1.47 × 10−91 |
| N/T | BIRC3 | 4.50 | 0 | −4.79 | 8.37 × 10−277 |
| C | BMP4 | 3.78 | 1.88 × 10−38 | −3.57 | 3.03 × 10−36 |
| C/R/T | CCL2 | 4.26 | 0 | −4.25 | 4.01 × 10−292 |
| C/R/T | CCL20 | 5.39 | 1.13 × 10−2 | −3.57 | 8.66 × 10−12 |
| C/R | CCL3 | 6.65 | 3.09 × 10−8 | −2.10 | 2.45 × 10−5 |
| C/R/T | CCL5 | 4.33 | 2.99 × 10−111 | −3.86 | 5.14 × 10−89 |
| C/R/T | CSF2 | 7.01 | 2.41 × 10−27 | −4.92 | 1.42 × 10−11 |
| C/T | CXCL10 | 8.52 | 6.82 × 10−36 | −5.49 | 1.79 × 10−7 |
| C | CXCL11 | 7.69 | 4.85 × 10−34 | −7.12 | 3.62 × 10−37 |
| C/R/T | CXCL5 | 2.79 | 1.58 × 10−6 | −2.44 | 2.56 × 10−5 |
| C/R/T | CXCL8 (IL8) | 6.64 | 0 | −2.39 | 2.58 × 10−140 |
| C | CXCL9 | 5.60 | 3.51 × 10−2 | −5.44 | 2.57 × 10−2 |
| N | DDX58 | 3.10 | 1.38 × 10−194 | −3.47 | 1.89 × 10−200 |
| C | EBI3 | 3.11 | 2.40 × 10−4 | −2.31 | 3.15 × 10−3 |
| C | GDF6 | −2.32 | 6.02 × 10−11 | 2.37 | 1.19 × 10−10 |
| N/R/T | ICAM1 | 4.49 | 0 | −3.73 | 1.07 × 10−297 |
| C/R | IL1A | 5.46 | 1.11 × 10−100 | −3.68 | 8.14 × 10−78 |
| C/N/R/T | IL1B | 5.52 | 0 | −4.74 | 0 |
| C | IL32 | 3.65 | 1.25 × 10−128 | −3.53 | 4.70 × 10−101 |
| C | IL34 | 3.17 | 1.33 × 10−10 | −3.72 | 1.10 × 10−11 |
| C | IL3RA | 5.86 | 3.61 × 10−3 | −7.14 | 1.09 × 10−4 |
| C/R/T | IL6 | 5.05 | 0 | −3.47 | 9.57 × 10−29 |
| Cyto | INHBA | 2.09 | 8.81 × 10−111 | −2.57 | 3.21 × 10−128 |
| T | IRF1′ | 2.50 | 7.42 × 10−103 | −2.41 | 4.09 × 10−66 |
| C/T | LIF’ | 2.86 | 4.49 × 10−281 | −3.41 | 3.37 × 10−195 |
| T | MMP9 | 5.86 | 3.57 × 10−3 | −4.69 | 1.41 × 10−3 |
| N | NFKB2 | 2.74 | 1.33 × 10−125 | −2.54 | 2.31 × 10−91 |
| N/T | NFKBIA | 3.06 | 1.19 × 10−192 | −2.94 | 1.94 × 10−141 |
| N | PLCG2 | 2.39 | 3.31 × 10−2 | 3.64 | 1.04 × 10−28 |
| N | RELB | 2.79 | 3.15 × 10−2 | −2.36 | 7.73 × 10−65 |
| R | TLR2 | 2.84 | 2.27 × 10−66 | −2.69 | 1.49 × 10−52 |
| C/N/T/R | TNF’ | 6.04 | 2.18 × 10−18 | −2.22 | 4.41 × 10−10 |
| N/T | TNFAIP3 | 4.22 | 0 | −4.18 | 0 |
| C | TNFRSF11B | 2.38 | 1.44 × 10−74 | −2.12 | 1.20 × 10−52 |
| C | TNFRSF9 | 4.62 | 4.37 × 10−53 | −4.11 | 2.99 × 10−45 |
| C | TNFSF10 | 4.60 | 2.12 × 10−4 | −5.02 | 2.82 × 10−4 |
| C/N/R/T | TNFSF13B | 4.33 | 8.79 × 10−23 | −3.32 | 4.33 × 10−17 |
| N/T | TRAF1 | 4.73 | 3.09 × 10−237 | −4.20 | 1.13 × 10−167 |
| N/T | VCAM1 | 5.83 | 1.44 × 10−195 | −6.68 | 7.78 × 10−153 |
| Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| IL1B-F | GTACCTGTCCTGCGTGTTGA | 153 |
| IL1B-R | GGGAACTGGGCAGACTCAAA | |
| IL6-F | GAGGAGACTTGCCTGGTGAAA | 199 |
| IL6-R | TGGCATTTGTGGTTGGGTCA | |
| IL8-F | ACACTGCGCCAACACAGAAA | 89 |
| IL8-R | CAACCCTCTGCACCCAGTTT | |
| GAPDH-F | TGTTGCCATCAATGACCCCTT | 202 |
| GAPDH-R | CTCCACGACGTACTCAGCG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muneshige, K.; Inahashi, Y.; Itakura, M.; Iwatsuki, M.; Hirose, T.; Inoue, G.; Takaso, M.; Sunazuka, T.; Ohashi, Y.; Ohta, E.; et al. Jietacin Derivative Inhibits TNF-α-Mediated Inflammatory Cytokines Production via Suppression of the NF-κB Pathway in Synovial Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010005
Muneshige K, Inahashi Y, Itakura M, Iwatsuki M, Hirose T, Inoue G, Takaso M, Sunazuka T, Ohashi Y, Ohta E, et al. Jietacin Derivative Inhibits TNF-α-Mediated Inflammatory Cytokines Production via Suppression of the NF-κB Pathway in Synovial Cells. Pharmaceuticals. 2023; 16(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuneshige, Kyoko, Yuki Inahashi, Makoto Itakura, Masato Iwatsuki, Tomoyasu Hirose, Gen Inoue, Masashi Takaso, Toshiaki Sunazuka, Yoshihisa Ohashi, Etsuro Ohta, and et al. 2023. "Jietacin Derivative Inhibits TNF-α-Mediated Inflammatory Cytokines Production via Suppression of the NF-κB Pathway in Synovial Cells" Pharmaceuticals 16, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010005
APA StyleMuneshige, K., Inahashi, Y., Itakura, M., Iwatsuki, M., Hirose, T., Inoue, G., Takaso, M., Sunazuka, T., Ohashi, Y., Ohta, E., & Uchida, K. (2023). Jietacin Derivative Inhibits TNF-α-Mediated Inflammatory Cytokines Production via Suppression of the NF-κB Pathway in Synovial Cells. Pharmaceuticals, 16(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16010005






