The Past, Present, and Future of Clinically Applied Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T-Cell Therapy
Abstract
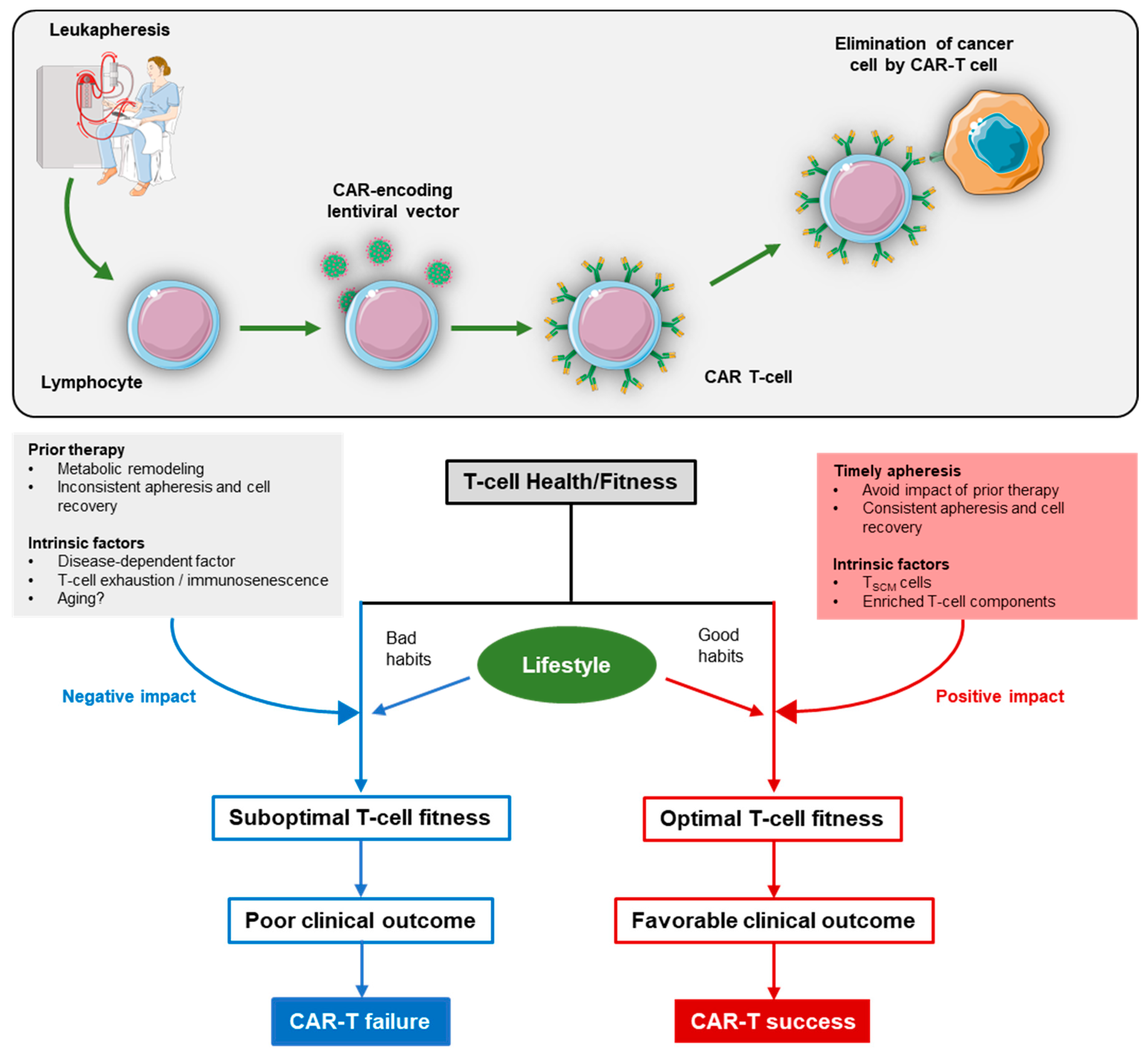
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of CAR-T-Cell Therapy Development and Clinical Trials
3. Establishment of an Ecosystem for Actual Clinical Use of Regenerative Medicine Products
4. Real-World Evidence of Clinically Applied CAR-T-Cell Therapy
| Reference | N Number of Infusions | Median Age (Range) | Histology (DLBCL/tFL/HGBCL) | ORR/CR | PFS/OS | CRS Any Gr/≥ Gr3 | ICANS Any Gr/≥ Gr3 | MEDIAN FU | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jaglowski S, Blood 2019 Suppl. [45] | 70 | 65 (19–89) | 63%/-/31% | 60%/38% a | -/- | -/4% b | -/4% b | - | CIBMTR registry |
| Jakub Svoboda, Blood 2019. [42] | 28 | 66 (38–81) | 64%/36%/- | 46%/38% (3 mo) | 52% (3 mo)/71% (6 mo) | 29%/0% c | 7%/4% d | 5.5 mo | Bendamustine as LD chemotherapy |
| Matthew J. Frigault, Blood, 2019. [43] | 8 | 50 (17–79) | 63%/-/24%, PMBCL 13% | 50%/25% | - | 88%/0% e | 13%/0% e | - | Secondary CNS Lymphoma |
| Marcelo C. Pasquini, Blood Adv 2020. [44] | 155 | 65 (18–89) | 55%/27%/- | 62%/40% (BOR) | 26% (12 mo)/56% (12 mo) | 45%/5% b | 18%/5% b | 11.9 mo | CIBMTR registry |
| Gloria Iacoboni, Cancer Med 2021. [46] | 75 (Apheresis: 91) | 60 (52–67) | 58%/23%/15% | 60%/32% | 32% (12 mo)/10.7 mo (median) | 57%/22% b | 20%/11% b | 14.1 mo | |
| S. J. Schuster, NEJM 2019. [41] | 111 | 56 (22–76) | 79%/19%/- | 52%/40% | EFS 35% (12 mo)/48% (12 mo) | 71%/5% c | 15%/1% | 28.6 mo | Pivotal trial (JULIET study) |
| Marcelo C. Pas-quini, Blood Adv 2020. [44] | 255 | 13.2 (0.41–26.17) | B-ALL | 85%(BOR) | EFS 52% (12 mo)/77% (12 mo) | 55%/16% b | 27%/9% b | 13.4 mo | CIBMTR registry |
| S. L. Maude, NEJM 2018. [47] | 75 | 11 (3–23) | B-ALL | 81%/61% | EFS 57% (12 mo)/77% (12 mo) | 77%/48% c | 40%/13% | 13.1 mo | Pivotal trial (ELIANA study) |
5. T-Cell Health/Fitness for CAR-T-Cell Therapy
5.1. Aging and Immune Cells
5.2. Diet, Exercise, and Immune Cells
5.3. Prior Therapy before Leukapheresis
5.4. Timely Leukapheresis and Cryopreservation
6. Future CAR-T-Cell Therapy
6.1. Antigen Loss
6.2. TME and CAR-T-Cell Exhaustion
6.3. Allogenic CAR-T Cells
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Steinman, R.M. Decisions about Dendritic Cells: Past, Present, and Future. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Yang, J.C.; Sherry, R.M.; Kammula, U.S.; Hughes, M.S.; Phan, G.Q.; Citrin, D.E.; Restifo, N.P.; Robbins, P.F.; Wunderlich, J.R.; et al. Durable Complete Responses in Heavily Pretreated Patients with Metastatic Melanoma Using T-Cell Transfer Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4550–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grupp, S.A.; Kalos, M.; Barrett, D.; Aplenc, R.; Porter, D.L.; Rheingold, S.R.; Teachey, D.T.; Chew, A.; Hauck, B.; Wright, J.F.; et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells for Acute Lymphoid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riddell, S.R.; Jensen, M.C.; June, C.H. Chimeric Antigen Receptor--Modified T Cells: Clinical Translation in Stem Cell Transplantation and Beyond. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2013, 19, S2–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riddell, S.R.; Sommermeyer, D.; Berger, C.; Liu, L.S.; Balakrishnan, A.; Salter, A.; Hudecek, M.; Maloney, D.G.; Turtle, C.J. Adoptive Therapy with Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells of Defined Subset Composition. Cancer J. 2014, 20, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sadelain, M.; Brentjens, R.; Rivière, I. The Basic Principles of Chimeric Antigen Receptor Design. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- June, C.H.; Sadelain, M. Chimeric Antigen Receptor Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.J.; Svoboda, J.; Chong, E.A.; Nasta, S.D.; Mato, A.R.; Anak, Ö.; Brogdon, J.L.; Pruteanu-Malinici, I.; Bhoj, V.; Landsburg, D.; et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells in Refractory B-Cell Lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2545–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restifo, N.P.; Dudley, M.E.; Rosenberg, S.A. Adoptive Immunotherapy for Cancer: Harnessing the T Cell Response. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, G.; Waks, T.; Eshhar, Z. Expression of Immunoglobulin-T-Cell Receptor Chimeric Molecules as Functional Receptors with Antibody-Type Specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 10024–10028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abate-Daga, D.; Davila, M.L. CAR Models: Next-Generation CAR Modifications for Enhanced T-Cell Function. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2016, 3, 16014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bretscher, P.A. A Two-Step, Two-Signal Model for the Primary Activation of Precursor Helper T Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maher, J.; Brentjens, R.J.; Gunset, G.; Rivière, I.; Sadelain, M. Human T-Lymphocyte Cytotoxicity and Proliferation Directed by a Single Chimeric TCRzeta/CD28 Receptor. Nat. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, C.; Mihara, K.; Andreansky, M.; Nicholson, I.C.; Pui, C.H.; Geiger, T.L.; Campana, D. Chimeric Receptors with 4–1BB Signaling Capacity Provoke Potent Cytotoxicity against Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2004, 18, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moreno-Cortes, E.; Forero-Forero, J.V.; Lengerke-Diaz, P.A.; Castro, J.E. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Oncology -Pipeline at a Glance: Analysis of the ClinicalTrials.gov Database. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 159, 103239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKay, M.; Afshinnekoo, E.; Rub, J.; Hassan, C.; Khunte, M.; Baskaran, N.; Owens, B.; Liu, L.; Roboz, G.J.; Guzman, M.L.; et al. The Therapeutic Landscape for Cells Engineered with Chimeric Antigen Receptors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuirk, J.; Waller, E.K.; Qayed, M.; Abhyankar, S.; Ericson, S.; Holman, P.; Keir, C.; Myers, G.D. Building Blocks for Institutional Preparation of CTL019 Delivery. Cytotherapy 2017, 19, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langebrake, C.; Admiraal, R.; van Maarseveen, E.; Bonnin, A.; Bauters, T.; EBMT Working Group. Consensus Recommendations for the Role and Competencies of the EBMT Clinical Pharmacist and Clinical Pharmacologist Involved in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2020, 55, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakoub-Agha, I.; Chabannon, C.; Bader, P.; Basak, G.W.; Bonig, H.; Ciceri, F.; Corbacioglu, S.; Duarte, R.F.; Einsele, H.; Hudecek, M.; et al. Management of Adults and Children Undergoing Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy: Best Practice Recomendations of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) and the Joint Accreditation Committee of ISCT and EBMT (JACIE). Haematologica 2020, 105, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzal-Alfaro, M.B.; Escudero-Vilaplana, V.; Revuelta-Herrero, J.L.; Collado-Borrell, R.; Herranz-Alonso, A.; Sanjurjo-Saez, M. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy Management and Safety: A Practical Tool from a Multidisciplinary Team Perspective. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 636068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaupierre, A.; Kahle, N.; Lundberg, R.; Patterson, A. Educating Multidisciplinary Care Teams, Patients, and Caregivers on CAR T-Cell Therapy. J. Adv. Pract. Oncol. 2019, 10, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, L.; Rodriguez, E.S.; Reese, A.; Anderson, K. Building a Program: Implications for Infrastructure, Nursing Education, and Training for CAR T-Cell Therapy. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2019, 23, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, K.; DiFilippo, H.; Henes, K.; Irwin, L.L.; Napier, E.; Weber, E. Tisagenlecleucel Therapy: Nursing Considerations for the Outpatient Setting. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2021, 37, 151178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastoupil, L.J.; Jain, M.D.; Spiegel, J.Y.; Ghobadi, A.; Lin, Y.; Dahiya, S.; Lunning, M.A.; Lekakis, L.J.; Reagan, P.M.; Oluwole, O.O.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel) CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy for Relapsed/Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Real World Experience. Blood 2018, 132 (Suppl. 1), 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.D.; Chavez, J.C.; Shah, B.D.; Khimani, F.; Lazaryan, A.; Davila, M.L.; Liu, H.D.; Falchook, A.D.; Robinson, T.; Kim, S.; et al. Radiation Therapy as a Bridging Strategy for Refractory Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Patients Awaiting CAR T Manufacturing of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel. Blood 2018, 132, 4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, C.A.; Hunter, B.; Armand, P.; Kamihara, Y.; Ritz, J.; Rodig, S.J.; Wright, K.; Lipschitz, M.; Redd, R.A.; Maus, M.V.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in the Real World: Outcomes and Predictors of Response, Resistance and Toxicity. Blood 2018, 132 (Suppl. 1), 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, M.C.; Locke, F.L.; Herrera, A.F.; Siddiqi, T.; Ghobadi, A.; Komanduri, K.V.; Hu, Z.-H.; Dong, H.; Hematti, P.; Nikiforow, S.; et al. Post-Marketing Use Outcomes of an Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cell Therapy, Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel), for the Treatment of Large B Cell Lymphoma (LBCL) in the United States (US). Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mian, A.; Wei, W.; Winter, A.M.; Khouri, J.; Jagadeesh, D.; Anwer, F.; Gerds, A.T.; Dean, R.M.; Sobecks, R.; Pohlman, B.; et al. Outcomes and Factors Impacting Use of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Refractory and Relapsed Large B-Cell Lymphoma: An Intent-to-Treat Analysis. Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Miklos, D.B.; Vose, J.M.; Rapoport, A.P.; Munoz, J.; Andreadis, C.; Vu, K.; Hill, B.T.; et al. Experience with Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel) in Patients with Secondary CNS Involvement: Results from the US Lymphoma CAR T Consortium. Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, T.; Sauter, C.S.; Shah, G.L.; Maloy, M.A.; Chan, J.; Scordo, M.; Avecilla, S.T.; Batlevi, Y.; Dahi, P.B.; Batlevi, C.W.; et al. Safety and Feasibility of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy after Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Relapsed/Refractory B Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2540–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinnix, C.C.; Gunther, J.R.; Dabaja, B.S.; Strati, P.; Fang, P.; Hawkins, M.C.; Adkins, S.; Westin, J.; Ahmed, S.; Fayad, L.; et al. Bridging Therapy Prior to Axicabtagene Ciloleucel for Relapsed/Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 2871–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbasi, A.; Peeke, S.; Shah, N.; Mustafa, J.; Khatun, F.; Lombardo, A.; Abreu, M.; Elkind, R.; Fehn, K.; de Castro, A.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CD19 CAR-T Cell Therapy Results in High Rates of Systemic and Neurologic Remissions in Ten Patients with Refractory Large B Cell Lymphoma Including Two with HIV and Viral Hepatitis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nastoupil, L.J.; Jain, M.D.; Feng, L.; Spiegel, J.Y.; Ghobadi, A.; Lin, Y.; Dahiya, S.; Lunning, M.; Lekakis, L.; Reagan, P.; et al. Standard-of-Care Axicabtagene Ciloleucel for Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results from the US Lymphoma CAR T Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, C.A.; Hunter, B.D.; Redd, R.; Rodig, S.J.; Chen, P.H.; Wright, K.; Lipschitz, M.; Ritz, J.; Kamihara, Y.; Armand, P.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in the Non-Trial Setting: Outcomes and Correlates of Response, Resistance, and Toxicity. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3095–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mian, A.; Wei, W.; Winter, A.M.; Khouri, J.; Jagadeesh, D.; Anwer, F.; Gerds, A.T.; Dean, R.M.; Sobecks, R.; Pohlman, B.; et al. Outcomes and Factors Impacting Use of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results from an Intention-to-Treat Analysis. Leuk. Lymphoma 2021, 62, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grana, A.; Gut, N.; Williams, K.; Maakaron, J.; Porter, K.; William, B.M.; Vasu, S.; Penza, S.; Brammer, J.E.; Saad, A.; et al. Safety of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel for the Treatment of Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 4, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuk, F.A.; Berger, C.; Badbaran, A.; Zabelina, T.; Sonntag, T.; Riecken, K.; Geffken, M.; Wichmann, D.; Frenzel, C.; Thayssen, G.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel In Vivo Expansion and Treatment Outcome in Aggressive B-Cell Lymphoma in a Real-World Setting. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2523–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, S.T.; Dholaria, B.R.; Sengsayadeth, S.M.; Savani, B.N.; Oluwole, O.O. Role of Bridging Therapy during Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy. eJHaem 2022, 3, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSelm, C. The Current and Future Role of Radiation Therapy in the Era of CAR T-Cell Salvage. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jäger, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svoboda, J.; Ballard, H.J.; Chong, E.A.; LaRose, M.I.; Bair, S.M.; Namoglu, E.C.; Hughes, M.E.; Dwivedy Nasta, S.; Landsburg, D.J.; Barta, S.K.; et al. Use of Bendamustine for Lymphodepletion before Tisagenlecleucel (Anti-CD19 CAR T Cells) for Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas. Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigault, M.J.; Dietrich, J.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Leick, M.; Choi, B.D.; DeFilipp, Z.; Chen, Y.B.; Abramson, J.; Crombie, J.; Armand, P.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Secondary CNS Lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquini, M.C.; Hu, Z.H.; Curran, K.; Laetsch, T.; Locke, F.; Rouce, R.; Pulsipher, M.A.; Phillips, C.L.; Keating, A.; Frigault, M.J.; et al. Real-World Evidence of Tisagenlecleucel for Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5414–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaglowski, S.; Hu, Z.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Kamdar, M.; Ghosh, M.; Lulla, P.; Sasine, J.; Perales, M.; Hematti, P.; Nikiforow, S.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy for Adults with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): Real World Experience from the Center for International Blood & Marrow Transplant Research (CIBMTR) Cellular Therapy (CT) Registry. Blood 2019, 134, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacoboni, G.; Villacampa, G.; Martinez-Cibrian, N.; Bailén, R.; Lopez Corral, L.; Sanchez, J.M.; Guerreiro, M.; Caballero, A.C.; Mussetti, A.; Sancho, J.M.; et al. Real-World Evidence of Tisagenlecleucel for the Treatment of Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 3214–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maude, S.L.; Laetsch, T.W.; Buechner, J.; Rives, S.; Boyer, M.; Bittencourt, H.; Bader, P.; Verneris, M.R.; Stefanski, H.E.; Myers, G.D.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, A.; Saygin, C.; Maakaron, J.; Hoelscher, T.; Purdin, Z.; Robinson, J.; Lamprecht, M.; Penza, S.; Brammer, J.E.; Efebera, Y.A.; et al. Cytopenias after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cells (CAR-T) Infusion; Patterns and Outcomes. Biol. Blood Marrow Transpl. 2019, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasta, S.D.; Hughes, M.E.; Namoglu, E.C.; Landsburg, D.J.; Chong, E.A.; Barta, S.K.; Frey, N.V.; Gerson, J.N.; Maity, A.; Plastaras, J.; et al. A Characterization of Bridging Therapies Leading up to Commercial CAR T-Cell Therapy. Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedell, P.A.; Walling, C.; Nastoupil, L.J.; Pennisi, M.; Maziarz, R.T.; McGuirk, J.P.; Oluwole, O.O.; Bachanova, V.; Hwang, W.-T.; Schuster, S.J.; et al. A Multicenter Retrospective Analysis of Clinical Outcomes, Toxicities, and Patterns of Use in Institutions Utilizing Commercial Axicabtagene Ciloleucel and Tisagenlecleucel for Relapsed/Refractory Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas. Blood 2019, 134, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sermer, D.; Batlevi, C.; Palomba, M.L.; Shah, G.; Lin, R.J.; Perales, M.A.; Scordo, M.; Dahi, P.; Pennisi, M.; Afuye, A.; et al. Outcomes in Patients with DLBCL Treated with Commercial CAR T Cells Compared with Alternate Therapies. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 4669–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafouri, S.; Fenerty, K.; Schiller, G.; de Vos, S.; Eradat, H.; Timmerman, J.; Larson, S.; Mead, M. Real-World Experience of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel and Tisagenlecleucel for Relapsed or Refractory Aggressive B-Cell Lymphomas: A Single-Institution Experience. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021, 21, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.J.; Lobaugh, S.M.; Pennisi, M.; Chan, H.T.; Batlevi, Y.; Ruiz, J.D.; Elko, T.A.; Maloy, M.A.; Batlevi, C.L.; Dahi, P.B.; et al. Impact and Safety of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy in Older, Vulnerable Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Haematologica 2021, 106, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.S.; Srour, S.A.; Whisenant, M.; Subbiah, I.M.; Chen, T.H.; Ponce, D.; Gonzalez, A.G.; Kamal, M.; Mendoza, T.; Cleland, C.S.; et al. Patient-Reported Symptom and Functioning Status During the First 12 Months after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy for Hematologic Malignancies. Transpl. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 930.e1–930.