Doxorubicin-Induced Platelet Activation and Clearance Relieved by Salvianolic Acid Compound: Novel Mechanism and Potential Therapy for Chemotherapy-Associated Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
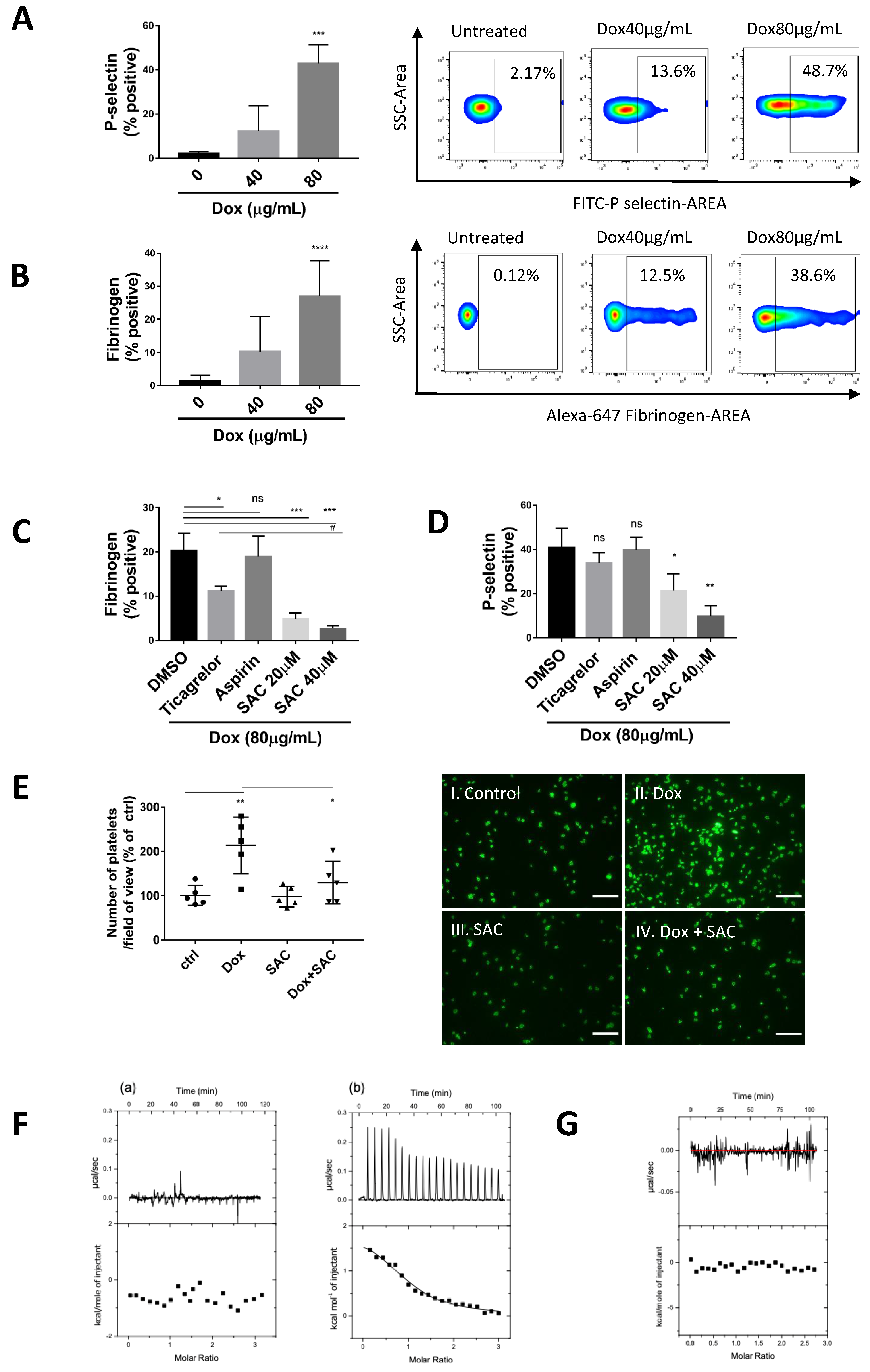
2.1. Dox Induced Platelet Activation and Degranulation Inhibited by SAC
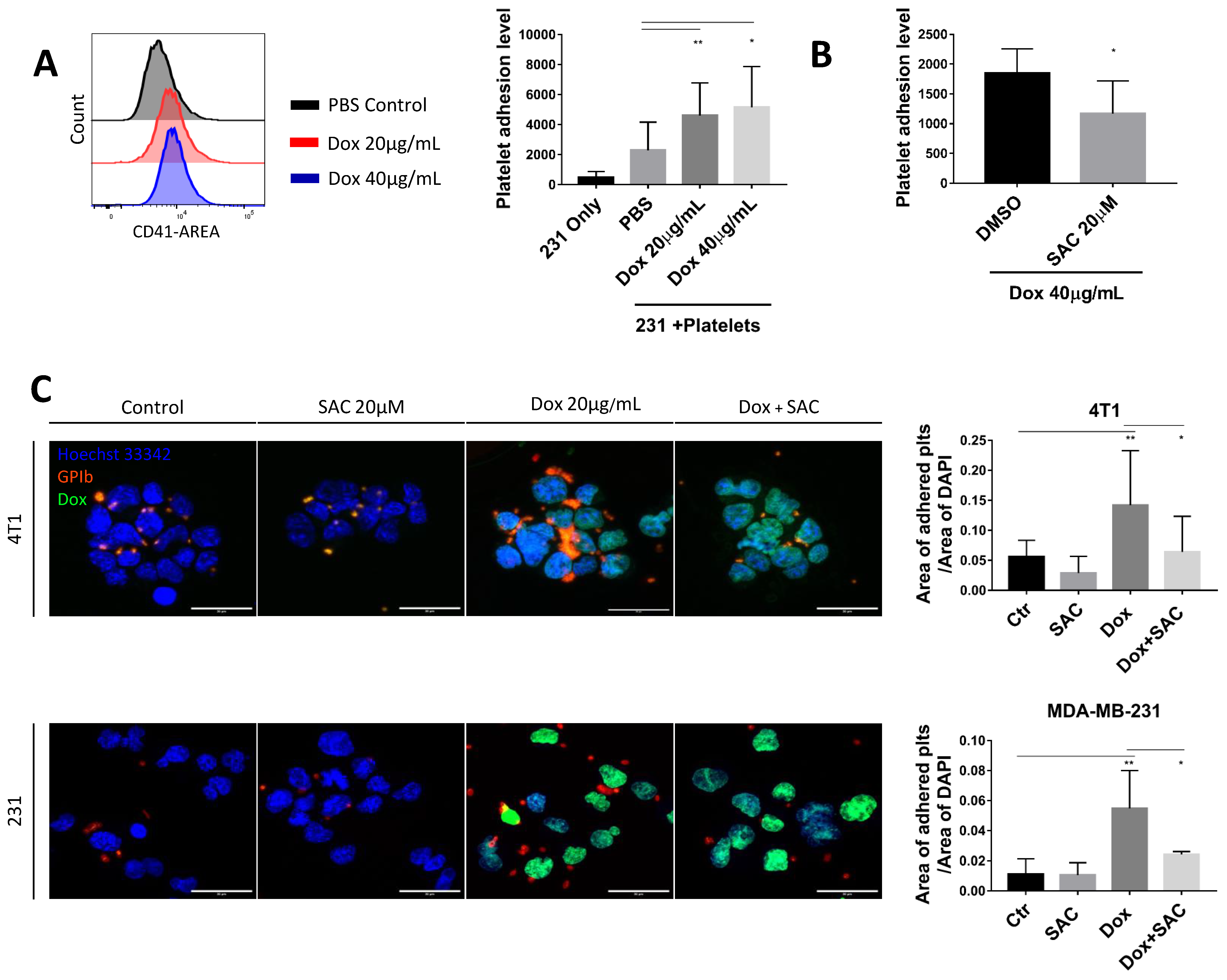
2.2. SAC Inhibited Cancer-Platelet Interaction Enhanced by Dox
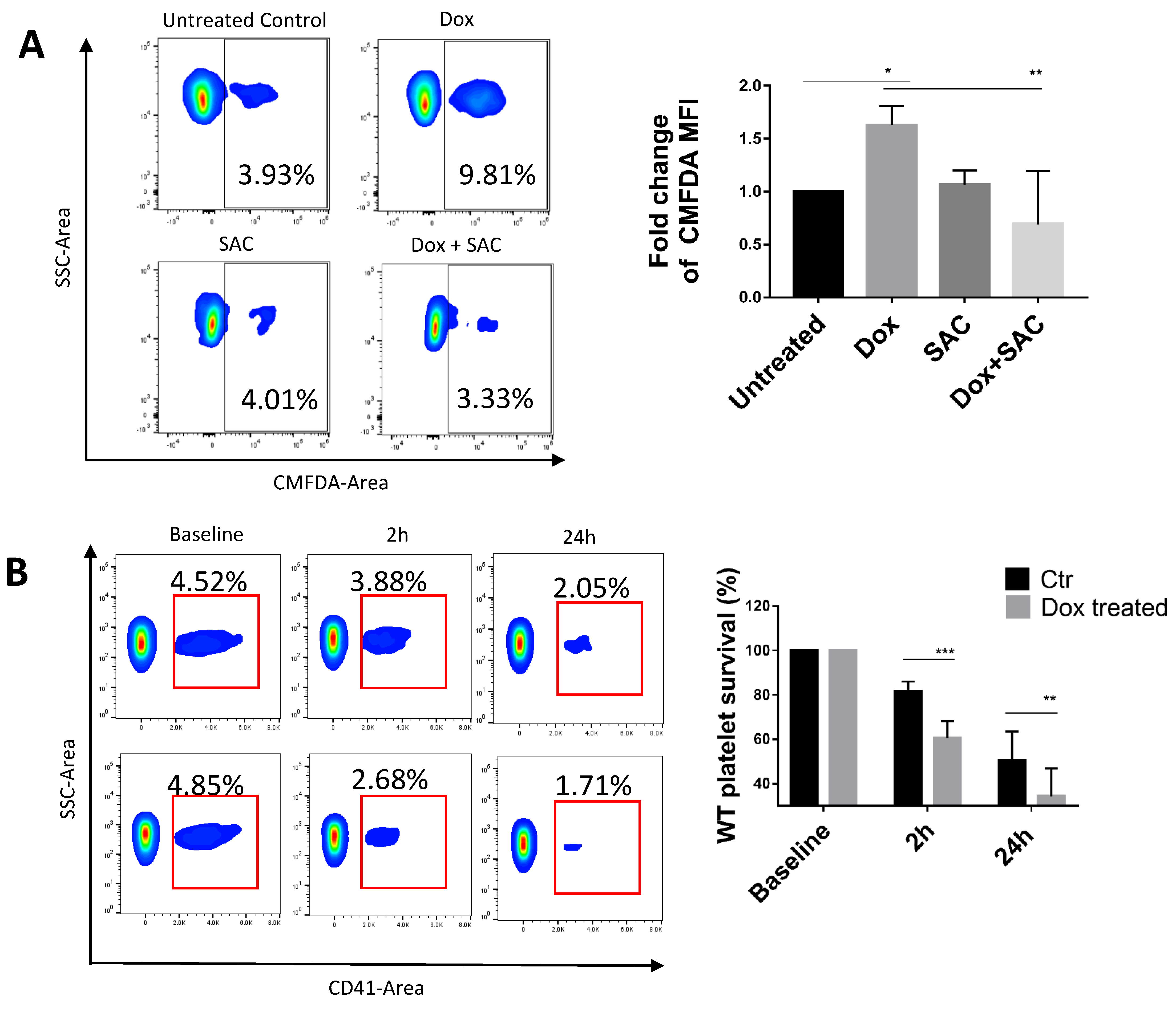
2.3. SAC Protected Platelets from Macrophage Phagocytosis
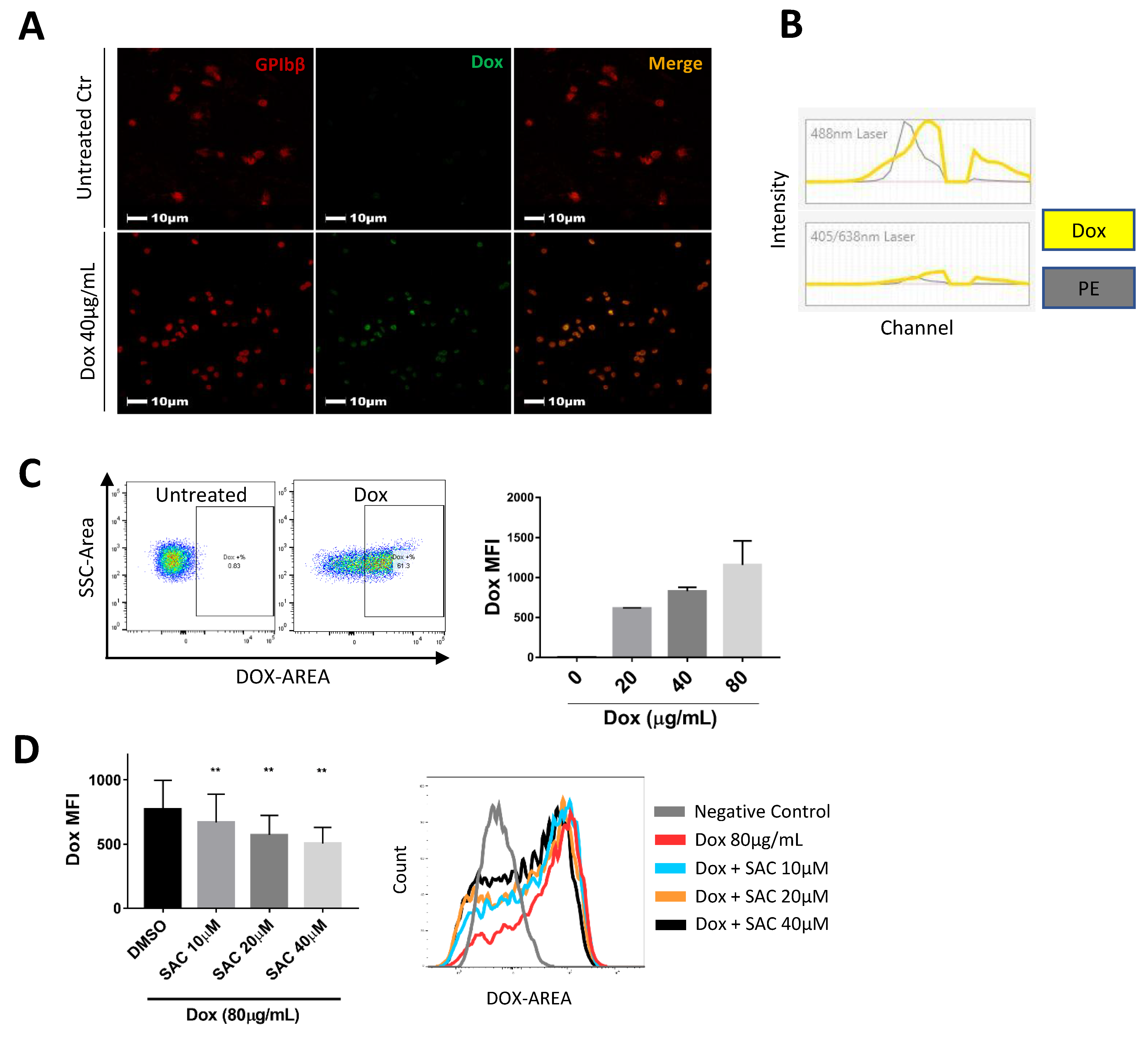
2.4. SAC Reduced Dox Uptake by Platelets
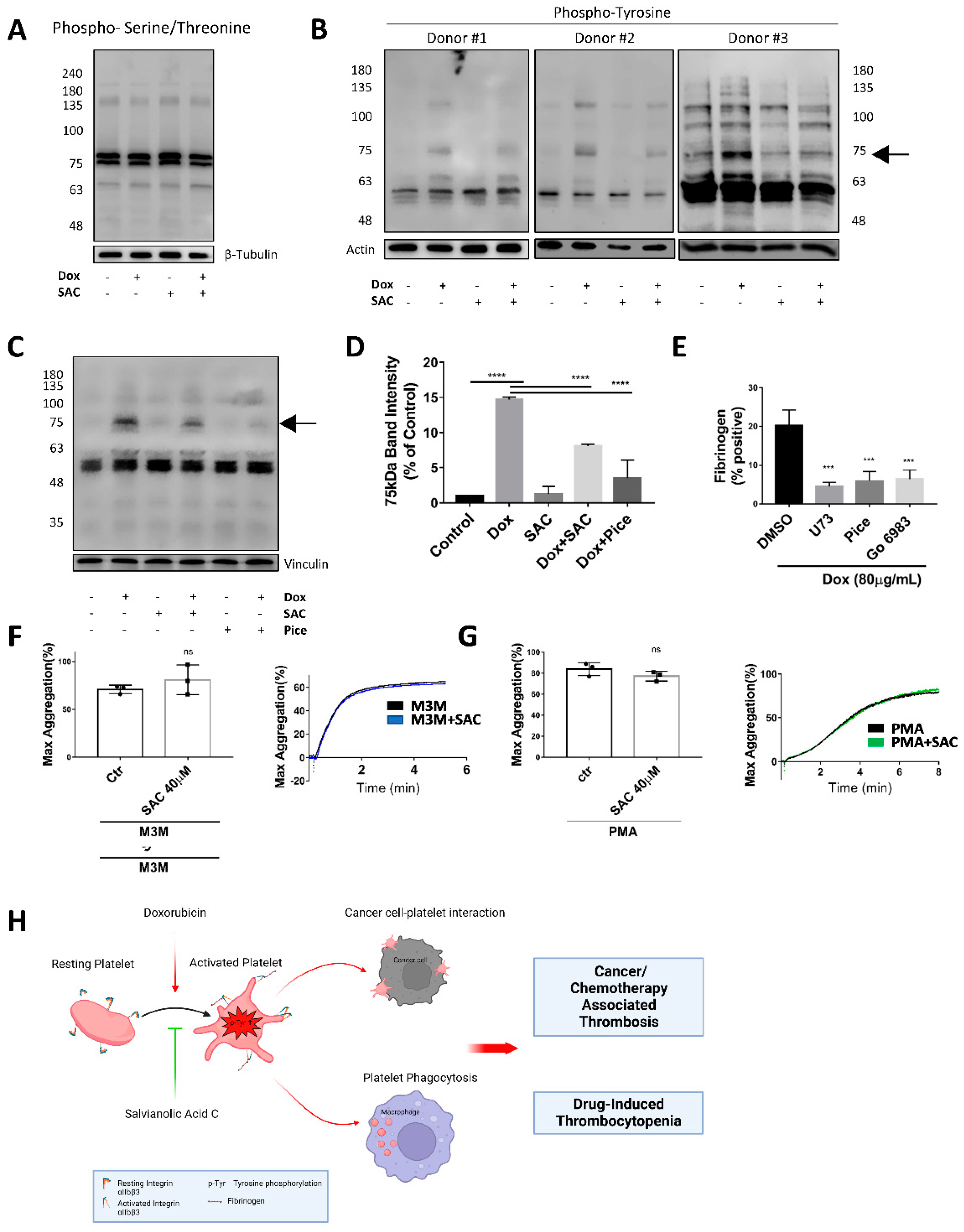
2.5. SAC Ameliorated Dox-Induced Increase in Tyrosine Phosphorylation of Platelet Protein
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Mice
4.3. Platelet Aggregation
4.4. Preparation of Human and Mouse Platelets
4.5. Dox/SAC Treatment of Platelets
4.6. Measurement of Platelet Adhesion to Cancer Cell by Flow Cytometry
4.7. Measurement of Platelet and Cancer Cell Interaction by Immunofluorescent Staining
4.8. Determination of Platelet Activation by Flow Cytometry
4.9. Platelet Spreading on Immobilized Fibrinogen
4.10. Preparation of Total Platelet Lysate Protein for Western Blot
4.11. Evaluation of Platelet Phagocytosis
4.12. Platelet Survival Assay
4.13. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
4.14. UV-Vis Measurements
4.15. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, X.R.; Zhang, D.; Oswald, B.E.; Carrim, N.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lavalle, C.; McKeown, T.; Marshall, A.H.; et al. Platelets are versatile cells: New discoveries in hemostasis, thrombosis, immune responses, tumor metastasis and beyond. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016, 53, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefrancais, E.; Ortiz-Munoz, G.; Caudrillier, A.; Mallavia, B.; Liu, F.; Sayah, D.M.; Thornton, E.E.; Headley, M.B.; David, T.; Coughlin, S.R.; et al. The lung is a site of platelet biogenesis and a reservoir for haematopoietic progenitors. Nature 2017, 544, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggeri, Z.M.; Mendolicchio, G.L. Interaction of von Willebrand factor with platelets and the vessel wall. Hamostaseologie 2015, 35, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jackson, S.P. The growing complexity of platelet aggregation. Blood 2007, 109, 5087–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Reheman, A.; Chen, P.; Zhu, G.; Hynes, R.O.; Freedman, J.; Wagner, D.D.; Ni, H. Fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor-independent platelet aggregation in vitro and in vivo. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 2230–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Denis, C.V.; Subbarao, S.; Degen, J.L.; Sato, T.N.; Hynes, R.O.; Wagner, D.D. Persistence of platelet thrombus formation in arterioles of mice lacking both von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen. J. Clin. Invest. 