Synthesis, Characterization, and Anticancer Activity of Benzothiazole Aniline Derivatives and Their Platinum (II) Complexes as New Chemotherapy Agents
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization
2.2. Anticancer Effects and Cytotoxicity
2.3. Selective Antitumor Activity
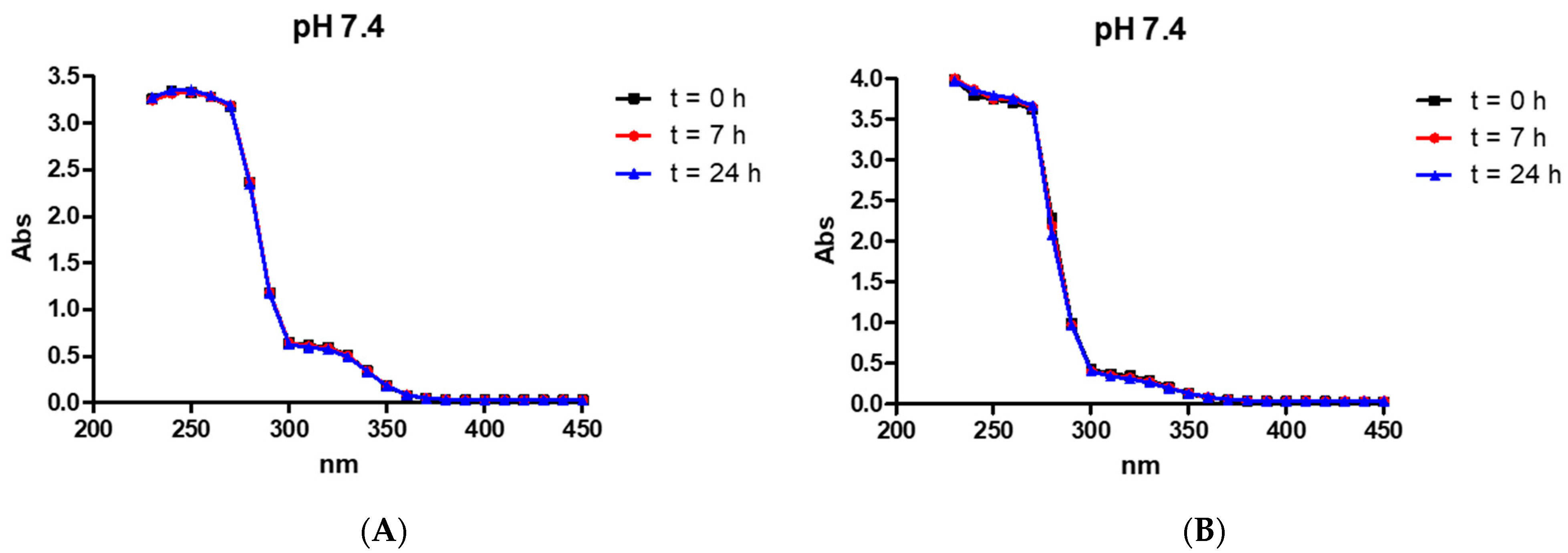
2.4. Stability of the Compounds in an Aqueous Solution
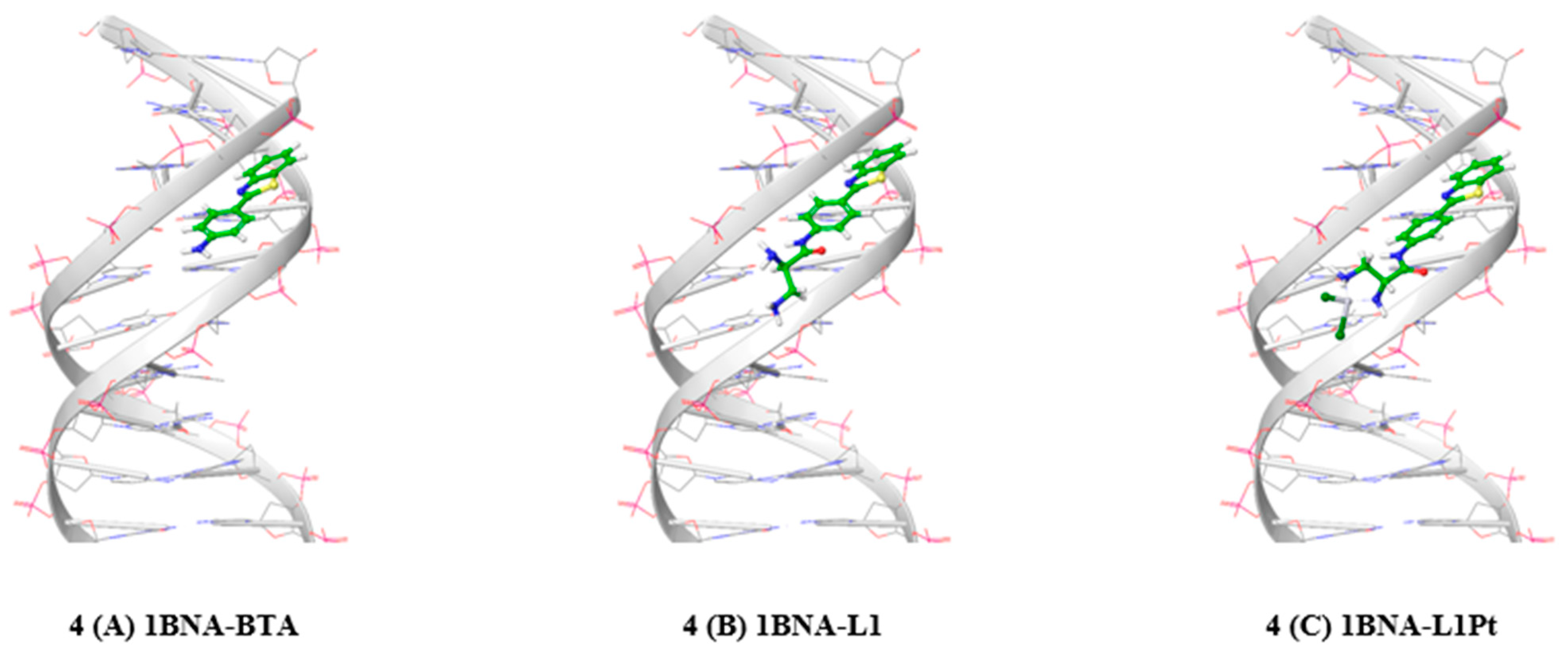
2.5. Protein-Ligand Docking Simulation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Instruments
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization
3.2.1. 2,3-Diamino-N-(4-benzothiazol-2-yl-phenyl)-propionamide (L1)
3.2.2. N-(4-Benzothiazol-2-yl-phenyl)-2,3-bis-[(2-hydroxy-benzylidene)amino] propionamide (L2)
3.2.3. 2-Pyridin-2-yl-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylic acid (4-benzothiazol-2-yl-phenyl)amide (L3)
3.2.4. Synthesis of Complex L1Pt
3.2.5. Synthesis of Complex L2Pt
3.2.6. Synthesis of Complex L3Pt
3.3. Stability of the Compounds in Aqueous Solution
3.4. Cell Culture
3.5. Cell Viability Assay
3.6. Molecular Docking
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BTA | Benzothiazole aniline |
| RT | Room temperature |
| CCK-8 | Cell counting kit-8 |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DI | Deionized |
| SAR | Structure-activity relationship |
| FTIR | Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy |
| MALDI-TOF | Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered solution |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
References
- Olszewski, U.; Hamilton, G. A better platinum-based anticancer drug yet to come? Anti Cancer Agents Med. Chem. Former. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti Cancer Agents 2010, 10, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, T.C.; Suntharalingam, K.; Lippard, S.J. The next generation of platinum drugs: Targeted Pt (II) agents, nanoparticle delivery, and Pt (IV) prodrugs. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3436–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bellamy, W.T. P-glycoproteins and multidrug resistance. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1996, 36, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, R.C.; Lippard, S.J. Inhibition of transcription by platinum antitumor compounds. Metallomics 2009, 1, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Lippard, S.J. Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usanova, S.; Piee-Staffa, A.; Sied, U.; Thomale, J.; Schneider, A.; Kaina, B.; Koberle, B. Cisplatin sensitivity of testis tumour cells is due to deficiency in interstrand-crosslink repair and low ERCC1-XPF expression. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakai, W.; Swisher, E.M.; Karlan, B.Y.; Agarwal, M.K.; Higgins, J.; Friedman, C.; Villegas, E.; Jacquemont, C.; Farrugia, D.J.; Couch, F.J.; et al. Secondary mutations as a mechanism of cisplatin resistance in BRCA2-mutated cancers. Nature 2008, 451, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dempke, W.; Voigt, W.; Grothey, A.; Hill, B.T.; Schmoll, H.J. Cisplatin resistance and oncogenes—A review. Anticancer Drugs 2000, 11, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McWhinney, S.R.; Goldberg, R.M.; McLeod, H.L. Platinum neurotoxicity pharmacogenetics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, Y.; Mao, C.Q.; Chen, S.; Ma, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Combating the drug resistance of cisplatin using a platinum prodrug based delivery system. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 6742–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.M.; Lippard, S.J. Cisplatin: From DNA damage to cancer chemotherapy. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 2001, 67, 93–130. [Google Scholar]
- Wheate, N.J.; Walker, S.; Craig, G.E.; Oun, R. The status of platinum anticancer drugs in the clinic and in clinical trials. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 8113–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chovanec, M.; Abu Zaid, M.; Hanna, N.; El-Kouri, N.; Einhorn, L.H.; Albany, C. Long-term toxicity of cisplatin in germ-cell tumor survivors. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2670–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelland, L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, H.; Loos, W.J.; Eechoute, K.; Verweij, J.; Mathijssen, R.H.; Wiemer, E.A. Drug transporters of platinum-based anticancer agents and their clinical significance. Drug Resist. Updates 2011, 14, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-H.; Chang, J.-Y. New insights into mechanisms of cisplatin resistance: From tumor cell to microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cincinelli, R.; Musso, L.; Dallavalle, S.; Artali, R.; Tinelli, S.; Colangelo, D.; Zunino, F.; De Cesare, M.; Beretta, G.L.; Zaffaroni, N. Design, modeling, synthesis and biological activity evaluation of camptothecin-linked platinum anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 63, 387–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovejoy, K.S.; Todd, R.C.; Zhang, S.; McCormick, M.S.; D’Aquino, J.A.; Reardon, J.T.; Sancar, A.; Giacomini, K.M.; Lippard, S.J. cis-Diammine(pyridine)chloroplatinum(II), a monofunctional platinum(II) antitumor agent: Uptake, structure, function, and prospects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8902–8907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yellol, G.S.; Donaire, A.; Yellol, J.G.; Vasylyeva, V.; Janiak, C.; Ruiz, J. On the antitumor properties of novel cyclometalated benzimidazole Ru(II), Ir(III) and Rh(III) complexes. Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 2013, 49, 11533–11535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.-F.; Bradshaw, T.D.; Wrigley, S.; McCall, C.J.; Lelieveld, P.; Fichtner, I.; Stevens, M.F. Antitumor benzothiazoles. 