Pharmacokinetic Study of Anti-osteoarthritic Compounds of a Standardized Fraction from Sphaeralcea Angustifolia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
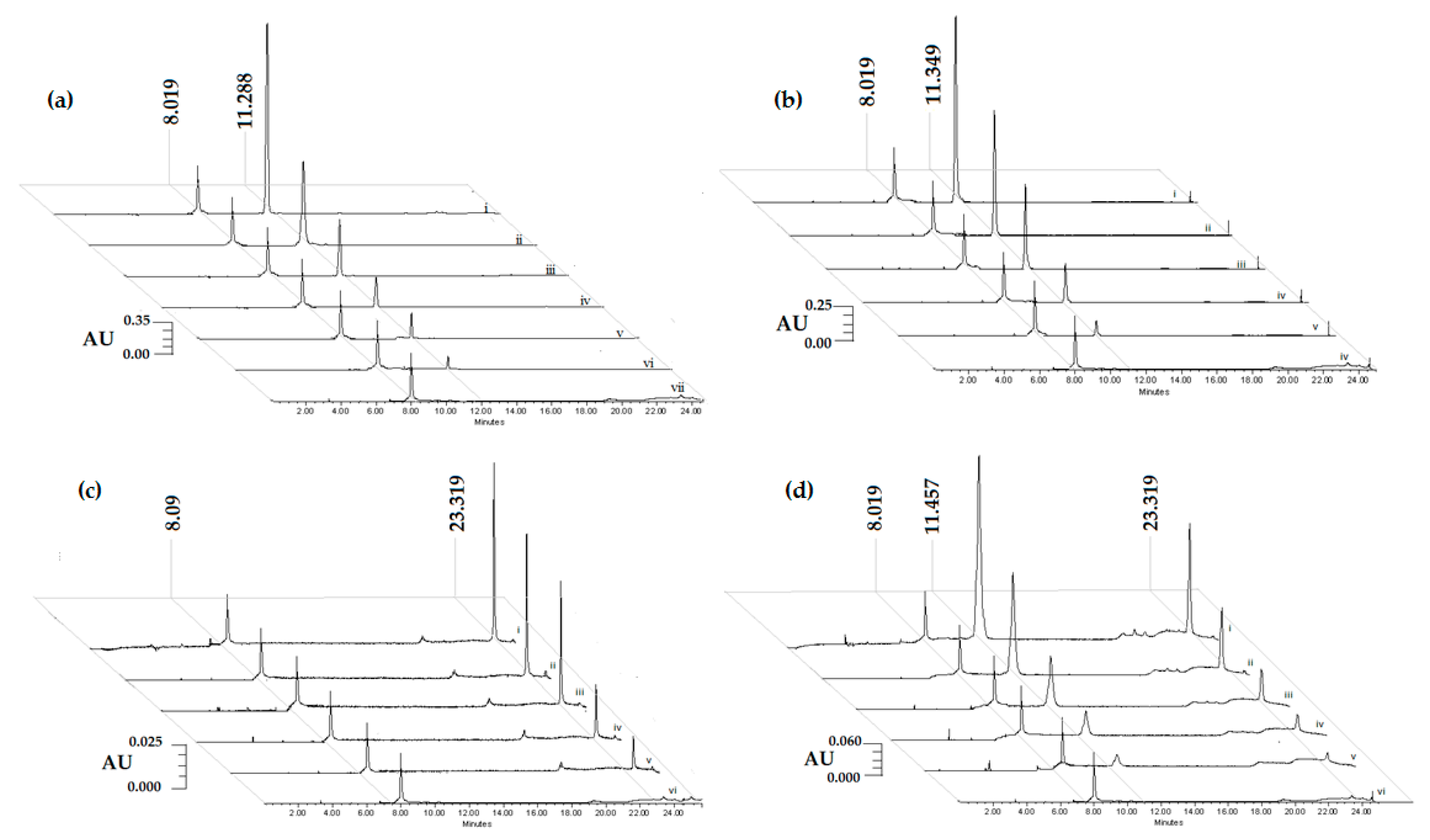
2.1. Chromatographic Profiling of Tomentin, Scopoletin, Sphaeralcic Acid, and SaTSS Standardized Fraction
2.2. Validation Methods
2.2.1. Standardization of Chromatographic Process
2.2.2. Standardization of the Extraction Process
2.3. Plasma Level of Active Compounds
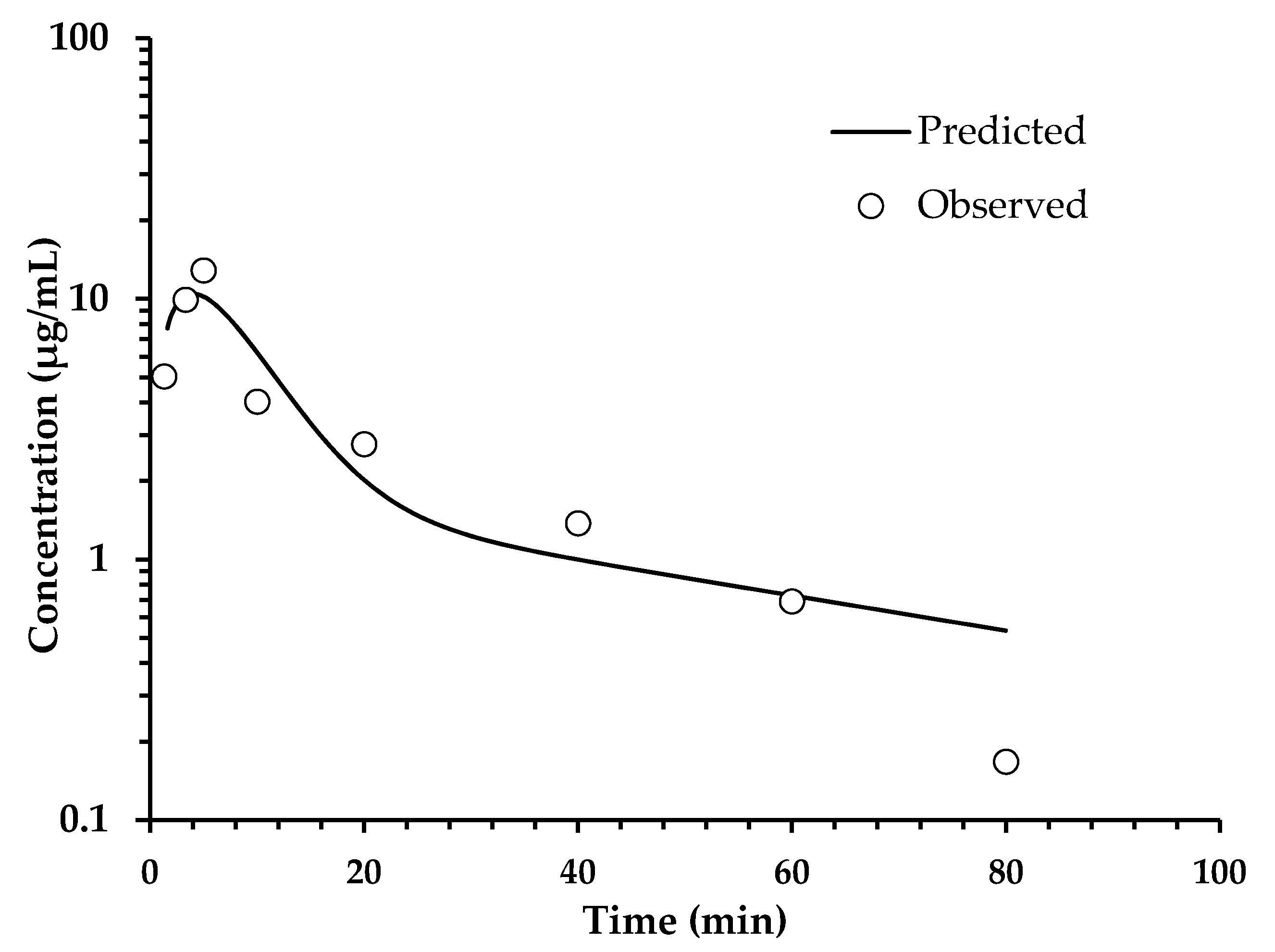
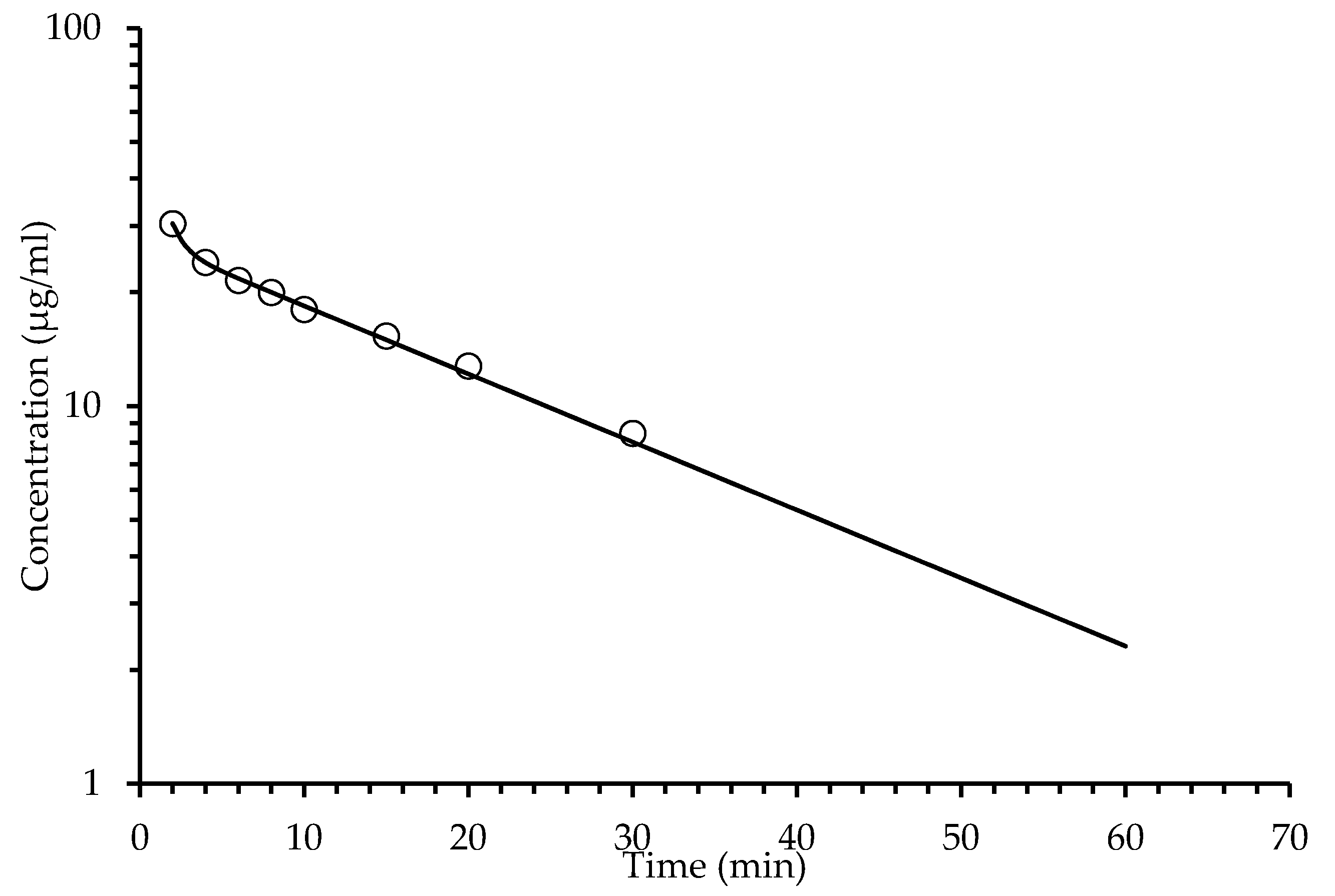
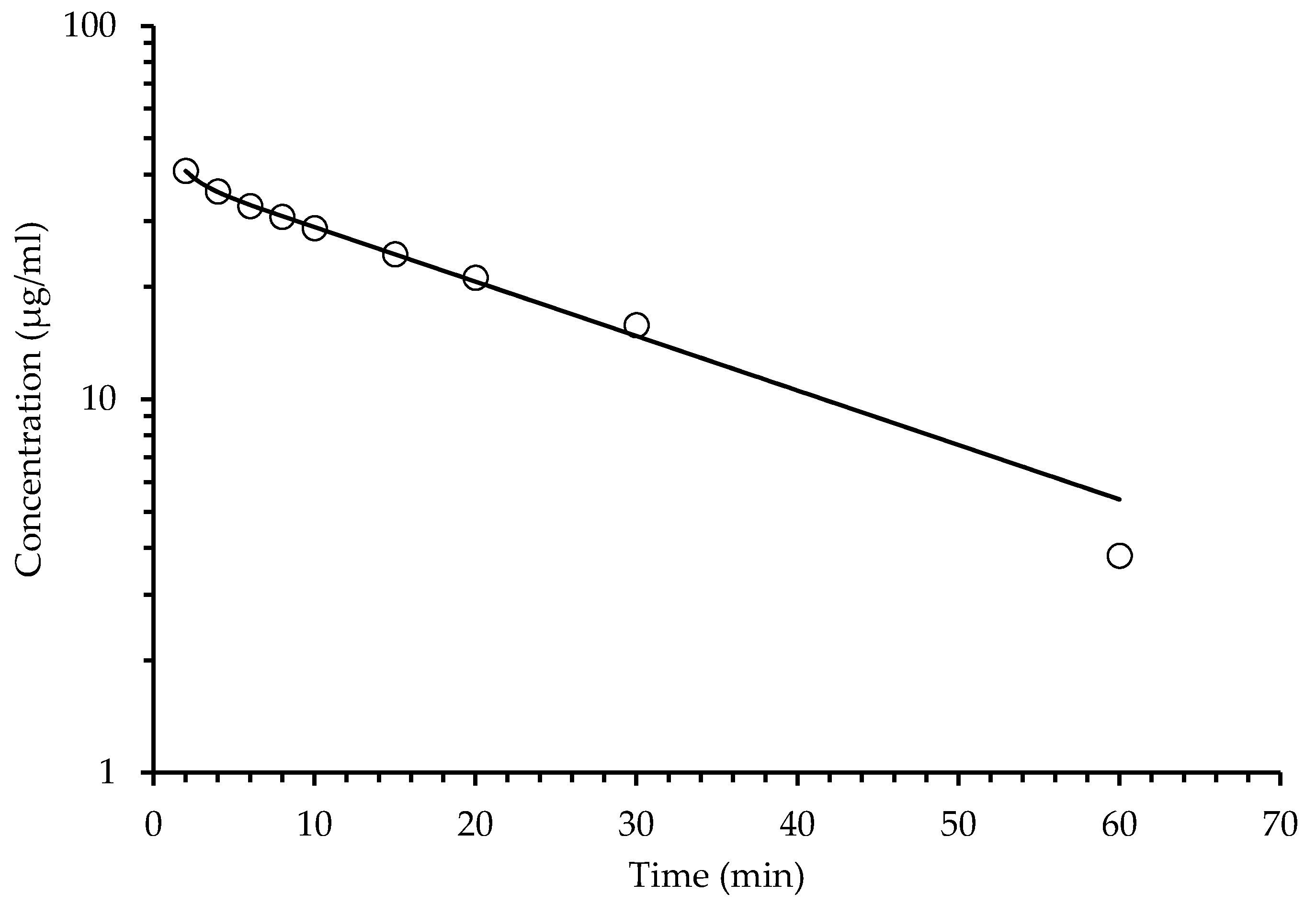
2.4. Pharmacokinetic Assay
2.4.1. Pharmacokinetic Oral Administration
2.4.2. Pharmacokinetic Intravenous Administration
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Cell Suspension Culture
4.2. Extraction and Purification Process of Sphaeralcea Angustifolia Cell Suspension
4.3. Preparation of the Sates Active Fraction
4.4. Isolation of Tomentin and Sphaeralcic Acid
4.5. HPLC Calibration Curves of Tomentin, Scopoletin, and Sphaeralcic Acid
4.6. Conditions of HPLC Analysis
4.7. Standards and Internal Standard Stock Solutions for Chromatographic Profiling
4.8. Animals
4.9. Obtaining Mouse Plasma
4.10. HPLC Calibration Curves of Tomentin, Scopoletin, and Sphaeralcic Acid In Plasma
4.11. Extraction of Active Compounds in Plasma
4.12. Method Validation
4.12.1. Linearity and Sensitivity Test
4.12.2. Recovery (Extraction Efficiency)
4.12.3. Specificity Test
4.12.4. Accuracy and Precision Test
4.12.5. Stability Study