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, B.; Argnani, L.; Guadagnuolo, S.; Pellegrini, C.; Stefoni, V.; Broccoli, A.; Nanni, L.; Morigi, A.; Lolli, G.; Guarino, M.; et al. Real World Evidence of CAR T-Cell Therapies for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Monocentric Experience. Cancers 2021, 13, 4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamure, S.; Van Laethem, F.; De Verbizier, D.; Lozano, C.; Gehlkopf, E.; Tudesq, J.J.; Serrand, C.; Benzaoui, M.; Kanouni, T.; Quintard, A.; et al. Clinical and Product Features Associated with Outcome of DLBCL Patients to CD19-Targeted CAR T-Cell Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnet, F.M. The Concept of Immunological Surveillance. Prog. Exp. Tumor Res. 1970, 13, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Lotze, M.T.; Muul, L.M.; Chang, A.E.; Avis, F.P.; Leitman, S.; Linehan, W.M.; Robertson, C.N.; Lee, R.E.; Rubin, J.T. A Progress Report on the Treatment of 157 Patients with Advanced Cancer Using Lymphokine-Activated Killer Cells and Interleukin-2 or High-Dose Interleukin-2 Alone. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 316, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, G.P.; Bruce, A.T.; Ikeda, H.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. Cancer immunoediting: From immunosurveillance to tumor escape. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 991–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagogo-Jack, I.; Shaw, A.T. Tumour Heterogeneity and Resistance to Cancer Therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, C.T.; Hassan, M.; Morris, A.B.; Jeffery, J.; Lee, K.; Jagirdar, N.; Staton, A.D.; Raikar, S.S.; Spencer, H.T.; Sulchek, T.; et al. Improving T-Cell Expansion and Function for Adoptive T-Cell Therapy Using Ex Vivo Treatment with PI3Kdelta Inhibitors and VIP Antagonists. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lesch, S.; Benmebarek, M.R.; Cadilha, B.L.; Stoiber, S.; Subklewe, M.; Endres, S.; Kobold, S. Determinants of Response and Resistance to CAR T Cell Therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 65, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrucci, L.; Fabbri, E. Inflammageing: Chronic Inflammation in Ageing, Cardiovascular Disease, and Frailty. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, J.F. Immunological Function of the Thymus. Lancet 1961, 2, 748–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Feigelson, S.W.; Montresor, A.; Shimoni, E.; Roncato, F.; Legler, D.F.; Laudanna, C.; Haran, G.; Alon, R. CCR7 Signalosomes Are Preassembled on Tips of Lymphocyte Microvilli in Proximity to LFA-1. Biophys. J. 2021, 120, 4002–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, R.; Westermann, J. The Role of the Spleen in Lymphocyte Migration. Scanning Microsc. 1991, 5, 1075–1079. [Google Scholar]
- Szeto, C.; Lobos, C.A.; Nguyen, A.T.; Gras, S. TCR Recognition of Peptide-MHC-I: Rule Makers and Breakers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dustin, M.L. The Immunological Synapse. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, L. Advances in Targeting Cell Surface Signalling Molecules for Immune Modulation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Courtney, A.H.; Lo, W.L.; Weiss, A. TCR Signaling: Mechanisms of Initiation and Propagation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaud, G.; Lesourne, R.; Love, P.E. Regulatory Mechanisms in T Cell Receptor Signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natoli, G.; Ostuni, R. Adaptation and Memory in Immune Responses. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurosaki, T.; Kometani, K.; Ise, W. Memory B Cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanley, D.P.; Aw, D.; Manley, N.R.; Palmer, D.B. An Evolutionary Perspective on the Mechanisms of Immunosenescence. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callender, L.A.; Carroll, E.C.; Beal, R.W.J.; Chambers, E.S.; Nourshargh, S.; Akbar, A.N.; Henson, S.M. Human CD8+ EMRA T Cells Display a Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype Regulated by p38 MAPK. Aging Cell. 2018, 8, e12675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jergović, M.; Smithey, M.J.; Nikolich-Žugich, J. Intrinsic and Extrinsic Contributors to Defective CD8+ T Cell Responses with Aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 105, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wherry, E.J.; Kurachi, M. Molecular and Cellular Insights into T Cell Exhaustion. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 486–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLane, L.M.; Abdel-Hakeem, M.S.; Wherry, E.J. CD8 T Cell Exhaustion during Chronic Viral Infection and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 37, 457–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choe, S.S.; Huh, J.Y.; Hwang, I.J.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, J.B. Adipose Tissue Remodeling: Its Role in Energy Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders. Front. Endocrinol. 2016, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kusminski, C.M.; Bickel, P.E.; Scherer, P.E. Targeting Adipose Tissue in the Treatment of Obesity-Associated Diabetes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 639–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbudi, A.; Rahmadika, N.; Tjahjadi, A.I.; Ruslami, R. Type 2 Diabetes and Its Impact on the Immune System. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2020, 16, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, S.H.; Cantrell, D.A. Signaling and Function of Interleukin-2 in T Lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 411–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in Inflammation, Immunity, and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.W.; de Waal Malefyt, R.; Coffman, R.L.; O’Garra, A. Interleukin-10 and the Interleukin-10 Receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 683–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.L.; Hassi, H.O.; English, N.R.; Blakemore, A.I.; Stagg, A.J.; Knight, S.C. Methylglyoxal Modulates Immune Responses: Relevance to Diabetes. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Interaction between Microbiota and Immunity in Health and Disease. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D.; Jordan, B.F. Gut Microbiota-Mediated Inflammation in Obesity: A Link with Gastrointestinal Cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpaia, N.; Campbell, C.; Fan, X.; Dikiy, S.; van der Veeken, J.; deRoos, P.; Liu, H.; Cross, J.R.; Pfeffer, K.; Coffer, P.J.; et al. Metabolites Produced by Commensal Bacteria Promote Peripheral Regulatory T-Cell Generation. Nature 2013, 504, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, A.; Lauterbach, M.; Latz, E. Western Diet and the Immune System: An Inflammatory Connection. Immunity 2019, 51, 794–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schluter, J.; Peled, J.U.; Taylor, B.P.; Markey, K.A.; Smith, M.; Taur, Y.; Niehus, R.; Staffas, A.; Dai, A.; Fontana, E.; et al. The Gut Microbiota Is Associated with Immune Cell Dynamics in Humans. Nature 2020, 588, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, W.K.; Williams, J.; Atherton, P.; Larvin, M.; Lund, J.; Narici, M. Sarcopenia, Dynapenia, and the Impact of Advancing Age on Human Skeletal Muscle Size and Strength; a Quantitative Review. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- von Haehling, S.; Ebner, N.; Dos Santos, M.R.; Springer, J.; Anker, S.D. Muscle Wasting and Cachexia in Heart Failure: Mechanisms and Therapies. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 323–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clegg, A.; Young, J.; Iliffe, S.; Rikkert, M.O.; Rockwood, K. Frailty in Elderly People. Lancet 2013, 381, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duggal, N.A.; Niemiro, G.; Harridge, S.D.R.; Simpson, R.J.; Lord, J.M. Can Physical Activity Ameliorate Immunosenescence and Thereby Reduce Age-Related Multi-Morbidity? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiuza-Luces, C.; Garatachea, N.; Berger, N.A.; Lucia, A. Exercise Is the Real Polypill. Physiology 2013, 28, 330–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spielmann, G.; McFarlin, B.K.; O’Connor, D.P.; Smith, P.J.; Pircher, H.; Simpson, R.J. Aerobic Fitness Is Associated with Lower Proportions of Senescent Blood T-Cells in Man. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.J.; Cosgrove, C.; Ingram, L.A.; Florida-James, G.D.; Whyte, G.P.; Pircher, H.; Guy, K. Senescent T-Lymphocytes Are Mobilised into the Peripheral Blood Compartment in Young and Older Humans after Exhaustive Exercise. Brain Behav. Immun. 2008, 22, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooren, F.C.; Krüger, K. Apoptotic Lymphocytes Induce Progenitor Cell Mobilization after Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 119, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravussin, E. Physiology. A NEAT Way to Control Weight? Science 2005, 307, 530–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, W.A.; Deal, A.M.; Reeve, B.B.; Abernethy, A.P.; Basch, E.; Mitchell, S.A.; Shatten, C.; Hie Kim, Y.; Whitley, J.; Serody, J.S.; et al. Cardiopulmonary Fitness in Patients Undergoing Hematopoietic SCT: A Pilot Study. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2013, 48, 1342–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.K.; O’Connor, R.S.; Grupp, S.A.; Barrett, D.M. Lingering Effects of Chemotherapy on Mature T Cells Impair Proliferation. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 4653–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.K.; Vernau, L.; Grupp, S.A.; Barrett, D.M. Naïve T-Cell Deficits at Diagnosis and after Chemotherapy Impair Cell Therapy Potential in Pediatric Cancers. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.; Perazzelli, J.; Grupp, S.A.; Barrett, D.M. Early Memory Phenotypes Drive T Cell Proliferation in Patients with Pediatric Malignancies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 320ra3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klebanoff, C.A.; Scott, C.D.; Leonardi, A.J.; Yamamoto, T.N.; Cruz, A.C.; Ouyang, C.; Ramaswamy, M.; Roychoudhuri, R.; Ji, Y.; Eil, R.L.; et al. Memory T Cell-Driven Differentiation of Naive Cells Impairs Adoptive Immunotherapy. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 126, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mika, T.; Ladigan-Badura, S.; Maghnouj, A.; Mustafa, B.; Klein-Scory, S.; Baraniskin, A.; Döhring, S.; Fuchs, I.; Ehl, S.; Hahn, S.A.; et al. Altered T-Lymphocyte Biology Following High-Dose Melphalan and Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation with Implications for Adoptive T-Cell Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 568056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, M.J.; Niederle, N.; Maschmeyer, G.; Banat, G.A.; von Grünhagen, U.; Losem, C.; Kofahl-Krause, D.; Heil, G.; Welslau, M.; Balser, C.; et al. Bendamustine plus Rituximab versus CHOP plus Rituximab as First-Line Treatment for Patients with Indolent and Mantle-Cell Lymphomas: An Open-Label, Multicentre, Randomised, phase 3 Non-Inferiority Trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Maruyama, D.; Maeshima, A.M.; Makita, S.; Kitahara, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Fukuhara, S.; Munakata, W.; Suzuki, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; et al. Prolonged Lymphocytopenia after Bendamustine Therapy in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Indolent B-Cell and Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2015, 5, e362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Calle, N.; Hartley, S.; Ahearne, M.; Kasenda, B.; Beech, A.; Knight, H.; Balotis, C.; Kennedy, B.; Wagner, S.; Dyer, M.J.S.; et al. Kinetics of T-Cell Subset Reconstitution Following Treatment with Bendamustine and Rituximab for Low-Grade Lymphoproliferative Disease: A Population-Based Analysis. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, V.; Muralidharan, K.; Meng, W.; Bagashev, A.; Oldridge, D.A.; Rosenthal, J.; Van Arnam, J.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Mohan, D.; DiNofia, A.M.; et al. CAR T-Cell Therapy Is Effective for CD19-dim B-Lymphoblastic Leukemia but Is Impacted by Prior Blinatumomab Therapy. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 3539–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourthe, M.E.; Rabian, F.; Yakouben, K.; Chevillon, F.; Cabannes-Hamy, A.; Méchinaud, F.; Grain, A.; Chaillou, D.; Rahal, I.; Caillat-Zucman, S.; et al. Determinants of CD19-Positive vs. CD19-Negative Relapse after Tisagenlecleucel for B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3383–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceppi, F.; Rivers, J.; Annesley, C.; Pinto, N.; Park, J.R.; Lindgren, C.; Mgebroff, S.; Linn, N.; Delaney, M.; Gardner, R.A. Lymphocyte Apheresis for Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Manufacturing in Children and Young Adults with Leukemia and Neuroblastoma. Transfusion 2018, 58, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouziana, S.; Bouzianas, D. Anti-CD19 CAR-T Cells: Digging in the Dark Side of the Golden Therapy. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 157, 103096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, A.D.; Assenmacher, M.; Schröder, B.; Meyer, M.; Orentas, R.; Bethke, U.; Dropulic, B. Towards a Commercial Process for the Manufacture of Genetically Modified T Cells for Therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagarajan, S.; Schmitt, D.; Acker, C.; Rutjens, E. Autologous Cryopreserved Leukapheresis Cellular Material for Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T Cell Manufacture. Cytotherapy 2019, 21, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Rossi, J.M.; Neelapu, S.S.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Ghobadi, A.; Oluwole, O.O.; Reagan, P.M.; Lekakis, L.J.; Lin, Y.; et al. Tumor Burden, Inflammation, and Product Attributes Determine Outcomes of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 4898–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panch, S.R.; Srivastava, S.K.; Elavia, N.; McManus, A.; Liu, S.; Jin, P.; Highfill, S.L.; Li, X.; Dagur, P.; Kochenderfer, J.N.; et al. Effect of Cryopreservation on Autologous Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Characteristics. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1275–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, D.M. Improving CAR T Cell Immunotherapy-Mediated Remissions for Pediatric Leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 1842–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaeger, U.; Bishop, M.R.; Salles, G.; Schuster, S.J.; Maziarz, R.T.; Han, X.; Savchenko, A.; Roscoe, N.; Orlando, E.; Knoblock, D.; et al. Myc Expression and Tumor-Infiltrating T Cells Are Associated with Response in Patients (Pts) with Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (r/r DLBCL) Treated with Tisagenlecleucel in the Juliet Trial. Blood 2020, 136 (Suppl. 1), 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finney, O.C.; Brakke, H.M.; Rawlings-Rhea, S.; Hicks, R.; Doolittle, D.; Lopez, M.; Futrell, B.; Orentas, R.J.; Li, D.; Gardner, R.A.; et al. CD19 CAR T Cell Product and Disease Attributes Predict Leukemia Remission Durability. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, R.D.; Powell, J.D. Metabolism of Immune Cells in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 516–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, M.; Del Bufalo, F.; De Angelis, B.; Quintarelli, C.; Caruana, I.; de Billy, E. Manipulating the Metabolism to Improve the Efficacy of CAR T-Cell Immunotherapy. Cells 2021, 10, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Activity of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A Single-Arm, Multicentre, phase 1–2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Fry, T.J. Mechanisms of Resistance to CAR T Cell Therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, C.; Zhou, J. Understanding the Mechanisms of Resistance to CAR T-Cell Therapy in Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sotillo, E.; Barrett, D.M.; Black, K.L.; Bagashev, A.; Oldridge, D.; Wu, G.; Sussman, R.; Lanauze, C.; Ruella, M.; Gazzara, M.R.; et al. Convergence of Acquired Mutations and Alternative Splicing of CD19 Enables Resistance to CART-19 Immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 1282–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orlando, E.J.; Han, X.; Tribouley, C.; Wood, P.A.; Leary, R.J.; Riester, M.; Levine, J.E.; Qayed, M.; Grupp, S.A.; Boyer, M.; et al. Genetic Mechanisms of Target Antigen Loss in CAR19 Therapy of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1504–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.; Wu, D.; Cherian, S.; Fang, M.; Hanafi, L.A.; Finney, O.; Smithers, H.; Jensen, M.C.; Riddell, S.R.; Maloney, D.G.; et al. Acquisition of a CD19-negative Myeloid Phenotype Allows Immune Escape of MLL-rearranged B-ALL from CD19 CAR-T-cell Therapy. Blood 2016, 127, 2406–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, J.; Zuo, S.; Deng, B.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Zheng, Q.; Ling, Z.; Song, W.; Xu, J.; Duan, J.; et al. Sequential CD19-22 CAR T Therapy Induces Sustained Remission in Children with r/r B-ALL. Blood 2020, 135, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Cheng, J.; Li, T.; Huang, J.; Li, C.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Mao, X.; Zhu, L.; et al. Efficacy and Toxicity for CD22/CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Aggressive B-Cell Lymphoma Involving the Gastrointestinal Tract. Cytotherapy 2020, 22, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Hu, X.; Cao, W.; Li, C.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Gu, C.