Cell-Free DNA for the Management of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Classical Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (cHL) Particularities
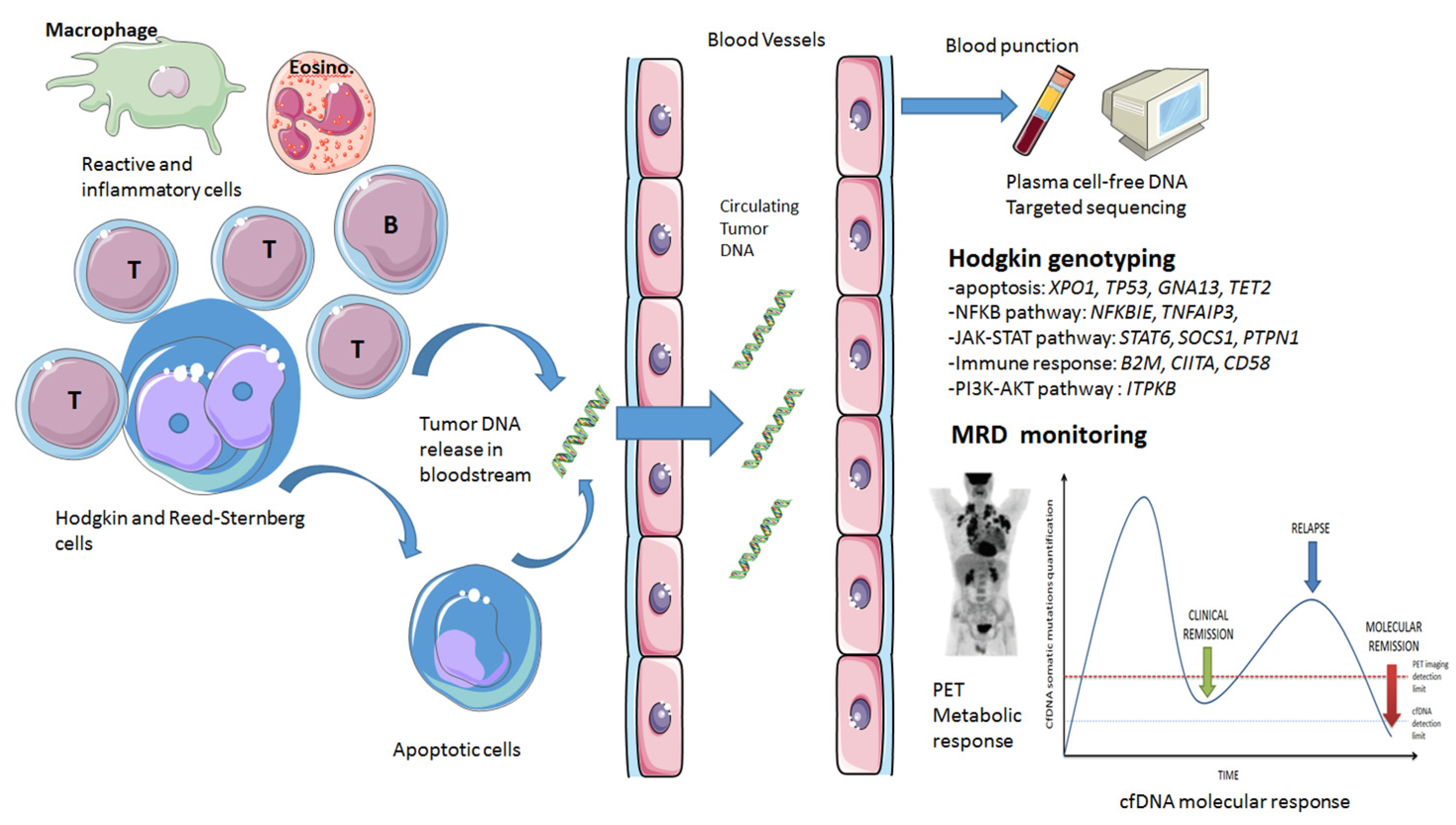
1.2. Cell-Free DNA Physiopathology
1.3. Cell-Free DNA Molecular Tools
2. Genotyping Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma Using cfDNA
2.1. Mutational Landscape Obtained by cfDNA Sequencing
2.2. Comparisons between cfDNA and Tumor DNA
2.3. Comparisons between cfDNA Results and cHL Histological Subtypes
2.4. Potential Interest in the Differential Diagnosis with Other Lymphomas (Gray-Zone, Primary Mediastinal B Cell Lymphoma)
3. Association of cfDNA Level with Clinical Features
4. cfDNA and Pediatric cHL Specificities
5. cfDNA as A MRD Biomarker in cHL
6. Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diehl, V.; Thomas, R.K.; Re, D. Part II: Hodgkin’s lymphoma--diagnosis and treatment. Lancet Oncol. 2004, 5, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasenclever, D.; Diehl, V. A prognostic score for advanced Hodgkin’s disease. International Prognostic Factors Project on Advanced Hodgkin’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casasnovas, R.-O.; Bouabdallah, R.; Brice, P.; Lazarovici, J.; Ghesquieres, H.; Stamatoullas, A.; Dupuis, J.; Gac, A.-C.; Gastinne, T.; Joly, B.; et al. PET-Adapted Treatment for Newly Diagnosed Advanced Hodgkin Lymphoma (AHL2011): A Randomised, Multicentre, Non-Inferiority, Phase 3 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, M.; Loft, A.; Hansen, M.; Pedersen, L.M.; Buhl, T.; Jurlander, J.; Buus, S.; Keiding, S.; D’Amore, F.; Boesen, A.-M.; et al. FDG-PET after Two Cycles of Chemotherapy Predicts Treatment Failure and Progression-Free Survival in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2006, 107, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.; Stanelle, J.; Hansmann, M.-L.; Küppers, R. Pathogenesis of classical and lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2009, 4, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderLaan, P.A. Fine-needle aspiration and core needle biopsy: An update on 2 common minimally invasive tissue sampling modalities: FNA Versus CNB. Cancer Cytopathol. 2016, 124, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camus, V.; Stamatoullas, A.; Mareschal, S.; Viailly, P.-J.; Sarafan-Vasseur, N.; Bohers, E.; Dubois, S.; Picquenot, J.M.; Ruminy, P.; Maingonnat, C.; et al. Detection and Prognostic Value of Recurrent Exportin 1 Mutations in Tumor and Cell-Free Circulating DNA of Patients with Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Haematologica 2016, 101, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spina, V.; Bruscaggin, A.; Cuccaro, A.; Martini, M.; Di Trani, M.; Forestieri, G.; Manzoni, M.; Condoluci, A.; Arribas, A.; Terzi-Di-Bergamo, L.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Reveals Genetics, Clonal Evolution, and Residual Disease in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2413–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessi, L.; Viailly, P.-J.; Bohers, E.; Ruminy, P.; Maingonnat, C.; Bertrand, P.; Vasseur, N.; Beaussire, L.; Cornic, M.; Etancelin, P.; et al. Somatic Mutations of Cell-Free Circulating DNA Detected by Targeted next-Generation Sequencing and Digital Droplet PCR in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 60, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camus, V.; Viennot, M.; Lequesne, J.; Viailly, P.-J.; Bohers, E.; Bessi, L.; Marcq, B.; Etancelin, P.; Dubois, S.; Picquenot, J.