The Evaluation of Drug Delivery Nanocarrier Development and Pharmacological Briefing for Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): An Update
Abstract
1. From NAFLD to MAFLD—What Is Going on?
2. Available MAFLD Treatments and Their Efficacy
2.1. Non-Pharmacological Approach
2.2. Pharmacological Approach
2.2.1. Anti-Obesity Drugs
2.2.2. Hypoglycemic Agents
2.2.3. Lipid-Lowering Agents
2.2.4. Cytoprotective and Antioxidant Agents
2.3. Surgical Intervention
3. Nanomedicine Alternatives for MAFLD Smart Drug Delivery
4. Opportunities and Limitations of Nanosystems for MAFLD Therapy
4.1. Nanoparticles
4.1.1. Polymeric Nanoparticles
4.1.2. Metal-Oxide-Based Nanoparticles
4.1.3. Nanographene Oxide Particles
4.2. Lipid-Based Formulations
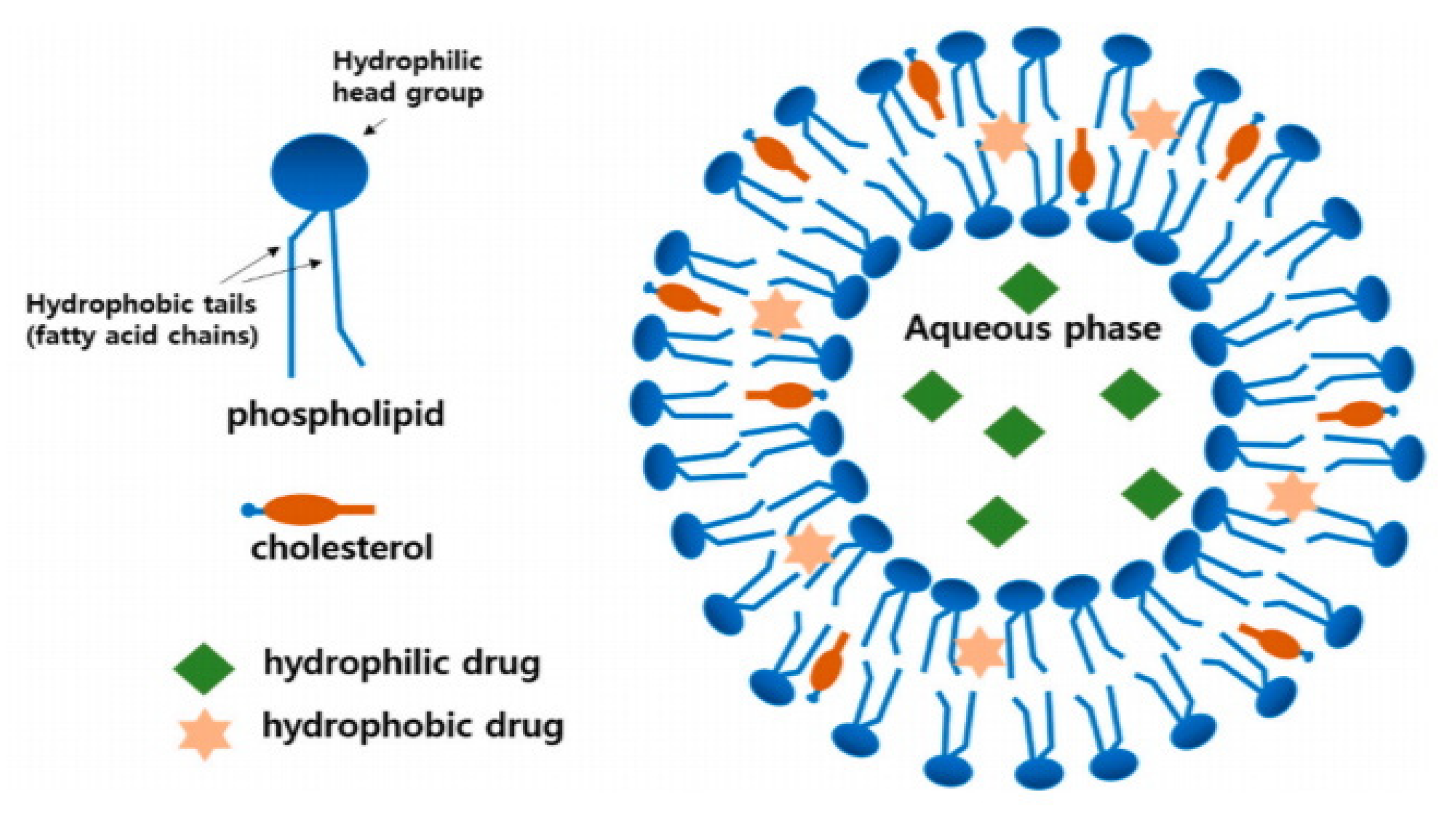
4.2.1. Liposomes
4.2.2. Hybrid Lipid–Polymer Nanoparticles
4.2.3. Solid Lipid Nanocarriers
4.2.4. Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System and Nano-Structured Lipid Carrier
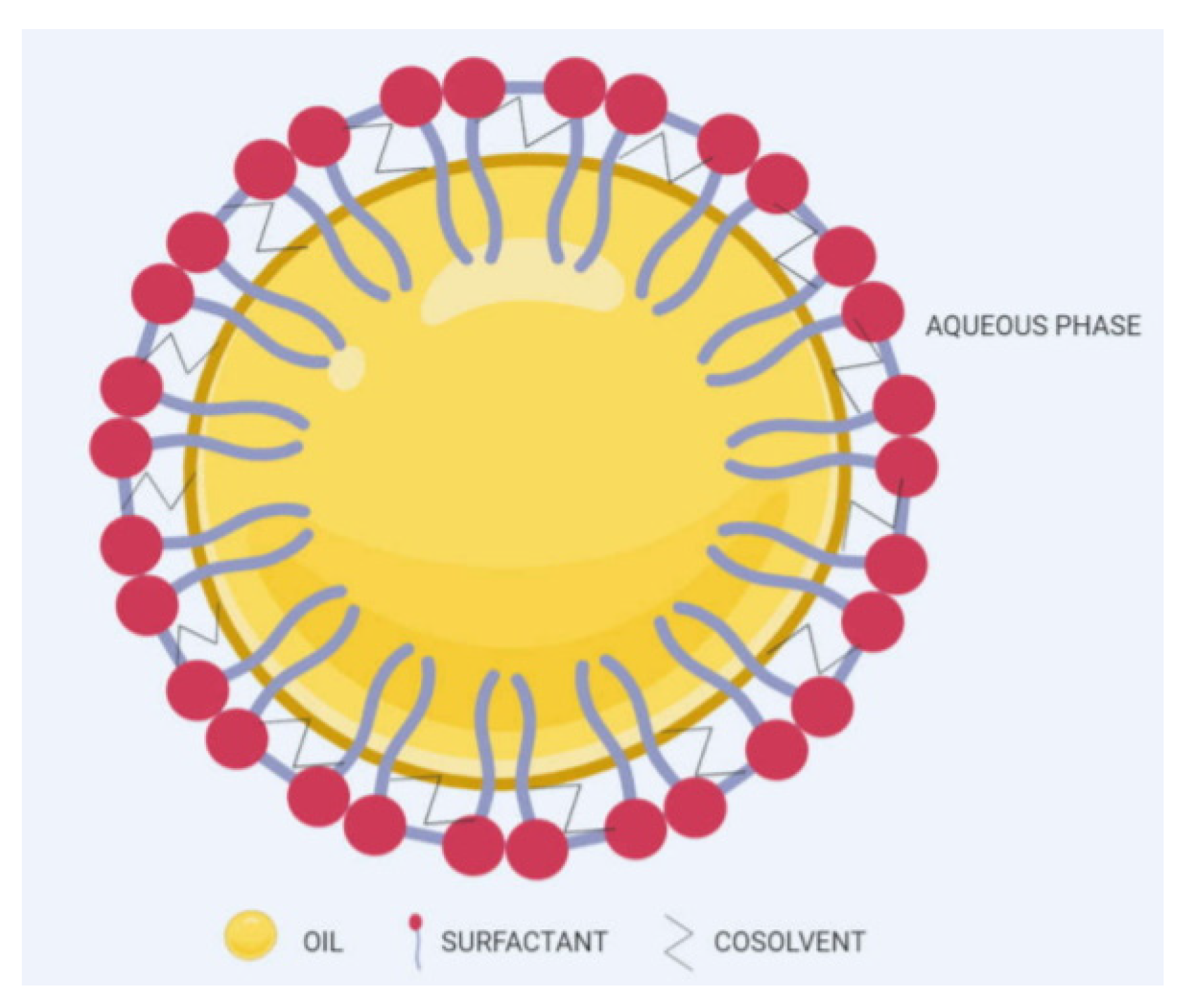
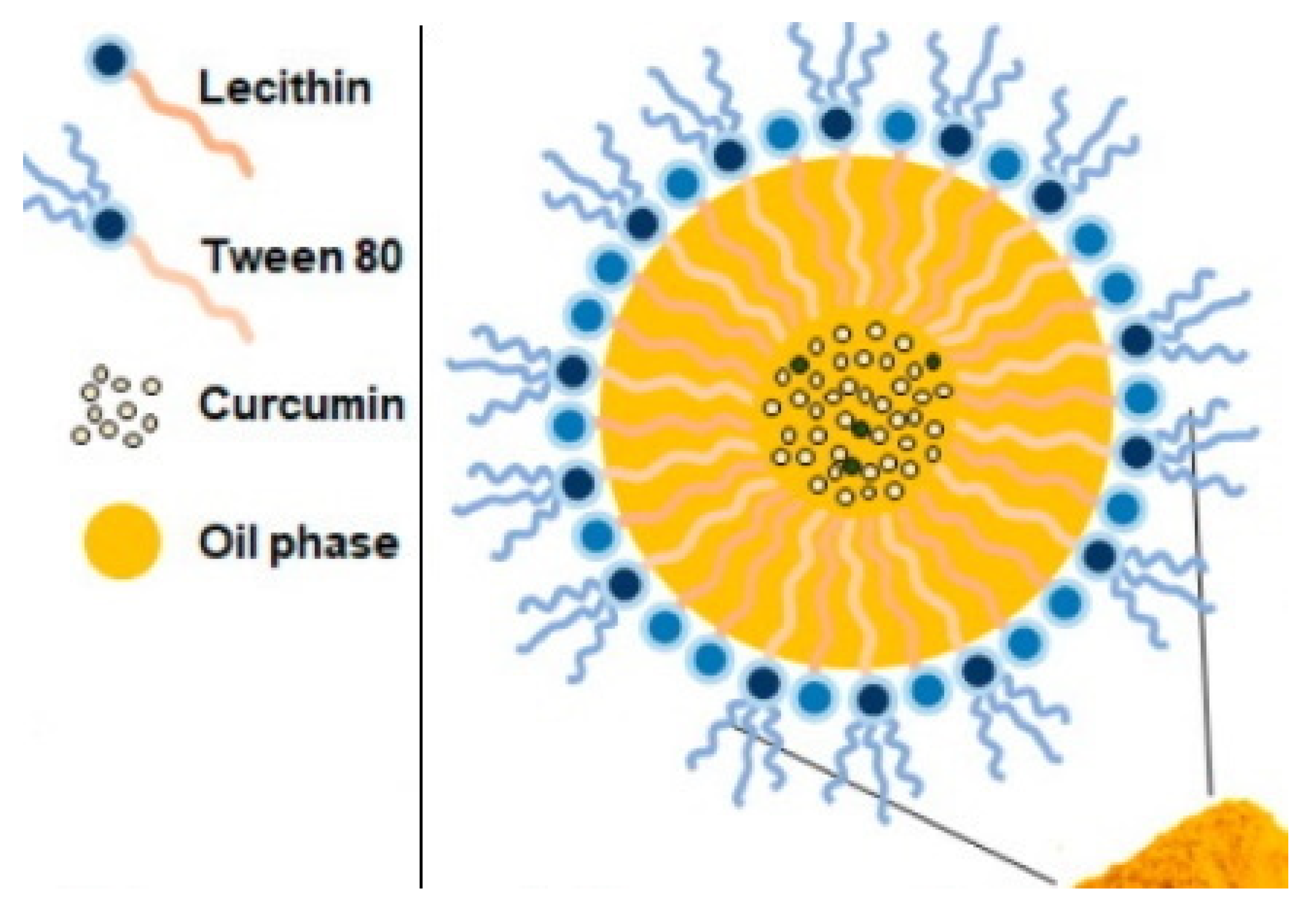
4.2.5. Nanoemulsion
4.2.6. Micelles
4.2.7. Nanocrystals
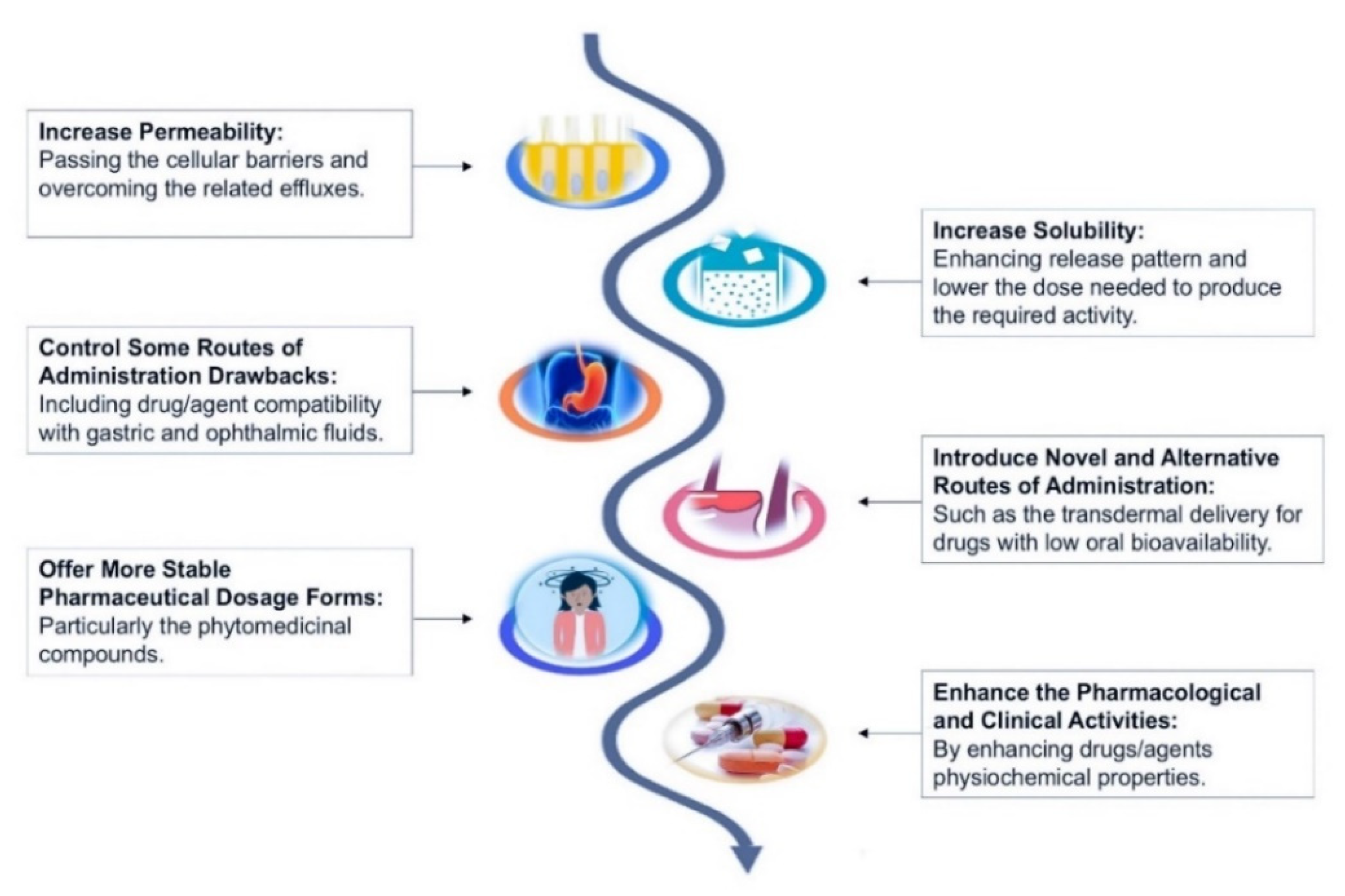
5. Future Perspectives
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basaranoglu, M.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Clinical Features and Pathogenesis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 2, 282–291. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, K. NAFLD—The next global epidemic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarin, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Al Mahtab, M.; Akbar, S.M.F.; Jia, J.; Tian, Q.; Aggarwal, R.; Muljono, D.H. Liver diseases in the Asia-Pacific region: A Lancet Gastroenterology & hepatology Commission. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 167–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fouad, Y.; Waked, I.; Bollipo, S.; Gomaa, A.; Ajlouni, Y.; Attia, D. What’s in a name? Renaming ‘NAFLD’ to ‘MAFLD’. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 1254–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åberg, F.; Helenius-Hietala, J.; Puukka, P.; Färkkilä, M.; Jula, A. Interaction between alcohol consumption and metabolic syndrome in predicting severe liver disease in the general population. Hepatology 2018, 67, 2141–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Lancet Gastroenterology Hepatology. Redefining non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: What’s in a name? Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J.; Sanyal, A.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.; Tiribelli, C.; Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.; Bugianesi, E.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; et al. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Effenberger, M. From NAFLD to MAFLD: When pathophysiology succeeds. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 387–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Blissett, D.; Blissett, R.; Henry, L.; Stepanova, M.; Younossi, Y.; Racila, A.; Hunt, S.; Beckerman, R. The economic and clinical burden of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the United States and Europe. Hepatology 2016, 64, 1577–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, J.; Viggiano, T.R.; McGill, D.B.; Oh, B.J. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1980, 55, 434–438. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, R.G. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A study of 49 patients. Hum. Pathol. 1989, 20, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurin, J.; Lindor, K.D.; Crippin, J.S.; Gossard, A.; Gores, G.J.; Ludwig, J.; Rakela, J.; McGill, D.B. Ursodeoxycholic acid or clofibrate in the treatment of non-alcohol-induced steatohepatitis: A pilot study. Hepatology 1996, 23, 1464–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, T.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.; Mishra, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in the Female Population. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 3, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, M.; Hu, Z.; Shrestha, U.K. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its metabolic risk factors in women of different ages and body mass index. Menopause 2015, 22, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.D.; Stengel, J.; Asike, M.I.; Torres, D.M.; Shaw, J.; Contreras, M.; Landt, C.L.; Harrison, S.A. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis among a largely middle-aged population utilizing ultrasound and liver biopsy: A prospective study. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browning, J.D.; Szczepaniak, L.S.; Dobbins, R.; Nuremberg, P.; Horton, J.D.; Cohen, J.C.; Grundy, S.M.; Hobbs, H.H. Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: Impact of ethnicity. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, B.R.; Farahvash, M.J.; Janney, C.G.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: An expanded clinical entity. Gastroenterology 1994, 107, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballestri, S.; Nascimbeni, F.; Baldelli, E.; Marrazzo, A.; Romagnoli, D.; Lonardo, A. NAFLD as a Sexual Dimorphic Disease: Role of Gender and Reproductive Status in the Development and Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Inherent Cardiovascular Risk. Adv. Ther. 2017, 34, 1291–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaz, A.; Ali, Z.; Nayyar, S.; Fatima, N. Prevalence of NAFLD in Healthy and Young Male Individuals. ISRN Gastroenterol. 2011, 2011, 363546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mencin, A.A.; Lavine, J.E. Advances in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Pediatr. Clin. 2011, 58, 1375–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vajro, P.; Lenta, S.; Socha, P.; Dhawan, A.; McKiernan, P.; Baumann, U.; Durmaz, O.; Lacaille, F.; McLin, V.; Nobili, V. Diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: Position paper of the ESPGHAN Hepatology Committee. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 700–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobili, V.; Alisi, A.; Valenti, L.; Miele, L.; Feldstein, A.E.; Alkhouri, N. NAFLD in children: New genes, new diagnostic modalities and new drugs. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 517–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, J.M.; Henry, L.; De Avila, L.; Younossi, E.; Racila, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Mortality Related to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Increasing in the United States. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, C.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Chien, R.N.; Chuang, W.-L.; Fung, J.; Goh, G.B.-B.; Hu, T.H.; Huang, J.-F.; Jang, B.K.; Jun, D.W.; et al. Modelling NAFLD disease burden in four Asian regions-2019-2030. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estes, C.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; Bantel, H.; Bellentani, S.; Caballeria, J.; Colombo, M.; Craxi, A.; Crespo, J.; Day, C.P.; et al. Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016–2030. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesini, G.; Brizi, M.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Bianchi, G.; Bugianesi, E.; McCullough, A.J.; Forlani, G.; Melchionda, N. Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with insulin resistance. Am. J. Med. 1999, 107, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Agroudy, N.N.; Kurzbach, A.; Rodionov, R.N.; O’Sullivan, J.; Roden, M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Pesta, D.H. Are Lifestyle Therapies Effective for NAFLD Treatment? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, M.-S.; Kim, D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and lifestyle modifications, focusing on physical activity. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promrat, K.; Kleiner, D.E.; Niemeier, H.M.; Jackvony, E.; Kearns, M.; Wands, J.R.; Fava, J.L.; Wing, R.R. Randomized controlled trial testing the effects of weight loss on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, J.B.; Bhathal, P.S.; Hughes, N.R.; O’Brien, P.E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Improvement in liver histological analysis with weight loss. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1647–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, E.R.; Sallam, S.; Perumpail, B.J.; Iqbal, U.; Shah, N.D.; Kwong, W.; Cholankeril, G.; Kim, D.; Ahmed, A. When to Initiate Weight Loss Medications in the NAFLD Population. Diseases 2018, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, K. Multidisciplinary Pharmacotherapeutic Options for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 950693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, W.T.; Mechanick, J.I.; Brett, E.M.; Garber, A.J.; Hurley, D.L.; Jastreboff, A.M.; Nadolsky, K.; Pessah-Pollack, R.; Plodkowski, R. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology Comprehensive Clinical Practice Guidelines for Medical Care Of Patients with Obesity. Endocr. Pract. 2016, 22, 842–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, H.S.; Sakaan, S.A.; March, K.L.; Siddique, O.; Cholankeril, R.; Cummings, C.D.; Gadiparthi, C.; Satapathy, S.K.; Ahmed, A.; Cholankeril, G. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Review of Anti-diabetic Pharmacologic Therapies. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2018, 6, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, M.; Rahimlou, M.; Mahmoodi, M.; Moosavian, S.P.; Symonds, M.E.; Jalali, R.; Zare, M.; Imanieh, M.H.; Stasi, C. The effects of metformin administration on liver enzymes and body composition in non-diabetic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and/or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: An up-to date systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 159, 104799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, D. Metformin in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed. Rep. 2013, 1, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, S.; Diehl, A.M.; Wiseman, M.; Farr, G.H., Jr.; Perrillo, R.P. Metformin in the treatment of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A pilot open label trial. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 20, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haukeland, J.W.; Konopski, Z.; Eggesbø, H.B.; von Volkmann, H.L.; Raschpichler, G.; Bjøro, K.; Haaland, T.; Løberg, E.M.; Birkeland, K. Metformin in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, controlled trial. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazina, I.; Selph, S. Diabetes drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2019, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Harrison, S.A.; Belfort-Aguilar, R.; Hardies, L.J.; Balas, B.; Schenker, S.; Cusi, K. Importance of changes in adipose tissue insulin resistance to histological response during thiazolidinedione treatment of patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutchman, G.; Modi, A.; Kleiner, D.E.; Promrat, K.; Heller, T.; Ghany, M.; Borg, B.; Loomba, R.; Liang, T.J.; Premkumar, A.; et al. The effects of discontinuing pioglitazone in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2007, 46, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacelli, M.; Celsa, C.; Magro, B.; Giannetti, A.; Pennisi, G.; Spatola, F.; Petta, S. Antidiabetic Drugs in NAFLD: The Accomplishment of Two Goals at Once? Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguli, S.; DeLeeuw, P.; Satapathy, S.K. A Review of Current and Upcoming Treatment Modalities in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepat. Med. 2019, 11, 159–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelas, A.; Tsoulkani, A.; Perrea, D. Effects of lipid-lowering drugs on adiponectin. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2010, 8, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimbeni, F.; Pellegrini, E.; Lugari, S.; Mondelli, A.; Bursi, S.; Onfiani, G.; Carubbi, F.; Lonardo, A. Statins and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the era of precision medicine: More friends than foes. Atherosclerosis 2019, 284, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argo, C.K.; Loria, P.; Caldwell, S.H.; Lonardo, A. Statins in liver disease: A molehill, an iceberg, or neither? Hepatology 2008, 48, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastori, D.; Polimeni, L.; Baratta, F.; Pani, A.; Del Ben, M.; Angelico, F. The efficacy and safety of statins for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casula, M.; Mozzanica, F.; Scotti, L.; Tragni, E.; Pirillo, A.; Corrao, G.; Catapano, A.L. Statin use and risk of new-onset diabetes: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakker, D.; Nair, S.; Pagada, A.; Jamdade, V.; Malik, A. Statin use and the risk of developing diabetes: A network meta-analysis. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2016, 25, 1131–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, D.I.; Preiss, D.; Kuchenbaecker, K.B.; Holmes, M.V.; Engmann, J.E.L.; Shah, T.; Sofat, R.; Stender, S.; Johnson, P.C.D.; Scott, R.A.; et al. HMG-coenzyme A reductase inhibition, type 2 diabetes, and bodyweight: Evidence from genetic analysis and randomised trials. Lancet 2015, 385, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Miranda, C.; Pérez-Carreras, M.; Colina, F.; López-Alonso, G.; Vargas, C.; Solís-Herruzo, J. A pilot trial of fenofibrate for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2008, 40, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostapanos, M.S.; Kei, A.; Elisaf, M.S. Current role of fenofibrate in the prevention and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Hepatol. 2013, 5, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippatos, T.D.; Elisaf, M.S. Role of ezetimibe in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Hepatol. 2011, 3, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, Y.; Takamura, T.; Honda, M.; Kita, Y.; Zen, Y.; Kato, K.-I.; Misu, H.; Ota, T.; Nakamura, M.; Yamada, K.; et al. The effects of ezetimibe on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and glucose metabolism: A randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 878–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindor, K.D.; Kowdley, K.V.; Heathcote, E.J.; Harrison, M.E.; Jorgensen, R.; Angulo, P.; Lymp, J.F.; Burgart, L.; Colin, P. Ursodeoxycholic acid for treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Results of a randomized trial. Hepatology 2004, 39, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, J.F.; Oneta, C.M.; Gonvers, J.J.; Bihl, F.; Cerny, A.; Cereda, J.M.; Zala, J.F.; Helbling, B.; Steuerwald, M.; Zimmermann, A. Randomized placebo-controlled trial of ursodeoxycholic acid with vitamin e in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 4, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Wier, B.; Koek, G.H.; Bast, A.; Haenen, G.R. The potential of flavonoids in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 834–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Cheung, F.; Hong, M.; Feng, Y. The Potential and Action Mechanism of Polyphenols in the Treatment of Liver Diseases. Oxid Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 8394818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elvira-Torales, L.I.; García-Alonso, J.; Periago-Castón, M.J. Nutritional Importance of Carotenoids and Their Effect on Liver Health: A Review. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Freitas Carvalho, M.M.; Lage, N.N.; de Souza Paulino, A.H.; Pereira, R.R.; de Almeida, L.T.; da Silva, T.F.; de Brito Magalhães, C.L.; de Lima, W.G.; Silva, M.E.; Pedrosa, M.L.; et al. Effects of açai on oxidative stress, ER stress, and inflammation-related parameters in mice with high fat diet-fed induced NAFLD. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hadi, H.; Vettor, R.; Rossato, M. Vitamin E as a Treatment for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Reality or Myth? Antioxidants 2018, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colica, C.; Boccuto, L.; Abenavoli, L. Silymarin: An option to treat non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 8437–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, G.B.-B.; Pagadala, M.R.; Dasarathy, J.; Unalp-Arida, A.; Sargent, R.; Hawkins, C.; Sourianarayanane, A.; Khiyami, A.; Yerian, L.; Pai, R.K.; et al. Clinical spectrum of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in diabetic and non-diabetic patients. BBA Clin. 2014, 3, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, T.L.; Hagemann, C.A.; Wei, C.; Kazankov, K.; Thomsen, K.L.; Knop, F.K.; Grønbæk, H. Bariatric surgery in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—From pathophysiology to clinical effects. World J. Hepatol. 2019, 11, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vander Naalt, S.J.; Gurria, J.P.; Holterman, A.L. Surgical treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in severely obese patients. Hepat. Med. 2014, 6, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, Y.; Doumouras, A.G.; Yu, J.; Brar, K.; Banfield, L.; Gmora, S.; Anvari, M.; Hong, D. Complete resolution of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease after bariatric surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 1040–1060.e1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciejewski, M.L.; Arterburn, D.E. Cost-effectiveness of bariatric surgery. JAMA 2013, 310, 742–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bzowej, N.H. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: The new frontier for liver transplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2018, 23, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Therapeutic landscape for NAFLD in 2020. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1984–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.-Y.; He, K.-M.; Chen, J.-L.; Xu, Y.-M.; Lau, A.T.Y. Phytofabrication of Nanoparticles as Novel Drugs for Anticancer Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United State National Nanotechnology Institute. What is Nanotechnology. Available online: https://www.nano.gov/nanotech-101/what/definition (accessed on 26 November 2020).
- Krishnaswamy, K.; Orsat, V. Chapter 2—Sustainable Delivery Systems through Green Nanotechnology. In Nano- and Microscale Drug Delivery Systems; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, A.; Carreiró, F.; Oliveira, A.M.; Neves, A.; Pires, B.; Venkatesh, D.N.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Eder, P.; Silva, A.M. Polymeric nanoparticles: Production, characterization, toxicology and ecotoxicology. Molecules 2020, 25, 3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.-Y.; Wu, D.-C.; Li, Z.-J.; Chen, G.-Q. Chpater 7—Polymer Nanoparticles. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Villaverde, A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 104, pp. 299–323. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, T.; Lai, T.C.; Kwon, G.S.; Sako, K. pH-and ion-sensitive polymers for drug delivery. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 1497–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, V.; Sharma, R. Chapter 5—Recent Advances in Development of Nano Drug Delivery. In Applications of Targeted Nano Drugs and Delivery Systems; Mohapatra, S.S., Ranjan, S., Dasgupta, N., Mishra, R.K., Thomas, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 93–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhao, D.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, K. Polymer-Based Nanomaterials and Applications for Vaccines and Drugs. Polymers 2018, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.-Y.; Imm, J.-Y. Lipase inhibition and cholesterol-lowering activities of laccase-catalyzed catechin polymers. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 1703–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, S.B.; Joshua, D.B.; Zachary, O.; Bryan, M.; Mardel, C.; Kurt, M.; Kyle, P.; Jodi, H.; Lisa-Marie, B.; Larisa, G.; et al. Lipid-Lowering Effects of Polymers Derived from Halophenyl Pyrroles. Lett. Drug Des. 2011, 8, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.K.; Park, J.B.; Song, C.H. Hypolipidemic effect of exo-polymer produced in submerged mycelial culture of five different mushrooms. J. Microb. Biotech. 2002, 12, 957–961. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, L.; Calvo, M.V.; Fontecha, J. The Influence of β-Cyclodextrin on the Reduction of Cholesterol Content in Egg and Duck Liver Pâté. Foods 2019, 8, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, L.; Fox, P.F.; Calvo, M.V.; Fontecha, J. Effect of Beta Cyclodextrin on the Reduction of Cholesterol in Ewe’s Milk Manchego Cheese. Molecules 2018, 23, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, I.S.; Loughrey, B.V. Chapter 88—Lipid-Lowering Therapy. In Comprehensive Hypertension; Lip, G.Y.H., Hall, J.E., Eds.; Mosby: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 1087–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korotkova, V.D.; Perelygina, A.A.; Lobanova, A.M.; Stoilov, L.D. Effect of dietary supplements with different cellulose content on the blood glucose and insulin levels in type II diabetes mellitus. Probl. Endokrinol. 1983, 29, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Geleva, D.; Thomas, W.; Gannon, M.C.; Keenan, J.M. A Solubilized Cellulose Fiber Decreases Peak Postprandial Cholecystokinin Concentrations after a Liquid Mixed Meal in Hypercholesterolemic Men and Women. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 2194–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, D.R.M.; Mendonça, M.H.; Helm, C.V.; Magalhães, W.L.E.; de Muniz, G.I.B.; Kestur, S.G. Assessment of Nano Cellulose from Peach Palm Residue as Potential Food Additive: Part II: Preliminary Studies. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 5641–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, H.; Xiao, X.; Hu, L.; Xin, F.; Yu, X. Inulin-type fructan improves diabetic phenotype and gut microbiota profiles in rats. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patki, A.; Shelgaonkar, V. Effect of 6% hydroxyethyl starch-450 and low molecular weight dextran on blood sugar levels during surgery under subarachnoid block: A prospective randomised study. Indian J. Anaesth. 2010, 54, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrnes, S.; Brand-Miller, J.; Denyer, G. Amylopectin starch promotes the development of insulin resistance in rats. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazono, T.; Nakamoto, H.; Kasai, K.; Kuriyama, S.; Sugimoto, T.; Nakayama, M.; Hamada, C.; Furuya, R.; Hasegawa, H.; Kasahara, M.; et al. Effects of Icodextrin on Glycemic and Lipid Profiles in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Peritoneal Dialysis. Am. J. Nephrol. 2007, 27, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, R.; González, T.; Fulladosa, X.; Castelao, A.M.; Grinyó, J.M. False hyperglycemies in diabetic patients using icodextrin in peritoneal dialysis. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 37, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Food and Drug Administration, FDA. 2012. GRAS Notices: Shrimp-Derived Chitosan. 2013. Available online: https://www.cfsanappsexternal.fda.gov/scripts/fdcc/index.cfm?set=GRASNotices&id=443&sort=GRN_No&order=DESC&startrow=1&type=basic&search=chitosan (accessed on 12 November 2020).
