Metformin Increases Survival in Hypopharyngeal Cancer Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Retrospective Cohort Study and Cell-Based Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Metformin Increased Overall Survival in DM Patients with Hypopharyngeal Cancer
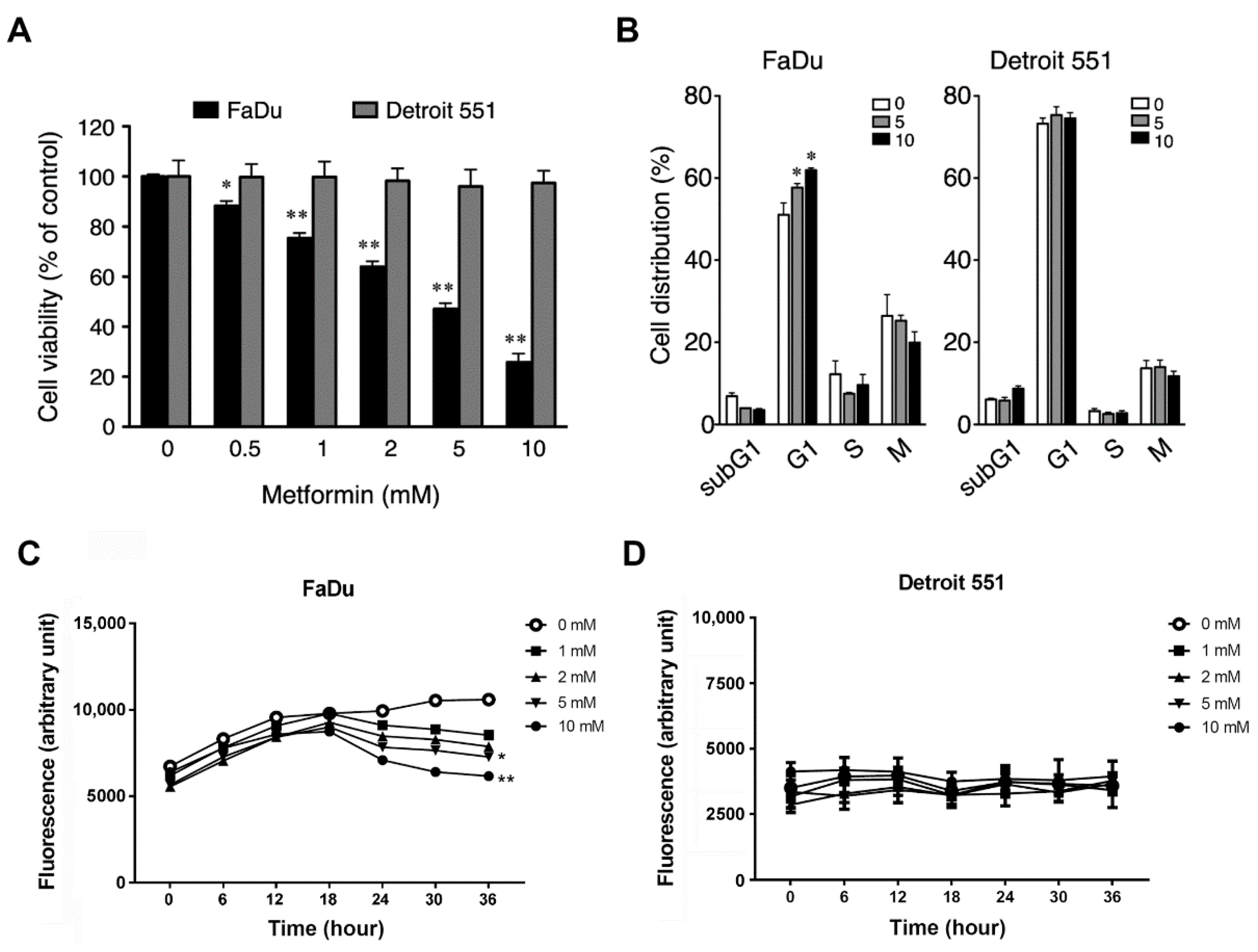
2.2. Metformin Inhibited Cell Growth and Induced Cell Cycle Arrest in Hypopharyngeal Cancer Cells
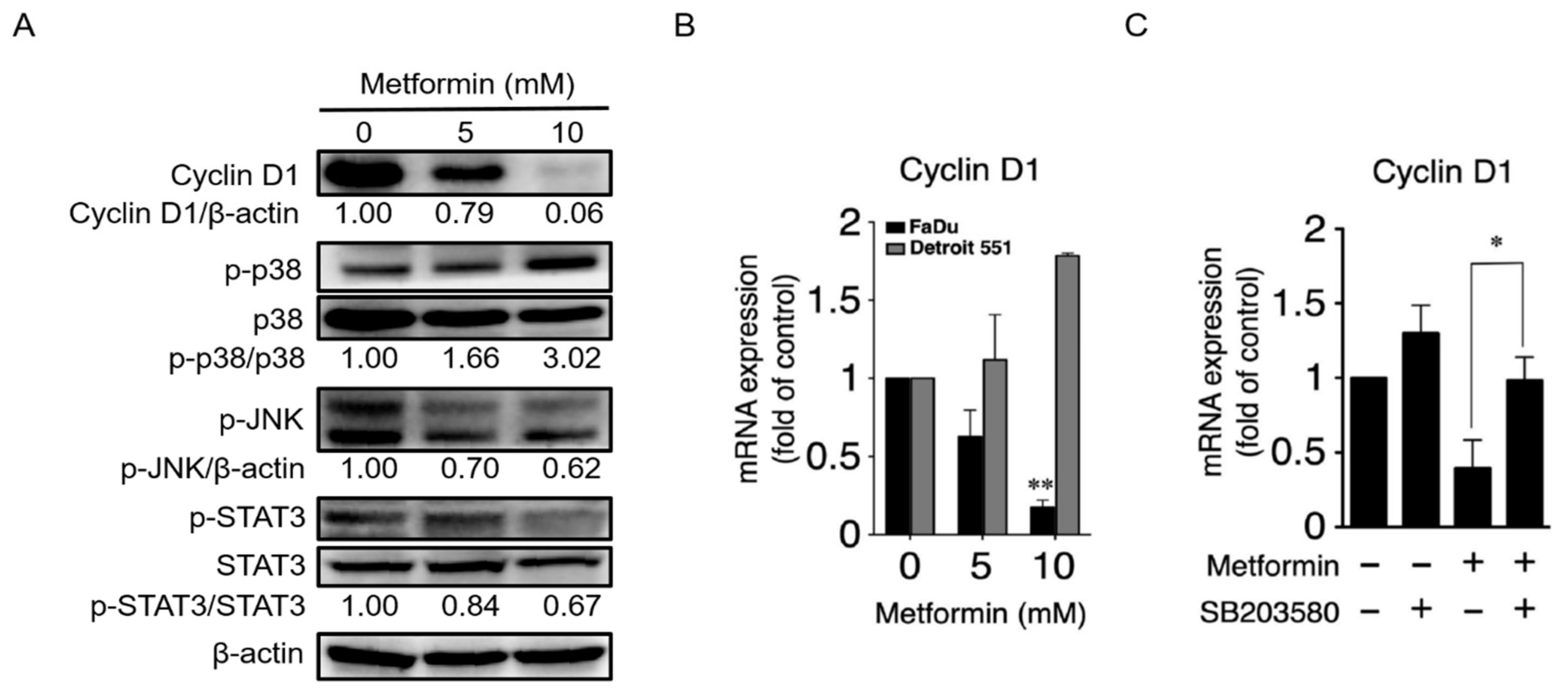
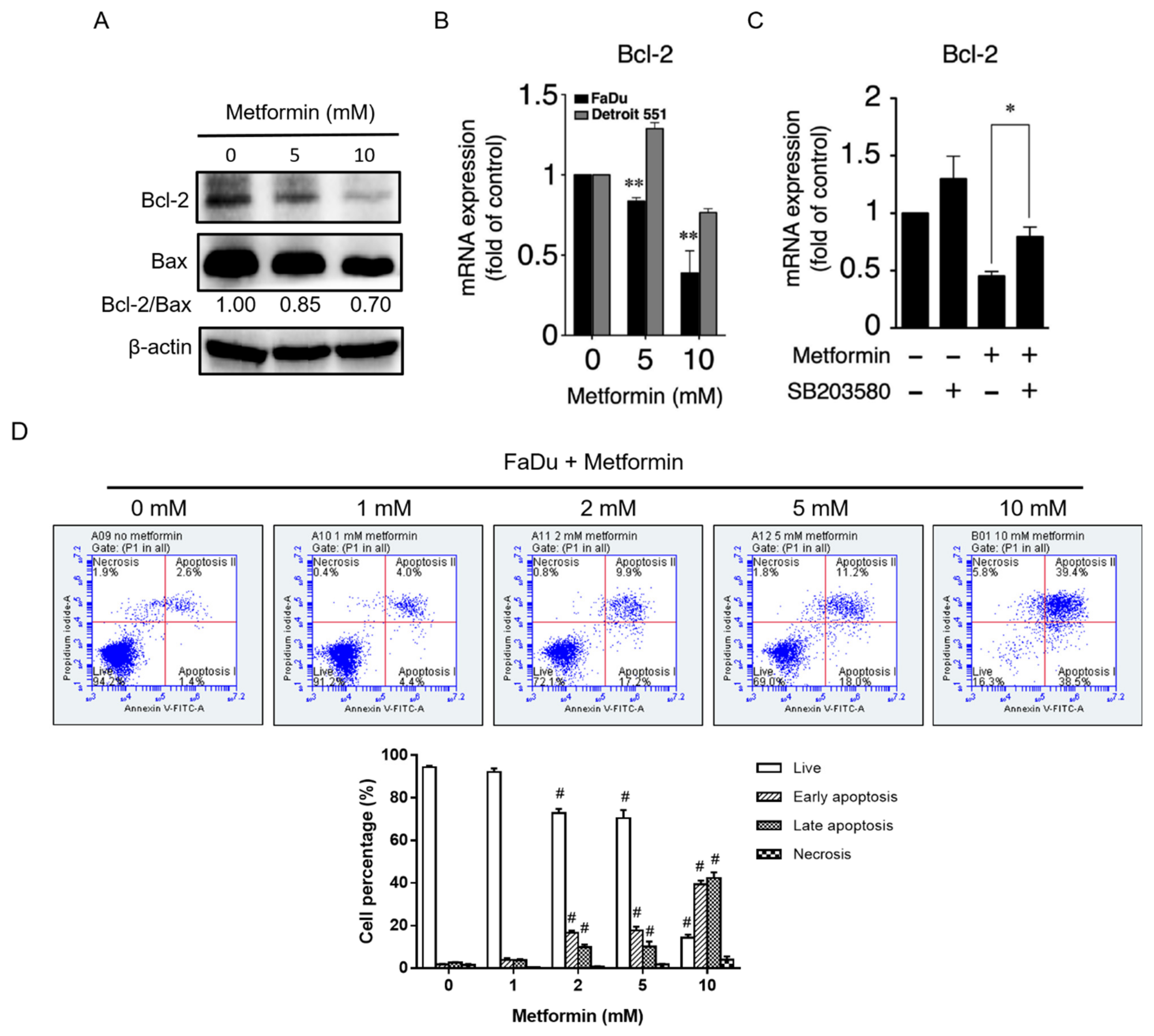
2.3. Metformin Downregulated Cyclin D1 and Bcl-2 and Induced Apoptosis
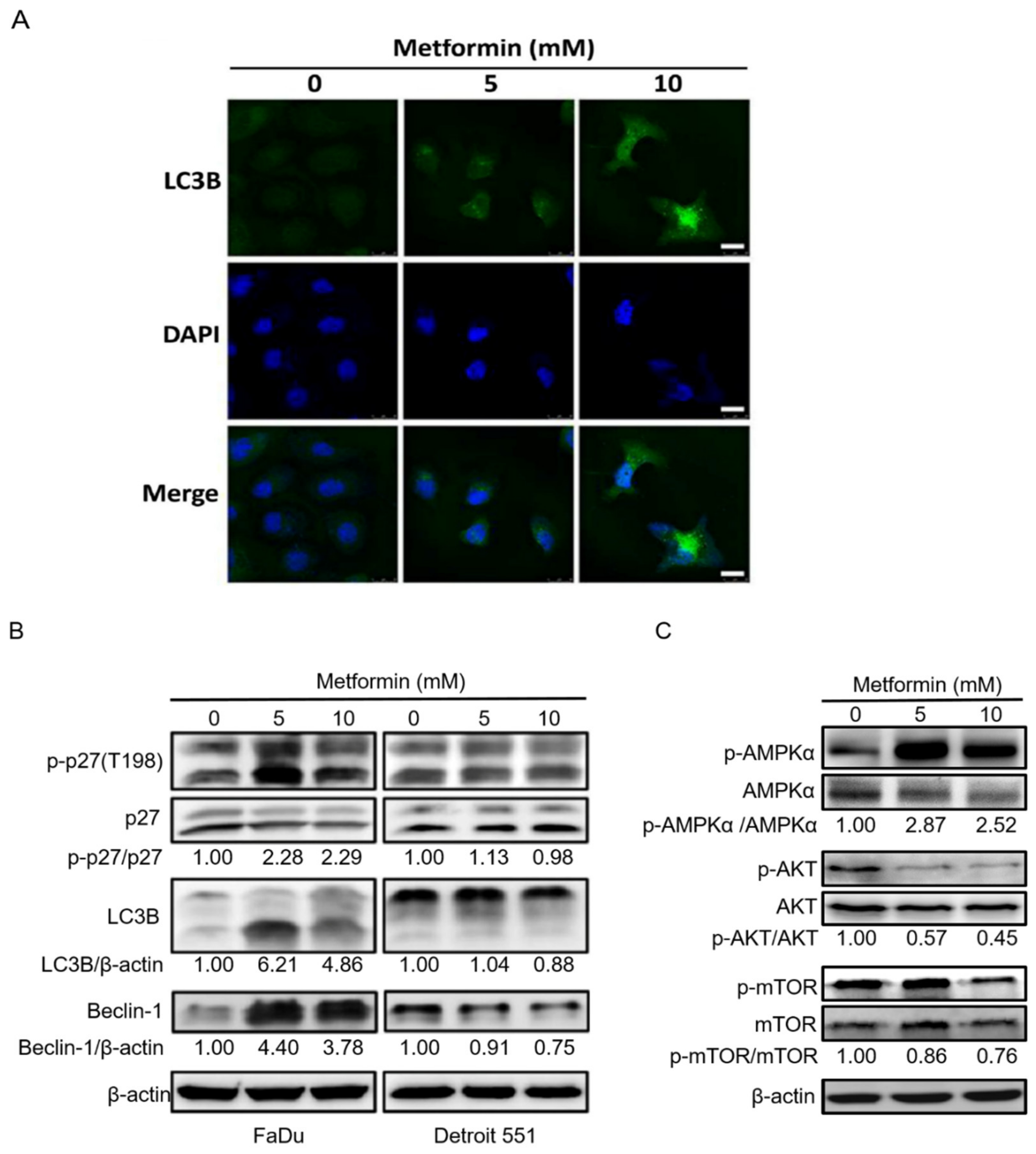
2.4. Treatment of Hypopharyngeal Cancer Cells with Metformin Also Induced Autophagy
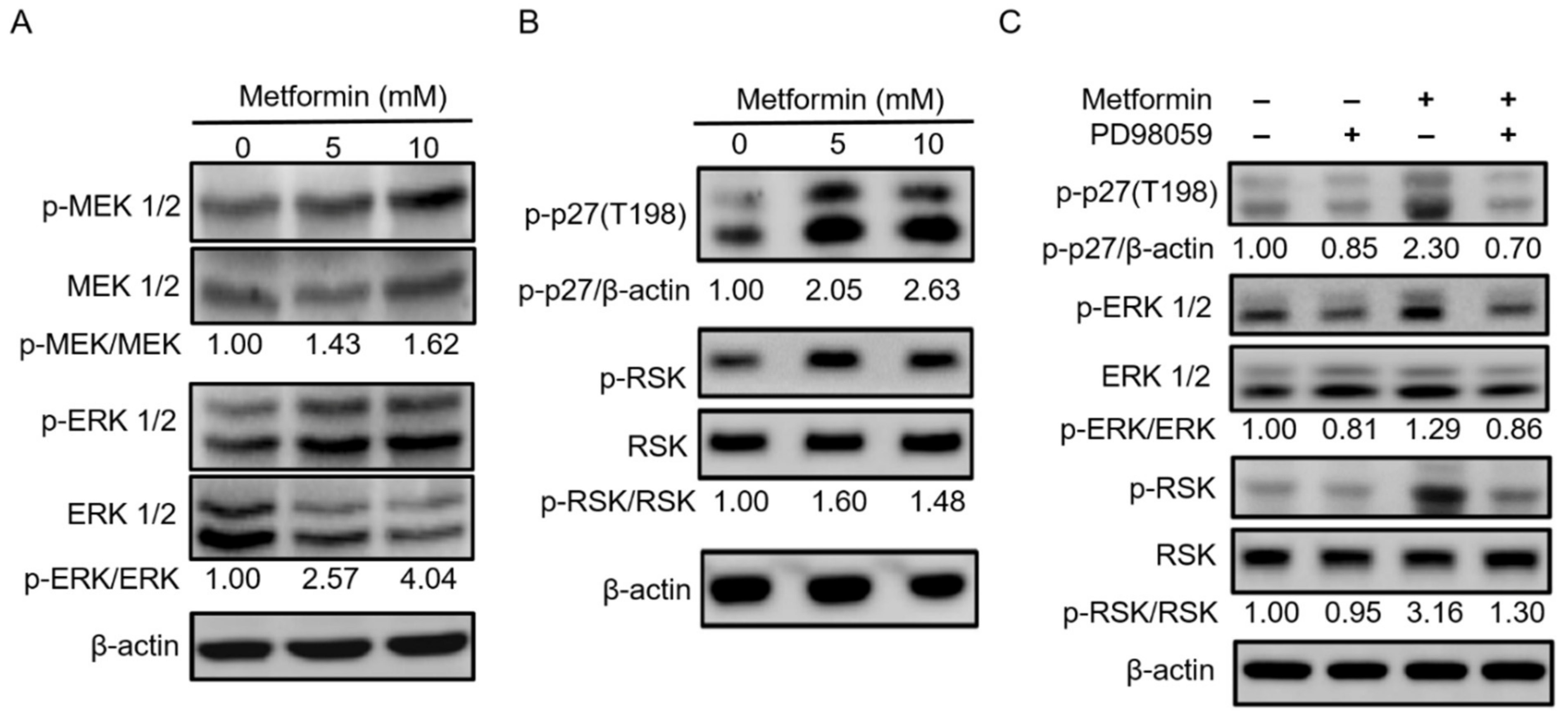
2.5. Metformin Inhibited Hypopharyngeal Cancer Cells via the MEK/ERK/RSK Signaling Pathways
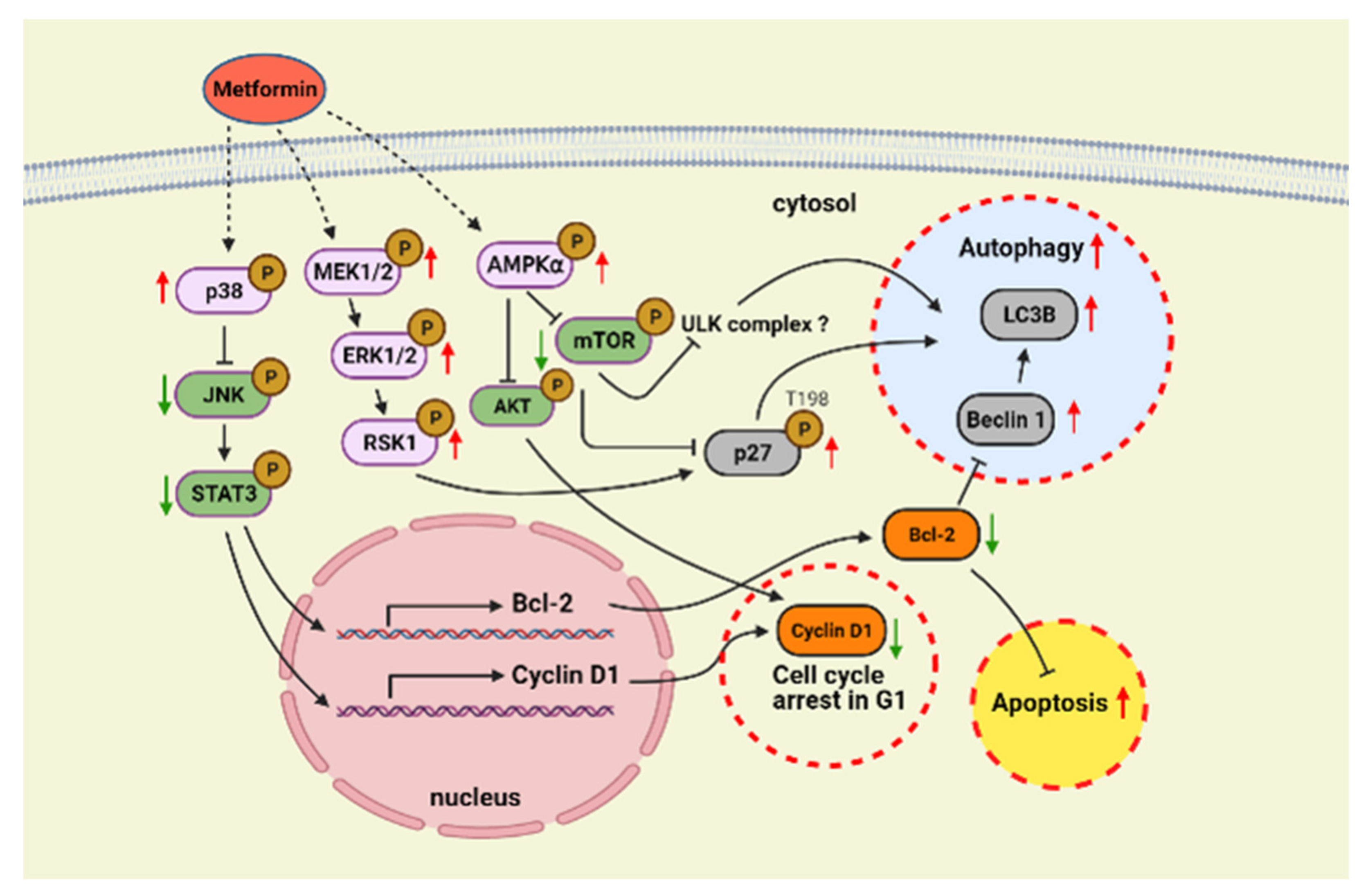
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Selection and Data Collection
4.2. Antibodies
4.3. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.4. Cell Viability and Proliferation Assay
4.5. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.6. Apoptosis Assay
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.8. Western Blot Assay
4.9. Immunofluorescence Staining and Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garneau, J.C.; Bakst, R.L.; Miles, B.A. Hypopharyngeal cancer: A state of the art review. Oral Oncol. 2018, 86, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.Y.; Kim, E.H.; Cho, J.; Jung, J.H.; Oh, D.; Ahn, Y.C.; Son, Y.I.; Jeong, H.S. Comparison of Oncological and Functional Outcomes between Initial Surgical versus Non-Surgical Treatments for Hypopharyngeal Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 2054–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S. Organ preservation in laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2019, 90, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munscher, A.; Prochnow, S.; Gulati, A.; Sauter, G.; Lorincz, B.; Blessmann, M.; Hanken, H.; Bottcher, A.; Clauditz, T.S. Survivin expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas is frequent and correlates with clinical parameters and treatment outcomes. Clin. Oral Investig. 