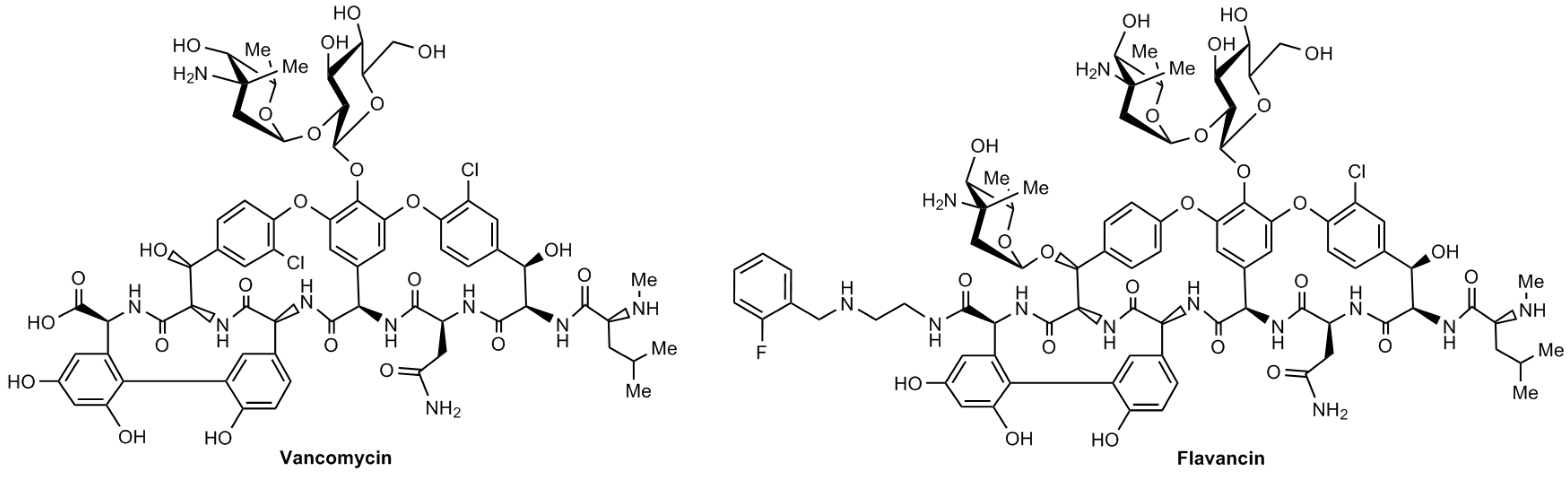
Evaluation of Toxic Properties of New Glycopeptide Flavancin on Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Acute Toxicity
2.2. Chronic Toxicity
2.2.1. Observations, Functional Indicators, and Clinical Laboratory Tests
2.2.2. Histological Evaluation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Acute Toxicity
4.2. Chronic Toxicity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blaskovich, M.; Hansford, K.A.; Butler, M.S.; Jia, Z.; Mark, A.E.; Cooper, M.A. Developments in Glycopeptide Antibiotics. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 11, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moiseenko, E.I.; Erdei, R.; Grammatikova, N.E.; Mirchink, E.P.; Isakova, E.B.; Pereverzeva, E.R.; Batta, G.; Shchekotikhin, A.E. Aminoalkylamides of Eremomycin Exhibit an Improved Antibacterial Activity. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauze, G.F.; Brazhnikova, M.G.; Laĭko, A.V.; Sveshnikova, M.A.; Preobrazhenskaia, T.P. Eremomycin—A new antibiotic from the cyclic glycopeptide group. Antibiot. Med. Biotekhnol. 1987, 32, 571–576. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malkova, I.V. Experimental study of the antibacterial activity and chemotherapeutic efficacy of the novel glycopeptide eremomycin. Antibiot. Chemother. 1989, 34, 52–56. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Filippos’iants, S.T.; Malkova, I.V.; Gol’dberg, L.E. Glycopeptide antibiotics: Eremomycin, vancomycin, and teicoplanin. Comparison of several parameters of pharmacokinetics and antimicrobial activity. Antibiot. Chemother. 1989, 34, 523–526. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Filippos’iants, S.T.; Shevniuk, L.A. Experimental study of histamine-liberating properties of eremomycin. Antibiot. Chemother. 1989, 34, 209–212. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Moiseenko, E.I.; Grammatikova, N.E.; Shchekotikhin, A.E. Eremomycin Picolylamides and Their Cationic Lipoglycopeptides: Synthesis and Antimicrobial Properties. Macroheterocycles 2019, 12, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Groesen, E.; Slingerland, C.J.; Innocenti, P.; Mihajlovic, M.; Masereeuw, R.; Martin, N.I. Vancomyxins: Vancomycin-Polymyxin Nonapeptide Conjugates That Retain Anti-Gram-Positive Activity with Enhanced Potency against Gram-Negative Strains. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 10, 2746–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.C.; Cameron, M.D.; Boger, D.L. Vancomycin C-Terminus Guanidine Modifications and Further Insights into an Added Mechanism of Action Imparted by a Peripheral Structural Modification. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 14, 2169–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, Y.; Dhanda, G.; Sarkar, P.; Haldar, J. Pursuit of next-generation glycopeptides: A journey with vancomycin. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 1881–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mühlberg, E.; Umstätter, F.; Kleist, C.; Domhan, C.; Mier, W.; Uhl, P. Renaissance of vancomycin: Approaches for breaking antibiotic resistance in multidrugresistant bacteria. Can. J. Microbiol. 2020, 66, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedl, M.A.; Casillas, A.M. Adverse drug reactions: Types and treatment options. Am. Fam. Phys. 2003, 68, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar]
