Abstract
Magnesium complexes of phthalocyanines (Pcs) and their aza-analogues have a great potential in medical applications or fluorescence detection. They are known to demetallate to metal-free ligands in acidic environments, however, detailed investigation of this process and its possible prevention is lacking. In this work, a conversion of lipophilic and water-soluble magnesium complexes of Pcs and tetrapyrazinoporphyrazines (TPyzPzs) to metal-free ligands was studied in relation to the acidity of the environment (organic solvent, water) including the investigation of the role of delivery systems (microemulsion or liposomes) in improvement in their acido-stability. The mechanism of the demetallation in organic solvents was based on an acidoprotolytic mechanism with the protonation of the azomethine nitrogen as the first step and a subsequent conversion to non-protonated metal-free ligands. In water, the mechanism seemed to be solvoprotolytic without any protonated intermediate. The water-soluble magnesium complexes were stable in a buffer with a physiological pH 7.4 while a time-dependent demetallation was observed in acidic pH. The demetallation was immediate at pH < 2 while the full conversion to metal-free ligand was done within 10 min and 45 min for TPyzPzs at pH 3 and pH 4, respectively. Incorporation of lipophilic magnesium complexes into microemulsion or liposomes substantially decreased the rate of the demetallation with the latter delivery system being much more efficient in the protection from the acidic environment. A comparison of two different macrocyclic cores revealed significantly higher kinetic inertness of magnesium TPyzPz complexes than their Pc analogues.
1. Introduction
Magnesium phthalocyanines (Pcs), similarly to their various aza-analogues and lower homologues, have attracted the attention of researchers since their first reports by Linstead in the 1930s [1,2]. Their synthesis is simple and they are readily accessible by the reaction of suitable substituted dinitriles with magnesium alkoxides [3,4,5]. They were investigated in several applications, e.g., for panchromatic light-harvesting, [6] for the formation of Langmuir–Shaefer films, [7] or as coatings for electrodes by porphyrazine/multiwalled carbon nanotube hybrids. [8] Magnesium is a light atom and therefore its Pc and porphyrazine complexes are often characterized by a strong fluorescence that is utilized in the development of fluorescent sensors [9,10,11]. The magnesium complexes of Pcs and porphyrazines are also able to efficiently produce a singlet oxygen and for this reason they have been tested several times in photodynamic applications in the treatment of cancer [12,13,14] or bacterial infections [15,16,17,18]. If required, the singlet oxygen production of magnesium complexes in these medical applications can be further increased by the peripheral substitution of heavy-atoms [19,20]. The central magnesium cation in Pcs and their analogues is, however, not very stable and can be removed using various acids [21,22,23]. This is advantageously utilized in the synthesis of metal-free ligands that are firstly prepared using magnesium alkoxide-assisted cyclotetramerization and subsequently demetallated [24,25]. On the other hand, the low resistance of magnesium complexes against acids and easy dissociation to metal-free derivatives in acidic media may be undesirable properties if the intended compounds for various applications are magnesium derivatives. The demetallation may have unexpected consequence since the compounds are often tested under acidic conditions (e.g., cancer tissues have an acidic pH or lysosomes (a typical target of many hydrophilic PSs) also have a pH value of around 5) without any care about the stability of the central magnesium cation. As efficient photosensitizers and/or diagnostic fluorescence imaging tools, Pc and TPyzPzs can meet acidic environments in vivo, typically in some cancer tissues and inflamed areas. Also, in the case of development of targeted third generation photosensitizers by conjugation of a Pc/TPyzPzs with monoclonal antibodies, specific oligonucleotides (antisense or aptamers) or other targeting tools (e.g., liver cells targeting N-acetylgalactosamine) will enter the cells via endosomes or lysosomes. Therefore, the detailed knowledge about their behavior in various pH conditions is crucial to properly design efficient molecules. The unintentionally arisen metal-free ligands of Pcs and porphyrazines often suffer from a low fluorescence or singlet oxygen quantum yields that completely change their usability in photodynamic application or in fluorescence sensing [10,26].
The aim of this project was, therefore, to evaluate and discuss the kinetic inertness of the magnesium complexes of Pc and its aza-analogue of tetrapyrazinoporphyrazine (TPyzPz) type in various acidic environments. Besides water and organic solvent, microemulsion and liposomes were selected for testing as well since both were recently applied as delivery systems in several studies and the access of acid may be potentially restricted by the lipophilic environment [11,19,27,28].
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Design of the Study
The study was focused on two types of Pcs (lipophilic and hydrophilic) and their aza-analogues TPyzPzs (Figure 1). Both of these structural types have been previously extensively studied in photodynamic applications or fluorescence sensing [11,12]. The magnesium complexes PcMg and TPyzPzMg are highly lipophilic with bulky peripheral substituents to decrease the aggregation and were selected for the study in organic solvent (benzene) and in the lipophilic delivery systems of microemulsions and liposomes (Figure 1a,c,d). The water-soluble analogues ws-PcMg and ws-TPyzPzMg are substituted by charged cationic substituents that ensure a high water-solubility (Figure 1b). The electronic effects of alkylsulfanyl substituents in all studied compounds (lipophilic and hydrophilic) are the same and thus the influences of different environments (solvent, delivery systems or water) can be easily studied without being affected by the electron density of the macrocyclic ligand.
