Significant Associations of lncRNA H19 Genotypes with Susceptibility to Childhood Leukemia in Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Comparisons of Basic Characters between the Case and Control Groups
2.2. The Relationships between H19 rs2839698 Polymorphism and Risk of Childhood Leukemia
2.3. The Relationships between H19 rs217727 Polymorphism and Risk of Childhood Leukemia
2.4. The Relationships between H19 rs2839698 Polymorphism with Clinical Features (Immunophenotypes, Risk Classification, and Survival Time)
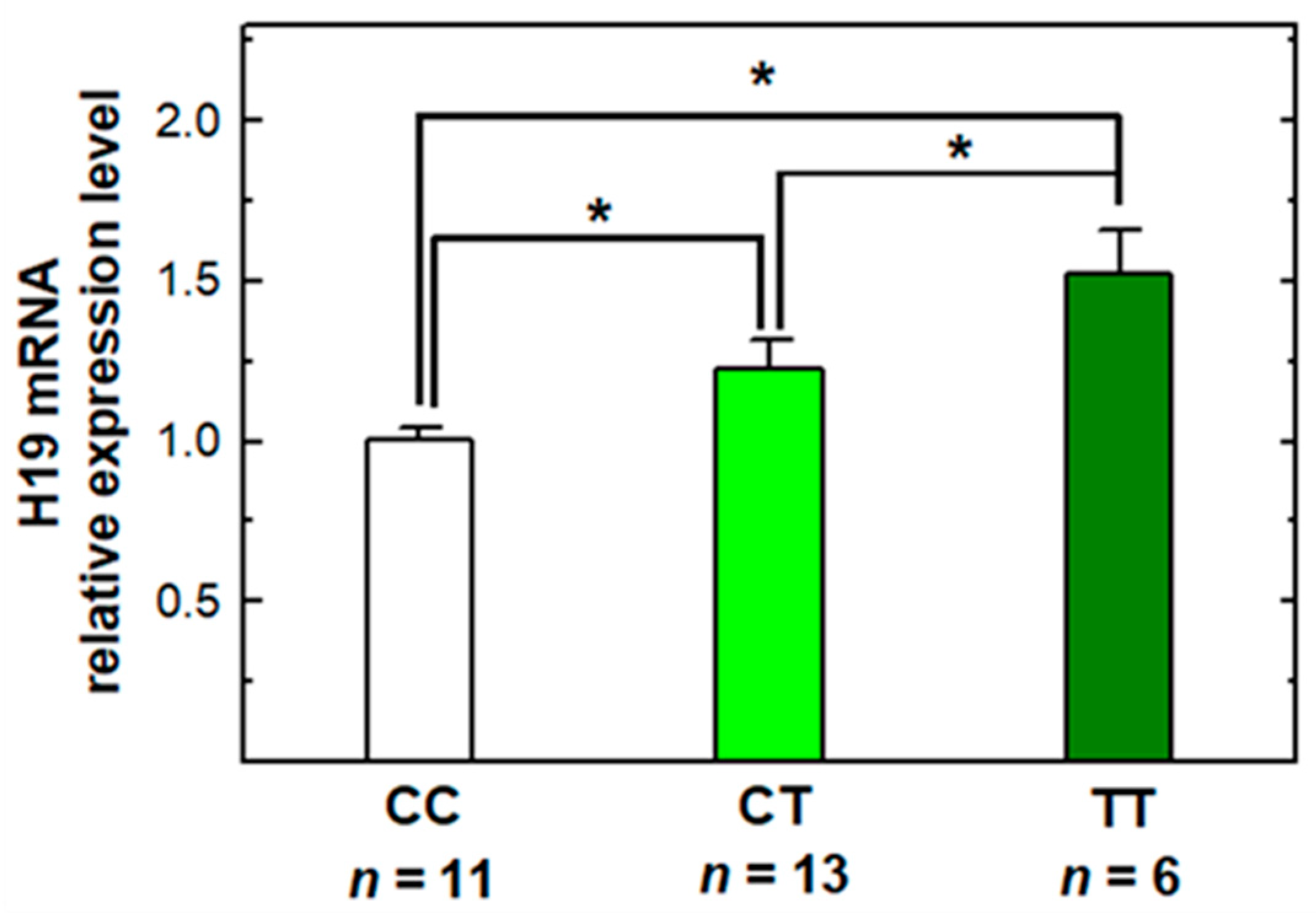
2.5. The Genotype–Phenotype Correlation of H19 rs2839698 Polymorphism
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Recruitment of Childhood Leukemia and Control Participants
4.2. DNA Extraction and Genotyping
4.3. Quantitative RT-PCR Assay of H19 mRNA Expression
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trevino, L.R.; Yang, W.; French, D.; Hunger, S.P.; Carroll, W.L.; Devidas, M.; Willman, C.; Neale, G.; Downing, J.; Raimondi, S.C.; et al. Germline genomic variants associated with childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Lo, H.H.; Hsu, Y.N.; Lin, S.S.; Bau, D.T. Association of X-ray repair cross-complementing-6 genotypes with childhood leukemia. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 5395–5399. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, J.S.; Hsu, C.M.; Tsai, C.W.; Chang, W.S.; Ji, H.X.; Hsiao, C.L.; Miao, C.E.; Hsu, Y.N.; Bau, D.T. The association of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase genotypes with the risk of childhood leukemia in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.S.; Chang, W.S.; Hsu, P.C.; Tsai, C.W.; Hsu, C.M.; Ji, H.X.; Hsiao, C.L.; Hsu, Y.N.; Bau, D.T. The Association of Flap Endonuclease 1 Genotypes with the Risk of Childhood Leukemia. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2016, 13, 69–74. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, J.S.; Hsu, P.C.; Chou, A.K.; Tsai, C.W.; Chang, W.S.; Hsiao, C.L.; Hsu, Y.N.; Cheng, S.P.; Bau, D.T. Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 Genotype Contributes to the Risk of Non-solid Tumor in Childhood Leukemia. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 5127–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.S.; Chou, A.K.; Hsu, P.C.; Tsai, C.W.; Chang, W.S.; Wu, M.F.; Wu, M.H.; Hsia, T.C.; Cheng, S.P.; Bau, D.T. Contribution of Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 Genotypes to the Risk of Non-solid Tumor, Childhood Leukemia. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 6679–6684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.S.; Chang, W.S.; Hsu, P.C.; Chen, C.C.; Cheng, S.P.; Wang, Y.C.; Tsai, C.W.; Shen, T.C.; Bau, D.T. The contribution of XRCC3 genotypes to childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 5677–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.C.; Pei, J.S.; Chen, C.C.; Chang, W.S.; Kuo, C.C.; Cheng, S.P.; Tsai, C.W.; Bau, D.T.; Gong, C.L. Association of Matrix Metallopeptidase-2 Promoter Polymorphisms With the Risk of Childhood Leukemia. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.C.; Chen, C.C.; Tzeng, H.E.; Hsu, Y.N.; Kuo, C.C.; Lin, M.L.; Chang, W.S.; Wang, Y.C.; Tsai, C.W.; Pei, J.S.; et al. HOGG1 rs1052133 Genotypes and Risk of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in a Taiwanese Population. In Vivo 2019, 33, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, J.S.; Chang, W.S.; Hsu, P.C.; Chen, C.C.; Chin, Y.T.; Huang, T.L.; Hsu, Y.N.; Kuo, C.C.; Wang, Y.C.; Tsai, C.W.; et al. Significant Association Between the MiR146a Genotypes and Susceptibility to Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Taiwan. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2020, 17, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, V.A.; Szymanski, M.; Hochberg, A.; Groot, N.; Barciszewski, J. Non-coding, mRNA-like RNAs database Y2K. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilusz, J.E.; Sunwoo, H.; Spector, D.L. Long noncoding RNAs: Functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1494–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taft, R.J.; Pang, K.C.; Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.; Mattick, J.S. Non-coding RNAs: Regulators of disease. J. Pathol. 2010, 220, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, T.R.; Qureshi, I.A.; Gokhan, S.; Dinger, M.E.; Li, G.; Mattick, J.S.; Mehler, M.F. Long noncoding RNAs in neuronal-glial fate specification and oligodendrocyte lineage maturation. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Carmichael, G.G. Decoding the function of nuclear long non-coding RNAs. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinger, M.E.; Amaral, P.P.; Mercer, T.R.; Pang, K.C.; Bruce, S.J.; Gardiner, B.B.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E.; Ru, K.; Solda, G.; Simons, C.; et al. Long noncoding RNAs in mouse embryonic stem cell pluripotency and differentiation. Genome. Res. 2008, 18, 1433–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loewer, S.; Cabili, M.N.; Guttman, M.; Loh, Y.H.; Thomas, K.; Park, I.H.; Garber, M.; Curran, M.; Onder, T.; Agarwal, S.; et al. Large intergenic non-coding RNA-RoR modulates reprogramming of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q. H19 promotes the gastric carcinogenesis by sponging miR-29a-3p: Evidence from lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network analysis. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, C.; Ungerleider, N.; Chen, W.; Song, K.; Wang, Y.; Kwon, H.; Ma, W.; Wu, T. A Transforming Growth Factor-beta and H19 Signaling Axis in Tumor-Initiating Hepatocytes That Regulates Hepatic Carcinogenesis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, H.; Matsuda, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Kamiya, S.; Ishiwata, T. Expression and role of long non-coding RNA H19 in carcinogenesis. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 614–625. [Google Scholar]
- Brannan, C.I.; Dees, E.C.; Ingram, R.S.; Tilghman, S.M. The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol. Cell Biol. 1990, 10, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabory, A.; Jammes, H.; Dandolo, L. The H19 locus: Role of an imprinted non-coding RNA in growth and development. Bioessays 2010, 32, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabory, A.; Ripoche, M.A.; Le Digarcher, A.; Watrin, F.; Ziyyat, A.; Forne, T.; Jammes, H.; Ainscough, J.F.; Surani, M.A.; Journot, L.; et al. H19 acts as a trans regulator of the imprinted gene network controlling growth in mice. Development 2009, 136, 3413–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raveh, E.; Matouk, I.J.; Gilon, M.; Hochberg, A. The H19 Long non-coding RNA in cancer initiation, progression and metastasis—A proposed unifying theory. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaegh, G.W.; Verkleij, L.; Vermeulen, S.H.; den Heijer, M.; Witjes, J.A.; Kiemeney, L.A. Polymorphisms in the H19 gene and the risk of bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2008, 54, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Z.; Yan, R.; Duan, F.; Song, C.; Wang, P.; Wang, K. Genetic Polymorphisms in Long Noncoding RNA H19 Are Associated With Susceptibility to Breast Cancer in Chinese Population. Medicine 2016, 95, e2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Q.; Lv, X.; Gu, X.; Chen, Y.; Chu, H.; Du, M.; Gong, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z. Genetic variants in lncRNA H19 are associated with the risk of bladder cancer in a Chinese population. Mutagenesis 2016, 31, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, F.; Yuan, J.H.; Yuan, S.X.; Zhou, W.P.; Huo, X.S.; Xu, D.; Bi, H.S.; Wang, F.; Sun, S.H. Epigenetic activation of the MiR-200 family contributes to H19-mediated metastasis suppression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, M.; Suzuki, H.; Ueda, R.; Osada, H.; Takagi, K.; Takahashi, T.; Takahashi, T. Frequent loss of imprinting of the H19 gene is often associated with its overexpression in human lung cancers. Oncogene 1995, 10, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar]