4.13. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, A.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Zhong, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H. Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 2020, 100587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hame, S.L.; Alexander, R.A. Knee osteoarthritis in women. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet Med. 2013, 6, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Cáceres, A.E.; Rodriguez-Amado, J.; Peláez-Ballestas, I.; Vega-Morales, D.; Garza-Elizondo, M.A. Factors associated with treatment of osteoarthritis: Analysis of a COPCORD study in Nuevo León, México. Reumatol. Clin. 2015, 11, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, A.S.; Loeser, R.F. Why is Osteoarthritis an Age-Related Disease? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 24, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, H.; Walker, A.; Williams, J.; Hasty, K.A. Study of osteoarthritis treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs: Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor and steroids. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 595273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Argueta, A.; Cano, L.; Rodarte, M. Atlas de las Plantas de la Medicina Tradicional Mexicana; Instituto Nacional Indigenista (INI) Publisher: México D.F., México, 1994; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Meckes, M.; David-Rivera, A.; Nava-Aguilar, V.; Jimenez, A. Activity of some Mexican medicinal plant extracts on carrageenan-induced rat paw edema. Phytomedicine 2004, 11, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Rodríguez, R.V.; Chamorro-Cevallos, G.; Siordia, G.; Jiménez-Arellanes, M.A.; Chávez-Soto, M.A.; Meckes-Fischer, M. Sphaeralcea angustifolia (Cav.) G. Don extract, a potential phytomedicine to treat chronic inflammation. Boletín Latinoam. Caribe Plantas Med. Aromáticas 2012, 11, 454–463. [Google Scholar]
- Juárez-Ciriaco, M.; Román-Ramos, R.; González-Márquez, H.; Meckes-Fisher, M. Efecto de Sphaeralcea angustifolia sobre la expresión de citocinas pro y antiinflamatorias. LabCiencia 2008, 2, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Cerecero, O.; Meckes-Fischer, M.; Zamilpa, A.; Enrique Jiménez-Ferrer, J.; Nicasio-Torres, P.; Pérez-García, D.; Tortoriello, J. Clinical trial for evaluating the effectiveness and tolerability of topical Sphaeralcea angustifolia treatment in hand osteoarthritis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 147, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, R.; Dai, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Yao, X.; Xia, Y. Anti-angiogenic potential of scopoletin is associated with the inhibition of ERK1/2 activation. Drug Dev. Res. 2009, 70, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-059-SEMARNAT-2010. Protección Ambiental-Especies Nativas de México de Flora y Fauna Silvestres-Categorías de Riesgo y Especificaciones Para su Inclusión, Exclusión o Cambio-Lista de Especies en Riesgo. Available online: https://www.biodiversidad.gob.mx/especies/pdf/NOM_059_SEMARNAT_2010.pdf (accessed on 22 August 2019).