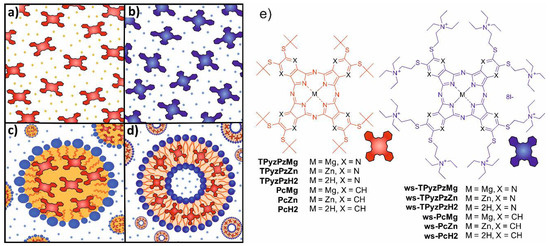
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the studied systems: (a) organic solvent (benzene) with the dissolved lipophilic dyes; (b) water with the dissolved hydrophilic dyes; (c) microemulsion with the lipophilic dyes incorporated in the oil particles; (d) liposomes with the lipophilic dyes incorporated in the lipidic bilayer; and (e) structures of the concerned compounds shown on the right.
In the case of water and benzene, the zinc analogues were studied as well to allow a comparison with a macrocycle which is not demetallated under acidic conditions and to distinguish between a demetallation and other possible processes (e.g., a protonation of the porphyrazine core).
The stability under acidic conditions was monitored spectroscopically by observing changes in the Q-band area of the absorption spectra. The metal complexes (both Mg and Zn) are characterized by the sharp and unsplit Q-band. On the other hand, the produced metal-free derivatives possess the split Q-band due to the lower D2h symmetry.
2.2. Organic Solvent
Several works have suggested that the process of the dissociation of magnesium Pcs and analogues in organic solvents involves several intermediates (some of them appearing only very shortly) depending on the type of solvent used. In benzene, they suggested an acidoprotolytic mechanism where the acid acts as a proton donor and the anion at the same time [29,30]. As the first typical step of this mechanism, a protonation of the azomethine nitrogen (Figure 2, Intermediate I) and an anion coordination to central magnesium were suggested.
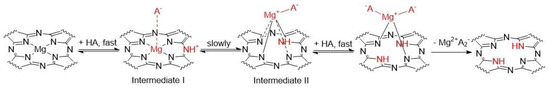
Figure 2.
The acidoprotolytic mechanism of dissociation of Mg complexes in organic solvent in presence of acid HA. Based on ref. [29].
To confirm this mechanism, we examined the protonation of the macrocycles leading to Intermediate I first. A stepwise addition of dichloroacetic acid (DCA) into benzene solution of PcMg and TPyzPzMg led to a decrease in the intensity of the Q-band with an appearance of the novel, red-shifted band at approximately 756 nm and 701 nm, respectively (Figure 3). Based on the literature data, this band can be attributed to the formation of the monoprotonated form of the macrocycle (PcMgH+, TPyzPzMgH+) on azomethine nitrogen (Figure 2, Intermediate I) [31,32,33,34]. The association constant of the macrocycle and DCA in benzene were determined from the titration data (Figure 3, insets) to be Ka = 4.33 ± 0.31 × 103 M−1 and 1.67 ± 0.026 × 103 M−1 for PcMg and TPyzPzMg, respectively, indicating a lower basicity of the latter macrocycle due to the presence of electron-withdrawing pyrazine rings. When the titration of TPyzPzMg was performed with more acidic trifluoroacetic acid (TFA, Figure S1), the Ka value increased to 4.24 ± 0.20 × 104 M−1.
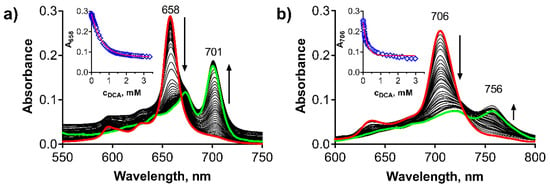
Figure 3.
Changes in absorption spectra during the protonation of (a) TPyzPzMg and (b) PcMg in benzene (cdye = 1 μM) after the addition of DCA. Insets: Changes of the absorbance of the main absorption Q-band of the non-protonated form, red line = nonlinear fit. All data were corrected for a dilution.
Similar spectral changes (Figure S2) after the addition of DCA were observed also for the corresponding zinc complexes confirming that the protonation of an azomethine nitrogen is taking place in acidic environments irrespective of the central metal. Their Ka values were, however, considerably lower than for the corresponding magnesium complexes (1.17 ± 0.02 × 103 M−1 and 3.47 ± 0.05 × 102 M−1, for TPyzPzZn and PcZn, respectively). This finding is in line with observations of the increased basicity of magnesium Pcs in comparison with other metal complexes which have been already noted in the literature [35].
While no qualitative changes were observed for the monoprotonated zinc complexes in time even after 24 h (besides a slight decomposition of PcZn indicated by overall decrease of the absorption at all wavelengths, Figure S2f) due to known high kinetic inertness of these complexes, the spectra of the protonated magnesium macrocycles evolved in time. The spectrum of monoprotonated TPyzPzMgH+ (Intermediate I) was replaced by a new spectrum with the split Q-band and the blue-shifted maxima at 675 nm and 645 nm (Figure 4a) with clear isosbestic points indicating a transformation of one species to another. The change was irreversible. The shape of the spectrum after 24 h of treatment with 4.75 mM DCA perfectly overlapped the spectrum of metal-free TPyzPzH2 (the last structure on Figure 2) with only a small residue of non-demetallated TPyzPzMgH+ appearing as the shoulder at 701 nm (Figure 4a,b). This further supported the mechanism suggested in Figure 2. The fact that the final product of this reaction, TPyzPzH2, is in non-protonated form, has been confirmed by dissolving TPyzPzH2 in benzene and after the addition of DCA (c = 4.75 mM, Figure 4b). The spectra overlapped each other indicating no protonation at this acid concentration which is again in agreement with the reported very low basicity of metal-free Pcs and TPyzPzs [31]. In the case of the demetallation of PcMgH+, similar changes were observed as for the pyrazine analogue, but they were accompanied by its decomposition as deduced from an overall decrease of the absorption intensity at all wavelengths with no apparent isosbestic point (Figure 4c). Despite this, the final product after 24 h was characterized by the absorption maxima in the same position as for metal-free PcH2, similarly as in the case of the pyrazine analogue, indicating that also in this case, the final product is a non-protonated metal-free ligand as suggested in Figure 2.