2019, 23, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poel, D.; Rustenburg, F.; Sie, D.; van Essen, H.F.; Eijk, P.P.; Bloemena, E.; Elhorst Benites, T.; van den Berg, M.C.; Vergeer, M.R.; Leemans, R.C.; et al. Expression of let-7i and miR-192 is associated with resistance to cisplatin-based chemoradiotherapy in patients with larynx and hypopharynx cancer. Oral Oncol. 2020, 109, 104851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsahafi, E.; Begg, K.; Amelio, I.; Raulf, N.; Lucarelli, P.; Sauter, T.; Tavassoli, M. Clinical update on head and neck cancer: Molecular biology and ongoing challenges. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossen, D.M.; Verhagen, C.V.M.; van der Heijden, M.; Essers, P.B.M.; Bartelink, H.; Verheij, M.; Wessels, L.F.A.; van den Brekel, M.W.M.; Vens, C. Genetic Factors Associated with a Poor Outcome in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Receiving Definitive Chemoradiotherapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, C.J. Metformin: Historical overview. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1566–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Rangel, E.; Inzucchi, S.E. Metformin: Clinical use in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1586–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, R.J.; Goodwin, P.J.; Stambolic, V. Understanding the benefit of metformin use in cancer treatment. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.M.; Donnelly, L.A.; Emslie-Smith, A.M.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ 2005, 330, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, M.N. Investigating metformin for cancer prevention and treatment: The end of the beginning. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodmer, M.; Meier, C.; Krahenbuhl, S.; Jick, S.S.; Meier, C.R. Long-term metformin use is associated with decreased risk of breast cancer. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1304–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.W.; Liao, K.F.; Chen, P.C.; Tsai, P.Y.; Hsieh, D.P.; Chen, C.C. Antidiabetes drugs correlate with decreased risk of lung cancer: A population-based observation in Taiwan. Clin. Lung Cancer 2012, 13, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Hsu, C.C.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; Tsai, H.N.; Chang, Y.H.; Huang, Y.C. Type 2 diabetes increases and metformin reduces total, colorectal, liver and pancreatic cancer incidences in Taiwanese: A representative population prospective cohort study of 800,000 individuals. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraei, P.; Asadi, I.; Kakar, M.A.; Moradi-Kor, N. The beneficial effects of metformin on cancer prevention and therapy: A comprehensive review of recent advances. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3295–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, W.; Pan, H.; Xiao, M. Metformin: A Novel but Controversial Drug in Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 3783–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, R.J.; Niraula, S.; Stambolic, V.; Goodwin, P.J. Metformin in cancer: Translational challenges. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 48, R31–R43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edson, M.A.; Garden, A.S.; Takiar, V.; Glisson, B.S.; Fuller, C.D.; Gunn, G.B.; Beadle, B.M.; Morrison, W.H.; Frank, S.J.; Shah, S.J.; et al. Outcomes for hypopharyngeal carcinoma treated with organ-preservation therapy. Head Neck 2016, 38 (Suppl. 