3. Synthesis of 2-(4-aminophenyl) benzothiazoles and evaluation of their activities against breast cancer cell lines in vitro and in vivo. J. Med. Chem. 1996, 39, 3375–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, T.; Wrigley, S.; Shi, D.; Schultz, R.; Paull, K.; Stevens, M. 2-(4-Aminophenyl) benzothiazoles: Novel agents with selective profiles of in vitro anti-tumour activity. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 77, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, T.; Shi, D.; Schultz, R.; Paull, K.; Kelland, L.; Wilson, A.; Garner, C.; Fiebig, H.; Wrigley, S.; Stevens, M. Influence of 2-(4-aminophenyl) benzothiazoles on growth of human ovarian carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 78, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leong, C.-O.; Gaskell, M.; Martin, E.; Heydon, R.; Farmer, P.; Bibby, M.; Cooper, P.; Double, J.; Bradshaw, T.; Stevens, M. Antitumour 2-(4-aminophenyl) benzothiazoles generate DNA adducts in sensitive tumour cells in vitro and in vivo. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bradshaw, T.; Stevens, M.; Westwell, A. The discovery of the potent and selective antitumour agent 2-(4-amino-3-methylphenyl) benzothiazole (DF 203) and related compounds. Curr. Med. Chem. 2001, 8, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradshaw, T.; Westwell, A. The development of the antitumour benzothiazole prodrug, Phortress, as a clinical candidate. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiyama, E.; Hutchinson, I.; Chua, M.-S.; Stinson, S.F.; Phillips, L.R.; Kaur, G.; Sausville, E.A.; Bradshaw, T.D.; Westwell, A.D.; Stevens, M.F. Antitumor benzothiazoles. 8. Synthesis, metabolic formation, and biological properties of the C-and N-oxidation products of antitumor 2-(4-aminophenyl) benzothiazoles. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 4172–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noolvi, M.N.; Patel, H.M.; Kaur, M. Benzothiazoles: Search for anticancer agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 54, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chakraborty, M.; Cerda-Smith, C.G.; Bratton, R.N.; Maurer, N.E.; Senser, E.M.; Novak, M. Chemistry of Ring-Substituted 4-(Benzothiazol-2-yl) phenylnitrenium Ions from Antitumor 2-(4-Aminophenyl) benzothiazoles. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 6992–7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tzanopoulou, S.; Pirmettis, I.C.; Patsis, G.; Paravatou-Petsotas, M.; Livaniou, E.; Papadopoulos, M.; Pelecanou, M. Synthesis, characterization, and biological evaluation of M (I)(CO) 3 (NNO) complexes (M= Re, 99mTc) conjugated to 2-(4-aminophenyl) benzothiazole as potential breast cancer radiopharmaceuticals. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 5408–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanopoulou, S.; Sagnou, M.; Paravatou-Petsotas, M.; Gourni, E.; Loudos, G.; Xanthopoulos, S.; Lafkas, D.; Kiaris, H.; Varvarigou, A.; Pirmettis, I.C. Evaluation of Re and 99mTc complexes of 2-(4′-aminophenyl) benzothiazole as potential breast cancer radiopharmaceuticals. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 4633–4641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-K.; Kang, M.-K.; Jung, K.-H.; Kang, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Jung, J.-C.; Lee, G.H.; Chang, Y.; Kim, T.-J. Gadolinium complex of DO3A-benzothiazole aniline (BTA) conjugate as a theranostic agent. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8104–8111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroidi, B.; Sagnou, M.; Stamatakis, K.; Paravatou-Petsotas, M.; Pelecanou, M.; Methenitis, C. Palladium (II) and platinum (II) complexes of derivatives of 2-(4′-aminophenyl) benzothiazole as potential anticancer agents. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2016, 444, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagasser, J.; Ma, B.N.; Baecker, D.; Salcher, S.; Hermann, M.; Lamprecht, J.; Angerer, S.; Obexer, P.; Kircher, B.; Gust, R. A New Approach in Cancer Treatment: Discovery of Chlorido[N,N′-disalicylidene-1,2-phenylenediamine]iron(III) Complexes as Ferroptosis Inducers. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 8053–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Peng, B.; Ma, L.; Cao, S.L.; Bai, L.L.; Yang, C.R.; Wan, C.Q.; Yan, H.J.; Ding, P.P.; Li, Z.F.; et al. Synthesis, crystal structures and antitumor activity of two platinum(II) complexes with methyl hydrazinecarbodithioate derivatives of indolin-2-one. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomczyk, M.D.; Walczak, K.Z. l,8-Naphthalimide based DNA intercalators and anticancer agents. A systematic review from 2007 to 2017. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 159, 393–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weninger, A.; Baecker, D.; Obermoser, V.; Egger, D.; Wurst, K.; Gust, R. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Zeise’s Salt Derivatives with Acetylsalicylic Acid Substructure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Intini, F.P.; Zajac, J.; Novohradsky, V.; Saltarella, T.; Pacifico, C.; Brabec, V.; Natile, G.; Kasparkova, J. Novel Antitumor Platinum(II) Conjugates Containing the Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Agent Diclofenac: Synthesis and Dual Mechanisms of Antiproliferative Effects. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 1483–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, J.M.; Mendes, F.; Gama, S.; Santos, I.; Navarro Ranninger, C.; Cabrera, S.; Quiroga, A.G. Design and biological evaluation of new platinum(II) complexes bearing ligands with DNA-targeting ability. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 12627–12634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-K.; Park, S.; Lee, G.-H.; Kang, H.J.; Jung, J.-C.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, T.-J.; Chang, Y. Manganese Complex of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid (EDTA)–Benzothiazole Aniline (BTA) Conjugate as a Potential Liver-Targeting MRI Contrast Agent. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 2993–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Still, B.M.; Kumar, P.G.; Aldrich-Wright, J.R.; Price, W.S. 195Pt NMR--theory and application. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 665–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hille, A.; Ott, I.; Kitanovic, A.; Kitanovic, I.; Alborzinia, H.; Lederer, E.; Wolfl, S.; Metzler-Nolte, N.; Schafer, S.; Sheldrick, W.S.; et al. [N,N′-Bis(salicylidene)-1,2-phenylenediamine]metal complexes with cell death promoting properties. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 14, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenis-Rojas, O.A.; Robalo, M.P.; Tomaz, A.I.; Carvalho, A.; Fernandes, A.R.; Marques, F.; Folgueira, M.; Yanez, J.; Vazquez-Garcia, D.; Lopez Torres, M.; et al. Ru(II)( p-cymene) Compounds as Effective and Selective Anticancer Candidates with No Toxicity in Vivo. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 13150–13166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennelly, C.; Amaravadi, R.K. Lysosomal Biology in Cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1594, 293–308. [Google Scholar]
- Grazul, M.; Besic-Gyenge, E.; Maake, C.; Ciolkowski, M.; Czyz, M.; Sigel, R.K.; Budzisz, E. Synthesis, physico-chemical properties and biological analysis of newly obtained copper(II) complexes with pyrazole derivatives. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2014, 135, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Hu, S.; Liu, J.; Ji, L. Synthesis, characterization, antiproliferative and anti-metastatic properties of two ruthenium-DMSO complexes containing 2,2′-biimidazole. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fereidoonnezhad, M.; Niazi, M.; Ahmadipour, Z.; Mirzaee, T.; Faghih, Z.; Faghih, Z.; Shahsavari, H.R. Cyclometalated Platinum(II) Complexes Comprising 2-(Diphenylphosphino)pyridine and Various Thiolate Ligands: Synthesis, Spectroscopic Characterization, and Biological Activity. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 2017, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereidoonnezhad, M.; Niazi, M.; Shahmohammadi Beni, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Faghih, Z.; Faghih, Z.; Shahsavari, H.R. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Docking Studies on the DNA Binding Interactions of Platinum(II) Rollover Complexes Containing Phosphorus Donor Ligands. ChemMedChem 2017, 12, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fereidoonnezhad, M.; Faghih, Z.; Mojaddami, A.; Tabaei, S.M.H.; Rezaei, Z. Novel Approach Synthesis, Molecular Docking and Cytotoxic Activity Evaluation of N-phenyl-2,2-dichloroacetamide Derivatives as Anticancer Agents. J. Sci. Islamic Repub. Iran 2016, 27, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Schrödinger Release 2021-3, Glide; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2021.

