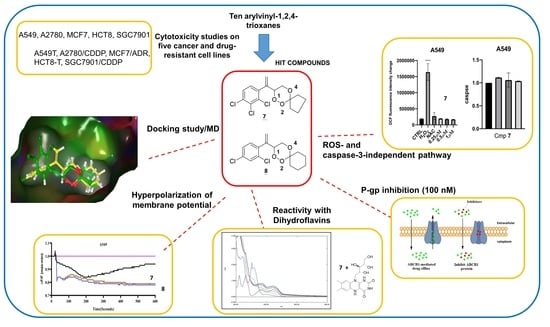
Biological Evaluation in Resistant Cancer Cells and Study of Mechanism of Action of Arylvinyl-1,2,4-Trioxanes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Studies
2.2.1. Cytotoxicity Studies
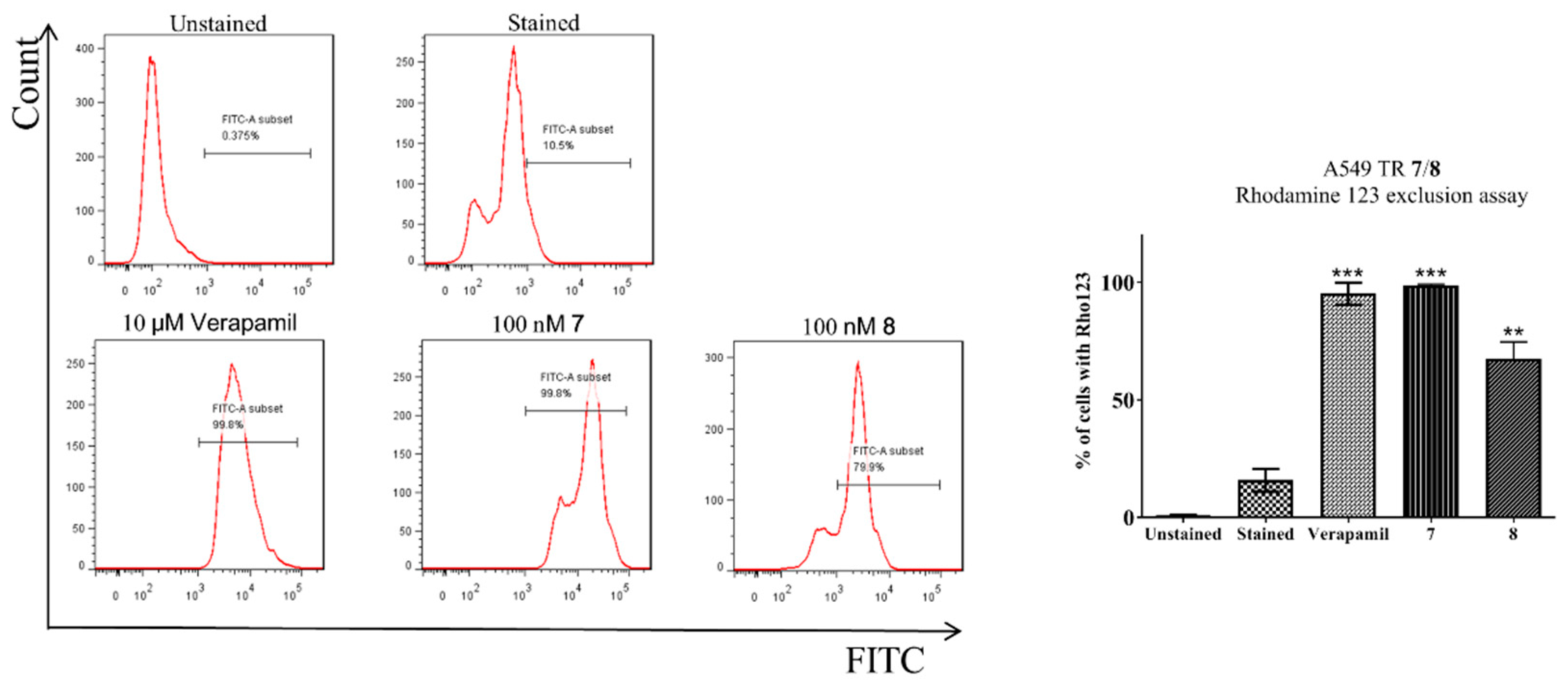
2.2.2. Rhodamine 123 Exclusion Assay
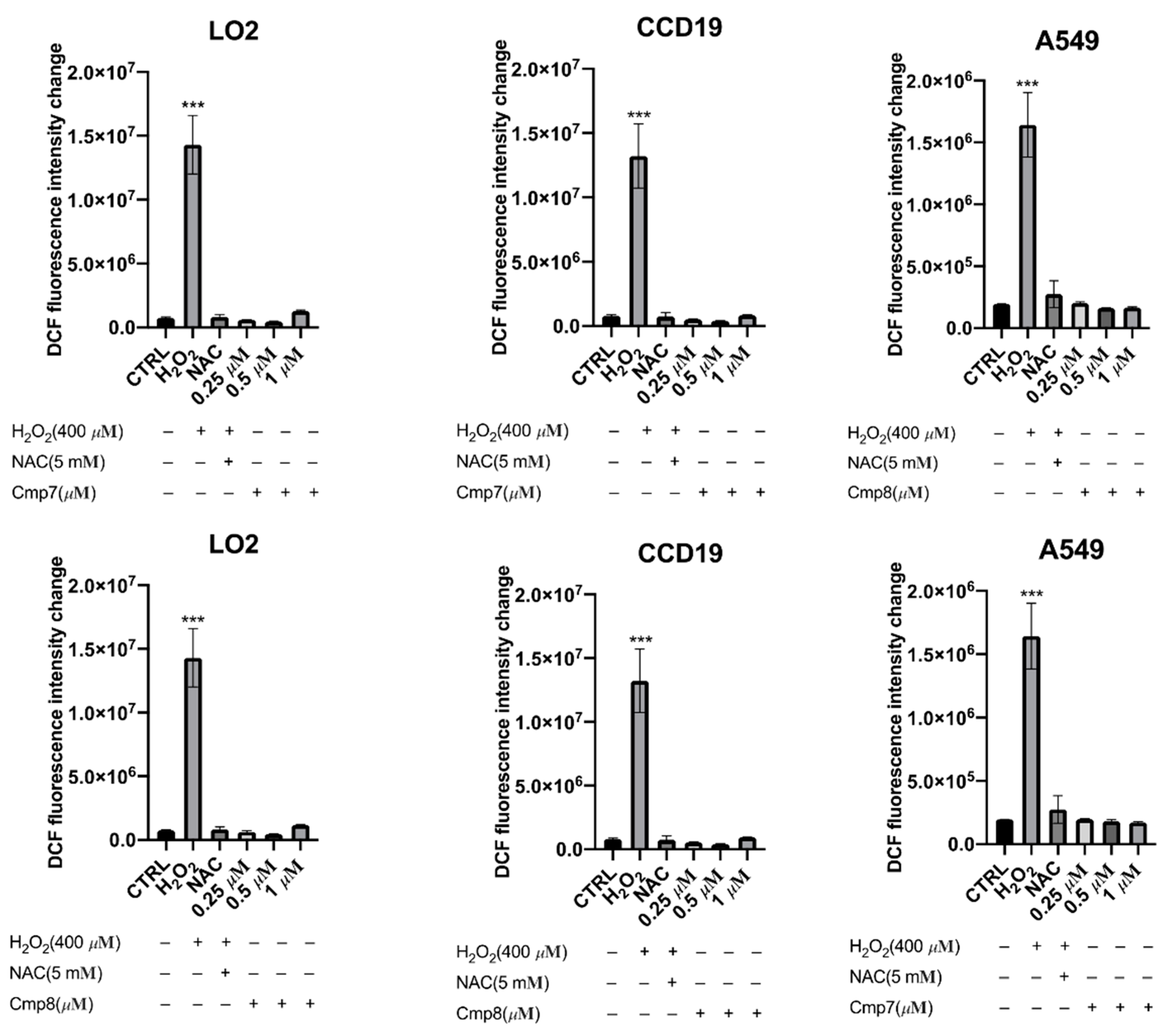
2.2.3. Measurement of ROS Generation
2.2.4. Measurement of Cell Membrane Potential
2.2.5. Caspase-3 Activity Assay
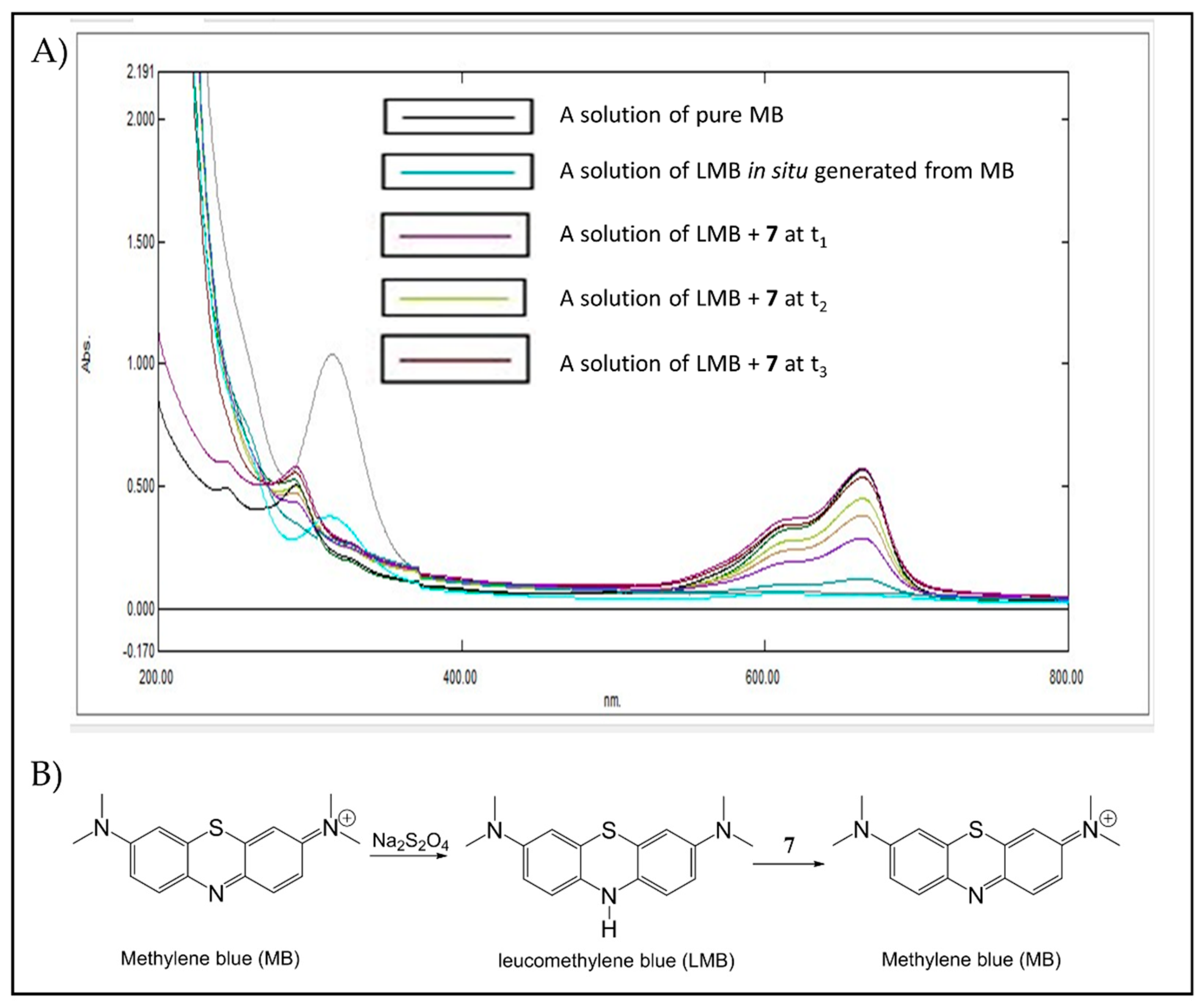
2.2.6. Reactivity Studies Using Dihydroflavins and Leucomethylene Blue
2.3. In Silico Studies
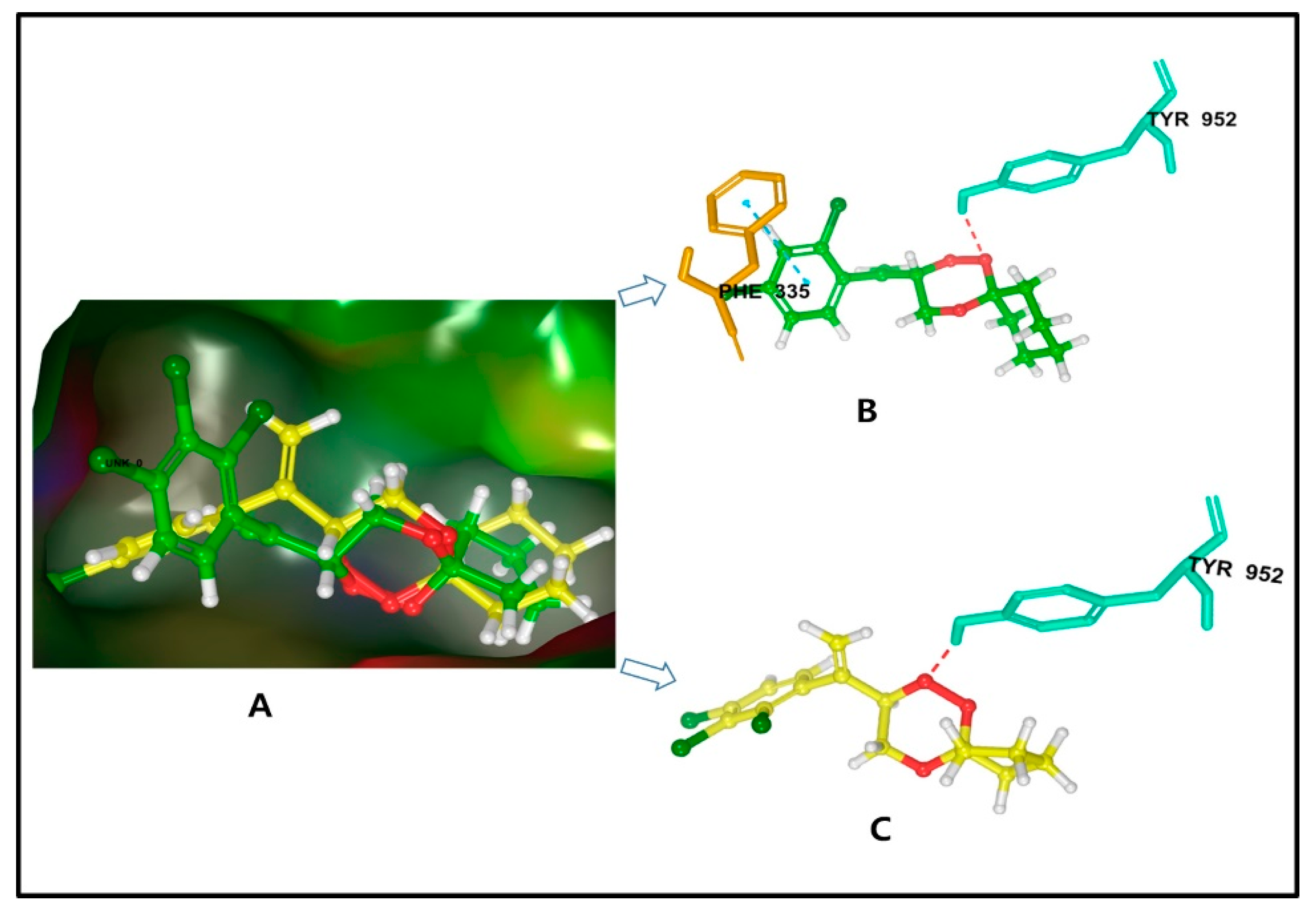
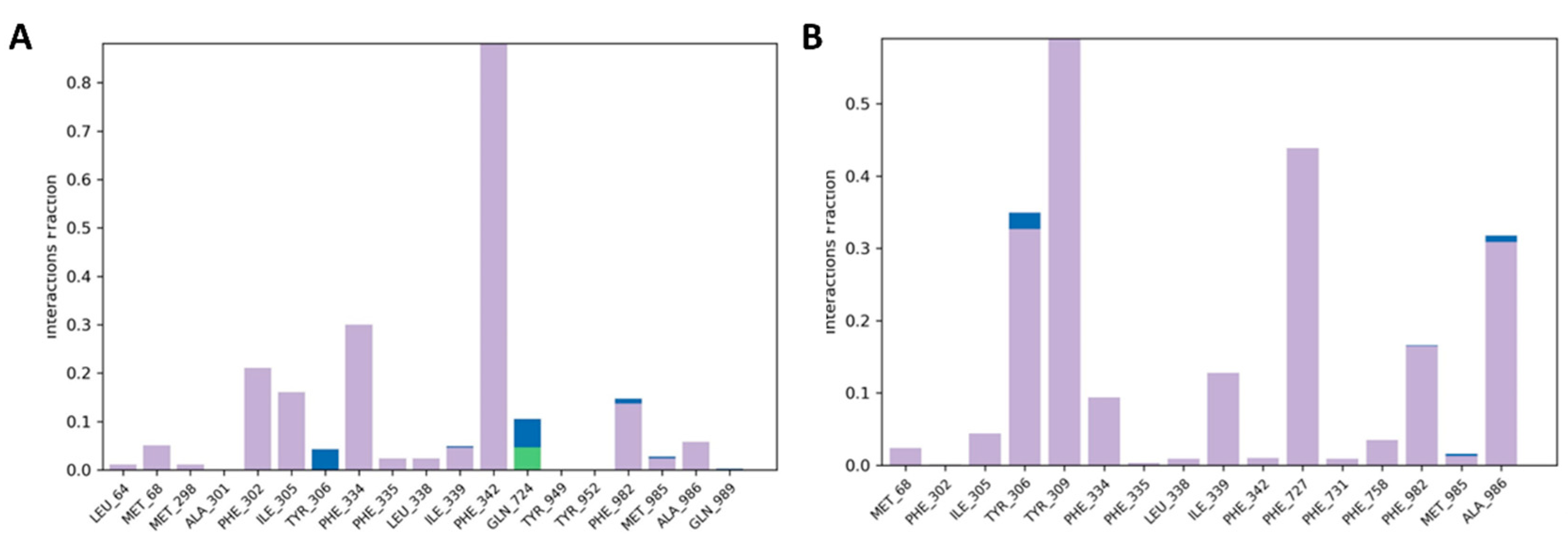
2.3.1. Molecular Docking of P-gp for 7 and 8
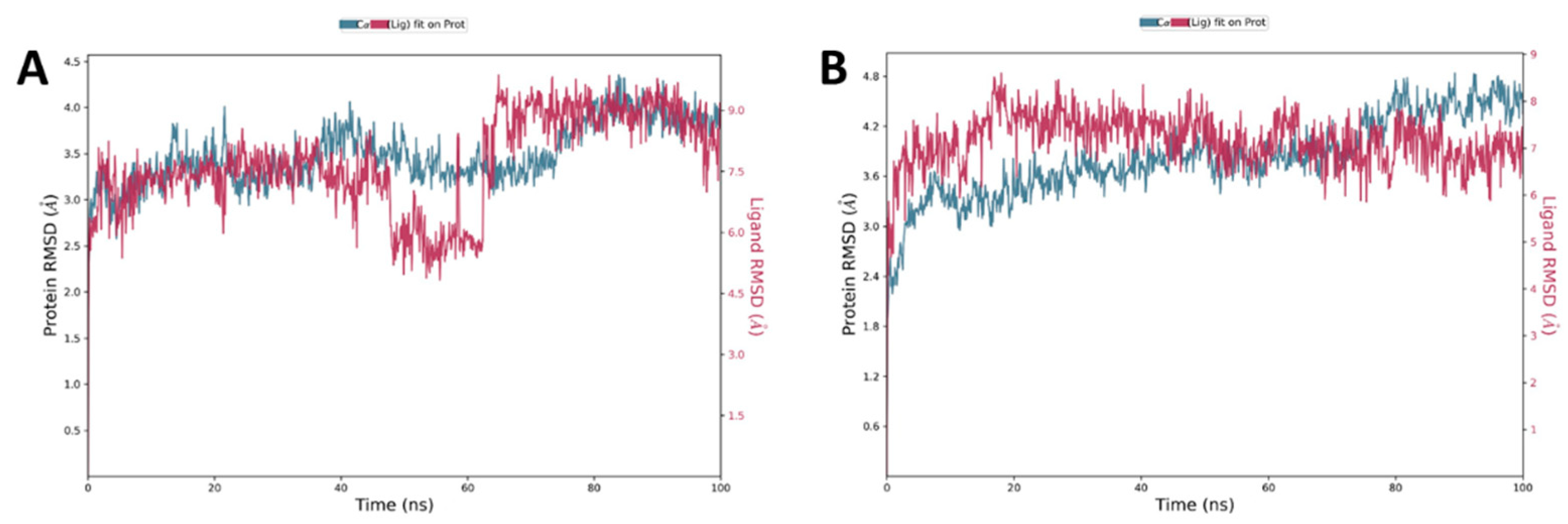
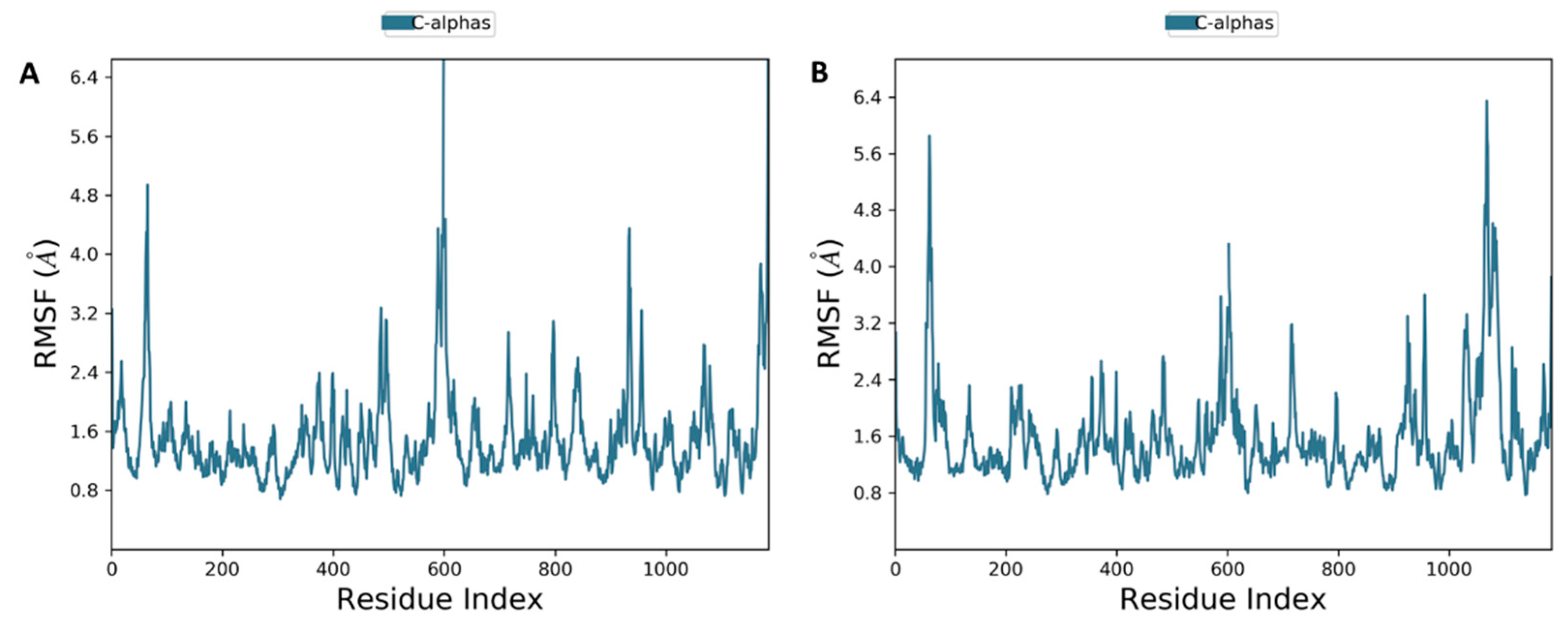
2.3.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of 7 and 8
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Chemistry
3.3. Biological Screening Studies
3.3.1. Cytotoxicity Drug Assay
3.3.2. Rhodamine 123 Exclusion Assay
3.3.3. Detection of ROS Generation Assay
3.3.4. Colorimetric Determination of Caspase-3 Activity
3.3.5. Measurement of Cell Membrane Potential
3.4. Reactivity Studies
3.4.1. Oxidation of Reduced Riboflavin (RFH2) by Peroxide 7
3.4.2. Oxidation of Reduced Leucomethylene (LMB) by Peroxide 7
3.5. In Silico Studies of Trioxanes with P-Glycoprotein Proteins
3.5.1. Molecular Docking
3.5.2. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2020; Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- World Health Organization. WHO Fact Sheet on Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 18 January 2022).