2000, 106, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reheman, A.; Yang, H.; Zhu, G.; Jin, W.; He, F.; Spring, C.M.; Bai, X.; Gross, P.L.; Freedman, J.; Ni, H. Plasma fibronectin depletion enhances platelet aggregation and thrombus formation in mice lacking fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor. Blood 2009, 113, 1809–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Reheman, A.; Spring, C.M.; Kalantari, J.; Marshall, A.H.; Wolberg, A.S.; Gross, P.L.; Weitz, J.I.; Rand, M.L.; Mosher, D.F.; et al. Plasma fibronectin supports hemostasis and regulates thrombosis. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 124, 4281–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.R.; Hoffman, M.; Monroe, D.M. A cell-based model of thrombin generation. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2006, 32 (Suppl. 1), 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gallant, R.C.; Ni, H. Extracellular matrix proteins in the regulation of thrombus formation. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2016, 23, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.P. Arterial thrombosis—Insidious, unpredictable and deadly. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1423–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ni, H. Fibronectin maintains the balance between hemostasis and thrombosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 3265–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.; Freedman, J. Platelets in hemostasis and thrombosis: Role of integrins and their ligands. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2003, 28, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdol Razak, N.B.; Jones, G.; Bhandari, M.; Berndt, M.C.; Metharom, P. Cancer-Associated Thrombosis: An Overview of Mechanisms, Risk Factors, and Treatment. Cancers 2018, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khorana, A.A.; Mackman, N.; Falanga, A.; Pabinger, I.; Noble, S.; Ageno, W.; Moik, F.; Lee, A.Y.Y. Cancer-associated venous thromboembolism. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2022, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imenez Silva, P.H.; Camara, N.O.; Wagner, C.A. Role of proton-activated G protein-coupled receptors in pathophysiology. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 323, C400–C414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meikle, C.K.; Kelly, C.A.; Garg, P.; Wuescher, L.M.; Ali, R.A.; Worth, R.G. Cancer and Thrombosis: The Platelet Perspective. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.P.; Hisada, Y.M.; Kasthuri, R.S.; Reeves, B.N.; Mackman, N. Cancer Therapy-Associated Thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2021, 41, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorana, A.A.; Francis, C.W.; Culakova, E.; Kuderer, N.M.; Lyman, G.H. Thromboembolism is a leading cause of death in cancer patients receiving outpatient chemotherapy. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 632–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniak, S.; Phungphong, S.; Cheng, Z.; Jensen, B.C. Novel Mechanisms of Anthracycline-Induced Cardiovascular Toxicity: A Focus on Thrombosis, Cardiac Atrophy, and Programmed Cell Death. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 817977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Tan, R.; Liao, J.; Hao, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xia, Y. Doxorubicin contributes to thrombus formation and vascular injury by interfering with platelet function. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020, 319, H133–H143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matera, C.; Falzarano, C.; Vacca, C.; Falciani, M.; Rossi, F. Effects of some antineoplastic drugs (vincristine, doxorubicin and epirubicin) on human platelet aggregation. J. Med. 1994, 25, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lim, K.M.; Noh, J.Y.; Kim, K.; Kang, S.; Chang, Y.K.; Shin, S.; Chung, J.H. Doxorubicin-induced platelet procoagulant activities: An important clue for chemotherapy-associated thrombosis. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 124, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Xie, R.; Liu, R.; Lu, Y. Mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species play an important role in Doxorubicin-induced platelet apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 11087–11100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, J.H.; Hong, C.Y. Salvianolic acids: Small compounds with multiple mechanisms for cardiovascular protection. J. Biomed. Sci. 2011, 18, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Song, J.; Du, L.; Zhang, L.; Qiang, G.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Fang, L. Chemical and pharmacological research on the polyphenol acids isolated from Danshen: A review of salvianolic acids. Adv. Pharmacol. 2020, 87, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.S.; Zeng, C.L.; Zhu, L.J.; Jiang, L.; Li, N.; Hu, H. Salvianolic acid A inhibits platelet activation and arterial thrombosis via inhibition of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Chang, L.; Zhang, B.; Lu, M.; Wang, X.; Orgah, J.O.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Yang, J.; Fan, G.; et al. Specific Combination of Salvianolic Acids As Core Active Ingredients of Danhong Injection for Treatment of Arterial Thrombosis and Its Derived Dry Gangrene. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Lim, K.M.; Kim, K.Y.; Bae, O.N.; Noh, J.Y.; Chung, S.M.; Shin, S.; Yun, Y.P.; Chung, J.H. Doxorubicin-induced platelet cytotoxicity: A new contributory factor for doxorubicin-mediated thrombocytopenia. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 1172–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Aharon, I.; Bar Joseph, H.; Tzabari, M.; Shenkman, B.; Farzam, N.; Levi, M.; Shalgi, R.; Stemmer, S.M.; Savion, N. Doxorubicin-induced vascular toxicity—Targeting potential pathways may reduce procoagulant activity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulop, Z.; Gref, R.; Loftsson, T. A permeation method for detection of self-aggregation of doxorubicin in aqueous environment. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menozzi, M.; Valentini, L.; Vannini, E.; Arcamone, F. Self-association of doxorubicin and related compounds in aqueous solution. J. Pharm. Sci. 1984, 73, 766–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, E.; Furuya, K.; Ueno, H.; Kuroda, T.; Moriyama, M.; Kondo, A. Visible Absorption and Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies on the Self-Association of Doxorubicin in Aqueous Solution. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1991, 39, 1009–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Perez-Arnaiz, C.; Busto, N.; Leal, J.M.; Garcia, B. New insights into the mechanism of the DNA/doxorubicin interaction. J. Phys. Chem. B 2014, 118, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari, S.; Osei, E.; Maftoon, N. Interactions of platelets with circulating tumor cells contribute to cancer metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 15477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, L.J.; Felding-Habermann, B. Contribution of platelets to tumour metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, J.S.; Talmage, K.E.; Massari, J.V.; La Jeunesse, C.M.; Flick, M.J.; Kombrinck, K.W.; Jirouskova, M.; Degen, J.L. Platelets and fibrin(ogen) increase metastatic potential by impeding natural killer cell-mediated elimination of tumor cells. Blood 2005, 105, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.R.; Yousef, G.M.; Ni, H. Cancer and platelet crosstalk: Opportunities and challenges for aspirin and other antiplatelet agents. Blood 2018, 131, 1777–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paridaens, R.; Biganzoli, L.; Bruning, P.; Klijn, J.G.; Gamucci, T.; Houston, S.; Coleman, R.; Schachter, J.; Van Vreckem, A.; Sylvester, R.; et al. Paclitaxel versus doxorubicin as first-line single-agent chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer: A European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Randomized Study with cross-over. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saphner, T.; Tormey, D.C.; Gray, R. Venous and arterial thrombosis in patients who received adjuvant therapy for breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1991, 9, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, M.N.; Gent, M.; Hirsh, J.; Arnold, A.; Goodyear, M.D.; Hryniuk, W.; De Pauw, S. The thrombogenic effect of anticancer drug therapy in women with stage II breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 1988, 318, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badlou, B.A.; Wu, Y.P.; Smid, W.M.; Akkerman, J.W. Platelet binding and phagocytosis by macrophages. Transfusion 2006, 46, 1432–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunapuli, S.P.; Bhavanasi, D.; Kostyak, J.C.; Manne, B.K. Platelet Signaling: Protein Phosphorylation. In Platelets in Thrombotic and Non-Thrombotic Disorders: Pathophysiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics: An Update; Gresele, P., Kleiman, N.S., Lopez, J.A., Page, C.P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Delaney, M.K.; O’Brien, K.A.; Du, X. Signaling during platelet adhesion and activation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 2341–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinstein, M.B.; Pumiglia, K.; Lau, L.F. Tyrosine phosphorylation in platelets: Its regulation and possible roles in platelet functions. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1993, 344, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; Zhu, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Deng, H.; et al. Platelet integrin alphaIIbbeta3: Signal transduction, regulation, and its therapeutic targeting. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.R.; Wang, Y.; Adili, R.; Ju, L.; Spring, C.M.; Jin, J.W.; Yang, H.; Neves, M.A.D.; Chen, P.; Yang, Y.; et al. Apolipoprotein A-IV binds alphaIIbbeta3 integrin and inhibits thrombosis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reheman, A.; Gross, P.; Yang, H.; Chen, P.; Allen, D.; Leytin, V.; Freedman, J.; Ni, H. Vitronectin stabilizes thrombi and vessel occlusion but plays a dual role in platelet aggregation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Reddy, E.C.; Carrim, N.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.R.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Ma, L.; et al. The integrin PSI domain has an endogenous thiol isomerase function and is a novel target for antiplatelet therapy. Blood 2017, 129, 1840–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dole, V.S.; Bergmeier, W.; Eichenberger, S.C.; Wagner, D.D. Downregulation of P-Selectin from Activated Platelets Involves Both Receptor Internalization and Shedding upon Binding to PSGL-1. Blood 2005, 106, 2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Acedo, A.L.; Langiu, M.; Crescence, L.; Mege, D.; Dubois, C.; Panicot-Dubois, L. Platelet and Cancer-Cell Interactions Modulate Cancer-Associated Thrombosis Risk in Different Cancer Types. Cancers 2022, 14, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Wang, L.; Agyin, J.; Tang, Y.; Lin, S.; Yeh, I.T.; De, K.; Sun, L.Z. Doxorubicin in combination with a small TGFbeta inhibitor: A potential novel therapy for metastatic breast cancer in mouse models. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Chang, B.; Li, Q.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L. Redox-Responsive Dual Drug Delivery Nanosystem Suppresses Cancer Repopulation by Abrogating Doxorubicin-Promoted Cancer Stemness, Metastasis, and Drug Resistance. Adv. Sci. (Weinh.) 2019, 6, 1801987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, S.; Shamseddine, A.A.; Newcomb, B.; Chavez, R.S.; Panzner, T.D.; Lee, A.H.; Canals, D.; Okeoma, C.M.; Clarke, C.J.; Hannun, Y.A. Sublethal doxorubicin promotes migration and invasion of breast cancer cells: Role of Src Family non-receptor tyrosine kinases. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachet, C.; Hanau, D.; Spehner, D.; Brisson, C.; Garaud, J.C.; Schmitt, D.A.; Ohlmann, P.; Cazenave, J.P. Alpha IIb beta 3 integrin dissociation induced by EDTA results in morphological changes of the platelet surface-connected canalicular system with differential location of the two separate subunits. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 120, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Yu, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, C.; Li, M. Dynamic trajectory of platelet counts after the first cycle of induction chemotherapy in AML patients. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, Y.; Suzuki-Inoue, K.; Inoue, O. Platelet receptors activated via mulitmerization: Glycoprotein VI, GPIb-IX-V, and CLEC-2. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11 (Suppl. 1), 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denslow, A.; Switalska, M.; Jarosz, J.; Papiernik, D.; Porshneva, K.; Nowak, M.; Wietrzyk, J. Clopidogrel in a combined therapy with anticancer drugs-effect on tumor growth, metastasis, and treatment toxicity: Studies in animal models. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.H.; Bhatt, D.L.; Topol, E.J. Aspirin and clopidogrel resistance: An emerging clinical entity. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, J.J.; Wolfe, R.; Woods, R.L.; Tonkin, A.M.; Donnan, G.A.; Nelson, M.R.; Reid, C.M.; Lockery, J.E.; Kirpach, B.; Storey, E.; et al. Effect of Aspirin on Cardiovascular Events and Bleeding in the Healthy Elderly. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Hu, H.Y.; Luo, J.C.; Peng, Y.L.; Hou, M.C.; Lin, H.C.; Lee, F.Y. Risk factors of gastrointestinal bleeding in clopidogrel users: A nationwide population-based study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.Y.; Fu, F.H.; Yang, M.Y.; Xu, H.; Zhang, A.H.; Liu, K. Antiplatelet and antithrombotic activities of salvianolic acid A. Thromb. Res. 2010, 126, e17–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ye, J.; Wen, Z.; Ding, J.; Kunapuli, S.P.; Luo, X.; Ding, Z. Salvianolic acid B inhibits platelets as a P2Y12 antagonist and PDE inhibitor: Evidence from clinic to laboratory. Thromb. Res. 2014, 134, 866–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.K.