Figure 4.
Changes of the absorption spectra of protonated (green line) (a) TPyzPzMgH+ and (c) PcMgH+ (cdye = 1 µM) during 24 h in solution of DCA (cDCA = 4.75 mM) in benzene at 25 °C. The normalized absorption spectra of (b) TPyzPzMg, (d) PcMg demetallated by DCA (blue line) in benzene (cDCA = 4.75 mM, 24 h treatment, data from boxes (a,c)). For comparison, the spectra of (b) TPyzPzH2 and (d) PcH2 in benzene (red) and benzene with DCA (cDCA = 4.75 mM, black dashed) are also shown indicating no protonation of metal-free ligands.
The kinetic data from Figure 4 were used to calculate the rate of the dissociation of TPyzPzMgH+ in benzene with DCA. It followed the first order kinetic (Figure 5a). The effective rate constants, keff, for the dissociation increased linearly with increasing DCA concentrations (Figure 5b) in a row 2.98 × 10−6, 4.90 × 10−6, 6.00 × 10−6, 5.41 × 10−6 and 7.54 × 10−6 s−1 for the DCA concentrations 7.17, 9.56, 11.95, 14.34 and 16.73 mM, respectively. From these data, the true rate constant kV = keff/cDCA was calculated to be kV = 4.52 ± 0.57 × 10−4 s−1 M−1. Also, the kinetic data therefore supported the acidoprotolytic mechanism suggested in the literature for this type of dissociation [30]. Due to the decomposition observed during the dissociation of PcMgH+, the kinetic data could not be properly analyzed for this compound.
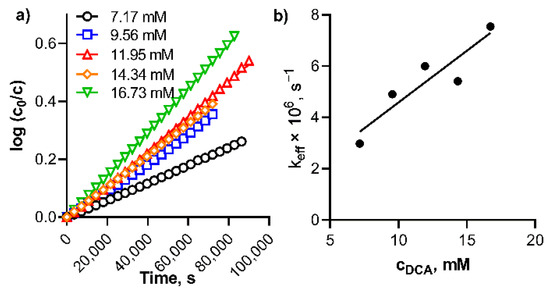
Figure 5.
(a) Plot of log(c0/c) against time for the dissociation of TPyzPzMgH+ in benzene at different concentrations of DCA at 20 °C, and (b) Plot of effective rate constant, keff, (calculated from the data in box (a)) versus the concentration of DCA.
The experiments in benzene, besides confirming the suggested mechanism of the acidoprotolytic dissociation, [30] led to further conclusions about the basicity of azomethine nitrogens, the point of the molecule where the dissociation of magnesium complexes starts. Firstly, the basicity of azomethine nitrogens in magnesium complexes of Pcs and TPyzPzs is substantially increased over zinc complexes and, in particular, over metal-free ligand. Second, the basicity of MgTPyzPz core was lower than that of PcMg.
2.3. Water
The behavior of Pcs and TPyzPzs was studied in Britton–Robinson buffers at acidic pH values (1–4) as well as at a physiological pH = 7.4. First, ws-TPyzPzZn, which is monomeric and kinetically inert in this buffer, was investigated. No changes were observed within 24 h at pH < 3 while at pH = 4, and even more significantly at pH = 7.4, a decrease in the absorbance at all wavelengths was detected without the change of the shape of the spectra (Figure 6b). This behavior can be attributed to a well-known phenomenon of an adsorption of cationic compounds to the negatively charged glass surface [36,37]. The silanol groups on the glass surface are acidic (several different silanol groups are present, the most acidic has pKa = 4.8) that introduces the negative charge to the surface at pH > 4 [38]. On the other hand, the charge density of glass is almost zero in the acidic environment at pH < 4 [39]. The results of our study with limited adsorption of cationic ws-TPyzPzZn at pH < 3 are in full agreement with these findings. To further support this explanation of the decreased absorbance, ws-TPyzPzZn in buffer of pH = 7.4 was left in a cuvette for 24 h; the cuvette was emptied; carefully washed three times with water and filled with distilled water to the same volume as used during the investigation. The absorption spectrum indicated that the cationic compound adsorbed to the glass surface was released back to the solution (Figure S3).
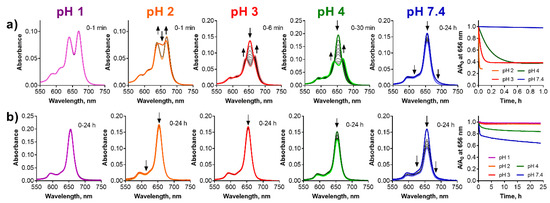
Figure 6.
Changes of the absorption spectra of (a) ws-TPyzPzMg and (b) ws-TPyzPzZn at different pH values of the buffer (cdye = 1 µM). The utmost right graphs show normalized decrease of the absorbance at the λmax of the parent magnesium complexes with time.
Similarly, to the zinc complex, ws-TPyzPzMg was also adsorbed to the glass at pH 7.4 without any qualitative changes observed in the spectrum indicating a full stability during the studied period of 24 h (Figure 6a). Lowering of the pH led to the demetallation, which was detected by a typical split of the Q-band of its product, ws-TPyzPzH2. The rate of the demetallation was also a function of time; the lower pH the faster demetallation. The demetallation was finished almost immediately at pH 1 after the adding of the sample to the buffer and potential residuals of the magnesium complex were not even detected. The residuals of the magnesium complex were observed at pH 2 just after the addition of the sample to the solution. The demetallation was finished in 10 min and in 45 min at pH 3 and pH 4, respectively. Contrary to the above observations in organic solvents, the azomethine-protonated form, ws-TPyzPzMgH+, was not observed at any pH indicating that the mechanism of the demetallation might be different in water, most likely solvoprotolytic as suggested by Berezin et al. for a polar DMSO/H2SO4 system [29]. In this mechanism, the magnesium complex is directly converted to metal-free ligand without any intermediates similarly as observed in our experiments.