- Wong, Y.K.; Xu, C.; Kalesh, K.A.; He, Y.; Lin, Q.; Wong, W.S.F.; Shen, H.M.; Wang, J. Artemisinin as an anticancer drug: Recent advances in target profiling and mechanisms of action. Med. Res. Rev. 2017, 37, 1492–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, D.; Goswami, A.; Saikia, P.P.; Barua, N.C.; Rao, P.G. Artemisinin and its derivatives: A novel class of anti-malarial and anti-cancer agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaremenko, I.A.; Syroeshkin, M.A.; Levitsky, D.O.; Fleury, F.; Terent’ev, A.O. Cyclic peroxides as promising anticancer agents: In vitro cytotoxicity study of synthetic ozonides and tetraoxanes on human prostate cancer cell lines. Med. Chem. Res. 2017, 26, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubush, D.M.; Morges, M.A.; Rose, B.J.; Thamm, D.H.; Rovis, T. An asymmetric synthesis of 1,2,4-trioxane anticancer agents via desymmetrization of peroxyquinols through a Brønsted acid catalysis cascade. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13554–13557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, V.; Chaudhry, A.; Chashoo, G.; Arora, R.; Arora, S.; Saxena, A.K.; Ishar, M.P.S. β-Ionone derived apoptosis inducing endoperoxides: Discovery of potent leads for anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 87, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, E.P.; Eastman, K.J.; Hill, M.D.; Donnelly, D.J.; Meanwell, N.A. Applications of fluorine in medicinal chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 8315–8359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesbeck, A.G.; Neudorfl, J.; Horauf, A.; Specht, S.; Raabe, A. Antimalarial peroxide dyads from natural artemisinin and hydroxyalkylated 1,2,4-trioxanes. