Arabinoxylans-Based Oral Insulin Delivery System Targeting the Colon: Simulation in a Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem and Evaluation in Diabetic Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
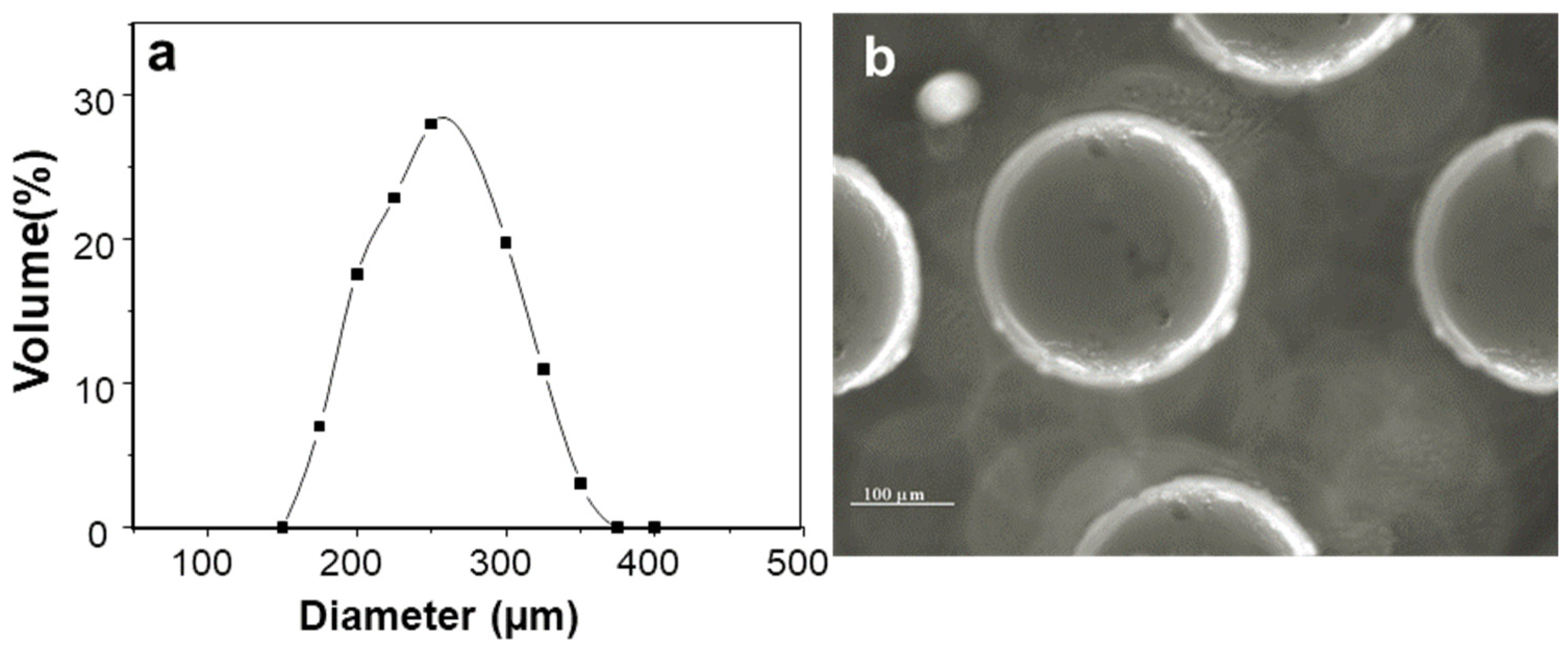
2.1. Characterization of Insulin-Loaded AX Microcapsules
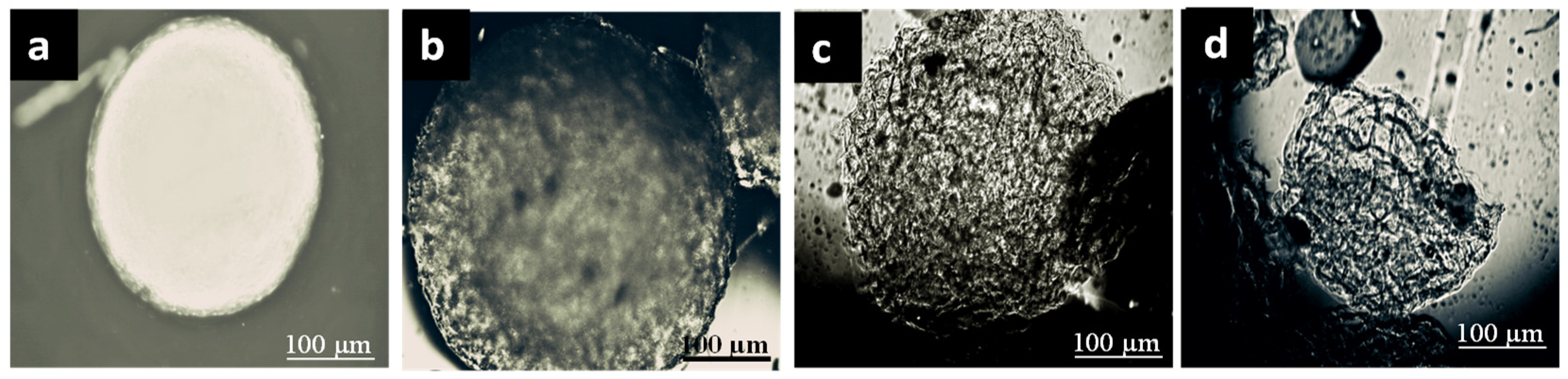
2.2. Morphology Changes of Insulin-Loaded AX Microcapsules in the Simulated Human G.I. Environment
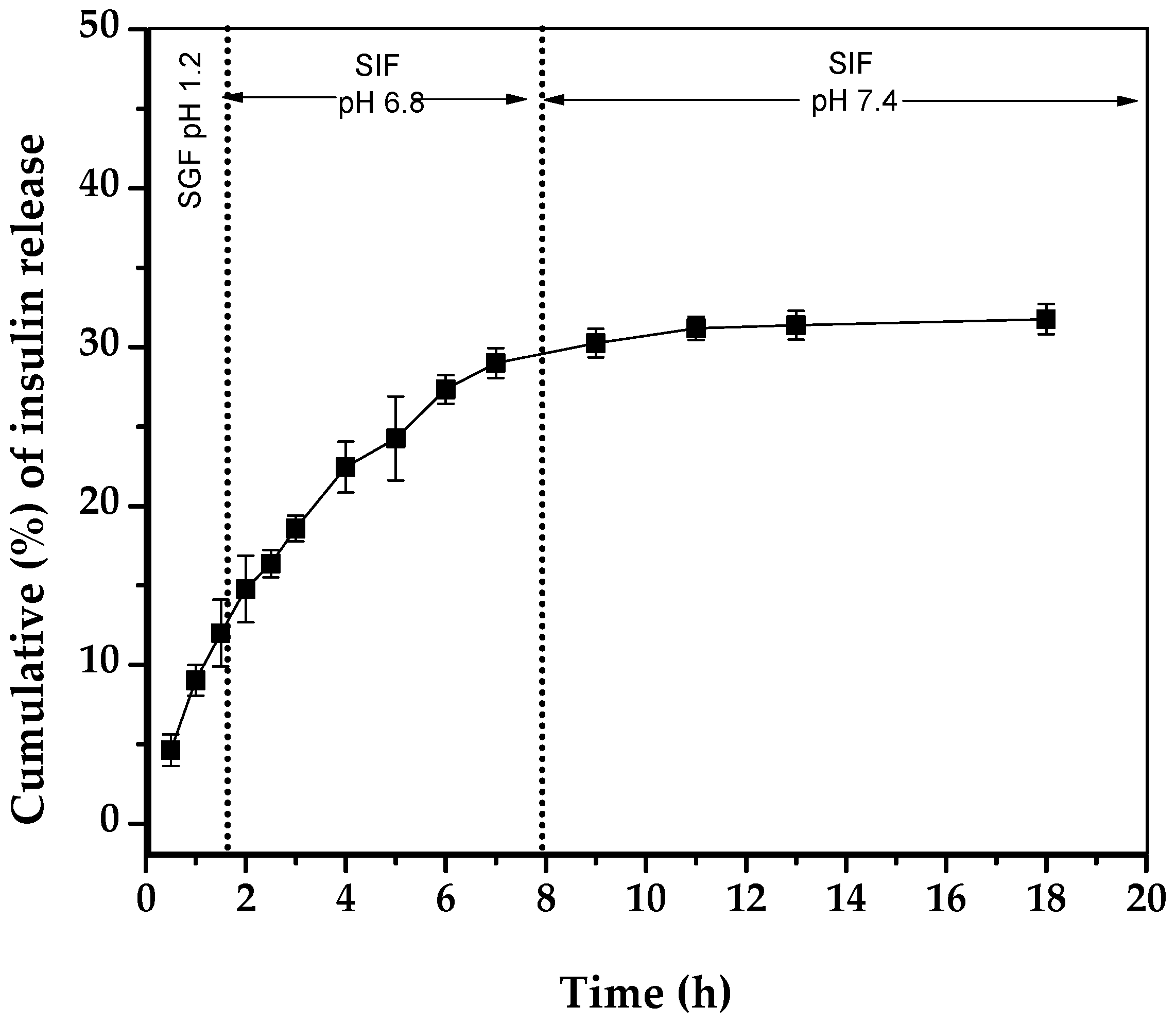
2.3. In Vitro Insulin Release
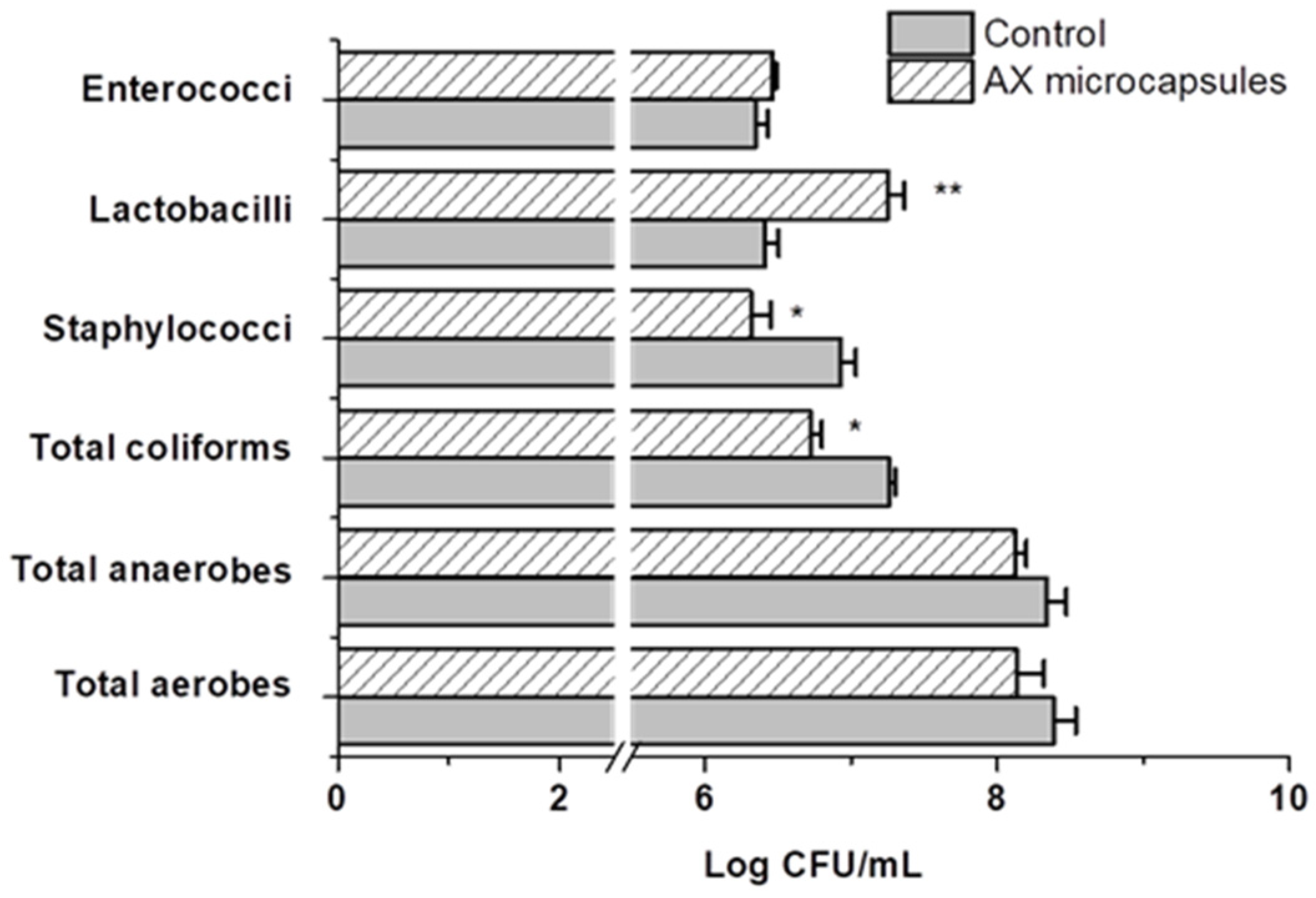
2.4. Effect of AX Microcapsules on the Simulated Gut Microbiota
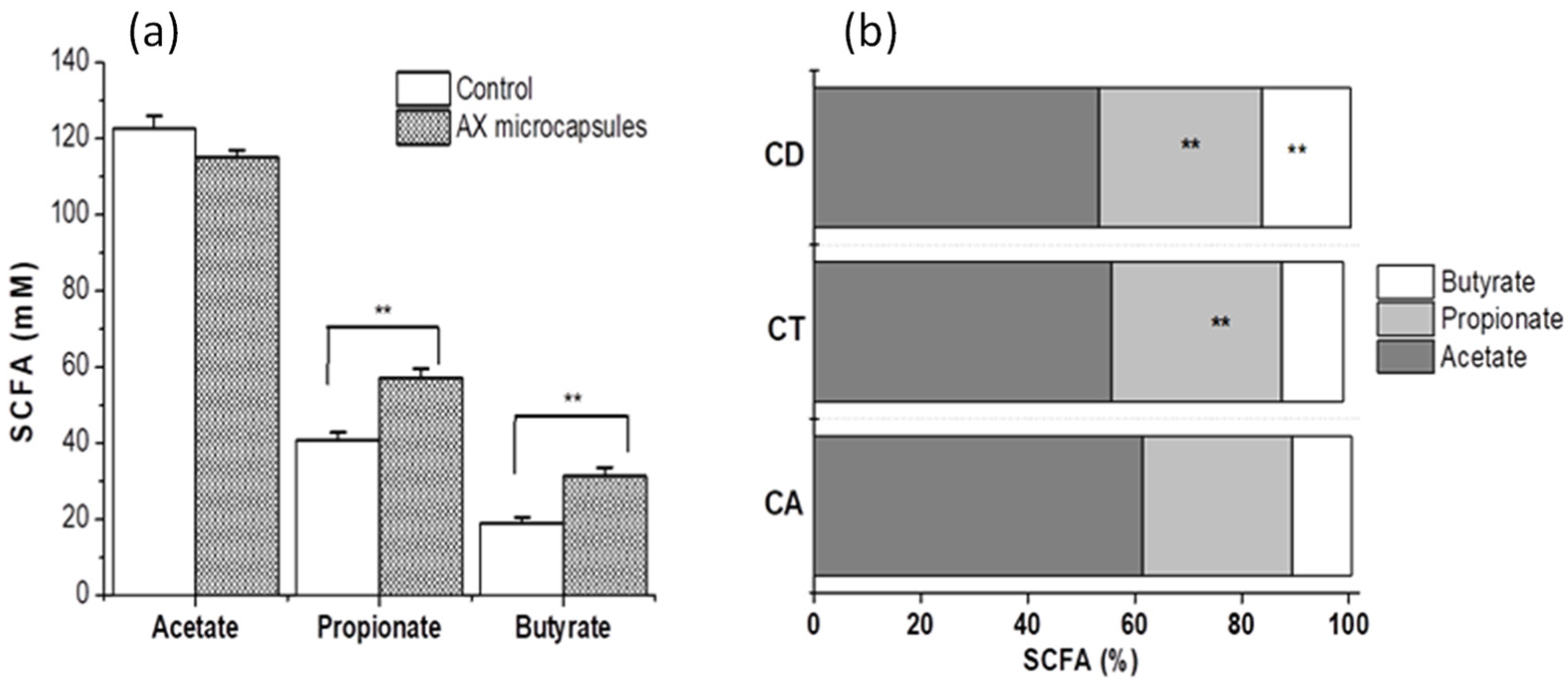
2.5. Metabolic Activity
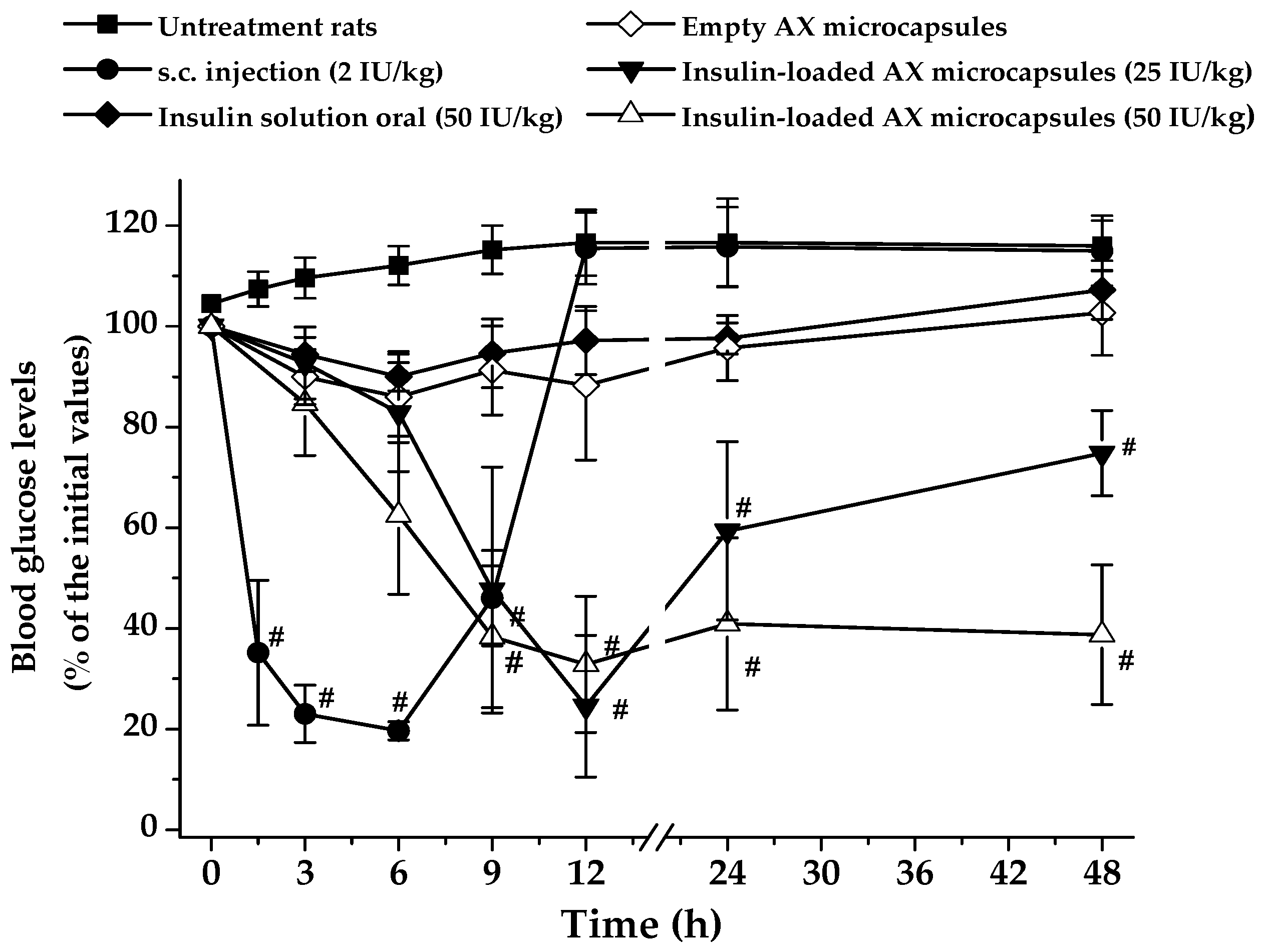
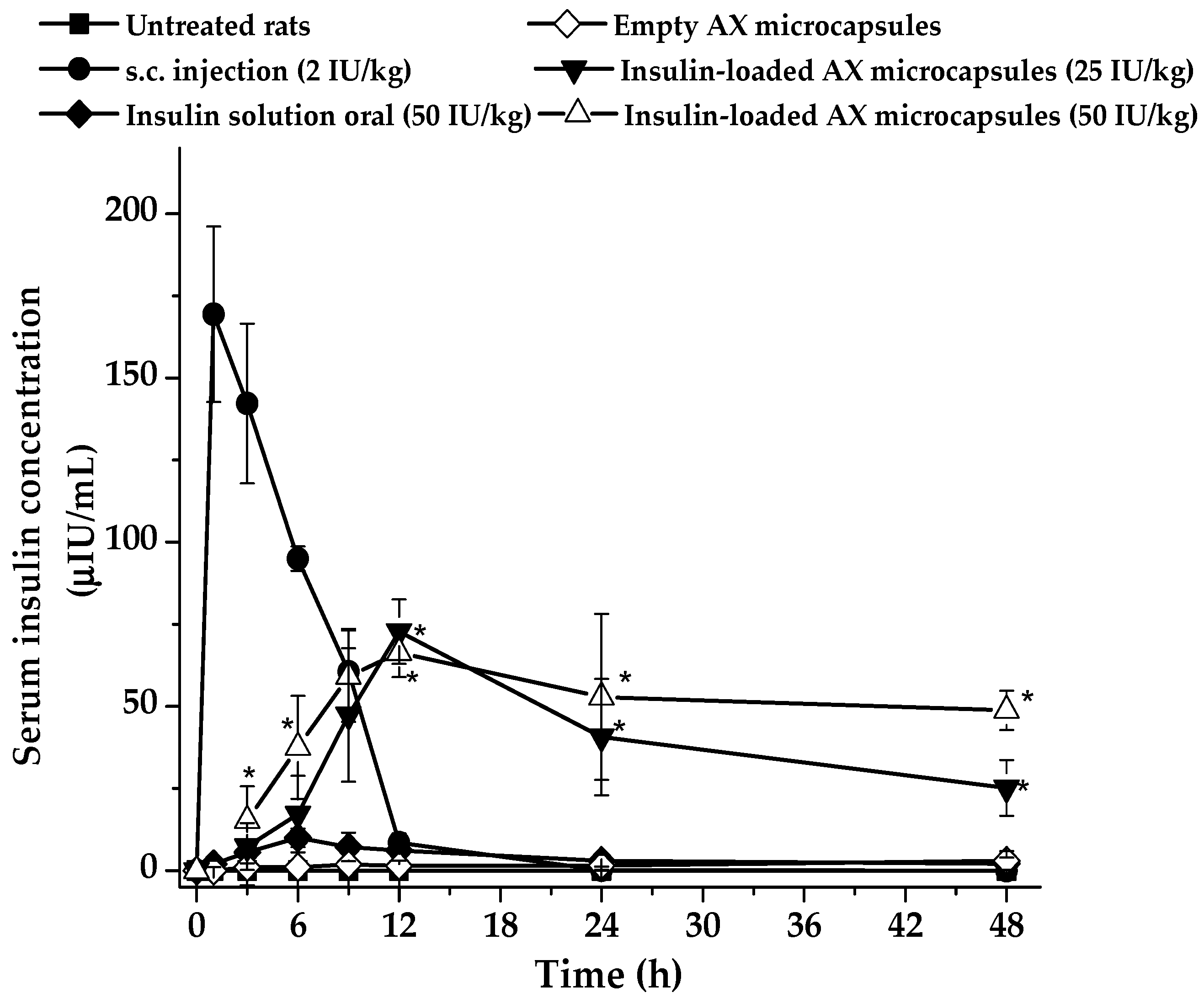
2.6. Hypoglycemic Effect and In Vivo Bioavailability of Insulin
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Microencapsulation of Insulin
3.3. Characterization of Insulin-Loaded AX Microcapsules
3.4. Study of Insulin-Loaded AX Microcapsules in a Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem (SHIME)
3.4.1. Simulation of the Human Gastrointestinal (G.I.) Tract
3.4.2. Morphology Changes of Insulin-Loaded AX Microcapsules in the Simulated Human G.I. Environment
3.4.3. Effect of AX Microcapsules on the Simulated Gut Microflora and Production of Metabolites
3.5. In Vitro Release of Insulin
3.6. Study of Insulin-Loaded AX Microcapsules in Diabetic Rats
3.6.1. Animals
3.6.2. Hypoglycemic Effect and Bioavailability
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iyer, G.; Dyawanapelly, S.; Jain, R.; Dandekar, P. An Overview of Oral Insulin Delivery Strategies (OIDS). Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 208, 565–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbagh, F.; Muhamad, I.I.; Niazmand, R.; Dikshit, P.K.; Kim, B.S. Recent Progress in Polymeric Non-Invasive Insulin Delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 203, 222–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroni, A.; Zema, L.; Dorly, M.; Curto, D.; Foppoli, A.; Gazzaniga, A. Oral Colon Delivery of Insulin with the Aid of Functional Adjuvants. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L. Biorelevant Dissolution Testing of Colon-Specific Delivery Systems Activated by Colonic Microflora. J. Control. Release 2008, 125, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Anda-Flores, Y.; Rascón-Chu, A.; Campa-Mada, A.C.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Tanori-Cordova, J.; Carvajal-Millan, E. Polysaccharides Nanoparticles as Oral Drug Delivery Systems. In Natural Polysaccharides in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, S.F.; Gullon, B.; Gullon, P.; Ferreira, S.; Maia, C.J.; Alonso, J.L.; Domingues, F.C.; Abu-Ghannam, N. Evaluation of the Prebiotic Potential of Arabinoxylans from Brewer’s Spent Grain. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9365–9373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assor Antoine, C.; Cassan, D.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Bouchoux, A.; Micard, V. Making Dense Covalent Arabinoxylan Gels with High Swelling Properties: A Strategy Based on Water Extraction through Osmotic Compression. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 6176–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alejandra Mendez-Encinas, M.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Rascon-Chu, A.; Astiazaran-Garcia, H.F.; Valencia-Rivera, D.E. Review Article Ferulated Arabinoxylans and Their Gels: Functional Properties and Potential Application as Antioxidant and Anticancer Agent. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 2314759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupfer, E.; Pak, S.C.; Wang, S.; Micalos, P.S.; Jeffries, T.; Ooi, S.L.; Golombick, T.; Harris, G.; El-Omar, E. The Effects and Benefits of Arabinoxylans on Human Gut Microbiota—A Narrative Review. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, A.L.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Micard, V.; Rascón-Chu, A.; Brown-Bojorquez, F.; Sotelo-Cruz, N.; López-Franco, Y.L.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J. In Vitro Degradation of Covalently Cross-Linked Arabinoxylan Hydrogels by Bifidobacteria. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 144, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, A.L.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Sotelo-Cruz, N.; Micard, V.; Rascón-Chu, A.; López-Franco, Y.L.