1), E2091–E2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnicki, S.; Kapral, M.; Weglarz, L. Molecular targets of metformin antitumor action. Pharm. Rep. 2016, 68, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, Y.A.; Chang, W.D.; Lu, J.J.; Wu, T.F.; Chen, H.L.; Chen, C.M.; Tsai, M.H. The effect of metformin use on hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma in diabetes mellitus patients. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Tang, Y.; Fang, X.; Xie, C.; Zeng, J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, S. Metformin Suppresses Hypopharyngeal Cancer Growth by Epigenetically Silencing Long Non-coding RNA SNHG7 in FaDu Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, G.; Poolman, R.A.; Li, J.M. Arresting developments in the cardiac myocyte cell cycle: Role of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. Cardiovasc. Res. 1998, 39, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duronio, R.J.; Xiong, Y. Signaling pathways that control cell proliferation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.P.; Cao, X. Serine phosphorylation and negative regulation of Stat3 by JNK. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 31055–31061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Gibson, T.B.; Robinson, F.; Silvestro, L.; Pearson, G.; Xu, B.; Wright, A.; Vanderbilt, C.; Cobb, M.H. MAP kinases. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 2449–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ke, C.; Tang, Q.; Dong, H.; Zheng, X.; Lin, W.; Ke, J.; Huang, J.; Yeung, S.C.; Zhang, H. Metformin promotes autophagy and apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by downregulating Stat3 signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattingre, S.; Tassa, A.; Qu, X.; Garuti, R.; Liang, X.H.; Mizushima, N.; Packer, M.; Schneider, M.D.; Levine, B. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell 2005, 122, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Shao, S.H.; Xu, Z.X.; Hennessy, B.; Ding, Z.; Larrea, M.; Kondo, S.; Dumont, D.J.; Gutterman, J.U.; Walker, C.L.; et al. The energy sensing LKB1-AMPK pathway regulates p27(kip1) phosphorylation mediating the decision to enter autophagy or apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farre, J.C.; Subramani, S. Mechanistic insights into selective autophagy pathways: Lessons from yeast. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuri, M.C.; Zalckvar, E.; Kimchi, A.; Kroemer, G. Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kossatz, U.; Vervoorts, J.; Nickeleit, I.; Sundberg, H.A.; Arthur, J.S.; Manns, M.P.; Malek, N.P. C-terminal phosphorylation controls the stability and function of p27kip1. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 5159–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zhou, P.; Xu, K.; Chen, T.; Jiao, J.; Wei, H.; Yang, X.; Xu, W.; Wan, W.; Xiao, J. Metformin induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and autophagy through ROS/JNK signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, C.J.; Vaux, D.L. Analysis of the role of bcl-2 in apoptosis. Immunol. Rev. 1994, 142, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.D.; Qin, Z.H. Beclin 1, Bcl-2 and Autophagy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1206, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Yan, Z.; Zhao, W.; Mi, J.; Li, J.; Yan, H. Metformin induces autophagy and G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest in myeloma by targeting the AMPK/mTORC1 and mTORC2 pathways. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alalem, M.; Ray, A.; Ray, B.K. Metformin induces degradation of mTOR protein in breast cancer cells. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3194–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Wu, Z.; Shang, J.; Xie, Z.; Chen, C.; Zhang, C. The effects of metformin on autophagy. Biomed. Pharm. 