- Hibi, K.; Nakamura, H.; Hirai, A.; Fujikake, Y.; Kasai, Y.; Akiyama, S.; Ito, K.; Takagi, H. Loss of H19 imprinting in esophageal cancer. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 480–482. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Zeng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, J. Upregulated H19 contributes to bladder cancer cell proliferation by regulating ID2 expression. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 1709–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yu, B.; Li, J.; Su, L.; Yan, M.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, B. Overexpression of lncRNA H19 enhances carcinogenesis and metastasis of gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2318–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Nong, K.; Zhu, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Ai, K. H19 promotes pancreatic cancer metastasis by derepressing let-7’s suppression on its target HMGA2-mediated EMT. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 9163–9169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Li, P.; Cao, P.; Qian, J.; Du, M.; Li, L.; Wang, M.; Qin, C.; Shao, P.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Genetic Variant in Long Non-Coding RNA H19 Modulates Its Expression and Predicts Renal Cell Carcinoma Susceptibility and Mortality. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.B.; Zeng, Y.; Li, T.L.; Wang, G. Correlation between polymorphisms in IGF2/H19 gene locus and epithelial ovarian cancer risk in Chinese population. Genomics 2020, 112, 2510–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Li, J.; Wen, Y.; Zou, Y.; Yang, J.; Pan, J.; Hu, C.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xin, Y.; et al. Association between lncRNA-H19 polymorphisms and hepatoblastoma risk in an ethic Chinese population. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 25, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, E.R.; Chou, Y.E.; Liu, Y.F.; Hsueh, K.C.; Lee, H.L.; Yang, S.F.; Su, S.C. Association of lncRNA H19 Gene Polymorphisms with the Occurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Genes 2019, 10, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.L.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Chen, H.H.; Ma, S.N.; Wu, R.; Cai, W.S. The association of polymorphisms in lncRNA-H19 with hepatocellular cancer risk and prognosis. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20171652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Tang, R.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.; Luo, D.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, L. Tag SNPs in long non-coding RNA H19 contribute to susceptibility to gastric cancer in the Chinese Han population. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15311–15320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Chen, J.; Hou, C.; Zhang, L.; Jia, J. LncRNA H19 gene rs2839698 polymorphism is associated with a decreased risk of colorectal cancer in a Chinese Han population: A case-control study. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2020, 34, e23311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Hua, Y.; Jin, J.; Wang, H.; Du, M.; Zhu, L.; Chu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M. Association of genetic variants in lncRNA H19 with risk of colorectal cancer in a Chinese population. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 25470–25477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari, M.R.; Mohammad Rezaei, F.; Dehghan, A.; Noroozi, R.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Genomic variants within the long non-coding RNA H19 confer risk of breast cancer in Iranian population. Gene 2019, 701, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y. LncRNA H19 polymorphisms associated with the risk of OSCC in Chinese population. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 3770–3774. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Liu, Q.; Cui, K.; Ma, A.; Zhang, H. Association between H19 polymorphisms and NSCLC risk in a Chinese Population. J. BUON 2019, 24, 913–917. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.C.; Chou, Y.H.; Shen, H.P.; Ng, S.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Sun, Y.H.; Hsu, C.F.; Yang, S.F.; Wang, P.H. The clinicopathological characteristic associations of long non-coding RNA gene H19 polymorphisms with uterine cervical cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 6191–6198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yao, J.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, N.; Xu, P.; Lyu, L.; et al. Associations of lncRNA H19 Polymorphisms at MicroRNA Binding Sites with Glioma Susceptibility and Prognosis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhuo, Z.J.; Zhou, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhou, H.; Li, S.; Li, M.; He, J.; et al. H19 gene polymorphisms and neuroblastoma susceptibility in Chinese children: A six-center case-control study. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 6358–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Yang, T.; Pan, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; He, J.; Zou, Y. Associations between H19 polymorphisms and neuroblastoma risk in Chinese children. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Fu, F.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, W.; Lin, S.; Yang, P.; Huang, M.; Wang, C. Genetic variants in long noncoding RNA H19 contribute to the risk of breast cancer in a southeast China Han population. Oncol Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 4369–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Yuan, W.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z.; Mao, L.; Tian, T.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; et al. Quantitative assessment of polymorphisms in H19 lncRNA and cancer risk: A meta-analysis of 13,392 cases and 18,893 controls. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78631–78639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chen, L.; You, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G.; Xu, B.; Chen, M. Association between lncRNA H19 polymorphisms and cancer susceptibility based on a meta-analysis from 25 studies. Gene 2020, 729, 144317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jiang, X.; Jin, X.; Yan, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, Z. Significant association between long non-coding RNA H19 polymorphisms and cancer susceptibility: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis and bioinformatics prediction. Medicine 2020, 99, e19322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Quantitative assessment of lncRNA H19 polymorphisms and cancer risk: A meta-analysis based on 48,166 subjects. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.F.; Yin, X.H.; Cai, J.W.; Wang, M.J.; Zeng, Y.Q.; Li, M.; Niu, Y.M.; Shen, M. Significant association between lncRNA H19 polymorphisms and cancer susceptibility: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 45143–45153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, M.; Moazeni-Roodi, A.; Sarabandi, S.; Karami, S.; Ghavami, S. Association between genetic polymorphisms of long noncoding RNA H19 and cancer risk: A meta-analysis. J. Genet. 2019, 98, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Cases, n = 266 | Controls, n = 266 | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | Mean ± SD | n | % | Mean ± SD | ||