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Canett-Romero, R. Enzymatically Cross-Linked Arabinoxylan Microspheres as Oral Insulin Delivery System. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 126, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Burgos, A.M.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Sotelo-Cruz, N.; Rascón-Chu, A.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; López-Franco, Y.L.; Martínez-Porchas, M.; Canett-Romero, R. Highly Cross-Linked Arabinoxylans Microspheres as a Microbiota-Activated Carrier for Colon-Specific Insulin Delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 163, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rascón-Chu, A.; Díaz-Baca, J.A.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Pérez-López, E.; Hotchkiss, A.T.; González-Ríos, H.; Balandrán-Quintana, R.; Campa-Mada, A.C. Electrosprayed Core-Shell Composite Microbeads Based on Pectin-Arabinoxylans for Insulin Carrying: Aggregation and Size Dispersion Control. Polymer 2018, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possemiers, S.; Verthé, K.; Uyttendaele, S.; Verstraete, W. PCR-DGGE-Based Quantification of Stability of the Microbial Community in a Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2004, 49, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molly, K.; Vande Woestyne, M.; Verstraete, W. Development of a 5-Step Multi-Chamber Reactor as a Simulation of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1993, 39, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassani, L.; Gomez-Zavaglia, A.; Simal-Gandara, J. Technological Strategies Ensuring the Safe Arrival of Beneficial Microorganisms to the Gut: From Food Processing and Storage to Their Passage through the Gastrointestinal Tract. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Kim, S.S. Multishell Encapsulation Using a Triple Coaxial Electrospray System. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4644–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Qiao, X.; Hong, W.; Dong, L. Core-Shell Microcapsules with Embedded Microactuators for Regulated Release. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 2013, 22, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, Q.; Qiao, J.; Gao, X.; Nie, J.; Yang, D. Preparation of Chitosan/Alginate Microcapsules by High-Voltage Electrostatic Method. Front. Chem. China 2011, 6, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crittenden, R.; Karppinen, S.; Ojanen, S.; Tenkanen, M.; Fagerstrm, R.; Mtt, J.; Saarela, M.; Mattila-Sandholm, T.; Poutanen, K. In Vitro Fermentation of Cereal Dietary Fibre Carbohydrates by Probiotic and Intestinal Bacteria. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 82, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Abbeele, P.; Venema, K.; van de Wiele, T.; Verstraete, W.; Possemiers, S. Different Human Gut Models Reveal the Distinct Fermentation Patterns of Arabinoxylan versus Inulin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 9819–9827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, H.K.; Gudmundsdottir, V.; Nielsen, H.B.; Hyotylainen, T.; Nielsen, T.; Jensen, B.A.H.; Forslund, K.; Hildebrand, F.; Prifti, E.; Falony, G.; et al. Human Gut Microbes Impact Host Serum Metabolome and Insulin Sensitivity. Nature 2016, 535, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Indias, I.; Sánchez-Alcoholado, L.; García-Fuentes, E.; Cardona, F.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I.; Tinahones, F.J. Insulin Resistance Is Associated with Specific Gut Microbiota in Appendix Samples from Morbidly Obese Patients. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 5672–5684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, M.J.; Englyst, H.N.; Macfarlane, S.; Furrie, E.; Macfarlane, G.T.; Andrew, J.; Mcbain, A.J. Degradation of Cross-Linked and Non-Cross-Linked Arabinoxylans by the Intestinal Microbiota in Children. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 6354–6360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grootaert, C.; van den Abbeele, P.; Marzorati, M.; Broekaert, W.F.; Courtin, C.M.; Delcour, J.A.; Verstraete, W.; van de Wiele, T. Comparison of Prebiotic Effects of Arabinoxylan Oligosaccharides and Inulin in a Simulator of the Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 69, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Long, W.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; Zhao, L.; Hamaker, B.R. Fiber-Utilizing Capacity Varies in Prevotella- versus Bacteroides-Dominated Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Abbeele, P.; Grootaert, C.; Marzorati, M.; Possemiers, S.; Verstraete, W.; Gérard, P.; Rabot, S.; Bruneau, A.; Aidy Ei, S.; Derrien, M.; et al. Microbial Community Development in a Dynamic Gut Model Is Reproducible, Colon Region Specific, and Selective for Bacteroidetes and Clostridium Cluster IX. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5237–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendis, M.; Simsek, S. Arabinoxylans and Human Health. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 42, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartvigsen, M.L.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Lærke, H.N.; Njabe, E.N.; Knudsen, K.E.B.; Hermansen, K. Concentrated Arabinoxylan in Wheat Bread Has Beneficial Effects as Rye Breads on Glucose and Changes in Gene Expressions in Insulin-Sensitive Tissues of Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5054–5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, B.; Gallaher, D.D.; Bunzel, M. Influence of Cross-Linked Arabinoxylans on the Postprandial Blood Glucose Response in Rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3847–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izydorczyk, M.S.; Biliaderis, C.G. Cereal Arabinoxylans: Advances in Structure and Physicochemical Properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 1995, 28, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, A.L.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; López-Franco, Y.L.; Rascón-Chu, A.; Salas-Muñoz, E.; Barron, C.; Micard, V. The Peroxidase/H2O2 System as a Free Radical-Generating Agent for Gelling Maize Bran Arabinoxylans: Rheological and Structural Properties. Molecules 2011, 16, 8410–8418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonaje, K.; Lin, Y.H.; Juang, J.H.; Wey, S.P.; Chen, C.T.; Sung, H.W. In Vivo Evaluation of Safety and Efficacy of Self-Assembled Nanoparticles for Oral Insulin Delivery. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2329–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Li, L. Modulation of Short-Chain Fatty Acids as Potential Therapy Method for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 6632266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, B.; Ribeiro, A.; Veiga, F.; Sampaio, P.; Neufeld, R.; Ferreira, D. Alginate/Chitosan Nanoparticles Are Effective for Oral Insulin Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 2198–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Ping, Q.; Huang, G.; Xu, W.; Cheng, Y.; Han, X. Lectin-Modified Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers for Oral Administration of Insulin. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 327, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchaurraga, L.; Martínez-López, A.L.; Martin-Arbella, N.; Irache, M. Zein-Based Nanoparticles for the Oral Delivery of Insulin. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2020, 10, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-López, A.L.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; López-Franco, Y.; Rascón-Chu, A.; Salas-Muñoz, E.; Ramírez-Wong, B. Ferulated Arabinoxylans as By-Product from Maize Wet-Milling Process: Characterization and Gelling Capability; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; ISBN 9781620815144. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Peppas, N.A.; Hennink, W.E.; de Jong, S.J.; Bos, G.W.; Veldhuis, T.F.J.; van Nostrum, C.F.; Han, Y.; Tian, H.; He, P.; et al. In Vitro Release Behavior and Stability of Insulin in Complexation Hydrogels as Oral Drug Delivery Carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 266, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Yu, W.; Liu, X.; Xie, H.; Wang, W.; Ma, X. In Vitro and in Vivo Characterization of Alginate-Chitosan-Alginate Artificial Microcapsules for Therapeutic Oral Delivery of Live Bacterial Cells. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2008, 105, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodes, L.; Saha, S.; Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Prakash, S. Microencapsulated Bifidobacterium Longum Subsp. Infantis ATCC 15697 Favorably Modulates Gut Microbiota and Reduces Circulating Endotoxins in F344 Rats. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 602832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodes, L.; Tomaro-Duchesneau, C.; Saha, S.; Arghya, P.; Meenaskhi, M.; Marinescu, D.; Shao, W.; Kahouli, I.; Prakash, S. Enrichment of Bifidobacterium Longum Subsp. Infantis ATCC 15697 within the Human Gut Microbiota Using Alginate-Poly-l-lysine-alginate microencapsulation oral delivery system: An in vitro analysis using a computer-controlled dynamic human gastrointestinal model. J. Microencapsul. 