- Hermsen, E.D.; Hanson, M.; Sankaranarayanan, J.; Stoner, J.A.; Florescu, M.C.; Rupp, M.E. Clinical outcomes and nephrotoxicity associated with vancomycin trough concentrations during treatment of deep-seated infections. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2010, 9, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, E.; Keynan, Y. Vancomycin Revisited—60 Years Later. Front. Public Health 2014, 2, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, G.R.; Arhin, F.F.; Wikler, M.A.; Sahm, D.F.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; Mediavilla, J.R.; Good, S.; Fiset, C.; Jiang, H.; Moeck, G.; et al. SOLO I, SOLO II Investigators. Pooled analysis of single-dose oritavancin in the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin-structure infections caused by Grampositive pathogens, including a large patient subset with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 48, 528–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masterton, R.; Cornaglia, G.; Courvalin, P.; Lode, H.M.; Rello, J.; Torres, A. The clinical positioning of telavancin in Europe. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 45, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huband, M.D.; Castanheira, M.; Farrell, D.J.; Flamm, R.K.; Jones, R.N.; Sader, H.S.; Mendes, R.E. In vitro activity of dalbavancin against multidrugresistant Staphylococcus aureus and streptococci from patients with documented infections in Europe and surrounding regions (2011–2013). Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2016, 47, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plattner, J.; Chu, D.; Mirchink, E.P.; Isakova, E.B.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.N.; Olsufyeva, E.N. N’-(alpha-aminoacyl)- and N’-alpha-(N-alkylamino)acyl derivatives of vancomycin and eremomycin II. Antibacterial activity of N’-(alpha-aminoacyl)- and N’-alpha-(N-alkylamino)acyl derivatives of Vancomycin and Eremomycin. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moiseenko, E.I.; Grammatikova, N.E.; Shchekotikhin, A.E. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Aminoalkylamides of Eremomycin. Macroheterocycles 2020, 13, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izsépi, L.; Erdei, R.; Tevyashova, A.N.; Grammatikova, N.E.; Shchekotikhin, A.E.; Herczegh, P.; Batta, G. Bacterial Cell Wall Analogue Peptides Control the Oligomeric States and Activity of the Glycopeptide Antibiotic Eremomycin: Solution NMR and Antimicrobial Studies. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Printsevskaya, S.S.; Pavlov, A.Y.; Olsufyeva, E.N.; Mirchink, E.P.; Isakova, E.B.; Reznikova, M.I.; Goldman, R.C.; Branstrom, A.A.; Baizman, E.R.; Longley, C.B.; et al. Synthesis and mode of action of hydrophobic derivatives of the glycopeptide antibiotic eremomycin and des-(N-methyl-D-leucyl)eremomycin against glycopeptide-sensitive and -resistant bacteria. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maples, K.R.; Wheeler, C.; Ip, E.; Plattner, J.; Chu, D.; Zhang, Y.K.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.N.; Printsevskaya, S.S.; Solovieva, S.E.; Olsufyeva, E.N.; et al. Novel semisynthetic derivative of antibiotic eremomycin active against drug-resistant gram-positive pathogens including Bacillus anthracis. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 3681–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Printsevskaya, S.S.; Reznikova, M.I.; Korolev, A.M.; Lapa, G.B.; Olsufyeva, E.N.; Preobrazhenskaya, M.N.; Plattner, J.J.; Zhang, Y.K. Synthesis and study of antibacterial activities of antibacterial glycopeptide antibiotics conjugated with benzoxaboroles. Future Med. Chem. 2013, 5, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsufyeva, E.N.; Shchekotikhin, A.E.; Bychkova, E.N.; Pereverzeva, E.R.; Treshalin, I.D.; Mirchink, E.P.; Isakova, E.B.; Chernobrovkin, M.G.; Kozlov, R.S.; Dekhnich, A.V.; et al. Eremomycin pyrrolidide: A novel semisynthetic glycopeptide with improved chemotherapeutic properties. Drug Des. Devel 2018, 12, 2875–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.I. Biopsy-proved acute tubulointerstitial nephritis and toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with vancomycin. Pharmacotherapy 2001, 21, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancocin® HCl. Vancomycin Hydrochloride for Injection USP. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2021/060180s049lbl.pdf (accessed on 24 May 2022).
- Black, E.; Lau, T.T.; Ensom, M.H. Vancomycin-induced neutropenia: Is it dose- or duration-related? Ann. Pharm. 2011, 45, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.L.L.; Kondo, W.; Baptista, M.; Cunha, C.A.; Martins, L.T. Uncommon vancomycin-induced side effects. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 6, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepelevtseva, N.G.; Goldberg, L.E.; Vertogradova, T.P.; Shevniuk, L.A.; Stepanova, E.S. Preclinical toxicological study of a new antibiotic eremomycin. Chronic toxicity, impact on prenatal development of rats. Antibiot. Chemother. 1988, 33, 280–286. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Council of Europe European Convention for the Protection of Vertebrate Animals Used for Experimental and Other Purposes. Strasbourg: 1986, 18.III.1986, Council of Europe, ETS No.123. Available online: https://rm.coe.int/168007a67b (accessed on 28 August 2018).
- Directive 2010/63/EU on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes EN. Official Journal of the European Union, L 276/33-276/79 (20.10.2010). Available online: https://eurlex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2010:276:0033:0079:EN:PDF (accessed on 27 April 2020).
- National State Standard GOST 33044-2014 the Russian Federation Standard «The Principles of Good Laboratory Practice» (Approved and Put into Effect by the Order of the Federal Agency for Technical Regulation and Metrology of 20 October 2014), No 1700. Available online: https://docs.cntd.ru/document/1200115791 (accessed on 1 August 2015). (In Russian).
