Cardiac Events Potentially Associated to Remdesivir: An Analysis from the European Spontaneous Adverse Event Reporting System
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
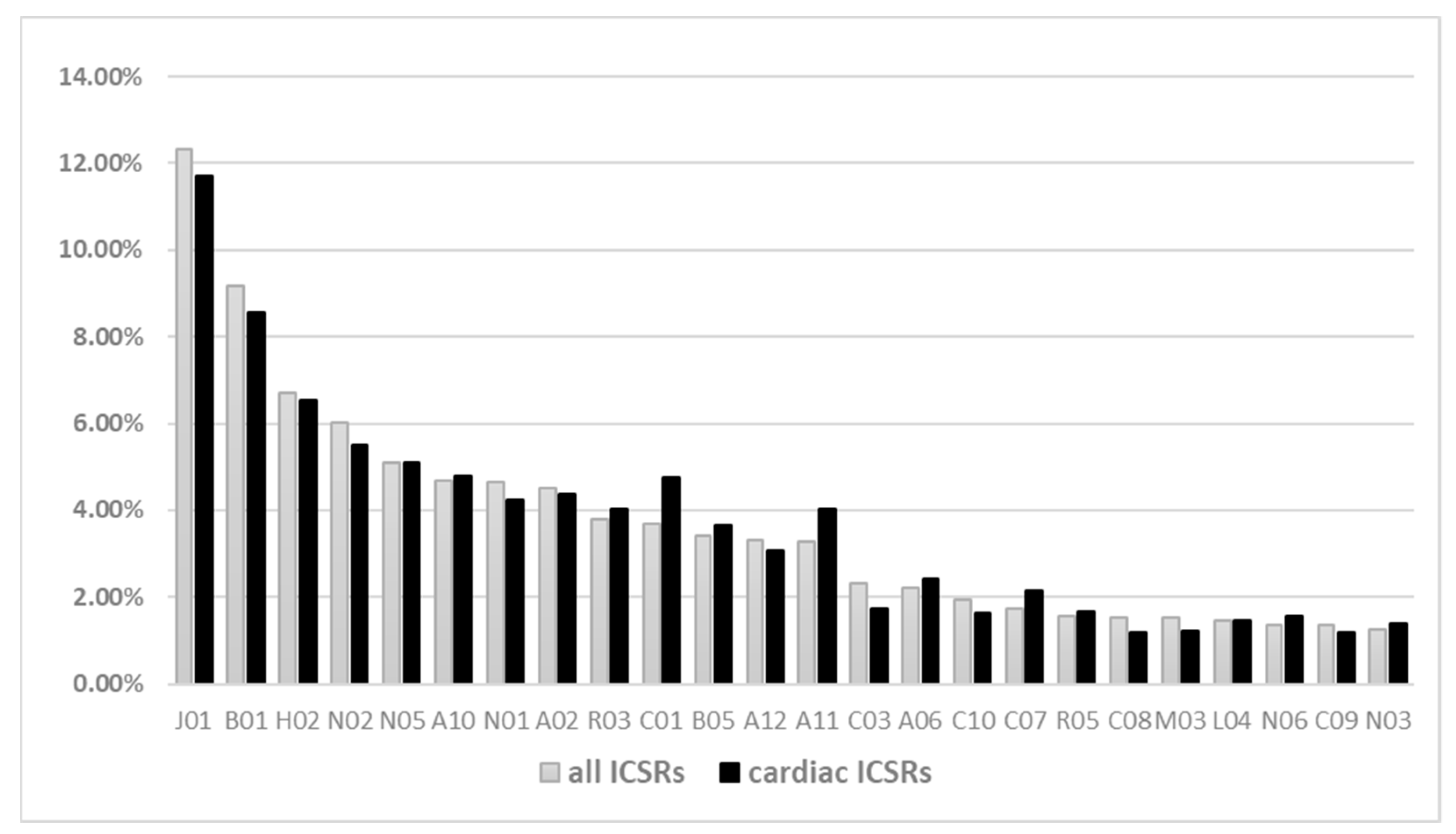
2.1. Characteristics of Individual Case Safety Reports (ICSRs)
2.2. Cardiac Events
2.3. Description of Other Medicines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Source
4.2. ICSRs Selection
4.3. Descriptive Analysis
4.4. Disproportionality Analysis
4.5. Ethical Consideration
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EMA—Veklury Authorisation Details. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/veklury (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Beigel, J.H.; Tomashek, K.M.; Dodd, L.E.; Mehta, A.K.; Zingman, B.S.; Kalil, A.C.; Hohmann, E.; Chu, H.Y.; Luetkemeyer, A.; Kline, S.; et al. Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19-Final Report. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1813–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochwerg, B.; Siemieniuk, R.A.C.; Agoritsas, T.; Lamontagne, F.; Askie, L.; Lytvyn, L.; Agarwal, A.; Leo, Y.-S.; Macdonald, H.; Zeng, L.; et al. A living WHO guideline on drugs for covid-19. BMJ 2020, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA—Risk Management Plan for Remdesivir. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/rmp/veklury-epar-risk-management-plan_en.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2020).