-M.; et al. Targeted Genotyping of Circulating Tumor DNA for Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma Monitoring: A Prospective Study. Haematologica 2020, 106, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, P.; Wlodarska, I.; Tousseyn, T.; Dehaspe, L.; Dierickx, D.; Verheecke, M.; Uyttebroeck, A.; Bechter, O.; Delforge, M.; Vandecaveye, V.; et al. Non-Invasive Detection of Genomic Imbalances in Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg Cells in Early and Advanced Stage Hodgkin’s Lymphoma by Sequencing of Circulating Cell-Free DNA: A Technical Proof-of-Principle Study. Lancet Haematol. 2015, 2, e55–e65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righolt, C.H.; Knecht, H.; Mai, S. DNA Superresolution Structure of Reed-Sternberg Cells Differs Between Long-Lasting Remission Versus Relapsing Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Patients: DNA Structure In Pre-Treatment Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. J. Cell Biochem. 2016, 117, 1633–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, F.; Shen, A.; Choi, A.; Gerner, E.W.; Shi, J. Extracellular DNA in Pancreatic Cancer Promotes Cell Invasion and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 4256–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendich, A.; Wilczok, T.; Borenfreund, E. Circulating DNA as a Possible Factor in Oncogenesis. Science 1965, 148, 374–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, L.A.; Bardelli, A. Liquid biopsies: Genotyping circulating tumor DNA. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowes, L.E.; Bratman, S.V.; Dittamore, R.; Done, S.; Kelley, S.O.; Mai, S.; Morin, R.D.; Wyatt, A.W.; Allan, A.L. Circulating Tumor Cells (CTC) and Cell-Free DNA (CfDNA) Workshop 2016: Scientific Opportunities and Logistics for Cancer Clinical Trial Incorporation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Aranda, V.; Bardelli, A.; Blanpain, C.; Bock, C.; Borowski, C.; Caldas, C.; Califano, A.; Doherty, M.; Elsner, M.; et al. Toward Understanding and Exploiting Tumor Heterogeneity. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroun, M.; Lyautey, J.; Lederrey, C.; Olson-Sand, A.; Anker, P. About the possible origin and mechanism of circulating DNA apoptosis and active DNA release. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2001, 313, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatouros, I.G.; Jamurtas, A.Z.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Destouni, A.; Michailidis, Y.; Vrettou, C.; Douroudos, I.I.; Avloniti, A.; Chatzinikolaou, A.; Taxildaris, K.; et al. Time of Sampling Is Crucial for Measurement of Cell-Free Plasma DNA Following Acute Aseptic Inflammation Induced by Exercise. Clin. Biochem. 2010, 43, 1368–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, E.M.; Hessas, E.; Müller, S.; Beiter, T.; Fisch, M.; Eibl, A.; Wolf, O.T.; Giebel, B.; Platen, P.; Kumsta, R.; et al. Cell-Free DNA Release under Psychosocial and Physical Stress Conditions. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Vaart, M.; Pretorius, P.J. The Origin of Circulating Free DNA. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronkhorst, A.J.; Ungerer, V.; Holdenrieder, S. The emerging role of cell-free DNA as a molecular marker for cancer management. BioMol. Detect. Quantif. 2019, 17, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamkovich, S.N.; Cherepanova, A.V.; Kolesnikova, E.V.; Rykova, E.Y.; Pyshnyi, D.V.; Vlassov, V.V.; Laktionov, P.P. Circulating DNA and DNase Activity in Human Blood. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1075, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botezatu, I.; Serdyuk, O.; Potapova, G.; Shelepov, V.; Alechina, R.; Molyaka, Y.; Ananév, V.; Bazin, I.; Garin, A.; Narimanov, M.; et al. Genetic Analysis of DNA Excreted in Urine: A New Approach for Detecting Specific Genomic DNA Sequences from Cells Dying in an Organism. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, F.; Li, M.; Dressman, D.; He, Y.; Shen, D.; Szabo, S.; Diaz, L.A.; Goodman, S.N.; David, K.A.; Juhl, H.; et al. Detection and Quantification of Mutations in the Plasma of Patients with Colorectal Tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2005, 102, 16368–16373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Mei, C.; Nan, X.; Hui, L. Evaluation and comparison of in vitro degradation kinetics of DNA in serum, urine and saliva: A qualitative study. Gene 2016, 590, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelobanov, B.P.; Laktionov, P.P.; Vlasov, V.V. Proteins involved in binding and cellular uptake of nucleic acids. Biochem. Mosc. 2006, 71, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thierry, A.R.; El Messaoudi, S.; Gahan, P.B.; Anker, P.; Stroun, M. Origins, structures, and functions of circulating DNA in oncology. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 347–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahr, S.; Hentze, H.; Englisch, S.; Hardt, D.; Fackelmayer, F.O.; Hesch, R.D.; Knippers, R. DNA Fragments in the Blood Plasma of Cancer Patients: Quantitations and Evidence for Their Origin from Apoptotic and Necrotic Cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fontanilles, M.; Marguet, F.; Bohers, E. Somatic Mutations Detected in Plasma Cell-Free DNA By Targeted Sequencing: Assessment of Liquid Biopsy in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Blood 2015, 126, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimelen, V.; Ahle, G.; Pencreach, E.; Zinniger, N.; Debliquis, A.; Zalmaï, L.; Harzallah, I.; Hurstel, R.; Alamome, I.; Lamy, F.; et al. Tumor Cell-Free DNA Detection in CSF for Primary CNS Lymphoma Diagnosis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2019, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streleckiene, G.; Reid, H.M.; Arnold, N.; Bauerschlag, D.; Forster, M. Quantifying cell free DNA in urine: Comparison between commercial kits, impact of gender and inter-individual variation. BioTechniques 2018, 64, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumagalli, C.; Bianchi, F.; Rafaniello Raviele, P.; Vacirca, D.; Bertalot, G.; Rampinelli, C.; Lazzeroni, M.; Bonnani, B.; Veronesi, G.; Fusco, N.; et al. Circulating and Tissue Biomarkers in Early-Stage Non-Small. Ecancermedicalscience 2017, 11, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, N.; Camacho-Vanegas, O.; Rykunov, D.; Dashkoff, M.; Camacho, S.C.; Schumacher, C.A.; Irish, J.C.; Harkins, T.T.; Freeman, E.; Garcia, I.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Uterine Lavage Fluid Detects Early Endometrial Cancers and Reveals a Prevalent Landscape of Driver Mutations in Women without Histopathologic Evidence of Cancer: A Prospective Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imperiale, T.F.; Ransohoff, D.F.; Itzkowitz, S.H.; Levin, T.R.; Lavin, P.; Lidgard, G.P.; Ahlquist, D.A.; Berger, B.M. Multitarget Stool DNA Testing for Colorectal-Cancer Screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1287–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, Y.K.; Davis, A.A.; Carneiro, B.A.; Chandra, S.; Mohindra, N.; Kalyan, A.; Kaplan, J.; Matsangou, M.; Pai, S.; Costa, R.; et al. Concordance between Genomic Alterations Assessed by Next-Generation Sequencing in Tumor Tissue or Circulating Cell-Free DNA. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S.-L.; Cao, Y.; Huang, X.-W.; Fan, J.; Yang, X.-R.; Zhou, J. Detecting Circulating Tumor DNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Using Droplet Digital PCR Is Feasible and Reflects Intratumoral Heterogeneity. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Yang, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Ge, P.; Ren, J.; Xu, W.; Lu, X.; Sang, X.; Zhong, S.; et al. Noninvasive Detection of Tumor-Associated Mutations from Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients by Targeted Deep Sequencing. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40481–40490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parackal, S.; Zou, D.; Day, R.; Black, M.; Guilford, P. Comparison of Roche Cell-Free DNA collection Tubes to Streck Cell-Free DNA BCT s for sample stability using healthy volunteers. Pract. Lab. Med. 2019, 16, e00125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merker, J.D.; Oxnard, G.R.; Compton, C.; Diehn, M.; Hurley, P.; Lazar, A.J.; Lindeman, N.; Lockwood, C.M.; Rai, A.J.; Schilsky, R.L.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Analysis in Patients With Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology and College of American Pathologists Joint Review. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 1242–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.; Henry, N.L.; Paoletti, C.; Jiang, H.; Vats, P.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Hayes, D.F.; Merajver, S.D.; Rae, J.M.; Tewari, M. Comparative Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA Stability In K3EDTA, Streck, and CellSave Blood Collection Tubes. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 49, 1354–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Messaoudi, S.; Rolet, F.; Mouliere, F.; Thierry, A.R. Circulating cell free DNA: Preanalytical considerations. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2013, 424, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaza, M.; Dawson, S.-J.; Tsui, D.W.Y.; Gale, D.; Forshew, T.; Piskorz, A.M.; Parkinson, C.; Chin, S.-F.; Kingsbury, Z.; Wong, A.S.C.; et al. Non-Invasive Analysis of Acquired Resistance to Cancer Therapy by Sequencing of Plasma DNA. Nature 2013, 497, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camus, V.; Sarafan-Vasseur, N.; Bohers, E.; Dubois, S.; Mareschal, S.; Bertrand, P.; Viailly, P.-J.; Ruminy, P.; Maingonnat, C.; Lemasle, E.; et al. Digital PCR for Quantification of Recurrent and Potentially Actionable Somatic Mutations in Circulating Free DNA from Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2016, 57, 2171–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küppers, R.; Rajewsky, K.; Zhao, M.; Simons, G.; Laumann, R.; Fischer, R.; Hansmann, M.L. Hodgkin Disease: Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg Cells Picked from Histological Sections Show Clonal Immunoglobulin Gene Rearrangements and Appear to Be Derived from B Cells at Various Stages of Development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 10962–10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.J.; Gocke, C.D.; Kasamon, Y.L.; Miller, C.B.; Perkins, B.; Barber, J.P.; Vala, M.S.; Gerber, J.M.; Gellert, L.L.; Siedner, M.; et al. Circulating Clonotypic B Cells in Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2009, 113, 5920–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, Y.; Neelapu, S.S.; Fanale, M.; Kwak, L.W.; Fayad, L.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Wallace, M.; Klinger, M.; Carlton, V.; Kong, K.; et al. Detection of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma Specific Sequence in Peripheral Blood Using a Next-Generation Sequencing Approach. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 169, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, J.; Licence, S.; Nanou, A.; Morgan, G.; Mårtensson, I.-L. Transcription of productive and nonproductive VDJ-recombined alleles after IgH allelic exclusion. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 4273–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohers, E.; Viailly, P.J.; Dubois, S.; Bertrand, P.; Maingonnat, C.; Mareschal, S.; Ruminy, P.; Picquenot, J.