- Adams, J.V.; Slaght, K.S.; Boogaard, M.A. An automated approach to Litchfield and Wilcoxon’s evaluation of dose-effect experiments using the R package LW1949. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 3058–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Bacterial Strain | Eremomycin | Vancomycin |
|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcusaureus ATCC 25,923 | 0.13–0.25 | 1.0–1.0 |
| Staphylococcus epidermicus 533 | 0.13–0.25 | 1.0–2.0 |
| Staphylococcus haemoliticus 602 | 0.13–0.13 | 1.0–1.0 |
| Enteroccus faecalis 559 | 0.25–0.25 | 1.0–1.0 |
| Enteroccus faecium 4 | 0.25–0.25 | 1.0–1.0 |
| Parameter | Doses, mg/kg | |
|---|---|---|
| Males | Females | |
| LD10 (MTD) | 94.8 | 98.1 |
| LD50 | 157.7 (126.0 ÷ 188.0) * | 159.4 (127.3 ÷ 190.0) * |
| LD100 | 236 | 242 |
| Organ | Day 1 | Day 30 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flavancin of 6 mg/kg/day | Flavancin of 10 mg/kg/day | Flavancin of 6 mg/kg/day | Flavancin of 10 mg/kg/day | |
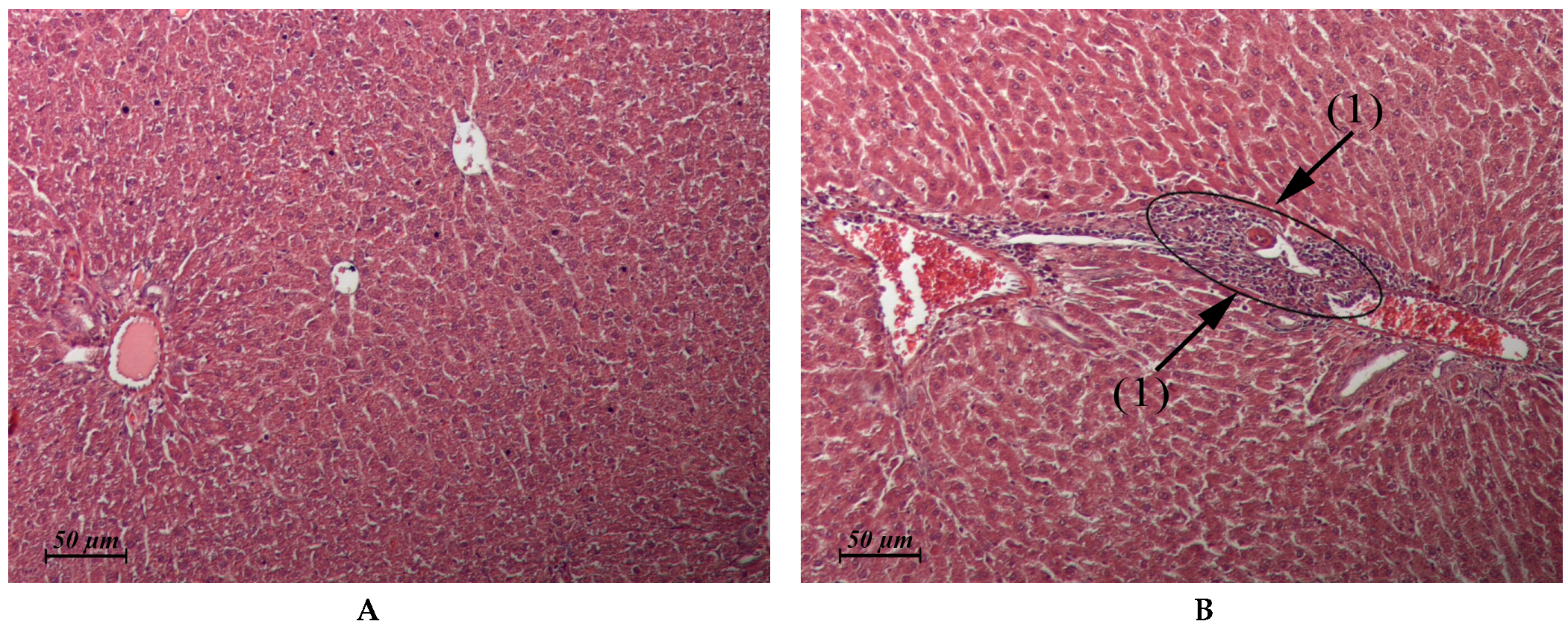
