Abstract
With the several targets of cancer treatment, inhibition of DNA topoisomerase activity is one of the well-known focuses in cancer chemotherapy. Here, we describe the design and synthesis of a novel series of pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolines with potential anticancer/topoisomerase inhibition activity. Forty newly designed pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline derivatives were synthesized via inverse imino Diels–Alder reaction. The antiproliferative activity of the synthesized derivatives was initially measured in the human NUGC-3 cancer cell line. Then, the selected compounds 1B, 1C, 1M, 2A, 2D, 2E, 2F, and 2R with higher activity among tested compounds were screened against six cancer cell lines, including ACHN, HCT-15, MM231, NCI-H23, NUGC-3, and PC-3. The results demonstrated that the compounds 1M, 2E, and 2P were most effective in all cancer cell lines exhibiting GI50 below 8 µM. Among them, 2E showed an equivalent inhibition pattern of topoisomerase IIα activity to that of etoposide, positive control at a 100 µM dose.
1. Introduction
Cancer is expected to be the leading cause of death and the only most critical barrier to increasing life expectancy in the 21st century due to its precipitously rising incidence and mortality rate globally [1,2,3]. Regardless of enormous efforts and achievements in cancer management and prophylaxis, the development of resistance to traditional chemotherapeutic drugs and/or novel targeted drugs, cancer cell selectivity, and relatively high toxicity remain a significant challenge [4,5]. As a result, the continued advancement of novel, more selective chemotherapeutics, as well as novel biological targets, notably for the most aggressive tumors, is highly desirable to address current and future treatment goals [6,7,8].
DNA topoisomerases (topos) are nuclear enzymes that help to restore DNA topology by relieving torsional strains produced during replication, transcription, segregation, and recombination [9,10]. Among two types, in the absence of ATP and Mg, human type I topoisomerase (topo I) splits and rejoins a single DNA strand while in the presence of ATP and Mg, type II (topo II), which behaves as a homodimer, breaks, and rejoins the double DNA strand. Based on their nuclear activities, topo II is further subdivided into two isoforms: topo IIα, which is frequently linked to proliferating cells and topo Iiβ, which is independent of cell proliferation [11,12,13,14]. Despite the fact that topoisomerase inhibitors such as etoposide, camptothecin, and irinotecan have been used as anticancer drugs for decades, they have well-defined shortcomings, such as dose-limiting toxicities like myelosuppression and diarrhea. Similarly, topo II inhibitors are also known to cause major side effects, such as cardiomyopathy and secondary leukemia [15,16,17,18]. In rapidly proliferating tumor cells, activities of topo enzymes are generally elevated. In this vain, topos have remained a promising target in medicinal chemistry due to high antitumor selectivity when compared with other DNA damaging agents [7,19].
Camptothecin and its structural derivatives have been studied extensively in the treatment of colon, ovarian, and lung malignancies in both research and clinical trials. However, as the lactone ring opens at physiological pH, they have substantial off-target consequences, such as poor solubility, limited potency, and structural instability [20]. With these considerations in mind and our long-standing interest in synthesizing heterocyclic motif carrying biological applications, our group reported a series of novel angularly fused pentacyclic scaffolds, such as 1,3-diphenylbenzo[f][1,7]naphthyridines, and 13H-benzo[f]chromeno[4,3-b][1,7]naphthyridines for their cytotoxic activities against cancer cells and topoisomerase enzyme activities in the past few years [21,22,23].
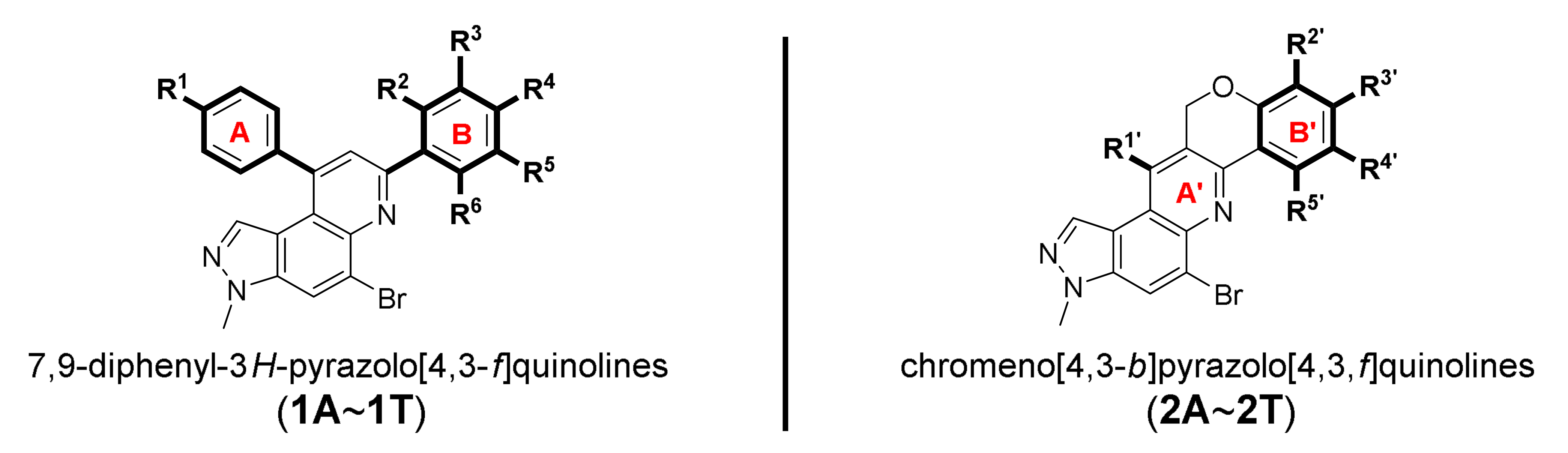
In the current research, we show the design, synthesis, and cytotoxicity evaluation of pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline derivatives as potential anticancer agents (Figure 1). In addition, several studies reported that pyrazoloquinolines synergized in a single nucleus have been linked to a variety of biological actions, including anticancer, antiviral, antibacterial, antimalarial, anti-inflammatory, immunostimulant, and high corrosion inhibition activity [24,25,26,27]. Based on a bioisosterism strategy, this study aimed to generate a string of more active molecules by fusion of our 6,6,6-heterocyclic skeleton-similar previous work and 5,6,6-heterocyclic skeleton-similar anticancer medicines such as camptothecin (Figure 1). The strategy is an efficient and practical tool for developing novel compounds in which a functional group substitution in the lead molecule improves affinity, efficacy, druggability, and/or toxicity by modifying the binding affinity to the biological target [28,29].
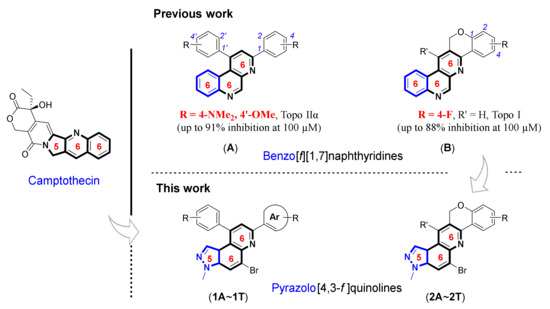
Figure 1.
Representation of bioisostere-based research design.
2. Results
2.1. Chemistry
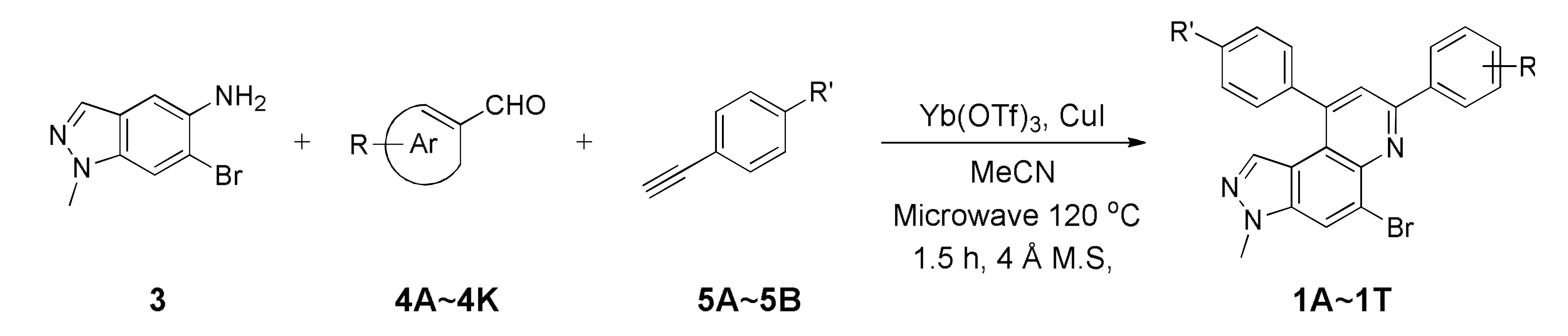
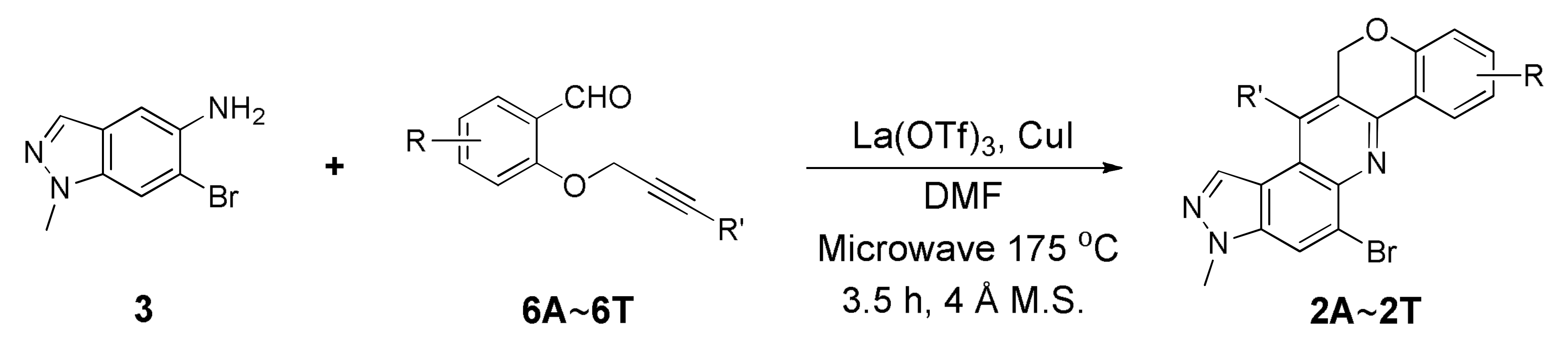
As shown in Scheme 1, we utilized one-pot inter- or intramolecular synthetic methods to prepare pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolines developed by us (i.e., synthesis of the compounds A and B). To replace the benzo[f][1,7]naphthyridine backbone (Figure 1, structures A and B) with pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline skeleton, we utilized 6-bromo-1-methyl-1H-indazol-5-amine (3) as a starting precursor. The precursor 3 in inverse imino Diels–Alder (DA) reaction mode was reacted either with the functionalized benzaldehydes 4A~4K and salicylaldehydes 5A~5B to achieve 5-bromo-3-methyl-7,9-diphenyl-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolines 1Ai~1T or with the 2-((3-phenylprop-2-yn-1-yl)oxy)benzaldehydes 6A~6T to achieve 5-bromo-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolines 2A~2T. Besides, the starting precursors 3 and 6 were synthesized using literature procedures as shown in Schemes S1 and S4 (see Supplementary Materials) [30,31,32,33,34,35].
