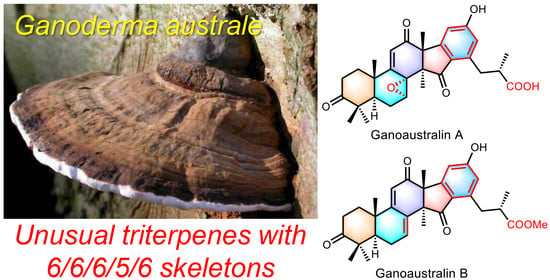
Ganoaustralins A and B, Unusual Aromatic Triterpenes from the Mushroom Ganoderma australe
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Structural Elucidation
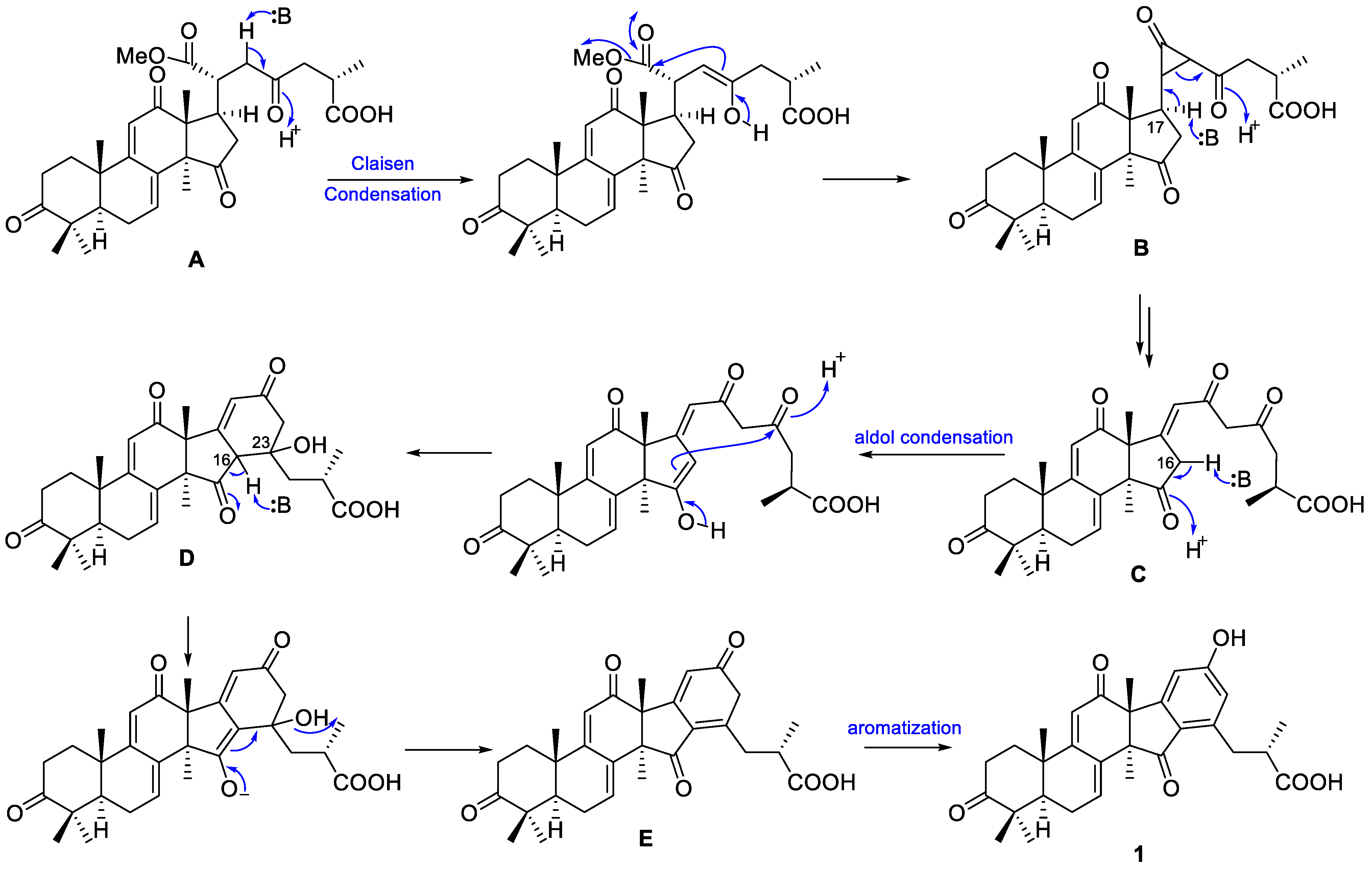
2.2. Proposed Biosynthetic Pathway of 1 and 2
2.3. Biological Activity Evaluation of 1 and 2
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Fungal Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation
4.4. Biological Activity Assays
4.5. Synthesis of the PGME Derivatives of 1
4.6. 13C NMR and ECD Calculation of 1 and 2
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, Y.; Wu, S.-H.; Dai, Y.-C. Species clarification of the prize medicinal Ganoderma mushroom “Lingzhi”. Fungal Divers. 2012, 56, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, C.; Wittstein, K.; Kirk, P.M.; Stadler, M. An assessment of the taxonomy and chemotaxonomy of Ganoderma. Fungal Divers. 2015, 71, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, S.; Johnson, A.J. Secondary metabolites from Ganoderma. Phytochemistry 2015, 114, 66–101. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.-Z.; Chen, H.-P.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.-H.; Zhang, L.; Feng, T.; Liu, J.-K. Lanostane triterpenoids from fruiting bodies of Ganoderma leucocontextum. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2016, 6, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, X.-C.; Liu, F.; Su, H.-G.; Peng, C.; Zhou, Q.-M.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.-J.; Guo, L.; Xiong, L. Twelve undescribed derivatives of ganoderic acid isolated from Ganoderma luteomarginatum and their cytotoxicity against three human cancer cell lines. Phytochemistry 2021, 183, 112617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Qiu, M. Meroterpenoids from Ganoderma species: A review of last five years. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2018, 8, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Su, H.; Wang, H.; Hu, G.; Hu, K.; Zhou, L.; Qiu, M. Applanmerotic acids A and B, two meroterpenoid dimers with an unprecedented polycyclic skeleton from Ganoderma applanatum that inhibit formyl peptide receptor 2. Org. Chem. Front. 2021, 8, 3381–3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, M.; Di, L.; Zhou, L.-L.; Yan, Y.-M.; Wang, X.-L.; Zhou, F.-J.; Yang, Z.-L.; Li, R.-T.; Hou, F.-F.; Cheng, Y.-X. Cochlearols A and B, polycyclic meroterpenoids from the fungus Ganoderma cochlear that have renoprotective activities. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 6064–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, H.; Peng, X.-R.; Hou, B.; Yu, M.-Y.; Dong, J.-R.; Li, X.-N.; Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Qiu, M.-H. (±)-Ganoapplanin, a pair of polycyclic meroterpenoid enantiomers from Ganoderma applanatum. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 6078–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Di, L.; Dai, W.-F.; Lu, Q.; Yan, Y.-M.; Yang, Z.-L.; Li, R.-T.; Cheng, Y.-X. Applanatumin A, a new dimeric meroterpenoid from Ganoderma applanatum that displays potent antifibrotic activity. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1110–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Tian, L.; Di, L.; Yan, Y.-M.; Wei, X.-Y.; Wang, X.-F.; Cheng, Y.-X. (±)-Sinensilactam A, a pair of rare hybrid metabolites with smad3 phosphorylation inhibition from Ganoderma sinensis. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1565–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.-R.; Liu, J.-Q.; Wan, L.-S.; Li, X.-N.; Yan, Y.-X.; Qiu, M.-H. Four new polycyclic meroterpenoids from Ganoderma cochlear. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 5262–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.-M.; Ai, J.; Zhou, L.L.; Chung, A.C.K.; Li, R.; Nie, J.; Fang, P.; Wang, X.-L.; Luo, J.; Hu, Q.; et al. Lingzhiols, unprecedented rotary door-shaped meroterpenoids as potent and selective inhibitors of p-Smad3 from Ganoderma lucidum. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 5488–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.-M.; Zhang, H.-X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, J.-B.; Li, Y.-P.; Cheng, Y.-X. (±)-Lucidumone, a COX-2 inhibitory caged fungal meroterpenoid from Ganoderma lucidum. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 8523–8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.-J.; Nian, Y.; Yan, Y.; Gong, Y.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hou, B.; Zuo, Z.-L.; Wang, S.-M.; Jiang, H.-H.; et al. Two new classes of t-type calcium channel inhibitors with new chemical scaffolds from Ganoderma cochlear. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 3082–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-P.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.-K. (+)- and (−)-Ganodilactone, a pair of meroterpenoid dimers with pancreatic lipase inhibitory activities from the macromycete Ganoderma leucocontextum. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 64469–64473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-Z.; Liang, X.-B.; Feng, W.-S.; Wu, Y.; Zhi, Y.-L.; Xue, G.-M.; Chen, H.-P.; Liu, J.-K. Unusual constituents from the medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lingzhi. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 36931–36939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-Z.; Chen, H.-P.; Feng, T.; Li, Z.-H.; Dong, Z.-J.; Liu, J.-K. Lucidimine A-D, four new alkaloids from the fruiting bodies of Ganoderma lucidum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 17, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Yang, Z.-L.; Yan, Y.-M.; Cheng, Y.-X. Ganotheaecolin A, a neurotrophic conjugated ergosterol with a naphtho [1,8-ef]azulene scaffold from Ganoderma theaecolum. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 718–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-P.; Liu, J.