2021, 137, 111286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.Y.; Tsai, C.H.; Yu, H.M.; Jao, Y.C.; Fang, J.M.; Wong, C.H. Latifolicinin A from a Fermented Soymilk Product and the Structure-Activity Relationship of Synthetic Analogues as Inhibitors of Breast Cancer Cell Growth. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9715–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Chou, L.C.; Huang, C.H.; Chung, J.G.; Huang, L.J.; Lee, K.H.; Hung, M.C.; Way, T.D.; Kuo, S.C. CHM-1 induces apoptosis via p38-mediated upregulation of DR5 expression in human ovarian cancer SKOV3 cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Kuo, I.C.; Lin, J.J.; Lu, Y.C.; Chen, C.T.; Back, H.T.; Lou, P.J.; Chang, T.C. A novel carbazole derivative, BMVC: A potential antitumor agent and fluorescence marker of cancer cells. Chem. Biodivers. 2004, 1, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFatta, R.J.; Nathan, C.O.; De Benedetti, A. Antisense RNA to eIF4E suppresses oncogenic properties of a head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Laryngoscope 2000, 110, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, Z.E.; Wang, C.; Vadan, F.; Yu, T.Y.; Ausio, J.; Kusalik, A.; Eskiw, C.H. Metformin induces the AP-1 transcription factor network in normal dermal fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Luo, J.; Yu, T.; Zhou, L.; Lv, H.; Shang, P. Anticancer mechanisms of metformin: A review of the current evidence. Life Sci. 2020, 254, 117717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.M.; Cory, S. Bcl-2-regulated apoptosis: Mechanism and therapeutic potential. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2007, 19, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhajda, F.P. AMP-activated protein kinase and human cancer: Cancer metabolism revisited. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32 (Suppl. 