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 3420–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, P.M.; Mukhtar, A.; Ward, S.A.; Bickley, J.F.; Davies, J.; Bachi, M.D.; Stocks, P.A. Application of thiol-olefin co-oxygenation methodology to a new synthesis of the 1,2,4-trioxane pharmacophore. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 3035–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efferth, T. Mechanistic perspectives for 1,2,4-trioxanes in anti-cancer therapy. Drug Resist. Updat. 2005, 8, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.K.; Chan, W.C.; Wong, H.N.; Li, K.Y.; Wu, W.K.; Fan, K.M.; Sung, H.H.Y.; Williams, I.D.; Prosperi, D.; Melato, S.; et al. Facile oxidation of leucomethylene blue and dihydroflavins by artemisinins: Relationship with flavoenzyme function and antimalarial mechanism of action. ChemMedChem 2010, 5, 1282–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, M.K.; Coghi, P.; Agrawal, P.; Yadav, D.K.; Yang, L.J.; Congling, Q.; Sahal, D.; Wong, V.K.W.; Chaudhary, S. Novel halogenated arylvinyl-1,2,4 trioxanes as potent antiplasmodial as well as anticancer agents: Synthesis, bioevaluation, structure-activity relationship and in-silico studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davou, G.I.; Chuwang, N.J.; Essien, U.C.; Choji, T.P.P.; Echeonwu, B.C.; Lugos, M.D. Cytotoxicity analysis of etoposide and cisplatin on cell lines from human lung cancer and normal human lung. Int. Res. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2019, 7, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Hu, B.; He, X.; Mao, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, J.