-K. Secondary metabolites from higher fungi. In Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products 106; Kinghorn, A.D., Falk, H., Gibbons, S., Kobayashi, J., Eds.; Secondary Metabolites from Higher Fungi; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2017; pp. 1–201. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Tuong, T.M.L.; Tian, J.-M.; Pescitelli, G.; Gao, J.-M. Ganorbifates A and B from Ganoderma orbiforme, determined by DFT calculations of NMR data and ECD spectra. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 10195–10198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-F.; Liu, J.-Q.; Yan, Y.-X.; Chen, J.-C.; Lu, Y.; Guo, Y.-H.; Qiu, M.-H. Three new triterpenoids containing four-membered ring from the fruiting body of Ganoderma sinense. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 1656–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Ren, J.; Han, J.; Bao, L.; Li, L.; Yao, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhou, B.; Liu, H. Ganoboninketals A–C, antiplasmodial 3,4-seco-27-norlanostane triterpenes from Ganoderma boninense Pat. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.-R.; Wang, X.; Zhou, L.; Hou, B.; Zuo, Z.-L.; Qiu, M.-H. Ganocochlearic acid A, a rearranged hexanorlanostane triterpenoid, and cytotoxic triterpenoids from the fruiting bodies of Ganoderma cochlear. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 95212–95222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, F.; Valencia, M.; Rivera, A.; Nieto, I.; Quintana, J.; Esté-vez, F.; Bermejo, J. Novel cytostatic lanostanoid triterpenes from Ganoderma australe. Helv. Chim. Acta 2003, 86, 3088–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaka, M.; Chinthanom, P.; Mayteeworakoon, S.; Laoteng, K.; Choowong, W.; Choeyklin, R. Lanostane triterpenoids from cultivated fruiting bodies of the basidiomycete Ganoderma australe. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-J.; Dong, Y.; Qin, F.-Y.; Yan, Y.-M.; Cheng, Y.-X. Meroterpenoids and alkaloids from Ganoderma australe. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 3226–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.C.; Gupta, S.K. The isolation of lanosta-7,9(11),24-trien-3β,21-diol from the fungus Ganoderma australe. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 686–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Guo, L.-L.; Isaka, M.; Li, Z.-H.; Chen, H.-P. [20(22)E]-Lanostane Triterpenes from the Fungus Ganoderma australe. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairul; Tokuyama, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Nishizawa, M.; Tokuda, H.; Chairul, S.M.; Hayashi, Y. Applanoxidic acids A, B, C and D, biologically active tetracyclic triterpenes from Ganoderma applanatum. Phytochemistry 1991, 30, 4105–4109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuuchi, T.; Kusumi, T. Phenylglycine methyl ester, a useful tool for absolute configuration determination of various chiral carboxylic acids. J. Org. Chem. 2000, 65, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofrenić, I.; Anđelković, B.; Todorović, N.; Stanojković, T.; Vujisić, L.; Novaković, M.; Milosavljević, S.; Tešević, V. Cytotoxic triterpenoids and triterpene sugar esters from the medicinal mushroom Fomitopsis betulina. Phytochemistry 2021, 181, 112580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Feng, T.; Li, Z.-H.; Chen, H.-P.; Liu, J.-K. Triterpenes with unusual modifications from the fruiting bodies of the medicinal fungus Irpex lacteus. Phytochemistry 2019, 162, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-P.; Zhao, Z.-Z.; Li, Z.-H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, S.-B.; Tang, Y.; Yao, J.-N.; Chen, L.; Isaka, M.; Feng, T.; et al. Anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory lanostane triterpenoids from the polish edible mushroom Macrolepiota procera. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3146–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.-F.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Yao, L.-G.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.