Electroconvulsive Therapy and Age: Effectiveness, Safety and Tolerability in the Treatment of Major Depression among Patients under and over 65 Years of Age
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Group
2.2. Efficacy of Electroconvulsive Therapy in Relation to Age
2.3. Safety of Electroconvulsive Therapy in Relation to Age
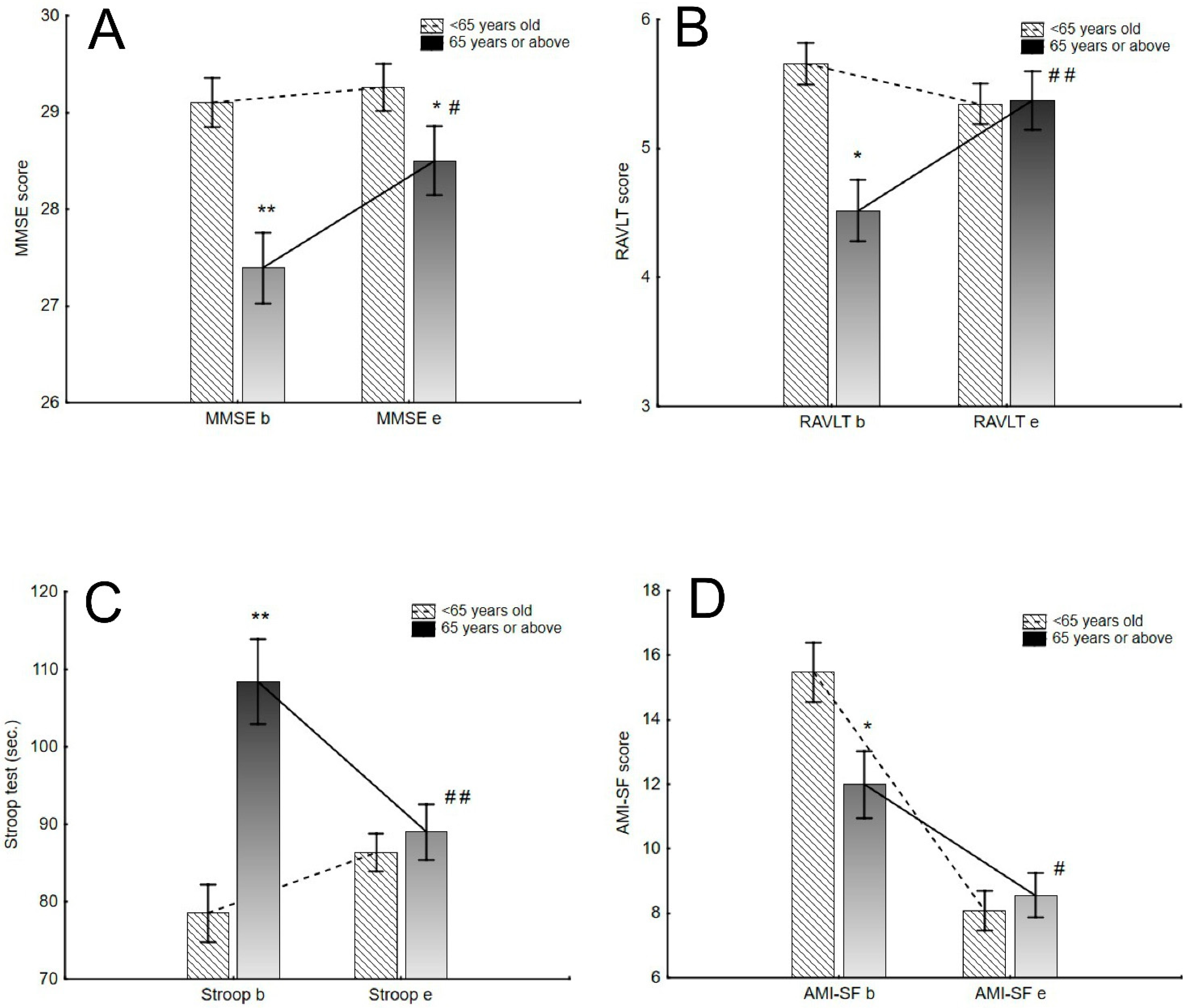
2.4. Tolerability of Electroconvulsive Therapy in Relation to Age
3. Discussion
Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Clinical Assessment
4.3. Procedures
4.4. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rush, A.J.; Trivedi, M.H.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Stewart, J.W.; Warden, D.; Niederehe, G.; Thase, M.E.; Lavori, P.W.; Lebowitz, B.D.; et al. Acute and Longer-Term Outcomes in Depressed Outpatients Requiring One or Several Treatment Steps: A STAR*D Report. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado-Vieira, R.; Baumann, J.; Wheeler-Castillo, C.; Latov, D.; Henter, I.; Salvadore, G.; Zarate, J.C.A. The Timing of Antidepressant Effects: A Comparison of Diverse Pharmacological and Somatic Treatments. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, S.J.; Grima, E.; Tan, M.; Rotzinger, S.; Lin, P.; McIntyre, R.S.; Kennedy, S.H. Treatment-Resistant Depression in Primary Care across Canada. Can. J. Psychiatry 2014, 59, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruberto, V.L.; Jha, M.K.; Murrough, J.W. Pharmacological Treatments for Patients with Treatment-Resistant Depression. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UK ECT Review Group. Efficacy and safety of electroconvulsive therapy in depressive disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2003, 361, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnin, D.; De Queiroz, V.; Pini, S.; Cassano, G.B. Efficacy of ECT in Depression: A Meta-Analytic Review. J. ECT 2004, 20, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaynes, B.N.; Warden, D.; Trivedi, M.H.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Fav, A.M.; Rush, A.J. What did STAR*D Teach Us? Results from a large-scale, practical, clinical trial for patients with depression. Psychiatr. Serv. 2009, 60, 1439–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlim, M.T.; Eynde, F.V.D.; Daskalakis, Z.J. Efficacy and acceptability of high frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (RTMS) versus electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) for major depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Depress. Anxiety 2013, 30, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacobbe, P.; Rakita, U.; Penner-Goeke, K.; Feffer, K.; Flint, A.J.; Kennedy, S.H.; Downar, J. Improvements in Health-Related Quality of Life With Electroconvulsive Therapy: A Meta-analysis. J. ECT 2018, 34, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-J.; Zhao, L.-B.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Fan, S.-H.; Xie, P. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of electroconvulsive therapy versus repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation for major depression: A systematic review and multiple-treatments meta-analysis. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 320, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooij, S.J.H.; Riva-Posse, P.; McDonald, W.M. The Efficacy and Safety of Neuromodulation Treatments in Late-Life Depression. Curr. Treat. Options Psychiatry 2020, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Quality Ontario. Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Treatment-Resistant Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Ont. Health Technol. Assess. Ser. 2016, 16, 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Mutz, J.; Vipulananthan, V.; Carter, B.; Hurlemann, R.; Fu, C.H.Y.; Young, A.H. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of non-surgical brain stimulation for the acute treatment of major depressive episodes in adults: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ 2019, 364, l1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottomley, J.M.; LeReun, C.; Diamantopoulos, A.; Mitchell, S.; Gaynes, B.N. Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) therapy in patients with treatment resistant depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Compr. Psychiatry 2020, 98, 152156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milev, R.V.; Giacobbe, P.; Kennedy, S.H.; Blumberger, D.M.; Daskalakis, Z.J.; Downar, J.; Modirrousta, M.; Patry, S.; Vila-Rodriguez, F.; Lam, R.W.; et al. Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) 2016 Clinical Guidelines for the Management of Adults with Major Depressive Disorder: Section 4. Neurostimulation Treatments. Can. J. Psychiatry 2016, 61, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, K.; Fink, M. The Chemical Induction of Seizures in Psychiatric Therapy. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 34, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veraart, J.K.; Smith-Apeldoorn, S.Y.; Spaans, H.-P.; Kamphuis, J.; Schoevers, R.A. Is ketamine an appropriate alternative to ECT for patients with treatment resistant depression? A systematic review. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 281, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, C. ECT in the 21st century: Optimizing treatment: State of the art in the 21st century. J. ECT 2010, 26, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heijnen, W.T.; Birkenhäger, T.K.; Wierdsma, A.I.; van den Broek, W.W. Antidepressant pharmacotherapy failure and response to subsequent electroconvulsive therapy: A meta-analysis. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 30, 616–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellner, C.H.; Knapp, R.; Husain, M.M.; Rasmussen, K.; Sampson, S.; Cullum, M.; McClintock, S.M.; Tobias, K.G.; Martino, C.; Mueller, M.; et al. Bifrontal, bitemporal and right unilateral electrode placement in ECT: Randomised trial. Br. J. Psychiatry 2010, 196, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordenskjold, A. ECT is superior to pharmacotherapy for the short-term treatment of medication-resistant in patients with bipolar depression. Evid. Based Ment. Health 2015, 18, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schoeyen, H.K.; Kessler, U.; Andreassen, O.A.; Auestad, B.H.; Bergsholm, P.; Malt, U.F.; Morken, G.; Oedegaard, K.J.; Vaaler, A. Treatment-Resistant Bipolar Depression: A Randomized Controlled Trial of Electroconvulsive Therapy Versus Algorithm-Based Pharmacological Treatment. Am. J. Psychiatry 2015, 172, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tielkes, C.E.M.; Comijs, H.C.; Verwijk, E.; Stek, M.L. The effects of ECT on cognitive functioning in the elderly: A review. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2008, 23, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antosik-Wójcińska, A.; Święcicki, Ł. The efficacy and safety of ECT in population before and after 60 years of age. Psychiatr. Pol. 2016, 50, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damm, J.; Eser, D.; Schüle, C.; Obermeier, M.; Möller, H.