Baloxavir Marboxil: An Original New Drug against Influenza
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Baloxavir Marboxil
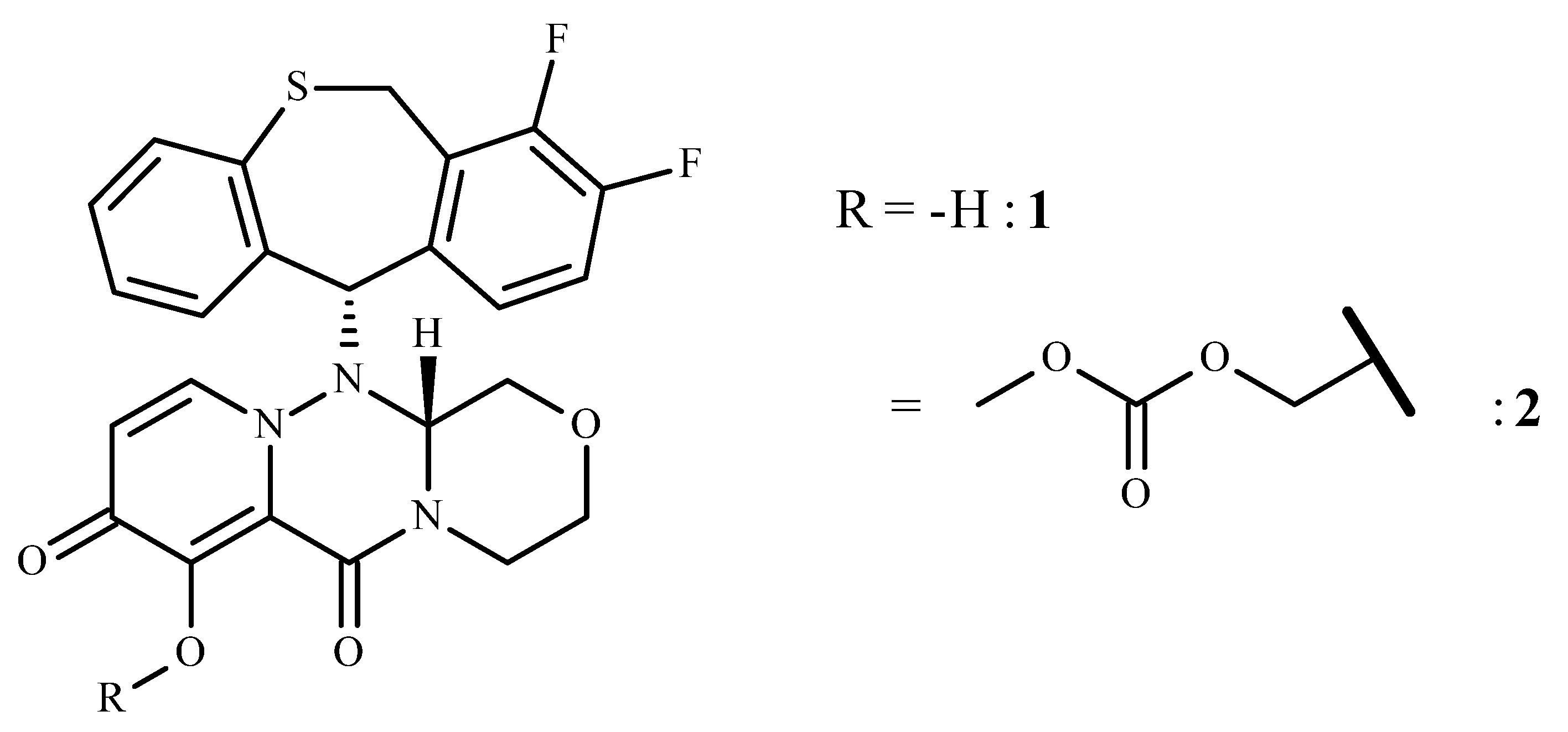
2.1. Name, Structure, Chemistry, and Rationale Development
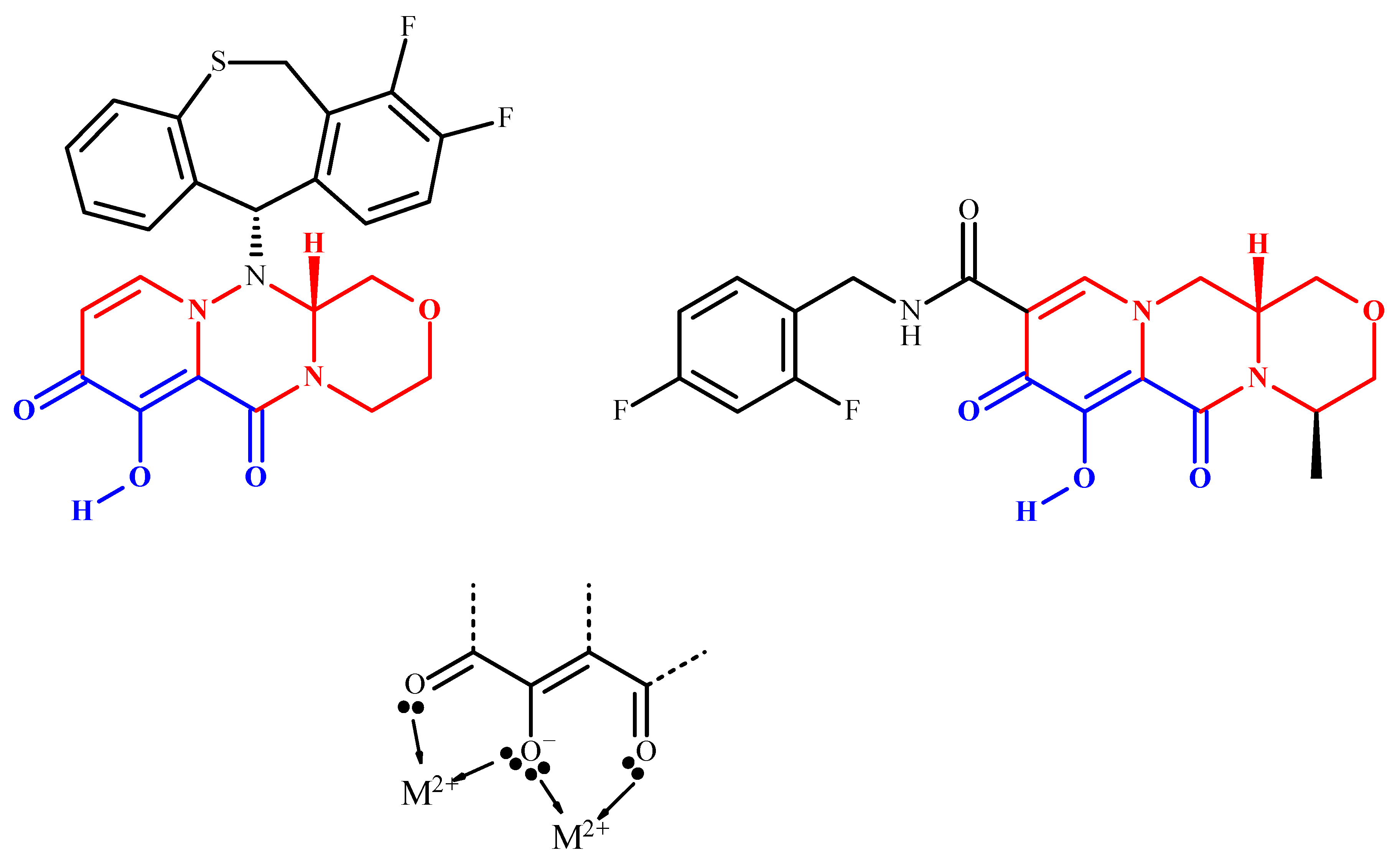
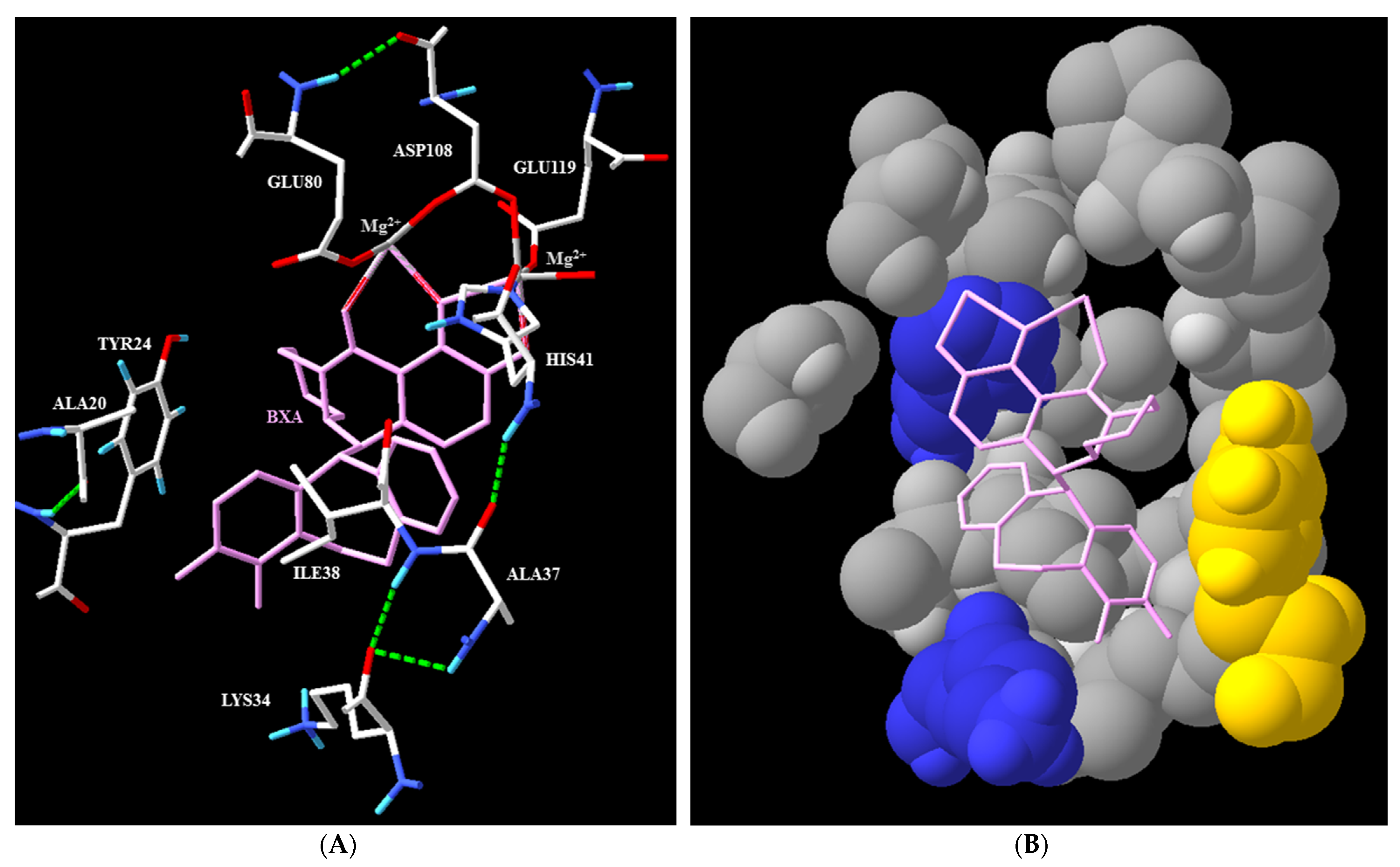
2.2. Mechanism of Action and In Vitro Characterization
2.3. Preclicinal and Clinical Trials, Toxicology, and Pharmacokinetics
2.4. Uses
2.5. Medical Interest
3. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawai, M.; Tomita, K.; Akiyama, T.; Okano, A.; Miyagawa, M. Preparation of Polycyclic Pyridone Derivatives as Cap-Dependent Endonuclease (CEN) Inhibitors and Prodrugs Thereof. Jpn. Tokkyo Koho JP5971830, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shishido, T.; Noshi, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Kitano, M. Medicine for Treating Influenza Comprising a Combination of Cap-Dependent Endonuclease Inhibitor with Anti-Influenza Drug. PCT Int. Appl. 201803246, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Noshi, T.; Kitano, M.; Taniguchi, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Omoto, S.; Baba, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Ishida, K.; Kushima, Y.; Hattori, K.; et al. In vitro characterization of baloxavir acid, a first-in-class cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor of the influenza virus polymerase PA subunit. Antivir. Res. 2018, 160, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omoto, S.; Speranzini, V.; Hashimoto, T.; Noshi, T.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kawai, M.; Kawaguchi, K.; Uehara, T.; Shishido, T.; Naito, A.; et al. Characterization of influenza virus variants induced by treatment with the endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir marboxil. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszalka, P.; Farrukee, R.; Mifsud, E.; Vijaykrishna, D.; Hurt, A.C. A rapid pyrosequencing assay for the molecular detection of influenza viruses with reduced baloxavir susceptibility due to PA/I38X amino acid substitutions. Influenza Other Respir. Viruses 2020, 14, 460–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, D.L. Review of the Patent Literature: Synthesis and Final Forms of Antiviral Drugs Tecovirimat and Baloxavir Marboxil. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2019, 23, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, D.; Elderfield, R.A.; Barclay, W.S. Molecular studies of influenza B virus in the reverse genetics era. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Wen, L.; Zhou, J. Inhibitors of Influenza A Virus Polymerase. ACS Infect. Dis. 2018, 4, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, B.; Kang, D.; Huang, B.; Liu, X.; Zhan, P. Inhibitors of Influenza Virus Polymerase Acidic (PA) Endonuclease: Contemporary Developments and Perspectives. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 3533–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, N.; Koshimichi, H.; Ishibashi, T.; Wajima, T. Evaluation of Drug-Drug Interaction Potential between Baloxavir Marboxil and Oseltamivir in Healthy Subjects. Clin. Drug Investig. 2018, 38, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heo, Y.-A. Baloxavir: First Global Approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, A.C.-Y. Influenza virus: A master tactician in innate immune evasion and novel therapeutic interventions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 743/1–743/11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takashita, E.; Daniels, R.S.; Fujisaki, S.; Gregory, V.; Gubareva, L.V.; Huang, W.; Hurt, A.C.; Lackenby, A.; Nguyen, H.T.; Pereyaslov, D.; et al. Global update on the susceptibilities of human influenza viruses to neuraminidase inhibitors and the cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir, 2017–2018. Antivir. Res. 2020, 175, 104718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszalka, P.; Tilmanis, D.; Roe, M.; Vijaykrishna, D.; Hurt, A.C. Baloxavir marboxil susceptibility of influenza viruses from the Asia-Pacific, 2012–2018. Antivir. Res. 2019, 164, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, F.G.; Sugaya, N.; Hirotsu, N.; Lee, N.; de Jong, M.D.; Hurt, A.C.; Ishida, T.; Sekino, H.; Yamada, K.; Portsmouth, S.; et al. Baloxavir marboxil for uncomplicated influenza in adults and adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukao, K.; Noshi, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Kitano, M.; Ando, Y.; Noda, T.; Baba, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Higuchi, N.; Ikeda, M.; et al. Combination treatment with the cap-dependent endonuclease inhibitor baloxavir marboxil and a neuraminidase inhibitor in a mouse model of influenza A virus infection. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koshimichi, H.; Ishibashi, T.; Kawaguchi, N.; Sato, C.; Kawasaki, A.; Wajima, T. Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of the Novel Anti-influenza Agent Baloxavir Marboxil in Healthy Adults: Phase I Study Findings. Clin. Drug Investig. 2018, 38, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Data Available on the RxList Website and in Xofluza® Package Insert. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/documents/product-information/xofluza-epar-product-information_en.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2021).