- Fan, Q.; Zhang, B.; Ma, J.; Zhang, S. Safety profile of the antiviral drug remdesivir: An update. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 130, 110532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA—Veklury-Summary of Product Characteristics. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/other/veklury-product-information-approved-chmp-25-june-2020-pending-endorsement-european-commission_en.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2021).
- EMA—Meeting Highlights from the Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC). 8–11 February 2021. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/meeting-highlights-pharmacovigilance-risk-assessment-committee-prac-8-11-february-2021 (accessed on 15 February 2021).
- de Vries, S.T.; Denig, P.; Ekhart, C.; Burgers, J.S.; Kleefstra, N.; Mol, P.G.M.; van Puijenbroek, E.P. Sex differences in adverse drug reactions reported to the National Pharmacovigilance Centre in the Netherlands: An explorative observational study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montastruc, J.L.; Lapeyre-Mestre, M.; Bagheri, H.; Fooladi, A. Gender differences in adverse drug reactions: Analysis of spontaneous reports to a Regional Pharmacovigilance Centre in France. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2002, 16, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugi, A.; Bonaiuti, R.; Maggini, V.; Moschini, M.; Tuccori, M.; Leone, R.; Rossi, M.; Motola, D.; Piccinni, C.; Ferrazin, F.; et al. Safety profile of antiviral medications: A pharmacovigilance study using the Italian spontaneous-reporting database. Am. J. Health Pharm. 2013, 70, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charan, J.; Kaur, R.J.; Bhardwaj, P.; Haque, M.; Sharma, P.; Misra, S.; Godman, B. Rapid review of suspected adverse drug events due to remdesivir in the WHO database; findings and implications. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 14, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouw, N.; van de Maat, J.; Veerman, K.; Ten Oever, J.; Janssen, N.; Abbink, E.; Reijers, M.; de Mast, Q.; Hoefsloot, W.; van Crevel, R.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of 952 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in The Netherlands: A retrospective cohort study. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavin, W.; Campbell, E.; Zaidi, S.-A.; Gavin, N.; Dbeibo, L.; Beeler, C.; Kuebler, K.; Abdel-Rahman, A.; Luetkemeyer, M.; Kara, A. Clinical characteristics, outcomes and prognosticators in adult patients hospitalized with COVID-19. Am. J. Infect. Control 2021, 49, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondi, F.; Novelli, L.; Ghirardi, A.; Russo, F.M.; Pellegrini, D.; Biza, R.; Trapasso, R.; Giuliani, L.; Anelli, M.; Amoroso, M.; et al. HPG23 Covid-19 Study Group. Covid-19 and gender: Lower rate but same mortality of severe disease in women-an observational study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2021, 21, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covid-19 Sex Disaggregated Data Tracker. Sex, Gender and Covid-19. Available online: http://globalhealth5050.org/covid19 (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- Grasselli, G.; Zangrillo, A.; Zanella, A.; Antonelli, M.; Cabrini, L.; Castelli, A.; Cereda, D.; Coluccello, A.; Foti, G.; Fumagalli, R.; et al. COVID-19 Lombardy ICU Network. Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy. JAMA 2020, 323, 1574–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bwire, G.M. Coronavirus: Why Men are More Vulnerable to Covid-19 Than Women? SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2020, 2, 874–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capuano, A.; Rossi, F.; Paolisso, G. Covid-19 Kills More Men Than Women: An Overview of Possible Reasons. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elezkurtaj, S.; Greuel, S.; Ihlow, J.; Michaelis, E.G.; Bischoff, P.; Kunze, C.A.; Sinn, B.V.; Gerhold, M.; Hauptmann, K.; Ingold-Heppner, B.; et al. Causes of death and comorbidities in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.D.; Lye, D.C.B.; Hui, D.S.; Marks, K.M.; Bruno, R.; Montejano, R.; Spinner, C.D.; Galli, M.; Ahn, M.-Y.; Nahass, R.G.; et al. Remdesivir for 5 or 10 Days in Patients with Severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1827–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampino, R.; Mele, F.; Florio, L.L.; Bertolino, L.; Andini, R.; Galdo, M.; De Rosa, R.; Corcione, A.; Durante-Mangoni, E. Liver injury in remdesivir-treated COVID-19 patients. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 881–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montastruc, F.; Thuriot, S.; Durrieu, G. Hepatic Disorders With the Use of Remdesivir for Coronavirus 2019. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 2835–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Laar, S.A.; de Boer, M.G.J.; Gombert-Handoko, K.B.; Guchelaar, H.-J.; Zwaveling, J. Liver and kidney function in patients with Covid-19 treated with remdesivir. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grein, J.; Ohmagari, N.; Shin, D.; Diaz, G.; Asperges, E.; Castagna, A.; Feldt, T.; Green, G.; Green, M.L.; Lescure, F.-X.; et al. Compassionate Use of Remdesivir for Patients with Severe Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gérard, A.O.; Laurain, A.; Fresse, A.; Parassol, N.; Muzzone, M.; Rocher, F.; Esnault, V.L.M.; Drici, M.-D. Remdesivir and Acute Renal Failure: A Potential Safety Signal From Disproportionality Analysis of the WHO Safety Database. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 109, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA—Update on Remdesivir-EMA Will Evaluate New Data from Solidarity Trial. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/update-remdesivir-ema-will-evaluate-new-data-solidarity-trial (accessed on 1 January 2021).
- Touafchia, A.; Bagheri, H.; Carrié, D.; Durrieu, G.; Sommet, A.; Chouchana, L.; Montastruc, F. Serious bradycardia and remdesivir for coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19): A new safety concerns. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubitosa, J.C.; Kakar, P.; Gerula, C.; Nossa, H.; Finkel, D.; Wong, K.; Khatri, M.; Ali, H. Marked Sinus Bradycardia Associated With Remdesivir in COVID-19: A Case and Literature Review. JACC. Case Rep. 2020, 2, 2260–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Parker, B.M.; Priyadarshi, V.; Parker, J. Cardiac Adverse Events With Remdesivir in COVID-19 Infection. Cureus 2020, 12, e11132. [Google Scholar]
- Barkas, F.; Styla, C.-P.; Bechlioulis, A.; Milionis, H.; Liberopoulos, E. Sinus Bradycardia Associated with Remdesivir Treatment in COVID-19: A Case Report and Literature Review. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2021, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 121304016, Remdesivir. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Remdesivir (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Gordon, C.J.; Tchesnokov, E.P.; Woolner, E.; Perry, J.K.; Feng, J.Y.; Porter, D.P.; Götte, M. Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 6785–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishiga, M.; Wang, D.W.; Han, Y.; Lewis, D.B.; Wu, J.C. COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease: From basic mechanisms to clinical perspectives. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzerini, P.E.; Boutjdir, M.; Capecchi, P.L. COVID-19, Arrhythmic Risk, and Inflammation: Mind the Gap! Circulation 2020, 142, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roshdy, A.; Zaher, S.; Fayed, H.; Coghlan, J.G. COVID-19 and the Heart: A Systematic Review of Cardiac Autopsies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 626975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatla, A.; Mayer, M.M.; Adusumalli, S.; Hyman, M.C.; Oh, E.; Tierney, A.; Moss, J.; Chahal, A.A.; Anesi, G.; Denduluri, S.; et al. COVID-19 and cardiac arrhythmias. Hear. Rhythm 2020, 17, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rubio, A.; Ascoeta, S.; Taibi, F.; Soldevila, J.G. Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Cardiac Arrhythmias. Eur. Cardiol. 2020, 15, e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Haqqani, H.; Wynn, G.; Pathak, R.K.; Lipton, J.; Mahajan, R.; Sanders, P.; Healey, S.; Wilsmore, B.; Mariani, J.A.; et al. Position Statement on the Management of Cardiac Electrophysiology and Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices in Australia During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Living Document. Heart Lung Circ. 2020, 29, e57–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA—EudraVigilance-European Database of Suspected Adverse Reactions Related to Medicines: User Manual for Online Access via the Adrreports.eu Portal. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/regulatory-procedural-guideline/eudravigilance-european-database-suspected-adverse-reactions-related-medicines-user-manual-online_en.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2020).
