2-Arylpropionic Acid Pyrazolamides as Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Inverse Agonists Endowed with Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Abstract
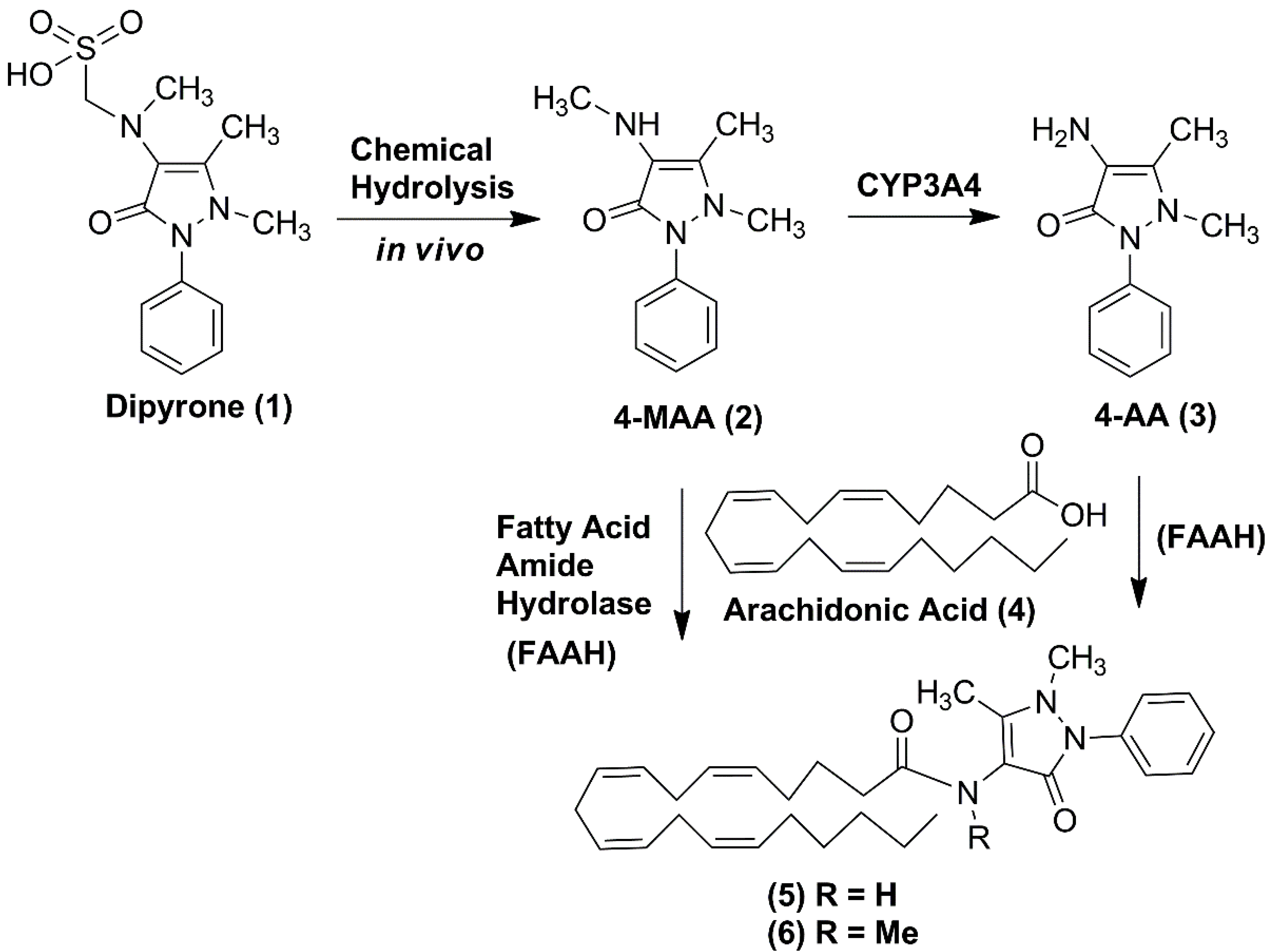
1. Introduction
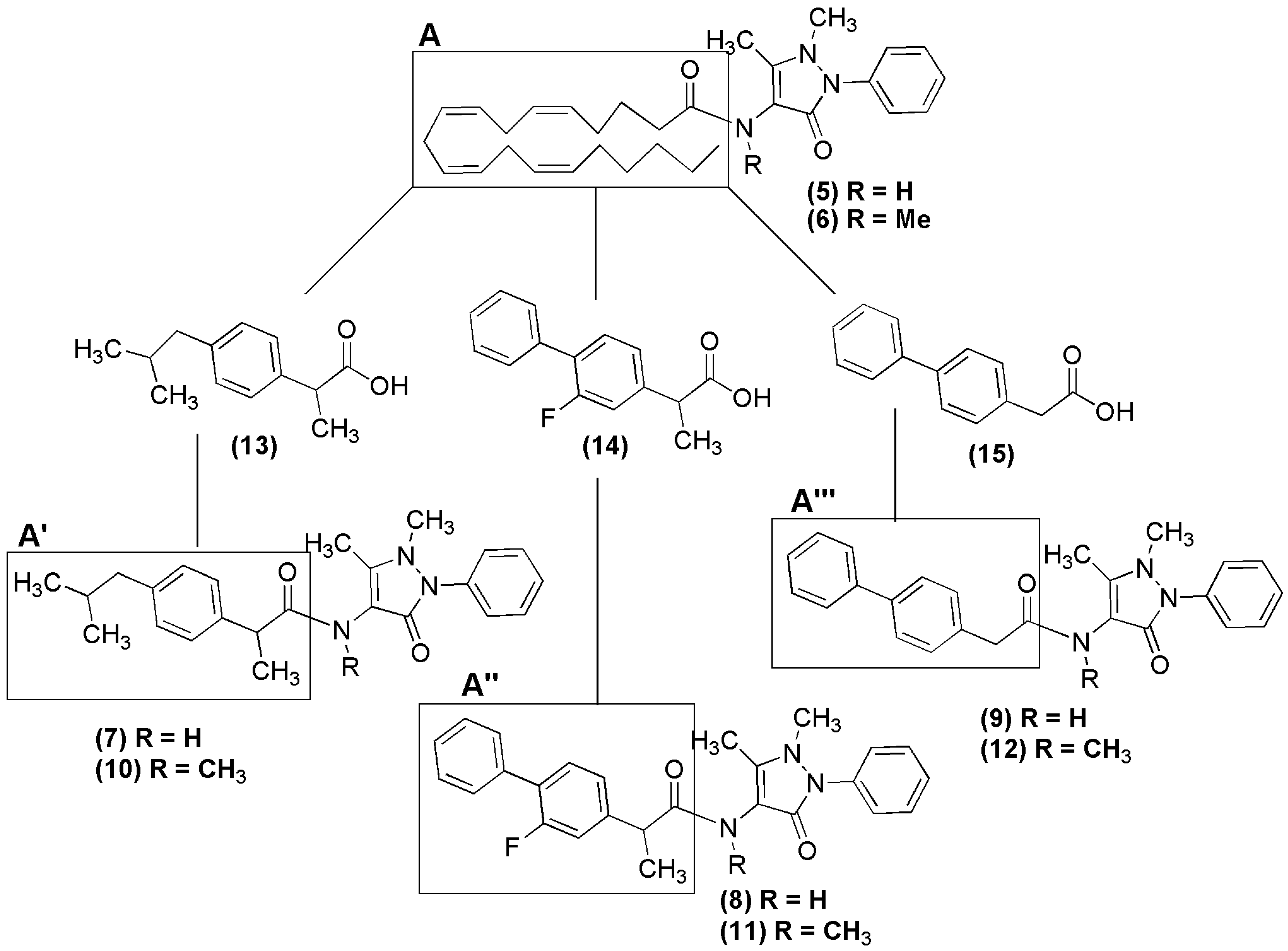
2. Results and Discussion
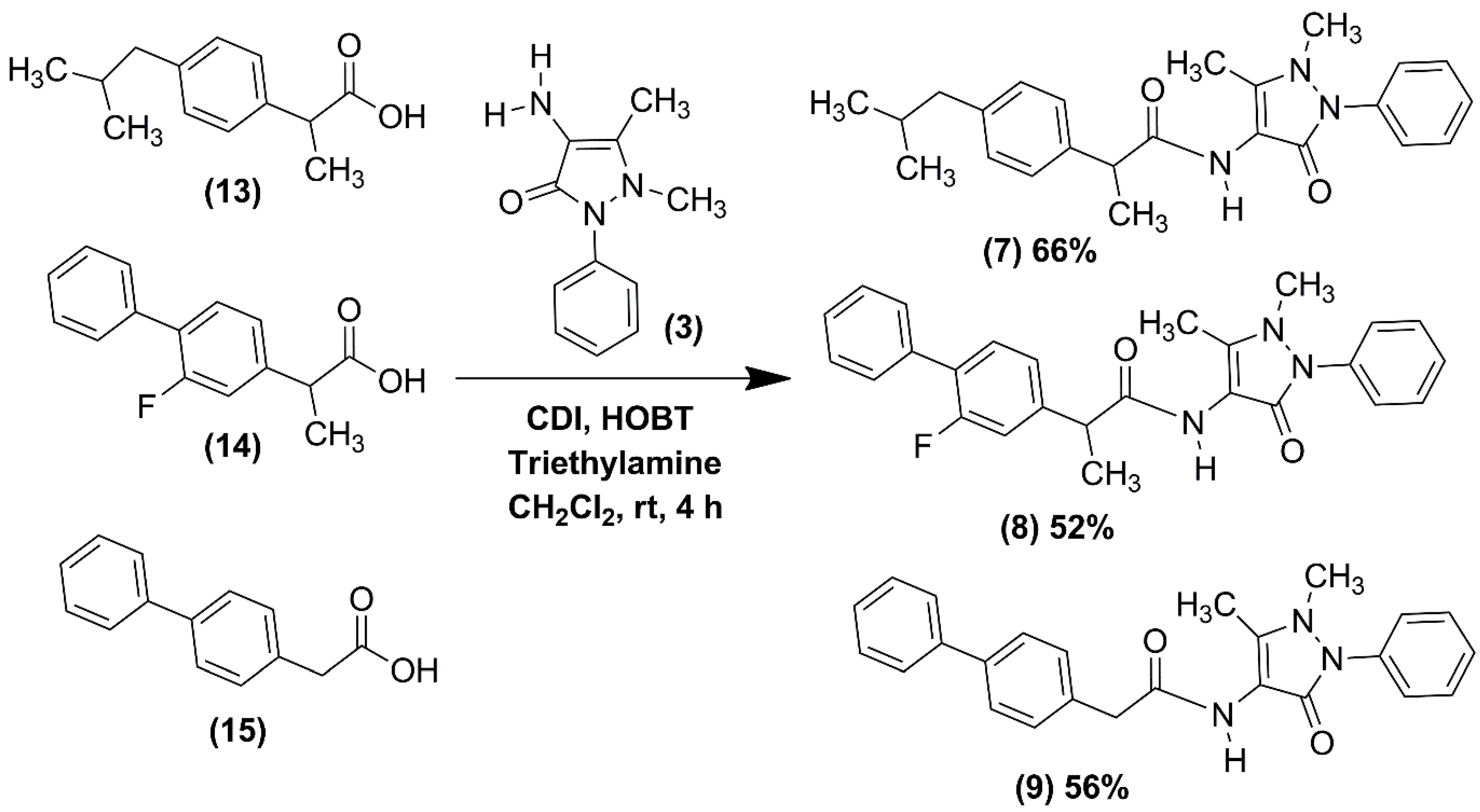
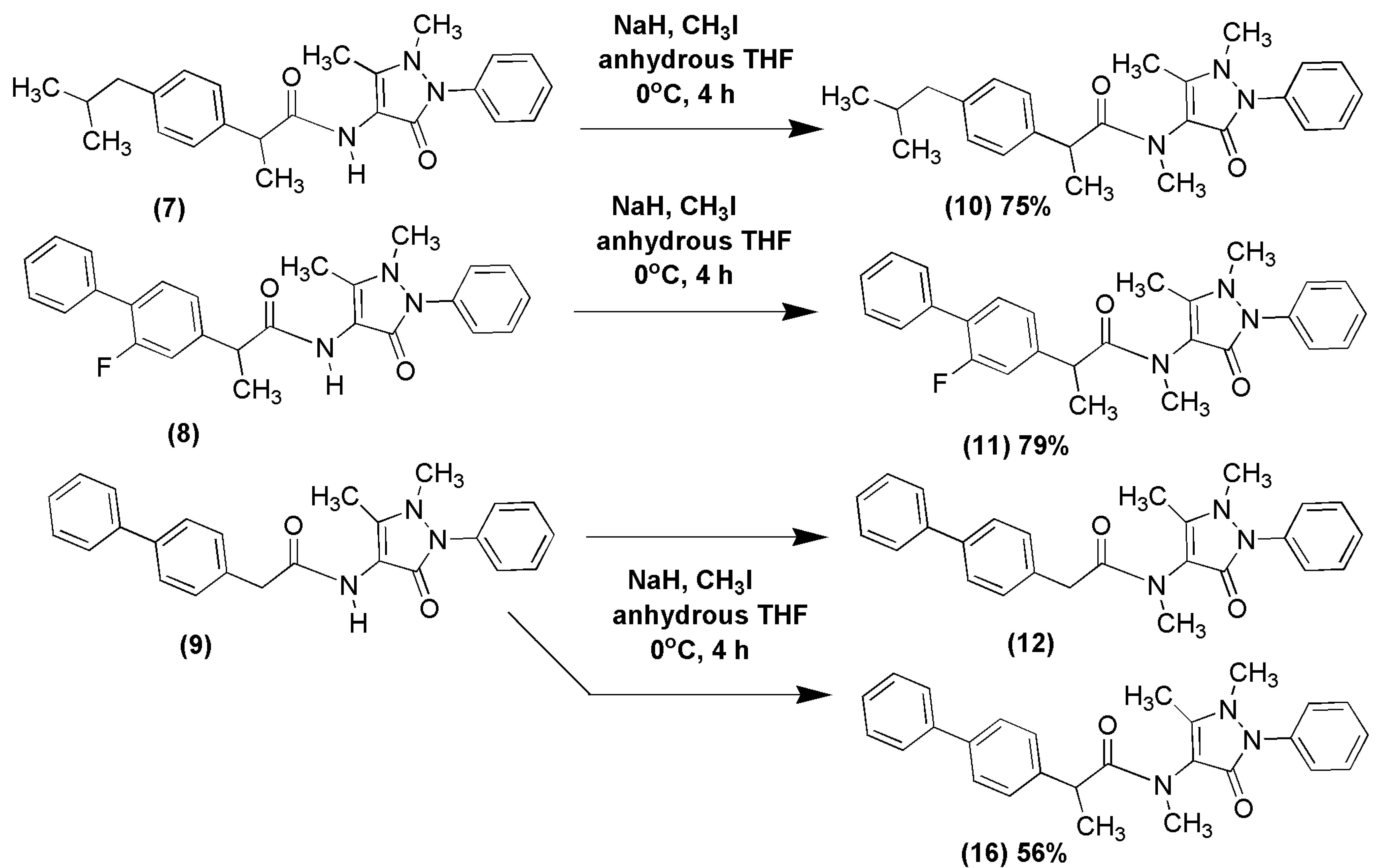
2.1. Chemical Synthesis of NSAID-Pyrazolamides (7–12)
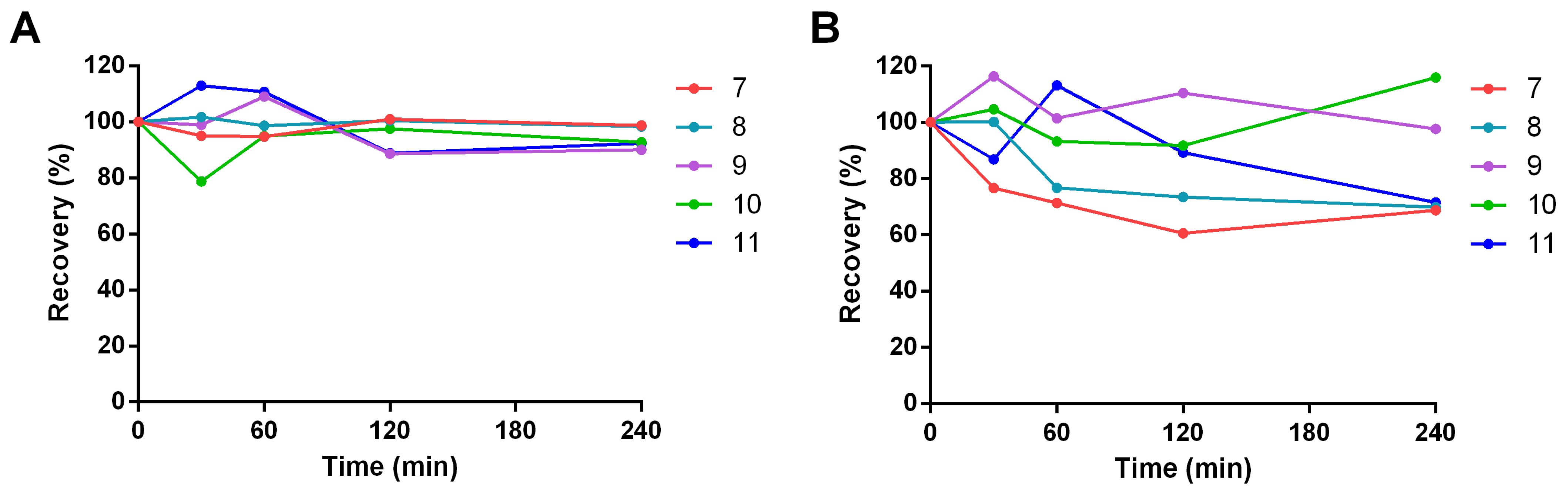
2.2. Drug-like Properties of Pyrazolamides 7–11
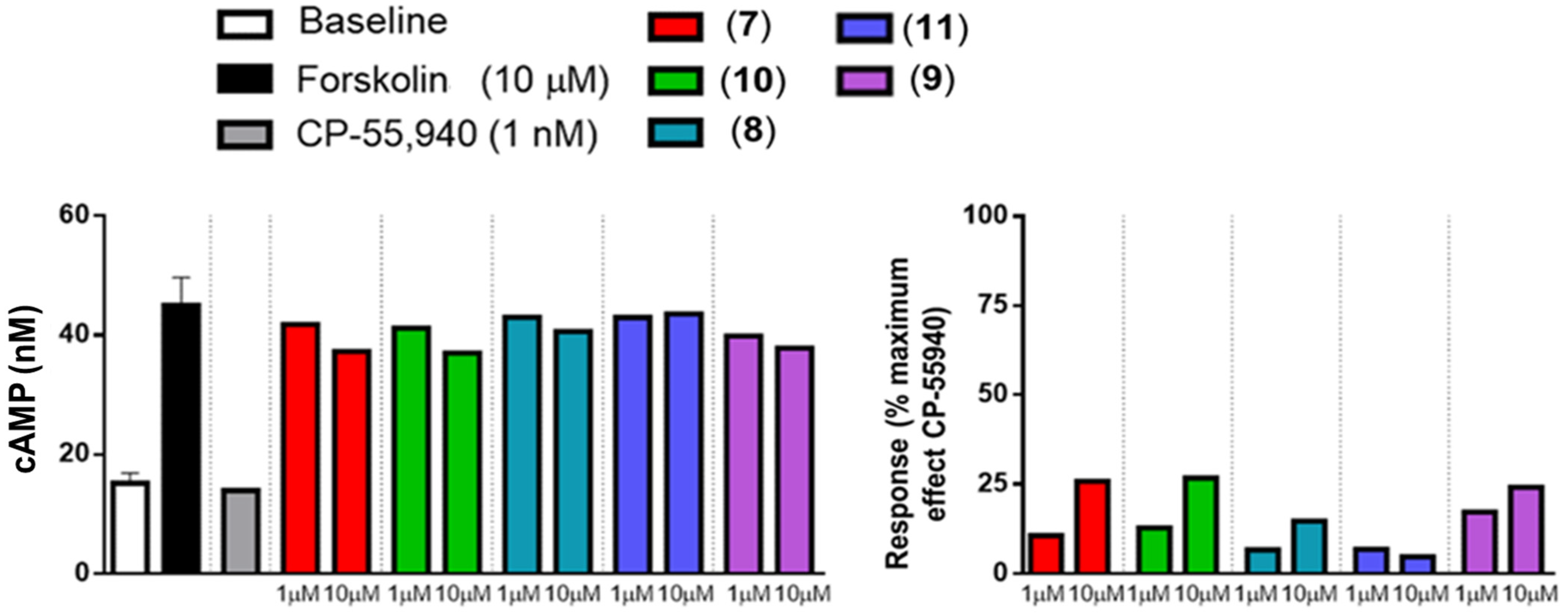
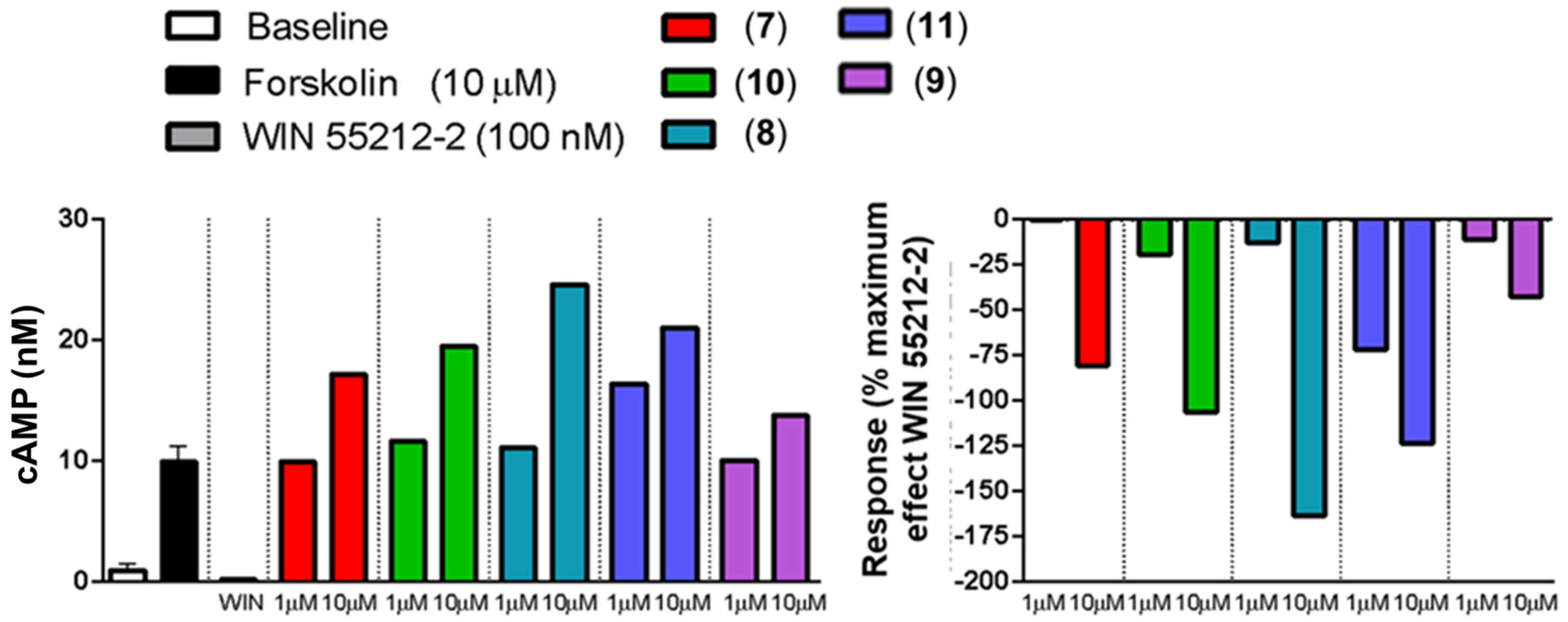
2.3. In Vitro Activity Profiles of Pyrazolamides 7–11
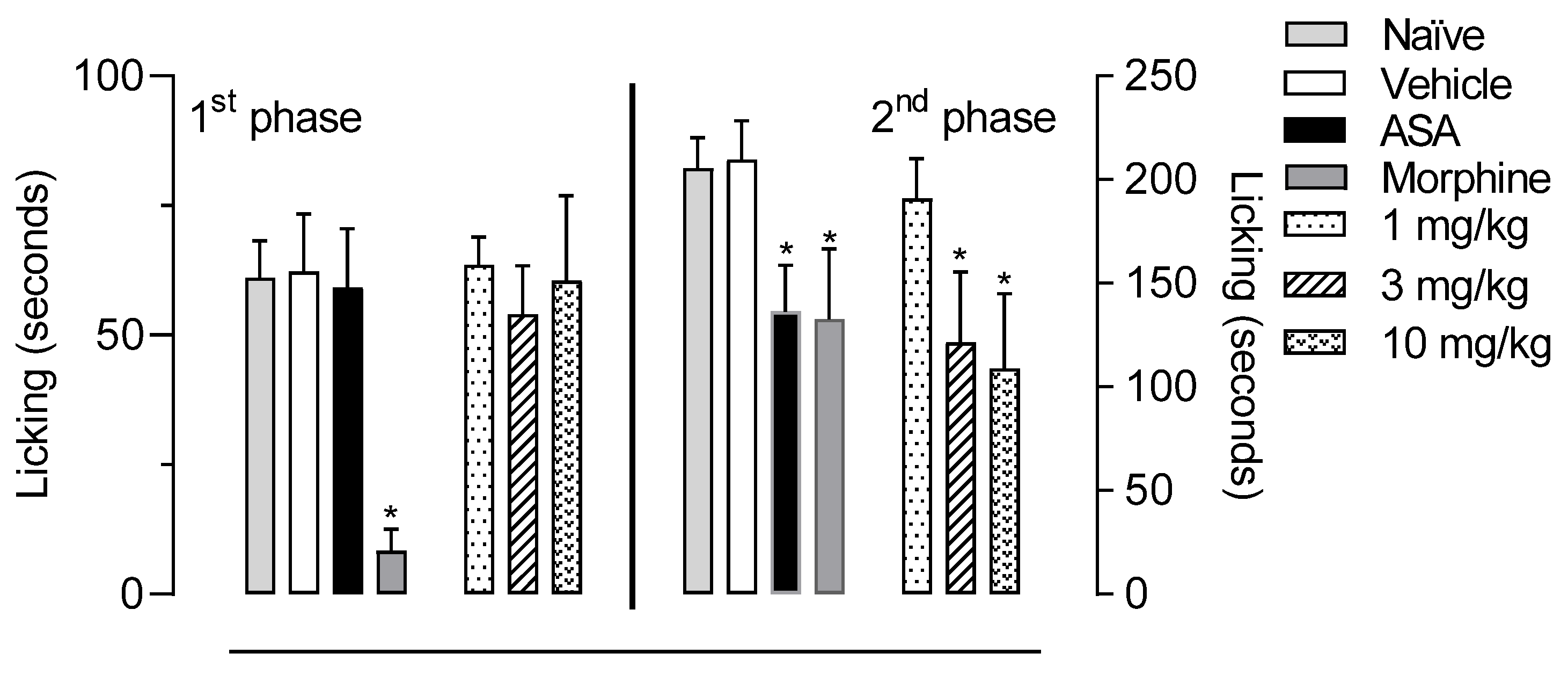
2.4. In Vivo Activity of LASSBio-2265 (11) in the Formalin-Induced Licking Response in Mice
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of the NSAID-Pyrazolamides (7–11)
3.2.1. Synthesis of the NSAID-Pyrazolamides (7–9)
3.2.2. Synthesis of N-Methylated Pyrazolamides (10) and (11)
3.3. Drug-like Properties of NSAID-Pyrazolamides (7–11)
3.3.1. Aqueous Solubility
3.3.2. Determination of the Distribution Coefficient at pH 7.4 (log D7.4)
3.3.3. Chemical Stability
3.3.4. Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay (PAMPA-GTI)
3.3.5. Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay (PAMPA-BBB)
3.3.6. Plasmatic Stability
3.4. In Vitro Experiments
3.4.1. Agonist Activity toward CB1 and CB2 Receptors
3.4.2. Inverse Agonist Activity toward CB2 Receptors [45]
3.4.3. Human CB2 (Agonist Radioligand) Receptor Binding Assay
3.5. In Vivo Experiments
3.5.1. Animals
3.5.2. Formalin-Induced Licking Behavior
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guindon, J.; Hohmann, A. The Endocannabinoid System and Pain. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets 2009, 8, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto-Reyes, V.; Llames, S.; Hidalgo, A.; Menéndez, L.; Baamonde, A. Spinal and Peripheral Analgesic Effects of the CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist AM1241 in Two Models of Bone Cancer-Induced Pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hama, A.; Sagen, J. Centrally Mediated Antinociceptive Effects of Cannabinoid Receptor Ligands in Rat Models of Nociception. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 100, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulieu, P.; Bisogno, T.; Punwar, S.; Farquhar-Smith, W.P.; Ambrosino, G.; Di Marzo, V.; Rice, A.S. Role of the Endogenous Cannabinoid System in the Formalin Test of Persistent Pain in the Rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 396, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, D.P.; Jhaveri, M.D.; Beckett, S.R.G.; Roe, C.H.; Kendall, D.A.; Marsden, C.A.; Chapman, V. Effects of Direct Periaqueductal Grey Administration of a Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist on Nociceptive and Aversive Responses in Rats. Neuropharmacology 2003, 45, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maione, S.; Bisogno, T.; de Novellis, V.; Palazzo, E.; Cristino, L.; Valenti, M.; Petrosino, S.; Guglielmotti, V.; Rossi, F.; Marzo, V. Di Elevation of Endocannabinoid Levels in the Ventrolateral Periaqueductal Grey through Inhibition of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase Affects Descending Nociceptive Pathways via Both Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1 and Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Type-1 Re. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 316, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahn, E.J.; Hohmann, A.G. Cannabinoids as Pharmacotherapies for Neuropathic Pain: From the Bench to the Bedside. Neurotherapeutics 2009, 6, 713–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos, E.; Pascual, D.; Martín, M.I.; Goicoechea, C. Antinociceptive Effect of the Cannabinoid Agonist, WIN 55,212-2, in the Orofacial and Temporomandibular Formalin Tests. Eur. J. Pain 2010, 14, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinsey, S.G.; Mahadevan, A.; Zhao, B.; Sun, H.; Naidu, P.S.; Razdan, R.K.; Selley, D.E.; Imad Damaj, M.; Lichtman, A.H. The CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor-Selective Agonist O-3223 Reduces Pain and Inflammation without Apparent Cannabinoid Behavioral Effects. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumella, J.; Hernández-Folgado, L.; Girón, R.; Sánchez, E.; Morales, P.; Hurst, D.P.; Gómez-Cañas, M.; Gómez-Ruiz, M.; Pinto, D.C.G.A.; Goya, P.; et al. Chromenopyrazoles: Non-Psychoactive and Selective CB 1 Cannabinoid Agonists with Peripheral Antinociceptive Properties. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, B.R.; Compton, D.R.; Thomas, B.F.; Prescott, W.R.; Little, P.J.; Razdan, R.K.; Johnson, M.R.; Melvin, L.S.; Mechoulam, R.; Susan, J.W. Behavioral, Biochemical, and Molecular Modeling Evaluations of Cannabinoid Analogs. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1991, 40, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.A.; Grieb, M.; Lutz, B. Central Side-Effects of Therapies Based on CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Agonists and Antagonists: Focus on Anxiety and Depression. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 23, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, J.; Hohmann, A.G. Cannabinoid CB 2 Receptors: A Therapeutic Target for the Treatment of Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, K.; Johnson, D.S.; Mileni, M.; Beidler, D.; Long, J.Z.; McKinney, M.K.; Weerapana, E.; Sadagopan, N.; Liimatta, M.; Smith, S.E.; et al. Discovery and Characterization of a Highly Selective FAAH Inhibitor That Reduces Inflammatory Pain. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comelli, F.; Giagnoni, G.; Bettoni, I.; Colleoni, M.; Costa, B. The Inhibition of Monoacylglycerol Lipase by URB602 Showed an Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Nociceptive Effect in a Murine Model of Acute Inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 152, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, J.; Desroches, J.; Beaulieu, P. The Antinociceptive Effects of Intraplantar Injections of 2-Arachidonoyl Glycerol Are Mediated by Cannabinoid CB 2 Receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 150, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, P.S.; Kinsey, S.G.; Guo, T.L.; Cravatt, B.F.; Lichtman, A.H. Regulation of Inflammatory Pain by Inhibition of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 334, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turcotte, C.; Chouinard, F.; Lefebvre, J.S.; Flamand, N. Regulation of Inflammation by Cannabinoids, the Endocannabinoids 2-Arachidonoyl-Glycerol and Arachidonoyl-Ethanolamide, and Their Metabolites. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 1049–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, B.; Cheremina, O.; Bachmakov, J.; Renner, B.; Zolk, O.; Fromm, M.F.; Brune, K. Dipyrone Elicits Substantial Inhibition of Peripheral Cyclooxygenases in Humans: New Insights into the Pharmacology of an Old Analgesic. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 2343–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogosch, T.; Sinning, C.; Podlewski, A.; Watzer, B.; Schlosburg, J.; Lichtman, A.H.; Cascio, M.G.; Bisogno, T.; Di Marzo, V.; Nüsing, R.; et al. Novel Bioactive Metabolites of Dipyrone (Metamizol). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, S.A.; Dick, F.; Herzog, C.; Eberhardt, M.J.; Leffler, A. Active Metabolites of Dipyrone Induce a Redox-Dependent Activation of the Ion Channels TRPA1 and TRPV1. Pain Rep. 2019, 4, e720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, W.; Ramirez, K.; Avila, C.; Limongi, R.; Vanegas, H.; Vazquez, E. Metamizol, a Non-Opioid Analgesic, Acts via Endocannabinoids in the PAG-RVM Axis during Inflammation in Rats. Eur. J. Pain 2012, 16, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, G.G.; Dias, E.V.; Teixeira, J.M.; Athie, M.C.P.; Bonet, I.J.M.; Tambeli, C.H.; Parada, C.A. The Analgesic Effect of Dipyrone in Peripheral Tissue Involves Two Different Mechanisms: Neuronal KATP Channel Opening and CB1 Receptor Activation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 741, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggan, K.C.; Hermanson, D.J.; Musee, J.; Prusakiewicz, J.J.; Scheib, J.L.; Carter, B.D.; Banerjee, S.; Oates, J.A.; Marnett, L.J. (R)-Profens Are Substrate-Selective Inhibitors of Endocannabinoid Oxygenation by COX-2. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, J.; Fowler, C.J. Inhibition of Endocannabinoid Metabolism by the Metabolites of Ibuprofen and Flurbiprofen. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkowski, M.G.; Ginell, S.L.; Smith, W.L.; Garavito, R.M. The Productive Conformation of Arachidonic Acid Bound to Prostaglandin Synthase. Science 2000, 289, 1933–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montalbetti, C.A.G.N.; Falque, V. Amide Bond Formation and Peptide Coupling. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 10827–10852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fones, W.S. The Use of Sodium Hydride in the Alkylation of N-Substituted Amides. J. Org. Chem. 1949, 14, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordwell, F.G.; Fried, H.E. Acidities of the Hydrogen-Carbon Protons in Carboxylic Esters, Amides, and Nitriles. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 4327–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordwell, F.G.; Ji, G.Z. Effects of Structural Changes on Acidities and Homolytic Bond Dissociation Energies of the Hydrogen-Nitrogen Bonds in Amidines, Carboxamides, and Thiocarboxamides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 8398–8401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Hosseiny, S.S.; Szczotka, M.; Jordan, V.; Schlitter, K. Rapid Solubility Determination of the Triterpenes Oleanolic Acid and Ursolic Acid by UV-Spectroscopy in Different Solvents. Phytochem. Lett. 2009, 2, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisneros, J.A.; Robertson, M.J.; Mercado, B.Q.; Jorgensen, W.L. Systematic Study of Effects of Structural Modifications on the Aqueous Solubility of Drug-like Molecules. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Iwasa, J.; Hansch, C. A New Substituent Constant, π, Derived from Partition Coefficients. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 5175–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.; Kerns, E.; Carter, G. Drug-Like Property Concepts in Pharmaceutical Design. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2184–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortuna, A.; Alves, G.; Soares-Da-Silva, P.; Falcão, A. Optimization of a Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay for the Fast and Simultaneous Prediction of Human Intestinal Absorption and Plasma Protein Binding of Drug Candidates: Application to Dibenz[b,f]Azepine-5-Carboxamide Derivatives. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, G.; Morales, P.; Rodríguez-Cueto, C.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Jagerovic, N.; Franco, R. Targeting Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors in the Central Nervous System. Medicinal Chemistry Approaches with Focus on Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Jiang, L.; Chen, T.-M.; Hwang, K.-K. A Comparative Study of Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay for High Throughput Profiling of Drug Absorption Potential. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 37, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, D.I.; Pistolozzi, M.; Palomo, V.; Redondo, M.; Fortugno, C.; Gil, C.; Felix, G.; Martinez, A.; Bertucci, C. 5-Imino-1,2-4-Thiadiazoles and Quinazolines Derivatives as Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β (GSK-3β) and Phosphodiesterase 7 (PDE7) Inhibitors: Determination of Blood–Brain Barrier Penetration and Binding to Human Serum Albumin. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 45, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konsoula, R.; Jung, M. In Vitro Plasma Stability, Permeability and Solubility of Mercaptoacetamide Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 361, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.A.; Ferreira-Silva, G.À.; Ferreira, A.C.S.; Fernandes, R.A.; Kwee, J.K.; Sant’Anna, C.M.R.; Ionta, M.; Fraga, C.A.M. Design, Synthesis, and Pharmacological Evaluation of Novel N -Acylhydrazone Derivatives as Potent Histone Deacetylase 6/8 Dual Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, E. Biochemical and Pharmacological Control of the Multiplicity of Coupling at G-Protein-Coupled Receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 99, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlett, A.C. Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling. In Cannabinoids; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 53–79. [Google Scholar]
- Seamon, K.B.; Padgett, W.; Daly, J.W. Forskolin: Unique Diterpene Activator of Adenylate Cyclase in Membranes and in Intact Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 3363–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felder, C.C.; Joyce, K.E.; Briley, E.M.; Mansouri, J.; Mackie, K.; Blond, O.; Lai, Y.; Ma, A.L.; Mitchell, R.L. Comparison of the Pharmacology and Signal Transduction of the Human Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 Receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 48, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khanolkar, A.D.; Palmer, S.L.; Makriyannis, A. Molecular Probes for the Cannabinoid Receptors. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2000, 108, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munro, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Abu-Shaar, M. Molecular Characterization of a Peripheral Receptor for Cannabinoids. Nature 1993, 365, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamura, H.; Suzuki, H.; Ueda, Y.; Kaya, T.; Inaba, T. In Vitro and in Vivo Pharmacological Characterization of JTE-907, a Novel Selective Ligand for Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 296, 420–425. [Google Scholar]