-J.; Rupprecht, R.; Baghai, T.C. Influence of Age on Effectiveness and Tolerability of Electroconvulsive Therapy. J. ECT 2010, 26, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, S.; Satapathy, A.; Chakrabarti, S.; Avasthi, A. Electroconvulsive Therapy among Elderly patients: Astudy from Tertiary care centre in north India. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2018, 31, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Zhu, X.-M.; Zheng, W.; Li, X.-H.; Ng, C.H.; Ungvari, G.S.; Xiang, Y.-T. Electroconvulsive therapy for older adult patients with major depressive disorder: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Psychogeriatrics 2018, 18, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dierman, L.; van den Ameele, S.; Kamperman, A.M.; Sabbe, B.C.G.; Vermeulen, T.; Schrijvers, D.; Birkenhager, T.K. Prediction of electroconvulsive therapy response and remission in major depression: Meta-analysis. Br. J. Psychiatry 2018, 212, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekadu, A.; Wooderson, S.; Donaldson, C.; Markopoulou, K.; Masterson, B.; Poon, L.; Cleare, A.J. A multidimensional tool to quantify treatment resistance in depression: The Maudsley staging method. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2009, 70, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominiak, M.; Goetz, Z.; Antosik-Wojcinska, A.Z.; Swiecicki, L. Right unilateral versus bilateral formula-based electroconvulsive therapy in the treatment of major depression in elderly patients: A randomised, open label, pilot controlled trial. Psychogeriatrics 2021, 21, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tew, J.D.; Mulsant, B.H.; Haskett, R.F.; Prudic, J.; Thase, M.E.; Crowe, R.R.; Dolata, D.; Begley, A.E.; Reynolds, C.F.; Sackeim, H.A. Acute efficacy of ECT in the treatment of major depression in the old-old. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 1102–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tew, J.D.; Mulsant, B.H.; Haskett, R.F.; Dolata, D.; Hixson, L.; Mann, J.J. A Randomized Comparison of High-Charge Right Unilateral Electroconvulsive Therapy and Bilateral Electroconvulsive Therapy in Older Depressed Patients Who Failed to Respond to 5 to 8 Moderate-Charge Right Unilateral Treatments. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2002, 63, 1102–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, M.K.; Knapp, R.; Husain, M.; Rummans, T.A.; Petrides, G.; Smith, G.; Mueller, M.; Snyder, K.; Bernstein, H.; Rush, A.J.; et al. The Influence of Age on the Response of Major Depression to Electroconvulsive Therapy: A C.O.R.E. Report. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2001, 9, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordenskjöld, A.; Von Knorring, L.; Engström, I. Predictors of the short-term responder rate of Electroconvulsive therapy in depressive disorders—A population based study. BMC Psychiatry 2012, 12, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fink, M. What was learned: Studies by the consortium for research in ECT (CORE) 1997-2011. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2014, 129, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.P.; Swetter, S.K.; Kellner, C.H. Electroconvulsive Therapy in Geriatric Psychiatry: A Selective Review. Psychiatr. Clin. North Am. 2018, 41, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socci, C.; Medda, P.; Toni, C.; Lattanzi, L.; Tripodi, B.; Vannucchi, G.; Perugi, G. Electroconvulsive therapy and age: Age-related clinical features and effectiveness in treatment resistant major depressive episode. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 227, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkenhäger, T.K.; Pluijms, E.M.; Ju, M.R.; Mulder, P.G.; Broek, W.W.V.D. Influence of age on the efficacy of electroconvulsive therapy in major depression: A retrospective study. J. Affect. Disord. 2010, 126, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, A.U.; Sitzmann, A.F.; Goldman, M.L.; Maixner, D.F.; Mickey, B.J. Response of depression to electroconvulsive therapy: A meta-analysis of clinical predictors. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2015, 76, 1374–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijnen, W.T.; Kamperman, A.; Tjokrodipo, L.D.; Hoogendijk, W.J.; Broek, W.W.V.D.; Birkenhager, T.K. Influence of age on ECT efficacy in depression and the mediating role of psychomotor retardation and psychotic features. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 109, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaakxs, R.; Comijs, H.C.; Lamers, F.; Beekman, A.T.F.; Penninx, B.W.J.H. Age-related variability in the presentation of symptoms of major depressive disorder. Psychol. Med. 2016, 47, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datka, W.; Rachel, W.; Zyss, T.; Szwajca, K.; Jabłoński, M.J. Effects of electroconvulsive therapy on cognitive function in the treatment of depression. Psychiatria 2014, 11, 148–154. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Sackeim, H.A.; Decina, P.; Kanzler, M.; Kerr, B.; Malitz, S. Effects of electrode placement on the efficacy of titrated, low-dose ECT. Am. J. Psychiatry 1987, 144, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obbels, J.; Verwijk, E.; Vansteelandt, K.; Dols, A.; Bouckaert, F.; Schouws, S.; Vandenbulcke, M.; Emsell, L.; Stek, M.; Sienaert, P. Long-term neurocognitive functioning after electroconvulsive therapy in patients with late-life depression. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2018, 138, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwijk, E.; Comijs, H.C.; Kok, R.M.; Spaans, H.-P.; Tielkes, C.E.; Scherder, E.J.; Stek, M.L. Short- and long-term neurocognitive functioning after electroconvulsive therapy in depressed elderly: A prospective naturalistic study. Int. Psychogeriatrics 2013, 26, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.; Lyketsos, C.G. The benefits and risks of ECT for patients with primary dementia who also suffer from depression. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2000, 15, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybedal, G.S.; Tanum, L.; Sundet, K.; Bjølseth, T.M. The Role of Baseline Cognitive Function in the Neurocognitive Effects of Electroconvulsive Therapy in Depressed Elderly Patients. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2015, 29, 487–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominiak, M.; Antosik-Wójcińska, A.Z.; Goetz, Z.; Sikorska, O.; Stefanowski, B.; Gorostiza, D.; Święcicki, Ł. Efficacy, safety and tolerability of formula-based unilateral vs bilateral electroconvulsive therapy in the treatment of major depression: A randomized open label controlled trial. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 133, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semkovska, M.; Noone, M.; Carton, M.; McLoughlin, D.M. Measuring consistency of autobiographical memory recall in depression. Psychiatry Res. 2012, 197, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackeim, H.A.; Prudic, J.; Nobler, M.S.; Fitzsimons, L.; Lisanby, S.H.; Payne, N.; Berman, R.M.; Brakemeier, E.-L.; Perera, T.; Devanand, D. Effects of pulse width and electrode placement on the efficacy and cognitive effects of electroconvulsive therapy. Brain Stimul. 