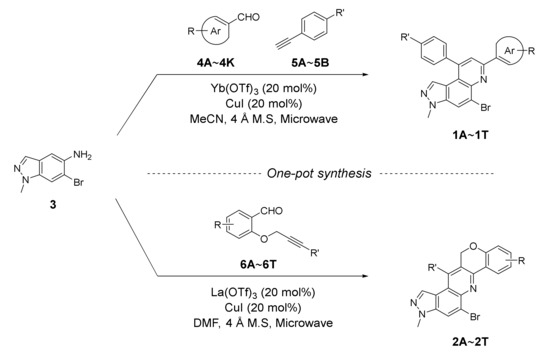
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolines.
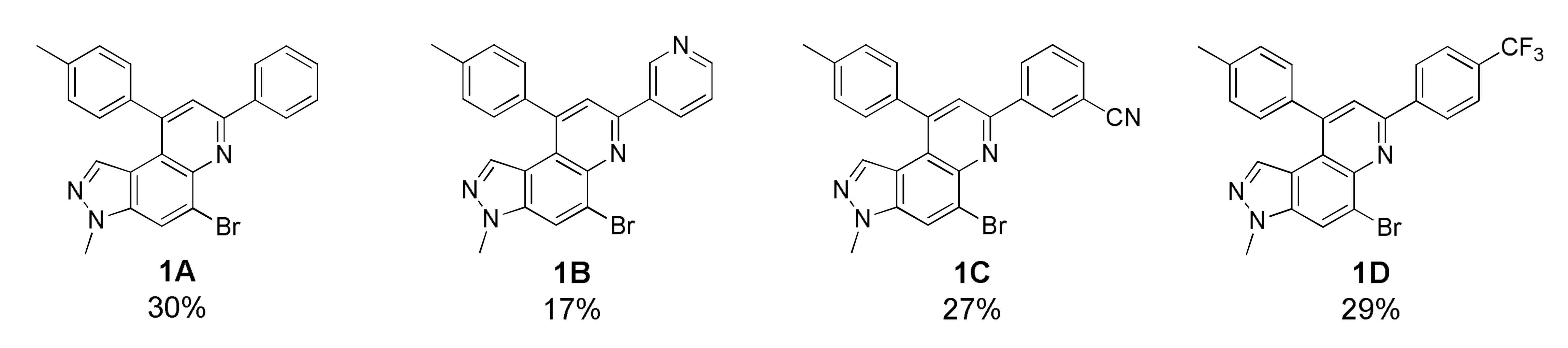
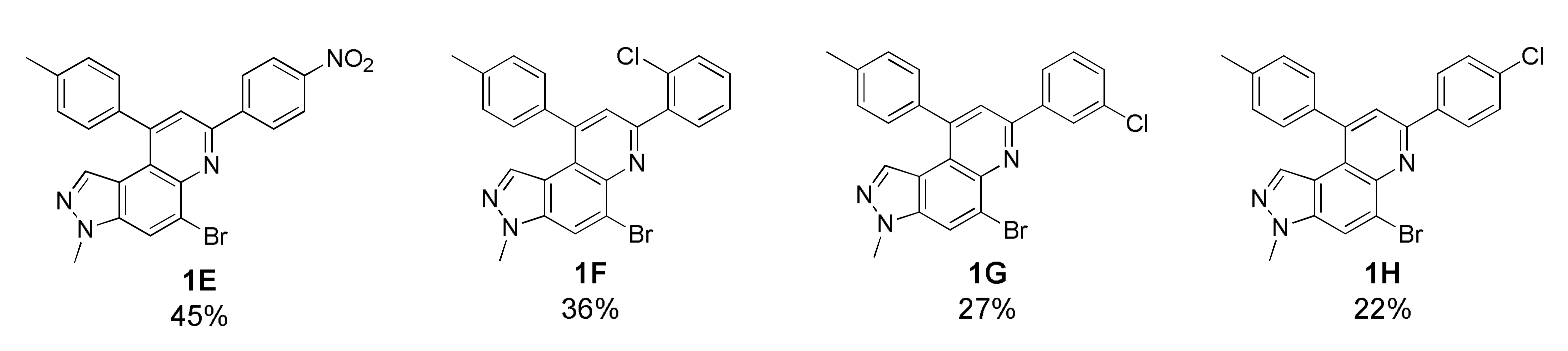
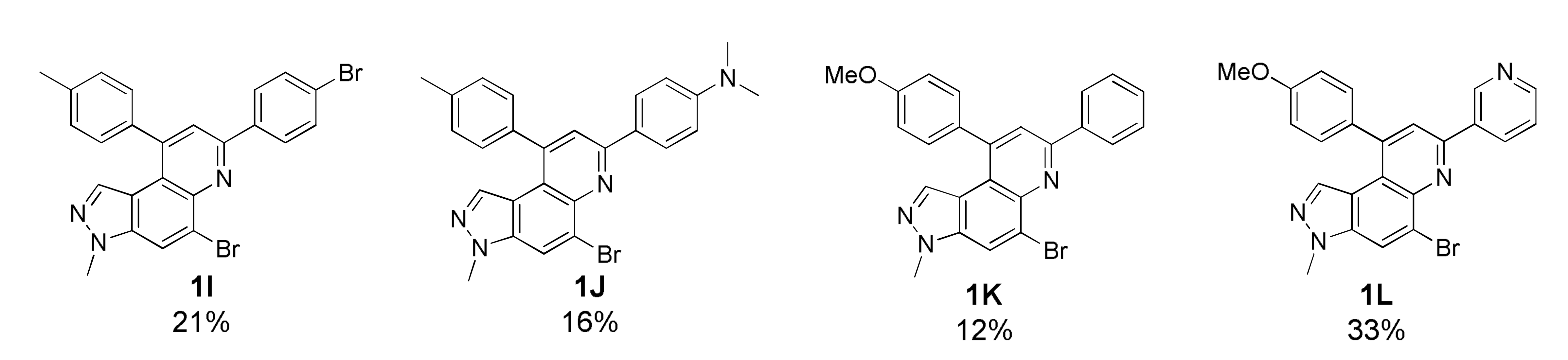
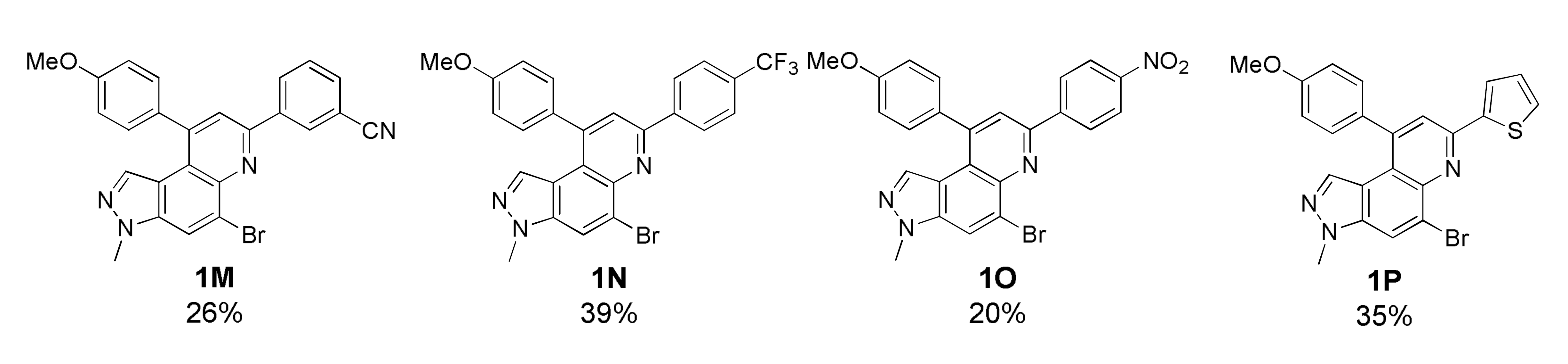
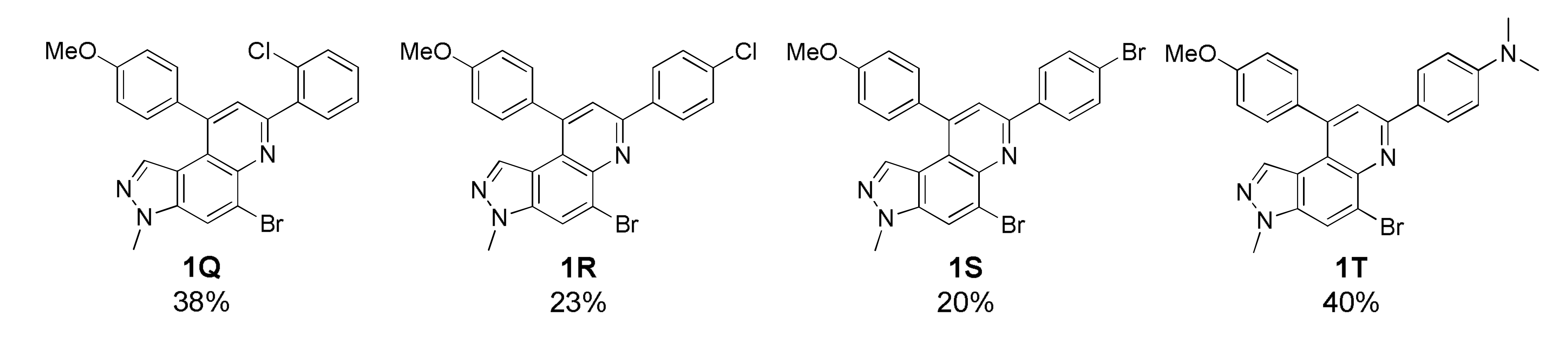
As depicted in Table 1, 20 new 7,9-diphenyl-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline derivatives 1 were prepared using the optimized condition developed previously [22]. The starting precursor 3 was condensed with 4A~4K and 5A~5B in intermolecular DA fashion in microwave condition. The microwave reactor progressed reactions more efficiently in a shorter time compared with conventional heating. The reaction yields for this transformation was low to moderate (Table 1, 1A~1T, 16~45%) because the intermediate (i.e., imine) derived from 3 and 4 acts as a proton acceptor during the aromatization process of product 1 formation (Scheme S2, see Supplementary Materials) [36]. Roughly, the amount of intermediate reduced (i.e., imine to amine) was observed to be directly proportional to the reaction time; however, microwave condition turned advantageous to increase product yield slightly. Thus, the role of air oxidation was also considered as anticipated in our previous work [21]. To further occlude the imine reduction phenomenon, AgSbF6 was added as an external oxidizing source [37]. Although the formation of an amine was remarkably prevented, the solidification of the reaction mixture caused complications in the purification process, which lowered the yield. Therefore, the use of AgSbF6 was not adapted to the further reactions.

