Dehydroisohispanolone as a Promising NLRP3 Inhibitor Agent: Bioevaluation and Molecular Docking
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
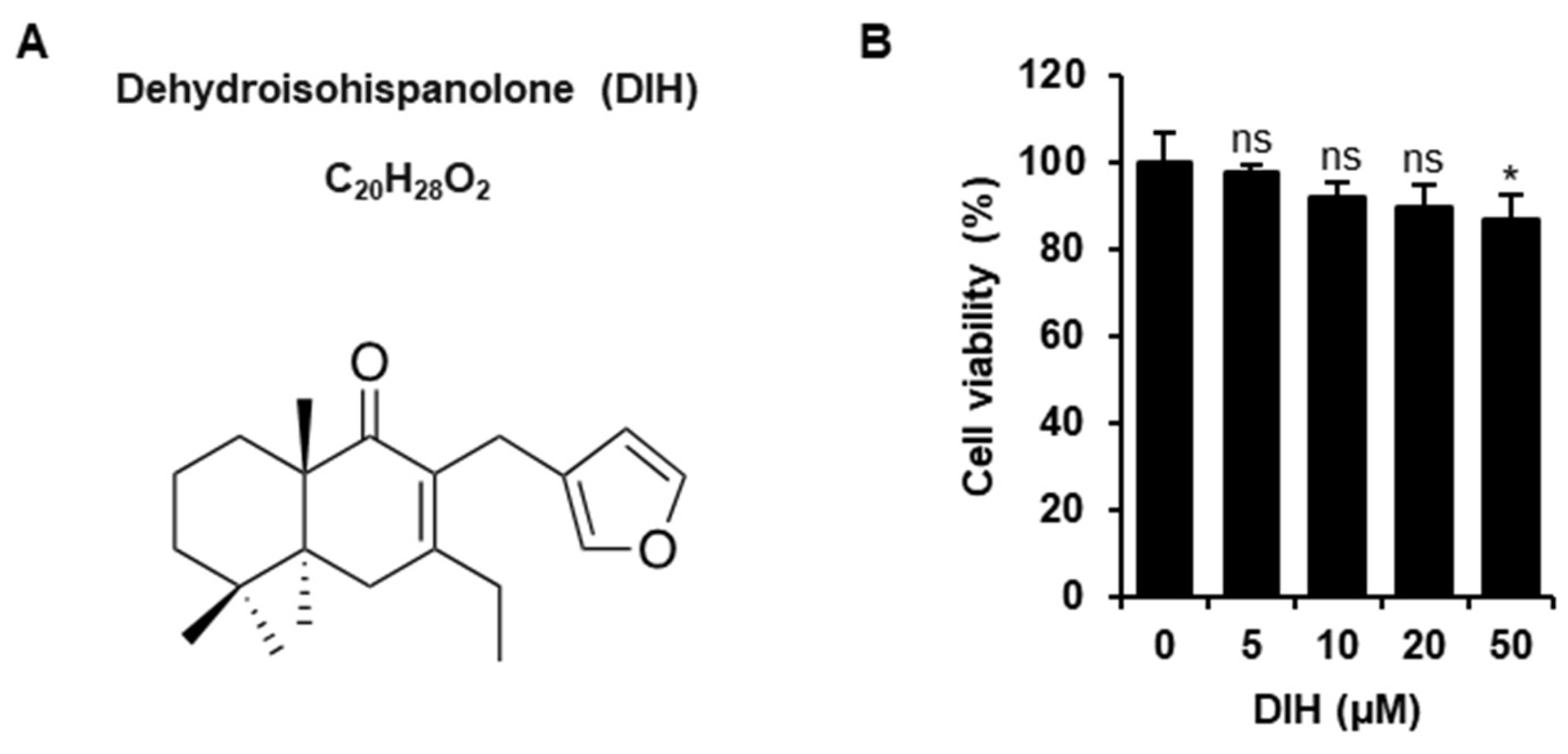
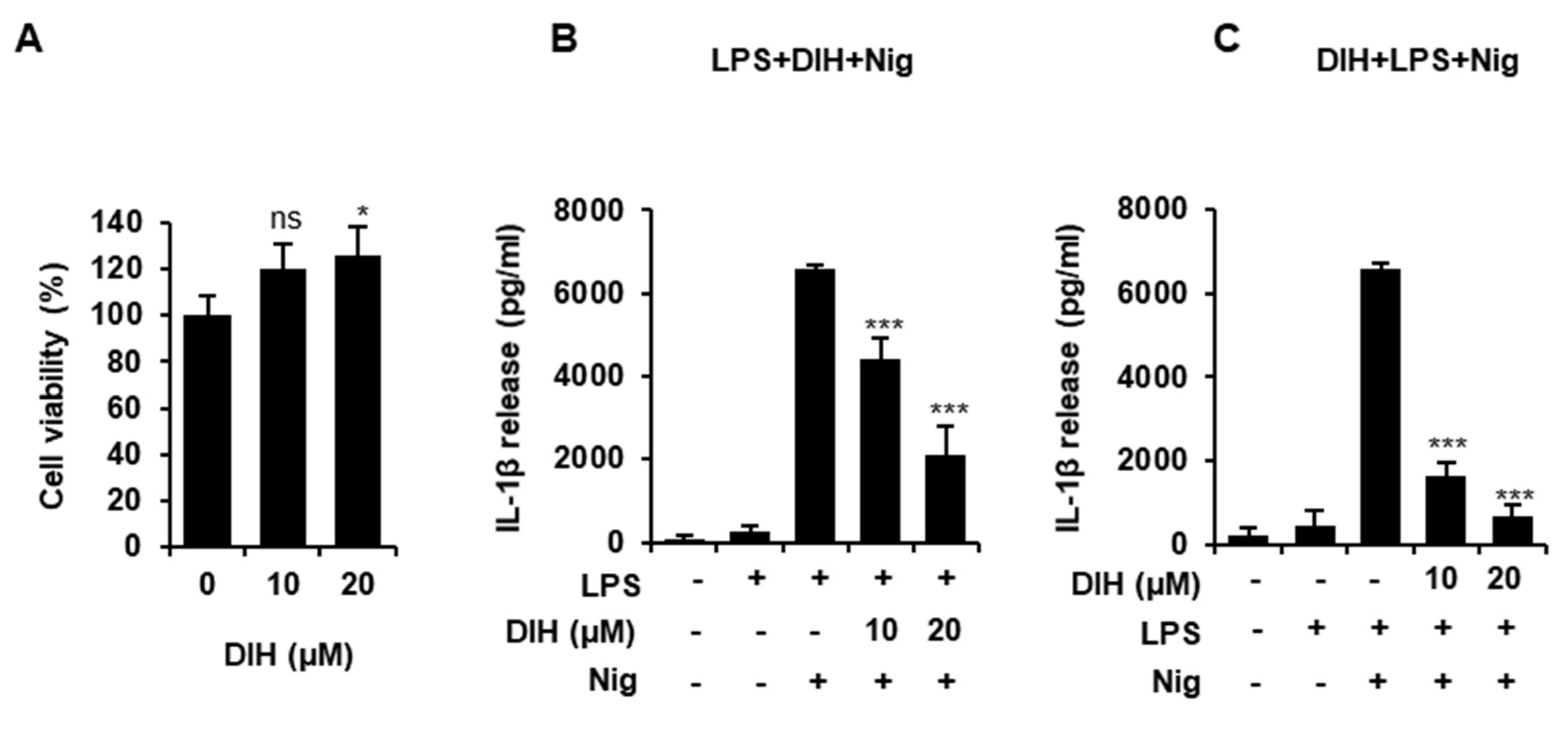
2.1. Cytotoxic Effects of DIH on Macrophages
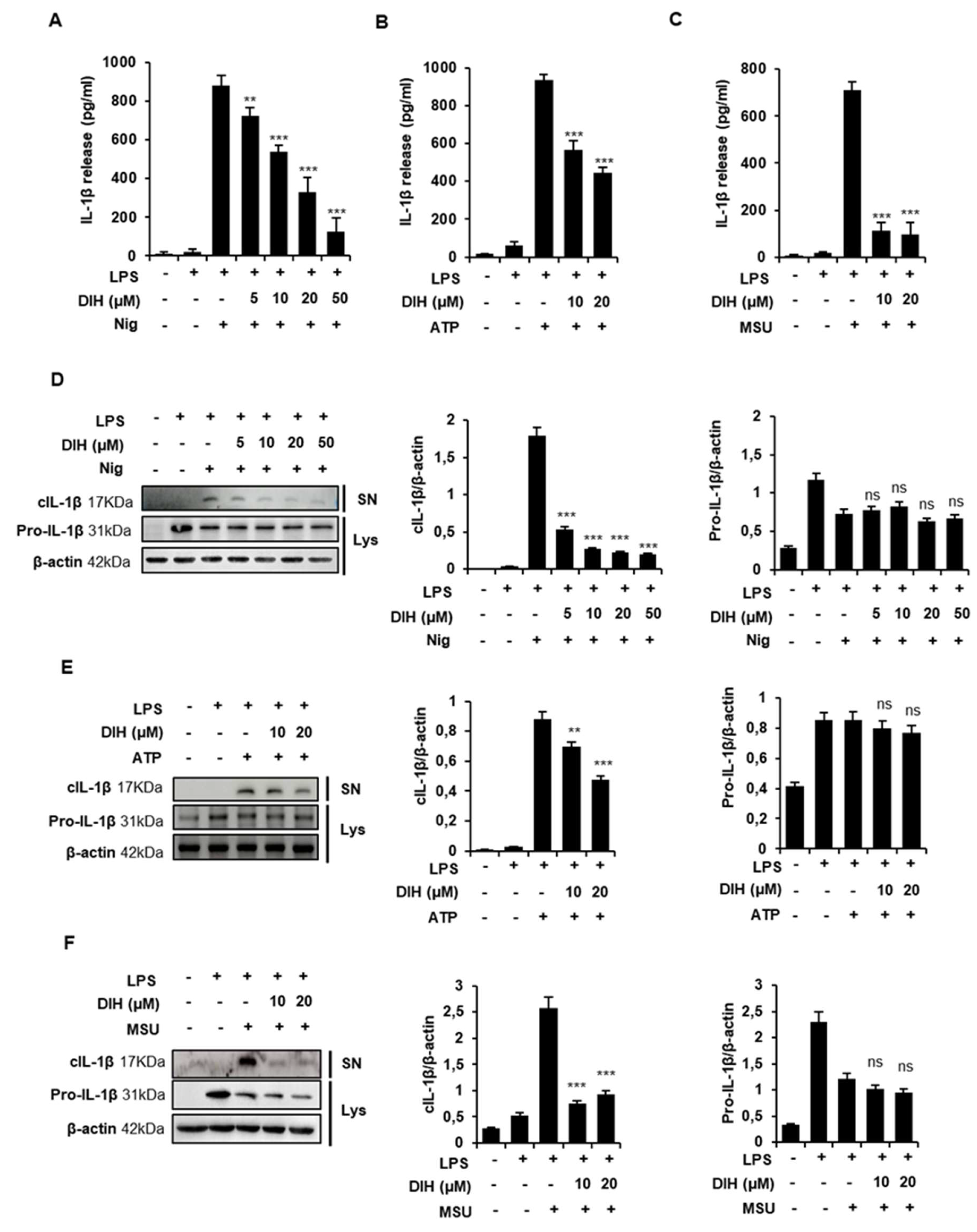
2.2. DIH Reduces IL-1β Secretion following NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
2.3. Caspase-1 Activation Is Inhibited by DIH Treatment
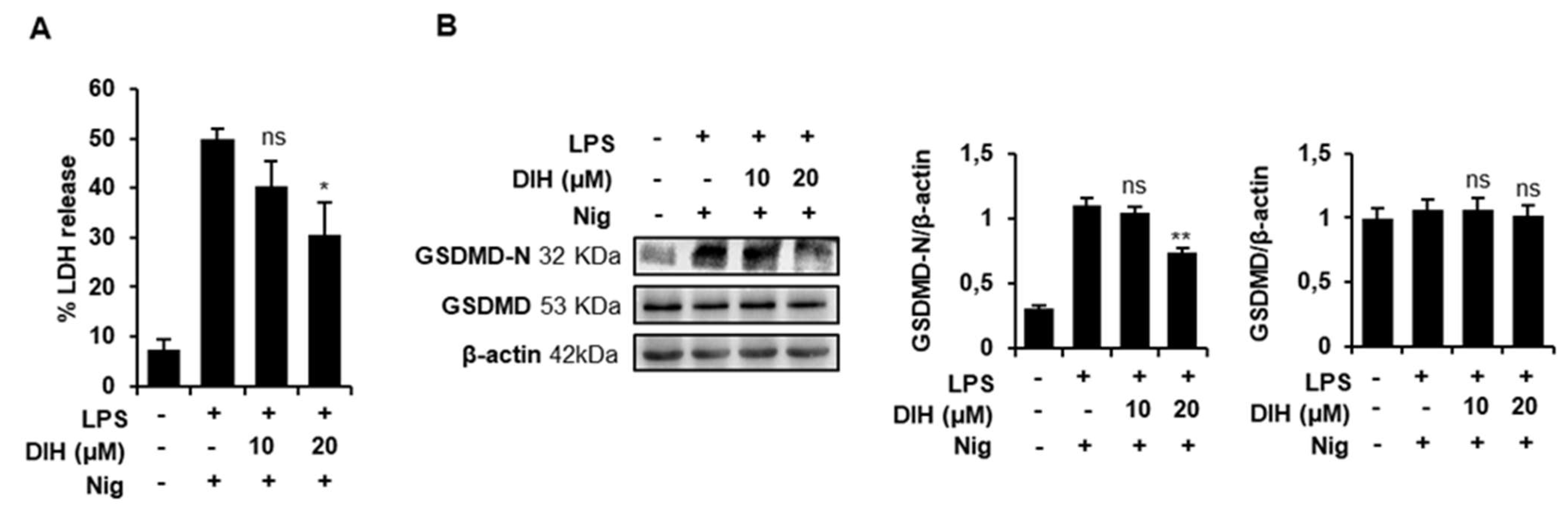
2.4. DIH Attenuates Inflammasome-Dependent Pyroptosis
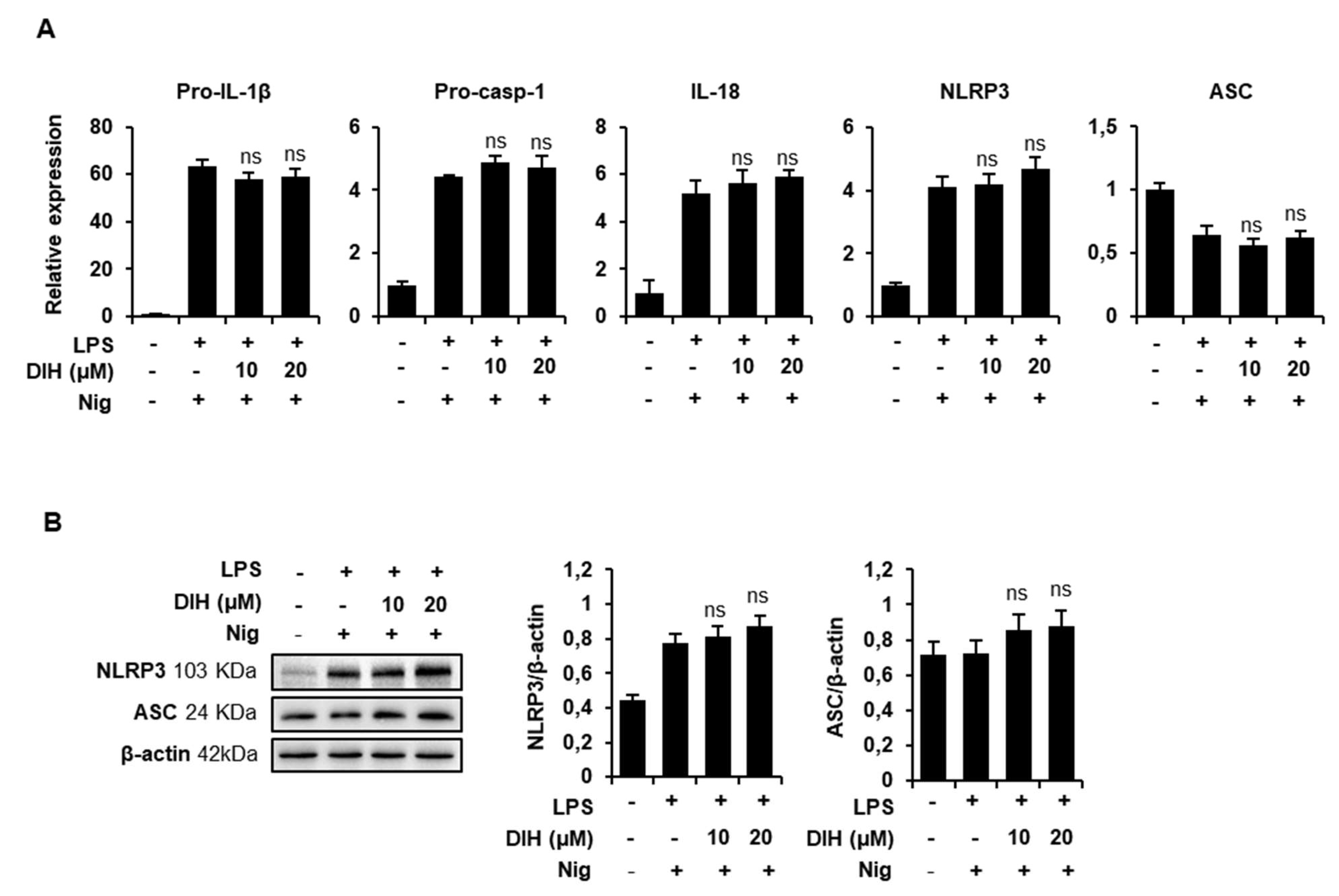
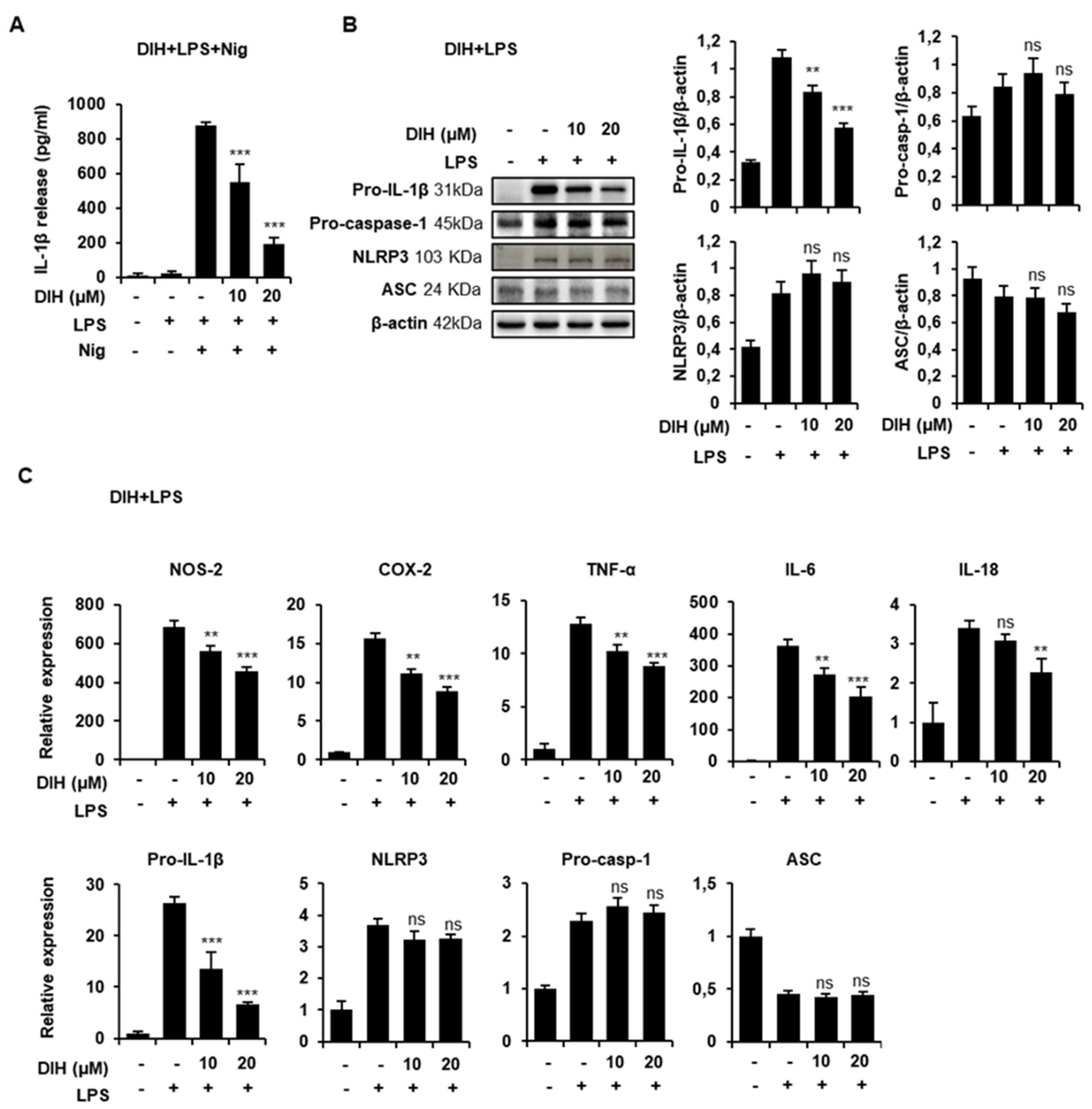
2.5. DIH Also Affects the Priming Step of Inflammasome Activation
2.6. Secretion of Pro-Inflammatory IL-1β Is Also Inhibited by the Treatment of DIH in BMDMs
2.7. Docking Studies on NLRP3
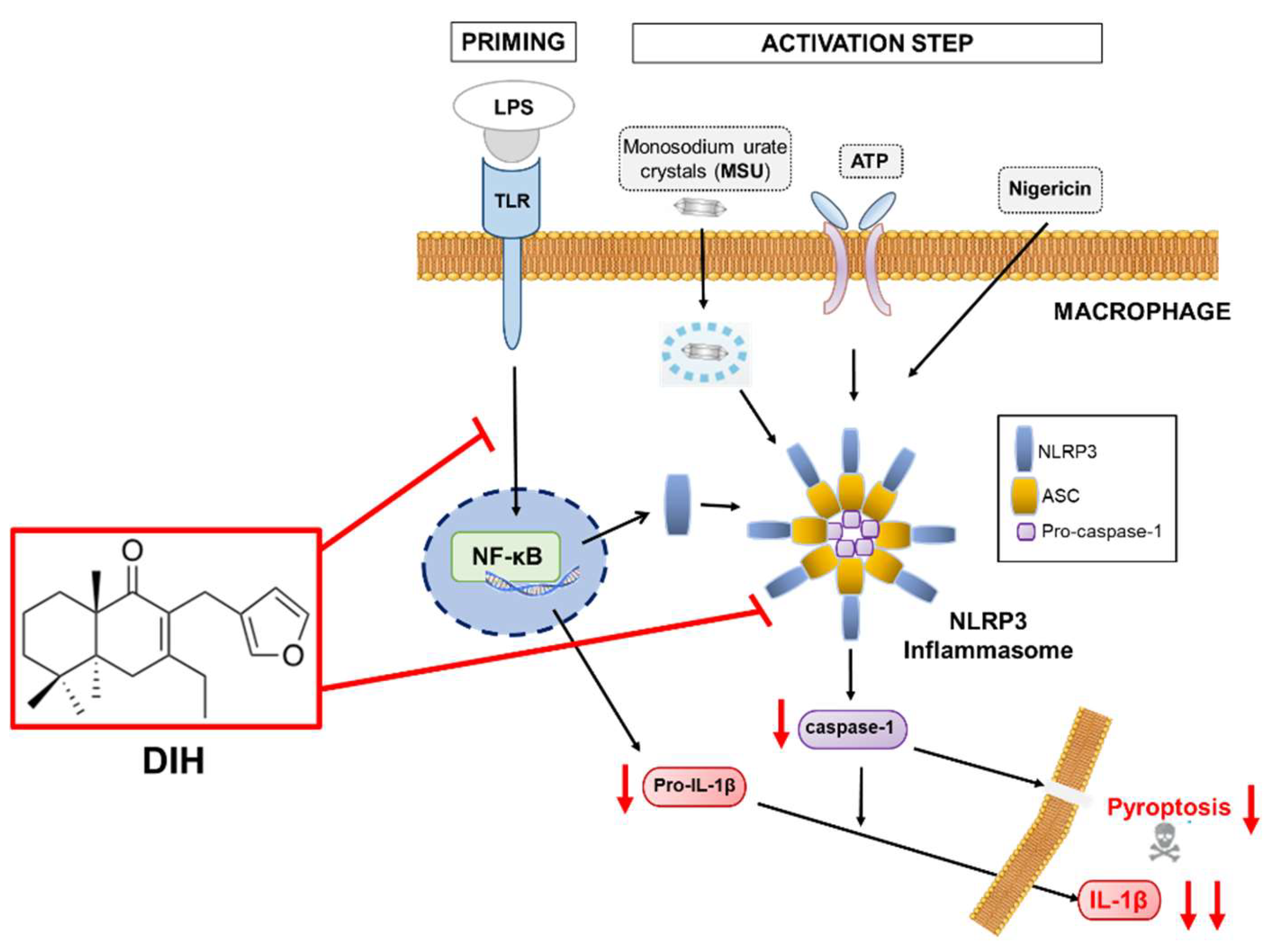
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Cultures and Inflammasome Stimulation
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4. IL-1β Measurement
4.5. Caspase-1 Activity Assay
4.6. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Assay
4.7. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR
4.8. Immunoblot Analysis
4.9. Protein Preparation and Molecular Docking
4.10. Covalent Docking
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADP | adenosine diphosphate |
| ASC | apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD |
| ATCC | American Type Cell Culture |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| BMDMs | bone marrow-derived macrophages |
| COX | Cyclooxygenase |
| Cryo-EM | cryogenic electron microscopy |
| DAMPs | danger-associated molecules patterns |
| DIH | dehydroisohispanolone diterpene |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| GSDMD | gasdermin D |
| IL | interleukin |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| MSU | monosodium urate |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| Nig | nigericin |
| NOS | Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| NLRP3 | NLR family pyrin domain-containing protein 3 |
| PAMPs | pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SD | standard deviation |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
References
- An, N.; Gao, Y.; Si, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Tian, C.; Yuan, M.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Shang, H.; et al. Regulatory mechanisms of the NLRP3 inflammasome, a novel immuneiInflammatory marker in cardiovascular diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nardo, D.; Latz, E. NLRP3 inflammasomes link inflammation and metabolic disease. Trends Immunol. 2011, 32, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamkanfi, M.; Vande Walle, L.; Kanneganti, T.D. Deregulated inflammasome signaling in disease. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 243, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, F.; Xia, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L. Expression of NLPR3 in psoriasis is associated with enhancement of interleukin-1β and caspase-1. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 7909–7913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abderrazak, A.; Syrovets, T.; Couchie, D.; El Hadri, K.; Friguet, B.; Simmet, T.; Rouis, M. NLRP3 inflammasome: From a danger signal sensor to a regulatory node of oxidative stress and inflammatory diseases. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, L.; Warner, N.; Viani, K.; Nuñez, G. Function of Nod-like receptors in microbial recognition and host defense. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 227, 106–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabal, M.; Calleja, D.J.; Simpson, D.S.; Lawlor, K.E. Stressing out the mitochondria: Mechanistic insights into NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 105, 377–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.K.; Wen, H.; Ting, J.P. The inflammasome NLRs in immunity, inflammation, and associated diseases. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latz, E.; Xiao, T.S.; Stutz, A. Activation and regulation of the inflammasomes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, S.M.; Karki, R.; Kanneganti, T.D. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 277, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinou, I. Labdanes of natural origin-biological activities (1981–2004). Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1295–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de las Heras, B.; Hortelano, S. Molecular basis of the anti-inflammatory effects of terpenoids. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2009, 8, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.T. Diterpenes and their derivatives as potential anticancer agents. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 691–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhuo, X.; Li, J.; Jiang, X.; Ye, X.Y.; Xie, T.; Bai, R. Natural terpenoids with anti-inflammatory activities: Potential leads for anti-inflammatory drug discovery. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 124, 105817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marco, J.L. Isolation, reactivity, pharmacological activities and total synthesis of hispanolone and structurally related diterpenes from Labiatae plants. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado-Berrocal, I.; Gómez-Gaviro, M.V.; Benito, Y.; Barrio, A.; Bermejo, J.; Fernández-Santos, M.E.; Sánchez, P.L.; Desco, M.; Fernández-Avilés, F.; Fernández-Velasco, M.; et al. A labdane diterpene exerts ex vivo and in vivo cardioprotection against post-ischemic injury: Involvement of AKT-dependent mechanisms. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 93, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cofrade, L.; Oramas-Royo, S.; Cuadrado, I.; Amesty, Á.; Hortelano, S.; Estevez-Braun, A.; de Las Heras, B. Dehydrohispanolone derivatives attenuate the inflammatory response through the modulation of inflammasome activation. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2155–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortelano, S.; González-Cofrade, L.; Cuadrado, I.; de Las Heras, B. Current status of terpenoids as inflammasome inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 172, 113739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Través, P.G.; López-Fontal, R.; Cuadrado, I.; Luque, A.; Boscá, L.; de las Heras, B.; Hortelano, S. Critical role of the death receptor pathway in the antitumoral effects induced by hispanolone derivatives. Oncogene 2013, 32, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girón, N.; Través, P.G.; Rodríguez, B.; López-Fontal, R.; Boscá, L.; Hortelano, S.; de las Heras, B. Suppression of inflammatory responses by labdane-type diterpenoids. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 228, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Sirvent, L.; Garcia-Alvarez, M.C.; Rodríguez, B.; Bruno, M.; Savona, G.; Piozzi, F. Transformaciones de hispanolona II. Reacción retroaldólica de hispanolona y condensación aldólica de δ-dicetonas diterpénicas. An. Quim. Ser. C 1981, 77, 324–329. [Google Scholar]
- Swanson, K.V.; Deng, M.; Ting, J.P.Y. The NLRP3 inflammasome: Molecular activation and regulation to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, T.; Nagar, A.; Duffy, E.B.; Okuda, K.; Silverman, N.; Harton, J.A. NLRP3 sensing of diverse inflammatory stimuli requires distinct structural features. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.; Liu, Z.S.; Xue, W.; Bai, Z.F.; Wang, Q.Y.; Dai, J.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.J.; Cai, H.; Zhan, X.Y.; et al. NLRP3 phosphorylation is an essential priming event for inflammasome activation. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid-Burgk, J.L.; Chauhan, D.; Schmidt, T.; Ebert, T.S.; Reinhardt, J.; Endl, E.; Hornung, V. A genome-wide CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) screen identifies NEK7 as an essential component of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhan, X.; Tang, M.; Fina, M.; Su, L.; Pratt, D.; Bu, C.H.; Hildebrand, S.; et al. NLRP3 activation and mitosis are mutually exclusive events coordinated by NEK7, a new inflammasome component. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zeng, M.Y.; Yang, D.; Motro, B.; Núñez, G. NEK7 is an essential mediator of NLRP3 activation downstream of potassium efflux. Nature 2016, 530, 354–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariathasan, S.; Weiss, D.S.; Newton, K.; McBride, J.; O’Rourke, K.; Roose-Girma, M.; Lee, W.P.; Weinrauch, Y.; Monack, D.M.; Dixit, V.M. Cryopyrin activates the inflammasome in response to toxins and ATP. Nature 2006, 440, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, A.A.; Cunningham, C.; Corr, E.; Ferreira Jr, W.A.; Costa, F.F.; Almeida, C.B.; Conran, N.; Dunne, A.J.B. Heme induces nlrp3 inflammasome formation in primary human macrophages and may