- Ding, Z.; Dai, Y.; Hao, H.; Pan, R.; Yao, X.; Wang, Z. Anti-inflammatory effects of scopoletin and underlying mechanisms. Pharm. Biol. 2008, 46, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Hernández, J.; González-Cortazar, M.; Marquina, S.; Herrera-Ruiz, M.; Meckes-Fischer, M.; Tortoriello, J.; Cruz-Sosa, F.; Nicasio-Torres, M.D.P. Sphaeralcic acid and tomentin, anti-inflammatory compounds produced in cell suspension cultures of Sphaeralcea angustifolia. Planta Med. 2014, 80, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicasio-torres, M.P.; Serrano-román, J.; Jiménez-ferrer, E.; Herrera-ruiz, M. Effect of Dichloromethane-Methanol Extract and Tomentin Obtained from Sphaeralcea angustifolia Cell Suspensions in a Model of Kaolin/Carrageenan-Induced Arthritis. Planta Med. Int. Open 2017, 4, 35–42. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Zhou, J.; Xie, S. PKSolver: An add-in program for pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data analysis in Microsoft Excel. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2010, 99, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Román, J.; Nicasio-Torres, M.P.; Hernández-Pérez, E.; Jiménez-Ferrer, E. Elimination pharmacokinetics of sphaeralcic acid, tomentin and scopoletin mixture from a standardized fraction of Sphaeralcea angustifolia (Cav.) G. Don orally administered. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 183, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludden, T.M.; Beal, S.L.; Sheiner, L.B. Comparison of the Akaike Information Criterion, the Schwarz criterion and the F test as guides to model selection. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharma. 