HIF-PH Encoded by EGLN1 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
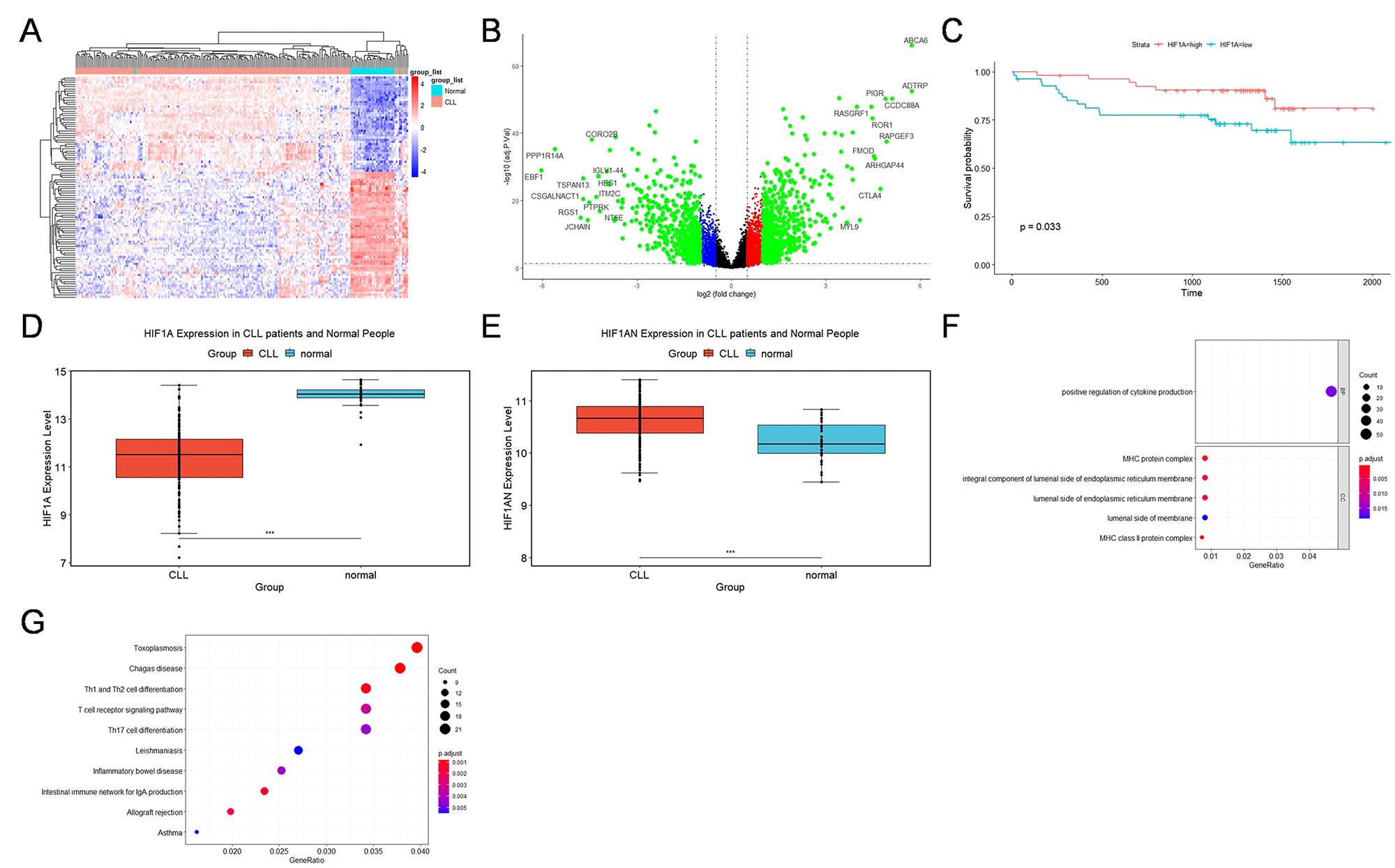
2.1. GEO Database Analysis of the Expression, Outcomes, and Functional Characteristics of the HIF1A in CLL
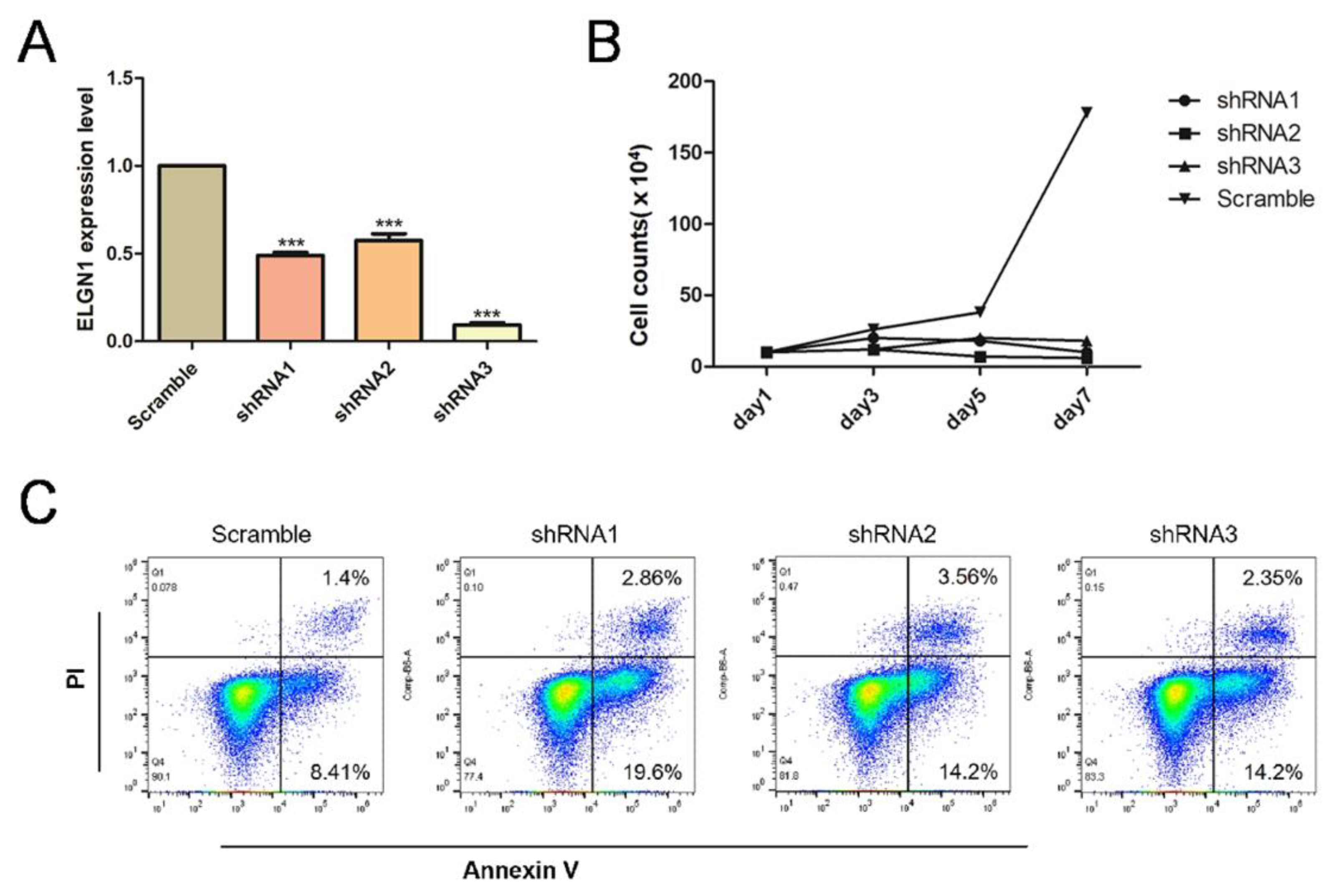
2.2. Knockdown of EGLN1, a Gene Encoding a HIF1A-Degrading Protein HIF-PH, Resulted in Apoptosis of CLL Cells
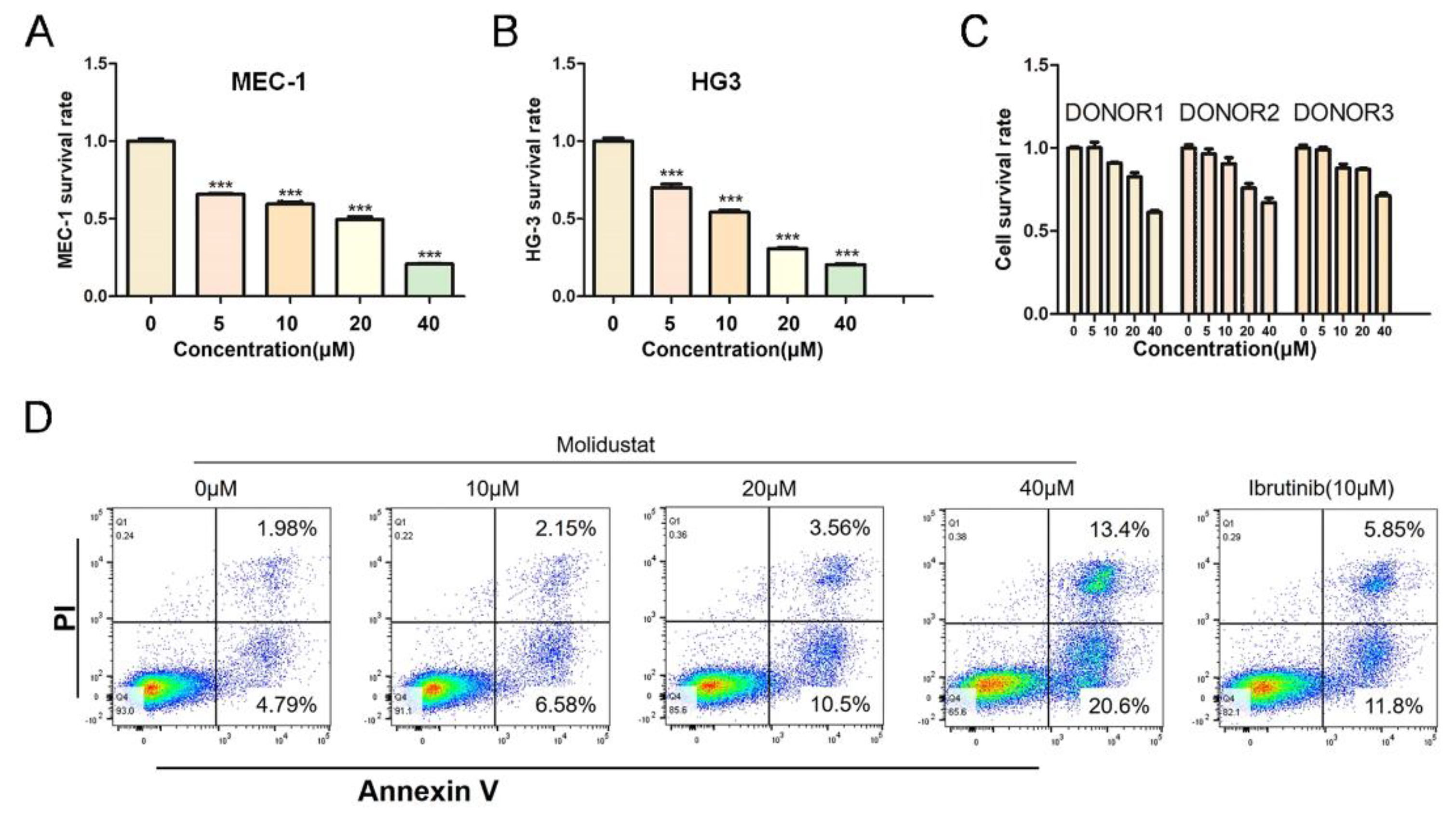
2.3. Molidustat Inhibited Proliferation and Promoted Apoptosis in CLL Cells
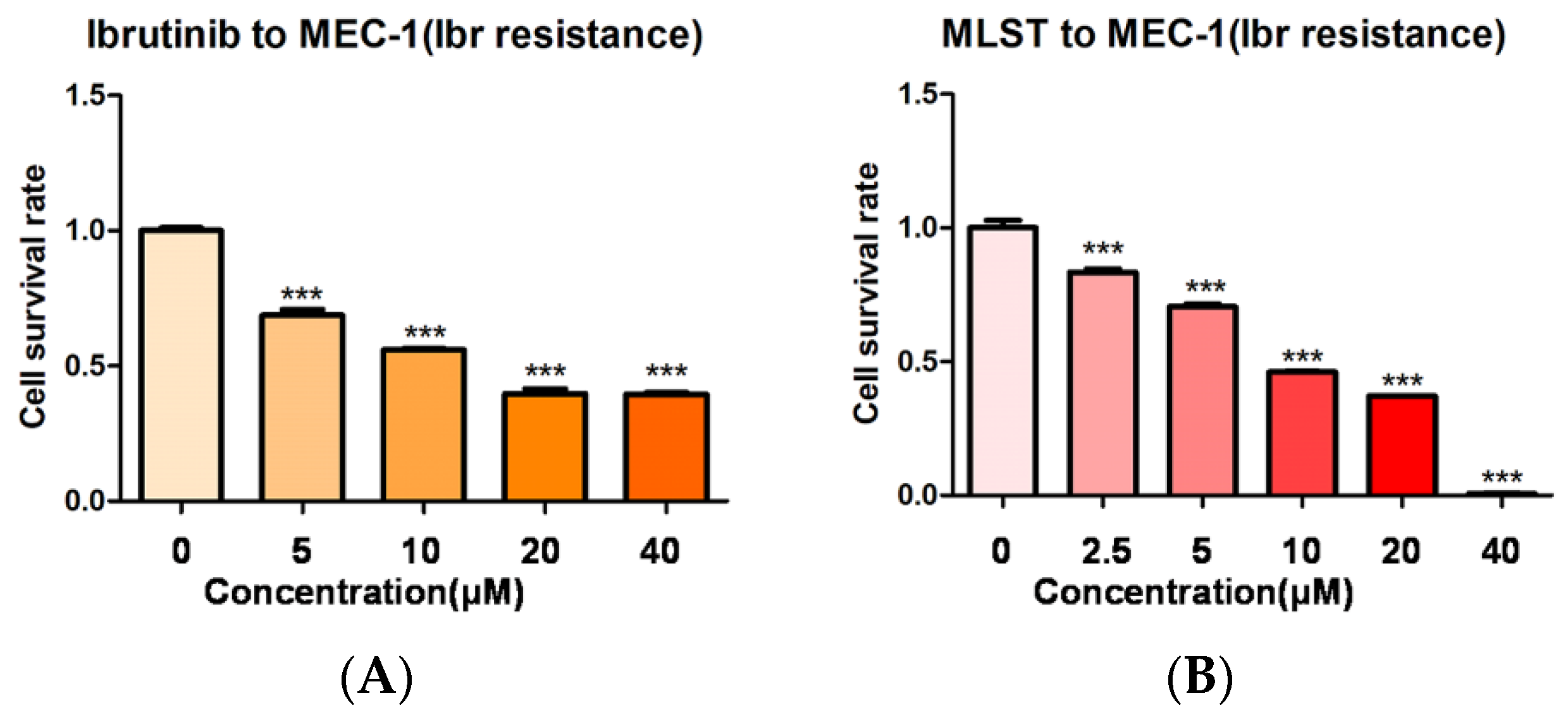
2.4. Molidustat Remains Effective against Ibrutinib-Resistant MEC-1 Cells
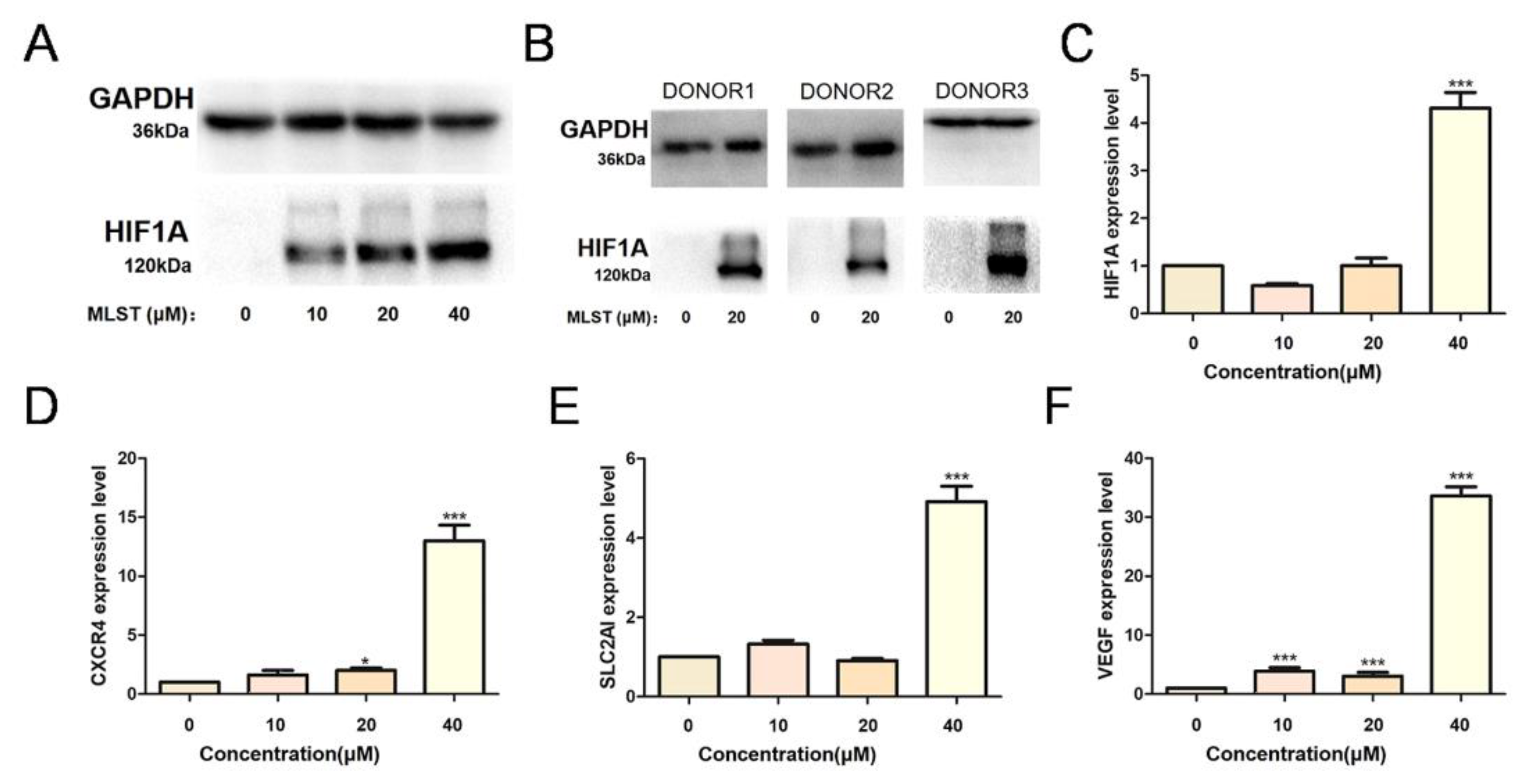
2.5. Molidustat Increased HIF1A Protein Expression and Induced Downstream Activation in CLL Cell Lines
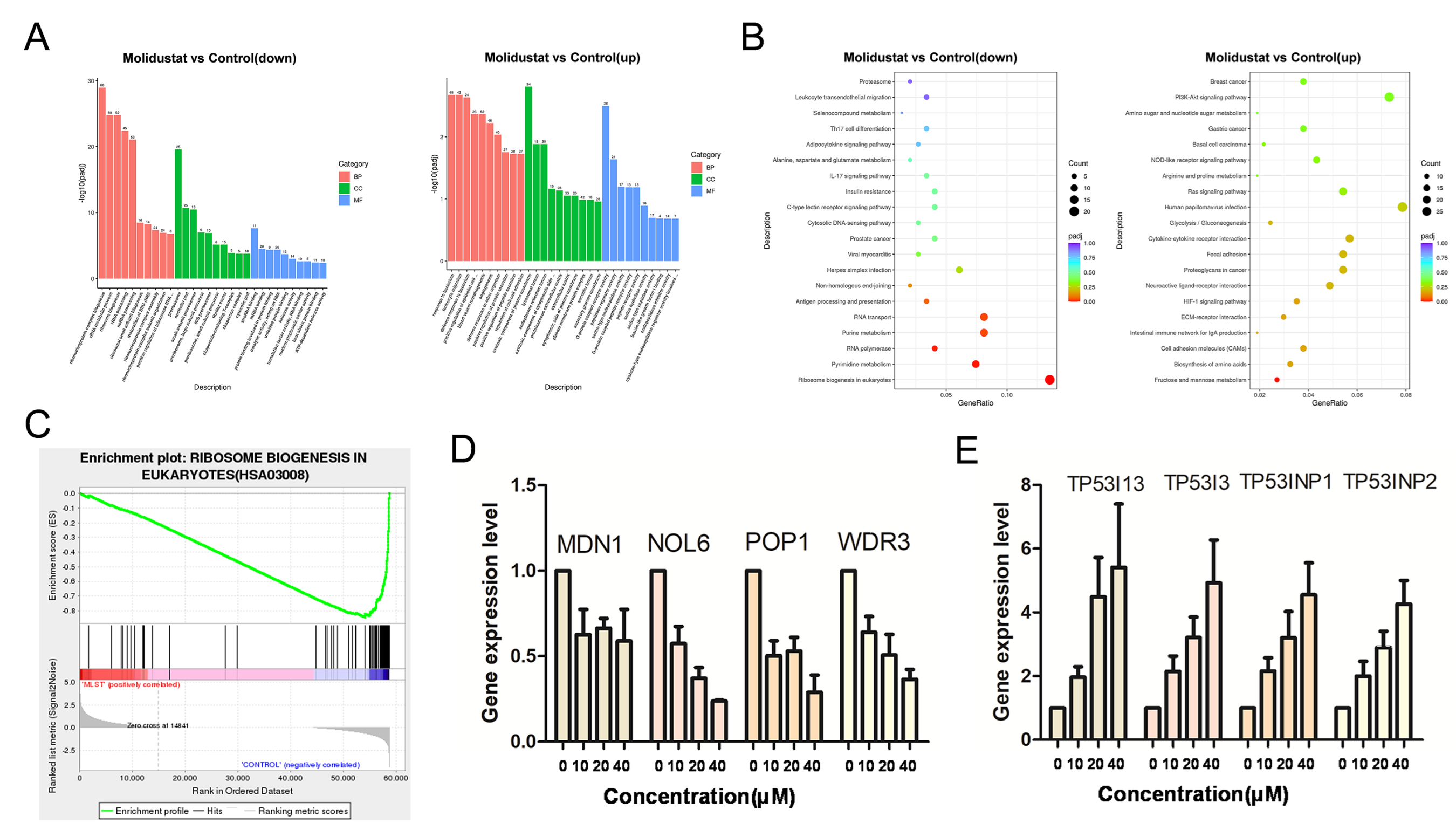
2.6. Molidustat Inhibited Ribosome Biogenesis and Increased TP53I Family Gene Expression in CLL Cells
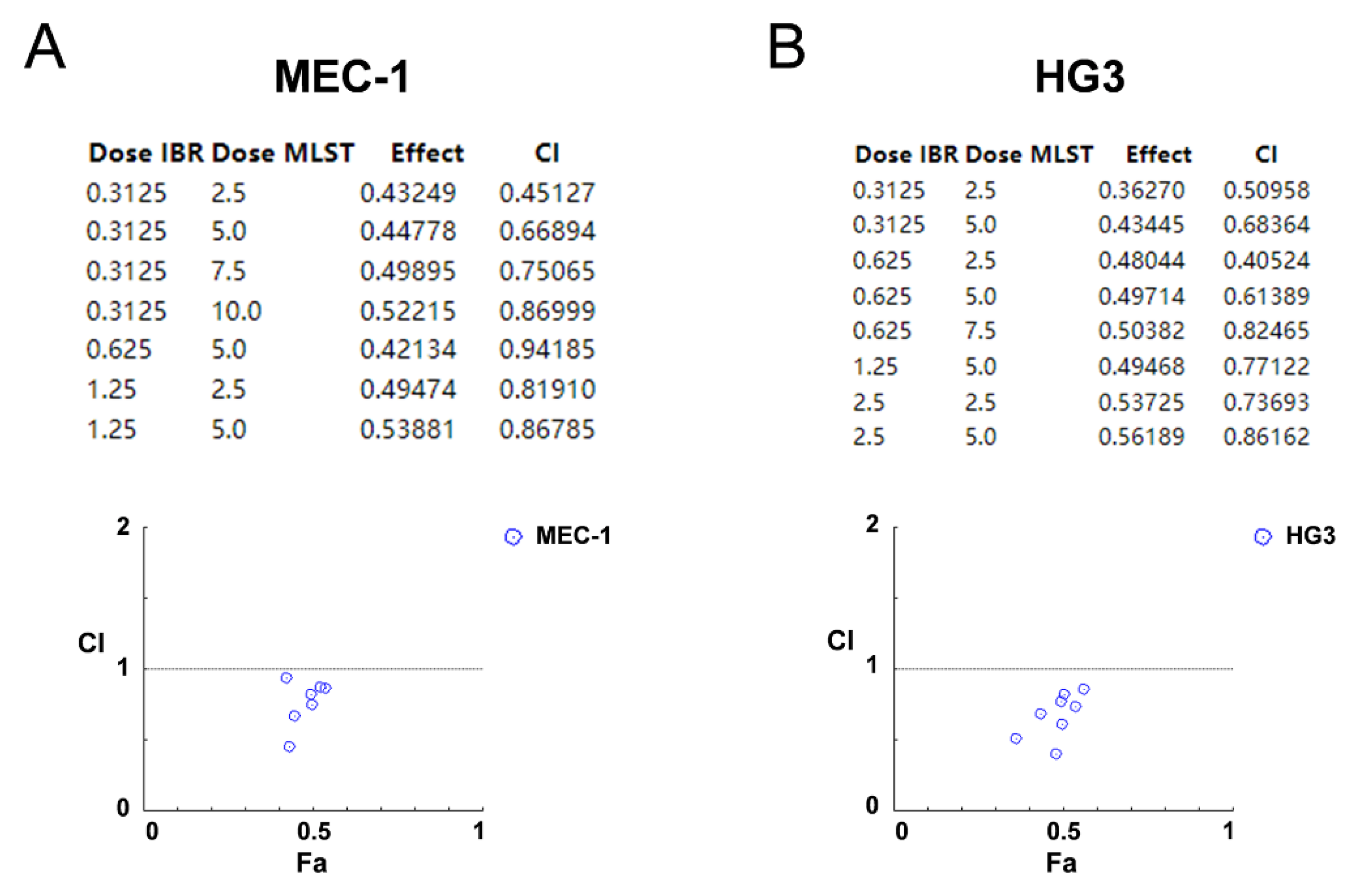
2.7. Synergistic Effects of Molidustat and Ibrutinib on CLL Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Materials
4.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.3. Virus Preparation and Transfection
4.4. Growth Curve of Cells after Transfection
4.5. Treatments
4.6. Cell Viability