- Gentili, M.; Ronchetti, S.; Ricci, E.; Di Paola, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Bereshchenko, O.; Migliorati, G.; Riccardi, C. Selective CB2 Inverse Agonist JTE907 Drives T Cell Differentiation towards a Treg Cell Phenotype and Ameliorates Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 141, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presley, C.; Abidi, A.; Suryawanshi, S.; Mustafa, S.; Meibohm, B.; Moore, B.M. Preclinical Evaluation of SMM-189, a Cannabinoid Receptor 2-specific Inverse Agonist. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunn, C.A.; Reich, E.-P.; Fine, J.S.; Lavey, B.; Kozlowski, J.A.; Hipkin, R.W.; Lundell, D.J.; Bober, L. Biology and Therapeutic Potential of Cannabinoid CB 2 Receptor Inverse Agonists. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascio, M.G.; Bolognini, D.; Pertwee, R.G.; Palazzo, E.; Corelli, F.; Pasquini, S.; Di Marzo, V.; Maione, S. In Vitro and in Vivo Pharmacological Characterization of Two Novel Selective Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Inverse Agonists. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 61, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubuisson, D.; Dennis, S.G. The Formalin Test: A Quantitative Study of the Analgesic Effects of Morphine, Meperidine, and Brain Stem Stimulation in Rats and Cats. Pain 1977, 4, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunskaar, S.; Hole, K. The Formalin Test in Mice: Dissociation between Inflammatory and Non-Inflammatory Pain. Pain 1987, 30, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Murawski, A.; Patel, K.; Crespi, C.L.; Balimane, P.V. A Novel Design of Artificial Membrane for Improving the PAMPA Model. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, J.P.B.; Silva, L.; Ceschi, M.A.; Lüdtke, D.S.; Zimmer, A.R.; Ruaro, T.C.; Dantas, R.F.; de Salles, C.M.C.; Silva-Jr, F.P.; Senger, M.R.; et al. Synthesis of New Lophine–Carbohydrate Hybrids as Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Cytotoxicity Evaluation and Molecular Modeling. Medchemcomm 2019, 10, 2089–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, W.; Shi, R.; Kang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Hou, A.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, K.; et al. Monoacylglycerol Lipase Regulates Cannabinoid Receptor 2-Dependent Macrophage Activation and Cancer Progression. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, L.; Kerns, E.H.; Fan, K.; McConnell, O.J.; Carter, G.T. High Throughput Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay for Blood–Brain Barrier. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, N.M.; Rezende, C.M.; Fontes, S.P.; Matheus, M.E.; Fernandes, P.D. Antinociceptive Activity of Amazonian Copaiba Oils. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 109, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cpd | Aqueous Solubility (a) (μM) | Log D7.4 (b) | PAMPA-GI (c) | PAMPA-BBB (d) | Plasma Metabolization Rate (e) (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pe Exp (10−6 cm/s) | Fa Exp (%) | Pe Exp (10−6 cm/s) | Score | ||||
| 7 | 12.14 | 2.47 | 15.38 | 99.71 | 12.77 | CNS+ | 56.13 |
| 8 | 59.07 | 1.94 | 9.69 | 97.49 | 17.25 | CNS+ | 18.66 |
| 9 | 21.32 | 2.14 | 11.00 | 98.47 | 4.51 | CNS+ | 24.56 |
| 10 | 47.66 | 2.43 | 2.51 | 61.51 | 12.68 | CNS+ | 32.50 |
| 11 | 68.47 | 1.98 | 10.18 | 97.91 | 9.26 | CNS+ | 13.04 |
| Compound (µM) | Ki (µM) |
|---|---|
| (5) | 5.4 (a) |
| (6) | 3.0 (a) |
| LASSBio-2265 (11) | 16.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Oliveira, D.R.; Maia, R.C.; de Carvalho França, P.R.; Fernandes, P.D.; Barbosa, G.; Lima, L.M.; Fraga, C.A.M. 2-Arylpropionic Acid Pyrazolamides as Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Inverse Agonists Endowed with Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121519
de Oliveira DR, Maia RC, de Carvalho França PR, Fernandes PD, Barbosa G, Lima LM, Fraga CAM. 2-Arylpropionic Acid Pyrazolamides as Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Inverse Agonists Endowed with Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(12):1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121519
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Oliveira, Daniela R., Rodolfo C. Maia, Patrícia R. de Carvalho França, Patrícia D. Fernandes, Gisele Barbosa, Lídia M. Lima, and Carlos A. Manssour Fraga. 2022. "2-Arylpropionic Acid Pyrazolamides as Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Inverse Agonists Endowed with Anti-Inflammatory Properties" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 12: 1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121519
APA Stylede Oliveira, D. R., Maia, R. C., de Carvalho França, P. R., Fernandes, P. D., Barbosa, G., Lima, L. M., & Fraga, C. A. M. (2022). 2-Arylpropionic Acid Pyrazolamides as Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Inverse Agonists Endowed with Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Pharmaceuticals, 15(12), 1519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121519