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, F. Overcoming Taxol-resistance in A549 cells: A comprehensive strategy of targeting P-gp transporter, AKT/ERK pathways, and cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP1B1 by 4-hydroxyemodin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 171, 113733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnan, A.M.; Kumar, N. Antimalarial action of artesunate involves DNA damage mediated by reactive oxygen species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, C. Preparation of β-hydroxyhydroperoxides by photooxygenation of allylic alcohols and their elaboration into 1,2,4-trioxanes. Tetrahedron Lett. 1990, 31, 6901–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, M.J.; Krasovskis, E.; Sutton, V.R.; Johnstone, R.W. The drug efflux protein, P-glycoprotein, additionally protects drug-resistant tumor cells from multiple forms of caspase-dependent apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7024–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaremenko, I.A.; Coghi, P.; Prommana, P.; Qiu, C.; Radulov, P.S.; Qu, Y.; Belyakova, Y.Y.; Zanforlin, E.; Kokorekin, V.A.; Wu, Y.Y.J.; et al. Synthetic peroxides promote apoptosis of cancer cells by inhibiting P-glycoprotein ABCB5. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 1118–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.U.; Haj-Yehia, A.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 2000, 5, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Ahn, J.H.; Cheon, H.G. Apoptotic action of PPARγ activation in human non-small cell lung cancer is mediated via proline oxidase-induced ROS formation. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 72, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.H.; Kim, S.Z.; Kim, S.H.; Park, W.H. Induction of apoptosis in arsenic trioxide-treated lung cancer A549 cells by buthionine sulfoximine. Mol. Cells 2008, 26, 158–164. [Google Scholar]