4.7. Construction of Ibrutinib-Resistant Strains
4.8. Apoptosis Assays
4.9. RNA Extraction and Real-Time qPCR
4.10. Western Blotting
4.11. Primary Cell Isolation, Culture, and Treatment
4.12. RNA Sequencing
4.13. Analysis of Synergistic Effects
4.14. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hallek, M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2020 update on diagnosis, risk stratification and treatment. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1266–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Kipps, T.J. The pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, S.; Rai, K.R. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treatment: So many choices, such great options. Cancer 2019, 125, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, N.; Gandhi, V. Ibrutinib combinations in CLL therapy: Scientific rationale and clinical results. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furstenau, M.; Eichhorst, B. Novel Agents in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: New Combination Therapies and Strategies to Overcome Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Furman, R.R.; Liu, T.M.; Ozer, H.G.; Zapatka, M.; Ruppert, A.S.; Xue, L.; Li, D.H.; Steggerda, S.M.; Versele, M.; et al. Resistance mechanisms for the Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2286–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, E.; Mi, X.; Thompson, M.C.; Montoya, S.; Notti, R.Q.; Afaghani, J.; Durham, B.H.; Penson, A.; Witkowski, M.T.; Lu, S.X.; et al. Mechanisms of Resistance to Noncovalent Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.K.; Forconi, F.; Kipps, T.J. Exploring the pathways to chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2021, 138, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.Y.; Widhopf, G.F., 2nd; Ghia, E.M.; Kidwell, R.L.; Hasan, M.K.; Yu, J.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Pittman, E.; et al. Phase I Trial: Cirmtuzumab Inhibits ROR1 Signaling and Stemness Signatures in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 951–959.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McWilliams, E.M.; Lucas, C.R.; Chen, T.; Harrington, B.K.; Wasmuth, R.; Campbell, A.; Rogers, K.A.; Cheney, C.M.; Mo, X.; Andritsos, L.A.; et al. Anti-BAFF-R antibody VAY-736 demonstrates promising preclinical activity in CLL and enhances effectiveness of ibrutinib. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.M.; Woyach, J.A.; Zhong, Y.; Lozanski, A.; Lozanski, G.; Dong, S.; Strattan, E.; Lehman, A.; Zhang, X.; Jones, J.A.; et al. Hypermorphic mutation of phospholipase C, gamma2 acquired in ibrutinib-resistant CLL confers BTK independency upon B-cell receptor activation. Blood 2015, 126, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valsecchi, R.; Coltella, N.; Belloni, D.; Ponente, M.; Ten Hacken, E.; Scielzo, C.; Scarfo, L.; Bertilaccio, M.T.; Brambilla, P.; Lenti, E.; et al. HIF-1alpha regulates the interaction of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells with the tumor microenvironment. Blood 2016, 127, 1987–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griggio, V.; Vitale, C.; Todaro, M.; Riganti, C.; Kopecka, J.; Salvetti, C.; Bomben, R.; Bo, M.D.; Magliulo, D.; Rossi, D.; et al. HIF-1alpha is over-expressed in leukemic cells from TP53-disrupted patients and is a promising therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 105, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Q.; Yang, H.; Sun, L.; Wei, R.; Fu, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.N.; Liu, W.J. Efficacy and safety of HIF prolyl-hydroxylase inhibitor vs epoetin and darbepoetin for anemia in chronic kidney disease patients not undergoing dialysis: A network meta-analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachamakova-Trojanowska, N.; Podkalicka, P.; Bogacz, T.; Barwacz, S.