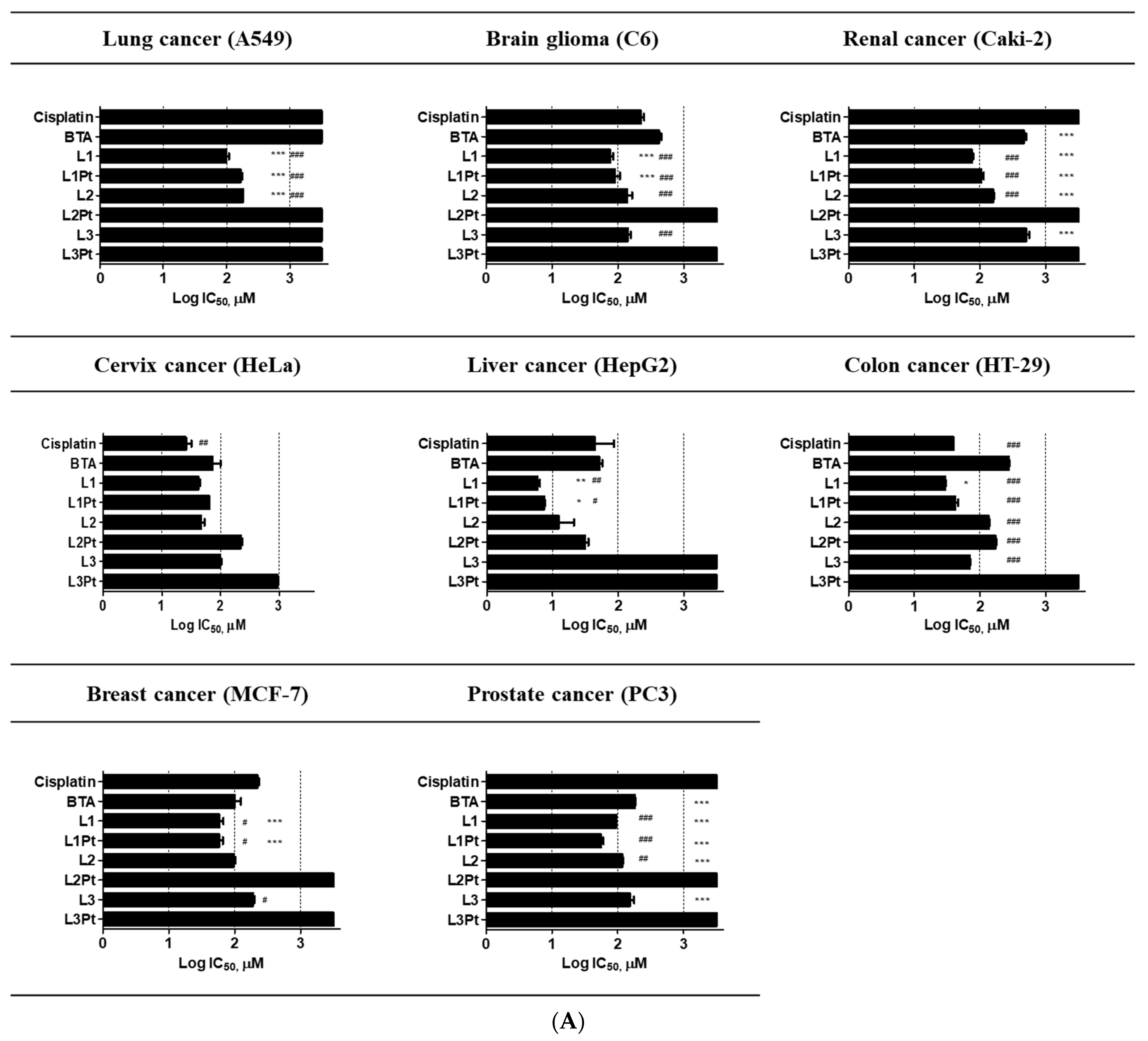
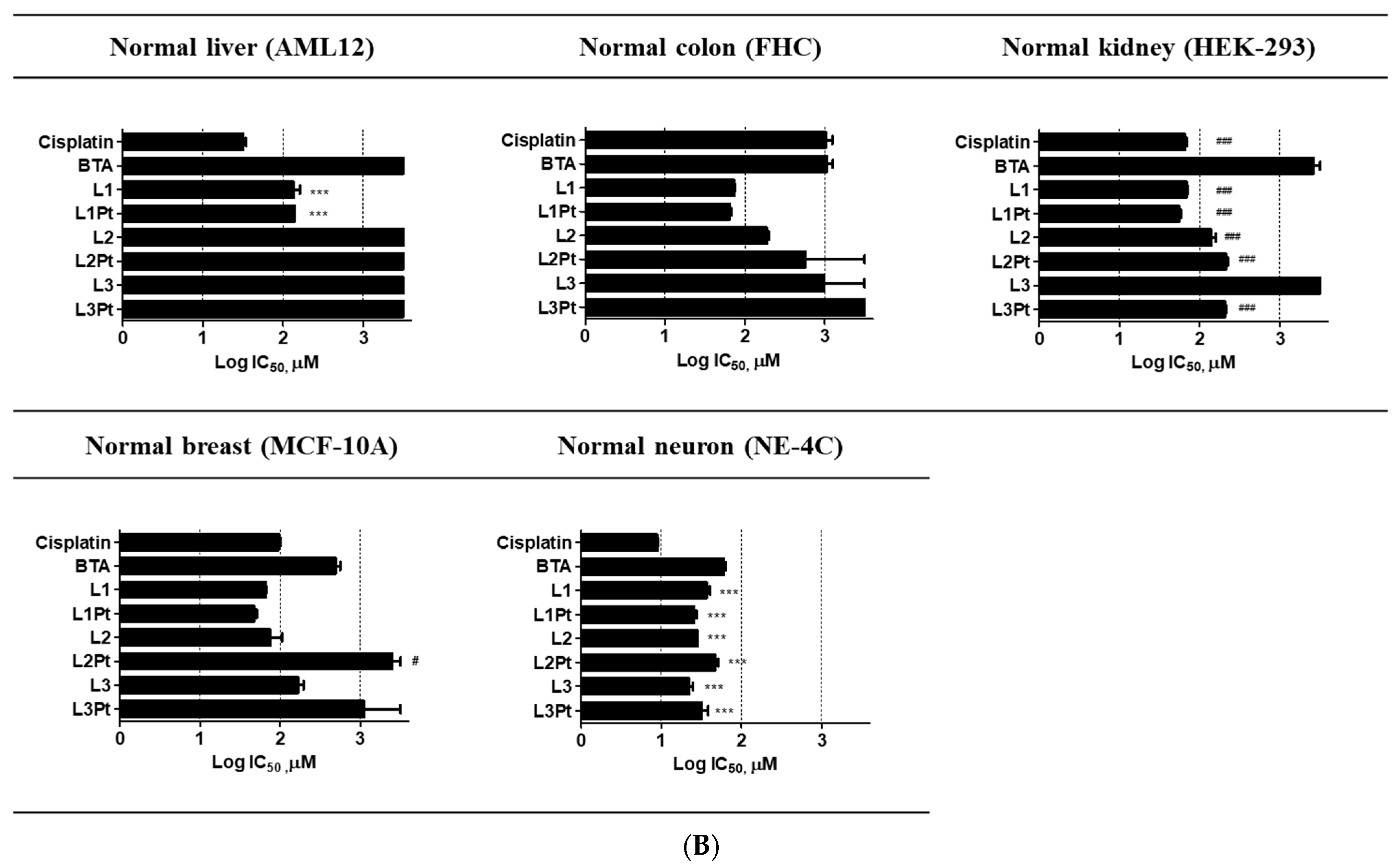
| Tissue Sources | Cell Lines | IC50 (μM) for | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisplatin | BTA | L1 | L1Pt | L2 | L2Pt | L3 | L3Pt | ||
| Human lung cancer | A549 | >500 | >500 | 100.16 ± 8.4 | 167.2 ± 11.2 | 182.4 ± 0.8 | >500 | >500 | >500 |
| Human brain glioma | C6 | 226.6 ± 34.3 | 424.7 ± 47.7 | 77.8 ± 9.7 | 93.3 ± 22.7 | 143.2 ± 32.7 | >500 | 142.4 ± 15.3 | >500 |
| Human renal cancer | Caki-2 | >500 | 462.8 ± 44.1 | 75.6 ± 3.4 | 105.7 ± 8.5 | 159.0 ± 4.3 | >500 | >500 | >500 |
| Human cervical cancer | HeLa | 26.2 ± 5.6 | 76.4 ± 23.4 | 41.9 ± 3.4 | 64.7 ± 0.3 | 47.0 ± 6.0 | 221.0 ± 15.8 | 98.9 ± 3.5 | >500 |
| Human hepatic carcinoma | HepG2 | 54.2 ± 31.8 | 52.0 ± 5.7 | 5.9 ± 0.5 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | 14.2 ± 7.0 | 31.6 ± 3.6 | >500 | >500 |
| Human colon cancer | HT-29 | 39.1 ± 0.6 | 275.3 ± 5.0 | 29.9 ± 0.3 | 42.6 ± 5.6 | 135.0 ± 4.4 | 172.6 ± 3.2 | 70.5 ± 0.2 | >500 |
| Human breast cancer | MCF-7 | 203.8 ± 27.3 | 103.9 ± 28.6 | 65.9 ± 12.3 | 59.0 ± 11.0 | 98.1 ± 7.9 | >500 | 190.3 ± 16.5 | >500 |
| Human prostate cancer | PC-3 | >500 | 181.7 ± 7.8 | 94.9 ± 0.8 | 55.7 ± 7.5 | 116.3 ± 5.0 | >500 | 130.2 ± 34.7 | >500 |