Table 1.
Synthesis of 7,9-diphenyl-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline a, b.
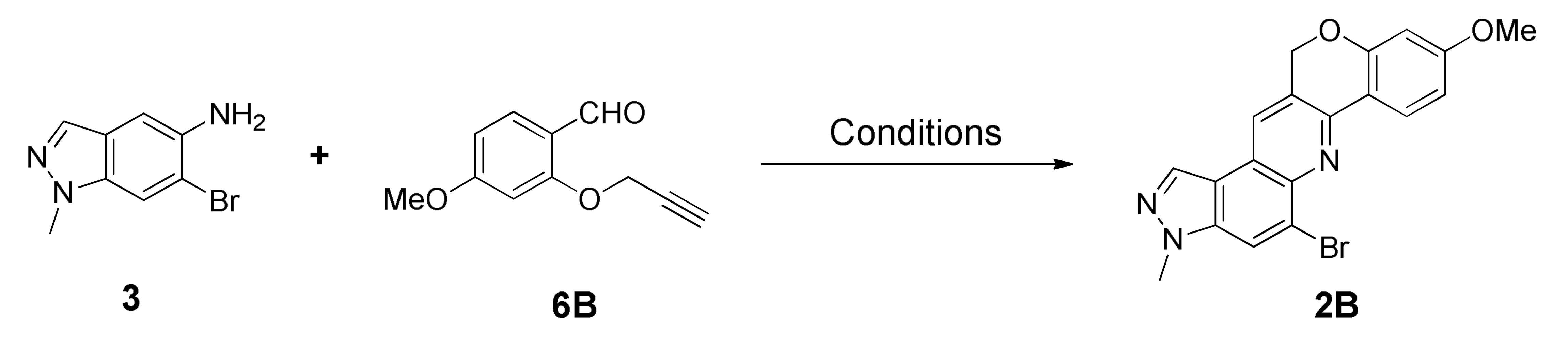
Likewise, the intramolecular inverse imino DA reactions were conducted between the precursors 3 and O-propargylated salicylaldehydes 6. The reaction was initially conducted in the conditions developed by us [23] using the substrate 6B; however, only a trace of the product 2B was obtained (Table 2, entry 1). Therefore, various transition metal triflates as a Lewis acid catalyst, such as Yb(OTf)3, La(OTf)3, and Sc(OTf)3, along with solvents such as MeCN, xylene, toluene, and DMF, were screened in order to optimize the reaction condition, and the results were summarized in Table 2. Among several trials in different parameters, entry 9 was found to be the suitable condition, which yielded 43% of the desired product 2B in 19 h reflux. Subsequently, the reaction was performed in a microwave reactor, which significantly reduced the reaction time and delivered 46% of the product 2B within a 3.5 h interval. Then the condition was utilized in further derivatization as an optimized condition (Table 2, entry 14). As in intermolecular conditions, when AgSbF6 was used as an external oxidizing agent, solidification of the reaction mixture noticeably decreased reaction yields (entries 16–18) even though the reduction of imine intermediate was considerably avoided (Scheme S3, see Supplementary Materials).

Table 2.
Optimization of reaction conditions for intramolecular DA reaction a.
Optimized condition (Table 2, entry 14) in hand, we utilized 3 as a starting precursor and coupled with the substituted O-propargylated salicylaldehydes 6A~6T to prepare 20 new chromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolines (yields: 23%~68%, Table 3, 2A~2T). The yields in the intramolecular series were moderately improved over the intermolecular series. However, the improvement with respect to the amount of amine formed was not as expected. Despite the small amounts of amines (i.e., imine to amine) compared with that of the intermolecular reactions, benzofurans directly from O-propargylated salicylaldehydes as an additional side reaction might lead to low yields of the desired products 2. The benzofuran was expected to generate as a result of hydration, followed by the intramolecular aldol condensation process (Scheme S5, See Supplementary Materials) [32].

Table 3.
Synthesis of chromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline a, b.
2.2. Biological Results
The cytotoxicity of new compounds including 7,9-diphenyl-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolines (1A~1T) and chromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolines (2A~2T) at a fixed concentration (30 µM) was first screened against a gastric cancer cell line (NUGC-3) using a cell-based in vitro system (see Supplementary Materials for procedure) [38]. Most of the compounds showed a smaller extent of effects against NUGC-3 cancer cells, where more than 60% cell proliferation was observed compared with control sets. A few compounds, 1B, 1C, 2A, 2D, 2F, and 2R, were relatively better antiproliferative (less than 30% cell proliferation), and three compounds, 1M, 2E, and 2P, were highly toxic against a tested cancer cell line (cells up to −30% less compared with an initial number of cells) at the experimental concentration (Table 4).

Table 4.
In vitro antiproliferative activity of synthesized pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline analogues in human NUGC-3 cell line at 30 µM concentration.
To clarify the cytotoxic effects, the compounds with a higher antiproliferative ability (less than 30% cell) were chosen for the follow-up antiproliferative evaluation in six different human cancer cell lines, namely, kidney cancer cell line (ACHN), colon cancer cell line (HCT-15), breast cancer cell line (MM231), lung cancer cell line (NCI-H23), gastric cancer cell line (NUGC-3), and prostate cancer cell line (PC-3). The antiproliferative ability of selected compounds was compared with doxorubicin (a positive control), and the data were expressed in 50% growth inhibition concentration (GI50) values (Table 5). Even though the tested compounds were less toxic to all human cancer cell lines compared with a positive control (GI50 less than 1 µM), growth inhibition (GI50) patterns were aligned with initial NUGC-3 cell screening results (Table 4). For example, the compounds 1M (−29.01 ± 0.84%), 2E (−17.83 ± 1.63%), and 2P (−22.67 ± 4.55%) with negative NUGC-3 cell proliferation values demonstrated minimum GI50 concentration within entire cancer cell lines except for 1C in MM231 (IG50 = 4.514 ± 0.170 µM) compared with 1M, 2E, and 2P, and in PC-3 (IG50 = 6.068 ± 1.101 µM) compared with 1M. It was proved that all compounds displayed significant inhibitions in six cancer cell lines at less than 14 µM concentrations. More specifically, the highly cytotoxic compounds 1M, 2E, and 2P in NUGC-3 cells (Table 4) even inhibited 50% growth of all cancer cell lines below an 8 µM range concentration (Table 5). Therefore, the current pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline skeleton may serve as a potential source of anticancer agents upon further investigation.

Table 5.
In vitro antiproliferative activity of selected compounds in six different human cancer cell lines.
To precisely access molecular targets for the lead compounds 2E and 2P (consistent GI50 values in six cancer cell lines, less than 7 µM), we examined their capacity to block the activity of topoisomerase enzymes in relaxing supercoiled plasmid DNA to its relaxed form (see Supplementary Materials for procedure) [39]. The camptothecin for topo I and the etoposide for topo IIα were taken as positive drug controls, and their relative topo inhibition patterns along with 2E and 2P were measured by Western blot analysis as demonstrated in Figure 2. Both the positive controls and compounds were used at a single-dose concentration (100 µM). As the results revealed, the compounds 2E and 2P were weakly effective in inhibiting topo I activity in respect to the camptothecin effect. The camptothecin blocked the catalytic activity of topo I in supercoiled DNA by 86.7%, where the activities were approximately 6 folds less for 2E and 7 folds less for 2P (Figure 2A).
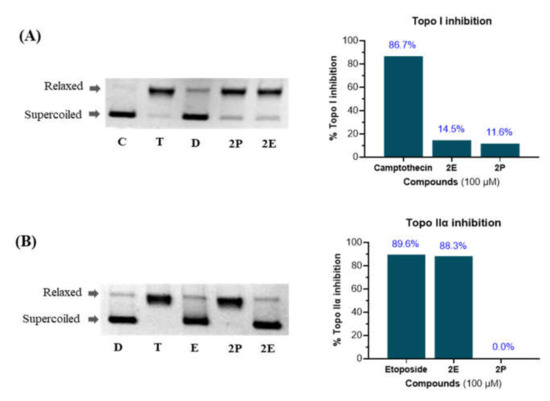
Figure 2.
Human DNA topo I (A) and human DNA topo IIα (B) inhibitory activity. Lane D (pBR322 DNA), Lane T (pBR322 DNA + topo I or topo IIα), Lane C (pBR322 DNA + topo I + camptothecin), Lane E (pBR322 DNA + topo IIα + etoposide), Lane 2E (pBR322 DNA + topo I or topo IIα + compound 2E), and Lane 2P (pBR322 DNA + topo I or topo IIα + compound 2P).
Additionally, the compounds 2E and 2P were evaluated against topo IIα activity in comparison with etoposide. Interestingly, the compound 2E was highly active in preventing topo IIα catalytic activity. It inhibited 88.3% of enzyme activity, which was similar to the activity of positive control (etoposide, 89.6% inhibition). However, the compound 2P with marginal inhibition activity in topo I (11.6%) was inactive in the intercalation of the topo IIα enzyme (Figure 2B).
3. Discussion
The bioisosteric replacement is taken as a powerful tool in medicinal chemistry for improving druglike properties, toxicity, and pharmacokinetics of experimental therapeutics [40,41]. Utilizing the key concept of bioisosterism, the 6,6,6-heterocyclic skeleton of benzo[f][1,7]naphthyridines was replaced to the 5,6,6-heterocyclic skeleton of pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolines (1A~1T and 2A~2T) and successfully prepared 40 different derivatives via inverse imino DA condition. A receptor interaction of new compounds for anticancer activity was expected to be consistent with previously studied compounds during the design process [21,22]. The molecular docking simulations of best analogues of benzo[f][4,3-b][1,7]naphthyridines (i.e., 1,3-diphenylbenzo[f][1,7]naphthyridines (A) and 3H-benzo[f]chromeno[4,3-b][1,7]naphthyridines (B), Figure 1) inhibiting topo IIα activity showed good fit at the DNA cleavage site where etoposide was located. Moreover, the compound B intercalates into a single-strand cleavage site as well for topo I activity by van der Waals interactions with Arg364, Pro431, and Asn722 residues and π–π stacking interactions with the stacked DNA bases.