-M.; Bastard, C.; Desmots, F.; et al. Somatic Mutations of Cell-Free Circulating DNA Detected by next-Generation Sequencing Reflect the Genetic Changes in Both Germinal Center B-Cell-like and Activated B-Cell-like Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas at the Time of Diagnosis. Haematologica 2015, 100, e280–e284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.M.; Bratman, S.V.; To, J.; Wynne, J.F.; Eclov, N.C.W.; Modlin, L.A.; Liu, C.L.; Neal, J.W.; Wakelee, H.A.; Merritt, R.E.; et al. An Ultrasensitive Method for Quantitating Circulating Tumor DNA with Broad Patient Coverage. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, D.M.; Scherer, F.; Newman, A.M.; Lovejoy, A.F.; Klass, D.M.; Chabon, J.J.; Gambhir, S.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Dynamic Noninvasive Genomic Monitoring for Outcome Prediction in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2015, 126, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, D.; Diop, F.; Spaccarotella, E.; Monti, S.; Zanni, M.; Rasi, S.; Deambrogi, C.; Spina, V.; Bruscaggin, A.; Favini, C.; et al. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Genotyping on the Liquid Biopsy. Blood 2017, 129, 1947–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, F.; Kurtz, D.M.; Newman, A.M.; Stehr, H.; Craig, A.F.M.; Esfahani, M.S.; Lovejoy, A.F.; Chabon, J.J.; Klass, D.M.; Liu, C.L.; et al. Distinct Biological Subtypes and Patterns of Genome Evolution in Lymphoma Revealed by Circulating Tumor DNA. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 364ra155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sater, V.; Viailly, P.-J.; Lecroq, T.; Prieur-Gaston, É.; Bohers, É.; Viennot, M.; Ruminy, P.; Dauchel, H.; Vera, P.; Jardin, F. UMI-VarCal: A New UMI-Based Variant Caller That Efficiently Improves Low-Frequency Variant Detection in Paired-End Sequencing NGS Libraries. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2718–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primerano, S.; Burnelli, R.; Carraro, E.; Pillon, M.; Elia, C.; Farruggia, P.; Sala, A.; Vinti, L.; Buffardi, S.; Basso, G.; et al. Kinetics of Circulating Plasma Cell-Free DNA in Paediatric Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, M. Digital PCR hits its stride. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavon, G.; Hrebien, S.; Garcia-Murillas, I.; Cutts, R.J.; Pearson, A.; Tarazona, N.; Fenwick, K.; Kozarewa, I.; Lopez-Knowles, E.; Ribas, R.; et al. Analysis of ESR1 Mutation in Circulating Tumor DNA Demonstrates Evolution during Therapy for Metastatic Breast Cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 313ra182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taly, V.; Pekin, D.; Benhaim, L.; Kotsopoulos, S.K.; Le Corre, D.; Li, X.; Atochin, I.; Link, D.R.; Griffiths, A.D.; Pallier, K.; et al. Multiplex Picodroplet Digital PCR to Detect KRAS Mutations in Circulating DNA from the Plasma of Colorectal Cancer Patients. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1722–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tone, A.A.; McConechy, M.K.; Yang, W.; Ding, J.; Yip, S.; Kong, E.; Wong, K.-K.; Gershenson, D.M.; Mackay, H.; Shah, S.; et al. Intratumoral Heterogeneity in a Minority of Ovarian Low-Grade Serous Carcinomas. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent-Puig, P.; Pekin, D.; Normand, C.; Kotsopoulos, S.K.; Nizard, P.; Perez-Toralla, K.; Rowell, R.; Olson, J.; Srinivasan, P.; Le Corre, D.; et al. Clinical Relevance of KRAS-Mutated Subclones Detected with Picodroplet Digital PCR in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Treated with Anti-EGFR Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugo, N.; Padula, F.; Mobili, L.; Brizzi, C.; D’Emidio, L.; Cignini, P.; Mesoraca, A.; Bizzoco, D.; Cima, A.; Giorlandino, C. Six Consecutive False Positive Cases from Cell-Free Fetal DNA Testing in a Single Referring Centre. J. Prenat. Med. 2014, 8, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilie, M.; Hofman, V.; Long, E.; Bordone, O.; Selva, E.; Washetine, K.; Marquette, C.H.; Hofman, P. Current Challenges for Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells and Cell-Free Circulating Nucleic Acids, and Their Characterization in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Patients. What Is the Best Blood Substrate for Personalized Medicine? Ann. Transl. Med. 2014, 2, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, C.L.; Ye, M.Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, L.T.; et al. Biological Background of the Genomic Variations of Cf-DNA in Healthy Individuals. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichel, J.B.; McCormick, J.; Fromm, J.R.; Elemento, O.; Cesarman, E.; Roshal, M. Flow-sorting and Exome Sequencing of the Reed-Sternberg Cells of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2017, 124, 54399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinnider, B.F.; Elia, A.J.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Patterson, B.; Trumper, L.; Kapp, U.; Mak, T.W. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 6 Is Frequently Activated in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg Cells of Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2002, 99, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desch, A.-K.; Hartung, K.; Botzen, A.; Brobeil, A.; Rummel, M.; Kurch, L.; Georgi, T.; Jox, T.; Bielack, S.; Burdach, S.; et al. Genotyping Circulating Tumor DNA of Pediatric Hodgkin Lymphoma. Leukemia 2020, 34, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Wang, J.; Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Hu, X.; Yu, W.; Song, G.; Lou, J.; Chen, J. Heterogeneous Mutation Pattern in Tumor Tissue and Circulating Tumor DNA Warrants Parallel NGS Panel Testing. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, S.; Huang, F.; Shen, M.; Jiang, H.; Yu, Y.; Yu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Analytical and Clinical Validation of a Novel Amplicon-Based NGS Assay for the Evaluation of Circulating Tumor DNA in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. CCLM 2019, 57, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdigones, N.; Murtaza, M. Capturing tumor heterogeneity and clonal evolution in solid cancers using circulating tumor DNA analysis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 174, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, S.J.; Bhagwate, A.; Sun, Z.; Wang, C.; Zschunke, M.; Gorman, J.A.; Kopp, K.J.; Cunningham, J.M. Use of FFPE-Derived DNA in next Generation Sequencing: DNA Extraction Methods. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0211400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 Revision of the World Health Organization Classification of Lymphoid Neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, V.; Sextro, M.; Franklin, J.; Hansmann, M.-L.; Harris, N.; Jaffe, E.; Poppema, S.; Harris, M.; Franssila, K.; van Krieken, J.; et al. Clinical Presentation, Course, and Prognostic Factors in Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin’s Disease and Lymphocyte-Rich Classical Hodgkin’s Disease: Report From the European Task Force on Lymphoma Project on Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin’s Disease. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, A.; Gloghini, A.; Aldinucci, D.; Gattei, V.; Dalla-Favera, R.; Gaidano, G. Expression pattern of MUM1/IRF4 in the spectrum of pathology of Hodgkin’s disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2002, 117, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiwa, N.M.; Kanavaros, P.; van der Valk, P.; Walboomers, J.M.; Horstman, A.; Vos, W.; Mullink, H.; Meijer, C.J. Expression of C-Myc and Bcl-2 Oncogene Products in Reed-Sternberg Cells Independent of Presence of Epstein-Barr Virus. J. Clin. Pathol. 