Human Enterovirus B: Selective Inhibition by Quinoxaline Derivatives and Bioinformatic RNA-Motif Identification as New Targets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Evaluation of Antiviral Efficacies of Quinoxaline Compounds (6–9) against a Representative Panel of Enterovirus Replication
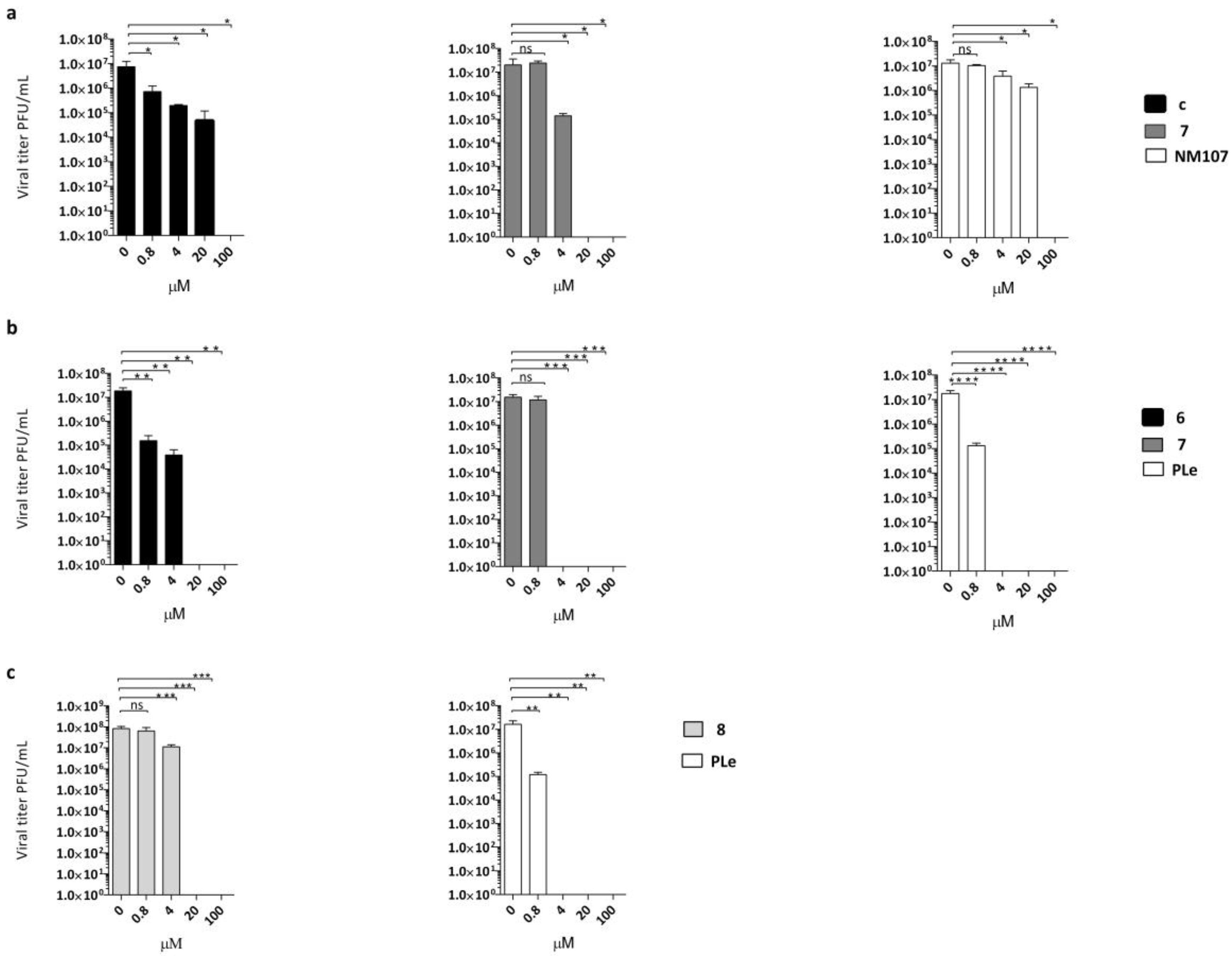
2.2. Effect of Quinoxalines on Viral Yield
2.3. Virucidal Activity Evaluation
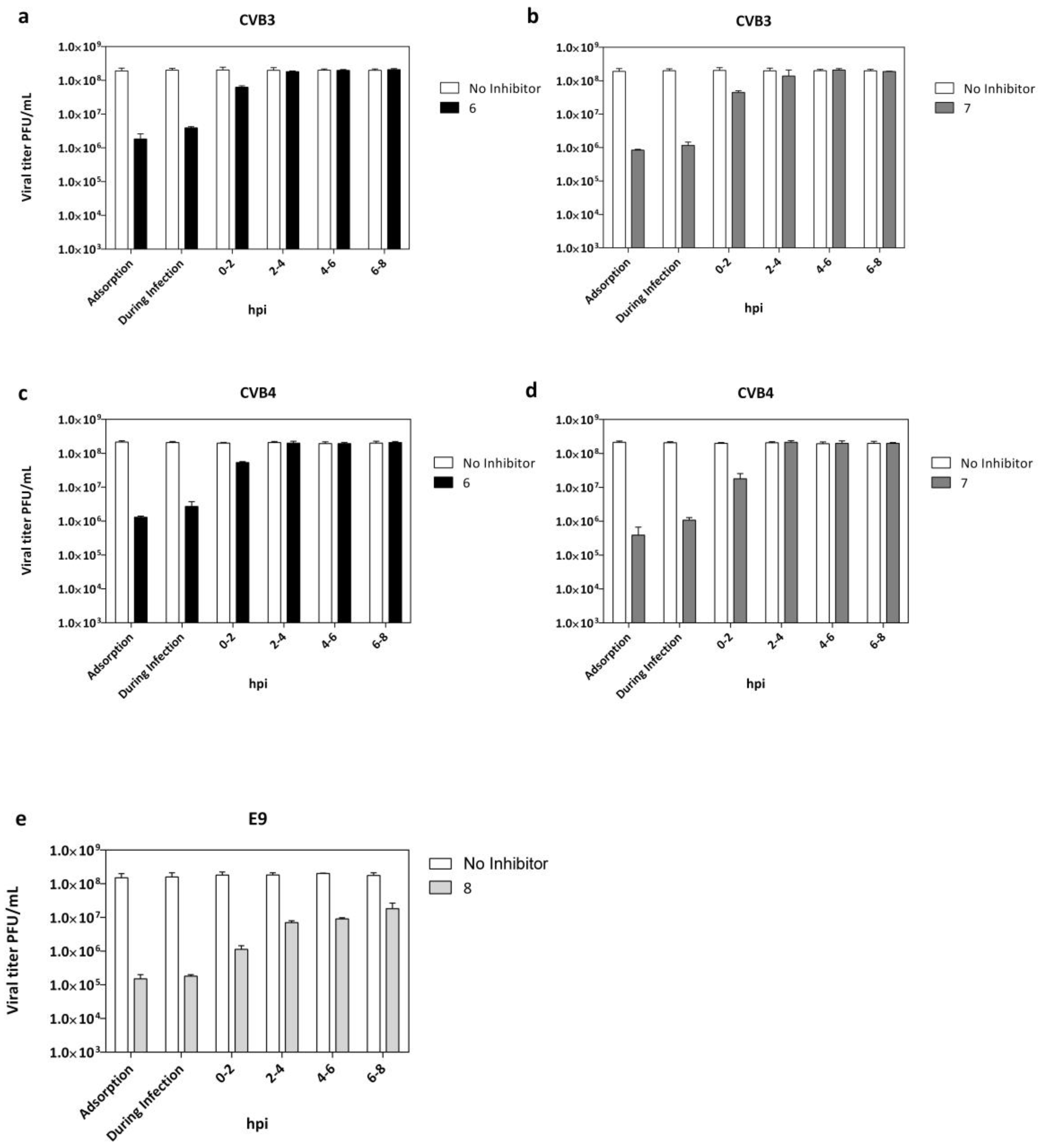
2.4. Adsorption Assay and Time Course Assay
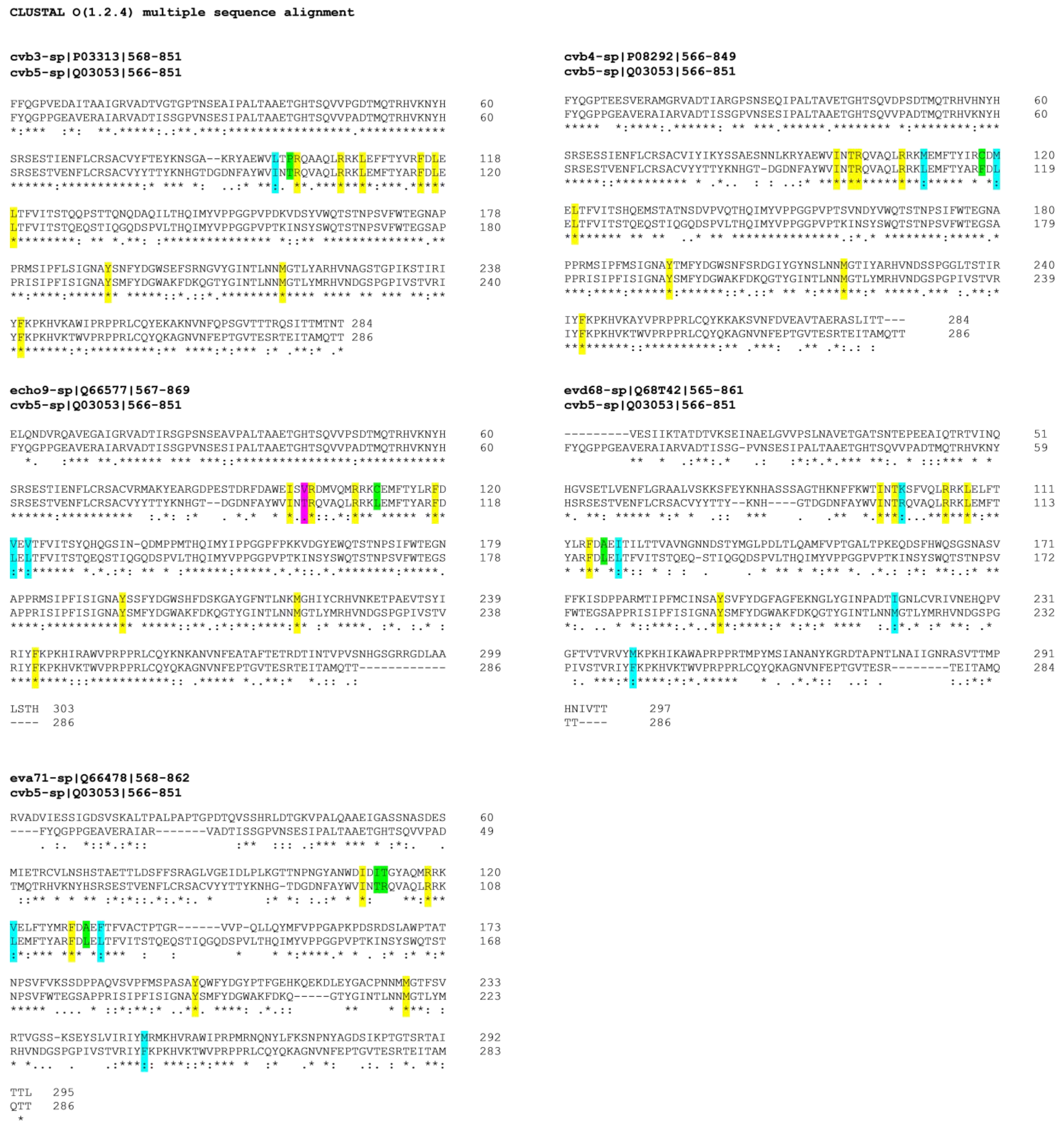
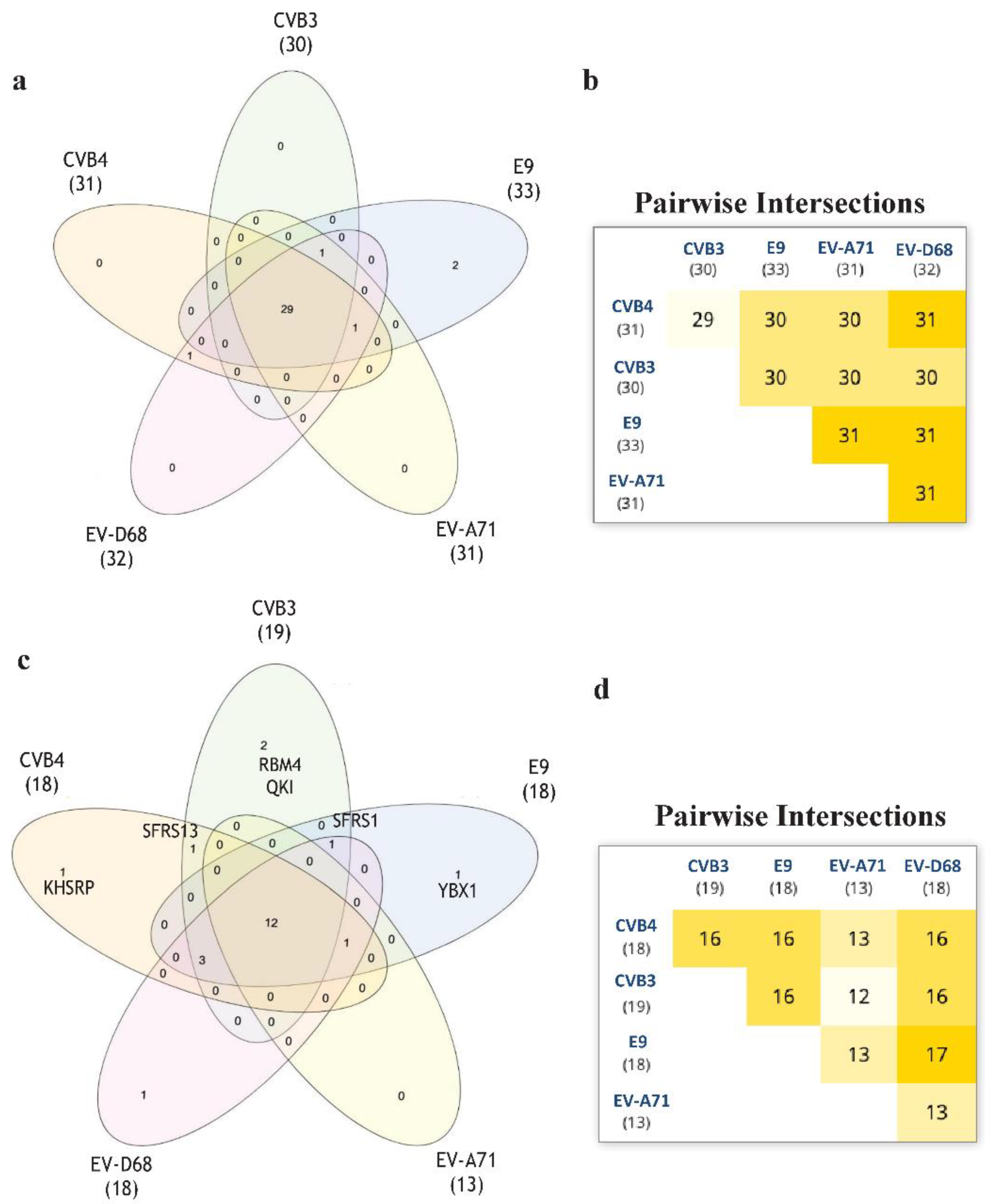
2.5. Alignment of VP1 Protein Sequences to Clarify Detected Activities amongTested EVs
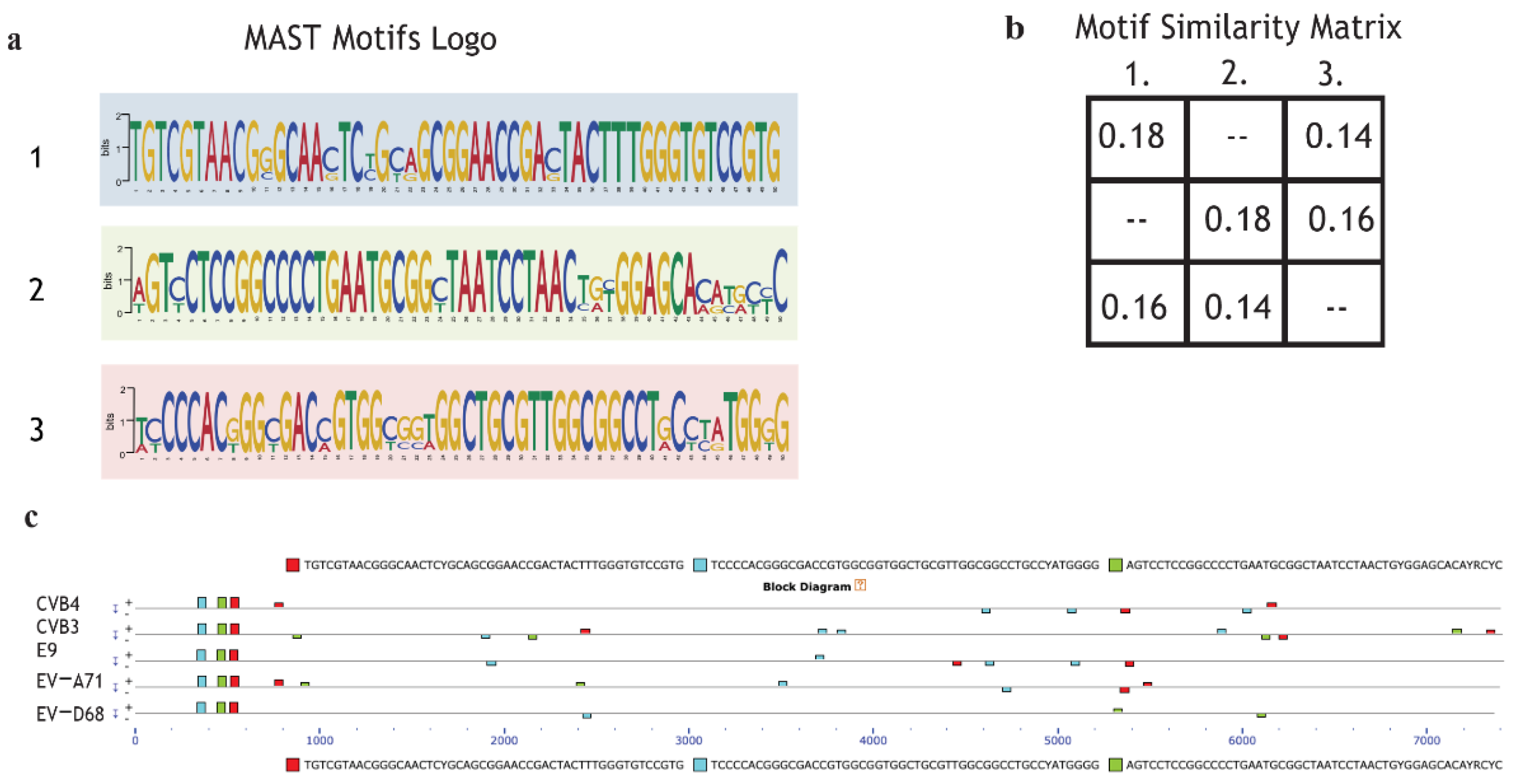
2.6. Motif Discoverinyvia MEME Suite Tools
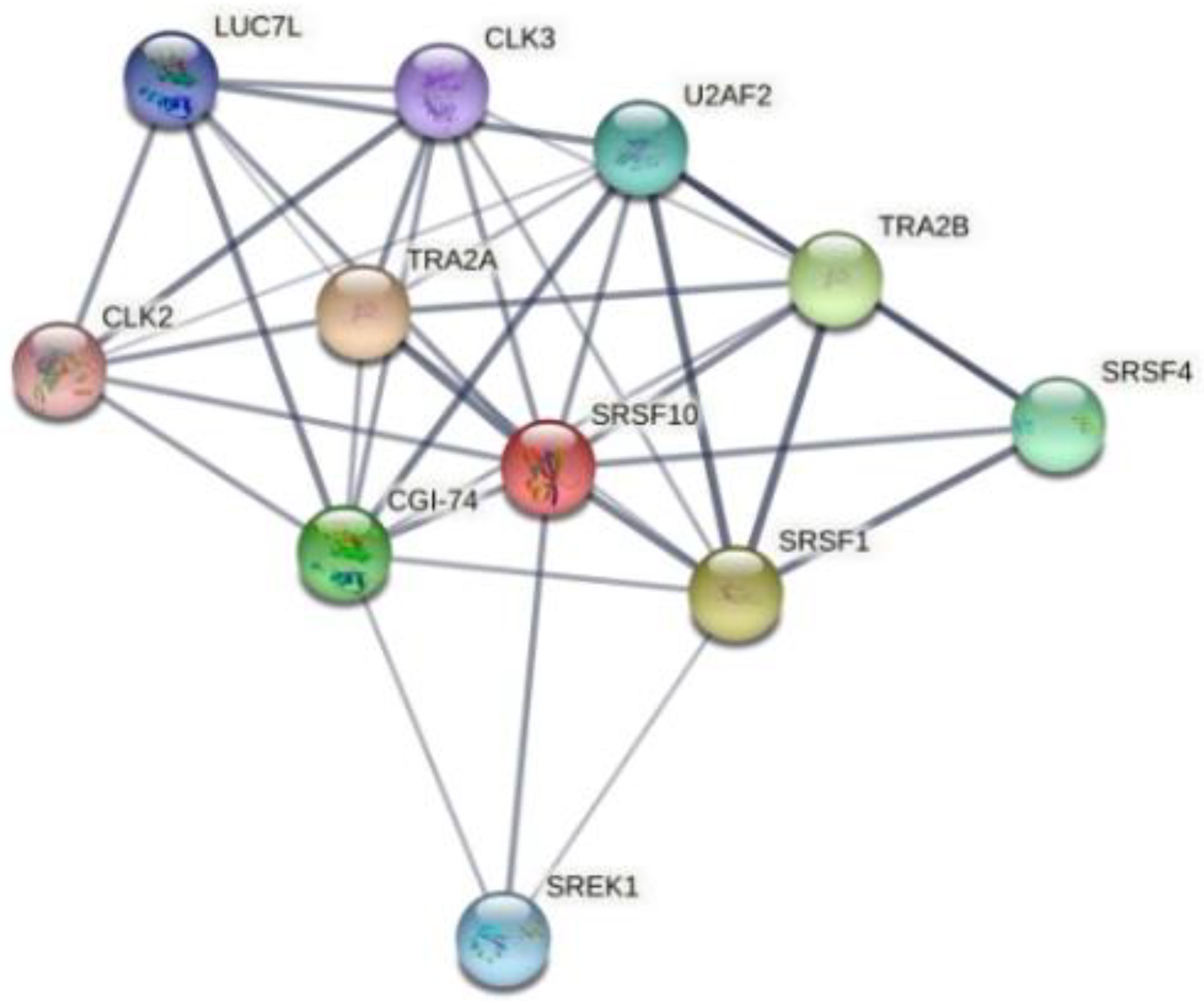
2.7. Enterovirus RNA Scanning via RNA-Binding Protein DataBase (RBPDB)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cells and Viruses
3.2. Cytotoxicity Assays
3.3. Antiviral Assays
3.4. Yield-Reduction Assay
3.5. Virucidal Activity Assay
3.6. Time Course Assay
3.7. Adsorption Assays
3.8. Statistical Analysis
3.9. Linear Regression Analysis
3.10. VP1 Protein Alignment
3.11. Novel Motif Discoveryvia MEME Suite Tools
3.12. Enterovirus RNA Scanning via RNA-Binding Protein DataBase