4), S36–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, C.; Gerhart-Hines, Z.; Feige, J.N.; Lagouge, M.; Noriega, L.; Milne, J.C.; Elliott, P.J.; Puigserver, P.; Auwerx, J. AMPK regulates energy expenditure by modulating NAD+ metabolism and SIRT1 activity. Nature 2009, 458, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.G.; Plas, D.R.; Kubek, S.; Buzzai, M.; Mu, J.; Xu, Y.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Thompson, C.B. AMP-activated protein kinase induces a p53-dependent metabolic checkpoint. Mol. Cell 2005, 18, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamargo-Gómez, I.; Mariño, G. AMPK: Regulation of metabolic dynamics in the context of autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldis, P. Another piece of the p27Kip1 puzzle. Cell 2007, 128, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nowosad, A.; Jeannot, P.; Callot, C.; Creff, J.; Perchey, R.T.; Joffre, C.; Codogno, P.; Manenti, S.; Besson, A. p27 controls Ragulator and mTOR activity in amino acid-deprived cells to regulate the autophagy-lysosomal pathway and coordinate cell cycle and cell growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 1076–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.Z.; Liu, Z.; Sun, L.L.; Zhou, M.; Liu, C.; Li, W.D.; Li, X.Q. Metformin inhibits angiogenesis of endothelial progenitor cells via miR-221-mediated p27 expression and autophagy. Future Med. Chem. 2019, 11, 2263–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.J.; Liu, H.H.; Lin, C.D.; Kao, M.C.; Chen, Y.A.; Chiang-Ni, C.; Jiang, Z.P.; Huang, M.Z.; Lin, C.J.; Lo, U.G.; et al. Cytolethal Distending Toxin Enhances Radiosensitivity in Prostate Cancer Cells by Regulating Autophagy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.J.; Jiang, Z.P.; Lo, H.R.; Feng, C.L.; Chen, C.J.; Yang, C.Y.; Huang, M.Z.; Wu, H.Y.; Chen, Y.A.; Chen, Y.; et al. Coalescence of RAGE in Lipid Rafts in Response to