- Haynes, R.K.; Cheu, K.-W.; N’Da, D.; Coghi, P.; Monti, D. Considerations on the mechanism of action of artemisinin antimalarials: Part 1—The ’carbon radical’ and ’heme’ hypotheses. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 13, 217–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, A.E.; Maggs, J.L.; Sun, X.M.; Cohen, G.M.; Chadwick, J.; O’Neill, P.M.; Park, B.K. Evidence for the involvement of carbon-centered radials in the induction of apoptotic cell death by artemisinin compounds. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 9372–9382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, M.; Mertens, C.; Tomat, E.; Brune, B. Iron as a central player and promising target in cancer progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, G.; Wu, L.; Liu, H.; Pang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wu, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, T. Artesunate induces apoptosis via a ROS-independent and Bax-mediated intrinsic pathway in HepG2 cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 336, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenshields, A.L.; Fernando, W.; Hoskin, D.W. The anti-malarial drug artesunate causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of triple-negative MDA-MB-468 and HER2-enriched SK-BR-3 breast cancer cells. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2019, 107, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, F.M., Jr.; Bortner, C.D.; Purdy, G.D.; Cidlowski, J.A. Intracellular K+ suppresses the activation of apoptosis in lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 30567–30576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bortner, C.D.; Hughes, F.M., Jr.; Cidlowski, J.A. A primary role for K+ and Na+ efflux in the activation of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 32436–32442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholson, D.W.; Thornberry, N.A. Caspases: Killer proteases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1997, 22, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, A.G.; Jänicke, R.U. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in Apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999, 6, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, A.; Benoit-Vical, F.; Meunier, B. The key role of heme to trigger the antimalarial activity of trioxanes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2005, 249, 1927–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coghi, P.; Yaremenko, I.A.; Prommana, P.; Radulov, P.S.; Syroeshkin, M.A.; Wu, Y.J.; Gao, J.Y.; Gordillo, F.M.; Mok, S.; Wong, V.K.W.; et al. Novel peroxides as promising anticancer agents with unexpected depressed antimalarial activity. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, C.; Gupta, N.; Tiwari, P. Chemistry of 1,2,4-trioxanes relevant to their mechanism of action. Part 1: Reaction with Fe(II) salts. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 4551–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Guo, J.; Wang, C. Localized Fe(II)-induced cytotoxic reactive oxygen species generating nanosystem for enhanced anticancer therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 