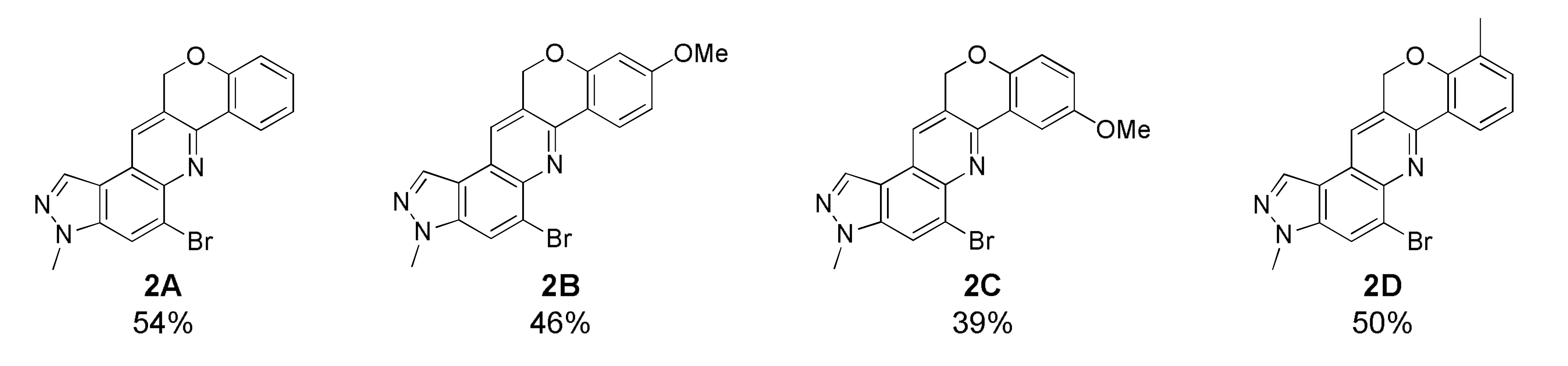
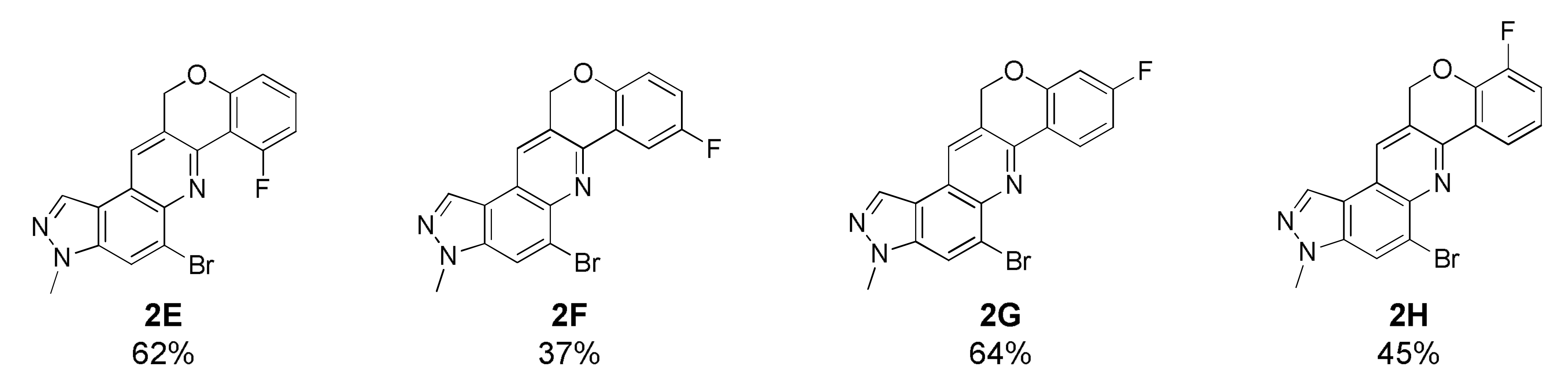
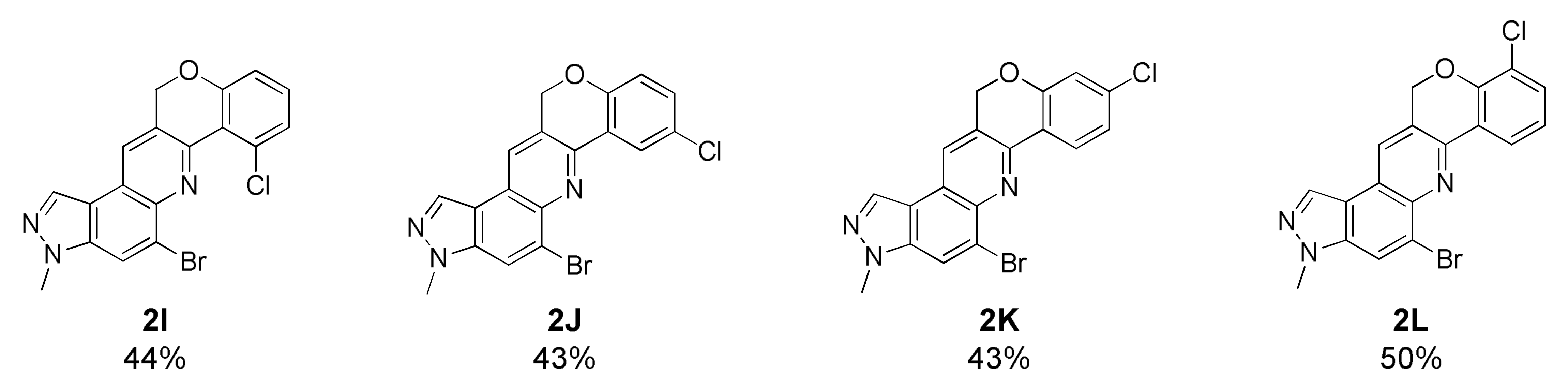
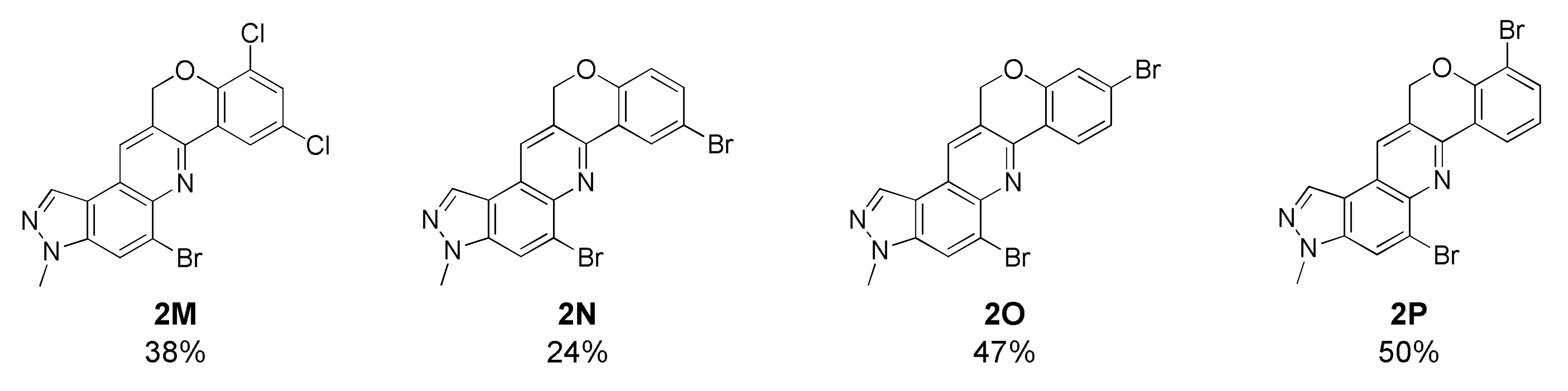
Unfortunately, most derivatives of the new series were less effective in antiproliferative activity against NUGC-3 cancer cells. We tried to figure out the effect of chemical properties of compounds in antiproliferative activity even though the data were acquired at a fixed dose of 30 µM concentration (Table 4). Initially, we thought of comparing substituents’ effect on ring B when R1 was methyl or methoxy on ring A in diphenyl-pyrazoloquinolines 1. The electron-withdrawing nitrile substituent on the R5 position showed higher activity in both compounds 1C (9.80% cell proliferation compared with drug untreated positive control) and 1M (−29.01% cells). However, neither the R5 position, the compound 1G, nor the electron-withdrawing property was consistent with the other compounds, 1D, 1E, 1N, and 1O. The effects of halogens, irrespective of their positions, were poorly effective against cancer cell proliferation (compounds 1F~1I, 1Q~1S). Similarly, very low effects were observed in the case of rings without substituents, the compounds 1A and 1K, or with electron-donating bulky substituents, the compounds 1J and 1T. The cytotoxic effect of pyridine heterocycle (ring B) was remarkably high when R1 was methyl (compound 1B, 22.89% cell proliferation), but the effect was not restored when the methyl was replaced with the methoxy substituent (compound 1L, 82.07% cell proliferation). Likewise, the thiophen-2-yl heterocycle 1P was also not effective in the inhibition of cancer cell proliferation. Next, the structure–activity relationship (SAR) study was concentrated in chromeno-pyrazoloquinoline skeleton 2. Six compounds most effectively inhibited NUGC-3 cell proliferation in this series. In the compounds 2A, 2D, 2E, 2F, 2P, and 2R, the cell proliferation was 19.41%, 27.68%, −17.83%, 14.67%, −22.67%, and 11.16%, respectively, compared with the positive control set. Unfortunately, as in the diphenyl-pyrazoloquinolines 1 series, the structure–activity relationship was not systematically established in chromeno-pyrazoloquinolines 2 too. Briefly, compounds having electron-releasing substituents (compounds 2B, 2C, and 2S) on ring B’ were weakly active. Conversely, the methyl at the R2′ position (2D, 27.68% growth) was slightly active in antiproliferative activity. We analyzed the effects of halogen substituents, and –Br at R2′ (2P) and –F at R6′ (2E) were highly toxic to NUGC-3 cancer cells. At the same time, –F or –Cl at R2′ and –Cl at the R6′ (2H, 2L, and 2I, respectively) positions did not show a notable effect on cell proliferation inhibition. Halogens at R3′ or R4′ (2G, 2J, 2K, 2N, and 2O) were also poorly active except for –F at the R4′ position (2F, showing 14.67% cell proliferation), which showed no evidence of linear correlation of activity to halogen atomic size, electronegativity, and their substituted positions. Further, the naphthalenes (compounds 2Q, 2R, and 2T) instead of ring B’ with a different orientation were evaluated, where 2R displayed higher activity out of three different naphthalene compounds. The activity of compound 2R was similar to that of compound 2F, whose relation is indescribable with respect to their structures and chemical properties.
Eight effective analogues, 1B, 1C, 1M, 2A, 2D, 2E, 2F, 2P, and 2R, were tested in six different human cancer cell lines for antitumorigenic ability, where only two chromeno analogues, 2E and 2P, were selected for follow-up evaluation (Table 5 and Figure 2). Both were less effective in blocking the catalytic activity of topo I enzyme activity. Interestingly, 2E showed strong inhibition of topo IIα activity in DNA religation.