- Rafaniello, C.; Ferrajolo, C.; Gaio, M.; Zinzi, A.; Scavone, C.; Sullo, M.G.; Rossi, F.; Berrino, L.; Capuano, A. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults: Reverse Translational Research by Using Real-World Safety Data. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Mauro, G.; Zinzi, A.; Scavone, C.; Mascolo, A.; Gaio, M.; Sportiello, L.; Ferrajolo, C.; Rafaniello, C.; Rossi, F.; Capuano, A. PCSK9 Inhibitors and Neurocognitive Adverse Drug Reactions: Analysis of Individual Case Safety Reports from the Eudravigilance Database. Drug Saf. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Individual Case Safety Reports 1375 (%) | |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 863 (62.8) |
| Female | 477 (34.7) |
| Not Specified | 35 (2.5) |
| Age group | |
| Paediatrics (>18 Years) | 12 (0.9) |
| Adult (18–64 Years) | 596 (43.3) |
| Elderly (65–85 Years) | 503 (36.6) |
| Very Elderly (>85 Years) | 93 (6.8) |
| Not Specified | 171 (12.4) |
| Type of reporter | |
| Health Care Professional | 1349 (98.1) |
| Non-Health Care Professional | 26 (1.9) |
| Country | |
| European Economic Area | 509 (37.0) |
| Non-European Economic Area | 866 (63.0) |
| Outcome 1 | |
| Fatal | 416 (30.3) |
| Recovered/Resolved | 338 (24.6) |
| Not Recovered/Not Resolved | 186 (13.5) |
| Recovering/Resolving | 151 (11.0) |
| Recovered/Resolved With Sequelae | 5 (0.4) |
| Unknown | 279 (20.3) |
| Adverse Events | |
| Total Number | 3166 |
| Mean AE per ICSR (±SD) | 2.3 (±2.24) |
| Number of Events 3166 (%) | |
|---|---|
| Seriousness | |
| Not Serious | 562 (17.8) |
| Seriousness Criteria, of which | 2604 (82.2) |
| Other Medically Important Condition | 1293 (49.7) |
| Results in Death | 703 (27.0) |
| Caused/Prolonged Hospitalisation | 398 (15.3) |
| Life Threatening | 179 (6.9) |
| Disabling | 29 (1.1) |
| Congenital Anomaly | 2 (0.1) |
| Outcome | |
| Fatal | 703 (22.2) |
| Not Recovered/Not Resolved | 577 (18.2) |
| Recovered/Resolved | 644 (20.3) |
| Recovering/Resolving | 293 (9.3) |
| Recovered/Resolved With Sequelae | 6 (0.2) |
| Unknown | 943 (29.8) |
| Adverse Event Duration, Days, Mean (±SD) | 4.16 (7.06) |
| Adverse Events by MedDRA SOC and HLGT | Adverse Events 3166 (%) |
|---|---|
| Investigations | 792 (25.0) |
| Hepatobiliary investigations | 496 (15.7) |
| Renal and urinary tract investigations and urinalyses | 95 (3.0) |
| Haematology investigations (incl. blood groups) | 54 (1.7) |
| Other | 147 (4.6) |
| General disorders and administration site conditions | 413 (13.0) |
| Fatal outcomes | 200 (6.3) |
| General system disorders NEC 1 | 140 (4.4) |
| Therapeutic and nontherapeutic effects (excluding toxicity) | 24 (0.8) |
| Other | 49 (1.5) |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | 286 (9.0) |
| Respiratory disorders NEC 1 | 195 (6.2) |
| Lower respiratory tract disorders (excluding obstruction and infection) | 38 (1.2) |
| Infections—pathogen unspecified | 14 (0.4) |
| Other | 39 (1.2) |
| Cardiac disorders | 266 (8.4) |
| Cardiac arrhythmias | 230 (7.3) |
| Coronary artery disorders | 16 (0.5) |
| Heart failures | 10 (0.3) |
| Other | 10 (0.3) |
| Renal and urinary disorders | 256 (8.1) |
| Renal disorders (excluding nephropathies) | 244 (7.7) |
| Urinary tract signs and symptoms | 6 (0.2) |
| Nephropathies | 4 (0.1) |
| Other | 2 (0.1) |
| Infections and infestations | 249 (7.9) |
| Viral infectious disorders | 147 (4.6) |
| Infections—pathogen unspecified | 63 (2.0) |
| Bacterial infectious disorders | 30 (0.9) |
| Other | 9 (0.3) |
| Hepatobiliary disorders | 117 (3.7) |
| Hepatic and hepatobiliary disorders | 115 (3.6) |
| Other | 2 (0.1) |
| Vascular disorders | 116 (3.7) |