propagate hemolytic inflammatory processes By inducing S100A8 expression. Blood 2016, 128, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinon, F.; Pétrilli, V.; Mayor, A.; Tardivel, A.; Tschopp, J.J.N. Gout-associated uric acid crystals activate the NALP3 inflammasome. Nature 2006, 440, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanneganti, T.D.; Ozören, N.; Body-Malapel, M.; Amer, A.; Park, J.H.; Franchi, L.; Whitfield, J.; Barchet, W.; Colonna, M.; Vandenabeele, P.; et al. Bacterial RNA and small antiviral compounds activate caspase-1 through cryopyrin/Nalp3. Nature 2006, 440, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaney, A.J.; Leppla, S.H.; Moayeri, M. Bacterial exotoxins and the inflammasome. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, L.; König, A.; Koenig, P.A.; Gresnigt, M.S.; Westman, J.; Drummond, R.A.; Lionakis, M.S.; Groß, O.; Ruland, J.; Naglik, J.R.; et al. The fungal peptide toxin Candidalysin activates the NLRP3 inflammasome and causes cytolysis in mononuclear phagocytes. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, J.A.; Bergstralh, D.T.; Wang, Y.; Willingham, S.B.; Ye, Z.; Zimmermann, A.G.; Ting, J.P. Cryopyrin/NALP3 binds ATP/dATP, is an ATPase, and requires ATP binding to mediate inflammatory signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8041–8046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glide Software, G; Version 9.1; Schrodinger Suite, Ed LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2021.
