Particle Size Effect of Curcumin Nanocrystals on Transdermal and Transfollicular Penetration by Hyaluronic Acid-Dissolving Microneedle Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
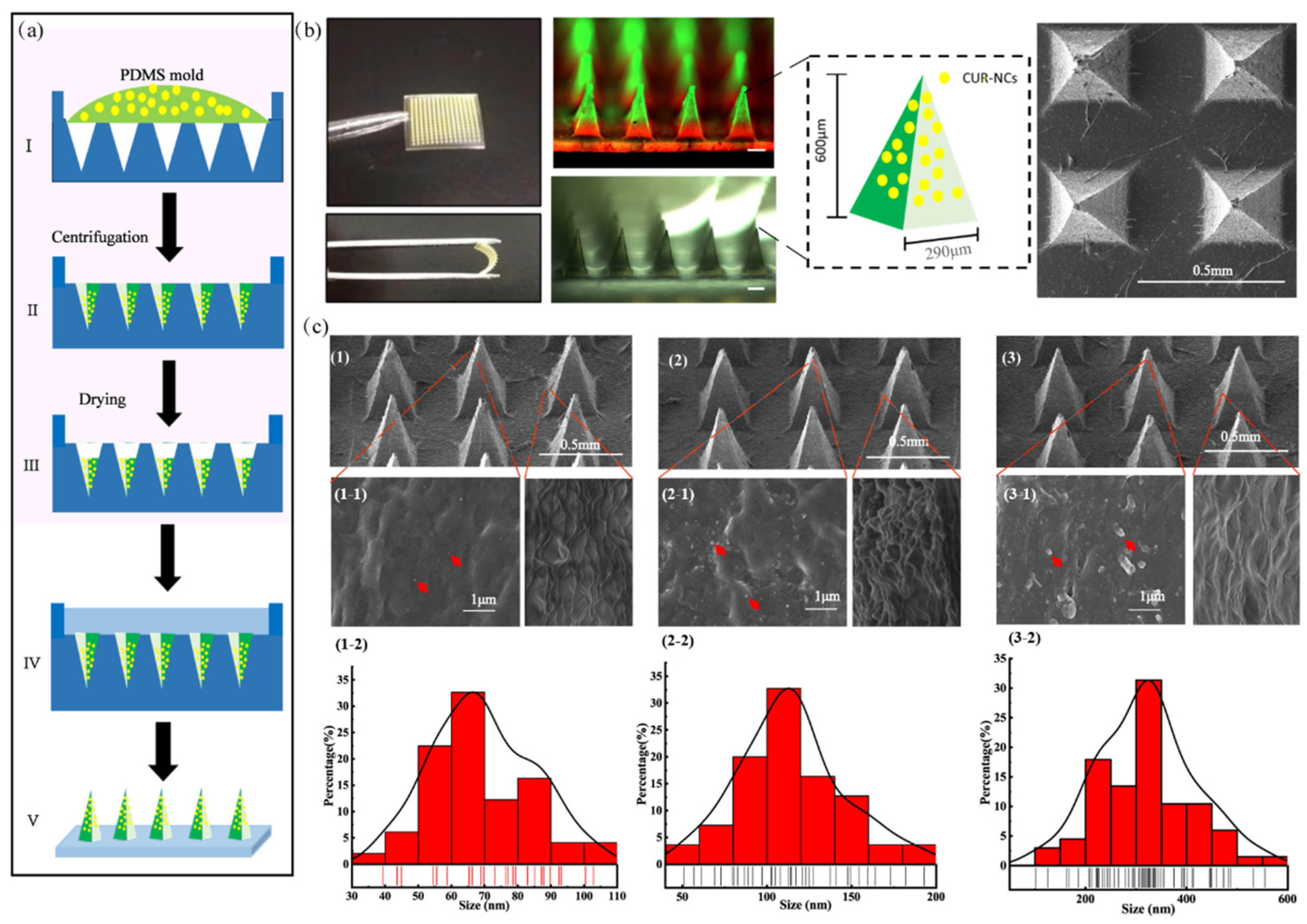
2.1. Characterization of CUR-NCs
2.2. Morphology and Structure of the MNs
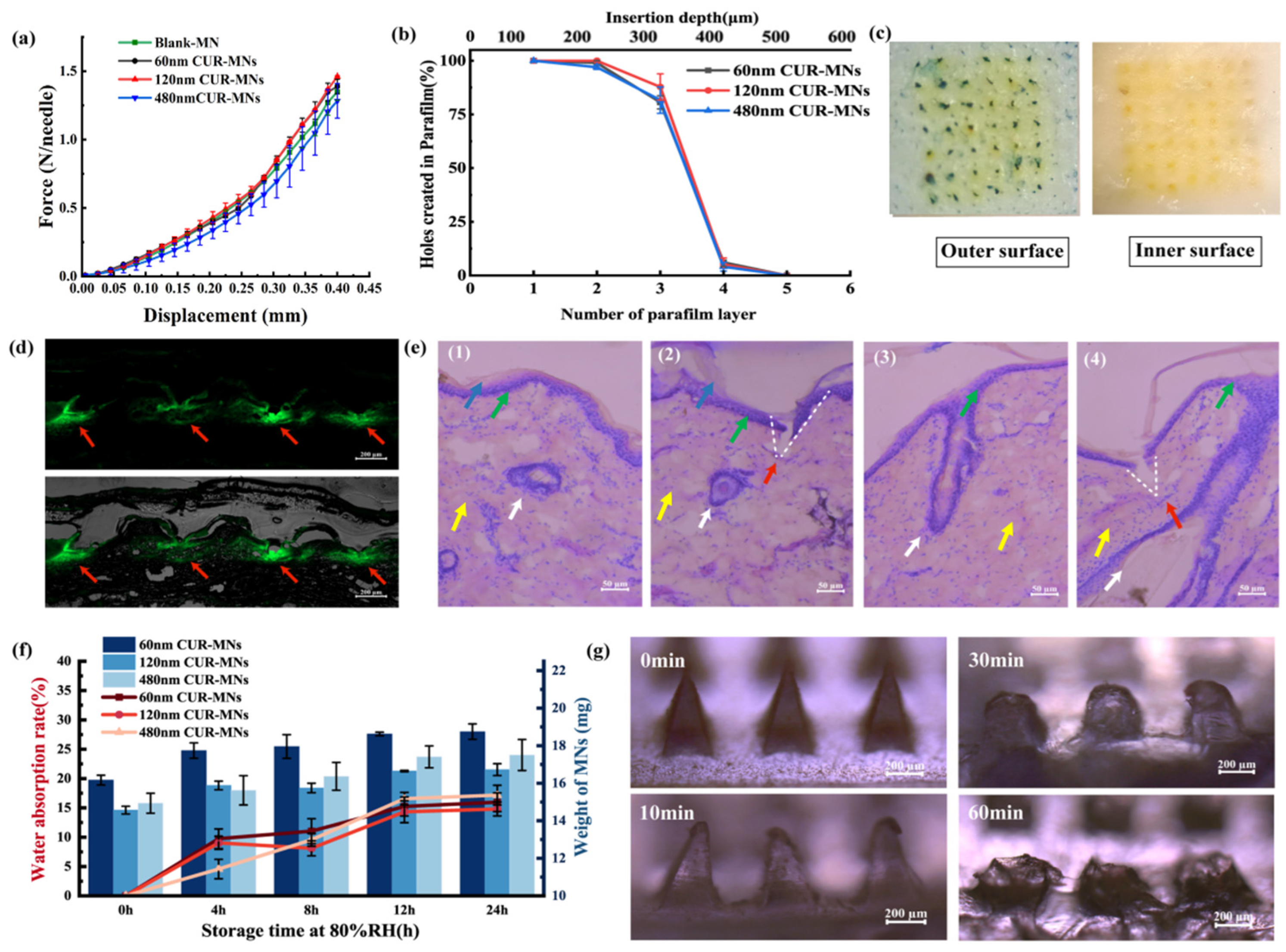
2.3. Mechanical and Insertion Properties of CUR-MNs
2.4. Hygroscopicity and Solubility of MNs
2.5. Ex-Vivo Transdermal Permeation
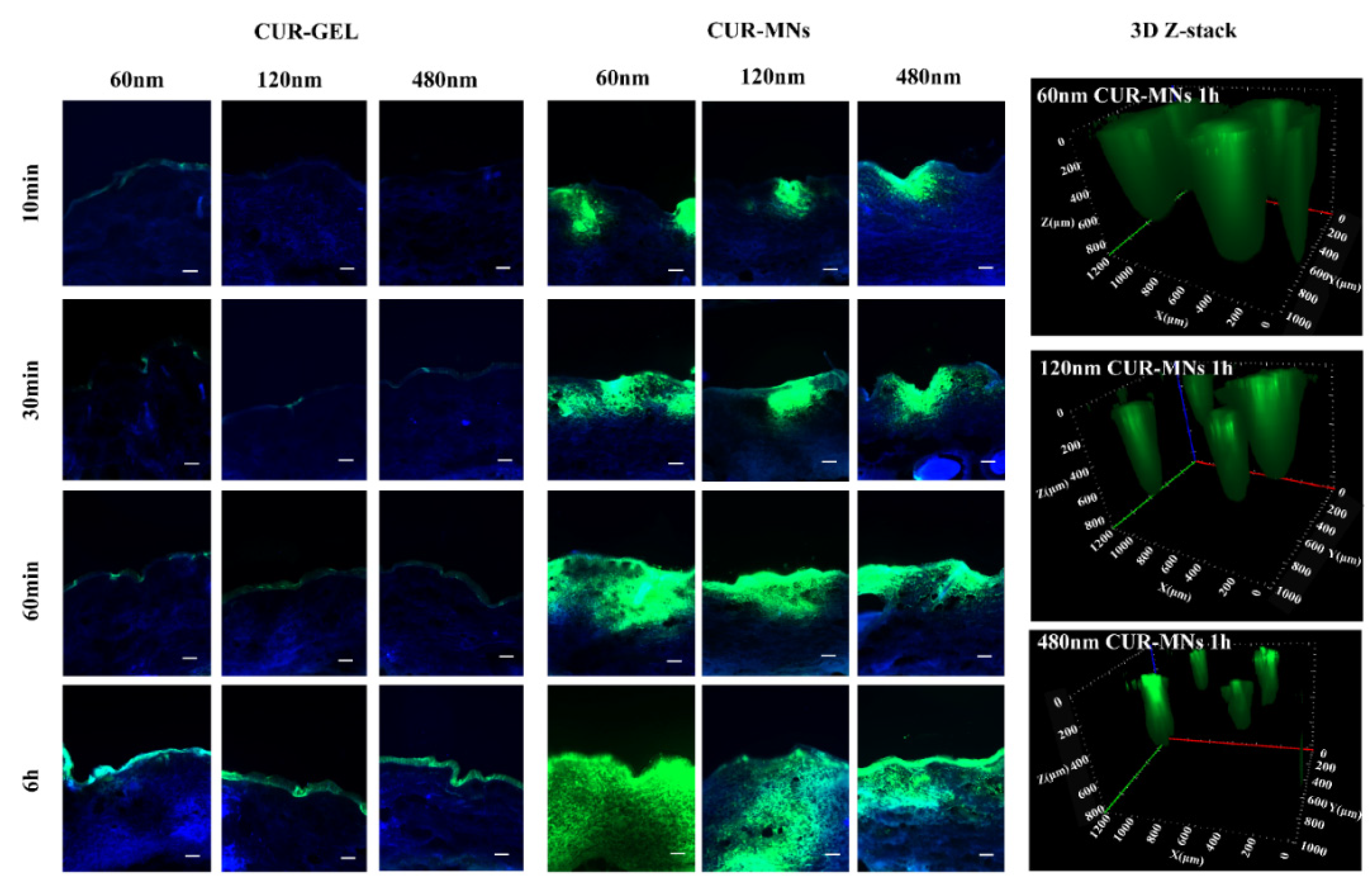
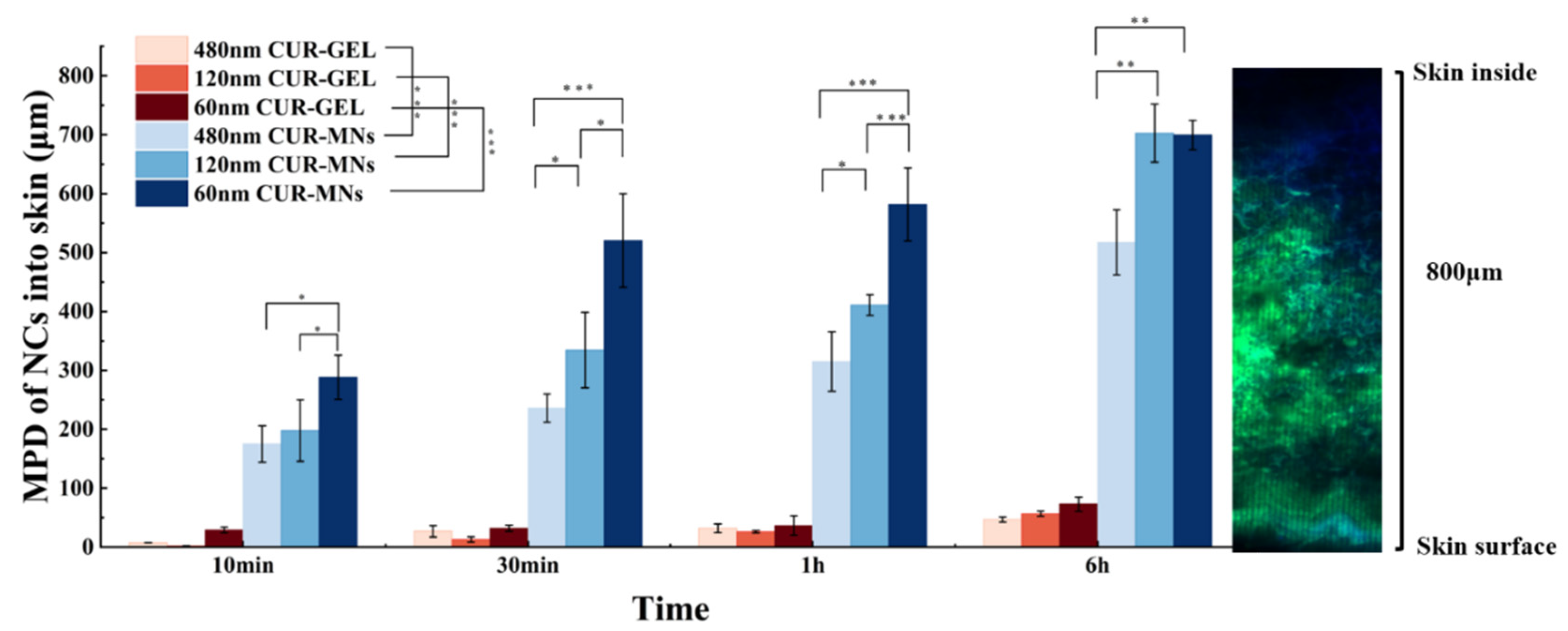
2.6. Dermal Penetration of CUR-MNs
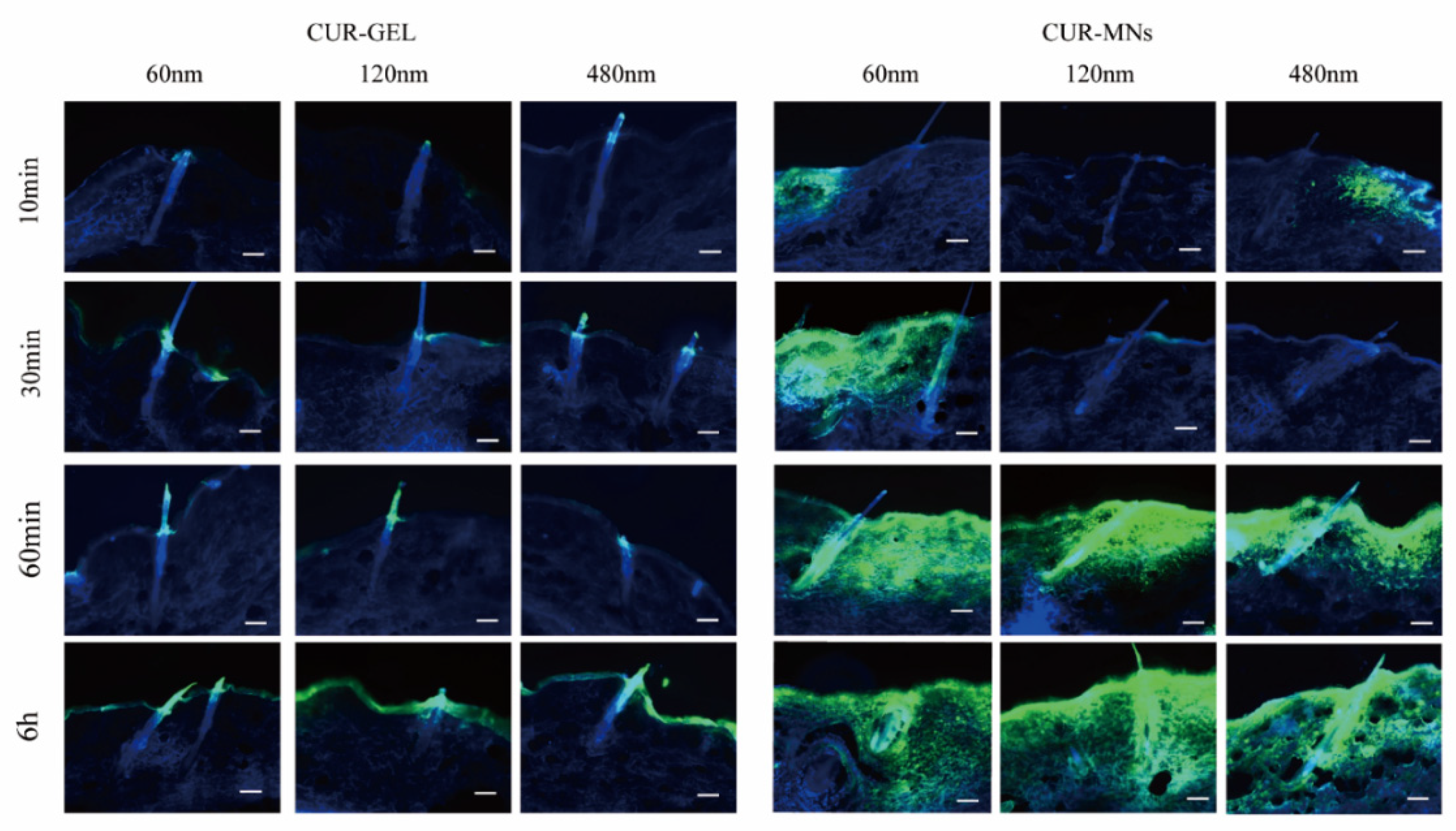
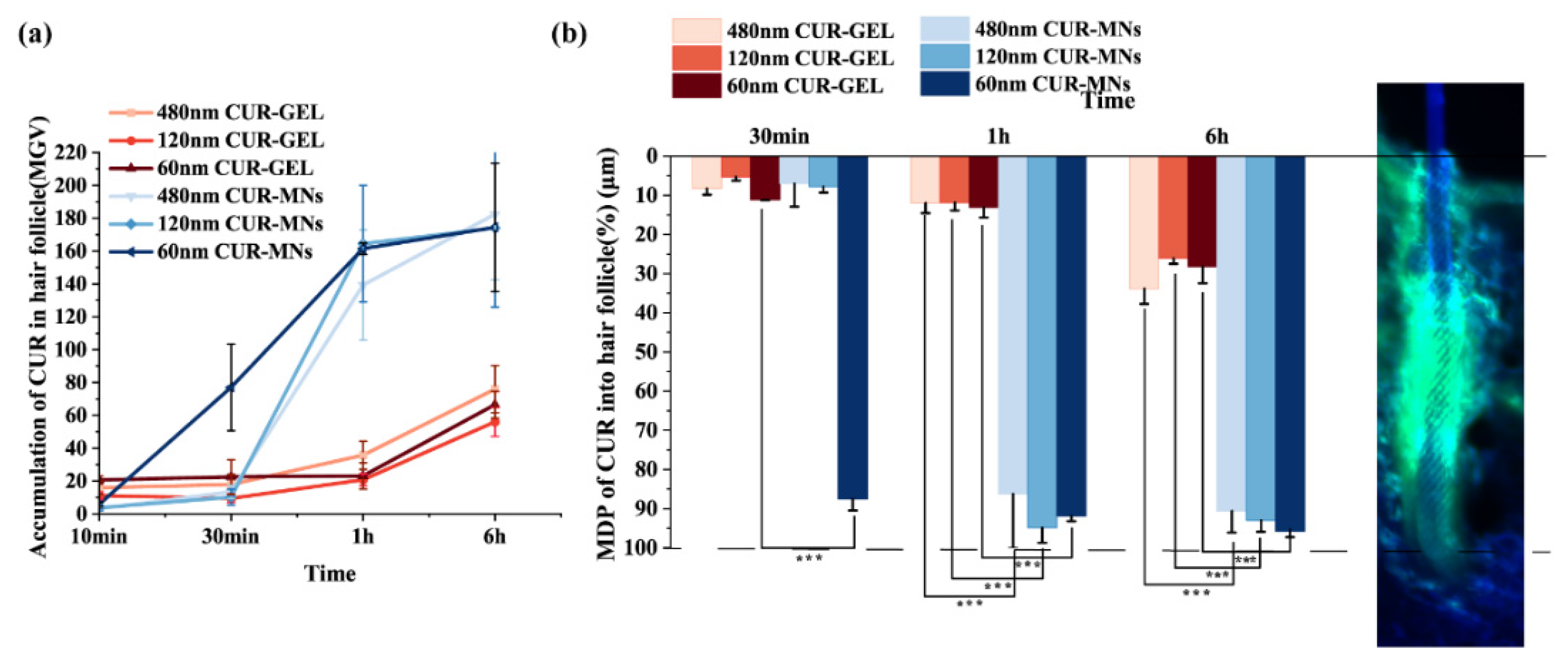
2.7. Hair-Follicle Accumulation of CUR-MNs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Fabrication of Three-Particle-Size CUR-NCs
3.3. Characterization of CUR-NCs
3.4. Fabrication of CUR-MNs
3.5. Morphology and Structure of CUR-MNs
3.6. Mechanical Properties Assessment of CUR-MNs
3.7. Insertion Properties of CUR-MNs and H&E Staining
3.8. Detection of Drug Loading in MNs
3.9. Hygroscopy of MNs
3.10. ExVivo Transdermal Permeation
3.11. Ex Vivo Model for Passive Dermal and Transfollicular Penetration
3.12. Digital Image Analysis
3.13. HPLC Analysis