1994, 22, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ya-Xin, Z.; Meng, W.; Wan-Ting, D.; Yang, L. Pharmacokinetics, bioavailability and metabolism of scopoletin in dog by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography combined with linear ion trap–Orbitrap tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2018, 33, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Yan-xu, C.; Qiu-Hong, Z.; Jin, L.; Ling, Z.; Xin-rong, G.; Jun, H.; Peng, Z.; Lin, M.; Yan-ru, D.; Bo-li, Z.; et al. Simultaneous determination of scopoletin, psoralen, bergapten, xanthotoxin, columbianetin acetate, imperatorin, osthole and isoimperatorin in rat plasma by LC–MS/MS for pharmacokinetic studies following oral administration of Radix Angelicae Pubescentis extract. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 77, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A Revised Medium for Rapid Growth and Bio Assays with Tobacco Tissue Cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicasio-Torres, M.P.; Pérez-Hernández, J.; González-Cortazar, M.; Meckes-Fischer, M.; Tortoriello, J.; Cruz-Sosa, F. Production of potential anti-inflammatory compounds in cell suspension cultures of Sphaeralcea angustifolia (Cav.) G. Don. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2016, 38, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- NORMA Oficial Mexicana NOM-062-ZOO-1999. Especificaciones Técnicas Para la Producción, Cuidado y Uso de los Animales de Laboratorio. Available online: http://dof.gob.mx/nota_detalle.php?codigo=764738&fecha=18/06/2001 (accessed on 22 August 2019).
