Enhanced In Vivo Wound Healing Efficacy of a Novel Hydrogel Loaded with Copper (II) Schiff Base Quinoline Complex (CuSQ) Solid Lipid Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Physicochemical Properties
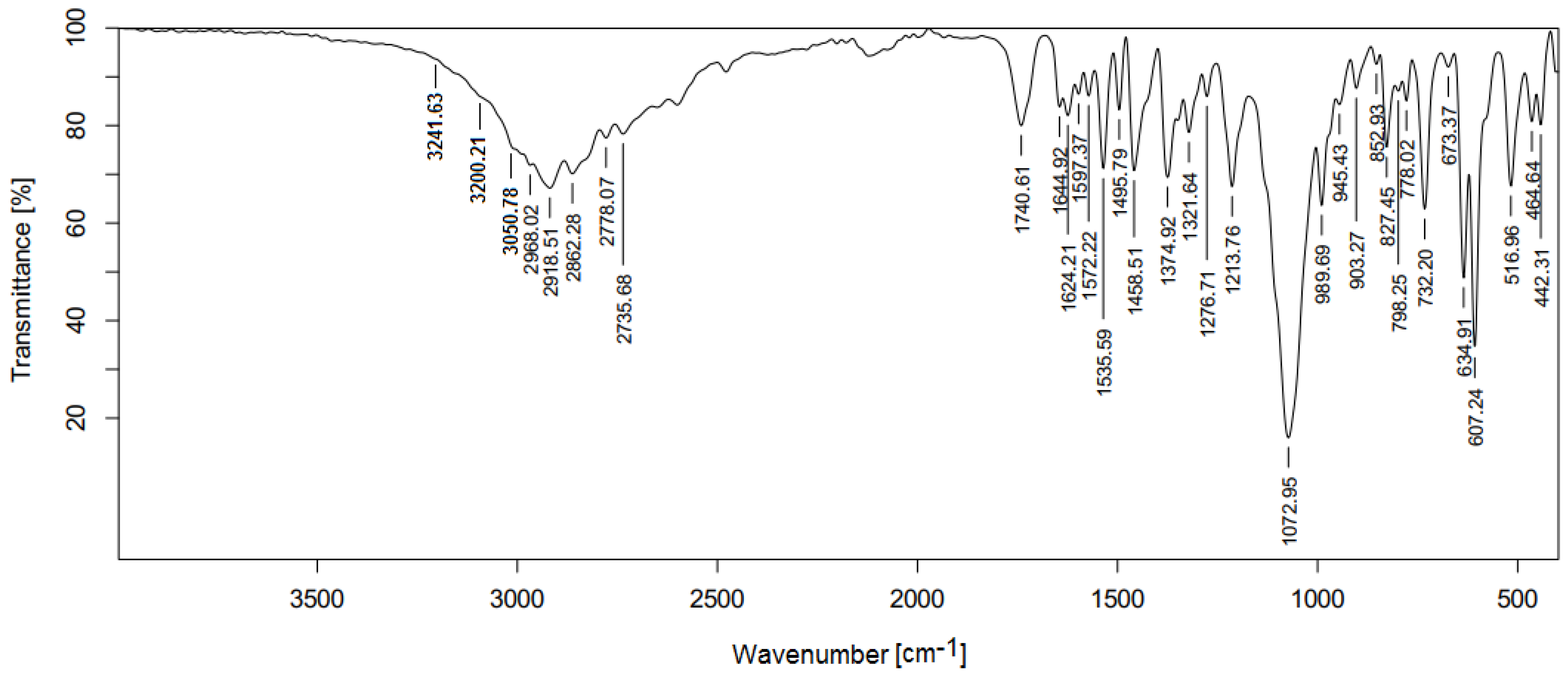
2.2. Fourier Transformation Infrared Spectra (FTIR)
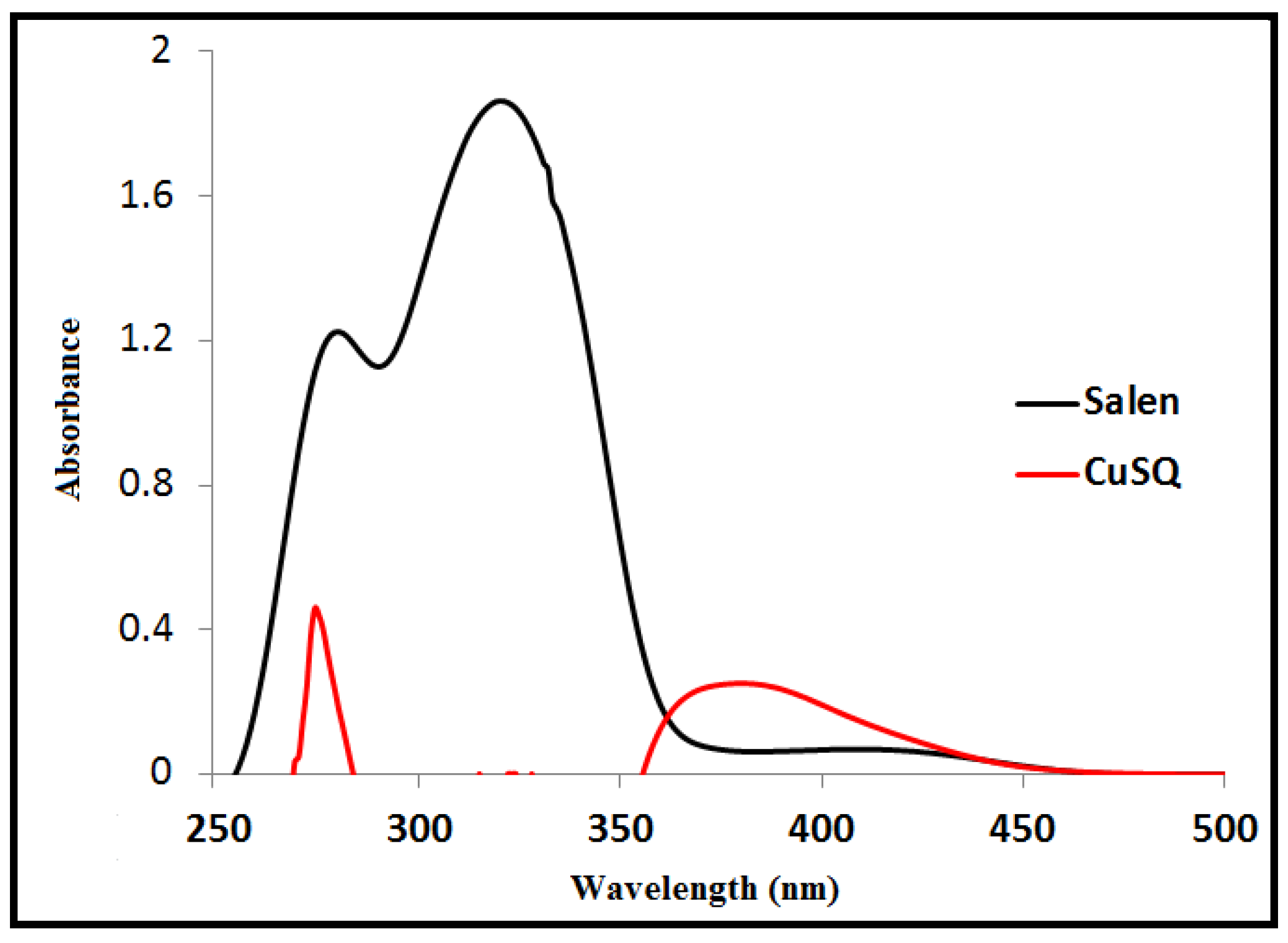
2.3. Electronic Spectra
2.4. Antimicrobial Bioassay
2.5. Characterization of CuSQ-Loaded SLNs
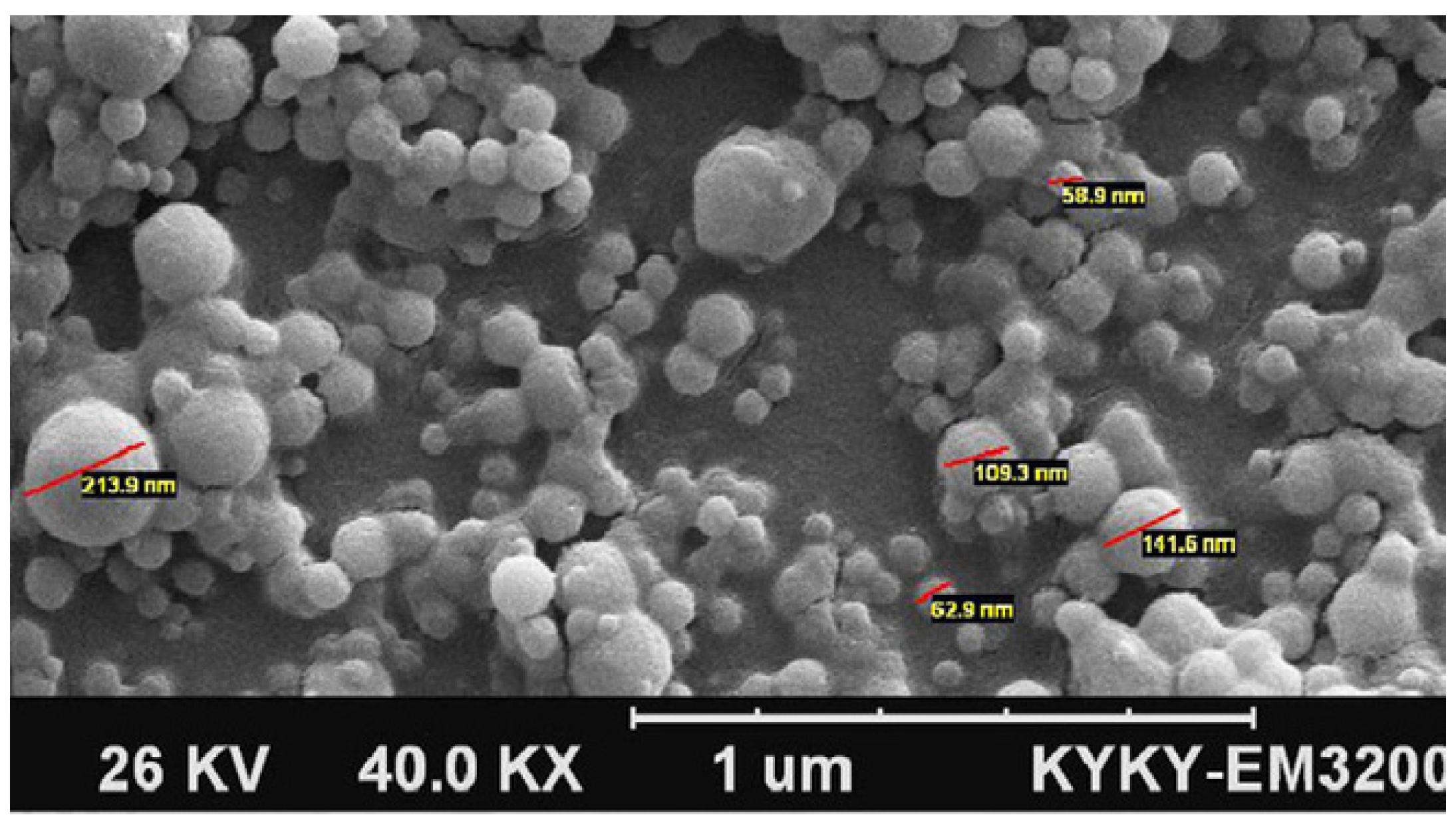
2.5.1. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.5.2. Particle Size, Polydispersity Index (PDI), and Zeta Potential Analysis
2.5.3. Entrapment Efficiency
2.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.7. Evaluation of Hydrogel Physical Characteristic
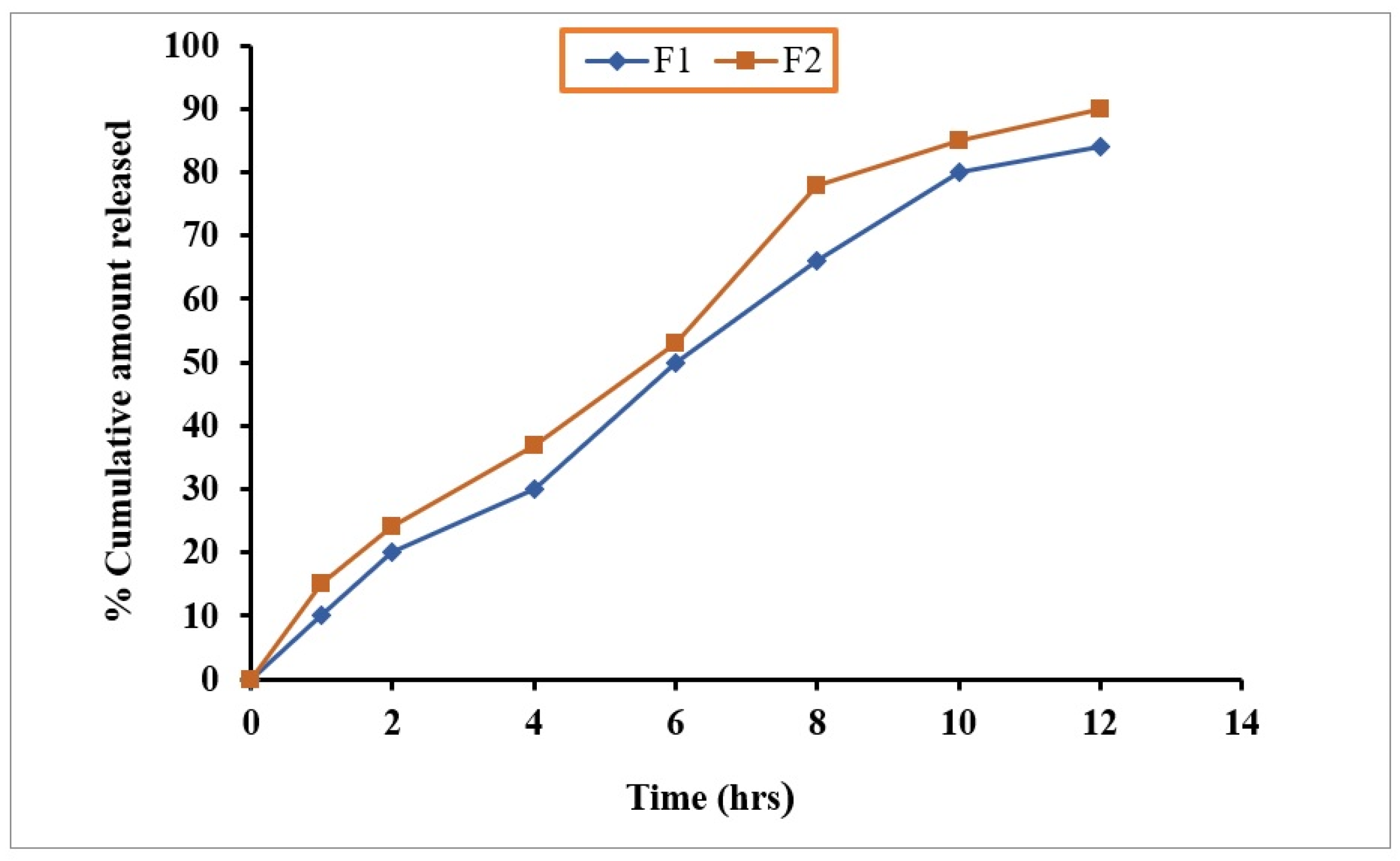
2.8. In Vitro Drug Dissolution of Hydrogel
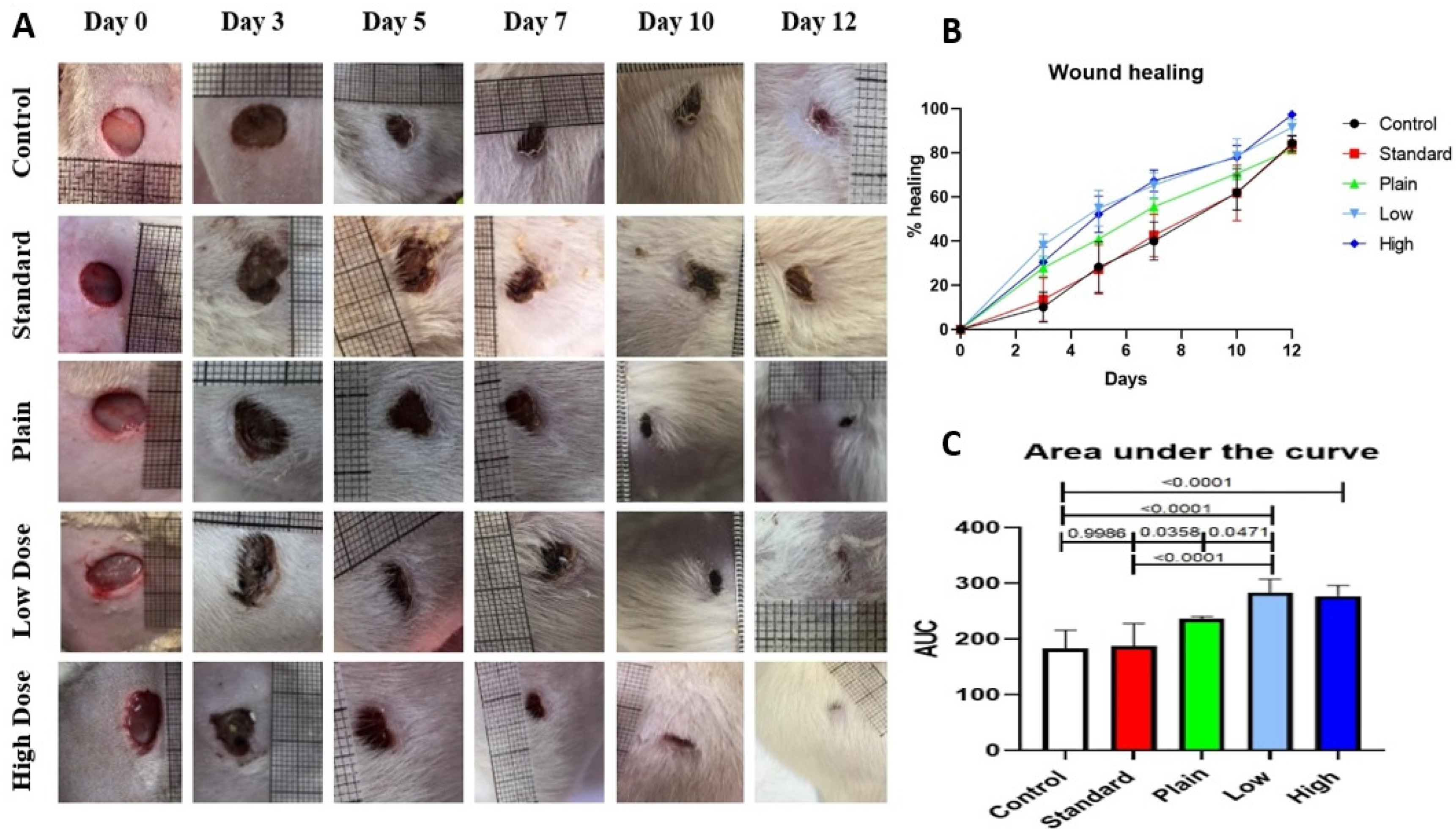
2.9. Effect of CuSQ Hydrogel on Wound Closure in Rats
2.10. Wound Healing Biomarkers
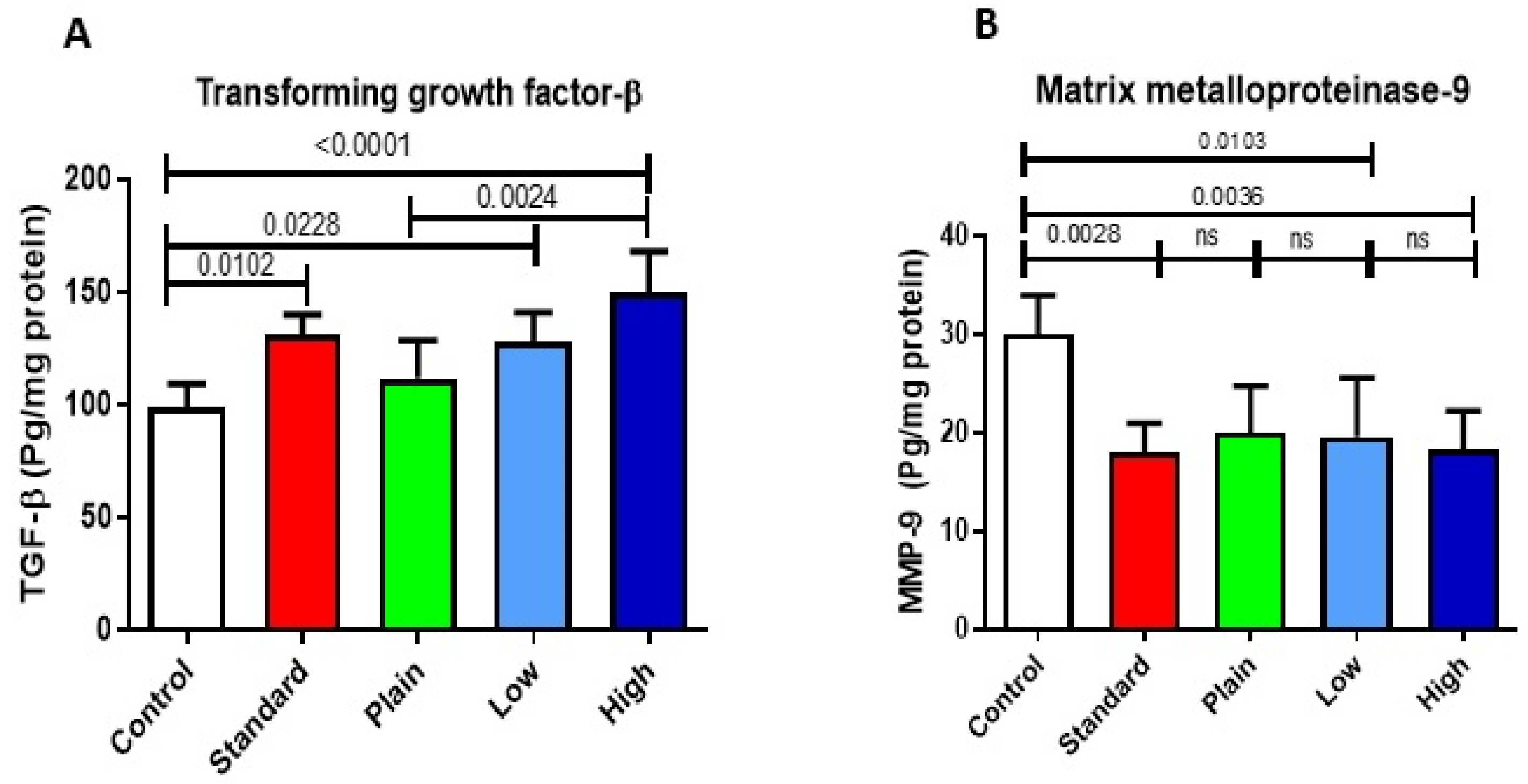
2.10.1. Effect of CuSQ Hydrogel on TGF Beta and MMP-9
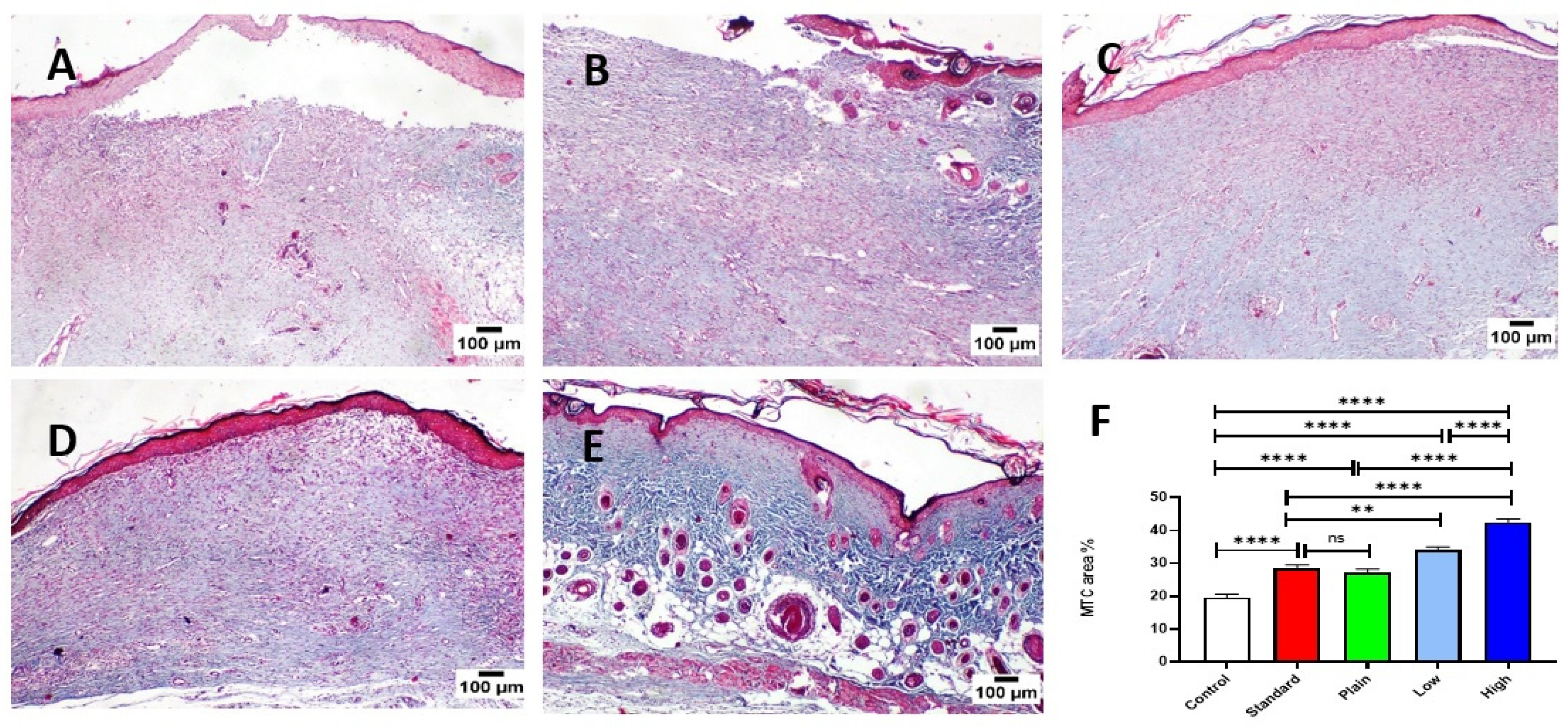
2.10.2. Histopathology and Healing Score
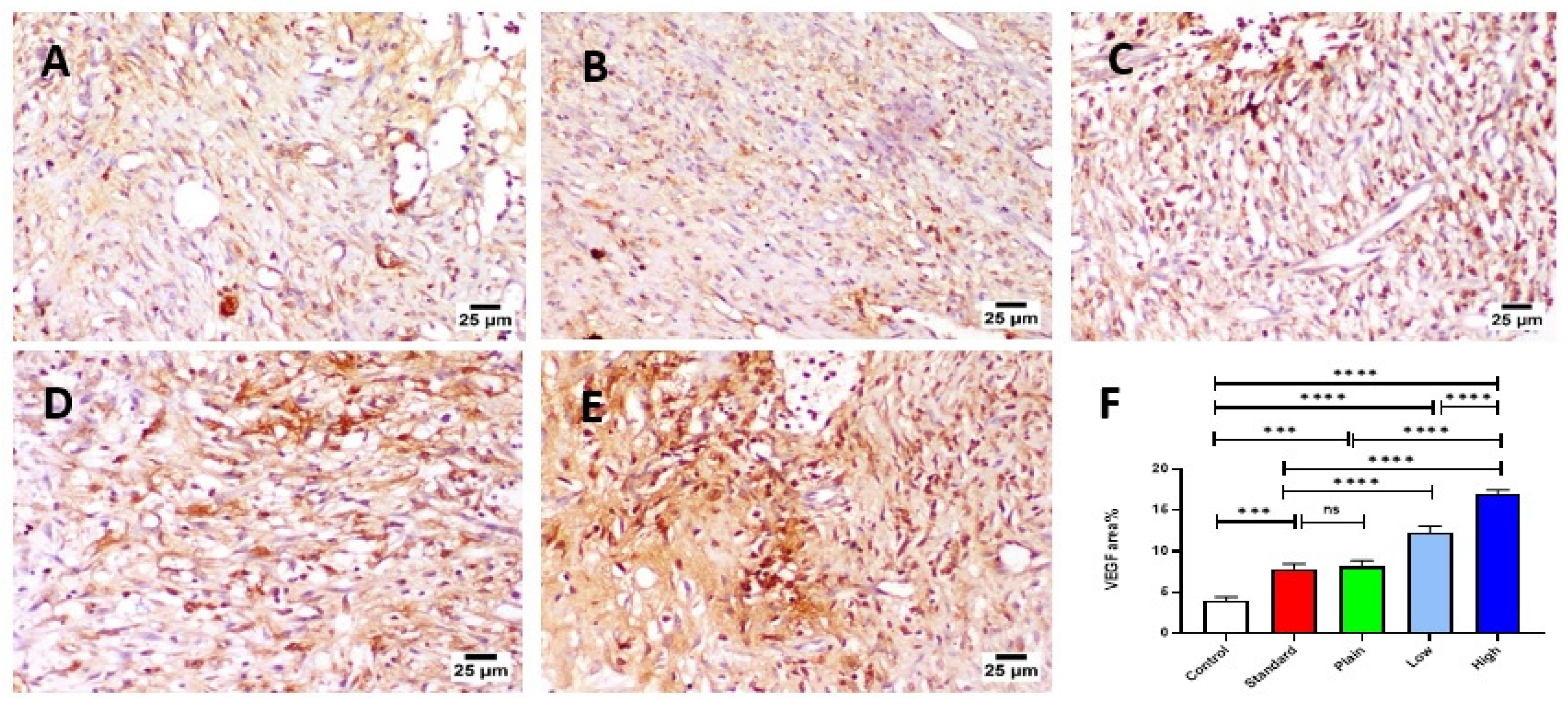
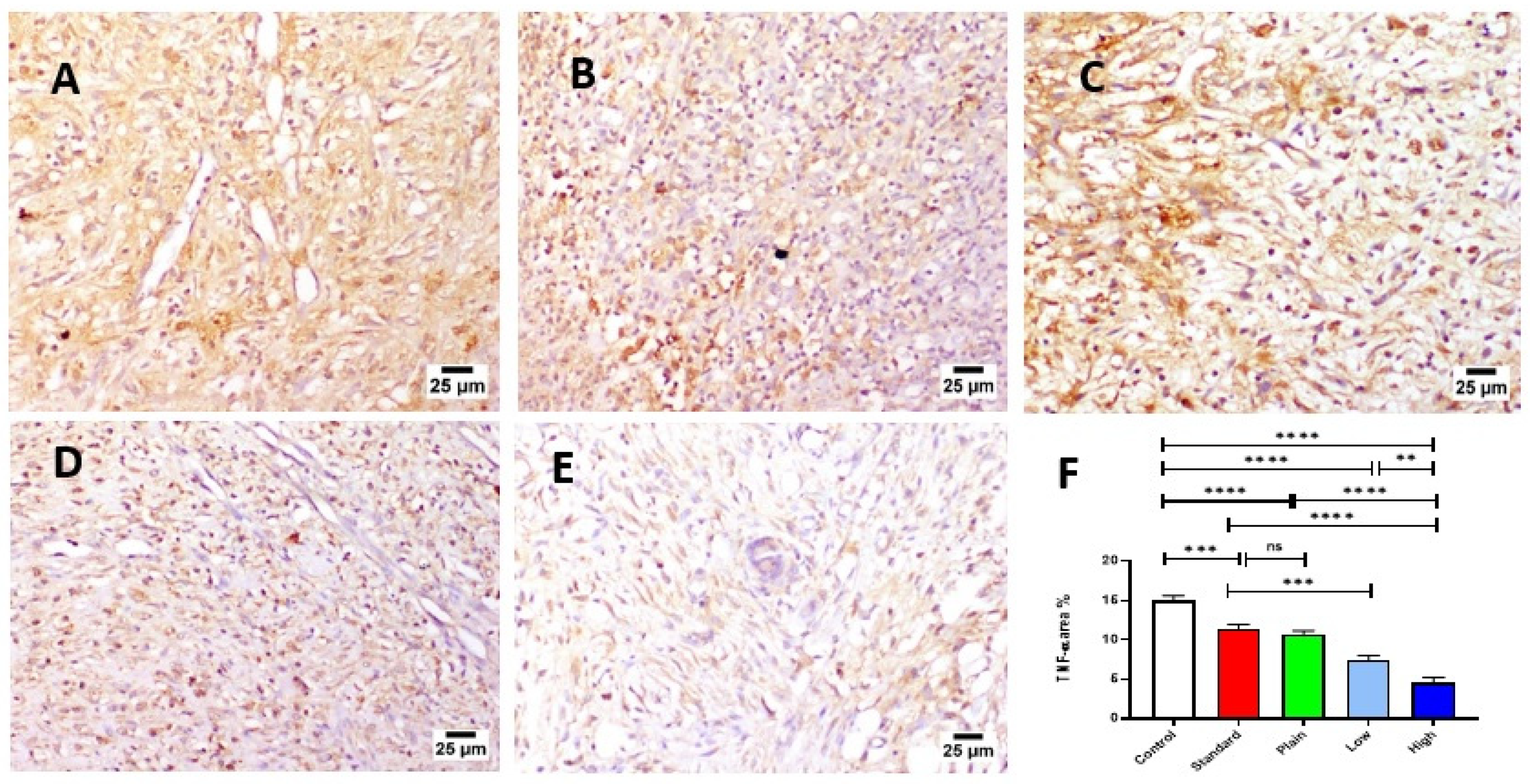
2.10.3. Immunohistochemistry
VEGF Expression
TNF-α Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Characterization
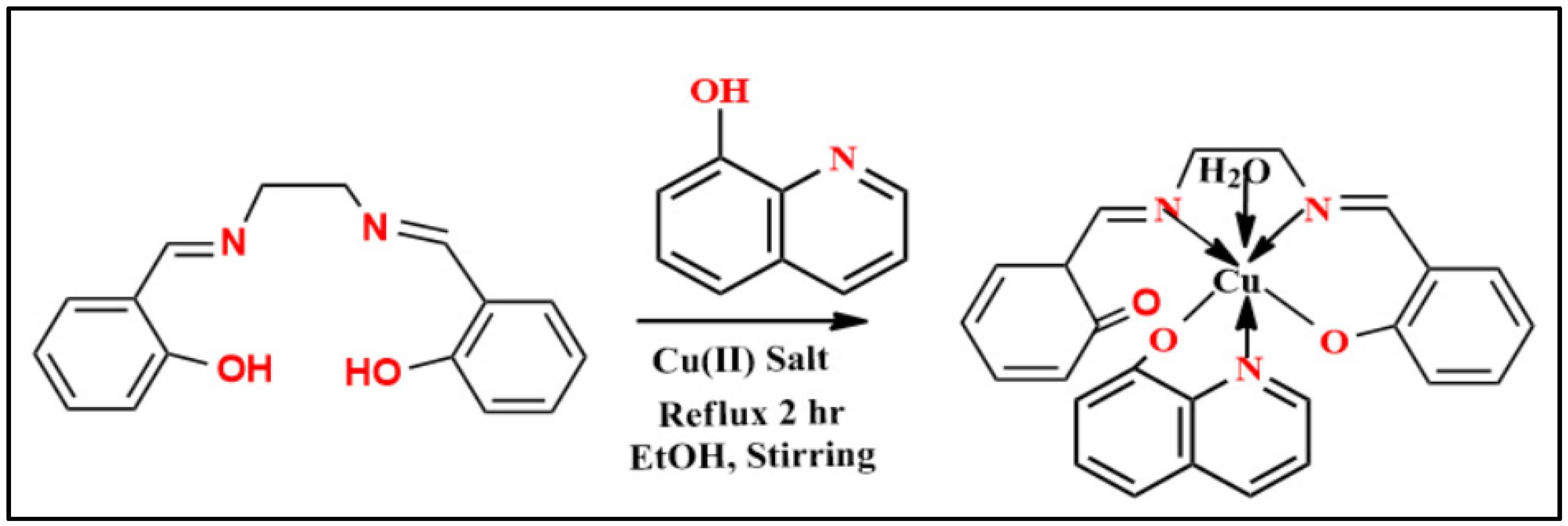
4.3. Synthesis of Schiff Base (Salen)
4.4. Synthesis of Mixed Complex (CuSQ)
4.5. Antimicrobial Potency
4.6. Synthesis of CuSQ Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN)
4.7. Characterization of CuSQ-Loaded SLNs
4.7.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.7.2. Particle Size Analysis, Polydispersity Index and Zeta Potential
4.7.3. Entrapment Efficiency
4.8. Cytotoxicity of CuSQ Loaded SLNs
4.8.1. Cell Culture
4.8.2. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.9. Preparation of CuSQ Nanoparticles Hydrogel
4.9.1. Evaluation of Hydrogel Physical Characteristics
4.9.2. Determination of pH
4.9.3. Washability
4.9.4. In Vitro Drug Dissolution of Hydrogel
4.10. In Vivo Assessment of the Wound Healing Activity
4.10.1. Animals
4.10.2. Excision Wound
4.10.3. Experimental Design
4.10.4. Estimation of the Rate of Wound Healing
4.11. Wound Healing Markers
4.11.1. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.11.2. Histopathological Examination
4.11.3. Immunohistochemistry