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.K.; Feng, Z.Y.; Xie, T.; Du, G.H. Pharmacokinetics of salvianolic acid A after single intravenous administration in Rhesus monkey. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2015, 50, 1142–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.T.; Chen, Y.F.; Hsieh, Y.J.; Jaw, I.; Shiao, M.S.; Tsai, T.H. Bioavailability of salvianolic acid B in conscious and freely moving rats. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 326, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.Y.; Song, Z.Y.; Gan, H.L.; Zheng, M.H.; Liu, Q.; Meng, X.T.; Pan, T.; Li, Z.Y.; Peng, R.X.; Liu, K.; et al. Non-clinical safety evaluation of salvianolic acid A: Acute, 4-week intravenous toxicities and genotoxicity evaluations. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2022, 23, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Tang, L.; Yi, Q. Salvianolic Acids: Potential Source of Natural Drugs for the Treatment of Fibrosis Disease and Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, B.; Zhao, F.; Wang, H.; Xu, H. Nanomicelles co-loaded with doxorubicin and salvianolic acid A for breast cancer chemotherapy. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2022, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.-Y.; Yang, M.-Y.; Qi, D.; Zhang, Z.-K.; Zhu, L.; Shang-Guan, X.-X.; Liu, K.; Xu, H.; Che, X. Salvianolic acid A as a multifunctional agent ameliorates doxorubicin-induced nephropathy in rats. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Pan, Y.; Cai, R.; Guo, S.; Zhang, X.; Xue, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Gu, Y.; et al. Salvianolic acid A increases the accumulation of doxorubicin in brain tumors through Caveolae endocytosis. Neuropharmacology 2020, 167, 107980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emambokus, N.R.; Frampton, J. The glycoprotein IIb molecule is expressed on early murine hematopoietic progenitors and regulates their numbers in sites of hematopoiesis. Immunity 2003, 19, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Lang, S.; Zhai, Z.; Li, L.; Kahr, W.H.; Chen, P.; Brkic, J.; Spring, C.M.; Flick, M.J.; Degen, J.L.; et al. Fibrinogen is required for maintenance of platelet intracellular and cell-surface P-selectin expression. Blood 2009, 114, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Liu, M.; Tian, H.; Li, J.; Xu, R.; Mwangi, J.; Lu, Q.; Hao, X.; Lai, R. Conformation-Specific Blockade of alphaIIbbeta3 by a Non-RGD Peptide to Inhibit Platelet Activation without Causing Significant Bleeding and Thrombocytopenia. Thromb. Haemost. 