4439–4449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, K.M.; Sauna, Z.E.; Ambudkar, S.V. Correlation between steady-state ATP hydrolysis and vanadate-induced ADP trapping in human P-glycoprotein: Evidence for ADP release as the rate-limiting step in the catalytic cycle and its modulation by substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8657–8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shang, C.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B.; Chen, X.; Xu, H.; Huang, B. Silence of cancer susceptibility candidate 9 inhibits gastric cancer and reverses chemoresistance. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15393–15398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Cmp | A549T Cells IC50 (μM) (SD) | S.I. a | A2780 Cells IC50 (μM) (SD) | A2780/CDDP Cells IC50 (μM) (SD) | S.I. | MCF7 Cells IC50a (μM) (SD) | MCF7/ADR Cells IC50 (μM) (SD) | S.I. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.06 ± 1.70 | 1.22 | 43.65 ± 0.35 | 65.81 ± 3.00 | 0.66 | >100 | 85.44 ± 2.90 | 1.17 |
| 2 | 18.29 ± 3.12 | 0.28 | 21.05 ± 6.45 | 53.08 ± 5.89 | 0.40 | >100 | >100 | --- |
| 3 | 2.63 ± 0.21 | 1.68 | 14.65 ± 2.77 | >100 | --- | >100 | 95.50 ± 3.80 | 1.04 |
| 4 | 0.92 ± 0.05 | 5.09 | 5.88 ± 10.43 | 24.08 ± 3.06 | 0.24 | >100 | 18.62 ± 0.77 | 5.37 |
| 5 | 1.21 ± 0.15 | 2.42 | 13.80 ± 3.09 | 22.90 ± 7.90 | 0.6 | >100 | 84.14 ± 2.88 | 1.18 |
| 6 | 0.57 ± 0.01 | 3.63 | 12.11 ± 4.77 | >100 | --- | >100 | >100 | --- |
| 7 | 2.93 ± 0.53 | 0.24 | 1.50 ± 1.50 | 14.18 ± 1.22 | 0.15 | 65.51 ± 3.06 | 12.50 ± 4.30 | 5.24 |
| 8 | 11.84 ± 0.28 | 0.07 | 2.86 ± 3.30 | 4.95 ± 3.40 | 0.58 | 69.71 ± 3.06 | 22.26 ± 2.80 | 3.13 |
| 9 | 1.94 ± 0.09 | 0.74 | 53.91 ± 4.77 | 52.4 ± 5.20 | 1.02 | >100 | 68.39 ± 1.22 | 1.46 |