2014, 2048, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinttilä, T.; Kassinen, A.; Malinen, E.; Krogius, L.; Palva, A. Development of an Extensive Set of 16S RDNA-Targeted Primers for Quantification of Pathogenic and Indigenous Bacteria in Faecal Samples by Real-Time PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 1166–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastell, H.; Westermann, P.; Meyer, A.S.; Tuomainen, P.; Tenkanen, M. In Vitro Fermentation of Arabinoxylan-Derived Carbohydrates by Bifidobacteria and Mixed Fecal Microbiota. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8598–8606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Xie, S. PKSolver: An Add-in Program for Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Data Analysis in Microsoft Excel. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2010, 99, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Bacterial Group | Group | SHIME Compartment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending | Transverse | Descending | ||
| All bacteria | Control | 8.6 ± 0.3 | 7.8 ± 0.5 | 8.0 ± 0.6 |
| Treatment | 8.8 ± 0.3 | 8.5 ± 0.3 | 8.5 ± 0.2 | |
| Genus Lactobacillus | Control | 6.0 ± 0.1 | 6.4 ± 0.05 | 6.3 ± 0.05 |
| Treatment | 6.9 ± 0.2 * | 6.6 ± 0.1 | 6.3 ± 0.3 | |
| Genus Bifidobacterium | Control | 5.6 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 5.6 ± 0.2 |
| Treatment | 6.4 ± 0.2* | 6.6 ± 0.2 * | 6.9 ± 0.2 * | |
| Phylum Bacteroidetes | Control | 7.6 ± 0.2 | 7.3 ± 0.1 | 6.8 ± 0.4 |
| Treatment | 7.7 ± 0.1 | 7.5 ± 0.2 | 7.3 ± 0.1 | |
| Genus Bacteroides/Prevotella | Control | 9.2 ± 0.3 | 9.1 ± 0.3 | 8.5 ± 0.4 |
| Treatment | 7.4 ± 0.04 * | 8.2 ± 0.2 * | 7.9 ± 0.2 | |
| Family Enterobacteriaceae | Control | 7.9 ± 0.3 | 8.4 ± 0.3 | 8.6 ± 0.3 |
| Treatment | 7.6 ± 0.2 | 7.3 ± 0.2 * | 7.3 ± 0.1 * | |
| Insulin Formulation | Dose (IU/Kg) | AAC(0–48 h) (% h) | Tmax (h) | Cmin (% Basal Glucose) | PA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AX microcapsules | 25 | 1800 ± 260 | 12 | 27.2 ± 9 | 19.9 ± 1.7 *** |
| AX microcapsules | 50 | 2700 ± 320 | 12 | 32.5 ± 7 | 14.2 ± 1.2 *** |