| Liver (Control: Figure 2A) | Similar to control | Micronecrotic foci in the vicinity of single triads (Figure 2B) | Similar to control | Similar to control |
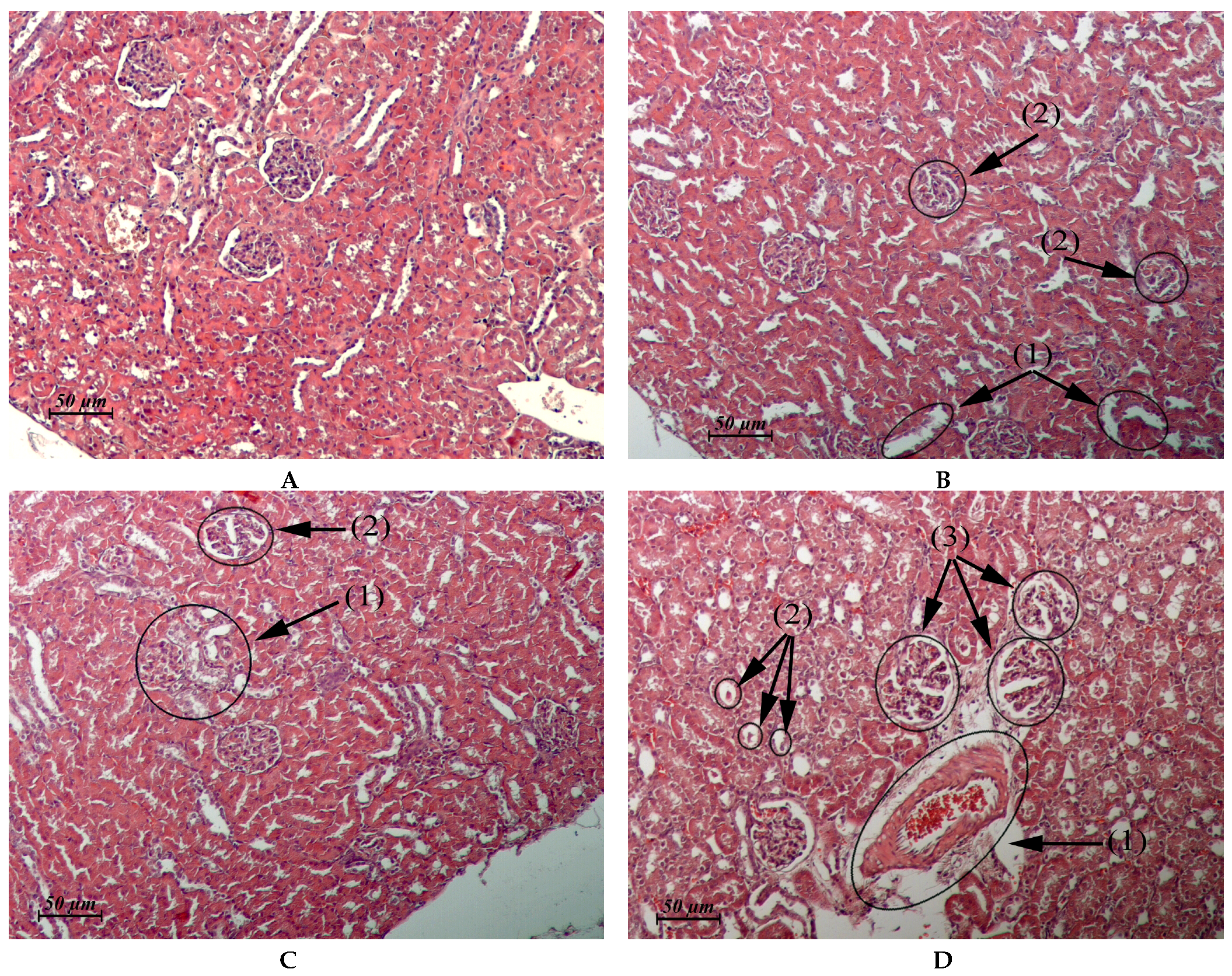
| Kidney (Control: Figure 3A) | Cortical and juxtamedullary zones: vacuolar dystrophy of the epithelium of some convoluted tubules. Thickening of the glomerular capsule and focal atrophy of the glomerular capillary network in single glomeruli (Figure 3B). | Cortical zone: small foci of granular and vacuolar dystrophy of the epithelium of some convoluted tubules in single-clawed glomeruli (Figure 3C). Juxtamedullary zone: moderate perivascular edema, multiple small foci of vacuolar dystrophy, single foci destruction in the epithelial layer of some convoluted tubules, clawed glomeruli with a sharply expanded lumen of the capsule (Figure 3D). | Similar to control | Similar to control. In one male, single glomeruli with a thickened capsule and single scarring glomeruli were found in the cortical and juxtamedullary zones. |