To this end, it was found that 2M of the diphenyl-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolines 1 and 2E and 2P of chromeno-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolines 2 showed high cytotoxicity regardless of structural relation to other analogues. Therefore, further experiments are essential to better understand the SAR relationship and mode of antiproliferative action to develop pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline scaffold as a potential source of anticancer drug candidates.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Information
Unless noted otherwise, all reagents were purchased from commercial sources (Aldrich, TCI, Alfa Aesar, and Acros) and used as received. Air or moisture labile reactions were conducted in oven-dried glassware under a nitrogen atmosphere. Reaction progress was monitored by thin-layer chromatography (TLC) using silica gel F254 plates. Products were purified by flash column chromatography using silica gel 60 (70–230 mesh) of Kieselgel60 (Merck, KGaA, 64271 Darmstadt, Germany) or by using the Biotage ‘Isolera One’ system with indicated solvents. High-resolution mass spectrometry was performed with LCQ Fleet, Thermo Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA), recorded in positive ion mode with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source. NMR spectra were recorded on a Jeol Resonance ECZ 400S (400 MHz for 1H NMR and 100 MHz for 13C NMR). Chemical shifts were reported in ppm from tetramethylsilane (TMS) with the solvent resonance resulting from incomplete deuteration as the internal reference (CDCl3: 7.26 ppm, CD3OD: 3.31 ppm, DMSO: 2.5 ppm, 3.33 ppm of water peak) or relative to TMS (δ 0.0). Data are reported as follows: chemical shift δ, multiplicity (s = singlet, d = doublet, t = triplet, m = multiplet, dd = doublet of doublet, td = triplet of doublet, ddd = doublet of doublets of doublets, ddt = doublet of doublet of triplets), coupling constants (Hz), number of protons.
4.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Diphenyl-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolines 1
The starting precursor 3 (98 mg, 0.44 mmol), intermediates 4 (0.44 mmol), 5 (0.44 mmol), Yb(OTf)3 (30 mol%), and CuI (20 mol%) in DMF (1 mL) with a molecular sieve was reacted under microwave conditions (175 °C) for 1.5 h. The reaction mixture was diluted with DCM and water, then extracted with DCM. Combined organic layers were dried over MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated. The concentrated crude was purified using silica gel column chromatography (Hex/EtOAc = 5:1) to afford the desired products 1 as solids.
5-Bromo-3-methyl-7-phenyl-9-(p-tolyl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1A)
White solid; 30% yield; Rf 0.6 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.34 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H), 8.18 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 7.94 (s, 1H), 7.54–7.52 (m, 2H), 7.46 (tt, J = 7.2, 2.4, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.39 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.36 (dd, J = 8.0, 2.0 Hz, 2H), 6.86 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 4.09 (s, 3H), 2.52 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 154.42, 148.48, 142.70, 138.97, 138.95, 137.78, 137.15, 134.63, 129.96, 129.61, 129.05, 128.59, 127.50, 126.38, 121.57, 120.95, 117.95, 117.46, 36.05, 21.58; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C24H19BrN3+: 428.0757; found: 428.0761.
5-Bromo-3-methyl-7-(pyridin-3-yl)-9-(p-tolyl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1B)
White solid; 17% yield; Rf 0.2 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 9.49 (s, 1H), 8.73–8.64 (m, 2H), 8.20 (d, J = 0.9 Hz, 1H), 7.94 (s, 1H), 7.48 (dd, J = 7.8, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 7.40 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 7.38–7.34 (m, 2H), 6.88 (d, J = 0.9 Hz, 1H), 4.10 (s, 3H), 2.53 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 151.75, 150.41, 148.86, 148.82, 142.86, 139.16, 137.87, 136.84, 134.93, 134.90, 134.55, 130.03, 128.53, 125.94, 123.92, 122.02, 120.61, 117.87, 36.11, 21.58; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C23H18BrN4+: 429.0709; found: 429.0711.
3-(5-Bromo-3-methyl-9-(p-tolyl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolin-7-yl)benzonitrile (1C)
Yellow solid; 27% yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.65 (s, 1H), 8.54 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 1H), 8.20 (s, 1H), 7.90 (s, 1H), 7.72 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 7.63 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.39 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.34 (d, J = 7.9 Hz, 2H), 6.87 (s, 1H), 4.09 (s, 3H), 2.51 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 151.72, 149.08, 142.78, 140.17, 139.26, 137.95, 136.72, 134.85, 132.72, 131.20, 130.07, 129.85, 128.49, 126.06, 122.20, 120.57, 119.03, 118.01, 117.79, 113.32, 36.11, 21.59; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C25H18BrN4+: 453.0709; found: 453.0713.
5-Bromo-3-methyl-9-(p-tolyl)-7-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1D)
Yellow solid; 29% yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 4:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.45 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 8.20 (s, 1H), 7.95 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.40 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.36 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 6.88 (s, 1H), 4.10 (s, 3H), 2.53 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 152.64, 148.79, 142.73, 142.29, 139.13, 137.88, 136.88, 134.89, 128.53, 127.72, 126.04, 125.94, 122.07, 120.93, 117.84, 36.11, 21.59; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C25H18BrF3N3+: 496.0631; found: 496.0635.
5-Bromo-3-methyl-7-(4-nitrophenyl)-9-(p-tolyl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1E)
Yellow solid; 45% yield; Rf 0.4 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.52 (dt, J = 9.5, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 8.39 (dt, J = 8.8, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 8.22 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 7.99 (s, 1H), 7.41 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 2H), 7.36 (dd, J = 6.4, 2.0 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (s, 1H), 4.11 (s, 3H), 2.53 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 151.49, 149.02, 148.48, 144.87, 142.84, 139.29, 138.02, 136.70, 135.04, 130.09, 128.50, 128.17, 126.00, 124.29, 122.42, 121.11, 118.15, 117.79, 36.16, 21.60; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C24H18BrN4O2+: 473.0608; found: 473.0611.
5-Bromo-7-(2-chlorophenyl)-3-methyl-9-(p-tolyl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1F)
White solid; 36% yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.18 (s, 1H), 7.97 (dd, J = 7.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.93 (s, 1H), 7.51 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.97 (dt, J = 7.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.40–7.35 (m, 5H), 6.92 (s, 1H), 4.10 (s, 3H), 2.51 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 154.27, 147.24, 142.77, 138.93, 137.90, 136.98, 134.99, 132.80, 132.65, 130.50, 130.03, 129.93, 128.67, 127.40, 125.82, 125.41, 121.65, 117.93, 117.45, 36.09, 21.57; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C24H18BrClN3+: 462.0367; found: 462.0376.
5-Bromo-7-(3-chlorophenyl)-3-methyl-9-(p-tolyl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1G)
Pale brown solid; 27% yield; Rf 0.6 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.33 (t, J = 1.6, 1H), 8.22–8.19 (m, 2H), 7.9 (s, 1H), 7.46–7.34 (m, 6H), 6.87 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 4.10 (s, 3H), 2.52 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 152.75, 148.69, 142.66, 140.80, 139.06, 137.84, 136.97, 135.13, 134.84, 130.25, 129.97, 129.49, 128.55, 127.59, 126.04, 125.51, 121.90, 120.77, 117.90, 117.71, 36.08, 21.57; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C24H18BrClN3+: 462.0367; found: 462.0373.
5-Bromo-7-(4-chlorophenyl)-3-methyl-9-(p-tolyl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1H)
Red solid; 22% yield; Rf 0.6 (Hex/EtOAc = 4:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.28 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 8.18 (s, 1H), 7.89 (s, 1H), 7.50 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.39 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.34 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 6.86 (s, 1H), 4.10 (s, 3H), 2.52 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 153.02, 148.60, 142.62, 139.01, 137.77, 137.41, 137.00, 135.69, 134.78, 129.96, 129.58, 129.20, 128.69, 128.54, 127.28, 126.00, 121.67, 120.55, 117.91, 117.64, 36.07, 21.57; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C24H18BrClN3+: 462.0367; found: 462.0374.
5-Bromo-7-(4-bromophenyl)-3-methyl-9-(p-tolyl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1I)
Pale brown solid; 21% yield; Rf 0.6 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.21 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 8.18 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 7.90 (s, 1H), 7.65 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.39 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.34 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 6.88 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 4.11 (s, 3H), 2.52 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 153.09, 148.65, 142.65, 139.04, 137.90, 137.80, 137.00, 134.80, 132.17, 129.97, 128.99, 128.55, 126.01, 124.12, 121.74, 120.52, 117.94, 117.98, 36.09, 21.58; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C24H18Br2N3+: 505.9862; found: 505.9872.
4-(5-Bromo-3-methyl-9-(p-tolyl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolin-7-yl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (1J)
Orange solid; 16% yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO): δ 8.58 (s, 1H), 8.26 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.96 (s, 1H), 7.44 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.38 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 6.86 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 6.57 (s, 1H), 4.07 (s, 3H), 3.00 (s, 6H), 2.48 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, DMSO): δ 153.72, 151.22, 147.68, 141.67, 138.36, 137.18, 136.93, 133.01, 129.68, 128.52, 128.13, 125.75, 124.60, 119.72, 119.22, 118.36, 117.16, 112.28, 40.07, 35.95, 21.05; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C26H24BrN4+: 471.1179; found: 471.1187.
5-Bromo-9-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-7-phenyl-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1K)
Brown solid; 12% yield; Rf 0.4 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.68 (dd, J = 8.4, 8.4 Hz, 2H), 8.18 (s, 1H), 7.94 (s, 1H), 7.56–7.52 (m, 2H), 7.48–7.44 (m, 1H), 7.39 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.11 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.95 (s, 1H), 4.11 (s, 3H), 3.94 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 160.23, 154.33, 148.12, 142.70, 138.96, 137.77, 134.72, 132.32, 129.99, 129.56, 129.03, 127.46, 126.18, 121.73, 121.11, 117.98, 117.45, 114.65, 55.59, 36.07, 31.72, 31.10, 29.85, 22.79, 14.27; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C24H19BrN3O+: 444.0706; found: 444.0706.
5-Bromo-9-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-7-(pyridin-3-yl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1L)
Orange solid; 33% yield; Rf 0.3 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 9.49 (s, 1H), 8.68 (tt, J = 3.9, 1.8 Hz, 2H), 8.19 (s, 1H), 7.93 (s, 1H), 7.47 (dd, J = 7.9, 4.8 Hz, 1H), 7.39 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.11 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.95 (s, 1H), 4.10 (s, 3H), 3.93 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 160.38, 151.74, 150.41, 148.82, 148.56, 142.90, 137.87, 134.91, 134.86, 134.53, 131.95, 129.95, 125.95, 123.90, 122.18, 120.81, 117.85, 114.76, 55.61, 36.11; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C23H18BrN4O+: 445.0659; found: 445.0667.
3-(5-Bromo-9-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolin-7-yl)benzonitrile (1M)
Yellow solid; 26% yield; Rf 0.4 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.65 (s, 1H), 8.56 (dt, J = 8.4, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 8.21 (s, 1H), 7.81 (s, 1H), 7.73 (dt, J = 8.0, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.64 (t, J = 7.6, 1H), 7.39 (dt, J = 8.8, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 7.12 (dt, J = 8.4, 2.4 Hz, 2H), 6.96 (s, 1H), 4.12 (s, 3H), 3.95 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 160.46, 151.78, 148.80, 142.86, 140.15, 137.97, 134.70, 132.73, 131.79, 131.55, 131.19, 129.90, 129.85, 126.85, 122.35, 120.81, 119.04, 117.97, 117.77, 114.83, 113.31, 55.64, 36.11; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C25H18BrN4O+: 469.0659; found: 469.0663.