| Onset age, year | 7.0 ± 4.4 | 8.3 ± 4.8 | 0.6483 a | ||||
| Gender | 1.0000 b | ||||||
| Boy | 148 | 55.6% | 148 | 55.6% | |||
| Girl | 118 | 44.4% | 118 | 44.4% | |||
| While blood cell counts (109/L) | 54.3 ± 75.9 | 7.5 ± 2.0 | <0.0001 | ||||
| t(1;19) | 11 | 4.1% | |||||
| t(4;11) | 4 | 1.5% | |||||
| t(9;22) | 6 | 2.3% | |||||
| ETV6-RUNX1 c | 28 | 10.5% | |||||
| Immunophenotype | |||||||
| B subtype | 227 | 85.3% | |||||
| T subtype | 39 | 14.7% | |||||
| Risk classification | |||||||
| Standard risk | 130 | 48.9% | |||||
| High risk | 67 | 25.2% | |||||
| Very high risk | 69 | 25.9% | |||||
| Survival time, year | |||||||
| <5 | 69 | 25.9% | |||||
| ≥5 | 197 | 74.1% | |||||
| Index | Genotype | Cases | Controls | p-Value | Crude OR (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs2839698 | CC | 91 (34.2%) | 119 (44.7%) | 1.00 (Ref) | |
| CT | 131 (49.3%) | 117 (44.0%) | 0.0429 * | 1.46 (1.08–2.14) | |
| TT | 44 (16.5%) | 30 (11.3%) | 0.0169 * | 1.94 (1.15–3.31) | |
| CT+TT | 175 (65.8%) | 147 (55.3%) | 0.0130 * | 1.68 (1.12–2.23) | |
| Ptrend | 0.0277 * | ||||
| PHWE | 0.8781 |
| Allele | Cases, n (%) (n = 532) | Controls, n (%) (n = 532) | Adjusted OR (95%CI) a | p-Value b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 313 (58.8) | 355 (66.7) | 1.00 (Reference) | 0.0077 * |
| T | 219 (41.2) | 177 (33.3) | 1.53 (1.13–1.79) |
| Index | Genotype | Cases | Controls | p-Value | Crude OR (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs217727 | CC | 111 (41.7%) | 114 (42.9%) | 1.00 (Ref) | |
| CT | 120 (45.1%) | 120 (45.1%) | 0.8857 | 1.04 (0.80–1.41) | |
| TT | 35 (13.2%) | 32 (12.0%) | 0.6763 | 1.10 (0.72–1.92) | |
| CT+TT | 155 (58.3%) | 152 (57.1%) | 0.7923 | 1.06 (0.74–1.45) | |
| Ptrend | 0.9165 | ||||
| PHWE | 0.9610 |
| Allele | Cases, n (%) (n = 532) | Controls, n (%) (n = 532) | Adjusted OR (95%CI) a | p-Value b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | 342 (64.3) | 348 (65.4) | 1.00 (Reference) | 0.7000 |
| T | 190 (35.7) | 184 (34.6) | 1.06 (0.84–1.39) |
| Index | CC | CT+TT | Adjusted OR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | (95%CI) a | |
| Immunophenotype | |||||
| B subtype | 77 | 33.9 | 150 | 66.1 | 1.26 (0.91–1.38) |
| T subtype | 14 | 35.9 | 25 | 64.1 | 1.22 (0.83–1.85) |
| Risk classification | |||||
| Standard risk | 47 | 36.2 | 83 | 63.8 | 1.28 (0.92–1.45) |
| High risk | 21 | 31.3 | 46 | 68.7 | 1.46 (1.04–1.87) |
| Very high risk | 23 | 33.3 | 46 | 66.7 | 1.38 (1.02–1.79) |
| Survival time (years) | |||||
| <5 | 22 | 31.9 | 47 | 68.1 | 1.43 (1.03–1.84) |
| ≥5 | 69 | 35.0 | 128 | 65.0 | 0.83 (0.64–1.23) |
| Author | Year | Cancer | Case/Control, n | Population | Highlight Findings | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Verhaegh | 2008 | Bladder cancer | 177/204 | Netherlands | CT but not TT genotype is associated with decreased bladder cancer risk | |
| Cao | 2020 | Renal cell carcinoma | 1094/1027 | China | TT but not CT genotype is associated with increased renal cell carcinoma risk | |
| Zhang | 2020 | Ovarian cancer | 219/203 | China | TT but not CT genotype is associated with increased ovarian cancer risk | |
| Tan | 2021 | Hepatoblastoma | 213/958 | China | TT but not CT genotype is associated with increased hepatoblastoma risk | |
| Wu | 2019 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | 359/1190 | Taiwan | CT but not TT genotype is associated with increased hepatocellular carcinoma risk | |
| Yang | 2018 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | 472/472 | China | CT plus TT genotype is associated with increased hepatocellular carcinoma risk | |
| Yang | 2015 | Gastric cancer | 500/500 | China | TT but not CT genotype is associated with increased gastric cancer risk | |