3.14. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dragicevic, N.; Maibach, H. Combined use of nanocarriers and physical methods for percutaneous penetration enhancement. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 127, 58–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Singh, V.; Yusuf, M.; Khan, R.A. Non-invasive drug delivery technology: Development and current status of transdermal drug delivery devices, techniques and biomedical applications. Biomed. Tech. 2020, 65, 243–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rai, V.K.; Mishra, N.; Yadav, K.S.; Yadav, N.P. Nanoemulsion as pharmaceutical carrier for dermal and transdermal drug delivery: Formulation development, stability issues, basic considerations and applications. J. Control. Release 2018, 270, 203–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcês, A.; Amaral, M.H.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Formulations based on solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for cutaneous use: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 112, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Tsai, P.C.; Ramezanli, T.; Michniak-Kohn, B.B. Polymeric nanoparticles-based topical delivery systems for the treatment of dermatological diseases. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 5, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, I.S.; Elnahas, O.S.; Assar, N.H.; Gad, A.M.; El Hosary, R. Nanocrystals of Fusidic Acid for Dual Enhancement of Dermal Delivery and Antibacterial Activity: In Vitro, Ex Vivo and In Vivo Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pelikh, O.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Keck, C.M. Dermal Penetration Analysis of Curcumin in an ex vivo Porcine Ear Model Using Epifluorescence Microscopy and Digital Image Processing. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2021, 34, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuckmann, P.; Meinke, M.C.; Jaenicke, T.; Krutmann, J.; Rasulev, U.; Keck, C.M.; Müller, R.H.; Klein, A.L.; Lademann, J.; Patzelt, A. Influence of nanocrystal size on the in vivo absorption kinetics of caffeine after topical application. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 167, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelikh, O.; Eckert, R.W.; Pinnapireddy, S.R.; Keck, C.M. Hair follicle targeting with curcumin nanocrystals: Influence of the formulation properties on the penetration efficacy. J. Control. Release 2021, 329, 598–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelikh, O.; Keck, C.M. Hair Follicle Targeting and Dermal Drug Delivery with Curcumin Drug Nanocrystals-Essential Influence of Excipients. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Lv, Y.; Huang, W.; Fang, Z.; Qi, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, W.; Wu, W.; Lu, Y. Enhanced transdermal delivery of curcumin nanosuspensions: A mechanistic study based on co-localization of particle and drug signals. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 588, 119737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Quan, G.; Sun, Y.; Yang, D.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Nanoparticles-encapsulated polymeric microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, L.K.; Vavia, P.R.; Larrañeta, E.; Bell, S.E.J.; Donnelly, R.F. Novel nanosuspension-based dissolving microneedle arrays for transdermal delivery of a hydrophobic drug. J. Interdiscip. Nanomed. 2018, 3, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, Y.A.; Garland, M.J.; McInnes, F.J.; Donnelly, R.F.; El-Khordagui, L.K.; Wilson, C.G. Microneedle/nanoencapsulation-mediated transdermal delivery: Mechanistic insights. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 86, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prausnitz, M.R. Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, P.K.; Wadhawan, J.; Bansal, A.K. Pharmaceutical nanocrystals: A promising approach for improved topical drug delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2021, 26, 2329–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Zhai, X.; Romero, G.B.; Keck, C.M. Nanocrystals for Passive Dermal Penetration Enhancement. In Percutaneous Penetration Enhancers Chemical Methods in Penetration Enhancement; Nanocarriers, D.N., Maibach, H.I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 283–295. [Google Scholar]
- Pawar, V.K.; Singh, Y.; Meher, J.G.; Gupta, S.; Chourasia, M.K. Engineered nanocrystal technology: In-vivo fate, targeting and applications in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2014, 183, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Patel, S.K.; Parniak, M.A.; Ballou, B.; Rohan, L.C. Nanocrystal Formulation Improves Vaginal Delivery of CSIC for HIV Prevention. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelt, A.; Knorr, F.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Hair follicles, their disorders and their opportunities. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2008, 5, e173–e181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patzelt, A.; Richter, H.; Knorr, F.; Schäfer, U.; Lehr, C.-M.; Dähne, L.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J. Selective follicular targeting by modification of the particle sizes. J. Control. Release 2011, 150, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Yang, X.; Tang, Y.; Pang, M.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.; Wu, C.; Xu, Y. Microneedles mediated bioinspired lipid nanocarriers for targeted treatment of alopecia. J. Control. Release 2021, 329, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, C.; Miao, X.Q.; Chow, S.F.; Wu, W.J.; Yan, R.; Liao, Y.H.; Chow, A.H.