5-Bromo-9-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-7-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1N)
Red solid; 8% yield; Rf 0.4 (Hex/EtOAc = 3:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.44 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 8.19 (s, 1H), 7.94 (s, 1H), 7.78 (d, J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.39 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.11 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.95 (s, 1H), 4.10 (s, 3H), 3.93 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 160.37, 152.64, 148.49, 142.79, 142.30, 137.91, 134.86, 132.02, 131.37, 131.05, 129.95, 127.72, 126.06, 125.96, 125.93, 125.71, 122.24, 117.83, 114.75, 55.61, 36.11; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C25H18BrF3N3O+: 512.0580; found: 512.0581.
5-Bromo-9-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-7-(4-nitrophenyl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1O)
Yellow solid; 20% yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.51 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 2H), 8.22 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 7.98 (s, 1H), 7.40 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.12 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.11 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.97 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 4.12 (s, 3H), 3.95 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 160.48, 151.52, 148.74, 148.48, 144.86, 142.92, 138.05, 134.98, 131.80, 129.92, 128.17, 126.08, 124.28, 122.59, 121.34, 118.13, 117.80, 114.83, 55.65, 36.15; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C24H19BrN4O3+: 489.0557; found: 489.0560.
5-Bromo-9-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-7-(thiophen-2-yl)-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1P)
Brown solid; 35% yield; Rf 0.3 (Hex/EtOAc = 4:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.15 (s, 1H), 8.12 (d, J = 3.0 Hz, 1H), 7.96 (d, J = 5.0 Hz, 1H), 7.77 (s, 1H), 7.43 (dd, J = 5.0, 3.0 Hz, 1H), 7.37 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.09 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.90 (s, 1H), 4.08 (s, 3H), 3.93 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 160.25, 150.80, 148.06, 142.64, 142.39, 137.70, 134.60, 132.21, 129.97, 126.91, 126.54, 125.86, 124.58, 121.51, 121.29, 118.06, 117.45, 114.66, 55.60, 36.06; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C22H17BrN3OS+: 450.0270; found: 450.0271.
5-Bromo-7-(2-chlorophenyl)-9-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1Q)
White solid; 38% yield; Rf 0.4 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.19 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.97 (dd, J = 7.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.93 (s, 1H), 7.51 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.47–7.36 (m, 4H), 7.10 (dt, J = 8.8, 2.8 Hz, 2H), 7.00 (d, J = 1.20 Hz, 1H), 4.11 (s, 3H), 3.93 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 160.24, 154.30, 146.94, 142.80, 138.80, 137.86, 134.69, 132.72, 132.58, 131.97, 130.44, 129.99, 127.36, 126.07, 125.64, 121.73, 117.80, 117.35, 114.65, 55.53, 36.01; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C24H18BrClN3O+: 478.0316; found: 478.0321.
5-Bromo-7-(4-chlorophenyl)-9-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1R)
Yellow solid; 23% yield; Rf 0.4 (Hex/EtOAc = 4:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.27 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 8.17 (s, 1H), 7.88 (s, 1H), 7.49 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.38 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.10 (d, J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 6.93 (s, 1H), 4.09 (s, 3H), 3.93 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 160.32, 153.06, 148.34, 142.71, 137.82, 137.45, 135.71, 134.78, 132.17, 129.97, 129.21, 128.72, 126.05, 121.87, 120.79, 117.95, 117.65, 114.71, 55.61, 36.08; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C24H18BrClN3O+: 478.0316; found: 478.0320.
5-Bromo-7-(4-bromophenyl)-9-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (1S)
Brown solid; 20% yield; Rf 0.3 (Hex/EtOAc = 4:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.21 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 8.17 (s, 1H), 7.88 (s, 1H), 7.65 (d, J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 7.38 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.10 (d, J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.93 (s, 1H), 4.09 (s, 3H), 3.93 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 160.30, 153.09, 148.35, 142.70, 137.89, 137.81, 134.77, 132.16, 129.96, 129.00, 126.03, 124.11, 121.91, 120.74, 117.94, 117.66, 114.70, 55.61, 36.09; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C24H18Br2N3O+: 521.9811; found: 521.9818.
4-(5-Bromo-9-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3-methyl-3H-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolin-7-yl)-N,N-dimethylaniline (1T)
Orange solid; 40% yield; Rf 0.4 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3): δ 8.25 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 8.13 (s, 1H), 7.84 (s, 1H), 7.39 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.10 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.88 (s, 1H), 6.84 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 4.08 (s, 3H), 3.94 (s, 3H), 3.05 (s, 6H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 160.11, 154.70, 151.53, 147.62, 142.68, 137.51, 134.47, 132.71, 130.05, 128.41, 126.87, 126.20, 120.76, 120.18, 118.22, 117.02, 114.57, 112.40, 55.60, 40.52, 36.02; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C26H24BrN4O+: 487.1128; found: 487.1132.
4.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Chromeno-pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinolines 2
The starting precursor 3 (98 mg, 0.44 mmol), substituted intermediates 6 (0.44 mmol), Yb(OTf)3 (30 mol%), and CuI (20 mol%) in DMF (1 mL) with a molecular sieve, was reacted under microwave conditions (175 °C) for 3.5 h. The reaction mixture was diluted with DCM and water, then extracted with DCM. Combined organic layers were dried over MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated. The concentrated crude was purified using silica gel column chromatography (Hex/EtOAc = 5:1) to afford the desired products 2 as solids.
5-Bromo-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f ]quinoline (2A)
Deep yellow solid; 54% yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.54 (dd, J = 7.6, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 8.30 (s, 1H), 8.17 (s, 1H), 8.09 (s, 1H), 7.37 (dd, J = 7.6, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (dd, J = 7.6, 0.8 Hz, 1H), 7.01 (dd, J = 7.6, 0.8 Hz, 1H), 5.44 (s, 2H), 4.14 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 157.05, 147.46, 142.00, 137.42, 131.94, 126.74, 126.69, 125.67, 125.33, 123.21, 122.82, 122.03, 118.71, 117.29, 117.09, 68.23, 36.23; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C18H13BrN3O+: 366.0237; found: 366.0235.
5-Bromo-9-methoxy-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2B)
Orange brown solid; 46% yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.45 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.29 (s, 1H), 8.14 (s, 1H), 8.08 (s, 1H), 6.75 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.53 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 5.42 (s, 2H), 4.15 (s, 3H), 3.86 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 163.08, 158.50, 147.75, 142.01, 137.29, 131.79, 126.90, 126.60, 125.80, 125.17, 121.48, 118.86, 116.94, 116.31, 109.95, 101.82, 68.54, 55.65, 36.22; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C19H15BrN3O2+: 396.0342; found: 396.0341.
5-Bromo-8-methoxy-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2C)
Brown solid; 39% yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.30 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 8.16 (s, 1H), 8.08 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.04 (t, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.93 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 2H), 5.37 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 2H), 4.14 (s, 3H), 3.92 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 155.30, 151.27, 147.49, 141.90, 137.45, 131.99, 127.04, 126.72, 125.26, 123.67, 122.12, 119.04, 118.75, 116.26, 117.06, 106.60, 68.31, 55.96, 36.24; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C19H15BrN3O2+: 396.0342; found: 396.0341.
5-Bromo-3,10-dimethyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f ]quinoline (2D)
Pale yellow solid; 50% yield; yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.39 (dd, J = 7.6, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.31 (s, 1H), 8.17 (s, 1H), 8.08 (s, 1H), 7.22 (dd, J = 7.6, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.08 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 5.44 (s, 2H), 4.14 (s, 3H), 2.30 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 155.36, 151.27, 147.49, 141.90, 137.45, 131.99, 127.04, 126.72, 125.26, 123.67, 122.12, 119.04, 118.75, 116.26, 117.08, 106.60, 68.31, 55.96, 36.24; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C19H15BrN3O+: 380.0393; found: 380.0392.
5-Bromo-7-fluoro-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2E)
Deep yellow solid; 62% yield; yield; Rf 0.4 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.54 (dd, J = 7.6, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 8.30 (s, 1H), 8.17 (s, 1H), 8.09 (s, 1H), 7.37 (dd, J = 7.6, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.18 (dd, J = 7.6, 0.8 Hz, 1H), 7.01 (dd, J = 7.6, 0.8 Hz, 1H), 5.44 (s, 2H), 4.14 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 162.55, 159.96, 158.75 (d, J = 19.2 Hz), 146.18 (d, J = 22.8 Hz), 142.31, 137.64, 132.07, 131.67 (d, J = 42.0 Hz), 126.96, 126.91, 125.45, 121.73, 118.53, 117.26, 113.21 (d, J = 15.2 Hz), 111.09 (d, J = 88.4 Hz), 68.58, 36.27; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C18H12BrFN3O+: 384.0142; found: 384.0142.
5-Bromo-8-fluoro-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2F)
Deep yellow solid; 37% yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.32 (s, 1H), 8.23–8.20 (m, 2H), 8.12 (s, 1H), 7.05 (td, J = 8.4, 3.2 Hz, 1H), 6.96 (dd, J = 8.4, 4.0 Hz, 1H), 5.42 (s, 2H), 4.15 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 159.83, 153.08 (d, J = 8.0 Hz), 146.69 (d, J = 7.6 Hz), 142.08, 137.59, 132.07, 126.91, 126.66, 125.28, 122.43, 118.72 (d, J = 34.8 Hz), 118.61 (d, J = 30.8 Hz), 118.52, 117.34, 111.70, 111.46, 68.33, 36.29; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C18H12BrFN3O+: 384.0142; found: 384.0141.
5-Bromo-9-fluoro-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2G)
Yellow solid; 64% yield; Rf 0.6 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.51 (d, J = 8.8, 6.8 Hz, 1H), 8.29 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.18 (s, 1H), 8.09 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 6.88 (td, J = 8.8, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 6.71 (dd, J = 9.6, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 5.45 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 2H), 4.14 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 166.39, 163.89, 158.28 (d, J = 50.0 Hz), 146.78, 142.03, 137.40, 131.95, 127.37 (d, J = 42.0 Hz), 126.86, 125.44 (d, J = 256.8 Hz), 121.96, 119.60 (d, J = 8.0 Hz), 118.71, 117.25, 110.34 (d, J = 88.0 Hz), 104.70 (d, J = 100.4 Hz), 68.58, 36.26; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C18H12BrFN3O+: 384.0142; found: 384.0142.