The investigation of the Pc analogues ws-PcMg and ws-PcZn was hampered by their clearly aggregated nature in the buffer at a pH above 2 (Figure 7, the utmost right graph). Despite this, the behavior of ws-PcZn was similar to the TPyzPz analogue. Strong adsorption of the cationic compound to glass surface was observed at pH 7.4 and slightly lower at pH 4. Almost no changes were detected at pH 2 and pH 3 (Figure 7b) for ws-PcZn. Surprisingly, a clearly monomeric spectrum was observed at pH 1 with appearance of a typical, red-shifted band corresponding to the small amount of azomethine-protonated species.
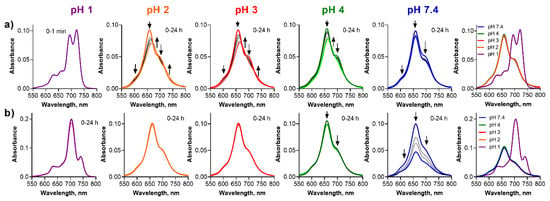
Figure 7.
Changes of the absorption spectra of (a) ws-PcMg and (b) ws-PcZn at different pH values of the buffer (cdye = 1 µM). The utmost right graphs show the absorption spectra just after addition of the stock solution of the dye to the buffer.
For ws-PcMg, the adsorption to the glass surface was clear at pH 7.4 without any qualitative changes to the absorption spectra suggesting a full stability (Figure 7a). The absorption spectra changed the shape with time at pH 2–4 suggesting a slight demetallation process, but this could not be unequivocally confirmed and analyzed due to a strongly aggregated nature of the spectra. However, the data suggested somewhat slower progress of the demetallation in a comparison to the corresponding TPyzPz (e.g., the demetallation of ws-TPyzPzMg was finished within 10 min while the progress was still observable even after 24 h for ws-PcMg). A plausible explanation might be that the aggregated species are less prone to the attack of the acid due to a restricted access of protons to the aggregates. Further, ws-PcMg was demetallated to ws-PcH2 at pH 1 immediately after the mixing of the solutions. At this pH, ws-PcH2 is monomeric and non-protonated confirming further the lower basicity of metal-free ligands.
2.4. Microemulsion
Ethoxylated castor oil/medium chain triglycerides in water microemulsions were employed as simple models of pegylated lipid nanoparticles, which are popular delivery systems for sensitive or purely water soluble pharmaceuticals. Microemulsions are clear, thermodynamically stable systems formed usually by oil particles stabilized in water by an addition of a suitable surfactant (see Figure 1c). The particles have hydrophobic core which may dissolve the lipophilic molecules, in our case the lipophilic PcMg and TPyzPzMg. Here, TPyzPzMg appeared to be fully stable in microemulsion at pH > 4 for at least 24 h. Only a small decrease in the absorbance of the Q-band due to demetallation was observed at pH 2 and 3 (Figure 8a). The data obtained at pH 1 could not be properly analyzed since this pH apparently led to the destruction of the delivery system as suggested by an increasing background during the measurements. Once the delivery system was destroyed, TPyzPzMg either precipitated from the solution or was destructed as indicated by the featureless absorption spectra in the Q-band area. The demetallation can potentially also take place during the destruction of microemulsion at pH 1, but this cannot be unequivocally confirmed or refuted from the obtained data. Contrary to the TPyzPz analogue, PcMg is stable in the microemulsion only at pH 7.4. At a lower pH, the changes in the absorption spectra indicated the demetallation process to PcH2 with the pH-dependent rate (Figure 8b). Similarly, pH 1 destroyed the microemulsion but PcMg was converted almost immediately to PcH2. The mechanism of the demetallation in microemulsions is most likely also solvoprotolytic since no protonated species were detected during the measurements and the conversion ran directly from the magnesium complex to the metal-free ligand. A direct comparison of the two macrocycles (PcMg and TPyzPzMg) clearly indicated much higher stability of the TPyzPzMg in the microemulsion.
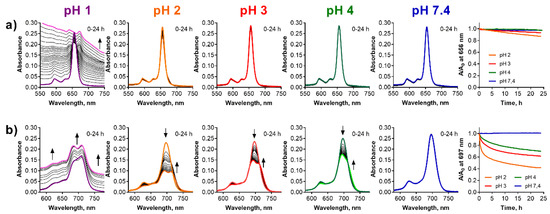
Figure 8.
Changes of the absorption spectra of (a) TPyzPzMg and (b) PcMg in the microemulsion (cdye = 1 µM) at different pH values of the buffer. The increasing backgrounds at pH = 1 are due to instability of the microemulsion in strongly acidic pH. The utmost right graphs show the normalized decrease of the absorbance at the λmax of the parent magnesium complexes with time.