- He, H.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Y.; Ye, J.; Wang, A.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q.; Liang, G.; Deng, X.; Jiang, W.; et al. Oridonin is a covalent NLRP3 inhibitor with strong anti-inflammasome activity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, M.E.; Davis, B.; Phillips, M.A. Medically useful plant terpenoids: Biosynthesis, occurrence, and mechanism of action. Molecules 2019, 24, 3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikezoe, T.; Yang, Y.; Bandobashi, K.; Saito, T.; Takemoto, S.; Machida, H.; Togitani, K.; Koeffler, H.P.; Taguchi, H. Oridonin, a diterpenoid purified from Rabdosia rubescens, inhibits the proliferation of cells from lymphoid malignancies in association with blockade of the NF-kappa B signal pathways. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, V.; Yarla, N.S.; Bishayee, A.; Putta, S.; Malla, R.; Neelapu, N.R.; Challa, S.; Das, S.; Shiralgi, Y.; Hegde, G.; et al. Multi-targeting andrographolide and its natural analogs as potential therapeutic agents. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wold, E.A.; Ding, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhou, J. Therapeutic potential of oridonin and its analogs: From anticancer and antiinflammation to neuroprotection. Molecules 2018, 23, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachove, I.; Chang, C. Anakinra and related drugs targeting interleukin-1 in the treatment of cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes. Open Access Rheumatol. 2014, 6, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Li, R.Z.; Shi, X.K.; Xi, R.Y.; Zhang, G.L.; Li, F.; Wang, F. A small molecule inhibitor of caspase-1 inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis to alleviate gouty inflammation. Immunol. Lett. 2022, 244, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, S.H.; Schipper, J.L.; Clark, A.C. The potential for caspases in drug discovery. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Devel. 2010, 13, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.T.; Bardaweel, S.K.; Mubarak, M.S.; Koch, W.; Gaweł-Beben, K.; Antosiewicz, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Immunomodulatory Effects of Diterpenes and Their Derivatives Through NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 572136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.W.; Lii, C.K.; Hong, J.J.; Chuang, W.T.; Yang, Y.C.; Huang, C.S.; Chen, H.W. Andrographolide inhibits IL-1β release in bone marrow-derived macrophages and monocyte infiltration in mouse knee joints induced by monosodium urate. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 410, 115341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.C.; Liu, Y.; Cen, Y.Y.; Xiong, Y.L.; Li, J.M.; Ding, Y.Y.; Tong, Y.F.; Liu, T.; Chen, X.H.; Zhang, H.G. Dual role of triptolide in interrupting the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway to attenuate cardiac fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Wang, L.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Fan, R.; Hao, T.; Yang, R.; et al. Isoandrographolide inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and attenuates silicosis in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 105, 108539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, F.; Shi, L.; Zhou, P. Phenols and terpenoids: Natural products as inhibitors of NLRP3 inflammasome in cardiovascular diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Que, W.; Hu, X.; Yu, X.; Guo, W.Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.K. Oridonin Prolongs the Survival of Mouse Cardiac Allografts by Attenuating the NF-κB/NLRP3 Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 719574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera, D.; Wree, A.; Povero, D.; Solís, N.; Hernandez, A.; Pizarro, M.; Moshage, H.; Torres, J.; Feldstein, A.E.; Cabello-Verrugio, C.; et al. Andrographolide ameliorates inflammation and fibrogenesis and attenuates inflammasome activation in experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra precision glide: Docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Borrelli, K.W.; Greenwood, J.R.; Day, T.; Abel, R.; Farid, R.S.; Harder, E. Docking covalent inhibitors: A parameter free approach to pose prediction and scoring. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
González-Cofrade, L.; Cuadrado, I.; Amesty, Á.; Estévez-Braun, A.; de las Heras, B.; Hortelano, S. Dehydroisohispanolone as a Promising NLRP3 Inhibitor Agent: Bioevaluation and Molecular Docking. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070825
González-Cofrade L, Cuadrado I, Amesty Á, Estévez-Braun A, de las Heras B, Hortelano S. Dehydroisohispanolone as a Promising NLRP3 Inhibitor Agent: Bioevaluation and Molecular Docking. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(7):825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070825
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonzález-Cofrade, Laura, Irene Cuadrado, Ángel Amesty, Ana Estévez-Braun, Beatriz de las Heras, and Sonsoles Hortelano. 2022. "Dehydroisohispanolone as a Promising NLRP3 Inhibitor Agent: Bioevaluation and Molecular Docking" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 7: 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070825
APA StyleGonzález-Cofrade, L., Cuadrado, I., Amesty, Á., Estévez-Braun, A., de las Heras, B., & Hortelano, S. (2022). Dehydroisohispanolone as a Promising NLRP3 Inhibitor Agent: Bioevaluation and Molecular Docking. Pharmaceuticals, 15(7), 825. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15070825