| 10 | 0.96 ± 0.15 | 0.41 | >100 | >100 | --- | >100 | >100 | --- |
| PTX | 33.24 ± 2.51 | --- | >100 | >100 | --- | >100 | >100 | --- |
| CDDP | 6.53 ± 0.39 | 0.41 | 7.56 ± 1.75 | 60.72 ± 3.06 | 0.12 | >100 | 28.84 ± 2.88 | 3.64 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ng, J.P.L.; Tiwari, M.K.; Nasim, A.A.; Zhang, R.L.; Qu, Y.; Sharma, R.; Law, B.Y.K.; Yadav, D.K.; Chaudhary, S.; Coghi, P.; et al. Biological Evaluation in Resistant Cancer Cells and Study of Mechanism of Action of Arylvinyl-1,2,4-Trioxanes. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15030360
Ng JPL, Tiwari MK, Nasim AA, Zhang RL, Qu Y, Sharma R, Law BYK, Yadav DK, Chaudhary S, Coghi P, et al. Biological Evaluation in Resistant Cancer Cells and Study of Mechanism of Action of Arylvinyl-1,2,4-Trioxanes. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(3):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15030360
Chicago/Turabian StyleNg, Jerome P. L., Mohit K. Tiwari, Ali Adnan Nasim, Rui Long Zhang, Yuanqing Qu, Richa Sharma, Betty Yuen Kwan Law, Dharmendra K. Yadav, Sandeep Chaudhary, Paolo Coghi, and et al. 2022. "Biological Evaluation in Resistant Cancer Cells and Study of Mechanism of Action of Arylvinyl-1,2,4-Trioxanes" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 3: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15030360
APA StyleNg, J. P. L., Tiwari, M. K., Nasim, A. A., Zhang, R. L., Qu, Y., Sharma, R., Law, B. Y. K., Yadav, D. K., Chaudhary, S., Coghi, P., & Wong, V. K. W. (2022). Biological Evaluation in Resistant Cancer Cells and Study of Mechanism of Action of Arylvinyl-1,2,4-Trioxanes. Pharmaceuticals, 15(3), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15030360