Combinations of Freeze-Dried Amorphous Vardenafil Hydrochloride with Saccharides as a Way to Enhance Dissolution Rate and Permeability
Abstract
1. Introduction
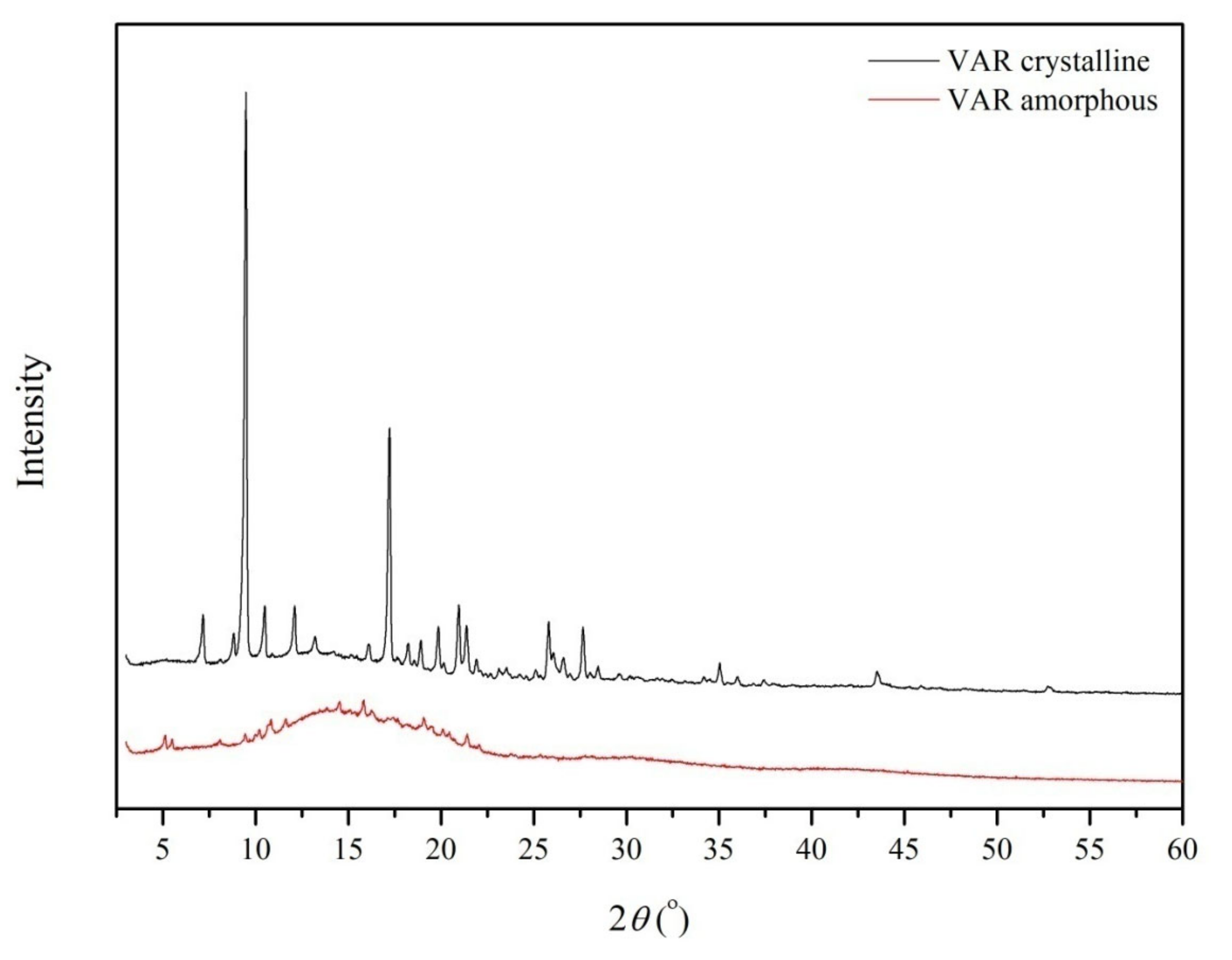
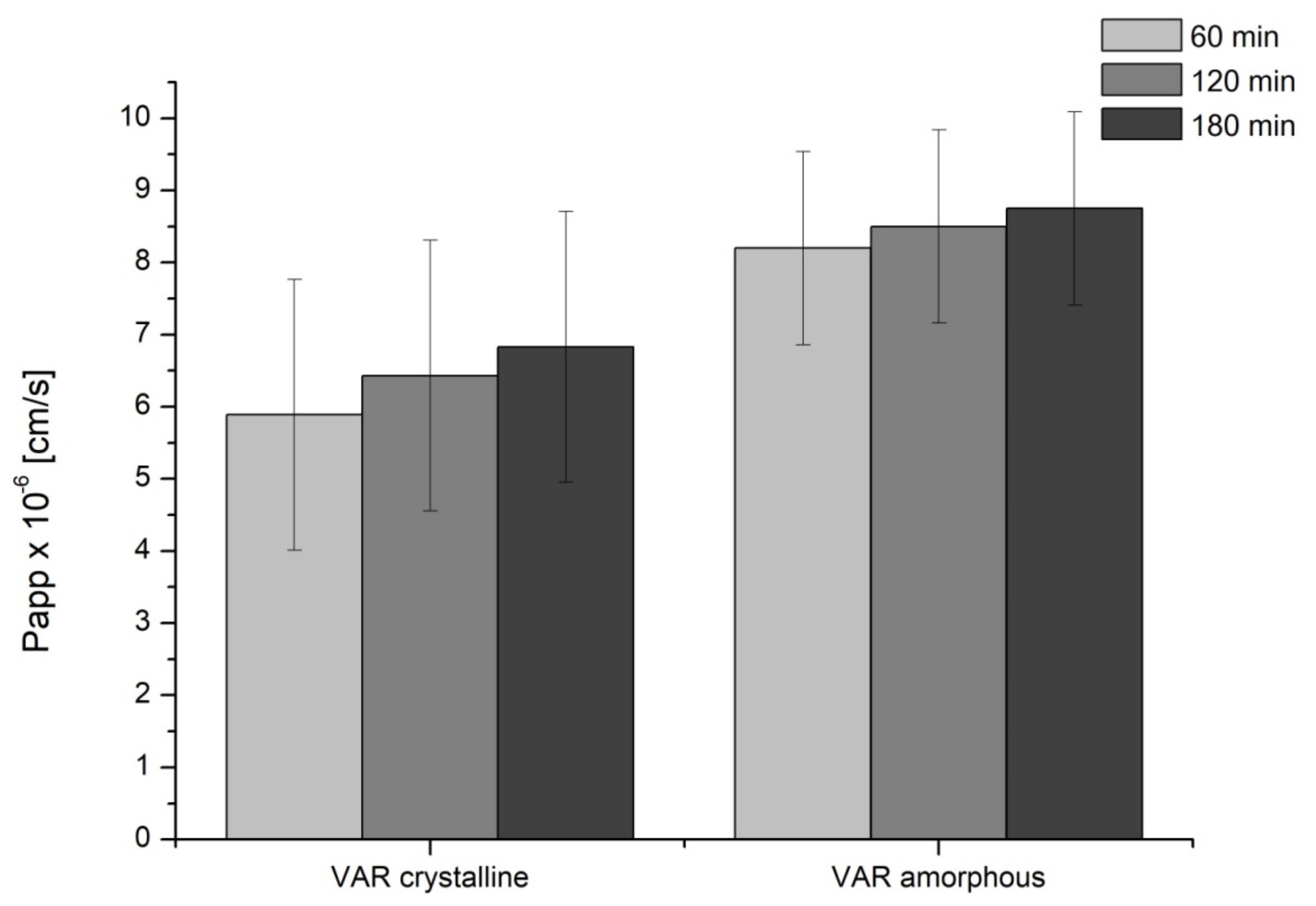
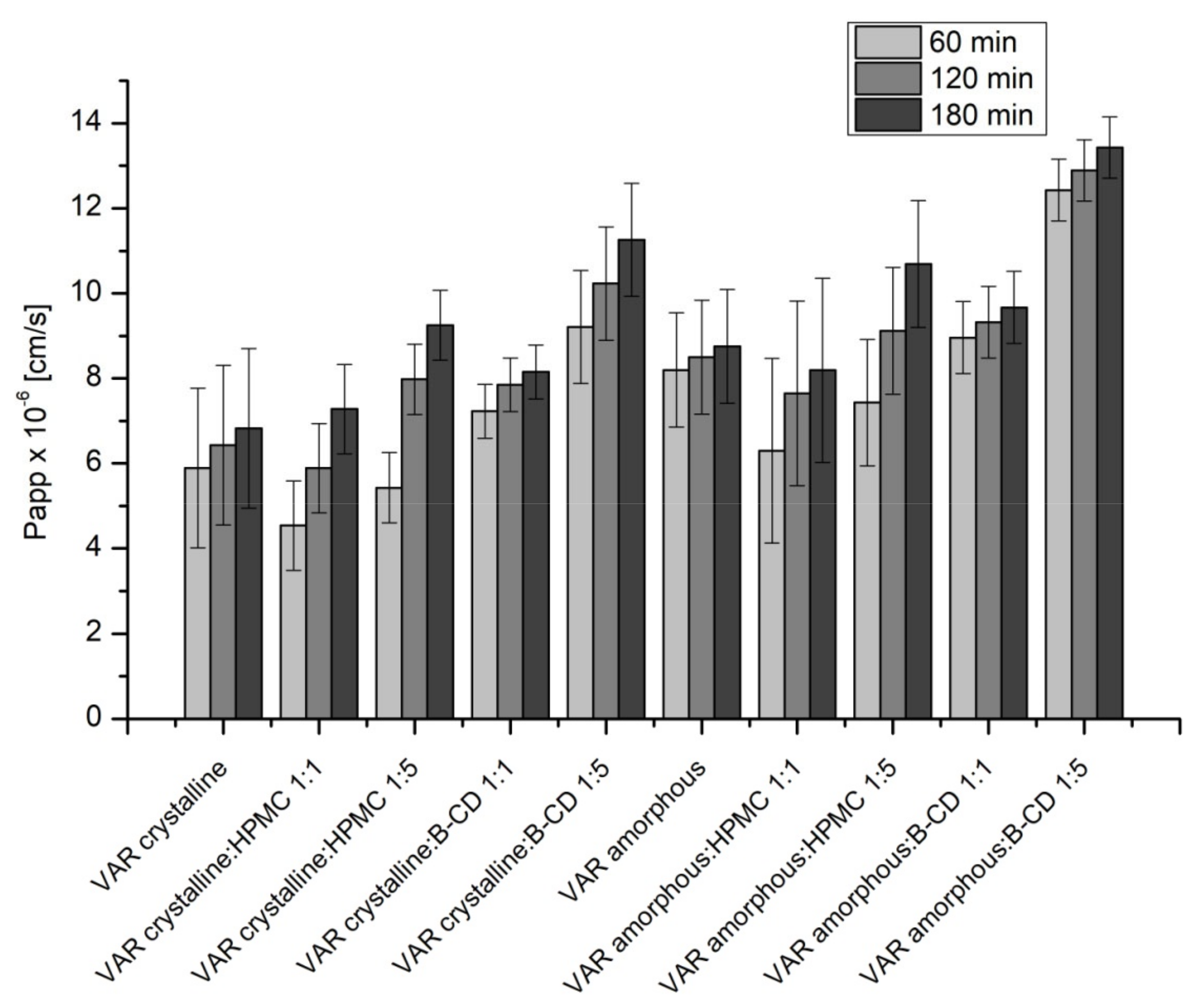
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of the Amorphous VAR
4.3. Preparation of the Physical Mixtures of Crystalline or Amorphous VAR with Excipients
4.4. Identification of Amorphous VAR
4.4.1. X-ray Powder Diffraction (PXRD)
4.4.2. Different Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.4.3. FT–IR Spectroscopy
4.5. Studies of Apparent Solubility and Permeability
4.5.1. Apparent Solubility
4.5.2. Permeability Studies
4.6. Studies of Chemical and Physical Stability
4.6.1. Chemical Stability Studies
4.6.2. Physical Stability Studies
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, S.A.; Lie, J.D. Phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitors in the management of erectile dysfunction. Pharm. Ther. 2013, 38, 407–419. [Google Scholar]
- Mátyás, C.; Németh, B.T.; Oláh, A.; Török, M.; Ruppert, M.; Kellermayer, D.; Barta, B.A.; Szabó, G.; Kökény, G.; Horváth, E.M.; et al. Prevention of the development of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction by the phosphodiesterase-5A inhibitor vardenafil in rats with type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbin, J.D. Mechanisms of action of PDE5 inhibition in erectile dysfunction. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2004, 16, S4–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Refai, K.; Teaima, M.H.; El-Nabarawi, M.A. Dual-purpose vardenafil hydrochloride/dapoxetine hydrochloride orodispersible tablets: In vitro formulation/evaluation, stability study and in vivo comparative pharmacokinetic study in healthy human subjects. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrotra, N.; Gupta, M.; Kovar, A.; Meibohm, B. The role of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor therapy. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2007, 19, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzichristou, D.; Montorsi, F.; Buvat, J.; Laferriere, N.; Bandel, T.