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simmonds, P.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Harvala, H.; Hovi, T.; Knowles, N.J.; Lindberg, A.M.; Oberste, M.S.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Reuter, G.; Skern, T.; et al. Recommendations for the Nomenclature of Enteroviruses and Rhinoviruses. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cherry, J.; Demmler-Harrison, G.; Kaplan, S.; Steinbach, W.; Hotez, P. Feigin and Cherry’s Textbook of Pediatric Infectious Disease, 8th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 1449–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Abzug, M.J. The Enteroviruses: Problems in Need of Treatments. J. Infect. 2014, 68 (Suppl.S1), S108–S114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, B.-K.; Ju, E.-S.; Lao, D.H.; Yun, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, D.-K.; Jeon, E.-S. Development of a Enterovirus Diagnostic Assay System for Diagnosis of Viral Myocarditis in Humans. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 57, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesvaderani, M.; Eslick, G.D.; Cox, M.R. Infectious Causes of Acute Pancreatitis. In Gastrointestinal Diseases and Their Associated Infections, 1st ed.; Eslick, G.D., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.-L.; Tang, R.-B. Why Zika Virus Infection Has Become a Public Health Concern? J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2016, 79, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chapman, N.M.; Kim, K.S. Persistent Coxsackievirus Infection: Enterovirus Persistence in Chronic Myocarditis and Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 323, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lugo, D.; Krogstad, P. Enteroviruses in the Early 21st Century: New Manifestations and Challenges. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2016, 28, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baggen, J.; Thibaut, H.J.; Strating, J.R.P.M.; van Kuppeveld, F.J.M. The Life Cycle of Non-Polio Enteroviruses and How to Target It. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, G.; Carr, M.J.; Kobayashi, M.; Hanaoka, N.; Fujimoto, T. Enterovirus-Associated Hand-Foot and Mouth Disease and Neurological Complications in Japan and the Rest of the World. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burrel, C.; Howard, C.; Murphy, F. Fenner and White’s Medical Virology, 5th ed.; Elsevier/Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 537–556. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, F.; Laessig, K. Safety and Efficacy Evaluation of Pleconaril for Treatment of the Common Cold. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2003, 37, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Palma, A.M.; Vliegen, I.; De Clercq, E.; Neyts, J. Selective Inhibitors of Picornavirus Replication. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28, 823–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, S.; Corona, P.; Ibba, R.; Riu, F.; Murineddu, G.; Sanna, G.; Madeddu, S.; Delogu, I.; Loddo, R.; Carta, A. Preliminary Anti-Coxsackie Activity of Novel 1-[4-(5,6-Dimethyl(H)-1H(2H)-Benzotriazol-1(2)-Yl)Phenyl]-3-Alkyl(Aryl)Ureas. Med. Chem. 2019, 16, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibba, R.; Corona, P.; Carta, A.; Giunchedi, P.; Loddo, R.; Sanna, G.; Delogu, I.; Piras, S. Antiviral Activities of 5-Chlorobenzotriazole Derivatives. Mon. Chem. 2018, 149, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, A.; Sanna, G.; Briguglio, I.; Madeddu, S.; Vitale, G.; Piras, S.; Corona, P.; Peana, A.T.; Laurini, E.; Fermeglia, M.; et al. Quinoxaline Derivatives as New Inhibitors of Coxsackievirus B5. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 145, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, K.L.; Heinz, B.A. RNA as a Target for Developing Antivirals. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2003, 14, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, K.B.; Kazan, H.; Zuberi, K.; Morris, Q.; Hughes, T.R. RBPDB: A Database of RNA-Binding Specificities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D301–D308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, C.; Manley, J.L. The SR Protein SRp38 Represses Splicing in M Phase Cells. Cell 2002, 111, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cowper, A.E.; Cáceres, J.F.; Mayeda, A.; Screaton, G.R. Serine-Arginine (SR) Protein-like Factors That Antagonize Authentic SR Proteins and Regulate Alternative Splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 48908–48914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahmud, B.; Horn, C.M.; Tapprich, W.E. Structure of the 5’ Untranslated Region of Enteroviral Genomic RNA. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01288-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chabrolles, H.; Auclair, H.; Vegna, S.; Lahlali, T.; Pons, C.; Michelet, M.; Couté, Y.; Belmudes, L.; Chadeuf, G.; Kim, Y.; et al. Hepatitis B Virus Core Protein Nuclear Interactome Identifies SRSF10 as a Host RNA-Binding Protein Restricting HBV RNA Production. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkreta, L.; Blanchette, M.; Toutant, J.; Wilhelm, E.; Bell, B.; Story, B.A.; Balachandran, A.; Cochrane, A.; Cheung, P.K.; Harrigan, P.R.; et al. Modulation of the Splicing Regulatory Function of SRSF10 by a Novel Compound That Impairs HIV-1 Replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 4051–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Platt, C.; Calimano, M.; Nemet, J.; Bubenik, J.; Cochrane, A. Differential Effects of Tra2ß Isoforms on HIV-1 RNA Processing and Expression. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, D.F.; Martin, M.A. Alternative Splicing of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 MRNA Modulates Viral Protein Expression, Replication, and Infectivity. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 6365–6378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, R.; Balachandran, A.; Mao, A.Y.; Dobson, W.; Gray-Owen, S.; Cochrane, A. Differential Effect of CLK SR Kinases on HIV-1 Gene Expression: Potential Novel Targets for Therapy. Retrovirology 2011, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pauwels, R.; Balzarini, J.; Baba, M.; Snoeck, R.; Schols, D.; Herdewijn, P.; Desmyter, J.; De Clercq, E. Rapid and Automated Tetrazolium-Based Colorimetric Assay for the Detection of Anti-HIV Compounds. J. Virol. Methods 1988, 20, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanna, G.; Madeddu, S.; Murgia, G.; Serreli, G.; Begala, M.; Caboni, P.; Incani, A.; Franci, G.; Galdiero, M.; Giliberti, G. Potent and Selective Activity against Human Immunodeficiency Virus 1 (HIV-1) of Thymelaea Hirsuta Extracts. Viruses 2020, 12, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibba, R.; Carta, A.; Madeddu, S.; Caria, P.; Serreli, G.; Piras, S.; Sestito, S.; Loddo, R.; Sanna, G. Inhibition of Enterovirus A71 by a Novel 2-Phenyl-Benzimidazole Derivative. Viruses 2021, 13, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D.; et al. The EMBL-EBI Search and Sequence Analysis Tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bailey, T.L.; Gribskov, M. Combining Evidence Using P-Values: Application to Sequence Homology Searches. Bioinformatics 