5-Bromo-10-fluoro-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2H)
Yellow solid; 45% yield; Rf 0.6 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.34 (s, 1H), 8.33 (td, J = 7.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 8.24 (s, 1H), 8.13 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 7.20–7.15 (m, 1H), 7.13–7.08 (m, 1H), 5.54 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 2H), 4.17 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 152.99, 150.55, 146.42 (d, J = 16.8 Hz), 144.83 (d, J = 46.0 Hz), 142.00, 137.47, 132.02, 127.00, 126.25, 125.41, 125.13, 122.21 (d, J = 30.8 Hz), 120.69 (d, J = 15.2 Hz), 118.59, 118.16 (d, J = 72.8 Hz), 117.36, 68.54, 36.22; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C18H12BrFN3O+: 384.0142; found: 384.0142.
5-Bromo-7-chloro-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2I)
Orange yellow solid; 44% yield; Rf 0.6 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.35 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 8.29 (s, 1H), 8.15 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.28–7.23 (m, 2H), 6.99 (dd, J = 6.4, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 5.33 (s, 2H), 4.17 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 155.97, 146.06, 142.00, 137.50, 134.47, 132.01, 128.17, 126.94, 128.56, 126.32, 124.86, 122.33, 119.24, 118.56, 117.39, 115.41, 68.24, 36.27; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C18H12BrClN3O+: 399.9847; found: 399.9846.
5-Bromo-8-chloro-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2J)
Deep yellow solid; 43% yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.48 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 8.32 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.21 (s, 1H), 8.12 (s, 1H), 7.30 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 6.95 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 5.45 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 2H), 4.16 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 155.52, 149.17, 146.30, 142.10, 137.58, 132.09, 131.62, 128.07, 126.99, 126.42, 125.26, 124.51, 122.43, 118.85, 118.64, 117.46, 68.31, 36.30; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C18H12BrClN3O+: 399.9847; found: 399.9846.
5-Bromo-9-chloro-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2K)
Pale yellow solid; 43% yield; Rf 0.4 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.47 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 8.32 (s, 1H), 8.19 (s, 1H), 8.12 (s, 1H), 7.15 (dd, J = 8.8, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.03 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 5.46 (s, 2H), 4.16 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 157.48, 146.61, 142.09, 137.50, 137.22, 132.05, 126.91, 126.74, 126.13, 125.15, 123.25, 122.22, 121.84, 118.71, 117.68, 117.38, 68.49, 36.30; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C18H12BrClN3O+: 399.9847; found: 399.9846.
5-Bromo-10-chloro-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2L)
Pale yellow solid; 50% yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.48 (dd, J = 7.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 8.33 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 8.23 (s, 1H), 8.12 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.43 (dd, J = 7.6, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.12 (t, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 5.56 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 2H), 4.15 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 152.55, 146.51, 142.08, 137.49, 132.13, 132.05, 126.94, 126.04, 125.16, 124.66, 124.13, 122.87, 122.30, 122.22, 118.59, 117.31, 68.64, 36.23; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C18H12BrClN3O+: 399.9847; found: 399.9846.
5-Bromo-8,10-dichloro-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2M)
Yellow solid; 38% yield; Rf 0.4 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.42 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 8.33 (s, 1H), 8.25 (s, 1H), 8.14 (s, 1H), 7.41 (d, J = 2.4 Hz, 1H), 5.56 (s, 2H), 4.17 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 151.24, 145.27, 142.09, 137.60, 132.19, 131.57, 127.75, 127.14, 125.81, 125.37, 125.06, 123.86, 123.17, 122.63, 118.51, 117.71, 68.72, 36.32; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C18H11BrCl2N3O+: 433.9457; found: 433.9456.
5-Bromo-8-bromo-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2N)
Pale yellow solid; 24% yield; Rf 0.4 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.57 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, 1H), 8.29 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 8.16 (s, 1H), 8.09 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 7.42 (dd, J = 8.4, 2.8 Hz, 1H), 6.88 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 5.44 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 2H), 4.15 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 156.00, 146.12, 142.06, 137.55, 134.48, 132.07, 128.22, 126.99, 126.36, 125.22, 124.92, 122.40, 119.25, 118.62, 117.44, 115.43, 68.26, 36.29; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C18H12Br2N3O+: 433.9342; found: 433.9341.
5-Bromo-9-bromo-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2O)
Pale yellow solid; 47% yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.50 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 8.30 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.19 (s, 1H), 8.09 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.05 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 5.55 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 2H), 4.14 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 157.47, 146.60, 142.07, 137.49, 137.22, 132.03, 126.91, 126.73, 126.13, 125.16, 123.25, 122.21, 121.82, 118.69, 117.67, 117.39, 48.49, 36.29; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C18H12Br2N3O+: 433.9342; found: 433.9341.
5-Bromo-10-bromo-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2P)
White yellow solid; 50% yield; Rf 0.3 (Hex/EtOAc = 2:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.50 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 8.30 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.19 (s, 1H), 8.09 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.58 (dd, J = 8.0, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.05 (t, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 5.55 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 2H), 4.14 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 153.59, 146.60, 142.18,137.57, 135.23, 132.12,126.96, 126.10, 125.25, 124.98, 124.73, 123.56, 122.39, 118.67, 117.45, 111.25, 68.75, 36.28; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C18H12Br2N3O+: 433.9342; found: 433.9341.
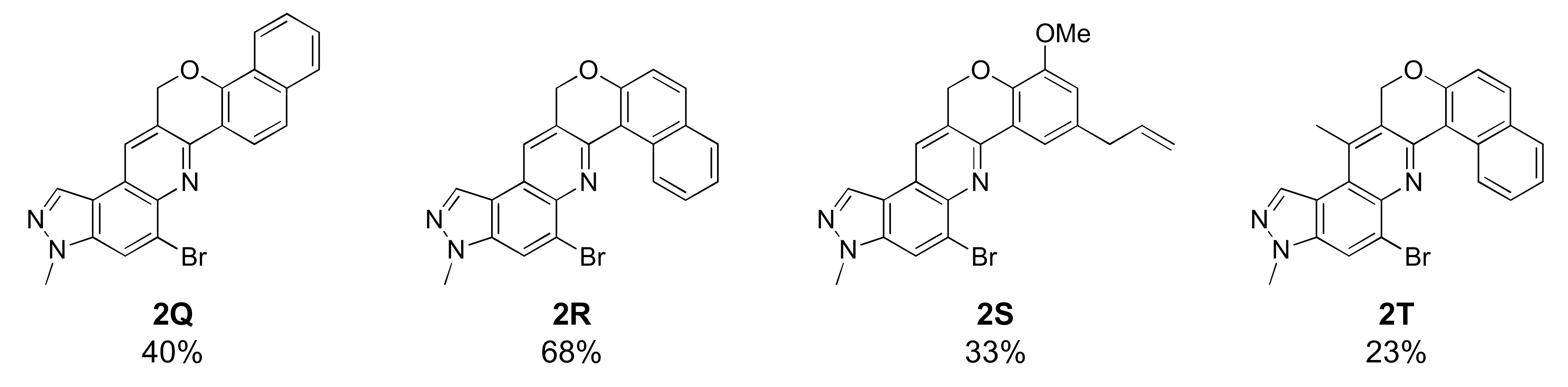
12-Bromo-10-methyl-6,10-dihydrobenzo[7,8]chromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2Q)
Orange brown solid; 40% yield; Rf 0.6 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.63 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 8.35 (s, 1H), 8.29 (d, J = 7.6 Hz, 1H), 8.24 (s, 1H), 8.12 (s, 1H), 7.84 (dd, J = 6.8, 2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.62 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.57–7.49 (m, 1H), 5.67 (s, 2H), 4.17 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 153.53, 148.03, 142.15, 137.46, 135.92, 131.98, 128.07, 127.73, 126.61, 126.23, 126.02, 125.37, 125.14, 122.54, 122.24, 121.99, 118.89, 117.66, 117.05, 68.78, 36.27; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C22H15BrN3O+: 416.0393; found: 416.0392.
14-Bromo-12-methyl-8,12-dihydrobenzo[5,6]chromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2R)
Brown solid; 68% yield; Rf 0.4 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 10.34 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 8.38 (s, 1H), 8.32 (s, 1H), 8.16 (s, 1H), 7.87 (d, J = 9.2 Hz, 1H), 7.85 (dd, J = 8.4, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.74 (ddd, J = 8.4, 6.8, 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.52–7.48 (m, 1H), 7.23 (d, J = 8.4 Hz, 1H), 5.42 (s, 2H), 4.19 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 157.59, 149.35, 142.03, 137.59, 133.36, 132.00, 131.28, 130.93, 128.58, 128.24, 127.97, 127.82, 126.87, 125.70, 124.75, 121.32, 118.66, 118.32, 116.95, 116.03, 68.60, 36.28; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C22H15BrN3O+: 416.0393; found: 416.0392.
8-Allyl-5-bromo-10-methoxy-3-methyl-3,12-dihydrochromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2S)
Brown solid; 33% yield; Rf 0.4 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 8.31 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 8.21 (s, 1H), 8.11 (d, J = 1.2 Hz, 1H), 7.98 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.82 (d, J = 2.0 Hz, 1H), 6.61–6.01 (m, 1H), 5.49 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 2H), 5.21–5.16 (m, 1H), 5.15–5.13 (m, 1H), 5.44 (s, 2H), 4.15 (s, 3H), 3.93 (s, 3H), 3.49 (d, J = 7.2 Hz, 2H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 148.73, 147.55, 144.87, 141.98, 137.60, 137.46, 134.25, 131.09, 126.83, 126.75, 125.29, 123.67, 122.10, 118.73, 117.12, 116.93, 116.15, 114.25, 68.62, 56.27, 40.38, 36.24; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C22H19BrN3O2+: 436.0655; found: 436.0653.
14-Bromo-9,12-dimethyl-8,12-dihydrobenzo[5,6]chromeno[4,3-b]pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline (2T)
Orange brown solid; 23% yield; Rf 0.5 (Hex/EtOAc = 1:1); 1H NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz): δ 10.28 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 8.46 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 8.19 (d, J = 0.8 Hz, 1H), 7.86 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 7.84 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.71 (ddd, J = 8.8, 6.8, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.48 (ddd, J = 8.0, 6.8, 2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.22 (d, J = 8.8 Hz, 1H), 5.53 (s, 2H), 4.21 (s, 3H), 2.90 (s, 3H); 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3): δ 157.29, 148.44, 141.73, 138.10, 137.88, 134.70, 133.15, 131.36, 131.00, 128.56, 128.04, 127.94, 126.75, 126.49, 124.62, 122.53, 118.11, 118.04, 116.90, 116.29, 66.04, 36.25, 17.76; HRMS m/z [M+H]+ calculated for C23H17BrN3O+: 430.0550; found: 430.0547.