- Ozcelik, E.; Uslu, S.; Erkasap, N.; Karimi, H. Protective effect of chitosan treatment against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2014, 30, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
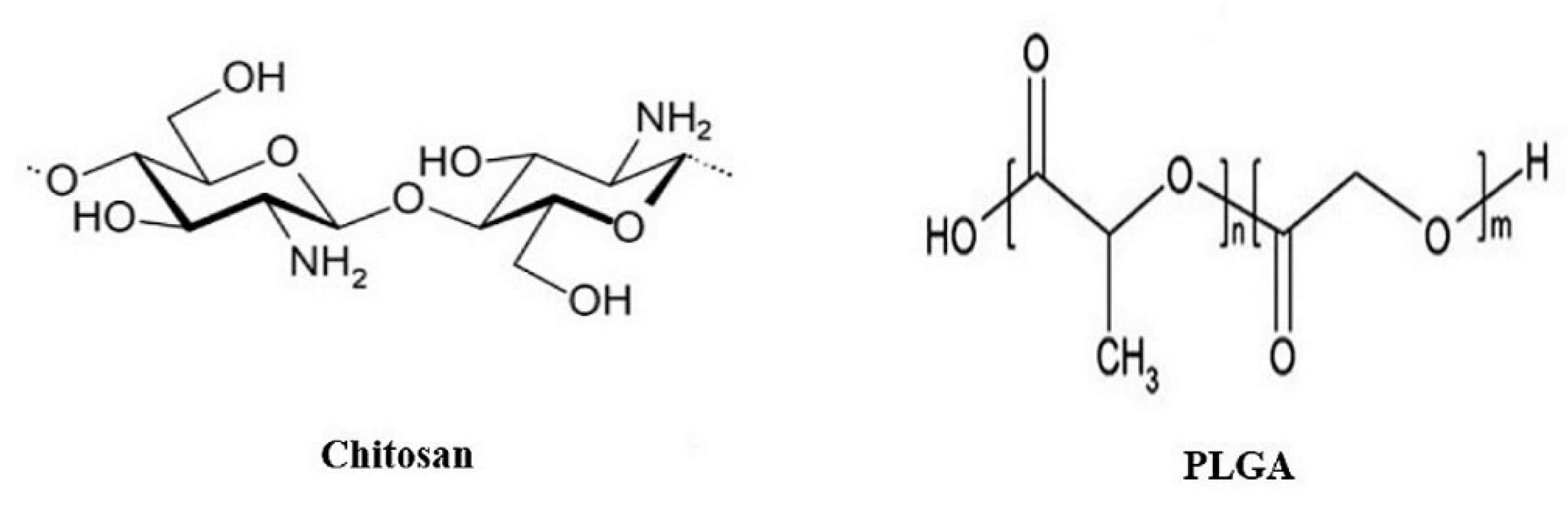
- Liang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Fan, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Yan, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, P.; Feng, N. Chitosan-functionalized lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles for oral delivery of silymarin and enhanced lipid-lowering effect in NAFLD. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.H.; Chiu, C.Y.; Shi, C.M.; Chiang, M.T. Functional Comparison of High and Low Molecular Weight Chitosan on Lipid Metabolism and Signals in High-Fat Diet-Fed Rats. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.F.; Wang, M.Y.; Yu, D.H.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H.M.; Zhong, S.; Sun, W.Y.; He, Y.F.; Niu, J.Q.; Gao, P.J.; et al. Therapeutic effect of chitosan on CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3211–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajapati, B. Chitosan a marine medical polymer and its lipid lowering capacity. Int. J. Health 2009, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Zhu, W.; Li, Q.; Dai, D.; Hou, Y. Anti-cancer efficacy of biotinylated chitosan nanoparticles in liver cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59068–59085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonferoni, M.C.; Gavini, E.; Rassu, G.; Maestri, M.; Giunchedi, P. Chitosan Nanoparticles for Therapy and Theranostics of Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver-Targeting. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, J.H.; Koo, H.; Lee, S.; Han, S.J.; Lee, K.E.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, K.; Kwon, I.C.; et al. Precise Targeting of Liver Tumor Using Glycol Chitosan Nanoparticles: Mechanisms, Key Factors, and Their Implications. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3700–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Allah, H.; Nasr, M.; Ahmed-Farid, O.A.H.; Ibrahim, B.M.M.; Bakeer, R.M.; Ahmed, R.F. Nicotinamide and ascorbic acid nanoparticles against the hepatic insult induced in rats by high fat high fructose diet: A comparative study. Life Sci. 2020, 263, 118540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makadia, H.K.; Siegel, S.J. Poly Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) as Biodegradable Controlled Drug Delivery Carrier. Polymers 2011, 3, 1377–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morelli, L.; Gimondi, S.; Sevieri, M.; Salvioni, L.; Guizzetti, M.; Colzani, B.; Palugan, L.; Foppoli, A.; Talamini, L.; Morosi, L.; et al. Monitoring the Fate of Orally Administered PLGA Nanoformulation for Local Delivery of Therapeutic Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazayeri-Tehrani, S.A.; Rezayat, S.M.; Mansouri, S.; Qorbani, M.; Alavian, S.M.; Daneshi-Maskooni, M.; Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.-J. Nano-curcumin improves glucose indices, lipids, inflammation, and Nesfatin in overweight and obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazayeri-Tehrani, S.A.; Rezayat, S.M.; Mansouri, S.; Qorbani, M.; Alavian, S.M.; Daneshi-Maskooni, M.; Hosseinzadeh-Attar, M.-J. Efficacy of nanocurcumin supplementation on insulin resistance, lipids, inflammatory factors and nesfatin among obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A trial protocol. BMJ Open 2017, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, H.; Sunagawa, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Imaizumi, A.; Fukuda, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Wada, H.; Katanasaka, Y.; Kakeya, H.; Fujita, M.; et al. Innovative Preparation of Curcumin for Improved Oral Bioavailability. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; Milic, N.; Luzza, F.; Boccuto, L.; De Lorenzo, A. Polyphenols Treatment in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2017, 5, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, S.; Zhang, L.; Quan, Y.; Wei, K. Resveratrol-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: Enhanced stability, solubility and bioactivity of resveratrol for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease therapy. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Guo, W.; Deng, F.; Chen, K.; Jiang, Y.; Dong, M.; Peng, L.; Chen, X. Targeted delivery of microRNA 146b mimic to hepatocytes by lactosylated PDMAEMA nanoparticles for the treatment of NAFLD. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boey, A.; Ho, H.K. All Roads Lead to the Liver: Metal Nanoparticles and Their Implications for Liver Health. Small 2020, 16, 2000153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crans, S.T.D.C. Metal Nanoparticles in Nanomedicine: Advantages and Scope. In Metal Nanoparticles; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 121–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, N.; Bhowmik, H.; Kuila, A. Metallic nanoparticle: A review. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2018, 4, 3765–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, V.V.; Siwale, R.; Singh, A.; Mody, H.R. Introduction to metallic nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2010, 2, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, I.; Saeed, K.; Khan, I. Nanoparticles: Properties, applications and toxicities. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 908–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbamaki, N.; Rasulev, B.; Cassano, A.; Marchese Robinson, R.L.; Benfenati, E.; Leszczynski, J.; Cronin, M.T.D. Correction: Genotoxicity of metal oxide nanomaterials: Review of recent data and discussion of possible mechanisms. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Tee, J.K.; Setyawati, M.I.; Ding, X.; Yeo, H.L.A.; Tan, Y.L.; Leong, D.T.; Ho, H.K. Inorganic Nanomaterials as Highly Efficient Inhibitors of Cellular Hepatic Fibrosis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 31938–31946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, K.E.; Al-Mutary, M.G.; Bakhiet, A.O.; Khan, H.A. Histopathology of the liver, kidney, and spleen of mice exposed to gold nanoparticles. Molecules 2018, 23, 1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal, S.; Perramón, M.; Oró, D.; Casals, E.; Fernández-Varo, G.; Casals, G.; Parra, M.; de la Presa, B.G.; Ribera, J.; Pastor, Ó.; et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticles display antilipogenic effect in rats with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oró, D.; Yudina, T.; Fernández-Varo, G.; Casals, E.; Reichenbach, V.; Casals, G.; de la Presa, B.G.; Sandalinas, S.; Carvajal, S.; Puntes, V.; et al. Cerium oxide nanoparticles reduce steatosis, portal hypertension and display anti-inflammatory properties in rats with liver fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra-Robert, M.; Casals, E.; Massana, N.; Zeng, M.; Perramón, M.; Fernández-Varo, G.; Morales-Ruiz, M.; Puntes, V.; Jiménez, W.; Casals, G. Beyond the Scavenging of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS): Direct Effect of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles in Reducing Fatty Acids Content in an In Vitro Model of Hepatocellular Steatosis. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Welsher, K.; Robinson, J.T.; Goodwin, A.; Zaric, S.; Dai, H. Nano-graphene oxide for cellular imaging and drug delivery. Nano Res. 2008, 1, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabish, T.A. Graphene-based materials: The missing piece in nanomedicine? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, G.; González-Domínguez, J.M.; Criado, A.; Vázquez, E.; Bianco, A.; Prato, M. Promises, facts and challenges for graphene in biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 4400–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marchi, L.; Pretti, C.; Gabriel, B.; Marques, P.A.; Freitas, R.; Neto, V. An overview of graphene materials: Properties, applications and toxicity on aquatic environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 1440–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, S.; Yang, G.; Yang, P.; He, F.; Lin, J.; Jin, D.; Xing, B. Recent advances in functional nanomaterials for light–triggered cancer therapy. Nano Today 2018, 19, 146–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enoki, T.; Prasad, B.L.V.; Shibayama, Y.; Takai, K.; Sato, H. Chapter 23—Magnetism of Nano-graphite. In Carbon Alloys; Yasuda, E.-I., Inagaki, M., Kaneko, K., Endo, M., Oya, A., Tanabe, Y., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro-Gahete, J.; Benítez, A.; Otero, R.; Esquivel, D.; Jiménez-Sanchidrián, C.; Morales, J.; Caballero, Á.; Romero-Salguero, F.J. A Comparative Study of Particle Size Distribution of Graphene Nanosheets Synthesized by an Ultrasound-Assisted Method. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Zhu, Z.; Gan, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Wan, Q.; Wang, J. PEGylated nano-graphene oxide as a nanocarrier for delivering mixed anticancer drugs to improve anticancer activity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoudipour, E.; Kashanian, S.; Maleki, N. A targeted drug delivery system based on dopamine functionalized nano graphene oxide. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 668, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.T.; LaChance, A.M.; Zeng, S.; Liu, B.; Sun, L. Synthesis, properties, and applications of graphene oxide/reduced graphene oxide and their nanocomposites. Nano Mater. Sci. 2019, 1, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdhouse, M.J.; Lalitha, P. Nanosilver-decorated nanographene and their adsorption performance in waste water treatment. Bioresour Bioprocess 2016, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majid, R.; Pegah, M.; Hadis, L.; Behzad, B.; Amirhossein, S. Conjugates of Curcumin with Graphene and Carbon Nanotubes: A Review on Biomedical Applications. Curr. Med. 2020, 27, 6849–6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugnano, M.; Lama, G.C.; Castaldo, R.; Marchesano, V.; Merola, F.; del Giudice, D.; Calabuig, A.; Gentile, G.; Ambrogi, V.; Cerruti, P.; et al. Cellular Uptake of Mildly Oxidized Nanographene for Drug-Delivery Applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasari Shareena, T.P.; McShan, D.; Dasmahapatra, A.K.; Tchounwou, P.B. A Review on Graphene-Based Nanomaterials in Biomedical Applications and Risks in Environment and Health. Nano-Micro Lett. 2018, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurunnabi, M.; Parvez, K.; Nafiujjaman, M.; Revuri, V.; Khan, H.A.; Feng, X.; Lee, Y.-K. Bioapplication of graphene oxide derivatives: Drug/gene delivery, imaging, polymeric modification, toxicology, therapeutics and challenges. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 42141–42161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, L.; Song, B.; Liang, H.; Liu, J.; Feng, X.; Deng, B.; Sun, T.; Shao, L. Toxicity of graphene-family nanoparticles: A general review of the origins and mechanisms. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Gou, X.; Sun, B.; Li, W.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Hu, F.; Li, Y. Porous graphene-black phosphorus nanocomposite modified electrode for detection of leptin. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 137, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Liu, Y.; Xiang, H.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Hong, G.; Hu, T.S.; et al. Membraneless reproducible MoS2 field-effect transistor biosensor for high sensitive and selective detection of FGF21. Sci. China Mater. 2019, 62, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, Y.-H.; Hsieh, C.-T.; Chiu, S.-T.; Tsai, P.-H.; Liu, C.-Y.; Ke, W.-J. Antibacterial Property of Composites of Reduced Graphene Oxide with Nano-Silver and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized Using a Microwave-Assisted Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangham, A.; Standish, M.M.; Watkins, J.C. Diffusion of univalent ions across the lamellae of swollen phospholipids. J. Mol. Bio. 1965, 13, 238-IN227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Rezaei-Sadabady, R.; Davaran, S.; Joo, S.W.; Zarghami, N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Samiei, M.; Kouhi, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, N.; Yadav, N.P.; Rai, V.K.; Sinha, P.; Yadav, K.S.; Jain, S.; Arora, S. Efficient Hepatic Delivery of Drugs: Novel Strategies and Their Significance. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 382184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himanshu, A.; Sitasharan, P.; Singhai, A. Liposomes as drug carriers. IJPLS 2011, 2, 945–951. [Google Scholar]