- FDA Analytical Procedures and Methods Validation for Drugs and Biologics. Guidance for Industry 2015. Available online: http://www.ich.org/fileadmin/Public_Web_Site/ICH_Products/Guidelines/Quaity/Q2_R1/Step4/Q2_R1__Guideline.pdf (accessed on 22 August 2019).


| Compound | Test | Concentration Nominal µg/mL) | Measured Concentration µg/mL± SD | Accuracy (% Bias) | Precision (% RDS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank plasma | Intra-assay | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Inter-assay | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Tomentin | Intra-assay | 2.5 | 2.41 ± 0.07 | −3.4 | 2.8 |
| 5 | 4.94 ± 0.06 | −1.2 | 1.1 | ||
| 10 | 9.95 ± 0.13 | −0.5 | 1.3 | ||
| 20 | 19.94 ± 0.22 | −0.3 | 1.1 | ||
| Inter-assay | 2.5 | 2.39 ± 0.09 | −4.6 | 3.6 | |
| 5 | 4.93 ± 0.11 | −1.5 | 2.3 | ||
| 10 | 9.96 ± 0.30 | −0.4 | 3.0 | ||
| 20 | 19.77 ± 0.19 | −1.1 | 1.0 | ||
| Scopoletin | Intra- assay | 2.5 | 2.33 ± 0.08 | −6.6 | 3.5 |
| 5 | 5.06 ± 0.06 | 1.1 | 1.1 | ||
| 10 | 9.98 ± 1.27 | −0.2 | 2.7 | ||
| 20 | 19.26 ± 0.25 | −3.7 | 1.3 | ||
| Inter- assay | 2.5 | 2.20 ± 0.04 | −12.0 | 1.9 | |
| 5 | 5.08 ± 0.05 | 1.6 | 0.9 | ||
| 10 | 9.78 ± 0.14 | −2.2 | 1.4 | ||
| 20 | 19.38 ± 0.45 | −3.1 | 2.3 | ||
| Sphaeralcic acid | Intra- assay | 2.5 | 2.33 ± 0.17 | −6.8 | 7.2 |
| 5 | 5.06 ± 0.09 | 1.3 | 1.7 | ||
| 10 | 9.96 ± 0.12 | −0.4 | 1.2 | ||
| 20 | 20.23 ± 1.31 | 1.2 | 6.5 | ||
| 40 | 39.52 ± 1.19 | −1.2 | 3.0 | ||
| Inter- assay | 2.5 | 2.18 ± 0.13 | −13.0 | 6.1 | |
| 5 | 4.91 ± 0.13 | −1.9 | 2.7 | ||
| 10 | 9.90 ± 0.7 | −1.0 | 0.7 | ||
| 20 | 19.91 ± 0.19 | −0.5 | 0.9 | ||
| 40 | 39.36 ± 0.75 | −1.6 | 1.9 |
| Condition | Compound | Nominal Concentration (μg/mL) | Observed Concentration (μg/mL) | Accuracy Bias (%) | RSD (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 8 h | 24 h | 0 h | 8 h | 24 h | 0 h | 8 h | 24 h | |||
| Room temperature | Tomentin | 2.5 | 2.39 ± 0.09 | 2.31 ± 0.08 | 2.35 ± 0.09 | −4.59 | −7.60 | −5.93 | 3.57 | 3.30 | 3.90 |
| 5 | 4.93 ± 0.11 | 4.96 ± 0.14 | 4.91 ± 0.17 | −1.48 | −0.86 | −1.73 | 2.31 | 2.88 | 3.42 | ||
| 10 | 9.96 ± 0.30 | 9.84 ± 0.40 | 9.55 ± 0.19 | −0.41 | −1.64 | −4.52 | 2.97 | 4.10 | 1.99 | ||
| Scopoletin | 2.5 | 2.49 ± 0.12 | 2.38 ± 0.08 | 2.38 ± 0.08 | −0.48 | −4.63 | −4.63 | 4.83 | 3.15 | 3.15 | |
| 5 | 5.02 ± 0.08 | 4.99 ± 0.14 | 5.02 ± 0.10 | 0.39 | −0.17 | 0.43 | 1.53 | 2.82 | 2.07 | ||
| 10 | 10.00 ± 0.37 | 9.80 ± 0.40 | 9.34 ± 0.27 | 0.04 | −2.02 | −6.61 | 3.65 | 4.05 | 2.89 | ||
| Sphaeralcic acid | 2.5 | 2.48 ± 0.03 | 2.25 ± 0.13 | 2.27 ± 0.11 | −0.60 | −9.98 | −9.03 | 1.10 | 5.97 | 5.01 | |
| 5 | 5.01 ± 0.06 | 4.59 ± 0.06 | 4.56 ± 0.10 | 0.17 | −8.10 | −8.73 | 1.11 | 1.27 | 2.09 | ||
| 10 | 9.95 ± 0.11 | 9.35 ± 0.11 | 9.26 ± 0.07 | −0.49 | −6.48 | −7.37 | 1.12 | 1.21 | 0.75 | ||
| Storage and stability | Nominal concentration (μg/mL) | Auto sampler (4 °C, 8 h) | Long-term (−70 °C, 1 month) | Autosampler (4 °C, 8 h) | Long-term (−70 °C, 1 month) | Auto sampler (4 °C, 8 h) | Long-term (−70 °C, 1 month) | ||||
