The p97 Inhibitor UPCDC-30245 Blocks Endo-Lysosomal Degradation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
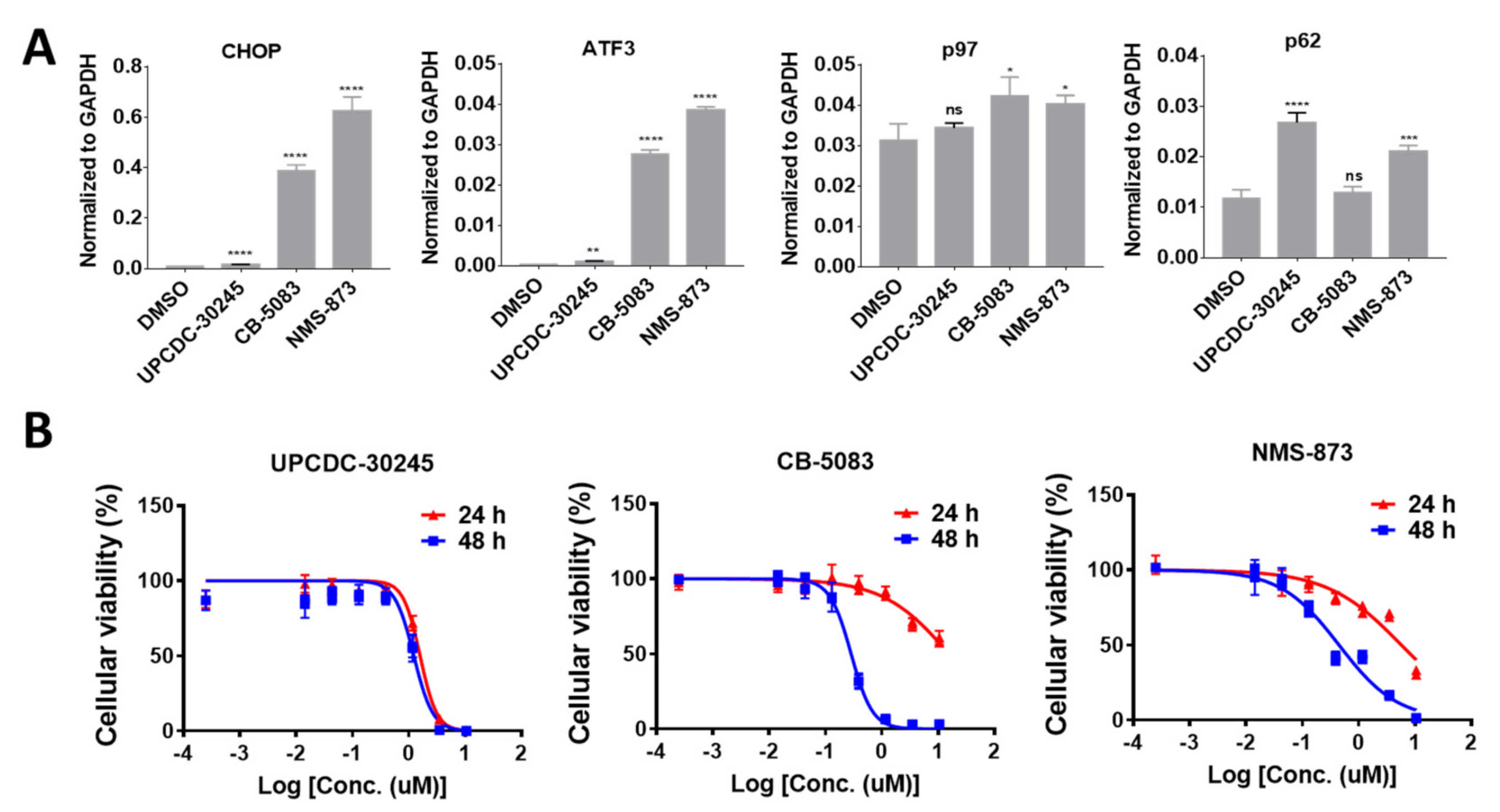
2.1. UPCDC-30245 Displays Unique Cellular Effects Compared to Two Other p97 Inhibitors
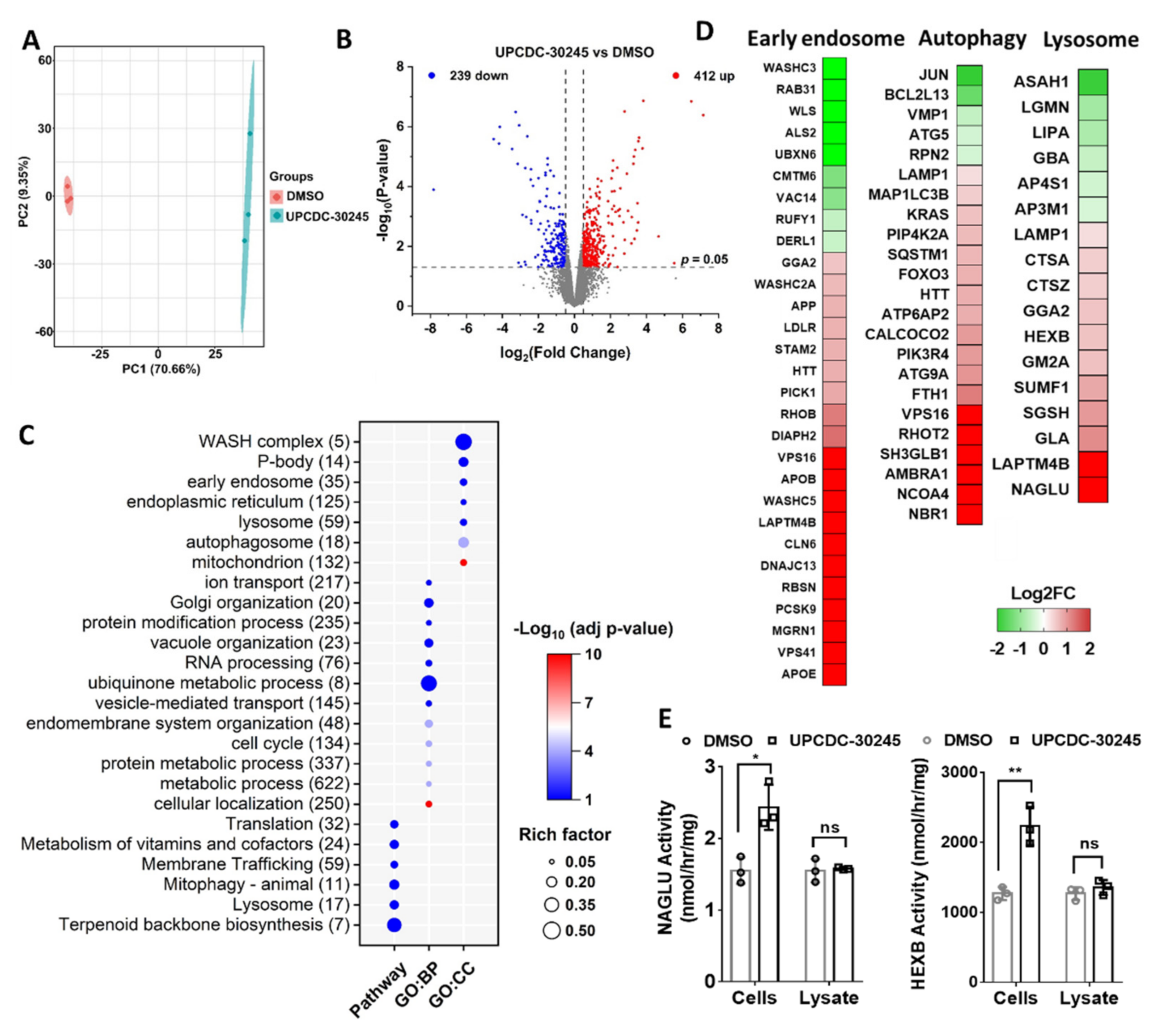
2.2. Proteomics Reveals Impairment of Endo-Lysosomal Pathways in Cells Treated with UPCDC-30245
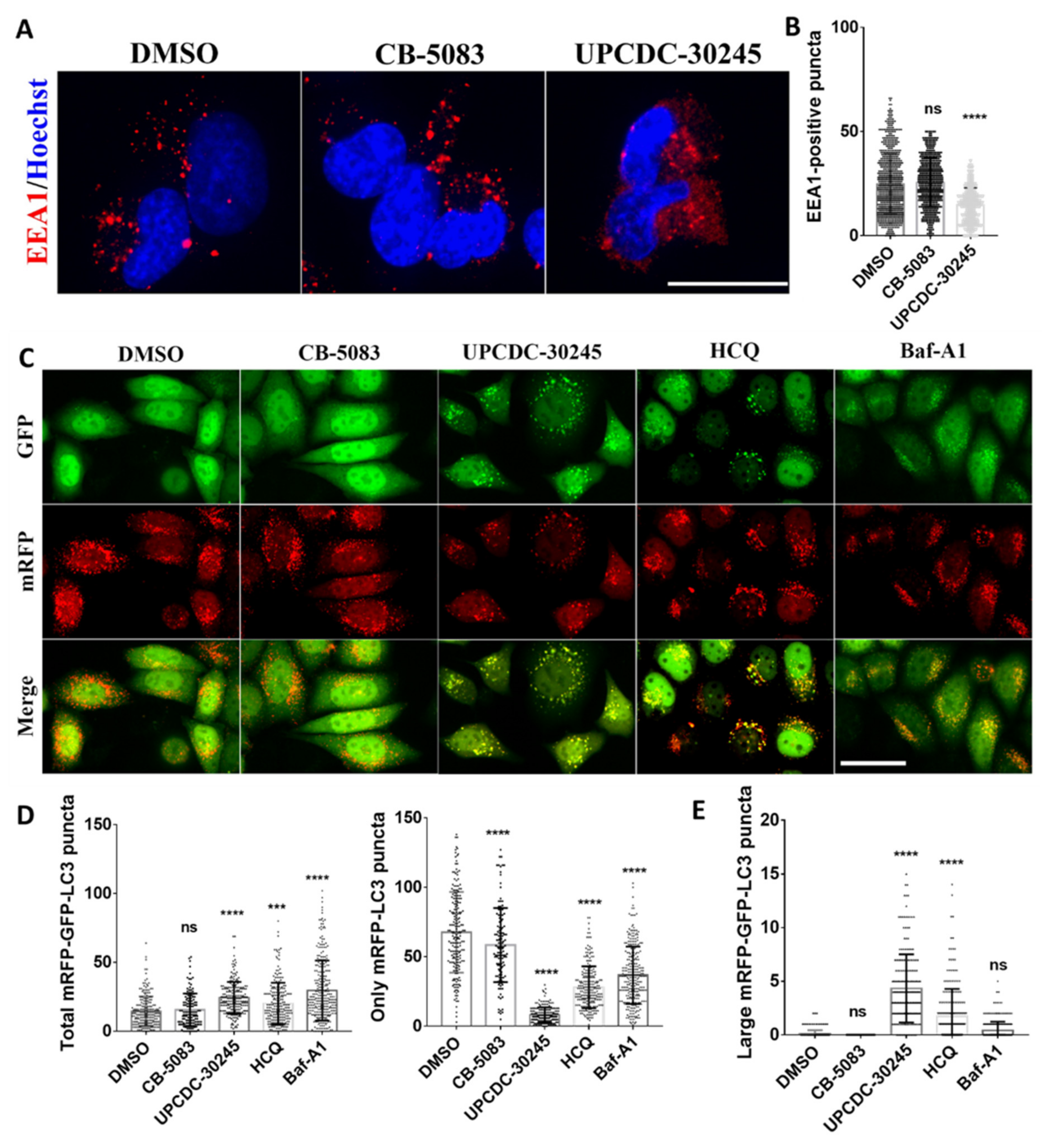
2.3. UPCDC-30245 Inhibits the Formation of Early Endosome and Autophagy Flux
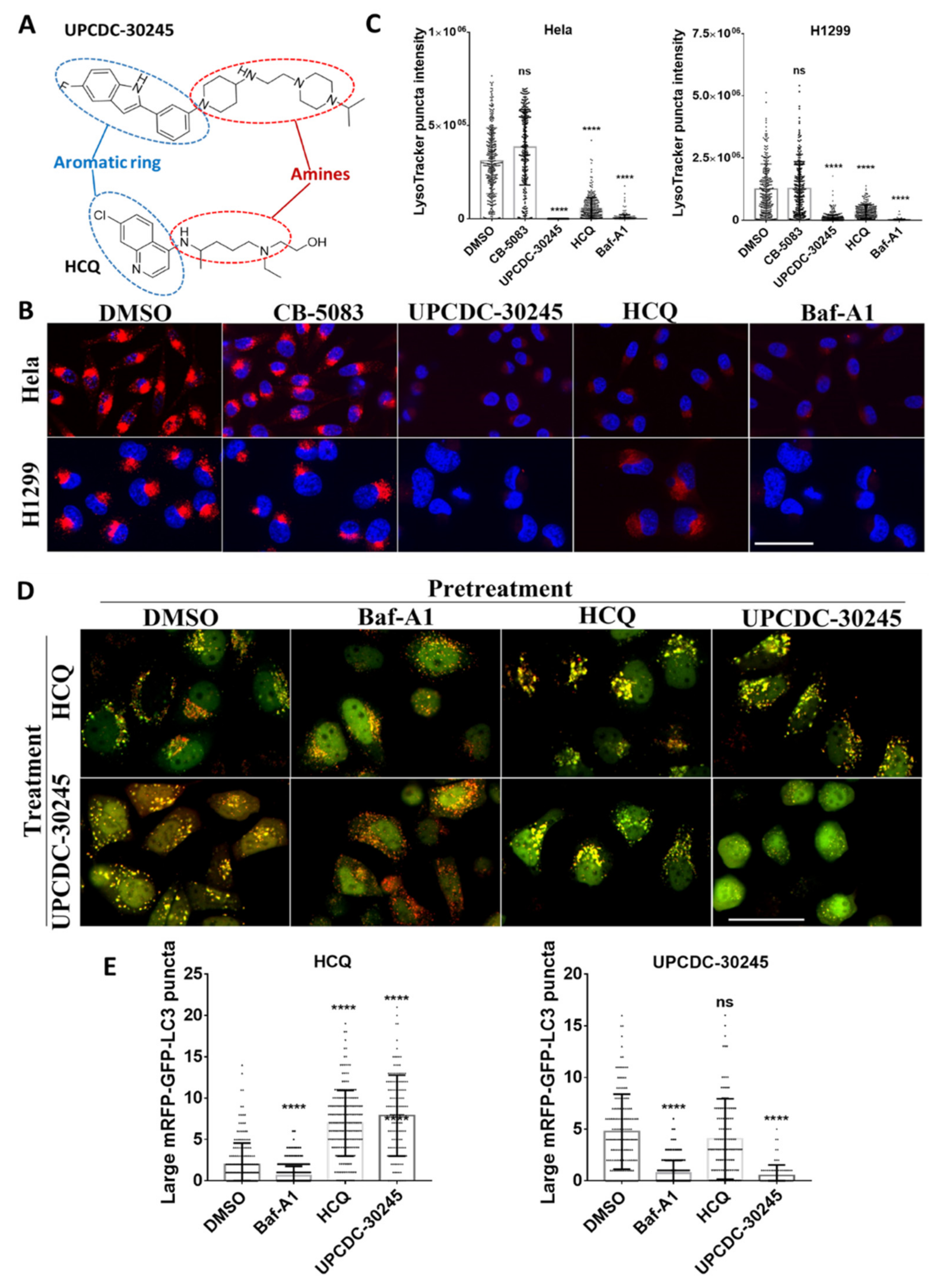
2.4. UPCDC-30245 Directly Disturbs the Acidic Environment of Lysosomes
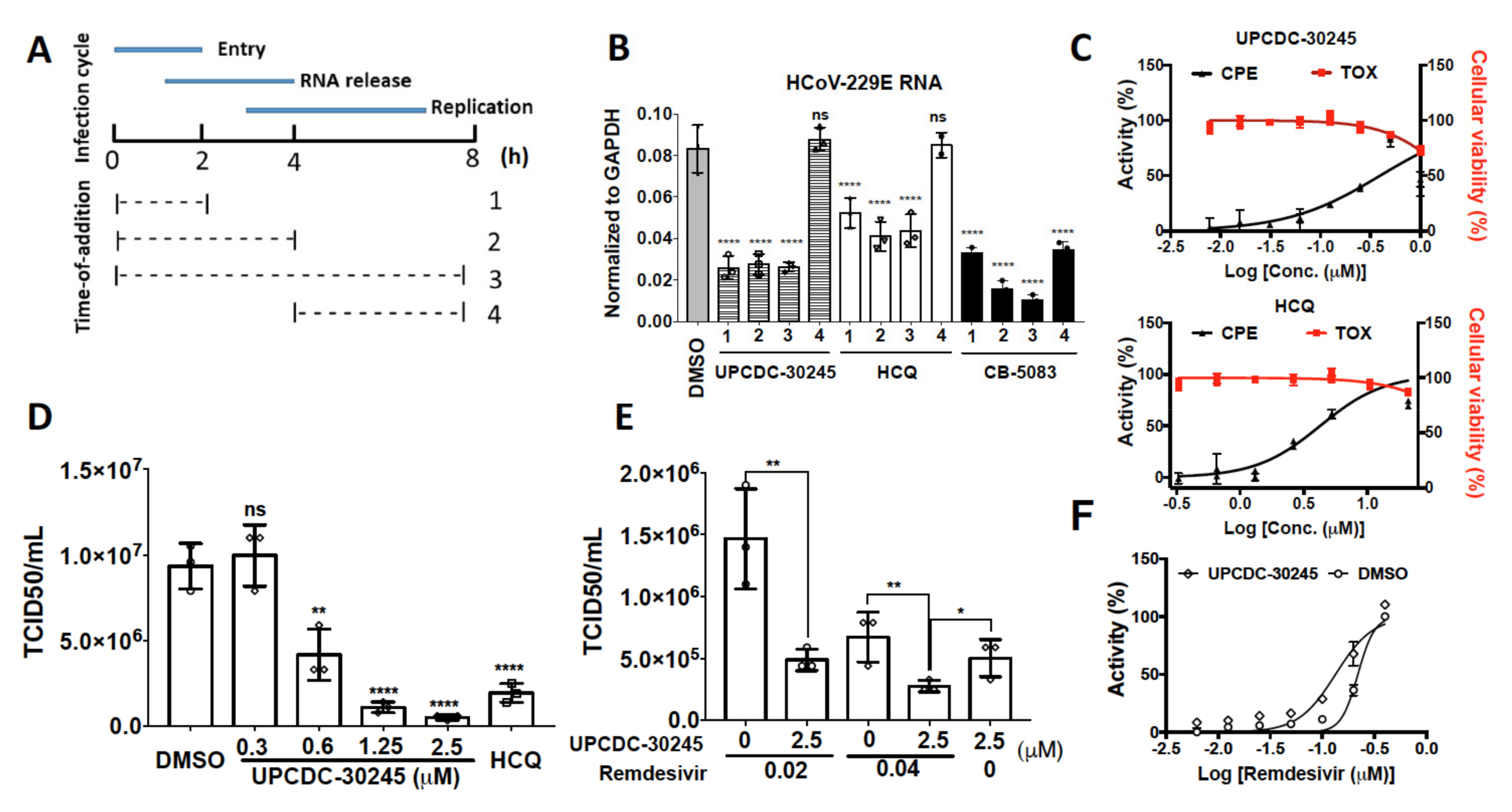
2.5. UPCDC-30245 Inhibits Coronavirus Infection at Viral Entry Stage
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. RNA Extraction and qPCR Analysis
4.3. Anti-Proliferative Activity
4.4. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.5. Enzymatic Activity Assays for NAGLU and HEXB
4.6. Tandem mRFP-GFP-LC3 Fluorescence Assay
4.7. Measuring the Cytotoxicity and Anti-CPE Effects of Compounds
4.8. Time-of Addition-Assay
4.9. TCID50 Assay
4.10. Label-Free Proteomics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, D.J.; Le Moigne, R.; Djakovic, S.; Kumar, B.; Rice, J.; Wong, S.; Wang, J.; Yao, B.; Valle, E.; Kiss von Soly, S.; et al. Targeting the AAA ATPase p97 as an Approach to Treat Cancer through Disruption of Protein Homeostasis. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magnaghi, P.; D’Alessio, R.; Valsasina, B.; Avanzi, N.; Rizzi, S.; Asa, D.; Gasparri, F.; Cozzi, L.; Cucchi, U.; Orrenius, C.; et al. Covalent and allosteric inhibitors of the ATPase VCP/p97 induce cancer cell death. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, S.; Gan, T.; Stott, G.M.; Flint, A.; Chou, T.F. Allosteric p97 Inhibitors Can Overcome Resistance to ATP-Competitive p97 Inhibitors for Potential Anticancer Therapy. ChemMedChem 2020, 15, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, N.G.; Toth, J.I.; Ma, C.T.; Wei, Y.; Motamedchaboki, K.; Sergienko, E.; Petroski, M.D. p97 Composition Changes Caused by Allosteric Inhibition Are Suppressed by an On-Target Mechanism that Increases the Enzyme’s ATPase Activity. Cell. Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burnett, J.C.; Lim, C.; Peyser, B.D.; Samankumara, L.P.; Kovaliov, M.; Colombo, R.; Bulfer, S.L.; LaPorte, M.G.; Hermone, A.R.; McGrath, C.F.; et al. A threonine turnstile defines a dynamic amphiphilic binding motif in the AAA ATPase p97 allosteric binding site. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 4096–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanzelmann, P.; Schindelin, H. The Interplay of Cofactor Interactions and Post-translational Modifications in the Regulation of the AAA+ ATPase p97. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2017, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.J.; Gui, L.; Zhang, X.; Moen, D.R.; Li, K.; Frankowski, K.J.; Lin, H.J.; Schoenen, F.J.; Chou, T.F. Evaluating p97 inhibitor analogues for their domain selectivity and potency against the p97-p47 complex. ChemMedChem 2015, 10, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gui, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Frankowski, K.J.; Li, S.; Wong, D.E.; Moen, D.R.; Porubsky, P.R.; Lin, H.J.; Schoenen, F.J.; et al. Evaluating p97 Inhibitor Analogues for Potency against p97-p37 and p97-Npl4-Ufd1 Complexes. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantzi, M.; Latosinska, A.; Mischak, H. Proteomics in Drug Development: The Dawn of a New Era? Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2019, 13, e1800087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedl, T.J.; San Gil., R.; Cheng, F.; Rayner, S.L.; Davidson, J.M.; De Luca, A.; Villalva, M.D.; Ecroyd, H.; Walker, A.K.; Lee, A. Proteomics Approaches for Biomarker and Drug Target Discovery in ALS and FTD. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barschke, P.; Oeckl, P.; Steinacker, P.; Ludolph, A.; Otto, M. Proteomic studies in the discovery of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2017, 14, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zheng, N. Accelerating protein biomarker discovery and translation from proteomics research for clinical utility. Bioanalysis 2020, 12, 1469–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saei, A.A.; Beusch, C.M.; Chernobrovkin, A.; Sabatier, P.; Zhang, B.; Tokat, Ü.G.; Stergiou, E.; Gaetani, M.; Végvári, Á.; Zubarev, R.A. ProTargetMiner as a proteome signature library of anticancer molecules for functional discovery. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gaetani, M.; Sabatier, P.; Saei, A.A.; Beusch, C.M.; Yang, Z.; Lundström, S.L.; Zubarev, R.A. Proteome Integral Solubility Alteration: A High-Throughput Proteomics Assay for Target Deconvolution. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 4027–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.H.; Ferguson, I.D.; Thornton, A.M.; Bastola, P.; Lam, C.; Lin, Y.T.; Choudhry, P.; Mariano, M.C.; Marcoulis, M.D.; Teo, C.F.; et al. Proteasome inhibitor-induced modulation reveals the spliceosome as a specific therapeutic vulnerability in multiple myeloma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Li, S.; Houerbi, N.; Chou, T.F. Temporal proteomics reveal specific cell cycle oncoprotein downregulation by p97/VCP inhibition. Cell Chem. Biol. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, H.N.; Ye, Y. The p97 ATPase associates with EEA1 to regulate the size of early endosomes. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, D.; Vuk, M.; Kirchner, P.; Bug, M.; Schütz, S.; Hayer, A.; Bremer, S.; Lusk, C.; Baloh, R.H.; Lee, H.; et al. Endolysosomal sorting of ubiquitylated caveolin-1 is regulated by VCP and UBXD1 and impaired by VCP disease mutations. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papadopoulos, C.; Kirchner, P.; Bug, M.; Grum, D.; Koerver, L.; Schulze, N.; Poehler, R.; Dressler, A.; Fengler, S.; Arhzaouy, K.; et al. VCP/p97 cooperates with YOD1, UBXD1 and PLAA to drive clearance of ruptured lysosomes by autophagy. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; van Laar, T.; Huang, H.; Zhang, L. APP and APLP1 are degraded through autophagy in response to proteasome inhibition in neuronal cells. Protein Cell 2011, 2, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blasiole, D.A.; Oler, A.T.; Attie, A.D. Regulation of ApoB secretion by the low density lipoprotein receptor requires exit from the endoplasmic reticulum and interaction with ApoE or ApoB. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 11374–11381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kan, S.H.; Aoyagi-Scharber, M.; Le, S.Q.; Vincelette, J.; Ohmi, K.; Bullens, S.; Wendt, D.J.; Christianson, T.M.; Tiger, P.M.; Brown, J.R.; et al. Delivery of an enzyme-IGFII fusion protein to the mouse brain is therapeutic for mucopolysaccharidosis type IIIB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14870–14875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Moen, D.R.; Sauni, C.; Kan, S.H.; Li, S.; Le, S.Q.; Lomenick, B.; Zhang, X.; Ekins, S.; Singamsetty, S.; et al. Enzyme Replacement Therapy for Mucopolysaccharidosis IIID using Recombinant Human alpha-N-Acetylglucosamine-6-Sulfatase in Neonatal Mice. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, J.M.; de Hoop, M.; Zorzi, N.; Toh, B.H.; Dotti, C.G.; Parton, R.G. EEA1, a tethering protein of the early sorting endosome, shows a polarized distribution in hippocampal neurons, epithelial cells, and fibroblasts. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 2657–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, D.J.; Yun, W.S.; Park, J.E.; Choi, J.S.; Key, J.; Seo, Y.J. Endocytic trafficking of polymeric clustered superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in mesenchymal stem cells. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhong, W.; Zhou, J.; Sheng, F.; Fang, Z.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Y.; Deng, X.; Xia, B.; Lin, J. Monitoring autophagic flux by an improved tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3 (mTagRFP-mWasabi-LC3) reveals that high-dose rapamycin impairs autophagic flux in cancer cells. Autophagy 2012, 8, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solomon, V.R.; Lee, H. Chloroquine and its analogs: A new promise of an old drug for effective and safe cancer therapies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 625, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauthe, M.; Orhon, I.; Rocchi, C.; Zhou, X.; Luhr, M.; Hijlkema, K.J.; Coppes, R.P.; Engedal, N.; Mari, M.; Reggiori, F. Chloroquine inhibits autophagic flux by decreasing autophagosome-lysosome fusion. Autophagy 2018, 14, 1435–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, E.J.; Siebers, A.; Altendorf, K. Bafilomycins: A class of inhibitors of membrane ATPases from microorganisms, animal cells, and plant cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 7972–7976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, X.; Ye, F.; Zhang, M.; Cui, C.; Huang, B.; Niu, P.; Liu, X.; Zhao, L.; Dong, E.; Song, C.; et al. In Vitro Antiviral Activity and Projection of Optimized Dosing Design of Hydroxychloroquine for the Treatment of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Cao, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Xu, M.; Shi, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, W.; Xiao, G. Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Cao, R.; Xu, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Hu, H.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z.; Zhong, W.; Wang, M. Hydroxychloroquine, a less toxic derivative of chloroquine, is effective in inhibiting SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro. Cell Discov. 2020, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Hau, R.; Musharrafieh, R.; Ma, C.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J. Identification of NMS-873, an allosteric and specific p97 inhibitor, as a broad antiviral against both influenza A and B viruses. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 133, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasoksuz, M.; Kilic, S.; Sarac, F. Coronaviruses and SARS-COV-2. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.J.; Won, J.J.; Graham, R.L.; Dinnon, K.H., 3rd; Sims, A.C.; Feng, J.Y.; Cihlar, T.; Denison, M.R.; Baric, R.S.; Sheahan, T.P. Broad spectrum antiviral remdesivir inhibits human endemic and zoonotic deltacoronaviruses with a highly divergent RNA dependent RNA polymerase. Antiviral Res. 2019, 169, 104541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.W.; Li, S.; Wang, F.; Ruiz-Lopez, N.M.; Houerbi, N.; Chou, T.F. Impacts of p97 on Proteome Changes in Human Cells during Coronaviral Replication. Cells 2021, 10, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, W.C.; Rolain, J.M.; Lee, N.Y.; Chen, P.L.; Huang, C.T.; Lee, P.I.; Hsueh, P.R. Arguments in favour of remdesivir for treating SARS-CoV-2 infections. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 55, 105933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, B.; Vaganay, C.; Vargas, J.D.; Alexe, G.; Benaksas, C.; Pardieu, B.; Fenouille, N.; Ellegast, J.M.; Malolepsza, E.; Ling, F.; et al. Targeting acute myeloid leukemia dependency on VCP-mediated DNA repair through a selective second-generation small-molecule inhibitor. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabg1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, H.; Cheng, C.; Pitkänen, M.; Sander, C.L.; Zhang, J.; Saeid, S.; Turunen, T.; Shmara, A.; Weiss, L.; Ta, L.; et al. A p97/Valosin-Containing Protein Inhibitor Drug CB-5083 Has a Potent but Reversible Off-Target Effect on Phosphodiesterase-6. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2021, 378, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwer, M.F.; Hamilton, K.E.; Jonker, P.B.; Kuiper, S.R.; Louters, L.L.; Looyenga, B.D. NMS-873 functions as a dual inhibitor of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Biochimie 2021, 185, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, S.; Rosser, M.F.; Cyr, D.M.; Hanson, P.I. Distinct roles for the AAA ATPases NSF and p97 in the secretory pathway. Mol. Biol. Cell 2004, 15, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Orme, C.M.; Bogan, J.S. The ubiquitin regulatory X (UBX) domain-containing protein TUG regulates the p97 ATPase and resides at the endoplasmic reticulum-golgi intermediate compartment. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6679–6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Escobar-Henriques, M.; Anton, V. Mitochondrial Surveillance by Cdc48/p97: MAD vs. Membrane Fusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, K.; Totsukawa, G.; Puhka, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Jokitalo, E.; Dreveny, I.; Beuron, F.; Zhang, X.; Freemont, P.; Kondo, H. p37 is a p97 adaptor required for Golgi and ER biogenesis in interphase and at the end of mitosis. Dev. Cell 2006, 11, 803–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stach, L.; Freemont, P.S. The AAA+ ATPase p97, a cellular multitool. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 2953–2976. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.L.; Geng, C.; Luo, G.; Lou, H. The p97-UBXD8 complex destabilizes mRNA by promoting release of ubiquitinated HuR from mRNP. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 1046–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bug, M.; Meyer, H. Expanding into new markets—VCP/p97 in endocytosis and autophagy. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 179, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgos, L.E.; Isaac, E.L.; Brooks, D.A.; Ravenscroft, E.M.; Davey, R.; Hopwood, J.J.; Meikle, P.J. Lysosomal biogenesis in lysosomal storage disorders. Exp. Cell Res. 1997, 234, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedele, A.O.; Proud, C.G. Chloroquine and bafilomycin A mimic lysosomal storage disorders and impair mTORC1 signalling. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20200905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, H.H.; Kumar, P.; Tay, F.P.; Moreau, D.; Liu, D.X.; Bard, F. Genome-Wide Screen Reveals Valosin-Containing Protein Requirement for Coronavirus Exit from Endosomes. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 11116–11128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.T.; Prendergast, J.; Grey, F. The host ubiquitin-dependent segregase VCP/p97 is required for the onset of human cytomegalovirus replication. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bojkova, D.; Klann, K.; Koch, B.; Widera, M.; Krause, D.; Ciesek, S.; Cinatl, J.; Münch, C. Proteomics of SARS-CoV-2-infected host cells reveals therapy targets. Nature 2020, 583, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehrawat, S.; Khasa, R.; Deb, A.; Prajapat, S.K.; Mallick, S.; Basu, A.; Surjit, M.; Kalia, M.; Vrati, S. Valosin-containing protein/p97 plays critical roles in the Japanese encephalitis virus life cycle. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e02336-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautret, P.; Lagier, J.C.; Parola, P.; Hoang, V.T.; Meddeb, L.; Mailhe, M.; Doudier, B.; Courjon, J.; Giordanengo, V.; Vieira, V.E.; et al. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: Results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2020, 56, 105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyaerts, E.; Li, S.; Vijgen, L.; Rysman, E.; Verbeeck, J.; Van Ranst, M.; Maes, P. Antiviral activity of chloroquine against human coronavirus OC43 infection in newborn mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 3416–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorshkov, K.; Chen, C.Z.; Bostwick, R.; Rasmussen, L.; Tran, B.N.; Cheng, Y.S.; Xu, M.; Pradhan, M.; Henderson, M.; Zhu, W.; et al. The SARS-CoV-2 Cytopathic Effect Is Blocked by Lysosome Alkalizing Small Molecules. ACS Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, 1389–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biacchesi, S.; Skiadopoulos, M.H.; Yang, L.; Murphy, B.R.; Collins, P.L.; Buchholz, U.J. Rapid human metapneumovirus microneutralization assay based on green fluorescent protein expression. J. Virol. Methods 2005, 128, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, S.; Wang, F.; Jones, A.C.; Goldberg, A.F.G.; Lin, B.; Virgil, S.; Stoltz, B.M.; Deshaies, R.J.; Chou, T.F. A covalent p97/VCP ATPase inhibitor can overcome resistance to CB-5083 and NMS-873 in colorectal cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 213, 113148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Li, S.; Cheng, K.-W.; Rosencrans, W.M.; Chou, T.-F. The p97 Inhibitor UPCDC-30245 Blocks Endo-Lysosomal Degradation. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020204
Wang F, Li S, Cheng K-W, Rosencrans WM, Chou T-F. The p97 Inhibitor UPCDC-30245 Blocks Endo-Lysosomal Degradation. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(2):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020204
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Feng, Shan Li, Kai-Wen Cheng, William M. Rosencrans, and Tsui-Fen Chou. 2022. "The p97 Inhibitor UPCDC-30245 Blocks Endo-Lysosomal Degradation" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 2: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020204
APA StyleWang, F., Li, S., Cheng, K.-W., Rosencrans, W. M., & Chou, T.-F. (2022). The p97 Inhibitor UPCDC-30245 Blocks Endo-Lysosomal Degradation. Pharmaceuticals, 15(2), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020204