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Cheng, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of CAR19/22 T-Cell Cocktail Therapy in Patients with Refractory/Relapsed B-Cell Malignancies. Blood 2020, 135, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Wu, Z.; Jia, H.; Tong, C.; Guo, Y.; Ti, D.; Han, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; et al. Bispecific CAR-T Cells Targeting Both CD19 and CD22 for Therapy of Adults with Relapsed or Refractory B Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, L.M.; Muffly, L.S.; Spiegel, J.Y.; Ramakrishna, S.; Hossain, N.; Baggott, C.; Sahaf, B.; Patel, S.; Craig, J.; Yoon, J.; et al. Phase I Trial Using CD19/CD22 Bispecific CAR T Cells in Pediatric and Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL). Blood 2019, 134, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrolia, P.J.; Wynn, R.; Hough, R.E.; Vora, A.; Bonney, D.; Veys, P.; Chiesa, R.; Rao, K.; Clark, L.; Al-Hajj, M.; et al. Phase I Study of AUTO3, a Bicistronic Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Therapy Targeting CD19 and CD22, in Pediatric Patients with Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (r/r B-ALL): Amelia Study. Blood 2019, 134, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, W.; Shi, M.; Yang, J.; Cao, J.; Xu, L.; Yan, D.; Yao, M.; Liu, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, B.; et al. Phase II Trial of Co-Administration of CD19- and CD20-Targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for Relapsed and Refractory Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 5827–5838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ji, X.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.; Han, X.; Ti, D.; Dai, H.; Wang, C.; et al. Optimized Tandem CD19/CD20 CAR-Engineered T Cells in Refractory/Relapsed B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2020, 136, 1632–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Zhu, F.; Taylor, C.; Schneider, D.; Krueger, W.; Worden, A.; Yim, S.; Fenske, T.S.; Hamadani, M.; Johnson, B.; et al. A phase 1 Study with Point-of-Care Manufacturing of Dual Targeted, Tandem Anti-CD19, Anti-CD20 Chimeric Antigen Receptor Modified T (CAR-T) Cells for Relapsed, Refractory, Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Zhu, F.; Schneider, D.; Taylor, C.; Krueger, W.; Worden, A.; Longo, W.L.; Hamadani, M.; Fenske, T.; Johnson, B.; et al. Results of a Phase I Study of Bispecific Anti-CD19, Anti-CD20 Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) Modified T Cells for Relapsed, Refractory, Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. JCO 2019, 37, 2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Johnson, B.D.; Schneider, D.; Zhu, F.; Szabo, A.; Keever-Taylor, C.A.; Krueger, W.; Worden, A.A.; Kadan, M.J.; Yim, S.; et al. Bispecific Anti-CD20, Anti-CD19 CAR T Cells for Relapsed B Cell Malignancies: A phase 1 Dose Escalation and Expansion Trial. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maude, S.L.; Teachey, D.T.; Porter, D.L.; Grupp, S.A. CD19-Targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood 2015, 125, 4017–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, E.A.; Ruella, M.; Schuster, S.J.; Lymphoma Program Investigators at the University of Pennsylvania. Five-Year Outcomes for Refractory B-Cell Lymphomas with CAR T-Cell Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemer, F.; Leisch, M.; Geisberger, R.; Melchardt, T.; Rinnerthaler, G.; Zaborsky, N.; Greil, R. Combination Strategies for Immune-Checkpoint Blockade and Response Prediction by Artificial Intelligence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraietta, J.A.; Lacey, S.F.; Orlando, E.J.; Pruteanu-Malinici, I.; Gohil, M.; Lundh, S.; Boesteanu, A.C.; Wang, Y.; O’Connor, R.S.; Hwang, W.T.; et al. Determinants of Response and Resistance to CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cell Therapy of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Mei, H. T Cell Exhaustion and CAR-T Immunotherapy in Hematological Malignancies. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6616391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, E.A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Lacey, S.F.; Ambrose, D.E.; Gonzalez, V.; Levine, B.L.; June, C.H.; Schuster, S.J. PD-1 Blockade Modulates Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-Modified T Cells: Refueling the CAR. Blood 2017, 129, 1039–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maude, S.L.; Hucks, G.E.; Seif, A.E.; Talekar, M.K.; Teachey, D.T.; Baniewicz, D.; Callahan, C.; Gonzalez, V.; Nazimuddin, F.; Gupta, M.; et al. The Effect of Pembrolizumab in Combination with CD19-Targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cells in Relapsed Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL). JCO 2017, 35, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardeshna, K.; Marzolini, M.A.V.; Osborne, W.; Al-Hajj, M.; Thomas, S.; Faulkner, J.; Pule, M.; Peddareddigari, V.G.R.; Khokhar, N.Z. Study of AUTO3, the First Bicistronic Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) Targeting CD19 and CD22, Followed by Anti-PD1 Consolidation in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory (r/r) Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): Alexander Study. Blood 2018, 132, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depil, S.; Duchateau, P.; Grupp, S.A.; Mufti, G.; Poirot, L. “Off-the-shelf” Allogeneic CAR T Cells: Development and Challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, W.; Zhan, H.; Samarasinghe, S.; Adams, S.; Amrolia, P.; Stafford, S.; Butler, K.; Rivat, C.; Wright, G.; Somana, K.; et al. Molecular Remission of Infant B-ALL after Infusion of Universal TALEN Gene-Edited CAR T Cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaaj2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcantara, M.; Tesio, M.; June, C.H.; Houot, R. CAR T-Cells for T-Cell Malignancies: Challenges in Distinguishing between Therapeutic, Normal, and Neoplastic T-Cells. Leukemia 2018, 32, 2307–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagarajan, S.; Spencer, T.; Smith, J. Optimizing CAR-T Cell Manufacturing Processes during Pivotal Clinical Trials. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 16, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Reference | N, Number of Infusions | Median Age (Range) | Histology (DLBCL/tFL/HGBCL) | BT Therapy Rates | ORR/CR | PFS/OS | CRS Any Gr/≥ Gr3 | ICANS Any Gr/≥ Gr3 | MEDIAN FU | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loretta J. Nastoupil, Blood 2018, Suppl. [25] | 165 (Apheresis: 211) | 59 (21–82) | 61%/31%/-, PMBCL 8% | 56% | 59%/49% (Day 100) | - | -/7% | -/31% | - | |