2.5. Liposomes
Liposomes are spherical-shaped vesicles formed by a lipophilic bilayer with a hydrophilic inner compartment (see Figure 1d). The lipophilic bilayer may host lipophilic compounds and, in addition to functioning as a delivery system or drug carrier, it can also serve as a simple model of biomembranes [40,41]. Contrary to the microemulsion, the liposomes as a delivery system were stable also at pH 1. The observation of the absorption spectra of TPyzPzMg in the liposomes did not indicate any change at any pH even after 24 h of the treatment and the compound in the liposomes was therefore fully protected against the attack of the acidic environment (Figure 9a). Similarly, PcMg in the liposomes appeared to be less stable in this delivery system than the TPyzPz analogue (Figure 9b). The compound was fully stable for 24 h only at a physiological pH 7.4. The decrease of the absorption at the Q-band at pH 4 and the typical increase of the absorption of PcH2 at longer wavelengths at pH 2 and pH 3 during 24 h suggested that the process of the demetallation occurred. This was confirmed by the full demetallation at pH 1 within 1.5 h of the treatment. Data from both PcMg and TPyzPzMg in liposomes can be compared also with the previous delivery system. The comparison of the results for both compounds clearly indicated a better protection of incorporated lipophilic compounds from the acidic environment in liposomes than in microemulsion.
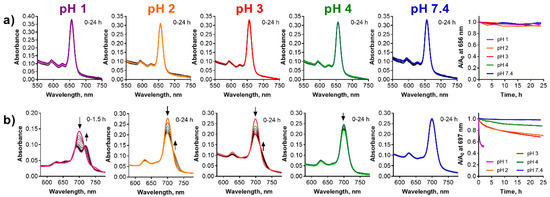
Figure 9.
Changes of absorption spectra of (a) TPyzPzMg and (b) PcMg in the liposomes (cdye = 1 µM) at different pH values of the buffer. The increased background is due to the light-scattering in the liposomal suspension. The utmost right graphs show the normalized decrease of the absorbance at the λmax of the parent magnesium complexes with time.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
All studied Pcs and TPyzPzs have been already prepared and published by our research group [10,12,42]. All organic solvents and other chemicals used for synthesis and spectral measurements were of analytical grade. The UV/Vis spectra were recorded using Shimadzu UV-2600 spectrophotometer at 20 °C or 25 °C (controlled by a Peltier cooled cuvette holder). All data were processed with UV Probe 2.42 software. The experiments in organic solvents were performed with anhydrous benzene (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA, water content <0.001%) with dichloroacetic acid (DCA, Carlo-Erba) or trifluoroacetic acid (TFA, Fluorochem). The Britton–Robinson buffer (containing 0.04 M H3BO3, 0.04 M H3PO4, 0.04 M CH3COOH—total volume 120 mL) was adjusted to desired pH values (7.4, 4.0, 3.0 and 2.0) by mixing with appropriate volume of 0.2 M NaOH (66; 23; 20; 6 mL, respectively). For the buffer of pH 1.0, an addition of H3PO4 and 98% acetic acid was used. The pH was measured using a pH 8+ DHS pH meter (XS Instruments) calibrated with a two-point calibration (pH 7.00 and 4.00) prior to use.
3.2. Lipophilic Samples in Organic Solvent
An anhydrous benzene solution (1 μM) of the lipophilic compounds (TPyzPzMg, TPyzPzZn, PcMg, PcZn, TPyzPzH2 and PcH2) was prepared and 2 mL were transferred into a quartz cuvette. For titration experiments, a specific volume of trifluoroacetic (TFA) or dichloroacetic (DCA) acid solutions in anh. benzene had been added. The absorption spectra were recorded immediately after every single addition of TFA or DCA. For the determination of keff, 2.49 mL of a prepared stock solution in benzene (1 μM) in a quartz cuvette was mixed with 10 μL of a prepared DCA solution in anh. benzene (final concentration of DCA in the cuvette was 7.17 mM, 9.56 mM, 11.95 mM, 14.34 mM and 16.73 mM); and the absorption spectra were recorded in a 24 h time-lapse sequence with time interval 1 h in the cuvette holder tempered at 20 °C. The effective rate constant, keff, for a dissociation of MgTPyzPzH+ to TPyzPzH2 in benzene/DCA, was determined from the linear regression of the dependence of the log(c0/c) on the time t, where c0 and c are the concentrations of protonated MgTPyzPzH+ in the beginning and in the time t, respectively. All spectra presented in the article were corrected for a dilution.
3.3. Water-Soluble Samples in Buffers
A water stock solution (100 μM) of the water-soluble compounds (ws-TPyzPzMg, ws-TPyzPzZn, ws-PcMg and ws-PcZn) was prepared and 25 μL of this stock solution was added to the tested buffer solution (2.48 mL) in a quartz cuvette to prepare a tested solution at a concentration of 1 μM. The absorption spectra were recorded immediately after the mixing and then in the selected time intervals (intervals were set between 30 s to 30 min depending on the speed of the process) typically up to 24 h.
3.4. Preparation of Microemulsions and Evaluation of Stability of the Complexes
A THF stock solution (100 μM) of lipophilic compounds TPyzPzMg or PcMg was prepared and a volume of 1.25 mL of this solution was added to a mixture of polyoxyl 35 hydrogenated castor oil (Cremophor® EL, BASF, Ludwigshafen, Germany) (72 mg) and medium-chain triacylglycerides (29 mg) (Ecogreen oleochemicals, meeting specifications of Ph. Eur.) dissolved in 4 mL of chloroform. The solvent was evaporated in a water bath tempered at 40 °C under reduced pressure and kept under the pressure of 5 mbar for 30 min to remove all residuals of solvents. Subsequently, the Britton–Robinson buffer of pH 7.40 (4 mL) was added and the mixture was vortexed for 5 min. After homogenization, the volume was adjusted to 5 mL in a volumetric flask. Prepared microemulsion (“stock microemulsion”) contained the dye at concentration of 25 μM incorporated in the oil particles. Microemulsions of such compositions have already been characterized using dynamic light scattering with the approximate size of the particles approximately 300 nm [43].