-W. Unprecedented diterpenoids as a PTP1B inhibitor from the Hainan soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum Marenzeller. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Wu, X.; Pan, J.; Hu, X.; Gong, D.; Zhang, G. New insights into the inhibition mechanism of betulinic acid on α-glucosidase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7065–7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsu, G.; Kino, Y.; Sasaki, H.; Satoh, J.-i.; Kinoshita, K.; Koyama, K. Meroterpenoids with BACE1 inhibitory activity from the fruiting body of Boletinus asiaticus. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1797–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Wu, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Q.; et al. Protoilludane, illudalane, and botryane sesquiterpenoids from the endophytic fungus Phomopsis sp. TJ507A. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Petersson, G.A.; Nakatsuji, H.; et al. Gaussian 16, Revision C.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bruhn, T.; Schaumlöffel, A.; Hemberger, Y.; Pescitelli, G. SpecDis Version 1.71, Berlin, Germany, 2017. Available online: https:/specdis-software.jimdo.com (accessed on 15 November 2022).
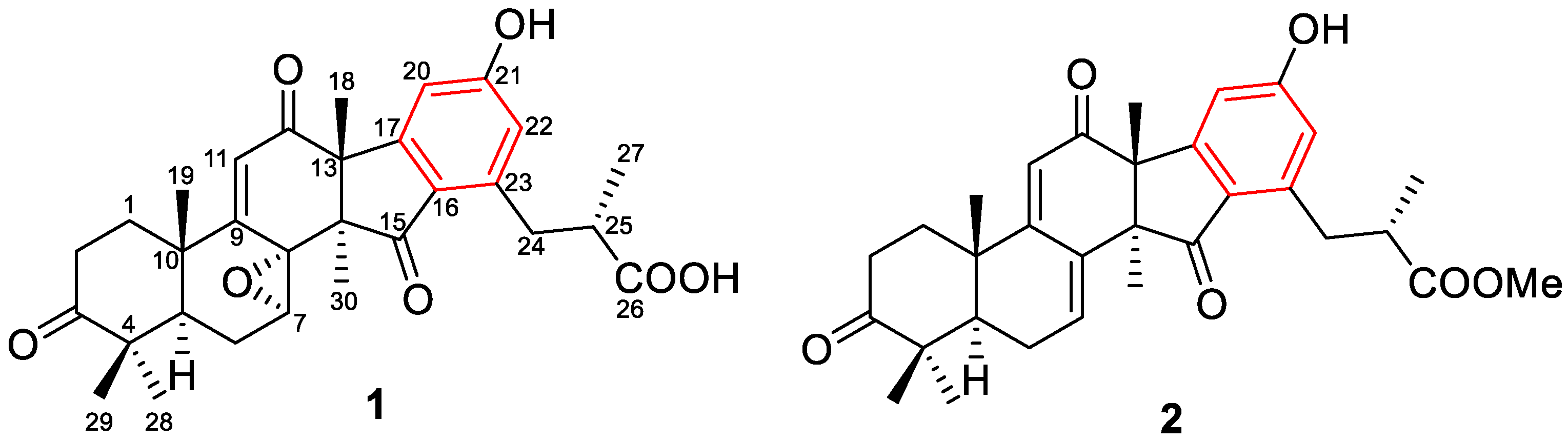
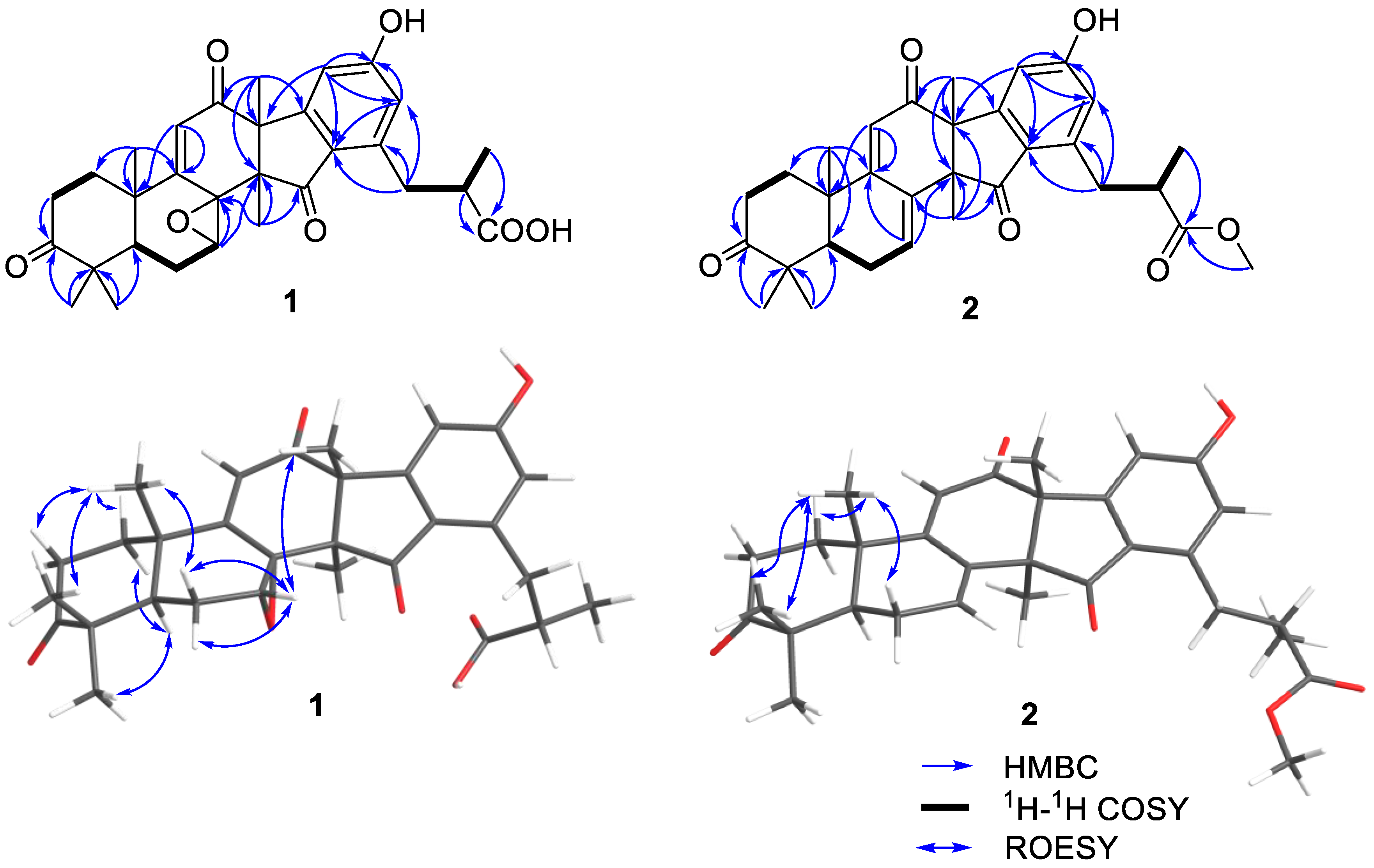
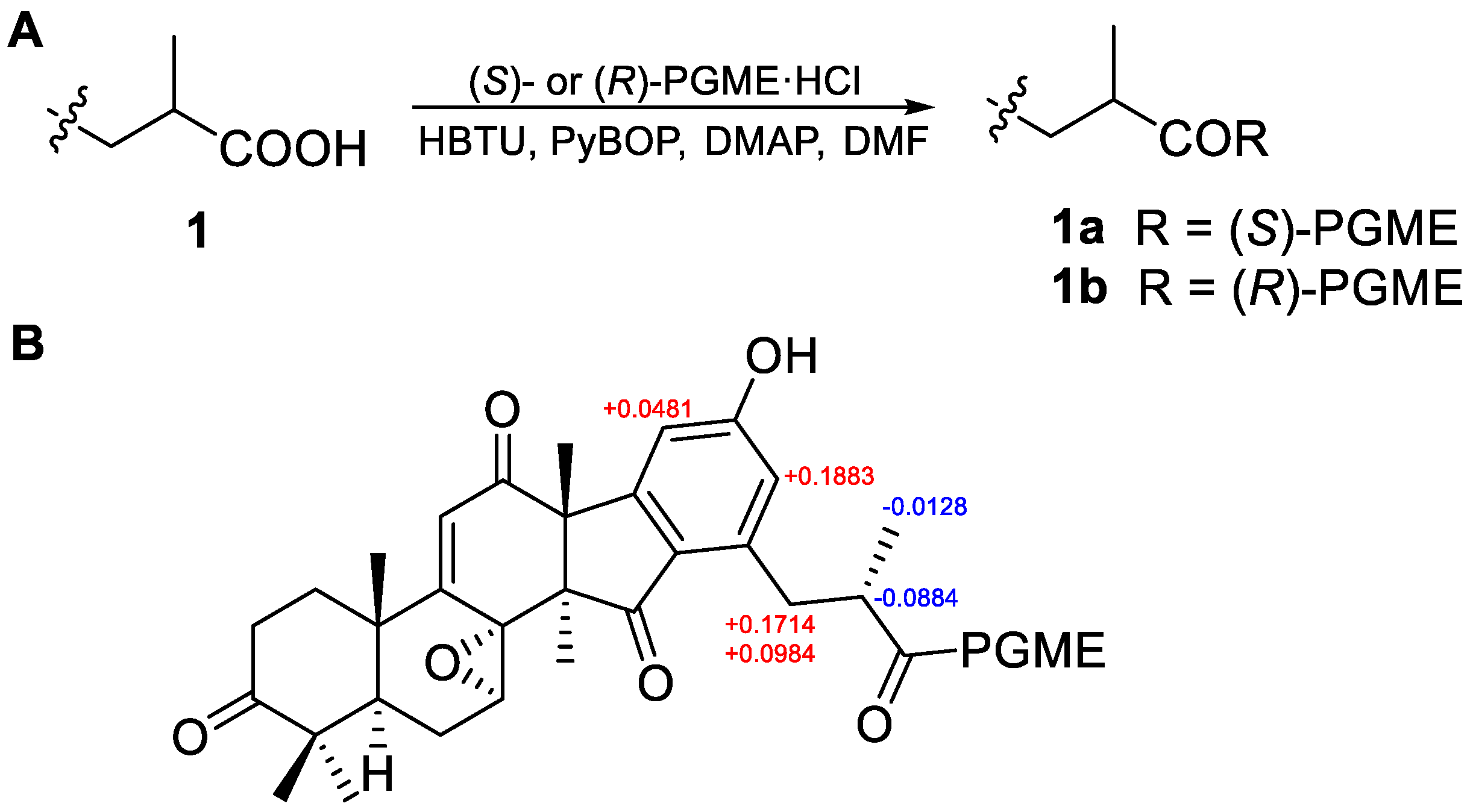

| No. | 1 a | 2 b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC, multi. | δH | δC, multi. | δH | |
| 1 | 36.2, CH2 | 1.98, overlapped, 2H | 35.8, CH2 | 2.35, ddd (13.8, 5.6, 2.8) 1.91, ddd (13.8, 13.8, 5.2) |
| 2 | 34.2, CH2 | 2.70, m 2.49, m | 34.5, CH2 | 2.82, ddd (15.3, 13.8, 5.2) 2.47, ddd (15.3, 5.6, 2.8) |
| 3 | 216.1, C | 214.8, C | ||
| 4 | 46.4, C | 47.5, C | ||
| 5 | 41.5, CH | 2.92, brd (12.8) | 49.7, CH | 1.78, dd (10.3, 5.6) |
| 6 | 23.2, CH2 | 2.08, brd (12.8) 1.74, brdd (12.8, 12.8) | 24.1, CH2 | 2.40, m, 2H |
| 7 | 59.4, CH | 5.07, brs | 135.0, CH | 7.56, m |
| 8 | 63.3, C | 134.9, C | ||
| 9 | 166.3, C | 163.2, C | ||
| 10 | 41.1, C | 38.8, C | ||