-J.; Porst, H.; European Vardenafil Study Group. The efficacy and safety of flexible-dose vardenafil (levitra) in a broad population of European men. Eur. Urol. 2004, 45, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, C.G.; McMahon, C.N.; Leow, L.J.; Winestock, C.G. Efficacy of Type-5 Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors in the Drug Treatment of Premature Ejaculation: A Systematic Review; Centre for Reviews and Dissemination: York, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jing, Z.-C.; Yu, Z.-X.; Shen, J.-Y.; Wu, B.-X.; Xu, K.-F.; Zhu, X.-Y.; Pan, L.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Liu, X.-Q.; Zhang, Y.-S.; et al. Vardenafil in pulmonary arterial hypertension: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Han, B.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Pang, T.; Fan, Y. The phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor vardenafil improves the activation of BMP signaling in response to hydrogen peroxide. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2020, 34, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.-F.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, X.; Wen, L.; Wu, D.-C.; Liu, D.; Yuan, P.; Wang, Y.-L.; Jing, Z.-C. The phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor vardenafil reduces oxidative stress while reversing pulmonary arterial hypertension. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 99, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-M.; Taneja, C.; Perez-Pena, H.; Ryu, V.; Gumerova, A.; Li, W.; Ahmad, N.; Zhu, L.-L.; Liu, P.; Mathew, M.; et al. Repurposing erectile dysfunction drugs tadalafil and vardenafil to increase bone mass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 14386–14394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Agamy, D.S.; Almaramhy, H.H.; Ahmed, N.; Bojan, B.; Alrohily, W.D.; Elkablawy, M.A. Anti-inflammatory effects of vardenafil against cholestatic liver damage in mice: A mechanistic study. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Government, Department of Health and Ageing, Therapeutic Goods Administration. Australian Public Assessment Report for Vardenafil; Therapeutic Goods Administration: Symonston, ACT, Australia, 2011; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff, E. Vardenafil preclinical trial data: Potency, pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and adverse events. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2004, 16, S34–S37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitra (Vardenafil HCl). Product Monograph; Bayer Inc.: Mississauga, ON, Canada, 2020; Available online: https://omr.bayer.ca/omr/online/levitra-pm-en.pdf (accessed on 26 April 2021).