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qu, J.; Zhao, X.; Liang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, P.X.; Guo, B. Degradable conductive injectable hydrogels as novel antibacterial, anti-oxidant wound dressings for wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preem, L.; Mahmoudzadeh, M.; Putrinš, M.; Meos, A.; Laidmäe, I.; Romann, T.; Aruväli, J.; Härmas, R.; Koivuniemi, A.; Bunker, A.; et al. Interactions between Chloramphenicol, Carrier Polymers, and Bacteria-Implications for Designing Electrospun Drug Delivery Systems Countering Wound Infection. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 4417–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guebitz, G.M.; Nyanhongo, G.S. Enzymes as Green Catalysts and Interactive Biomolecules in Wound Dressing Hydrogels. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1040–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Niu, L.; Liang, H.; Tan, H.; Liu, C.; Zhu, F. PH and Glucose Dual-Responsive Injectable Hydrogels with Insulin and Fibroblasts as Bioactive Dressings for Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 37563–37574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, L.; Gu, Z.; Wu, J. Red jujube-incorporated gelatin methacryloyl (GelMa) hydrogels with anti-oxidation and immunoregulation activity for wound healing. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2019, 15, 1357–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorasani, M.T.; Joorabloo, A.; Moghaddam, A.; Shamsi, H.; MansooriMoghadam, Z. Incorporation of ZnO nanoparticles into heparinised polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan hydrogels for wound dressing application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contardi, M.; Russo, D.; Suarato, G.; Heredia-Guerrero, J.A.; Ceseracciu, L.; Penna, I.; Margaroli, N.; Summa, M.; Spanò, R.; Tassistro, G.; et al. Polyvinylpyrrolidone/hyaluronic acid-based bilayer constructs for sequential delivery of cutaneous antiseptic and antibiotic. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasani, M.T.; Joorabloo, A.; Adeli, H.; Mansoori-Moghadam, Z.; Moghaddam, A. Design and optimization of process parameters of polyvinyl (alcohol)/chitosan/nano zinc oxide hydrogels as wound healing materials. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, E.M.; Abdel Rahman, L.H.; Abdelhamid, A.A.; Shehata, M.R.; Alothman, A.A.; Nafady, A. Synthesis, Characterization, Theoretical Studies, and Antimicrobial/Antitumor Potencies of Salen and Salen/Imidazole Complexes of Co (II), Ni (II), Cu (II), Cd (II), Al (III) and La (III). Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, M.I.; Rehan, R. Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications of Copper Nanoparticles. Anal. Lett. 2017, 50, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Farhan, B.S.; Basha, M.T.; Abdel Rahman, L.H.; El-Saghier, A.M.M.; El-Ezz, D.A.; Marzouk, A.A.; Shehata, M.R.; Abdalla, E.M. Synthesis, dft calculations, antiproliferative, bactericidal activity and molecular docking of novel mixed-ligand salen/8-hydroxyquinoline metal complexes. Molecules 2021, 26, 4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahnama, M.; Gwaram, N.S.; Abdel, I.; Ibrahim, A.; Shahzad, N.; Al-ghamdi, S.S.; Ayoub, N. Wound Curing Prospective of Copper (II) Bis [N´-((5-Chloro-1H-Indol-3-yl Methylene Nicotinohydrazide] on Experimentation Provoke Cutting Out Injury in Rats. Int. J. Drug Dev. Res. 2018, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Moty, S.; Abdel-Rahman, M.; Elsherief, H.; Kafafy, A.-H. Synthesis of some quinoline thiosemicarbazone derivatives of potential antimicrobial activity. Bull. Pharm. Sci. Assiut 2005, 28, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hussein, M.; Kafafy, A.H.; Abdel-Moty, S.; Abou-Ghadir, O. Synthesis and biological activities of new substituted thiazoline-quinoline derivatives. Acta Pharm. 2009, 59, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismael, M.; Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Abou El-ezz, D.; Ahmed, E.A.H.; Nafady, A. Synthesis, structural characterization, and biological studies of ATBS–M complexes (M(II) = Cu, Co, Ni, and Mn): Access for promising antibiotics and anticancer agents. Arch. Pharm. 2021, 354, 2000241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.S.S.; Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Abu-Dief, A.M.; Hashem, N.A. Synthesis, catalysis, antimicrobial activity, and DNA interactions of new Cu(II)-Schiff base complexes. Inorg. Nano-Metal Chem. 2020, 50, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; El-Khatib, R.M.; Nassr, L.A.; Abu-Dief, A.M.; Ismael, M.; Seleem, A.A. Metal based pharmacologically active agents: Synthesis, structural characterization, molecular modeling, CT-DNA binding studies and in vitro antimicrobial screening of iron(II) bromosalicylidene amino acid chelates. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Adam, M.S.; Abu-Dief, A.M.; Ahmed, H.E.S.; Nafady, A. Non-Linear Optical Property and Biological Assays of Therapeutic Potentials Under In Vitro Conditions of Pd(II), Ag(I) and Cu(II) Complexes of 5-Diethyl amino-2-({2-[(2-hydroxy-Benzylidene)-amino]-phenylimino}-methyl)-phenol. Molecules 2020, 25, 5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.M.M.; Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Abu-Dief, A.M.; Elshafaie, A.; Hamdan, S.K.; Ahmed, A.M. The electric and thermoelectric properties of Cu(II)-schiff base nano-complexes. Phys. Scr. 2018, 93, 055801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, E.M.; Hassan, S.S.; Elganzory, H.H.; Aly, S.A.; Alshater, H. Molecular docking, dft calculations, effect of high energetic ionizing radiation, and biological evaluation of some novel metal (Ii) heteroleptic complexes bearing the thiosemicarbazone ligand. Molecules 2021, 26, 5851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, S.A.; Elganzory, H.H.; Mahross, M.H.; Abdalla, E.M. Quantum chemical studies and effect of gamma irradiation on the spectral, thermal, X-ray diffraction and DNA interaction with Pd (II), Cu(I), and Cd (II) of hydrazone derivatives. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 35, e6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.T.; Lian, G.D.; Yin, D.W.; Su, B.J. Synthesis, characterization and biological activity of ferrocene-based Schiff base ligands and their metal (II) complexes. Spectrochim. Acta—Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 100, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, N.T.; Schultz, G.S. Growth factors and wound healing: Part II. Role in normal and chronic wound healing. Am. J. Surg. 1993, 166, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, N.T.; Schultz, G.S. Growth factors and wound healing: Biochemical properties of growth factors and their receptors. Am. J. Surg. 1993, 165, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, W.T. Physiology of the acute wound. Clin. Plast. Surg. 1998, 25, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harding, K.G.; Moore, K.; Phillips, T.J. Wound chronicity and fibroblast senescence—Implications for treatment. Int. Wound J. 2005, 2, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beanes, S.R.; Dang, C.; Soo, C.; Ting, K. Skin repair and scar formation: The central role of TGF-β. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2003, 5, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, H.N.; Hardman, M.J. Wound healing: Cellular mechanisms and pathological outcomes: Cellular Mechanisms of Wound Repair. Open Biol. 2020, 10, 200223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nur Amin Bitu, M. Anti-pathogenic Activity of Cu(II) Complexes Incorporating Schiff Bases: A Short Review. Am. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2019, 5, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.D.; Patel, H.S. Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization and thermal studies of some divalent transition metal complexes of 8-hydroxyquinoline. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1328–S1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérard, C.; Bordeleau, L.J.; Barralet, J.; Doillon, C.J. The stimulation of angiogenesis and collagen deposition by copper. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, R.; Raj Singh, T.; Garland, M.; Woolfson, A.; Donnelly, R. Mucoadhesive drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2011, 3, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, S.; Liu, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, P. Application of Nanomaterial in Hydrogels Related to Wound Healing. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 4656037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound healing: A cellular perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvin, M. Cutaneous wound repair. Wounds 1998, 10, 12–32. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, M.T.; Han, Y.P.; Yan, C.; Shaw, M.C.; Garner, W.L. TNF-α suppresses α-smooth muscle actin expression in human dermal fibroblasts: An implication for abnormal wound healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2645–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, G.F.; Mustoe, T.A.; Lingelbach, J.; Masakowski, V.R.; Griffin, G.L.; Senior, R.M.; Deuel, T.F. Platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor-β enhance tissue repair activities by unique mechanisms. J. Cell Biol. 1989, 109, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansbridge, J.N.; Hanawalt, P.C. Role of transforming growth factor beta in the maturation of human epidermal keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1988, 90, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weder, J.E.; Dillon, C.T.; Hambley, T.W.; Kennedy, B.J.; Lay, P.A.; Biffin, J.R.; Regtop, H.L.; Davies, N.M. Copper complexes of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: An opportunity yet to be realized. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2002, 232, 95–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borkow, G.; Gabbay, J.; Dardik, R.; Eidelman, A.I.; Lavie, Y.; Grunfeld, Y.; Ikher, S.; Huszar, M.; Zatcoff, R.C.; Marikovsky, M. Molecular mechanisms of enhanced wound healing by copper oxide-impregnated dressings. Wound Repair Regen. 