| Tomentin | 2.5 | 2.43 ± 0.11 | 2.31 ± 0.09 | −2.64 | −7.61 | 4.47 | 3.92 | ||||
| 5 | 4.92 ± 0.14 | 4.85 ± 0.18 | −1.65 | −2.90 | 2.82 | 3.75 | |||||
| 10 | 9.93 ± 0.62 | 9.63 ± 0.65 | −0.65 | −3.74 | 6.28 | 6.71 | |||||
| Scopoletin | 2.5 | 2.52 ± 0.09 | 2.32 ± 0.08 | 0.75 | −7.05 | 3.65 | 3.57 | ||||
| 5 | 4.95 ± 0.14 | 4.89 ± 0.17 | −0.94 | −2.27 | 2.76 | 3.48 | |||||
| 10 | 9.90 ± 0.61 | 9.95 ± 0.38 | −1.05 | −0.46 | 6.21 | 3.79 | |||||
| Sphaeralcic acid | 2.5 | 2.40 ± 0.04 | 2.38 ± 0.08 | −3.89 | −4.82 | 1.82 | 3.39 | ||||
| 5 | 4.92 ± 0.08 | 4.87 ± 0.10 | −1.69 | −2.61 | 1.61 | 2.10 | |||||
| 10 | 9.67 ± 0.12 | 9.65 ± 0.08 | −3.34 | −3.50 | 1.22 | 0.79 | |||||
| Oral Administration Plasma Concentration | Intravenous Administration Plasma Concentration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | Coumarins (Tomentin and Scopoletin) (μg/mL) | Sphaeralcic Acid (μg/mL) | Time (min) | Coumarins (Tomentin and Scopoletin) (μg/mL) | Sphaeralcic Acid (μg/mL) |
| 1.3 | 2.37 ± 0.05 | 5.04 ± 0.05 | 2.0 | 30.5 ± 0.12 | 40.88 ± 0.21 |
| 3.3 | 4.41 ± 0.07 | 9.92 ± 0.41 | 4.0 | 23.54 ± 0.47 | 36.28 ± 0.11 |
| 5 | 3.21 ± 0.15 | 12.84 ± 0.54 | 6.0 | 22.11 ± 0.85 | 33.90 ± 0.24 |
| 10 | 1.80 ± 0.09 | 4.03 ± 0.11 | 8.0 | 20.97 ± 0.40 | 31.78 ± 0.75 |
| 20 | 1.38 ± 0.05 | 2.77 ± 0.08 | 10 | 18.49 ± 0.41 | 28.71 ± 0.65 |
| 40 | 0.95 ± 0.03 | 1.38 ± 0.12 | 15 | 15.33 ± 0.18 | 24.43 ± 0.33 |
| 60 | 0.48 ± 0.01 | 0. 69 ± 0.03 | 20 | 12.76 ± 0.19 | 21.16 ± 0.51 |
| 80 | 0.12 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.03 | 30 | 8.46 ± 0.21 | 15.79 ± 0.57 |
| 120 | 0.00 ± 0.0 | 0.00 ± 0.0 | 60 | 0.68 ± 0.04 | 3.81 ± 0.09 |
| 240 | 0.00 ± 0.0 | 0.00 ± 0.0 | |||
| Pharmacokinetic Parameters | Sphaeralcic Acid | Coumarin (Tomentin and Scopoletin) | Units | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 413.646 | 71.468 | µg/mL | |
| B | 1.845 | 1.791 | µg/mL | |
| ka | 0.273 | 0.390 | 1/min | |
| k10 | 0.127 | 0.085 | 1/min | |
| k12 | 0.114 | 0.201 | 1/min | |
| k21 | 0.031 | 0.086 | 1/min | |
| t1/2α | 2.698 | 1.963 | min | |
| t1/2β | 44.653 | 32.946 | min | |
| t1/2ka | 2.537 | 1.774 | min | |
| α | 0.256 | 0.353 | 1/min | |
| β | 0.015 | 0.021 | 1/min | |
| V/F | 1.309 | 0.802 | (mg)/(µg/mL) | |
| CL/F | 0.166 | 0.068 | (mg)/(µg/mL)/min | |
| Tmax | 4.004 | 3.234 | min | |
| Cmax | 10.447 | 3.775 | µg/mL | |
| AUC 0→240 | 173.724 | 84.198 | µg/mL·min | |
| AUC 0→∞ | 208.058 | 100.020 | µg/mL·min | |
| MRT | 40.167 | 41.397 | min | |
| Diagnostics | ||||
| Statistical criteria | Sphaeralcic acid | Coumarin (Tomentin and scopoletin) | ||
| One-compartment model | Two-compartment model | One-compartment model | Two-compartment model | |
| SS | 18.469 | 15.62 | 1.918 | 0.835 |
| R2 | 0.941 | 0.950 | 0.953 | 0.979 |
| AIC | 37.739 | 32.245 | 11.862 | 8.379 |
| SC | 35.726 | 32.836 | 12.453 | 9.365 |