1993, 46, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiacci, E.; Döring, C.; Brune, V.; van Noesel, C.J.M.; Klapper, W.; Mechtersheimer, G.; Falini, B.; Küppers, R.; Hansmann, M.-L. Analyzing Primary Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg Cells to Capture the Molecular and Cellular Pathogenesis of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2012, 120, 4609–4620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devilard, E.; Bertucci, F.; Trempat, P.; Bouabdallah, R.; Loriod, B.; Giaconia, A.; Brousset, P.; Granjeaud, S.; Nguyen, C.; Birnbaum, D.; et al. Gene Expression Profiling Defines Molecular Subtypes of Classical Hodgkin’s Disease. Oncogene 2002, 21, 3095–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traverse-Glehen, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Gaulard, P.; Sorbara, L.; Alonso, M.A.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. Mediastinal Gray Zone Lymphoma: The Missing Link between Classic Hodgkin’s Lymphoma and Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 1411–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulino-Roth, L. How I treat primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 782–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardin, F.; Pujals, A.; Pelletier, L.; Bohers, E.; Camus, V.; Mareschal, S.; Dubois, S.; Sola, B.; Ochmann, M.; Lemonnier, F.; et al. Recurrent Mutations of the Exportin 1 Gene (XPO1) and Their Impact on Selective Inhibitor of Nuclear Export Compounds Sensitivity in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma: XPO1 Mutations in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunleavy, K.; Wilson, W.H. Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma and mediastinal gray zone lymphoma: Do they require a unique therapeutic approach? Blood 2015, 125, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunleavy, K.; Grant, C.; Eberle, F.C.; Pittaluga, S.; Jaffe, E.S.; Wilson, W.H. Gray zone lymphoma: Better treated like hodgkin lymphoma or mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma? Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2012, 7, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Slambrouck, C.; Huh, J.; Suh, C.; Song, J.Y.; Menon, M.P.; Sohani, A.R.; Duffield, A.S.; Goldberg, R.C.; Dama, P.; Kiyotani, K.; et al. Diagnostic Utility of STAT6YE361 Expression in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma and Related Entities. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussolin, L.; Burnelli, R.; Pillon, M.; Carraro, E.; Farruggia, P.; Todesco, A.; Mascarin, M.; Rosolen, A. Plasma Cell-Free DNA in Paediatric Lymphomas. J. Cancer 2013, 4, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohers, E.; Viailly, P.-J.; Becker, S.; Marchand, V.; Ruminy, P.; Maingonnat, C.; Bertrand, P.; Etancelin, P.; Picquenot, J.-M.; Camus, V.; et al. Non-Invasive Monitoring of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma by Cell-Free DNA High-Throughput Targeted Sequencing: Analysis of a Prospective Cohort. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delfau-Larue, M.-H.; van der Gucht, A.; Dupuis, J.; Jais, J.-P.; Nel, I.; Beldi-Ferchiou, A.; Hamdane, S.; Benmaad, I.; Laboure, G.; Verret, B.; et al. Total Metabolic Tumor Volume, Circulating Tumor Cells, Cell-Free DNA: Distinct Prognostic Value in Follicular Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decazes, P.; Camus, V.; Bohers, E.; Viailly, P.-J.; Tilly, H.; Ruminy, P.; Viennot, M.; Hapdey, S.; Gardin, I.; Becker, S.; et al. Correlations between Baseline 18F-FDG PET Tumour Parameters and Circulating DNA in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma and Hodgkin Lymphoma. EJNMMI Res. 2020, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachinel, N.; Salles, G. The host-tumor interface in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A new world to investigate. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2009, 4, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Decazes, P.; Vera, P.; Li, H.; Ruan, S. Detection and segmentation of lymphomas in 3D PET images via clustering with entropy-based optimization strategy. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 1715–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, D.M.; Scherer, F.; Jin, M.C.; Soo, J.; Craig, A.F.M.; Esfahani, M.S.; Chabon, J.J.; Stehr, H.; Liu, C.L.; Tibshirani, R.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA Measurements As Early Outcome Predictors in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2845–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, M.G.; Wesseling, P.; Wurdinger, T. Tumor-Educated Platelets as a Noninvasive Biomarker Source for Cancer Detection and Progression Monitoring. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3407–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, M.G.; Vancura, A.; Wurdinger, T. Platelet RNA as a circulating biomarker trove for cancer diagnostics. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- In ’t Veld, S.G.J.G.; Wurdinger, T. Tumor-educated platelets. Blood 2019, 133, 2359–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, M.G.; In ’t Veld, S.G.J.G.; Sol, N.; Wurdinger, T. RNA sequencing and swarm intelligence–enhanced classification algorithm development for blood-based disease diagnostics using spliced blood platelet RNA. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 1206–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Dieppa, D.R.; Steinberg, J.; Gonda, D.; Cheung, V.J.; Carter, B.S.; Chen, C.C. Extracellular vesicles as a platform for ‘liquid biopsy’ in glioblastoma patients. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekker, K.; Saare, M.; Roost, A.M.; Kubo, A.-L.; Zarovni, N.; Chiesi, A.; Salumets, A.; Peters, M. Comparison of Serum Exosome Isolation Methods for MicroRNA Profiling. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 47, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauro, B.J.; Greening, D.W.; Mathias, R.A.; Ji, H.; Mathivanan, S.; Scott, A.M.; Simpson, R.J. Comparison of Ultracentrifugation, Density Gradient Separation, and Immunoaffinity Capture Methods for Isolating Human Colon Cancer Cell Line LIM1863-Derived Exosomes. Methods 2012, 56, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.W.; Balaj, L.; Liau, L.M.; Samuels, M.L.; Kotsopoulos, S.K.; Maguire, C.A.; LoGuidice, L.; Soto, H.; Garrett, M.; Zhu, L.D.; et al. BEAMing and Droplet Digital PCR Analysis of Mutant IDH1 MRNA in Glioma Patient Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid Extracellular Vesicles. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2013, 2, e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Plasma Cell-Free DNA | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | Advantages | Disadvantages | |
| cfDNA source |
|
|
|
| cfDNA applications |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
| cfDNA tools |
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camus, V.; Jardin, F. Cell-Free DNA for the Management of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030207
Camus V, Jardin F. Cell-Free DNA for the Management of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(3):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030207
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamus, Vincent, and Fabrice Jardin. 2021. "Cell-Free DNA for the Management of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 3: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030207
APA StyleCamus, V., & Jardin, F. (2021). Cell-Free DNA for the Management of Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Pharmaceuticals, 14(3), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030207