- Koshimichi, H.; Tsuda, Y.; Ishibashi, T.; Wajima, T. Population Pharmacokinetic and Exposure-Response Analyses of Baloxavir Marboxil in Adults and Adolescents Including Patients with Influenza. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1896–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ison, M.G.; Portsmouth, S.; Yoshida, Y.; Shishido, T.; Mitchener, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Uehara, T.; Hayden, F.G. Early treatment with baloxavir marboxil in high-risk adolescent and adult outpatients with uncomplicated influenza (CAPSTONE-2): A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1204–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, N. Sixty seconds on baloxavir. BMJ 2018, 363, k4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.-C.; Lai, C.-C.; Wang, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Wang, C.-Y. Clinical efficacy and safety of baloxavir marboxil in the treatment of influenza: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2021, 54, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, N.; Morioka, I.; Nakano, T.; Furukawa, M.; Tanaka, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Manabe, A. Clinical and virological outcomes with baloxavir compared with oseltamivir in pediatric patients aged 6 to <12 years with in-fluenza: An open-label, randomized, active-controlled trial protocol. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 777. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, Y.; Kawai, N.; Tani, N.; Bando, T.; Takasaki, Y.; Shindo, S.; Ikematsu, H. Virological and clinical outcomes in outpatients treated with baloxavir or oseltamivir: A Japanese multicenter study in the 2019-2020 influenza season. Antivir. Res. 2021, 192, 105092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-W.; Lin, S.-H.; Wang, L.-C.; Chiu, H.-Y.; Lee, J.-A. Comparison of Antiviral Agents for Seasonal Influenza Outcomes in Healthy Adults and Children: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2119151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashita, E. Influenza polymerase inhibitors: Mechanisms of action and resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2021, 11, a038687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, M.; Takashita, E.; Katayose, M.; Nemoto, K.; Sakai, N.; Fujisaki, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Hosoya, M. Detection of variants with reduced baloxavir marboxil and oseltamivir susceptibility in children with influenza A during the 2019–2020 influenza season. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 222, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Haas, E.C.; Luijendijk, H.J. Baloxavir for influenza: Enrichment obscured lack of effect in North-American adults. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 62, e8–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Haas, E.C.; Luijendijk, H.J. Baloxavir for influenza: Enrichment obscured lack of effect in North-American adults. Author’s reply. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 72, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; De Clercq, E. Therapeutic options for the 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Codes and Completion Dates 2 | Title | Status | Main Clinical Results—Trial Characteristics 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02954354 (4/17) [15] | A study of S-033188 (BXM) compared with placebo or OMV in otherwise healthy patients with influenza (CAPSTONE 1) | Completed | Sponsor: Shionogi (Japan). Countries: not provided. Main outcomes: see [15]. |
| 2020-000696-20 (3/19) | A phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to confirm the efficacy of a single dose of BXM in the prevention of influenza virus infection | Completed | Sponsor: Shionogi (Japan). Country: Japan. 749 patients reenrolled: 374 received BXM and 375 received placebo. Main outcomes: proportion of subjects who are infected with influenza virus (RT-PCR positive), and present with fever and at least one respiratory symptom. |
| 2018-002169-21 (4/19) | A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, active (OMV)-controlled study to assess the safety, PK, and efficacy of BXM in otherwise healthy pediatric patients 1 to <12 years of age with influenza-like symptoms | Completed | Not available yet. Sponsor: Hoffmann-La Roche (Switzerland). Countries: USA. 173 patients enrolled in two groups: 115 received BXM and 58 received OMV. Main outcomes: percentage of participants with adverse events and serious adverse events and PK data. |