- Capogrosso, P.; Ventimiglia, E.; Boeri, L.; Serino, A.; Russo, A.; Croce, G.L.; Capitanio, U.; Dehò, F.; Montorsi, F.; Salonia, A. Time of onset of vardenafil orodispersible tablet in a real-life setting—Looking beyond randomized clinical trials. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 10, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldon, M.A.; Parsley, E.L.; Maurer, M.; Tarara, T.E.; Okikawa, J.; Weers, J.G. Safety, Tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of RT234 (vardenafil inhalation powder): A first-in-human, ascending single- and multiple-dose study in healthy subjects. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinig, R.; Weimann, B.; Dietrich, H.; Boettcher, M. Pharmacokinetics of a new orodispersible tablet formulation of vardenafil. J. Men Health 2010, 7, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalepu, S.; Nekkanti, V. Insoluble drug delivery strategies: Review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaiah, Y. Pharmaceutical technologies for enhancing oral bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs. J. Bioequiv. Bioavailab. 2010, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, M.M.; Makary, P.; Wlodarski, M.D. A Review of Polymorphism and the Amorphous State in the Formulation Strategy of Medicines and Marketed Drugs. Pharm. Biosci. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Mooter, G. The use of amorphous solid dispersions: A formulation strategy to overcome poor solubility and dissolution rate. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2012, 9, e79–e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, A.S.; Tiwari, K.J.; Mahajan, V.R. Solubility enhancement techniques for poorly water-soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 10, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Talaczynska, A.; Dzitko, J.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Benefits and limitations of polymorphic and amorphous forms of active pharmaceutical ingredients. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 4975–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Heng, W.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y. Coamorphous lurasidone hydrochloride–Saccharin with charge-assisted hydrogen bonding interaction shows improved physical stability and enhanced dissolution with ph-independent solubility behavior. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 2920–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapik-Kowalczuk, J.; Tu, W.; Chmiel, K.; Rams-Baron, M.; Paluch, M. Co-stabilization of amorphous pharmaceuticals—The case of nifedipine and nimodipine. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dengale, S.J.; Ranjan, O.P.; Hussen, S.S.; Krishna, B.S.M.; Musmade, P.B.; Gautham Shenoy, G.; Bhat, K. Preparation and characterization of co-amorphous ritonavir-indomethacin systems by solvent evaporation technique: Improved dissolution behavior and physical stability without evidence of intermolecular interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 62, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löbmann, K.; Laitinen, R.; Grohganz, H.; Gordon, K.C.; Strachan, C.; Rades, T. Coamorphous drug systems: Enhanced physical stability and dissolution rate of indomethacin and naproxen. Mol. Pharm. 2011, 8, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renuka, S.S.K.; Gulati, M.; Narang, R. Stable amorphous binary systems of glipizide and atorvastatin powders with enhanced dissolution profiles: Formulation and characterization. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, N.; Zeng, L.; Mangal, S.; Nie, H.; Rowles, M.R.; Guo, R.; Han, Y.; Park, J.H.; Zhou, Q.T. Effects of moisture-induced crystallization on the aerosol performance of spray dried amorphous ciprofloxacin powder formulations. Pharm. Res. 2018, 35, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Taylor, L.S. Effect of temperature and moisture on the physical stability of binary and ternary amorphous solid dispersions of celecoxib. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 106, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potes, N.; Kerry, J.P.; Roos, Y.H. Additivity of water sorption, alpha-relaxations and crystallization inhibition in lactose–maltodextrin systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzybowska, K.; Paluch, M.; Wlodarczyk, P.; Grzybowski, A.; Kaminski, K.; Hawelek, L.; Zakowiecki, D.; Kasprzycka, A.; Jankowska-Sumara, I. Enhancement of amorphous celecoxib stability by mixing it with octaacetylmaltose: The molecular dynamics study. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.M.A.; Ali, A.A.; Maghrabi, I.A. Clozapine-carboxylic acid plasticized co-amorphous dispersions: Preparation, characterization and solution stability evaluation. Acta Pharm. 2015, 65, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Yoshihashi, Y.; Yonemochi, E.; Fujii, K.; Uekusa, H.; Terada, K. Cocrystallization and amorphization induced by drug-excipient interaction improves the physical properties of acyclovir. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 422, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Wu, M. Carvedilol-Asccharin Amorphous Compound. CN103467363A, 25 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Borrego-Sánchez, A.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; Albertini, B.; Passerini, N.; Cerezo, P.; Viseras, C.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I. Ground calcium carbonate as a low cost and biosafety excipient for solubility and dissolution improvement of praziquantel. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego-Sánchez, A.; Sánchez-Espejo, R.; García-Villén, F.; Viseras, C.; Sainz-Díaz, C.I. Praziquantel–Clays as accelerated release systems to enhance the low solubility of the drug. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardenafil. Available online: https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00862 (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- Attia, A.K.; Souaya, E.R.; Soliman, E.A. Thermal analysis investigation of dapoxetine and vardenafil hydrochlorides using molecular orbital calculations. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- European Medicines Agency. Q 2 (R1) Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology; EMEA: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; p. 15. [Google Scholar]
- Europe PMC. Prediction of Human Intestinal Permeability Using Artificial Membrane Permeability. Abstract. Available online: http://europepmc.org/article/med/12711179 (accessed on 21 April 2020).