During the following experiment, the stock microemulsion (100 μL) was added to the tested buffer solution (2.4 mL) in a quartz cuvette to prepare the tested mixture at the final concentration of 1 μM. The absorption spectra were recorded immediately after mixing and then within 24 h in suitable time intervals (2–30 min) depending on the rate of the demetallation process.
3.5. Preparation of Liposomes and Evaluation of Stability of the Complexes
Large unilamellar vesicles formed by an extrusion technique (LUVETs) were prepared from a suspension of multilamellar vesicles (MLVs) using the following procedure. Dioleoylphosphatidylcholine (DOPC, 19.7 mg, 25 μmol) (Lipoid GmbH, Germany) was dissolved in chloroform and a THF stock solution (0.25 mL, 100 μM) of TPyzPzMg or PcMg was added. The solvents were evaporated in a 100 mL round-bottom flask on a water bath tempered at 37 °C and kept on the water bath for 30 min under the pressure of 5 mbar to remove all residues of organic solvents. The Britton–Robinson buffer of pH 7.4 (1.0 mL) was added and the lipids were removed from the flask walls by a gentle hand shaking. The prepared suspension was vortexed for 5 min to form MLVs and was left for 24 h at room temperature to complete the swelling. Subsequently, using a small hand extruder (LiposoFast Basic, Avestin), the suspension was passed back and forth 21 times through two stacked polycarbonate filters (pore size 100 nm) at room temperature. The final suspension of liposomes (“stock liposomal suspension”) contained the dye at a concentration of 25 μM incorporated in the unilamellar DOPC vesicles with a lipid concentration of 25 mM, i.e., with dye-to-lipid ratio 1:1000. Liposomes of such composition have already been characterized in our laboratory using a dynamic light scattering with the approximate size about 128 nm [44].
Subsequently, the stock liposomal suspension (100 μL) was added to the tested buffer solution (2.4 mL) in a quartz cuvette to prepare a tested mixture at the final concentration of dyes 1 μM. The absorption spectra were recorded immediately and then within 24 h with the time intervals selected according to the speed of changes from 2 min to 30 min.
4. Conclusions
The aim of the study was to determine the stability of the magnesium complexes of TPyzPzs and Pcs in different environments under acidic conditions. In organic solvents, the data suggested that basic azomethine nitrogens in the TPyzPz and Pc core are protonated after the addition of acid with a subsequent demetallation to non-protonated metal-free ligands, which confirmed the acidoprotolytic mechanism of the demetallation process in organic solvents. [29] However, the demetallation in water seems to proceed by a solvoprotolytic mechanism where the azomethine-protonated form was not detected and the magnesium derivative is converted directly to a metal-free ligand.
The demetallation of ws-TPyzPzMg in water was taking place already at pH 4 and was faster in a more acidic pH. Introduction of the lipophilic Pcs and TPyzPzs into delivery systems (microemulsions, liposomes) protected them substantially from the attack by the acidic environment. For example, while ws-TPyzPzMg in buffer was fully demetallated within few minutes at pH 2, the absorbance of lipophilic analogue TPyzPzMg at the same pH decreased only for approximately 10% within 24 h in the microemulsion and once incorporated into the liposomes the compound did not show any detectable changes at pH 2 for the same period of time. The data also indicated that liposomes offer a better protection against the acidity for magnesium complexes than the microemulsion system. The direct comparison between Pc and TPyzPz core could be carried out only for the delivery systems. Nevertheless, the data in both, the liposomes and the microemulsion, proved that the magnesium complexes of TPyzPz derivatives were more stable.
Findings from this study may lead to important consequences for the use of magnesium complexes of Pcs and TPyzPzs in in vitro or in vivo assays where a lower pH must be considered (for example, the acidic organelles lysosomes typically targeted by potential photosensitizers have a pH of 4–5 [45]). Once incorporated into lipidic bilayers, the risk of demetallation of lipophilic magnesium complexes is negligible at a physiologically achievable pH as suggested from the data in liposomes, the models of biological membranes, and the compounds may be considered as stable. Additionally, potential pH-sensing using magnesium TPyzPzs incorporated into liposomes (e.g., in a recent publication of pH-sensors [11]) should be achievable even at a much lower pH without any problems with stability of the central cation. At the same time, the microemulsions as a delivery system also proved to protect the lipophilic complexes sufficiently from low pH and therefore can be used in cellular systems without any limitations. On the other hand, well water-soluble and non-aggregating magnesium complexes of Pcs and TPyzPzs in cells are found in water environments in a lysosomal matrix. In this case, they are demetallated to the metal-free derivatives (in particular, at longer incubation times) and subsequently the tested compounds (e.g., for photodynamic activity or toxicity) are of the metal-free form and not the originally applied magnesium complexes. This consequence should be considered during the evaluation of the in vitro results.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ph15040409/s1, Figure S1: Protonation of TPyzPzMg in benzene by TFA; Figure S2: Protonation of TPyzPzZn and PcZn in benzene by DCA; Figure S3: Adsorption of ws-TPyzPzZn on the glass surface of cuvette. Figure S4: Absorption spectra of lipohilic compounds. Figure S5: Absorption spectra of water-soluble compounds. Analytical data for the studied compounds from literature. Reference [46] is cited in Supplementary Material.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition, writing, P.Z.; validation, writing—review and editing M.M., V.N.; formal analysis, P.Z., M.K.; investigation, M.K., A.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by EFSA-CDN [CZ.02.1.01/0.0/0.0/16_019/0000841], co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund, by Charles University [260 547 and PRIMUS/20/SCI/013] and by Czech Science Foundation [21-14919J]. The APC was funded by Charles University [PRIMUS/20/SCI/013].