| Decreased and nonspecific blood pressure disorders and shock | 87 (2.7) |
| Embolism and thrombosis | 11 (0.3) |
| Vascular hypertensive disorders | 8 (0.3) |
| Other | 10 (0.3) |
| Nervous system disorders | 110 (3.5) |
| Neurological disorders NEC 1 | 32 (1.0) |
| Central nervous system vascular disorders | 21 (0.7) |
| Seizures (incl. subtypes) | 13 (0.4) |
| Other | 44 (1.4) |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | 101 (3.2) |
| Epidermal and dermal conditions | 68 (2.1) |
| Skin appendage conditions | 13 (0.4) |
| Angioedema and urticaria | 10 (0.3) |
| Other | 10 (0.3) |
| Other SOCs | 920 (29.1) |
| Cardiac Individual Case Safety Reports 221 (%) | |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Female | 89 (40.3) |
| Male | 132 (59.7) |
| Age group | |
| 12–17 Years | 1 (0.5) |
| 18–64 Years | 83 (37.6) |
| 2 Months–2 Years | 1 (0.5) |
| 65–85 Years | 87 (39.4) |
| More Than 85 Years | 31 (14.0) |
| Not Specified | 18 (8.1) |
| Outcome | |
| Fatal | 69 (31.2) |
| Not Recovered/Not Resolved | 35 (15.8) |
| Recovered/Resolved | 60 (27.1) |
| Recovered/Resolved With Sequelae | 3 (1.4) |
| Recovering/Resolving | 9 (4.1) |
| Unknown | 45 (20.4) |
| N. of cardiac events per ICSR | |
| 1 | 178 (80.5) |
| 2 | 28 (12.7) |
| 3 | 9 (4.1) |
| 4 | 3 (1.4) |
| 5 | 3 (1.4) |
| Overall Adverse Events | |
| Total number | 841 |
| Median per ICSR | 2 (1–17) |
| Other drugs | |
| Total number | 2372 |
| Median per ICSR | 8 (0–52) |
| Other drugs for cardiovascular diseases | |
| Yes | 166 (75.1) |
| No | 55 (24.9) |
| Other cardiotoxic drugs (azithromycin or hydroxychloroquine) | |
| Yes | 56 (25.3) |
| No | 165 (74.7) |
| No. of Events | Mean of Time to Onset (Days) | StdDev | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac Events with time information | 196 | 3.3 | ±2.2 |
| Cardiac arrhythmias | 162 | 3.3 | ±2.3 |
| Coronary artery disorders | 12 | 3.3 | ±2.1 |
| Cardiac and vascular investigations (ex. enzyme tests) | 11 | 2.6 | ±1.4 |
| Heart failures | 7 | 3.1 | ±1.7 |
| Cardiac disorders, signs and symptoms NEC 1 | 2 | 5.5 | ±4.9 |
| Myocardial disorders | 2 | 2.5 | ±2.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rafaniello, C.; Ferrajolo, C.; Sullo, M.G.; Gaio, M.; Zinzi, A.; Scavone, C.; Gargano, F.; Coscioni, E.; Rossi, F.; Capuano, A. Cardiac Events Potentially Associated to Remdesivir: An Analysis from the European Spontaneous Adverse Event Reporting System. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070611
Rafaniello C, Ferrajolo C, Sullo MG, Gaio M, Zinzi A, Scavone C, Gargano F, Coscioni E, Rossi F, Capuano A. Cardiac Events Potentially Associated to Remdesivir: An Analysis from the European Spontaneous Adverse Event Reporting System. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(7):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070611
Chicago/Turabian StyleRafaniello, Concetta, Carmen Ferrajolo, Maria Giuseppa Sullo, Mario Gaio, Alessia Zinzi, Cristina Scavone, Francesca Gargano, Enrico Coscioni, Francesco Rossi, and Annalisa Capuano. 2021. "Cardiac Events Potentially Associated to Remdesivir: An Analysis from the European Spontaneous Adverse Event Reporting System" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 7: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070611
APA StyleRafaniello, C., Ferrajolo, C., Sullo, M. G., Gaio, M., Zinzi, A., Scavone, C., Gargano, F., Coscioni, E., Rossi, F., & Capuano, A. (2021). Cardiac Events Potentially Associated to Remdesivir: An Analysis from the European Spontaneous Adverse Event Reporting System. Pharmaceuticals, 14(7), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14070611