| Sphaeralcic Acid | Coumarin (Tomentin and Scopoletin) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pharmacokinetic Parameters | One-Compartment Model | Two-Compartment Model | One-Compartment Model | Two-Compartment Model | Units | |
| A | ------ | 18.027 | ------- | 63.57 | µg/mL | |
| B | ------ | 40.461 | ------ | 27.86 | µg/mL | |
| k10 | 0.032 | 0.048 | 0.047 | 0.126 | 1/min | |
| k12 | ------ | 0.249 | ------ | 0.787 | 1/min | |
| k21 | ------ | 0.624 | ------ | 0.424 | 1/min | |
| t1/2α | ------ | 0.781 | ------ | 0.534 | min | |
| t1/2β | ------ | 20.634 | ------ | 16.70 | min | |
| t1/2 | 21.245 | ------ | 14.641 | ------- | min | |
| α | ------- | 0.88 | ------- | 1.297 | 1/min | |
| β | ------- | 0.034 | ------- | 0.041 | 1/min | |
| C0 | 41.726 | 58.489 | 30.773 | 91.438 | µg/mL | |
| V | 0.828 | 0.591 | 0.220 | 0.068 | (mg)/(µg/mL) | |
| CL | 0.027 | 0.028 | 0.010 | 0.009 | (mg)/(µg/mL)/min | |
| AUC0-60 | 1098.375 | 1064.322 | 612.085 | 665.022 | µg/mL*min | |
| AUC0-inf ∞ | 1278.978 | 1224.828 | 650.047 | 720.770 | µg/mL*min | |
| AUMC | 39,202.118 | 35,880.304 | 13,731.187 | 16,230.343 | µg/mL*min2 | |
| MRT | 30.651 | 29.294 | 21.123 | 22.518 | Min | |
| Vss | 0.828 | 0.826 | 0.220 | 0.195 | mg/(µg/mL) | |
| Diagnostics | ||||||
| Sphaeralcic acid | Coumarin (Tomentin and scopoletin) | |||||
| Statistical criteria | One-compartment model | Two-compartment model | One-compartment model | Two-compartment model | ||
| SS | 28.44 | 3.937 | 14.58 | 3.587 | ||
| R2 | 0.996 | 0.999 | 0.995 | 0.999 | ||
| AIC | 34.13 | 20.333 | 28.116 | 19.497 | ||
| SC | 34.52 | 21.122 | 28.511 | 20.285 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serrano-Román, J.; Nicasio-Torres, P.; Hernández-Pérez, E.; Jiménez-Ferrer, E. Pharmacokinetic Study of Anti-osteoarthritic Compounds of a Standardized Fraction from Sphaeralcea Angustifolia. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070610
Serrano-Román J, Nicasio-Torres P, Hernández-Pérez E, Jiménez-Ferrer E. Pharmacokinetic Study of Anti-osteoarthritic Compounds of a Standardized Fraction from Sphaeralcea Angustifolia. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(7):610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070610
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerrano-Román, Jade, Pilar Nicasio-Torres, Elizabeth Hernández-Pérez, and Enrique Jiménez-Ferrer. 2021. "Pharmacokinetic Study of Anti-osteoarthritic Compounds of a Standardized Fraction from Sphaeralcea Angustifolia" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 7: 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070610
APA StyleSerrano-Román, J., Nicasio-Torres, P., Hernández-Pérez, E., & Jiménez-Ferrer, E. (2021). Pharmacokinetic Study of Anti-osteoarthritic Compounds of a Standardized Fraction from Sphaeralcea Angustifolia. Pharmaceuticals, 14(7), 610. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070610