| Michael D.Jain, Blood, 2018, Suppl. [26] | 8 | - | DLBCL 1, Double hit 5, tFL 2 | 100% | 50%/17% (Day 30) a | - | 86%/14% a | -/43% a | - | RT as Bridging therapy |
| Caron A. Jacobson, Blood 2018, Suppl. [27] | 76 | 64 | DHL/THL 21% | 36% | 64%/41% (4 mo as med FU, BOR) b | -/84% (4 mo) | 96%/17% | 76%/38% | - | |
| Marcelo C.Pasquini, Blood 2019, Suppl. [27,28] | 295 | 61 (19–81) | -/27%/-, DHL 36% | - | 70%/52% (BOR) | - | 83%/11% d | 61%/- | 6 mo | CIBMTR registry |
| Agrima Mian, Blood 2019, Suppl. [29] | 27 | 63 (25–77) | 74%/11%/PMBCL 15% | - | - | -/13 mo (median) | - | - | 5 mo | |
| N. Nora Bennani, Blood 2019, Suppl. [30] | 262 (Apheresis: 283) | 60 (21–80) | 67%/-/22% | 52% | 54% (3 mo)/- | EFS 9.5 mo (median) | 91%/6% | 67%/31% | 10.1 mo | Similar outcome between no CNS and secondary CNS |
| Tania Jain, Leukemia, 2019. [31] | 4 | 56 (38–66) | DLBCL 3, tFL 1 | 75% | 75%/50% (1 mo) | - | 50%/0% c | 25%/0% c | 112 days | After Allo-SCT |
| Chelsea C Pinnix, Blood Adv 2020. [32] | 124 (Apheresis: 148) | 60 (18–85) | 77%/16%/-, PMBCL 7% | 50% | 77%/48% | 37% (12 mo)/64% (12 mo) (median) | -/9% | -/40% | 11.1 mo | BT cohort/No BT cohort: 50%/50% |
| Ahmed Abbasi, J Hematol Oncol 2020. [33] | 10 | 66 (55–77) | 40%/30%/- | - | -/80% (3 mo) | -/80% (at data cut off) | 60%/20% (Gr ≥ 2) | 50%/30% (Gr ≥ 2) | - | Two patients with CNS involvement, two patients with HIV and viral hepatitis |
| Loretta J. Nastoupil, J Clin Oncol 2020. [34] | 275 (Apheresis: 298) | 60 (21–83) | 68%/26%/-, PMBCL 6% | 53% | 82%/64%(BOR) | 47%(12 mo)/68% (12 mo) | 91%/7% | 69%/31% | 12.9 mo | |
| Caron A. Jacobson, J Clin Oncol 2020. [35] | 122 | 62 (21–79) | 43%/14%/27%, PMBCL 7% | 45% | 70%/50%(BOR) | 40% (12 mo)/67% (12 mo) | 93%/16% | 70%/35% | 10.4 mo | |
| Allison Grana, Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2021. [36,37] | 37 | 59 (23–75) | 60%/24%/5%, PMBCL 11% | - | 49%/35% (6 mo) | 5.8 mo (median)/75% (7.5 mo) | 97%/16% | 73%/43% | 11 mo | |
| Francis A. Ayuk, Blood Adv 2021. [38] | 21 | 58 (24–67) | 67%/19%/-, PMBCL 14% | 90% | 67% (Day30)/- | 37%/49% (12 mo) | 71%/14% | 48%/19% | 121 days | Prospective study |
| Agrima Mian, LEUK& LYMP 2021. [36] | 27 | 63 (25–77) | 74%/11%/-, PMBCL 15% | 48% | 85%/48% (BOR) | 10.5 mo/13 mo (median) | - | - | 5 mo | |
| S. S. Neelapu, NEJM 2017. [9] | 111 | 58 (23–76) | 76%/16%/-, PMBCL 8% | 0%(only corrticosteroids were allowed) | 82%/54% | 44%/59% (12 mo) | 93%/13% d | 64%/28% | 15.4 mo | Pivotal trial (ZUMA-1 study) |
| NCT Number | Disease | Target Antigen | Treatment | Country | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02650999 | DLBCL, MCL, FL | CD19 | Pembrolizumab after CAR-T-cell therapy | USA | Completed |
| NCT03630159 | DLBCL | CD19 | Tisa-cel with Pembrolizumab | USA | Completed |
| NCT02926833 | DLBCL | CD19 | Axi-cel with Atezolizumab | USA | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT02706405 | NHL | CD19 | CAR-T (JCAR014) with Durvalumab | USA | Active, not recruiting |
| NCT03310619 | B-cell malignancies | CD19 | CAR T (JCAR017) with Durvalumab | USA | Recruiting |
| NCT04205409 | CLL, FL, DLBCL | CD19 | Nivolumab after CAR-T-cell therapy | USA | Recruiting |
| NCT04850560 | B-cell lymphoma | CD19 | CAR-T expressing PD-1/CD 28 switch-receptor | China | Recruiting |
| NCT04381741 | DLBCL | CD19 | CAR-T expressing IL7 and CCL 19 with PD-1 mAb | China | Recruiting |
| NCT04134325 | HL | CD30 | CAR-T-cell therapy with nivolumab/pembrolizumab | US | Recruiting |
| NCT03298828 | ALL, Burkitt lymphoma | CD19 | CAR-T-cell therapy with PD-1 knockout | China | Not yet recruiting |
| NCT04213469 | B-cell lymphoma | CD19 | CAR-T-cell therapy with PD-1 knockout | China | Recruiting |
| NCT04163302 | B-cell lymphoma | CD19 | CAR-T secreting mutant PD-1 | China | Recruiting |
| NCT04162119 | MM | BCMA | CAR-T secreting mutant PD-1 | China | Recruiting |
| NCT04539444 | B-cell lymphoma | CD19/22 | CAR-T with Tislelizumab | China | Recruiting |
| NCT03287817 | DLBCL | CD19/22 | CAR-T with pembrolizumab | US, UK | Recruiting |
| NCT03932955 | B-cell lymphoma | CD19 | CAR-T expressing PD-1/CD 28 switch-receptor | China | Unknown |
| NCT03540303 | B-cell lymphoma | CD19 | CAR-T cells carrying cytoplasmic activated PD-1 | China | Unknown |
| NCT03208556 | B-cell lymphoma | CD19 | CAR-T cells with cell-intrinsic PD1 inhibition | China | Unknown |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujiwara, Y.; Kato, T.; Hasegawa, F.; Sunahara, M.; Tsurumaki, Y. The Past, Present, and Future of Clinically Applied Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T-Cell Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020207
Fujiwara Y, Kato T, Hasegawa F, Sunahara M, Tsurumaki Y. The Past, Present, and Future of Clinically Applied Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T-Cell Therapy. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(2):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020207
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujiwara, Yuki, Toshiki Kato, Futoshi Hasegawa, Muha Sunahara, and Yoshie Tsurumaki. 2022. "The Past, Present, and Future of Clinically Applied Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T-Cell Therapy" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 2: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020207
APA StyleFujiwara, Y., Kato, T., Hasegawa, F., Sunahara, M., & Tsurumaki, Y. (2022). The Past, Present, and Future of Clinically Applied Chimeric Antigen Receptor-T-Cell Therapy. Pharmaceuticals, 15(2), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020207