2010, 18, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caley, M.P.; Martins, V.L.C.; O’Toole, E.A. Metalloproteinases and Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornblatt, A.P.; Nicoletti, V.G.; Travaglia, A. The neglected role of copper ions in wound healing. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 161, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Kang, Y. Role of Copper in Angiogenesis and Its Medicinal Implications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 1304–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, S.; Seyedalipour, B.; Shafieyan, S.; Kheime, A.; Mohammadi, P.; Aghdami, N. Copper nanoparticles promote rapid wound healing in acute full thickness defect via acceleration of skin cell migration, proliferation, and neovascularization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 517, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Basha, M.T.; Al-Farhan, B.S.; Shehata, M.R.; Abdalla, E.M. Synthesis, characterization, potential antimicrobial, antioxidant, anticancer, DNA binding, and molecular docking activities and DFT on novel Co(II), Ni(II), VO(II), Cr(III), and La(III) Schiff base complexes. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2022, 36, e6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, D.A.; Bayoumi, F.S.; Taher, H.M.; Abdelmonem, B.H.; Eissa, T.F. Antimicrobial potential of mentha spp. essential oils as raw and loaded solid lipid nanoparticles against dental caries. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2020, 13, 4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil Kumar, P.; Arivuchelvan, A.; Jagadeeswaran, A.; Subramanian, N.; Senthil Kumar, C.; Mekala, P. Formulation, optimization and evaluation of enrofloxacin solid lipid nanoparticles for sustained oral delivery. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2015, 8, 231–236. [Google Scholar]
- Skehan, P.; Storeng, R.; Scudiero, D.; Monks, A.; Mcmahon, J.; Vistica, D.; Warren, J.T.; Bokesch, H.; Kenney, S.; Boyd, M.R. New colorimetric cytotoxicity assay for anticancer-drug screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allam, R.M.; Al-Abd, A.M.; Khedr, A.; Sharaf, O.A.; Nofal, S.M.; Khalifa, A.E.; Mosli, H.A.; Abdel-Naim, A.B. Fingolimod interrupts the cross talk between estrogen metabolism and sphingolipid metabolism within prostate cancer cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 291, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, T.P.; Eswaraiah, M.C. Formulation and evaluation of topical hydrogel containing antifungal drug. Pharm. Pharmacol. Int. J. 2020, 8, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Chaubey, N. Design and Evaluation of Topical Hydrogel Formulation of Aceclofenac for Improved Therapy. J. Drug Deliv. Ther. 2019, 9, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Verpoorte, R.; Suresh, B. Evaluation of in-vivo wound healing activity of Hypericum patulum (Family: Hypericaceae) leaf extract on different wound model in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 70, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancroft, J.; Layton, C. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques—John D. Bancroft—Google Books. In Bancroft’s Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques; Elsevier: London, UK, 2018; pp. 126–176. ISBN 978-0-7020-6864-5. [Google Scholar]
- Bakr, R.O.; Amer, R.I.; Attia, D.; Abdelhafez, M.M.; Al-Mokaddem, A.K.; El Gendy, A.N.; El-Fishawy, A.M.; Fayed, M.A.A.; Gad, S.S. In vivo wound healing activity of a novel composite sponge loaded with mucilage and lipoidal matter of Hibiscus species. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 135, 111225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Molecular Formula | Molecular Weight | Color Yield% | Conductivity µs | M. P. °C | µeffµ B. M | Found (Cal.) % | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | N | M | ||||||
| Salen C16H16N2O2 | 268.31 | Yellow 95 | 0.830 | 127 | 0.58 | 71.32 | 5.95 | 10.28 | - |
| Cu (S) (Q) H2O C25H24CuN3O4 | 494.02 | Yellowish green 77 | 24.10 | 264 | 1.50 | 60.38 | 4.62 | 8.38 | 12.73 |
| Compound | ν (OH) | ν (NH) | ν (CH)arom | ν (CH)aliph | ν (C=O) | ν (C=N) | ν (C-O) | ν (H2O) Coordinated | ν (M-O) | ν (M-N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salen | 3292 | - | 3049–3007 | 2899–2867 | - | 1608 | 1247 | - | - | - |
| CuSQ | 3241 | 3200 | 3050 | 2968–2862 | 1740 | 1644 | 1213 | 945 | 516 | 442 |
| Compounds | λ max (nm) | Assignment |
|---|---|---|
| S | 280 | π—π * |
| 320 | n—π * | |
| 409 | n—π * | |
| CuSQ | 280 | π—π * |
| 380 | n—π * |
| Compound | S. aureus (+ve) | B. subtilis (+ve) | E. coli (−ve) | P. vulgaris (−ve) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 14 | 13 | 12 | 15 |
| Q | 16 | 14 | 13 | 16 |
| CuS | 25 | 20 | 13 | 22 |
| Gentamicin | 24 | 26 | 30 | 25 |
| CuSQ | 35 | 27 | 18 | 33 |