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J.; Loboda, A. HIF-1 stabilization exerts anticancer effects in breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 175, 113922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallek, M.; Al-Sawaf, O. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: 2022 update on diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1679–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, I.; Li, Y.; Sharma, A.; Zhu, H.; Bodo, J.; Xu, W.; Hsi, E.D.; Hill, B.T.; Almasan, A. Resistance to BTK inhibition by ibrutinib can be overcome by preventing FOXO3a nuclear export and PI3K/AKT activation in B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsinas, A.; Aggarwal, V.; Tan, E.J.; Levy, B.; Gorgoulis, V.G. PIG3: A novel link between oxidative stress and DNA damage response in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2012, 327, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ye, L.; Li, D.; Yao, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Tan, Z.; et al. MicroRNA-106a regulates autophagy-related cell death and EMT by targeting TP53INP1 in lung cancer with bone metastasis. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turi, Z.; Lacey, M.; Mistrik, M.; Moudry, P. Impaired ribosome biogenesis: Mechanisms and relevance to cancer and aging. Aging 2019, 11, 2512–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, C.; Griggio, V.; Riganti, C.; Todaro, M.; Kopecka, J.; Jones, R.; Salvetti, C.; Boccellato, E.; Perutelli, F.; Voena, C.; et al. Targeting HIF-1alpha Regulatory Pathways as a Strategy to Hamper Tumor-Microenvironment Interactions in CLL. Cancers 2021, 13, 2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Lu, C.C.; Yang, L.Y.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, B.S.; Cai, H.Q.; Hao, J.J.; Xu, X.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. ANXA2 promotes esophageal cancer progression by activating MYC-HIF1A-VEGF axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, A.L. Hypoxia—A key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouault-Pierre, K.; Hamilton, A.; Bonnet, D. Effect of hypoxia-inducible factors in normal and leukemic stem cell regulation and their potential therapeutic impact. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2016, 16, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Wish, J.B. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors: A Potential New Treatment for Anemia in Patients with CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penzo, M.; Montanaro, L.; Trere, D.; Derenzini, M. The Ribosome Biogenesis-Cancer Connection. Cells 2019, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Russo, A.; Russo, G. Ribosomal Proteins Control or Bypass p53 during Nucleolar Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, K.; Kumazawa, T.; Kuroda, T.; Katagiri, N.; Tsuchiya, M.; Goto, N.; Furumai, R.; Murayama, A.; Yanagisawa, J.; Kimura, K. Perturbation of ribosome biogenesis drives cells into senescence through 5S RNP-mediated p53 activation. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1310–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molavi, G.; Samadi, N.; Hosseingholi, E.Z. The roles of moonlight ribosomal proteins in the development of human cancers. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8327–8341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiffert, M.; Stilgenbauer, S.; Dohner, H.; Lichter, P. Efficient nucleofection of primary human B cells and B-CLL cells induces apoptosis, which depends on the microenvironment and on the structure of transfected nucleic acids. Leukemia 2007, 21, 1977–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, W.; Liang, D.; Wang, P.; Yin, L.; Zhang, H.; Xing, C.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Cheng, Z.; et al. HIF-PH Encoded by EGLN1 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060734
Guo W, Liang D, Wang P, Yin L, Zhang H, Xing C, Huang Z, Wu Y, Li H, Cheng Z, et al. HIF-PH Encoded by EGLN1 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(6):734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060734
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Wancheng, Daomiao Liang, Peilong Wang, Le Yin, Huifang Zhang, Cheng Xing, Zineng Huang, Yinghua Wu, Heng Li, Zhao Cheng, and et al. 2022. "HIF-PH Encoded by EGLN1 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 6: 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060734
APA StyleGuo, W., Liang, D., Wang, P., Yin, L., Zhang, H., Xing, C., Huang, Z., Wu, Y., Li, H., Cheng, Z., Xiao, X., Liu, J., Wang, Z., & Peng, H. (2022). HIF-PH Encoded by EGLN1 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Pharmaceuticals, 15(6), 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060734