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article and Supplementary Material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Linstead, R.P.; Lowe, A.R. 214. Phthalocyanines. Part III. Preliminary experiments on the preparation of phthalocyanines from phthalonitrile. J. Chem. Soc. 1934, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, G.T.; Linstead, R.P.; Lowe, A.R. 213. Phthalocyanines. Part II. The preparation of phthalocyanine and some metallic derivatives from o-cyanobenzamide and phthalimide. J. Chem. Soc. 1934, 1017–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Wang, K.; Ledoux-Rak, I.; Jiang, J.Z. ABAB-type phthalocyanines simultaneously bearing electron donating and electron accepting groups. Synthesis, spectroscopy, and structure. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonova, E.A.; Martynov, A.G.; Zolotarevskii, V.I.; Nefedov, S.E.; Gorbunova, Y.G.; Tsivadze, A.Y. Design of UV-Vis-NIR panchromatic crown-phthalocyanines with controllable aggregation. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 1366–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucinska, M.; Skupin-Mrugalska, P.; Szczolko, W.; Sobotta, L.; Sciepura, M.; Tykarska, E.; Wierzchowski, M.; Teubert, A.; Fedoruk-Wyszomirska, A.; Wyszko, E.; et al. Phthalocyanine Derivatives Possessing 2-(Morpholin-4-yl)ethoxy Groups As Potential Agents for Photodynamic Therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 2240–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhri, S.; Engelhardt, V.; Faust, R.; Guldi, D.M. En route towards panchromatic light harvesting: Photophysical and electrochemical properties of Bodipy-porphyrazine conjugates. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 2580–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kharitonova, N.V.; Maiorova, L.A.; Koifman, O.I. Aggregation behavior of unsubstituted magnesium porphyrazine in monolayers at air-water interface and in Langmuir-Schaefer films. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2018, 22, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falkowski, M.; Rebis, T.; Piskorz, J.; Popenda, L.; Jurga, S.; Mielcarek, J.; Milczarek, G.; Goslinski, T. Improved electrocatalytic response toward hydrogen peroxide reduction of sulfanyl porphyrazine/multiwalled carbon nanotube hybrids deposited on glassy carbon electrodes. Dyes Pigm. 2016, 134, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oter, O.; Aydin, A.C.; Zeyrek Ongun, M.; Celik, E. Development of a nanoscale-based optical chemical sensor for the detection of NO radical. Turk. J. Chem. 2018, 42, 1056–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimcik, P.; Novakova, V.; Kopecky, K.; Miletin, M.; Uslu Kobak, R.Z.; Svandrlikova, E.; Váchová, L.; Lang, K. Magnesium Azaphthalocyanines: An Emerging Family of Excellent Red-Emitting Fluorophores. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 4215–4223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlikova, M.; Cermakova, V.; Demuth, J.; Valer, V.; Miletin, M.; Novakova, V.; Zimcik, P. Magnesium tetrapyrazinoporphyrazines: Tuning of the pKa of red-fluorescent pH indicators. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 6162–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machacek, M.; Cidlina, A.; Novakova, V.; Svec, J.; Rudof, E.; Miletin, M.; Kucera, R.; Simunek, T.; Zimcik, P. Far-Red-Absorbing Cationic Phthalocyanine Photosensitizers: Synthesis and Evaluation of the Photodynamic Anticancer Activity and the Mode of Cell Death Induction. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 1736–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapshina, M.A.; Norko, S.I.; Baulin, V.E.; Terentiev, A.A.; Tsivadze, A.Y.; Goldshleger, N.F. Magnesium Octa[(4’-benzo-15-crown-5)oxy]phthalocyanine in Phosphate Buffer: Supramolecular Organization, Cytotoxicity and Accumulation/Localization in Tumor Cells HeLa. Macroheterocycles 2018, 11, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabaş, E.; Şahin-Bölükbaşı, S.; Şahin-İnan, Z.D. New water soluble magnesium phthalocyanine as a potential anticancer drug: Cytotoxic and apoptotic effect on different cancer cell lines. J. Porphyrins Phthalocyanines 2022, 26, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobotta, L.; Skupin-Mrugalska, P.; Piskorz, J.; Mielcarek, J. Porphyrinoid photosensitizers mediated photodynamic inactivation against bacteria. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 175, 72–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolarska, M.; Glowacka-Sobotta, A.; Ziental, D.; Dlugaszewska, J.; Falkowski, M.; Mielcarek, J.; Goslinski, T.; Sobotta, L. Photochemical properties and photocytotoxicities against wound bacteria of sulfanyl porphyrazines with bulky peripheral substituents. J. Organomet. Chem. 2021, 934, 121669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarczynska-Goslinska, B.; Stolarska, M.; Ziental, D.; Falkowski, M.; Glowacka-Sobotta, A.; Dlugaszewska, J.; Goslinski, T.; Sobotta, L. Photodynamic antimicrobial activity of magnesium(II) porphyrazine with bulky peripheral sulfanyl substituents. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2022. accepted. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolarska, M.; Glowacka-Sobotta, A.; Ziental, D.; Dlugaszewska, J.; Falkowski, M.; Goslinski, T.; Sobotta, L. Photochemical properties and promising activity against staphylococci of sulfanyl porphyrazines with dendrimeric moieties. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2021, 521, 120321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapok, L.; Cyza, M.; Gut, A.; Kepczynski, M.; Szewczyk, G.; Sarna, T.; Nowakowska, M. Synthesis, spectroscopic properties and interaction with a liposomal membrane of a novel iodinated magnesium phthalocyanine. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2014, 286, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, M.A.; Sundermeyer, J. Group 10 metal–thiocatecholate capped magnesium phthalocyanines—coupling chromophore and electron donor/acceptor entities and its impact on sulfur induced red-shifts. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 16255–16263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janczak, J. Solvothermal modification of magnesium phthalocyanine. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2018, 478, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossanyi, J.; Chahraoui, D. Electron transfer reaction and demetalation of phthalocyanines. Int. J. Photoenergy 2000, 2, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.K.; Byun, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, D.K.; Jaung, J.Y. Synthesis and optical properties of tetrapyrazinoporphyrazines containing camphorquinone group. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2009, 13, 794–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fang, W.; Wang, K.; Liu, W.; Jiang, J. Nonperipheral Tetrakis(dibutylamino)phthalocyanines. New Types of 1,8,15,22-Tetrakis(substituted)phthalocyanine Isomers. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 9289–9296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuzhin, P.A.; Bauer, E.M.; Ercolani, C. Tetrakis(thiadiazole)porphyrazines. 1. Syntheses and Properties of Tetrakis(thiadiazole)porphyrazine and Its Magnesium and Copper Derivatives. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, C.A.; Zeng, X.S.; Bettington, S.; Batsanov, A.S.; Bryce, M.R.; Beeby, A. Porphyrin, phthalocyanine and porphyrazine derivatives with multifluorenyl substituents as efficient deep-red emitters. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 6710–6717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobotta, L.; Dlugaszewska, J.; Ziental, D.; Szczolko, W.; Koczorowski, T.; Goslinski, T.; Mielcarek, J. Optical properties of a series of pyrrolyl-substituted porphyrazines and their photoinactivation potential against Enterococcus faecalis after incorporation into liposomes. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2019, 368, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskorz, J.; Konopka, K.; Düzgüneş, N.; Gdaniec, Z.; Mielcarek, J.; Goslinski, T. Diazepinoporphyrazines Containing Peripheral Styryl Substituents and Their Promising Nanomolar Photodynamic Activity against Oral Cancer Cells in Liposomal Formulations. ChemMedChem 2014, 9, 1775–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezin, B.D.; Shukhto, O.V.; Berezin, D.B. A new type of metal porphyrin dissociation reaction. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 47, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar]
- Berezin, B.D.; Shukhto, O.V.; Berezin, D.B. Unusual spectral and kinetic properties of magnesium phthalocyanine. Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved. Khim. Khim. Tekhnol. 2002, 45, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Petrik, P.; Zimcik, P.; Kopecky, K.; Musil, Z.; Miletin, M.; Loukotova, V. Protonation and deprotonation of nitrogens in tetrapyrazinoporphyrazine macrocycles. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2007, 11, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuzhin, P.A. Azaporphyrins and phthalocyanines as multicentre conjugated ampholites. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 1999, 3, 500–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, S.S.; Stuzhin, P.A. Indium(III) complexes of octaphenylporphyrazine: Effect of halide coordination on the basic properties and stability in acid media. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2011, 15, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuzumi, S.; Honda, T.; Kojima, T. Structures and photoinduced electron transfer of protonated complexes of porphyrins and metallophthalocyanines. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2012, 256, 2488–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuga, K.; Yashiki, K.; Sugimori, T.; Handa, M. Bathochromic shift of the Q-bands of octakis(p-t-butylbenzyloxy) phthalocyanines with magnesium(II), nickel(II) and copper(II) in a solvent mixture of chloroform and acetic acid. J. Porphyr. Phthalocyanines 2005, 9, 646–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, K.; Henriksen, J.R.; Andresen, T.L. Adsorption of Cationic Peptides to Solid Surfaces of Glass and Plastic. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinin, A.S.; Kalashnikova, I.V.; Rakhnyanskaya, A.A.; Yaroslavov, A.A. Adsorption of cationic polymers on the surfaces of anionic glass microspheres. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2012, 54, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, J.; Lu, X.; Wang, R. Surface acidity of quartz: Understanding the crystallographic control. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 26909–26916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, S.H.; Grier, D.G. The charge of glass and silica surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 6716–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, C.; Moutinho, C.; Lobao, P. Liposomes as a model for the biological membrane: Studies on daunorubicin bilayer interaction. J. Membr. Biol. 2012, 245, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peetla, C.; Stine, A.; Labhasetwar, V. Biophysical Interactions with Model Lipid Membranes: Applications in Drug Discovery and Drug Delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 1264–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimcik, P.; Miletin, M.; Radilova, H.; Novakova, V.; Kopecky, K.; Svec, J.; Rudolf, E. Synthesis, Properties and In Vitro Photodynamic Activity of Water-soluble Azaphthalocyanines and Azanaphthalocyanines. Photochem. Photobiol. 2010, 86, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novakova, V.; Laskova, M.; Vavrickova, H.; Zimcik, P. Phenol-Substituted Tetrapyrazinoporphyrazines: pH-Dependent Fluorescence in Basic Media. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 14382–14392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimcik, P.; Miletin, M.; Kopecky, K.; Musil, Z.; Berka, P.; Horakova, V.; Kucerova, H.; Zbytovska, J.; Brault, D. Influence of aggregation on interaction of lipophilic, water-insoluble azaphthalocyanines with DOPC vesicles. Photochem. Photobiol. 2007, 83, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellman, I.; Fuchs, R.; Helenius, A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1986, 55, 663–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostka, M.; Zimcik, P.; Miletin, M.; Klemera, P.; Kopecky, K.; Musil, Z. Comparison of aggregation properties and photodynamic activity of phthalocyanines and azaphthalocyanines. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2006, 178, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).