2008, 1, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaicu, A.; Bustuchina, V.M. New neuromodulation techniques for treatment resistant depression. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2020, 24, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerner, N.; Prudic, J. Current electroconvulsive therapy practice and research in the geriatric population. Neuropsychiatry 2014, 4, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElhiney, M.C.; Moody, B.J.; Sackeim, H.A. Manual for Administration and Scoring the Columbia University Autobiographical Memory Interview—Short Form; Version 3; New York State Psychiatric Institute: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Under 65 Years Old | 65 Years or Older | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients n (%) | 62 (68,1%) | 29 (31,9%) | |
| Mean age (in years) (SD) | 46.2 (12.4) | 70.9 (5.07) | <0.001 |
| Gender F/M | F–33 M-29 | F–14 M-15 | 0.659 |
| Type of ECT unilateral/bilateral | 31/31 | 15/14 | 0.878 |
| Score according to MSM Mean (SD) | 9.2 (1.5) | 8.9 (1.2) | 0.354 |
| Drug resistance—number of patients (n) | 60 | 28 | 0.324 |
| Number of patients with psychotic symptoms n (%) | 16 (25%) | 9 (31,0%) | 0.602 |
| Number of patients with at least one somatic disorder n (%) | 17 (27%) | 19 (65%) | 0.0005 |
| HDRS b M (SD) | 28.3 (6.43) | 30.1 (5.81) | 0.082 |
| HDRS e M (SD) | 11.5 (4.50) | 8.2 (3.96) | 0.001 |
| <65 Years Old (n = 62) | ≥65 Years Old (n = 29) | 95% CI | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | SD | M | SD | t | p | LL | UL | d Cohen | |
| Charge (mC) | 405.64 | 194.19 | 539.9 | 213.20 | 2.978 | 0.003 | −223.8 | −44.68 | 0.706 |
| Number of ECT treatments | 11.03 | 2.03 | 10.31 | 2.87 | 1.379 | 0.171 | −0.473 | 1.916 | 0.310 |
| Adverse Effects | <65 Years Old (n = 62) | ≥65 Years Old (n = 29) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood pressure elevation | 11.3% (n = 7) | 24.1 % (n = 9) | 0.044 |
| Cardiac arrythmias | 4.8% (n = 3) | 20.7 % (n = 6) | 0.047 |
| Disturbance of consciousness | 6.4% (n = 4) | 10.3% (n = 3) | 0.820 |
| Headaches | 11.3% (n = 7) | 10.3% (n = 3) | 0.821 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dominiak, M.; Antosik-Wójcińska, A.Z.; Wojnar, M.; Mierzejewski, P. Electroconvulsive Therapy and Age: Effectiveness, Safety and Tolerability in the Treatment of Major Depression among Patients under and over 65 Years of Age. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060582
Dominiak M, Antosik-Wójcińska AZ, Wojnar M, Mierzejewski P. Electroconvulsive Therapy and Age: Effectiveness, Safety and Tolerability in the Treatment of Major Depression among Patients under and over 65 Years of Age. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(6):582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060582
Chicago/Turabian StyleDominiak, Monika, Anna Z. Antosik-Wójcińska, Marcin Wojnar, and Paweł Mierzejewski. 2021. "Electroconvulsive Therapy and Age: Effectiveness, Safety and Tolerability in the Treatment of Major Depression among Patients under and over 65 Years of Age" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 6: 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060582
APA StyleDominiak, M., Antosik-Wójcińska, A. Z., Wojnar, M., & Mierzejewski, P. (2021). Electroconvulsive Therapy and Age: Effectiveness, Safety and Tolerability in the Treatment of Major Depression among Patients under and over 65 Years of Age. Pharmaceuticals, 14(6), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14060582