5. Conclusions
In summary, we have presented a design of 20 diphenyl-pyrazoloquinolines 1 and 20 chromeno-pyrazoloquinolines 2 and their successful synthesis via inverse imino Diels–Alder reaction in microwave conditions. The straightforward microwave protocol is advantageous in many ways, as it is economical, single-step reaction, multicomponent reaction and has broad functional group tolerance and so forth. In vitro cytotoxicity evaluation indicated strong activity of 8 (1B, 1C, 1M, 2A, 2D, 2E, 2F, and 2R) compounds out of 40 against NUGC-3 human cancer cell proliferation (less than 30% growth compared with vehicle-treated sets at 30 µM). Among the 8 compounds, 1M, 2E, and 2P demonstrated high inhibition of cancer cell proliferation (GI50 less than 8 µM) in six different human cancer cell lines (ACHN, HCT-15, MM231, NCI-H23, NUGC-3, and PC-3). Finally, the compounds 2E and 2P having consistent GI50 values in tested cancer cells were selected and accessed for their mode of action via topo I and topo IIα enzyme assay. The results demonstrated that cytotoxicity of the compound 2E was achieved via inhibition of the activity of the topo IIα enzyme and blocked relaxation of supercoiled plasmid DNA by 88.3%, which is almost equal to that of positive control, etoposide (89.6%), at 100 µM. Despite high cytotoxicity of the compounds 2E and 2P, marginal effects were observed against topo I activity compared with camptothecin. Unfortunately, 2P was completely inactive to topo IIα activity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ph15040399/s1, Scheme S1. Synthesis of starting precursor 3; Scheme S2. A plausible mechanism of intermolecular Diels-Alder reaction; Scheme S3. A plausible mechanism of intramolecular Diels-Alder reaction; Scheme S4. Representative synthetic method of compounds 6; Scheme S5. A plausible mechanism of benzofuran formation.
Author Contributions
Writing—original draft preparation, C.L.C., S.K.; conceptualization and supervision, H.L.; validation, writing—review and editing, J.-K.J., Y.K. (Youngjoo Kwon), J.-S.K.; data curation and investigation, C.L.C., S.K., C.L., Y.K. (Yerin Kim), C.J., S.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (NRF-2019R1F1A1057601) and the Medical Research Center Program (2017R1A5A2015541).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, X.; Wu, Q.; Luan, S.; Yin, Z.; He, C.; Yin, L.; Zou, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Li, L.; Song, X.; et al. A comprehensive review of topoisomerase inhibitors as anticancer agents in the past decade. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 171, 129–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.-M.; Lee, D.; Kong, H.-J.; Lee, S.; Won, Y.-J.; Jung, K.-W.; Cho, H. Causes of death among cancer patients in the era of cancer survivorship in Korea: Attention to the suicide and cardiovascular mortality. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Drug resistance and combating drug resistance in cancer. Cancer Drug Resist. 2019, 2, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matias-Barrios, V.M.; Radaeva, M.; Song, Y.; Alperstein, Z.; Lee, A.R.; Schmitt, V.; Lee, J.; Ban, F.; Xie, N.; Qi, J.; et al. Discovery of New Catalytic Topoisomerase II Inhibitors for Anticancer Therapeutics. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 633142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhaes, L.G.; Ferreira, L.L.G.; Andricopulo, A.D. Recent Advances and Perspectives in Cancer Drug Design. An. Acad. Bras. Ciênc. 2018, 90 (Suppl. S2), 1233–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Dou, Z.; Xiong, Z.; Wang, N.; He, S.; Yan, X.; Jin, H. Design, synthesis and biological research of novel N-phenylbenzamide-4-methylamine acridine derivatives as potential topoisomerase I/II and apoptosis-inducing agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 126714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Aouidate, A.; Wang, S.; Yu, Q.; Li, Y.; Yuan, S. Discovering Anti-Cancer Drugs via Computational Methods. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitiss, J.L. DNA topoisomerase II and its growing repertoire of biological functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2009, 9, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeon, K.H.; Park, S.; Jang, H.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Shrestha, A.; Lee, E.S.; Kwon, Y. AK-I-190, a New Catalytic Inhibitor of Topoisomerase II with Anti-Proliferative and Pro-Apoptotic Activity on Androgen-Negative Prostate Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.L.; Hsieh, C.M.; Chan, N.L.; Hiasa, H. Topoisomerases as anticancer targets. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 373–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanke, A.; Ziraldo, R.; Levene, S.D. DNA-Topology Simplification by Topoisomerases. Molecules 2021, 26, 3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunwar, S.; Hwang, S.-Y.; Katila, P.; Park, S.; Jeon, K.-H.; Kim, D.; Kadayat, T.M.; Kwon, Y.; Lee, E.-S. Discovery of a 2,4-diphenyl-5,6-dihydrobenzo(h)quinolin-8-amine derivative as a novel DNA intercalating topoisomerase IIα poison. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 226, 113860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunwar, S.; Hwang, S.-Y.; Katila, P.; Man Kadayat, T.; Jung, A.-R.; Kwon, Y.; Lee, E.-S. Topoisomerase IIα inhibitory and antiproliferative activity of dihydroxylated 2,6-diphenyl-4-fluorophenylpyridines: Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 60, 128606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommier, Y. Drugging topoisomerases: Lessons and challenges. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dalvie, E.D.; Gopas, J.; Golan-Goldhirsh, A.; Osheroff, N. 6,6′-Dihydroxythiobinupharidine as a poison of human type II topoisomerases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 1881–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tse-Dinh, Y.C. Recent Advances in Use of Topoisomerase Inhibitors in Combination Cancer Therapy. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes, M.; Selas, A.; Trejo, A.; Knudsen, B.R.; Palacios, F.; Alonso, C. Synthesis of hybrid phosphorated indenoquinolines and biological evaluation as topoisomerase I inhibitors and antiproliferative agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 57, 128517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Guo, M. Screening for Natural Inhibitors of Topoisomerases I from Rhamnus davurica by Affinity Ultrafiltration and High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martín-Encinas, E.; Selas, A.; Tesauro, C.; Rubiales, G.; Knudsen, B.R.; Palacios, F.; Alonso, C. Synthesis of novel hybrid quinolino[4,3-b][1,5]naphthyridines and quinolino[4,3-b][1,5]naphthyridin-6(5H)-one derivatives and biological evaluation as topoisomerase I inhibitors and antiproliferatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 195, 112292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arepalli, S.K.; Park, B.; Jung, J.-K.; Lee, K.; Lee, H. A facile one-pot regioselective synthesis of functionalized novel benzo[f]chromeno[4,3-b][1,7]naphthyridines and benzo[f][1,7]naphthyridines via an imino Diels-Alder reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arepalli, S.K.; Park, B.; Lee, K.; Jo, H.; Jun, K.Y.; Kwon, Y.; Kang, J.S.; Jung, J.K.; Lee, H. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 1,3-diphenylbenzo[f][1,7]naphthyrdines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 5586–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arepalli, S.K.; Lee, C.; Sim, S.; Lee, K.; Jo, H.; Jun, K.Y.; Kwon, Y.; Kang, J.S.; Jung, J.K.; Lee, H. Development of 13H-benzo[f]chromeno[4,3-b][1,7]naphthyridines and their salts as potent cytotoxic agents and topoisomerase I/IIα inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 5181–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, S.-J.; Wu, S.-S.; Zhang, X.-H.; Han, Z.-G.; Cao, X.-D.; Hao, W.-J. One-Step Efficient Synthesis of Pyrazolo[3,4-f]quinoline Derivatives Under Microwave Irradiation. Synth. Commun. 2010, 40, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Zhang, S.; Wu, S.-S.; Gao, Y.; Tu, S.-J. A diversity-oriented synthesis of pyrazolo[4,3-f]quinoline derivatives with potential bioactivities via microwave-assisted multi-component reactions. Mol. Divers. 2011, 15, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaboina, S.; Ramineni, V.; Banu, S.; Bandi, Y.; Nagarapu, L.; Dumala, N.; Grover, P. Iodine mediated pyrazolo-quinoline derivatives as potent anti-proliferative agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, R.; Kaya, S.; Zahedifar, M.; Ahmadi, S.A. Simulation and surface topology of activity of pyrazoloquinoline derivatives as corrosion inhibitor on the copper surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patani, G.A.; LaVoie, E.J. Bioisosterism: A Rational Approach in Drug Design. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 3147–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmacharya, U.; Guragain, D.; Chaudhary, P.; Jee, J.-G.; Kim, J.-A.; Jeong, B.-S. Novel Pyridine Bioisostere of Cabozantinib as a Potent c-Met Kinase Inhibitor: Synthesis and Anti-Tumor Activity against Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, K.; Sarkar, S.; Biswas, S.; Maiti, S.; Jana, U. Iron-Catalyzed Synthesis of Functionalized 2H-Chromenes via Intramolecular Alkyne−Carbonyl Metathesis. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 76, 3539–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusakabe, K.-i.; Ide, N.; Daigo, Y.; Tachibana, Y.; Itoh, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Hashizume, H.; Hato, Y.; Higashino, K.; Okano, Y.; et al. Indazole-Based Potent and Cell-Active Mps1 Kinase Inhibitors: Rational Design from Pan-Kinase Inhibitor Anthrapyrazolone (SP600125). J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 4343–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, R.M.; Prochnow, T.; Back, D.F.; Zeni, G.R.J.T. Base-mediated intramolecular cyclization of (2-propargyl ether) arylimines: An approach to 3-amino-benzofurans. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 3751–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Cole, K.P.; Fennell, J.W.; Maloney, T.D.; Mitchell, D.; Subbiah, R.; Ramadas, B. An Alternative Indazole Synthesis for Merestinib. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2018, 22, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Xing, Z.; Chen, X.; Zou, X.; Lu, X. Highly Active and Chemoselective Reduction of Halogenated Nitroarenes Catalyzed by Ordered Mesoporous Carbon Supported Platinum Nanoparticles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 8908–8916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, D.-F.; Jiao, Z.-F.; Liang, Z.-P.; Wang, Y.-W.; Guo, X.-N.; Guo, X.-Y. Selectivity control of Pt/SiC catalysts for photothermocatalytic hydrogenation of 3-nitrostyrene. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 526, 146616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddam, V.; Ramesh, S.; Nagarajan, R. CuI/La(OTf)3 catalyzed, one-pot synthesis of isomeric ellipticine derivatives in ionic liquid. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 4218–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thombal, R.S.; Lee, Y.R. Synergistic Indium and Silver Dual Catalysis: A Regioselective [2 + 2 + 1]-Oxidative N-Annulation Approach for the Diverse and Polyfunctionalized N-Arylpyrazoles. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 4681–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten, F.R.; Eckmann, L.; Greten, T.F.; Park, J.M.; Li, Z.-W.; Egan, L.J.; Kagnoff, M.F.; Karin, M. IKKβ Links Inflammation and Tumorigenesis in a Mouse Model of Colitis-Associated Cancer. Cell 2004, 118, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Hwang, S.-Y.; Shin, J.; Jo, H.; Na, Y.; Kwon, Y. A chromenone analog as an ATP-competitive, DNA non-intercalative topoisomerase II catalytic inhibitor with preferences toward the alpha isoform. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 12857–12860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, A.; Cocklin, S. Bioisosteric Replacement as a Tool in Anti-HIV Drug Design. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arabi, A.A. Routes to drug design via bioisosterism of carboxyl and sulfonamide groups. Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 2167–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).