| Yu | 2020 | Colorectal cancer | 315/441 | China | CT plus TT genotype is associated with decreased colorectal cancer risk | |
| Li | 2016 | Colorectal cancer | 1147/1203 | China | TT but not CT genotype is associated with increased colorectal cancer risk | |
| Safari | 2019 | Breast cancer | 111/130 | Iron | CT and TT genotypes are associated with increased breast cancer risk | |
| Lin | 2017 | Breast cancer | 1005/1020 | China | No association | |
| Guo | 2017 | Oral cancer | 362/741 | China | No association | |
| Wang | 2019 | Lung cancer | 564/1536 | China | No association | |
| Huang | 2019 | Cervical cancer | 235/325 | Taiwan | No association | |
| Deng | 2020 | Glioma | 605/1300 | China | No association | |
| Li | 2019 | Neuroblastoma | 700/1516 | China | No association | |
| Hu | 2019 | Child neuroblastoma | 393/812 | China | No association |
| Author | Year | Cancer | Case/Control, n | Population | Highlight Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Verhaegh | 2008 | Bladder cancer | 177/204 | Netherlands | No association |
| Cao | 2020 | Renal cell carcinoma | 1094/1027 | China | No association |
| Tan | 2021 | Hepatoblastoma | 213/958 | China | CT but not TT genotype is associated with decreased hepatoblastoma risk |
| Wu | 2019 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | 359/1190 | China | No Association |
| Yang | 2015 | Gastric cancer | 500/500 | China | TT but not CT genotype is associated with increased gastric cancer risk |
| Li | 2016 | Colorectal cancer | 1147/1203 | China | No association |
| Safari | 2019 | Breast cancer | 111/130 | Iron | CT and TT genotypes are associated with decreased breast cancer risk |
| Lin | 2017 | Breast cancer | 1005/1020 | China | CT and TT genotypes are associated with increased breast cancer risk |
| Xia | 2016 | Breast cancer | 464/467 | China | No association |
| Guo | 2017 | Oral cancer | 362/741 | China | TT but not CT genotype is associated with increased oral cancer risk |
| Wang | 2019 | Lung cancer | 564/1536 | China | TT but not CT genotype is associated with increased lung cancer risk |
| Huang | 2019 | Cervical cancer | 235/325 | Taiwan | No association |
| Cao | 2020 | Renal cell carcinoma | 1027/1094 | China | No association |
| Deng | 2020 | Glioma | 605/1300 | China | No association |
| Li | 2019 | Neuroblastoma | 700/1516 | China | No association |
| Hu | 2019 | Child neuroblastoma | 393/812 | China | No association |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pei, J.-S.; Chen, C.-C.; Chang, W.-S.; Wang, Y.-C.; Chen, J.-C.; Hsiau, Y.-C.; Hsu, P.-C.; Hsu, Y.-N.; Tsai, C.-W.; Bau, D.-T. Significant Associations of lncRNA H19 Genotypes with Susceptibility to Childhood Leukemia in Taiwan. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030235
Pei J-S, Chen C-C, Chang W-S, Wang Y-C, Chen J-C, Hsiau Y-C, Hsu P-C, Hsu Y-N, Tsai C-W, Bau D-T. Significant Associations of lncRNA H19 Genotypes with Susceptibility to Childhood Leukemia in Taiwan. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(3):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030235
Chicago/Turabian StylePei, Jen-Sheng, Chao-Chun Chen, Wen-Shin Chang, Yun-Chi Wang, Jaw-Chyun Chen, Yu-Chen Hsiau, Pei-Chen Hsu, Yuan-Nian Hsu, Chia-Wen Tsai, and Da-Tian Bau. 2021. "Significant Associations of lncRNA H19 Genotypes with Susceptibility to Childhood Leukemia in Taiwan" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 3: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030235
APA StylePei, J.-S., Chen, C.-C., Chang, W.-S., Wang, Y.-C., Chen, J.-C., Hsiau, Y.-C., Hsu, P.-C., Hsu, Y.-N., Tsai, C.-W., & Bau, D.-T. (2021). Significant Associations of lncRNA H19 Genotypes with Susceptibility to Childhood Leukemia in Taiwan. Pharmaceuticals, 14(3), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030235