| Tissue Sources | Cell Lines | IC50 (μM) for | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cisplatin | BTA | L1 | L1Pt | L2 | L2Pt | L3 | L3Pt | ||
| Mouse liver hepatocyte | AML12 | 32.1 ± 4.4 | >500 | 137.6 ± 24.1 | 139.0 ± 0.8 | >500 | >500 | >500 | >500 |
| Human colon epithelial | FHC | >500 | >500 | 72.7 ± 2.0 | 64.3 ± 2.4 | 189.2 ± 10.3 | >500 | >500 | >500 |
| Human embryonic kidney | HEK-293 | 65.5 ± 4.1 | >500 | 68.1 ± 2.8 | 54.9 ± 2.8 | 138.9 ± 20.1 | 211.5 ± 14.9 | >500 | 205.9 ± 7.4 |
| Human breast epithelial | MCF-10A | 95.9 ± 6.7 | 401.4 ± 136.3 | 65.1 ± 1.9 | 46.9 ± 5.1 | 79.3 ± 25.4 | >500 | >500 | >500 |
| Mouse brain neural stem cell | NE-4C | 9.0 ± 0.3 | 60.9 ± 2.9 | 36.8 ± 3.7 | 25.7 ± 1.7 | 28.2 ± 0.1 | 47.0 ± 4.1 | 22.4 ± 2.4 | 32.4 ± 6.0 |
| Docking Binding Energy (kcal/mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | 1BNA | 3CO3 | 1LU5 |
| L1 | −6.697 | −5.839 | −4.636 |
| L1Pt | −7.150 | −5.695 | −4.164 |
| BTA | −6.658 | −6.495 | −5.037 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.K.; Baek, A.-R.; Sung, B.; Yang, B.-W.; Choi, G.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, M.; Ha, S.; Lee, G.-H.; et al. Synthesis, Characterization, and Anticancer Activity of Benzothiazole Aniline Derivatives and Their Platinum (II) Complexes as New Chemotherapy Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080832
Islam MK, Baek A-R, Sung B, Yang B-W, Choi G, Park H-J, Kim Y-H, Kim M, Ha S, Lee G-H, et al. Synthesis, Characterization, and Anticancer Activity of Benzothiazole Aniline Derivatives and Their Platinum (II) Complexes as New Chemotherapy Agents. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(8):832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080832
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Md. Kamrul, Ah-Rum Baek, Bokyung Sung, Byeong-Woo Yang, Garam Choi, Hyun-Jin Park, Yeoun-Hee Kim, Minsup Kim, Seongmin Ha, Gang-Ho Lee, and et al. 2021. "Synthesis, Characterization, and Anticancer Activity of Benzothiazole Aniline Derivatives and Their Platinum (II) Complexes as New Chemotherapy Agents" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 8: 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080832
APA StyleIslam, M. K., Baek, A.-R., Sung, B., Yang, B.-W., Choi, G., Park, H.-J., Kim, Y.-H., Kim, M., Ha, S., Lee, G.-H., Kim, H.-K., & Chang, Y. (2021). Synthesis, Characterization, and Anticancer Activity of Benzothiazole Aniline Derivatives and Their Platinum (II) Complexes as New Chemotherapy Agents. Pharmaceuticals, 14(8), 832. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14080832