- Riaz, M. Liposomes preparation methods. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 1996, 9, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Li, Z.-P.; Tian, G.-X.; Pan, R.-Y.; Xu, C.-M.; Zhang, B.; Wu, J.-L. Liver-targeted liposomes for codelivery of curcumin and combretastatin A4 phosphate: Preparation, characterization, and antitumor effects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1789–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-J.; Lian, Y.-W.; Guan, Q.-S.; Li, N.; Liang, W.-J.; Liu, W.-X.; Huang, Y.-B.; Cheng, Y.; Luo, H. Liver-targeted delivery of liposome-encapsulated curcumol using galactosylated-stearate. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sercombe, L.; Veerati, T.; Moheimani, F.; Wu, S.Y.; Sood, A.K.; Hua, S. Advances and Challenges of Liposome Assisted Drug Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, R. Fenofibrate nanoliposome: Preparation and its inhibitory effects on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Nanomedicine 2016, 12, 2449–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-K. Liposomes for Enhanced Bioavailability of Water-Insoluble Drugs: In Vivo Evidence and Recent Approaches. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Jie, X.; Ou, Y.; Cao, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Qi, R. Nanoliposome improves inhibitory effects of naringenin on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Verma, N.; Kumar, K. Chapter 2—Hybrid composites: A revolutionary trend in biomedical engineering. In Materials for Biomedical Engineering; Grumezescu, V., Grumezescu, A.M., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narvekar, M.; Xue, H.Y.; Wong, H.L. A novel hybrid delivery system: Polymer-oil nanostructured carrier for controlled delivery of highly lipophilic drug all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA). Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 436, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narvekar, M.; Xue, H.Y.; Tran, N.T.; Mikhael, M.; Wong, H.L. A new nanostructured carrier design including oil to enhance the pharmaceutical properties of retinoid therapy and its therapeutic effects on chemo-resistant ovarian cancer. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghitman, J.; Biru, E.I.; Stan, R.; Iovu, H. Review of hybrid PLGA nanoparticles: Future of smart drug delivery and theranostics medicine. Mater. Des. 2020, 193, 108805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Waters, A.K.; Kalyan, P.; Achrol, A.S.; Kesari, S.; Yenugonda, V.M. Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a next-generation drug delivery platform: State of the art, emerging technologies, and perspectives. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 1937–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, V.; Yadav, R.B.; Kushwaha, K.; Yadav, S.; Sharma, S.; Agrawal, U. Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles: Development & statistical optimization of norfloxacin for topical drug delivery system. Bioact. Mater. 2017, 2, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, R.H.; Aryal, S.; Hu, C.M.; Zhang, L. Quick synthesis of lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles with low polydispersity using a single-step sonication method. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16958–16962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lee Chung, B.; Ma, M.; Mulder, W.J.; Fayad, Z.A.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Langer, R. Mass production and size control of lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles through controlled microvortices. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3587–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sah, H.; Thoma, L.A.; Desu, H.R.; Sah, E.; Wood, G.C. Concepts and practices used to develop functional PLGA-based nanoparticulate systems. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z. Lipid-enveloped hybrid nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 860–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamaly, N.; Yameen, B.; Wu, J.; Farokhzad, O.C. Degradable controlled-release polymers and polymeric nanoparticles: Mechanisms of controlling drug release. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2602–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadinoto, K.; Sundaresan, A.; Cheow, W.S. Lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2013, 85, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabok, A.; Shamsipur, M.; Yeganeh-Faal, A.; Molaabasi, F.; Molaei, K.; Sarparast, M. A highly selective semiconducting polymer dots-based “off–on” fluorescent nanoprobe for iron, copper and histidine detection and imaging in living cells. Talanta 2019, 194, 752–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perni, S.; Prokopovich, P. Poly-beta-amino-esters nano-vehicles based drug delivery system for cartilage. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishak, R.A.H.; Mostafa, N.M.; Kamel, A.O. Stealth lipid polymer hybrid nanoparticles loaded with rutin for effective brain delivery—Comparative study with the gold standard (Tween 80): Optimization, characterization and biodistribution. Drug Deliv. 2017, 24, 1874–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Yu, M.; Feng, N. Wheat germ agglutinin modification of lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles: Enhanced cellular uptake and bioadhesion. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 36125–36135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Uthaman, S.; Park, I.-K. Utilization of Polymer-Lipid Hybrid Nanoparticles for Targeted Anti-Cancer Therapy. Molecules 2020, 25, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajid, M.; Cameotra, S.S.; Ahmad Khan, M.S.; Ahmad, I. Chapter 23—Nanoparticle-Based Delivery of Phytomedicines: Challenges and Opportunities. In New Look to Phytomedicine; Ahmad Khan, M.S., Ahmad, I., Chattopadhyay, D., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 597–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.; Freitas, V.D.; Mateus, N.; Fernandes, I.; Oliveira, J. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles as Carriers of Natural Phenolic Compounds. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Eldridge, D.; Palombo, E.; Harding, I. Composition and structure. In Lipid Nanoparticles: Production, Characterization and Stability; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca-Santos, B.; Gremião, M.P.D.; Chorilli, M. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 4981–5003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badrealam, K.F.; Owais, M. Nanoscale drug delivery systems: An updated view. Nanobiotechnology 2014, 180, 180. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Dhar, A.; Patel, C.; Khimani, M.; Neogi, S.; Sharma, P.; Siva Kumar, N.; Vekariya, R.L. A brief review on solid lipid nanoparticles: Part and parcel of contemporary drug delivery systems. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 26777–26791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.P.; Tiyaboonchai, W.; Patankar, S.; Madhusudhan, B.; Souto, E.B. Curcuminoids-loaded lipid nanoparticles: Novel approach towards malaria treatment. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 81, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Ray, S.; Thakur, R.S. Solid lipid nanoparticles: A modern formulation approach in drug delivery system. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 71, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, L.; Gallarate, M.; Panciani, P.P.; Ugazio, E.; Sapino, S.; Peira, E.; Chirio, D. Techniques for the Preparation of Solid Lipid Nano and Microparticles; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, N.; Valizadeh, H.; Zakeri-Milani, P. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: Structure, Preparation and Application. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 5, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battu, S.K.; Repka, M.A.; Maddineni, S.; Chittiboyina, A.G.; Avery, M.A.; Majumdar, S. Physicochemical characterization of berberine chloride: A perspective in the development of a solution dosage form for oral delivery. AAPS PharmSciTech 2010, 11, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Yang, M.-X.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.-M.; Gao, D.-H.; Ou, Z.-M.; Li, Z.-P.; Liu, S.-H.; Li, X.-J.; Yang, S.-Y. Characterization, pharmacokinetics, and hypoglycemic effect of berberine loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 4677–4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.-X.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.-M.; Ou, Z.-M.; Li, Z.-P.; Liu, S.-H.; Li, X.-J.; Yang, S.-Y. Berberine-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles are concentrated in the liver and ameliorate hepatosteatosis in db/db mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 5049–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Baboota, S.; Ali, J.; Khan, S.; Narang, R.S.; Narang, J.K. Nanostructured lipid carriers: An emerging platform for improving oral bioavailability of lipophilic drugs. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 5, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Beg, S.; Khurana, R.K.; Sandhu, P.S.; Kaur, R.; Katare, O.P. Recent advances in self-emulsifying drug delivery systems (SEDDS). Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 2014, 31, 121–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Pang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, A.; Feng, J. Self-emulsifying drug delivery system and the applications in herbal drugs. Drug Deliv. 2015, 22, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salimi, A.; Sharif Makhmal Zadeh, B.; Hemati, A.A.; Akbari Birgani, S. Design and Evaluation of Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery System (SEDDS) Of Carvedilol to Improve the Oral Absorption. Jundishapur. J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2014, 9, e16125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akula, S.; Gurram, A.K.; Devireddy, S.R. Self-Microemulsifying Drug Delivery Systems: An Attractive Strategy for Enhanced Therapeutic Profile. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 964051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouton, C.W. Lipid formulations for oral administration of drugs: Non-emulsifying, self-emulsifying and ‘self-microemulsifying’ drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 11, S93–S98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouton, C.W. Formulation of poorly water-soluble drugs for oral administration: Physicochemical and physiological issues and the lipid formulation classification system. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 29, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eltobshi, A.A.; Mohamed, E.A.; Abdelghani, G.M.; Nouh, A.T. Self-nanoemulsifying drug-delivery systems for potentiated anti-inflammatory activity of diacerein. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 6585–6602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardouh, A.R.; Nasef, A.M.; Mostafa, Y.; Gad, S. Design and evaluation of combined atorvastatin and ezetimibe optimized self- nano emulsifying drug delivery system. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 102093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolakakis, I.; Partheniadis, I. Self-emulsifying granules and pellets: Composition and formation mechanisms for instant or controlled release. Pharmaceutics 2017, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Izham, M.N.; Hussin, Y.; Aziz, M.N.M.; Yeap, S.K.; Rahman, H.S.; Masarudin, M.J.; Mohamad, N.E.; Abdullah, R.; Alitheen, N.B. Preparation and characterization of self nano-emulsifying drug delivery system loaded with citraland its antiproliferative effect on colorectal cells in vitro. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Assi, R.; Abdulbaqi, M.I.; Seok Ming, T.; Siok Yee, C.; Wahab, A.H.; Asif, S.M.; Darwis, Y. Liquid and Solid Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems (SEDDs) as Carriers for the Oral Delivery of Azithromycin: Optimization, In Vitro Characterization and Stability Assessment. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershanik, T.; Benita, S. Positively charged self-emulsifying oil formulation for improving oral bioavailability of progesterone. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 1996, 1, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkawi, A.; Jalil, A.; Nazir, I.; Matuszczak, B.; Kennedy, R.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Self-Emulsifying Drug Delivery Systems: Hydrophobic Drug Polymer Complexes Provide a Sustained Release in Vitro. Mol. Pharm. 2020, 17, 3709–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piyush Chudiwal, S. Solid self-microemulsifying drug delivery system (SMEDDS) of primaquine: Bio-distribution and enhanced liver uptake. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Rajpoot, K.; Tekade, M.; Pandey, V.; Nagaraja, S.; Youngren-Ortiz, S.R.; Tekade, R.K. Chapter 9—Self-microemulsifying drug-delivery system: Ongoing challenges and future ahead. In Drug Delivery Systems; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 393–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristote, B.; Buya, A.B.; Patrick, B. Memvanga and Véronique Préat. Self-Nano-Emulsifying Drug-Delivery Systems: From the Development to the Current Applications and Challenges in Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, W.; Mäder, K. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles: Production, Characterization and Applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S.A. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic and dermatological preparations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, S131–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S. Nanostructured lipid matrices for improved microencapsulation of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 242, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosa, A.; Reddi, S.; Saha, R.N. Nanostructured lipid carriers for site-specific drug delivery. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 598–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uprit, S.; Kumar Sahu, R.; Roy, A.; Pare, A. Preparation and characterization of minoxidil loaded nanostructured lipid carrier gel for effective treatment of alopecia. Saudi Pharm. J. 2013, 21, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramaniam, B.; Siddik, Z.H.; Nagoor, N.H. Optimization of nanostructured lipid carriers: Understanding the types, designs, and parameters in the process of formulations. J. Nanopart Res. 2020, 22, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, I.; Yasir, M.; Verma, M.; Singh, A.P. Nanostructured Lipid Carriers: A Groundbreaking Approach for Transdermal Drug Delivery. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 10, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Xu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Huang, F.; Yin, D.; Huang, H. Tumor targeted nanostructured lipid carrier co-delivering paclitaxel and indocyanine green for laser triggered synergetic therapy of cancer. Rsc Adv. 2017, 7, 35086–35095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, D.; Duan, C.; Wang, Y.; Jia, L.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, Q. Preparation, characterization and biodistribution of nanostructured lipid carriers for parenteral delivery of bifendate. J. Microencapsul. 2011, 28, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Chen, C.J.; Elzoghby, A.O.; Yeh, T.S.; Fang, J.Y. Self-assembly and directed assembly of lipid nanocarriers for prevention of liver fibrosis in obese rats: A comparison with the therapy of bariatric surgery. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Ou, Y.; Hu, G.; Wen, C.; Yue, S.; Chen, C.; Xu, L.; Xie, J.; Dai, H.; Xiao, H.; et al. Naringenin attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by down-regulating the NLRP3/NF-κB pathway in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 1806–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Liu, S.; Anwaier, G.; Wang, Q.; Shen, W.; Shen, Q.; Qi, R. Formulation and intestinal absorption of naringenin loaded nanostructured lipid carrier and its inhibitory effects on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nanomedicine 2021, 32, 102310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Bishnoi, R.S.; Shukla, A.K.; Jain, C.P. Techniques for Formulation of Nanoemulsion Drug Delivery System: A Review. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2019, 24, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboalnaja, K.O.; Yaghmoor, S.; Kumosani, T.A.; McClements, D.J. Utilization of nanoemulsions to enhance bioactivity of pharmaceuticals, supplements, and nutraceuticals: Nanoemulsion delivery systems and nanoemulsion excipient systems. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, H.; Gorain, B.; Karmakar, S.; Biswas, E.; Dey, G.; Barik, R.; Mandal, M.; Pal, T.K. Improvement of cellular uptake, in vitro antitumor activity and sustained release profile with increased bioavailability from a nanoemulsion platform. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 460, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Das, B.; Patra, S. Chapter 10—Drug Resistance in Tuberculosis: Nanomedicines at Rescue. In Antimicrobial Nanoarchitectonics; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxmi, M.; Bhardwaj, A.; Mehta, S.; Mehta, A. Development and characterization of nanoemulsion as carrier for the enhancement of bioavailability of artemether. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2015, 43, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Sharma, A.; Arora, S.; Gupta, S.; Bishnoi, M. Formulation, optimization and evaluation of atorvastatin calcium loaded microemulsion. J. Pharm. Drug Deliv. Res. 2012, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.H.; Hussein, A.A. Oral nanoemulsions of candesartan cilexetil: Formulation, characterization and in vitro drug release studies. AAPS Open 2017, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Liao, W.; Charcosset, C. Recent advances in encapsulation of curcumin in nanoemulsions: A review of encapsulation technologies, bioaccessibility and applications. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, D.K. Engineering of nanoemulsions for drug delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.J.; Zhang, X.; Kang, M.G.; Kim, G.J.; Shin, S.Y.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, B.N.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, J.T.; Hong, K. Cytotoxicity evaluation of turmeric extract incorporated oil-in-water nanoemulsion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, N.P.; Macedo, A.S.; Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B.; Kim, S.; Chang, P.-S.; Ko, S. Development and evaluation of lipid nanocarriers for quercetin delivery: A comparative study of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN), nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC), and lipid nanoemulsions (LNE). LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gönüllü, Ü.; Üner, M.; Yener, G.; Karaman, E.F.; Aydoğmuş, Z. Formulation and characterization of solid lipid nanoparticles, nanostructured lipid carriers and nanoemulsion of lornoxicam for transdermal delivery. Acta Pharm. 2015, 65, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puglia, C.; Damiani, E.; Offerta, A.; Rizza, L.; Tirendi, G.G.; Tarico, M.S.; Curreri, S.; Bonina, F.; Perrotta, R.E. Evaluation of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) and nanoemulsions as carriers for UV-filters: Characterization, in vitro penetration and photostability studies. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 51, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, F.; Wafa, R.; Shafiq, S. Solubility and Dissolution Improvement of Aceclofenac using Different Nanocarriers. J. Bioequivalence Bioavailab. 2009, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammak, I.; Sobral, P.J.D.A.; Aquino, A.; Neves, M.A.D.; Conte-Junior, C.A. Nanoemulsions: Using emulsifiers from natural sources replacing synthetic ones—A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2721–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norouzi, P.; Rastegari, A.; Mottaghitalab, F.; Farokhi, M.; Zarrintaj, P.; Saeb, M.R. 24—Nanoemulsions for intravenous drug delivery. In Nanoengineered Biomaterials for Advanced Drug Delivery; Mozafari, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 581–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; He, X.; Feng, X. Developing neobavaisoflavone nanoemulsion suppresses lung cancer progression by regulating tumor microenvironment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.K.; Vingkar, S.K. Formulation, antimalarial activity and biodistribution of oral lipid nanoemulsion of primaquine. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 347, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simion, V.; Stan, D.; Constantinescu, C.A.; Deleanu, M.; Dragan, E.; Tucureanu, M.M.; Gan, A.-M.; Butoi, E.; Constantin, A.; Manduteanu, I.; et al. Conjugation of curcumin-loaded lipid nanoemulsions with cell-penetrating peptides increases their cellular uptake and enhances the anti-inflammatory effects in endothelial cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, D.; Quan, E.; Yuan, X.; Xie, Q.; Li, Z.; Wu, B. Sodium Oleate-Based Nanoemulsion Enhances Oral Absorption of Chrysin through Inhibition of UGT-Mediated Metabolism. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 2864–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S. Enhanced Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Pea (Pisum sativum) Protein by pH-Shifting and Ultrasonication Combined Process; University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign: Champaign, IL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sherbiny, M.; Eldosoky, M.; El-Shafey, M.; Othman, G.; Elkattawy, H.A.; Bedir, T.; Elsherbiny, N.M. Vitamin D nanoemulsion enhances hepatoprotective effect of conventional vitamin D in rats fed with a high-fat diet. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 288, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, R.; Kompella, U.B. Nanomicellar formulations for sustained drug delivery: Strategies and underlying principles. Nanomedicine 2010, 5, 485–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velagaleti, P.; Anglade, E.; Khan, I.; Gilger, B.; Mitra, A. Topical delivery of hydrophobic drugs using a novel mixed nanomicellar technology to treat diseases of the anterior and posterior segments of the eye. Drug Deliv. Technol. 2010, 10, 42–47. [Google Scholar]