2020, 120, 1432–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wang, G.; Xu, R.; Shen, C.; Ni, H.; Lai, R. Soy Isoflavones Inhibit Both GPIb-IX Signaling and alphaIIbbeta3 Outside-In Signaling via 14-3-3zeta in Platelet. Molecules 2021, 26, 4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Liu, M.; Xu, R.; Wang, G.; Li, J.; Chen, P.; Ma, W.; Mwangi, J.; Lu, Q.; Duan, Z.; et al. The 14-3-3zeta-c-Src-integrin-beta3 complex is vital for platelet activation. Blood 2020, 136, 974–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Liu, M.; Mackeigan, D.T.; Chen, Z.Y.; Chen, P.; Karakas, D.; Li, J.; Norris, P.A.A.; Li, J.; Deng, Y.; et al. Viper venoms drive the macrophages and hepatocytes to sequester and clear platelets: Novel mechanism and therapeutic strategy for venom-induced thrombocytopenia. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 3589–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; van der Wal, D.E.; Zhu, G.; Xu, M.; Yougbare, I.; Ma, L.; Vadasz, B.; Carrim, N.; Grozovsky, R.; Ruan, M.; et al. Desialylation is a mechanism of Fc-independent platelet clearance and a therapeutic target in immune thrombocytopenia. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, P.A.A.; Kaur, G.; Khan, R.; Zhu, G.; Ni, H.; Lazarus, A.H. Anti-inflammatory activity of CD44 antibodies in murine immune thrombocytopenia is mediated by Fcgamma receptor inhibition. Blood 2021, 137, 2114–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, W.; Rousseau, Z.; Slavkovic, S.; Shen, C.; Yousef, G.M.; Ni, H. Doxorubicin-Induced Platelet Activation and Clearance Relieved by Salvianolic Acid Compound: Novel Mechanism and Potential Therapy for Chemotherapy-Associated Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121444
Ma W, Rousseau Z, Slavkovic S, Shen C, Yousef GM, Ni H. Doxorubicin-Induced Platelet Activation and Clearance Relieved by Salvianolic Acid Compound: Novel Mechanism and Potential Therapy for Chemotherapy-Associated Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(12):1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121444
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Wenjing, Zackary Rousseau, Sladjana Slavkovic, Chuanbin Shen, George M. Yousef, and Heyu Ni. 2022. "Doxorubicin-Induced Platelet Activation and Clearance Relieved by Salvianolic Acid Compound: Novel Mechanism and Potential Therapy for Chemotherapy-Associated Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 12: 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121444
APA StyleMa, W., Rousseau, Z., Slavkovic, S., Shen, C., Yousef, G. M., & Ni, H. (2022). Doxorubicin-Induced Platelet Activation and Clearance Relieved by Salvianolic Acid Compound: Novel Mechanism and Potential Therapy for Chemotherapy-Associated Thrombosis and Thrombocytopenia. Pharmaceuticals, 15(12), 1444. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15121444