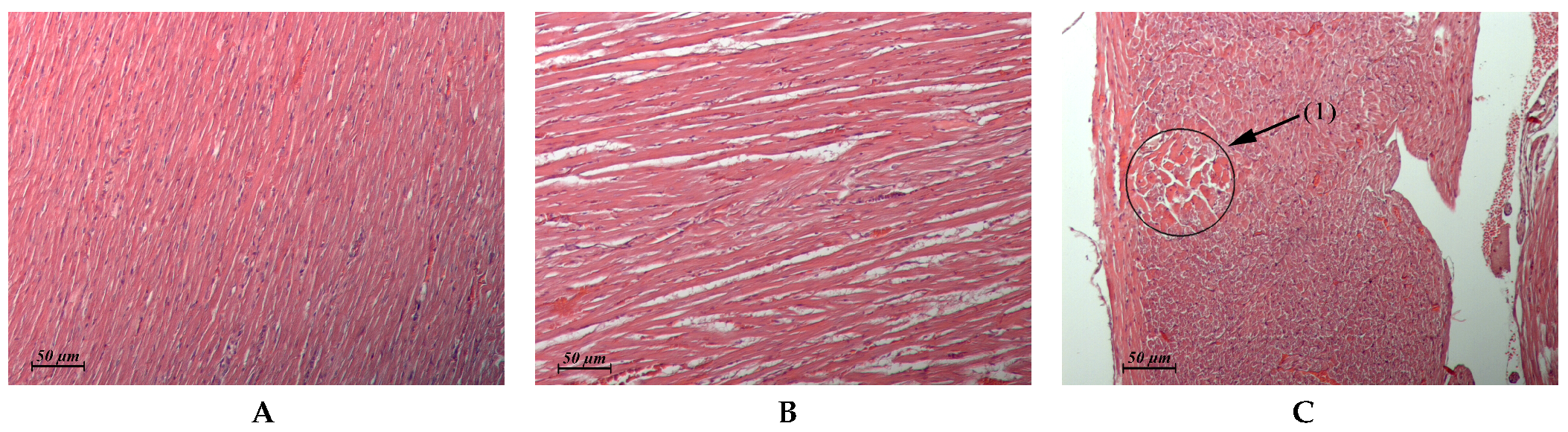
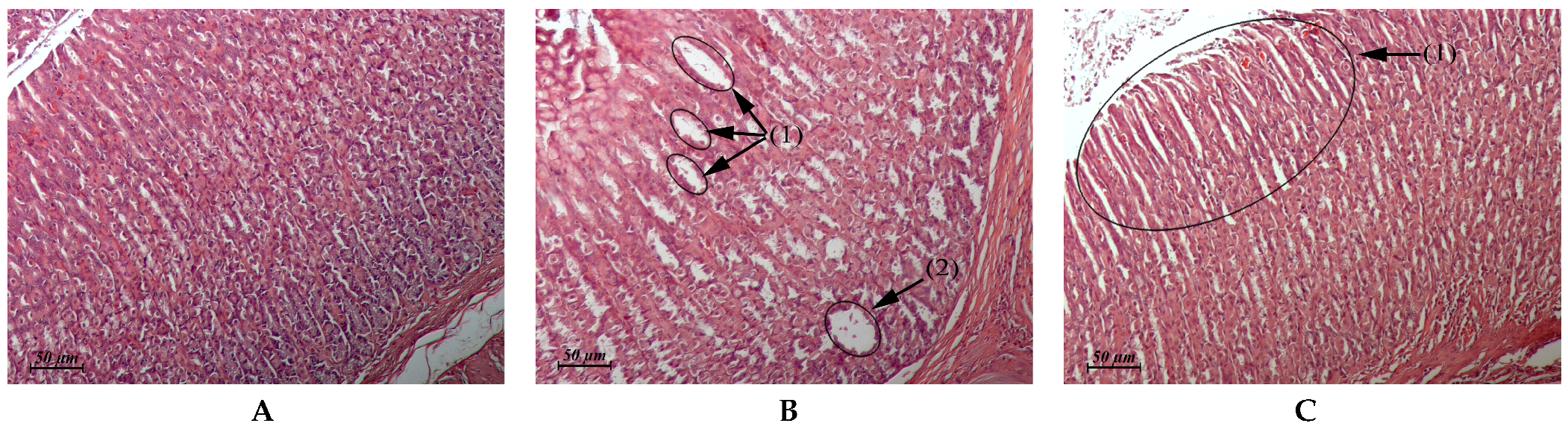
| Myocardium (Control: Figure 4A) | Similar to control | Foci of interstitial edema (Figure 4B). Some animals exhibited single foci of interstitial edema that was associated with toxic cardiomyopathy (Figure 4C) | Similar to control | Similar to control |
| Stomach (Control: Figure 5A) | Similar to control | Sharp expansion of the glands lumen of mucosa, which was sometimes accompanied by the formation of cysts lined with squamous or cuboidal epithelial cells. Parietal cells prevailed in the glands. The destruction of the parietal cells in single glands was observed (Figure 5B). We observed deep focal atrophy of the gastric gland epithelium with replacement of the glandular epithelium by the surface epithelium in these areas (Figure 5C). | Similar to control | Similar to control |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Treshchalin, M.I.; Polozkova, V.A.; Moiseenko, E.I.; Treshalina, H.M.; Shchekotikhin, A.E.; Pereverzeva, E.R. Evaluation of Toxic Properties of New Glycopeptide Flavancin on Rats. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060661
Treshchalin MI, Polozkova VA, Moiseenko EI, Treshalina HM, Shchekotikhin AE, Pereverzeva ER. Evaluation of Toxic Properties of New Glycopeptide Flavancin on Rats. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(6):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060661
Chicago/Turabian StyleTreshchalin, Michael I., Vasilisa A. Polozkova, Elena I. Moiseenko, Helen M. Treshalina, Andrey E. Shchekotikhin, and Eleonora R. Pereverzeva. 2022. "Evaluation of Toxic Properties of New Glycopeptide Flavancin on Rats" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 6: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060661
APA StyleTreshchalin, M. I., Polozkova, V. A., Moiseenko, E. I., Treshalina, H. M., Shchekotikhin, A. E., & Pereverzeva, E. R. (2022). Evaluation of Toxic Properties of New Glycopeptide Flavancin on Rats. Pharmaceuticals, 15(6), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15060661