| Particle Size (nm) | PDI (%) | Zeta Potential (mv) | EE (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 | 111 ± 0.26 | 0.52 ± 0.11 | −11.8 ± 0.13 | 88 ± 0.12 |
| F2 | 136 ± 0.32 | 0.43 ± 0.12 | −40 ± 0.23 | 85 ± 0.11 |
| Materials | F1 | F2 |
|---|---|---|
| CuSQ (mg) | 25 | 50 |
| Soy Lecithin (mg) | 10 | 10 |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 30 | 30 |
| Dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) (mL) | 10 | 10 |
| Tween 80 (mL) | 2 | 2 |
| 2% w/v of polyvinyl alcohol (mL) | 2 | 2 |
| H2O (mL) | 30 | 30 |
| Ingredients | Formula with Low Concentration (F1) | Formula with High Concentration (F2) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbopol 940 | 0.7 mg | 0.7 mg |
| Copper shiff base dispersions | 5 mL | 15 mL |
| Water | 15 mL | 15 mL |
| 0.1 NaoH | 2 mL | 2 mL |
| Isopropyl myristate | 1% | 1% |
| Benzalkonium chloride | 0.25 | 0.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abou El-ezz, D.; Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Al-Farhan, B.S.; Mostafa, D.A.; Ayad, E.G.; Basha, M.T.; Abdelaziz, M.; Abdalla, E.M. Enhanced In Vivo Wound Healing Efficacy of a Novel Hydrogel Loaded with Copper (II) Schiff Base Quinoline Complex (CuSQ) Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080978
Abou El-ezz D, Abdel-Rahman LH, Al-Farhan BS, Mostafa DA, Ayad EG, Basha MT, Abdelaziz M, Abdalla EM. Enhanced In Vivo Wound Healing Efficacy of a Novel Hydrogel Loaded with Copper (II) Schiff Base Quinoline Complex (CuSQ) Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(8):978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080978
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbou El-ezz, Doaa, Laila H. Abdel-Rahman, Badriah Saad Al-Farhan, Dalia A. Mostafa, Eman G. Ayad, Maram T. Basha, Mahmoud Abdelaziz, and Ehab M. Abdalla. 2022. "Enhanced In Vivo Wound Healing Efficacy of a Novel Hydrogel Loaded with Copper (II) Schiff Base Quinoline Complex (CuSQ) Solid Lipid Nanoparticles" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 8: 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080978
APA StyleAbou El-ezz, D., Abdel-Rahman, L. H., Al-Farhan, B. S., Mostafa, D. A., Ayad, E. G., Basha, M. T., Abdelaziz, M., & Abdalla, E. M. (2022). Enhanced In Vivo Wound Healing Efficacy of a Novel Hydrogel Loaded with Copper (II) Schiff Base Quinoline Complex (CuSQ) Solid Lipid Nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals, 15(8), 978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15080978