1998, 14, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heberle, H.; Meirelles, G.V.; da Silva, F.R.; Telles, G.P.; Minghim, R. InteractiVenn: A Web-Based Tool for the Analysis of Sets through Venn Diagrams. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Morris, J.H.; Cook, H.; Kuhn, M.; Wyder, S.; Simonovic, M.; Santos, A.; Doncheva, N.T.; Roth, A.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING Database in 2017: Quality-Controlled Protein-Protein Association Networks, Made Broadly Accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D362–D368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cmp | Vero76 | CVB4 | CVB4 | CVB3 | CVB3 | EV-A71 | HeLa | EV-D68 | LLC-MK2 | E9 | E9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aCC50 | dEC50 | eEC90 | dEC50 | eEC90 | fEC50 | bCC50 | gEC50 | cCC50 | dEC50 | eEC90 | |
| 6 | >100 | 1.7 | 12 | 2.5 | 13 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | >100 | Nd |
| 7 | 100 | 1.45 | 3.2 | 2 | 14 | >100 | 95 | >95 | 100 | >100 | Nd |
| 8 | >100 | >100 | nd | >100 | nd | >100 | >100 | 50 | >100 | 6 | 16 |
| 9 | 100 | >100 | nd | 100 | nd | >100 | >100 | 70 | 100 | 55 | Nd |
| PLe | >100 | 2 ± 1 | - | - | - | - | >100 | 0.4 ± 0.2 | >100 | 0.1 ± 0.05 | - |