-L.; Zheng, Y. Particle size effect of curcumin nanosuspensions on cytotoxicity, cellular internalization, in vivo pharmacokinetics and biodistribution. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2017, 13, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Han, N.; Zhao, B.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S. Enhanced dissolution rate and oral bioavailability of simvastatin nanocrystal prepared by sonoprecipitation. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2012, 38, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Terry, R.N.; Tang, J.; Feng, M.R.; Schwendeman, S.P.; Prausnitz, M.R. Rapidly separable microneedle patch for the sustained release of a contraceptive. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 3, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Luo, Z.; Baidya, A.; Kim, H.-J.; Wang, C.; Jiang, X.; Qu, M.; Zhu, J.; Ren, L.; Vajhadin, F.; et al. Biodegradable β-Cyclodextrin Conjugated Gelatin Methacryloyl Microneedle for Delivery of Water-Insoluble Drug. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2020, 9, e2000527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrañeta, E.; Moore, J.; Vicente-Pérez, E.M.; González-Vázquez, P.; Lutton, R.; Woolfson, A.D.; Donnelly, R.F. A proposed model membrane and test method for microneedle insertion studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 472, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, H.; Xu, S.; Li, J.; Pan, S.; Miao, X. Particle Size Effect of Curcumin Nanocrystals on Transdermal and Transfollicular Penetration by Hyaluronic Acid-Dissolving Microneedle Delivery. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020206
Xiang H, Xu S, Li J, Pan S, Miao X. Particle Size Effect of Curcumin Nanocrystals on Transdermal and Transfollicular Penetration by Hyaluronic Acid-Dissolving Microneedle Delivery. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(2):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020206
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Hong, Sai Xu, Jingyuan Li, Shihui Pan, and Xiaoqing Miao. 2022. "Particle Size Effect of Curcumin Nanocrystals on Transdermal and Transfollicular Penetration by Hyaluronic Acid-Dissolving Microneedle Delivery" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 2: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020206
APA StyleXiang, H., Xu, S., Li, J., Pan, S., & Miao, X. (2022). Particle Size Effect of Curcumin Nanocrystals on Transdermal and Transfollicular Penetration by Hyaluronic Acid-Dissolving Microneedle Delivery. Pharmaceuticals, 15(2), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020206