- Determan, M.D.; Cox, J.P.; Mallapragada, S.K. Drug release from pH-responsive thermogelling pentablock copolymers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2007, 81, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yan, M.; Jin, Y.; Zhu, K. Reverse self-assemblies based on amphiphilic polyphosphazenes for encapsulation of water-soluble molecules. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 475602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Li, Z. The perspectives of using unimolecular micelles in nanodrug formulation. Ther. Deliv. 2019, 10, 333–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadlapudi, A.D.; Mitra, A.K. Nanomicelles: An emerging platform for drug delivery to the eye. Ther. Deliv. 2013, 4, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, N.; Kataoka, K. Current state, achievements, and future prospects of polymeric micelles as nanocarriers for drug and gene delivery. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 112, 630–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Deng, X.; Ding, J.; Zhou, W.; Zheng, X.; Tang, G. Mechanisms of drug release in pH-sensitive micelles for tumour targeted drug delivery system: A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V.P. Micellar nanocarriers: Pharmaceutical perspectives. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulthe, S.S.; Choudhari, Y.M.; Inamdar, N.N.; Mourya, V. Polymeric micelles: Authoritative aspects for drug delivery. Des. Monomers Polym. 2012, 15, 465–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, Y.H.; Youssry, M. Polymeric micelles of biodegradable diblock copolymers: Enhanced encapsulation of hydrophobic drugs. Materials 2018, 11, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; Hou, J.; Xia, X.; Wang, J.; Ning, Q.; Jiang, S. Promising positive liver targeting delivery system based on arabinogalactan-anchored polymeric micelles of norcantharidin. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, S630–S640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avramović, N.; Mandić, B.; Savić-Radojević, A.; Simić, T. Polymeric Nanocarriers of Drug Delivery Systems in Cancer Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Han, J.; Li, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Xu, W. Synthetic glycopolypeptide micelle for targeted drug delivery to hepatic carcinoma. Polymers 2018, 10, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.P.; Tian, G.X.; Jiang, H.; Pan, R.Y.; Lian, B.; Wang, M.; Gao, Z.Q.; Zhang, B.; Wu, J.L. Liver-Targeting and pH-Sensitive Sulfated Hyaluronic Acid Mixed Micelles for Hepatoma Therapy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 9437–9452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Mondal, G.; Dutta, R.; Mahato, R.I. Co-delivery of small molecule hedgehog inhibitor and miRNA for treating liver fibrosis. Biomaterials 2016, 76, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, I.S.; Hu, H.; Yin, L.; He, W. Drug nanocrystals: Fabrication methods and promising therapeutic applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 562, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-L.; Zhan, H.; Liang, D.; Liang, J.F. Nanocrystal technology for drug formulation and delivery. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2015, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junyaprasert, V.B.; Morakul, B. Nanocrystals for enhancement of oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.-Y.; Lee, H.-E.; Jin, K.; Nam, K.T. Extended gold nano-morphology diagram: Synthesis of rhombic dodecahedra using CTAB and ascorbic acid. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 6861–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C. Poor aqueous solubility—an industry wide problem in drug discovery. Am. Pharm. Rev. 2002, 5, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Couvreur, P.; Tulkenst, P.; Roland, M.; Trouet, A.; Speiser, P. Nanocapsules: A new type of lysosomotropic carrier. FEBS Lett. 1977, 84, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crommelin, D.J.A.; Storm, G. Liposomes: From the Bench to the Bed. J. Liposome Res. 2003, 13, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, H.R.; Shegokar, R.; Keck, M.C. 20 years of lipid nanoparticles (SLN & NLC): Present state of development & industrial applications. Curr. Drug Discov. Technol. 2011, 8, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, Y.; Meher, J.G.; Raval, K.; Khan, F.A.; Chaurasia, M.; Jain, N.K.; Chourasia, M.K. Nanoemulsion: Concepts, development and applications in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 252, 28–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, J.; Müller, R.H.; Möschwitzer, J.P. Combinative particle size reduction technologies for the production of drug nanocrystals. J. Pharm. 2014, 2014, 265754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.-K.; Kwok, P.C.L. Production methods for nanodrug particles using the bottom-up approach. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, Y. Structure evolution of curcumin nanoprecipitation from a micromixer. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 1021–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhakar, B.; NagaJyothi, K.; Ramana Murthy, K. Nanosuspensions as a versatile carrier based drug delivery system–An overview. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, E.; Güngör, S.; Özsoy, Y. Potential enhancement and targeting strategies of polymeric and lipid-based nanocarriers in dermal drug delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2017, 8, 967–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-W.; Cambre, M.; Lee, H.-J. The toxicity of nanoparticles depends on multiple molecular and physicochemical mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Hu, Y.; Yin, L.; Tang, C.; Yin, C. Effects of particle size and surface charge on cellular uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3657–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, M.; Krishnan, V.; Mitragotri, S. Nanocrystals: A perspective on translational research and clinical studies. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2018, 4, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petronella, F.; Pagliarulo, A.; Striccoli, M.; Calia, A.; Lettieri, M.; Colangiuli, D.; Curri, M.L.; Comparelli, R. Colloidal nanocrystalline semiconductor materials as photocatalysts for environmental protection of architectural stone. Crystals 2017, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, W. Injected nanocrystals for targeted drug delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.R.; Park, J.S.; Bae, I.H.; Lee, Y.; Kim, B.M. Liquid crystal nanoparticle formulation as an oral drug delivery system for liver-specific distribution. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 853–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobyliak, N.; Abenavoli, L.; Falalyeyeva, T.; Virchenko, O.; Natalia, B.; Beregova, T.; Bodnar, P.; Spivak, M. Prevention of NAFLD development in rats with obesity via the improvement of pro/antioxidant state by cerium dioxide nanoparticles. Clujul. Med. 2016, 89, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobyliak, N.; Virchenko, O.; Falalyeyeva, T.; Kondro, M.; Beregova, T.; Bodnar, P.; Shcherbakov, O.; Bubnov, R.; Caprnda, M.; Delev, D.; et al. Cerium dioxide nanoparticles possess anti-inflammatory properties in the conditions of the obesity-associated NAFLD in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobyliak, N.M.; Falalyeyeva, T.M.; Kuryk, O.G.; Beregova, T.V.; Bodnar, P.M.; Zholobak, N.M.; Shcherbakov, O.B.; Bubnov, R.V.; Spivak, M.Y. Antioxidative effects of cerium dioxide nanoparticles ameliorate age-related male infertility: Optimistic results in rats and the review of clinical clues for integrative concept of men health and fertility. EPMA J. 2015, 6, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, Y.; Deb, P.K.; Bandopadhyay, S.; Bandyopadhyay, N.; Tekade, R.K. Chapter 3—Role of Physicochemical Parameters on Drug Absorption and Their Implications in Pharmaceutical Product Development. In Dosage Form Design Considerations; Tekade, R.K., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2018; pp. 85–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorad, R.S.; Mandlik, S.K.; Gujar, K.N. Liver Specific Drug Targeting Strategies: A Review. Int. J. Pharma. Sci. Res. 2013, 11, 4145–4157. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers as novel drug delivery systems: Applications, advantages and disadvantages. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 288. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Gao, Y.; Song, Z.; Zheng, Q.C. Ligand-based targeted therapy: A novel strategy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 5645–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, S.; Costa, C.P.; Moreira, J.N.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Silva, A.C. Using the quality by design (QbD) approach to optimize formulations of lipid nanoparticles and nanoemulsions: A review. Nanomedicine 2020, 28, 102206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanthamneni, N.; Valiveti, S.; Patel, M.; Xia, H.; Tseng, Y.-C. Enhanced bioavailability of danazol nanosuspensions by wet milling and high-pressure homogenization. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2016, 6, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D. Recent advances in the nanotechnology-based drug delivery of Silybin. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 543–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, W.; Hu, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, B. Pharmacokinetics and liver uptake of three Schisandra lignans in rats after oral administration of liposome encapsulating β-cyclodextrin inclusion compound of Schisandra extract. J. Liposome Res. 2019, 29, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, T.; Yan, N.; Wang, P.; Xia, Y.; Hao, H.; Wang, G.; Gonzalez, F.J. Herbal drug discovery for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musolino, V.; Gliozzi, M.; Scarano, F.; Bosco, F.; Scicchitano, M.; Nucera, S.; Carresi, C.; Ruga, S.; Zito, M.C.; Maiuolo, J.; et al. Bergamot Polyphenols Improve Dyslipidemia and Pathophysiological Features in a Mouse Model of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, D.; Barba, F.J.; Kovačević, D.B.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Cruz, A.G.; Putnik, P. Functional Foods: Product Development, Technological Trends, Efficacy Testing, and Safety. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 11, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, W.Y.; Chrisfield, B.J.; Sae-tan, S.; Lambert, J.D. Mitigation of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat-fed mice by the combination of decaffeinated green tea extract and voluntary exercise. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 76, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, P.; Talukdar, A.D.; Nath, R.; Sarker, S.D.; Nahar, L.; Sahu, J.; Choudhury, M.D. Role of Natural Phenolics in Hepatoprotection: A Mechanistic Review and Analysis of Regulatory Network of Associated Genes. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, J.; Sun, P.; Yi, R.; Han, X.; Zhao, X. Raw Bowl Tea (Tuocha) Polyphenol Prevention of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating Intestinal Function in Mice. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O. Polyphenols and the human brain: Plant “secondary metabolite” ecologic roles and endogenous signaling functions drive benefits. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 515–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Qiu, N.; Ding, H.; Yao, R. Polyphenols contents and antioxidant capacity of 68 Chinese herbals suitable for medical or food uses. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.-M.; Li, H.-B. Natural Polyphenols for Prevention and Treatment of Cancer. Nutrients 2016, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Rauf Khan, A.; Fu, M.; Zhai, Y.; Ji, J.; Bobrovskaya, L.; Zhai, G. Advances in curcumin-loaded nanopreparations: Improving bioavailability and overcoming inherent drawbacks. J. Drug Target 2019, 27, 917–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogaru, G.; Bulboaca, A.E.; Gheban, D.; Boarescu, P.M.; Rus, V.; Festila, D.; Sitar-taut, A.-V.; Stanescu, I. Effect of Liposomal Curcumin on Acetaminophen Hepatotoxicity by Down-regulation of Oxidative Stress and Matrix Metalloproteinases. In Vivo 2020, 34, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, S.; Sasani, M.R.; Akhlaghi, M.; Kohanmoo, A. Flaxseed oil in the context of a weight loss programme ameliorates fatty liver grade in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomised double-blind controlled trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 123, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherniya, M.; Nobili, V.; Blesso, C.N.; Sahebkar, A. Medicinal plants and bioactive natural compounds in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A clinical review. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 130, 213–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beji, R.S.; Khemir, S.; Wannes, W.A.; Ayari, K.; Ksouri, R. Antidiabetic, antihyperlipidemic and antioxidant influences of the spice cinnamon (Cinnamomum zeylanicumon) in experimental rats. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 54, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, J.K.; Sasaki, G.Y.; Bruno, R.S. Anti-inflammatory activities of green tea catechins along the gut–liver axis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Lessons learned from preclinical and human studies. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 85, 108478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhong, H.; Leng, L.; Jiang, Z. Effects of soy isoflavone on hepatic steatosis in high fat-induced rats. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2017, 61, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yan, T.; Wang, H.; Cao, L.; Wang, Q.; Takahashi, S.; Yagai, T.; Li, G.; Krausz, K.W.; Wang, G.; Gonzalez, F.J.; et al. Glycyrrhizin Alleviates Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis via Modulating Bile Acids and Meta-Inflammation. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2018, 46, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, F.; Tan, H.Y.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Feng, Y. Herbal Medicine in the Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases-Efficacy, Action Mechanism, and Clinical Application. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnoy, A.; Saenphet, K.; Lumyong, S.; Saenphet, S.; Chomdej, S. Monascus purpureus-fermented Thai glutinous rice reduces blood and hepatic cholesterol and hepatic steatosis concentrations in diet-induced hypercholesterolemic rats. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, B.; Qi, F.; Wu, J.; Yin, G.; Hua, J.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, L. Red Yeast Rice: A Systematic Review of the Traditional Uses, Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Quality Control of an Important Chinese Folk Medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Li, M.; Zhou, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, L.; Ji, G. Qianggan extract improved nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by modulating lncRNA/circRNA immune ceRNA networks. BMC Complement Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M.; Aliashrafi, S.; Javadzadeh, Y.; Asghari Jafarabadi, M. The Effect of Chlorella vulgaris Supplementation on Liver En-zymes, Serum Glucose and Lipid Profile in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Health Promot. Perspect. 2014, 4, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fan, J.-G.; Shanghai Multicenter Clinical Cooperative Group of Danning Pian Trial. Evaluating the efficacy and safety of Danning Pian in the short-term treatment of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A multicenter clinical trial. HBPD INT 2004, 3, 375–380. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, S.Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, W.H.; Ying, J.; He, Y.M.; Wang, W.J. Effects of Yiqi Sanju Formula on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2008, 6, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhong, R.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Tang, X.; Li, Z.; Xia, M.; Ling, W. Effects of bayberry juice on inflammatory and apoptotic markers in young adults with features of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutrition 2014, 30, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Ramiro, I.; Vauzour, D.; Minihane, A. Polyphenols and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Impact and mechanisms. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundermann, K.-J.; Gundermann, S.; Drozdzik, M.; Mohan Prasad, V.G. Essential phospholipids in fatty liver: A scientific update. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyod, S.; Wu, W.-K.; Ho, C.-T.; Lu, K.-H.; Liu, C.-T.; Yung-lin, C.; Lai, Y.-S.; Chen, W.-C.; Lin, Y.-E.; Lin, S.-H.; et al. Diet Supplementation with Allicin Protects against Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice by Improving Anti-Inflammation and Antioxidative Functions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7104–7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seif el-Din, S.; Sabra, A.-N.; Hammam, O.; Ebeid, F.; El-Lakkany, N. Pharmacological and Antioxidant Actions of Garlic and—Or Onion in Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (Nafld) in Rats. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2014, 44, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.; Yang, K.; Chen, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Wu, L. The Versatile Effects of Dihydromyricetin in Health. Evid. Based Complement Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 1053617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, S.; Chakraborty, R. Chapter 19—Herbs, Gastrointestinal Protection, and Oxidative Stress. In Gastrointestinal Tissue; Gracia-Sancho, J., Salvadó, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2017; pp. 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faran, S.A.; Asghar, S.; Khalid, S.H.; Khan, I.U.; Asif, M.; Khalid, I.; Farooq Gohar, U.; Hussain, T. Hepatoprotective and Renoprotective Properties of Lovastatin-Loaded Ginger and Garlic Oil Nanoemulsomes: Insights into Serum Biological Parameters. Medicina 2019, 55, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahadori, E.; Farjami, Z.; Rezayi, M.; Lngari, H.; Darroudi, M.; Avan, A.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M. Recent advances in nanotechnology for the treatment of metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousavi, Z.; Hassanpourezatti, M.; Najafizadeh, P.; Rezagholian, S.; Rhamanifar, M.S.; Nosrati, N. Effects of subcutaneous injection MnO2 micro-and nanoparticles on blood glucose level and lipid profile in rat. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 41, 518–524. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.; Li, F.; Zhou, H.; Bai, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Yan, B. Oral Exposure to Silver Nanoparticles or Silver Ions May Aggravate Fatty Liver Disease in Overweight Mice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9334–9343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
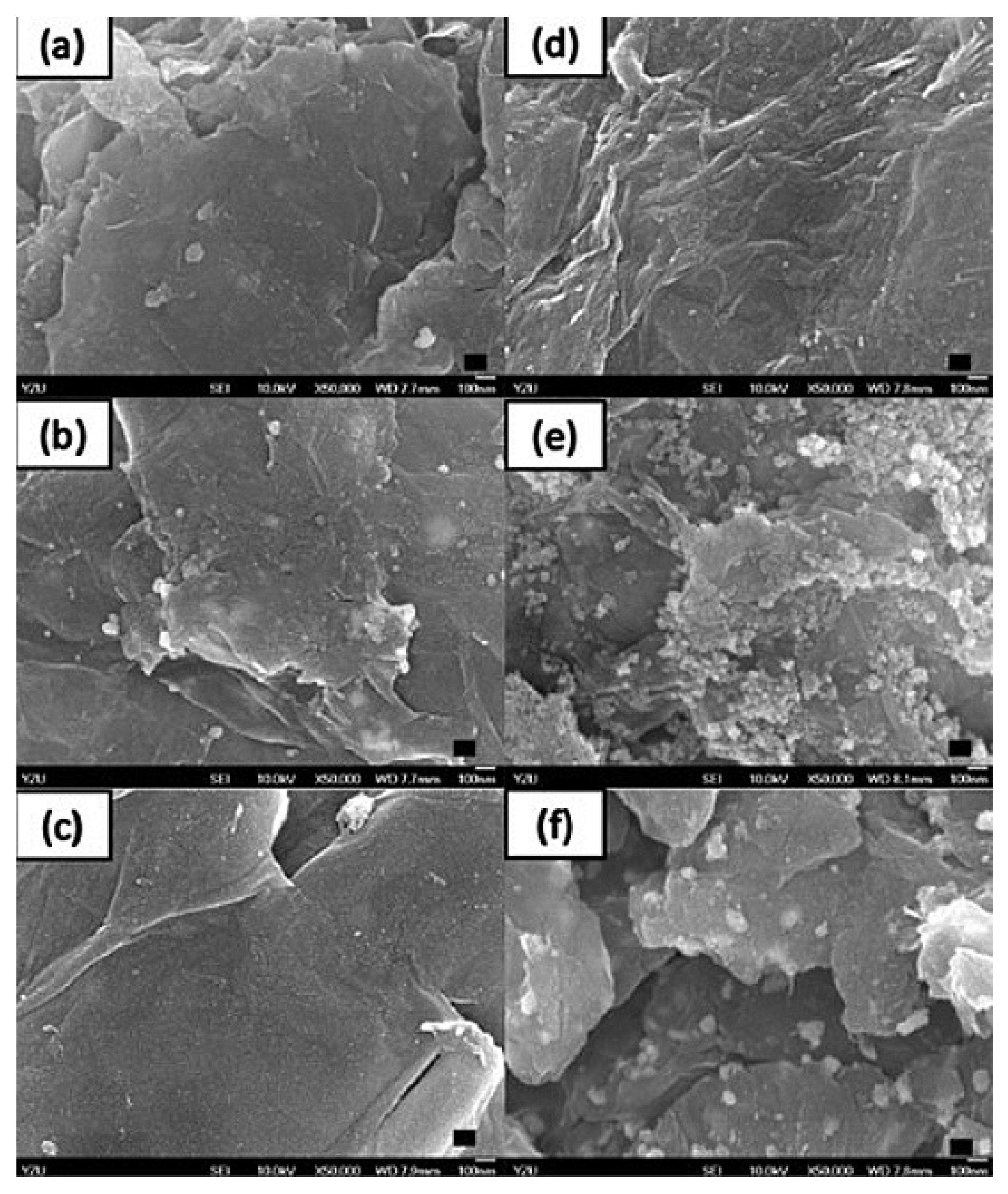





| Phytochemical Compound Name | Source | Reported Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| α-linolenic acid | Flaxseed | Weight loss, reducing the risk of atherosclerosis, diabetes, metabolic syndrome and dyslipidemia | [293,294] |
| Flavonoids, steroids, terpenoids and phenolic acids | Cinnamon | Antioxidant, anti-hyperglycemic effect, improves lipid profiles | [294,295] |
| Flavonoids (catechins) | Green Tea | Antioxidant | [294,296] |
| Isoflavones | Soybeans | Protection and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, decreasing hepatic lipid deposition, and increasing antioxidant capacity | [294,297] |
| Glycyrrhizin | Licorice root | Reduce liver inflammation, antioxidant, anti-diabetic, reduce ALT, AST, and hepato-protective | [294,298] |
| Xuezhikang, unsaturated fatty acids, and flavonoids | Red yeast rice | Lowering serum total glycerides, total cholesterol | [294,299,300,301] |
| Qianggan | A combination of 16 Chines herbs | Anti-fibrotic | [294,302] |
| Chlorophyll, tocopherols, and ubiquinone | Chlorella green algae | Prevention and treatment of several metabolic disorders (e.g., dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, hypertension, obesity) | [294,303] |
| Danning Pian | A combination of several herbs | Similar to ursodeoxycholic acid in terms of antioxidant and cytoprotective efficacy | [294,304] |
| Yiqi Sanju | A combination of several herbs | Improved the MAFLD grade | [294,305] |
| Anthocyanins and a variety of phenolic acids, including caffeic, ferulic, sinapic, and salicylic acids | Bayberry | High antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacity | [294,306,307] |
| Dietary phospholipids (dilinoleoylphosphatidylcholine) | Soybeans | Anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, and lipid and regulating effects | [294,308] |
| Allicin, and flavonoids | Garlic | Anti-hepatic oxidative stress potentials | [294,309,310] |
| Dihydromyricetin | Ampelopsis grossedentata | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective and glucose-regulatory activities | [294,311] |
| Phyllanthus | Phyllanthus urinaria | Hepatoprotective and strong antioxidant capacities | [294,312] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abou Assi, R.; Abdulbaqi, I.M.; Siok Yee, C. The Evaluation of Drug Delivery Nanocarrier Development and Pharmacological Briefing for Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): An Update. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030215
Abou Assi R, Abdulbaqi IM, Siok Yee C. The Evaluation of Drug Delivery Nanocarrier Development and Pharmacological Briefing for Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): An Update. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(3):215. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030215
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbou Assi, Reem, Ibrahim M. Abdulbaqi, and Chan Siok Yee. 2021. "The Evaluation of Drug Delivery Nanocarrier Development and Pharmacological Briefing for Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): An Update" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 3: 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030215
APA StyleAbou Assi, R., Abdulbaqi, I. M., & Siok Yee, C. (2021). The Evaluation of Drug Delivery Nanocarrier Development and Pharmacological Briefing for Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD): An Update. Pharmaceuticals, 14(3), 215. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030215