| Oral insulin | 50 | 190 ± 90 | 6 | 89.7 ± 3 | 0.9 ± 0.4 |
| Insulin Formulation | Dose (IU/Kg) | Cmax (µIU/mL) | Tmax (h) | AUC0–48 h (µIU*h/mL) | Kel (h−1) | t1/2 (h) | FR (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| s.c. injection | 2 | 178 ± 27 | 2 | 1197 ± 190 | 0.40 ± 0.041 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 100 |
| AX microcapsules | 25 | 78 ± 19 | 12 * | 1897 ± 390 * | 0.052 ±0.008 | 13 ± 2 | 13 ± 1 |
| AX microcapsules | 50 | 73 ± 25 | 12 * | 2597 ± 650 * | 0.027 ±0.007 | 25 ± 8 | 8.7 ± 0.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-López, A.L.; Carvajal-Millan, E.; Canett-Romero, R.; Prakash, S.; Rascón-Chu, A.; López-Franco, Y.L.; Lizardi-Mendoza, J.; Micard, V. Arabinoxylans-Based Oral Insulin Delivery System Targeting the Colon: Simulation in a Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem and Evaluation in Diabetic Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091062
Martínez-López AL, Carvajal-Millan E, Canett-Romero R, Prakash S, Rascón-Chu A, López-Franco YL, Lizardi-Mendoza J, Micard V. Arabinoxylans-Based Oral Insulin Delivery System Targeting the Colon: Simulation in a Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem and Evaluation in Diabetic Rats. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(9):1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091062
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-López, Ana L., Elizabeth Carvajal-Millan, Rafael Canett-Romero, Satya Prakash, Agustín Rascón-Chu, Yolanda L. López-Franco, Jaime Lizardi-Mendoza, and Valerie Micard. 2022. "Arabinoxylans-Based Oral Insulin Delivery System Targeting the Colon: Simulation in a Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem and Evaluation in Diabetic Rats" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 9: 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091062
APA StyleMartínez-López, A. L., Carvajal-Millan, E., Canett-Romero, R., Prakash, S., Rascón-Chu, A., López-Franco, Y. L., Lizardi-Mendoza, J., & Micard, V. (2022). Arabinoxylans-Based Oral Insulin Delivery System Targeting the Colon: Simulation in a Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem and Evaluation in Diabetic Rats. Pharmaceuticals, 15(9), 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15091062