- Chavan, R.; Thipparaboina, R.; Kumar, D.; Shastri, N. Co Amorphous systems: A product development perspective. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- View of Excipients Updates for Orally Disintegrating Dosage Forms. Available online: https://pharmascope.org/ijrps/article/view/157/149 (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Conceição, J.; Adeoye, O.; Cabral-Marques, H.M.; Lobo, J.M.S. Cyclodextrins as excipients in tablet formulations. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-khattawi, A.; Mohammed, A.R. Compressed orally disintegrating tablets: Excipients evolution and formulation strategies. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucamp, M.; Odendaal, R.; Liebenberg, W.; Hamman, J. Amorphous azithromycin with improved aqueous solubility and intestinal membrane permeability. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepek, P.; Sawicki, W.; Wlodarski, K.; Wojnarowska, Z.; Paluch, M.; Guzik, L. Effect of amorphization method on telmisartan solubility and the tableting process. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 83, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craye, G.; Löbmann, K.; Grohganz, H.; Rades, T.; Laitinen, R. Characterization of amorphous and co-amorphous simvastatin formulations prepared by spray drying. Molecules 2015, 20, 21532–21548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Jain, C.P. Preparation and characterization of solid dispersions of carvedilol with PVP K30. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 5, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kolodziejczyk, K.; Paluch, M.; Grzybowska, K.; Grzybowski, A.; Wojnarowska, Z.; Hawelek, L.; Ziolo, J.D. Relaxation dynamics and crystallization study of sildenafil in the liquid and glassy states. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 2270–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura Ramos, J.J.; Piedade, M.F.M.; Diogo, H.P.; Viciosa, M.T. thermal behavior and slow relaxation dynamics in amorphous efavirenz: A study by DSC, XRPD, TSDC, and DRS. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1254–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schammé, B.; Couvrat, N.; Malpeli, P.; Delbreilh, L.; Dupray, V.; Dargent, É.; Coquerel, G. crystallization kinetics and molecular mobility of an amorphous active pharmaceutical ingredient: A case study with biclotymol. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 490, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, P.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Modeling and comparison of dissolution profiles. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 13, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Compared Systems | f1 | f2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VARcrystalline | VARcrystalline:HPMC (1:1) | 10.02 | 47.09 |
| VARcrystalline | VARcrystalline:HPMC (1:5) | 18.64 | 33.75 |
| VARcrystalline | VARcrystalline:β-CD (1:1) | 8.87 | 67.28 |
| VARcrystalline | VARcrystalline:β-CD (1:5) | 13.06 | 42.06 |
| VARcrystalline:HPMC (1:1) | VARcrystalline:HPMC (1:5) | 13.69 | 50.49 |
| VARcrystalline:β-CD (1:1) | VARcrystalline:β-CD (1:5) | 9.32 | 49.93 |
| VARcrystalline | VARamorphous | 40.24 | 16.97 |
| VARamorphous | VARamorphous:HPMC (1:1) | 28.75 | 16.93 |
| VARamorphous | VARamorphous:HPMC (1:5) | 34.88 | 36.21 |
| VARamorphous | VARamorphous:β-CD (1:1) | 18.43 | 57.10 |
| VARamorphous | VARamorphous:β-CD (1:5) | 28.99 | 16.74 |
| VARamorphous:HPMC (1:1) | VARamorphous:HPMC (1:5) | 30.20 | 28.42 |
| VARamorphous:β-CD (1:1) | VARamorphous:β-CD (1:5) | 23.47 | 20.38 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiergowska, G.; Ludowicz, D.; Wdowiak, K.; Miklaszewski, A.; Lewandowska, K.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Combinations of Freeze-Dried Amorphous Vardenafil Hydrochloride with Saccharides as a Way to Enhance Dissolution Rate and Permeability. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050453
Wiergowska G, Ludowicz D, Wdowiak K, Miklaszewski A, Lewandowska K, Cielecka-Piontek J. Combinations of Freeze-Dried Amorphous Vardenafil Hydrochloride with Saccharides as a Way to Enhance Dissolution Rate and Permeability. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(5):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050453
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiergowska, Gabriela, Dominika Ludowicz, Kamil Wdowiak, Andrzej Miklaszewski, Kornelia Lewandowska, and Judyta Cielecka-Piontek. 2021. "Combinations of Freeze-Dried Amorphous Vardenafil Hydrochloride with Saccharides as a Way to Enhance Dissolution Rate and Permeability" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 5: 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050453
APA StyleWiergowska, G., Ludowicz, D., Wdowiak, K., Miklaszewski, A., Lewandowska, K., & Cielecka-Piontek, J. (2021). Combinations of Freeze-Dried Amorphous Vardenafil Hydrochloride with Saccharides as a Way to Enhance Dissolution Rate and Permeability. Pharmaceuticals, 14(5), 453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14050453