| NM107 | >100 | - | - | 29 ± 3 | - | 6 ± 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madeddu, S.; Ibba, R.; Sanna, G.; Piras, S.; Riu, F.; Marongiu, A.; Ambrosino, A.; Caria, P.; Onnis, V.; Franci, G.; et al. Human Enterovirus B: Selective Inhibition by Quinoxaline Derivatives and Bioinformatic RNA-Motif Identification as New Targets. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020181
Madeddu S, Ibba R, Sanna G, Piras S, Riu F, Marongiu A, Ambrosino A, Caria P, Onnis V, Franci G, et al. Human Enterovirus B: Selective Inhibition by Quinoxaline Derivatives and Bioinformatic RNA-Motif Identification as New Targets. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(2):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020181
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadeddu, Silvia, Roberta Ibba, Giuseppina Sanna, Sandra Piras, Federico Riu, Alessandra Marongiu, Annalisa Ambrosino, Paola Caria, Valentina Onnis, Gianluigi Franci, and et al. 2022. "Human Enterovirus B: Selective Inhibition by Quinoxaline Derivatives and Bioinformatic RNA-Motif Identification as New Targets" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 2: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020181
APA StyleMadeddu, S., Ibba, R., Sanna, G., Piras, S., Riu, F., Marongiu, A., Ambrosino, A., Caria, P., Onnis, V., Franci, G., Manzin, A., & Carta, A. (2022). Human Enterovirus B: Selective Inhibition by Quinoxaline Derivatives and Bioinformatic RNA-Motif Identification as New Targets. Pharmaceuticals, 15(2), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15020181