| NCT03629184 (4/19) | Study to assess the safety, PK, and efficacy of BXM in healthy pediatric participants with influenza-like symptoms | Completed | Sponsor: Hoffmann-La Roche (USA). Countries: Costa Rica, Israel, Mexico, Poland, Russian Federation, Spain, USA. 173 patients enrolled, 115 in the BXM group, 58 in the OMV group. Main outcomes: PK data, time to alleviation of symptoms, time to cessation of viral shedding. |
| NCT03959332 (7/19) | Study to assess the PK, safety, and tolerability of BXM in healthy Chinese participants (phase I) | Active Not recruiting | Sponsor: Hoffmann-La Roche (China). In collaboration with Shionogi. Country: China. 32 patients enrolled, 16 in two groups (40 and 80 mg). Main outcomes: PK data, adverse effects. |
| NCT02949011 (11/19) [20] | Study of S-033188 (BXM) compared with placebo or OMV in otherwise healthy patients with influenza (CAPSTONE-2) | Completed | Sponsor: Shionogi. Countries: worldwide. Main outcomes: see [20]. |
| 2021-001026-22 (3/20) | An open-label study to assess the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of BXM 2% granules after administration of a single dose to otherwise healthy pediatric patients with influenza | Completed | Sponsor: Shionogi. Countries: Japan. 45 patients enrolled. Divided in two groups: 9 patients (weight < 10 kg) received 2 mg/kg of BXM and 36 (weight ≥ 10 kg and < 20 kg) received 20 mg of BXM. Main outcomes: time to alleviation of influenza illness. |
| NCT03684044 2018-001416-30 (3/20) | A phase III, randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled, multicenter study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of BXM in combination with standard-of-care NI in hospitalized patients with severe influenza | Completed | Sponsor: Hoffmann-La Roche (USA). Countries: worldwide. 363 patients enrolled, 239 in the BXM group, 124 in the placebo group. Main outcomes: clinical improvement and PK data. |
| NCT04141917 (3/21) | Test-and-treat for influenza in homeless shelters | Terminated | Reason of the termination was operational futility. |
| NCT04141930 (4/21) | Pilot of cohort of households for influenza monitoring and evaluation in Seattle (pCHIMES) | Completed | Sponsor: University of Washington (USA). In collaboration with Genentech (USA). Country: USA. 481 patients enrolled in two groups: 302 patients were eligible to receive either 40 or 80 mg single dose oral BXM and 179 were not eligible to receive on-label use of BXM due to age or medical history. Main outcome: symptom onset after drug administration up to 48 h. |
| NCT03653364 (8/22) | Study to assess the safety, PK, and efficacy of BXM in healthy pediatric participants from birth to < 1 year with influenza-like symptoms | Recruiting | Sponsor: Hoffmann-La Roche (USA). Countries: worldwide. Main outcomes: PK data, time to alleviation of symptoms, time to cessation of viral shedding. |
| NCT04327791 (12/22) | Combination therapy with baloxavir and oseltamivir 1 for hospitalized patients with influenza (The COMBO Trial 1) (COMBO 1) | Recruiting | Sponsor: Bassett Healthcare (USA). In collaboration with: Genentech (USA) and Viroclinics Biosciences (the Netherlands). Phases II and III. Main outcomes: time to clearance of viral shedding. |
| NCT03969212 (2/23) | Study to assess the efficacy of BXM versus placebo to reduce onward transmission of influenza A or B in households | Recruiting | Sponsor: Hoffmann-La Roche (USA). Countries: worldwide. Main outcomes: virological transmission by day 5. |
| NCT04712539 (3/23) | BX and OMV for the treatment of severe influenza infection in immunocompromised patients | Not yet recruiting | Sponsor: M.D. Anderson Cancer Center (USA). Country: USA. Main outcomes: changes in viral loads, incidence of complicated hospital stay. |
| NCT05012189 (12/23) | BX versus OMV for nursing home influenza outbreaks | Recruiting | Sponsor: Insight Therapeutics (USA). Country: USA. Main outcomes: To demonstrate the non-inferiority of prophylactic BX vs. OMV to prevent influenza-like illness (ILI) after an index influenza case in nursing homes. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dufrasne, F. Baloxavir Marboxil: An Original New Drug against Influenza. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15010028
Dufrasne F. Baloxavir Marboxil: An Original New Drug against Influenza. Pharmaceuticals. 2022; 15(1):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15010028
Chicago/Turabian StyleDufrasne, François. 2022. "Baloxavir Marboxil: An Original New Drug against Influenza" Pharmaceuticals 15, no. 1: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15010028
APA StyleDufrasne, F. (2022). Baloxavir Marboxil: An Original New Drug against Influenza. Pharmaceuticals, 15(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph15010028