| 11 | 130.9, CH | 6.45, s | 117.6, CH | 5.80, s |
| 12 | 198.5, C | 200.5, C | ||
| 13 | 56.7, C | 54.4, C | ||
| 14 | 55.2, C | 56.0, C | ||
| 15 | 201.3, C | 203.3, C | ||
| 16 | 124.2, C | 124.8, C | ||
| 17 | 157.2, C | 156.5, C | ||
| 18 | 31.5, CH3 | 1.58, s | 31.9, CH3 | 1.35, s |
| 19 | 25.1, CH3 | 1.09, s | 21.7, CH3 | 1.36, s |
| 20 | 112.2, CH | 7.93, s | 111.3, CH | 7.54, d (2.0) |
| 21 | 164.8, C | 161.0, C | ||
| 22 | 118.2, CH | 7.30, s | 116.9, CH | 6.60, d (2.0) |
| 23 | 145.5, C | 143.9, C | ||
| 24 | 36.3, CH2 | 3.62, m 3.68, m | 35.9, CH2 | 3.26, dd (13.0, 7.1) 3.07, dd (13.0, 8.0) |
| 25 | 42.2, CH | 3.25, m | 40.6, CH | 2.80, ddd (8.0, 7.1, 7.0) |
| 26 | 179.1, C | 176.7, C | ||
| 27 | 18.2, CH3 | 1.42, d (6.7) | 17.2, CH3 | 1.17, d (7.0) |
| 28 | 28.9, CH3 | 1.09, s | 22.7, CH3 | 1.19, s |
| 29 | 22.2, CH3 | 1.13, s | 25.5, CH3 | 1.16, s |
| 30 | 24.5, CH3 | 1.64, s | 29.0, CH3 | 1.26, s |
| OMe | 51.8, CH3 | 3.59, s | ||
| 21-OH | 6.74, brs | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, L.; Chen, H.-P.; Li, X.; Liu, J.-K. Ganoaustralins A and B, Unusual Aromatic Triterpenes from the Mushroom Ganoderma australe. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121520
Zhou L, Chen H-P, Li X, Liu J-K. Ganoaustralins A and B, Unusual Aromatic Triterpenes from the Mushroom Ganoderma australe. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(12):1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121520
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Lin, He-Ping Chen, Xinyang Li, and Ji-Kai Liu. 2022. "Ganoaustralins A and B, Unusual Aromatic Triterpenes from the Mushroom Ganoderma australe" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 12: 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121520
APA StyleZhou, L., Chen, H.-P., Li, X., & Liu, J.-K. (2022). Ganoaustralins A and B, Unusual Aromatic Triterpenes from the Mushroom Ganoderma australe. Pharmaceuticals, 15(12), 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121520