Cytolethal Distending Toxin-Induced Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.W.; Huang, M.Z.; Chen, C.L.; Kuo, C.Y.; Yang, C.Y.; Chiang-Ni, C.; Chen, Y.M.; Hsieh, C.M.; Wu, H.Y.; Kuo, M.L.; et al. PM2.5 impairs macrophage functions to exacerbate pneumococcus-induced pulmonary pathogenesis. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.C.; Huang, M.Z.; Wang, M.L.; Lin, C.J.; Lu, T.L.; Lo, H.R.; Pan, Y.J.; Sun, Y.C.; Kao, M.C.; Lim, H.J.; et al. Statin Decreases Helicobacter pylori Burden in Macrophages by Promoting Autophagy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 6, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsou, Y.-A.; Chang, W.-C.; Lin, C.-D.; Chang, R.-L.; Tsai, M.-H.; Shih, L.-C.; Staniczek, T.; Wu, T.-F.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Chang, W.-D.; et al. Metformin Increases Survival in Hypopharyngeal Cancer Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Retrospective Cohort Study and Cell-Based Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030191
Tsou Y-A, Chang W-C, Lin C-D, Chang R-L, Tsai M-H, Shih L-C, Staniczek T, Wu T-F, Hsu H-Y, Chang W-D, et al. Metformin Increases Survival in Hypopharyngeal Cancer Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Retrospective Cohort Study and Cell-Based Analysis. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(3):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030191
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsou, Yung-An, Wei-Chao Chang, Chia-Der Lin, Ro-Lin Chang, Ming-Hsui Tsai, Liang-Chun Shih, Theresa Staniczek, Tsu-Fang Wu, Hui-Ying Hsu, Wen-Dien Chang, and et al. 2021. "Metformin Increases Survival in Hypopharyngeal Cancer Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Retrospective Cohort Study and Cell-Based Analysis" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 3: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030191
APA StyleTsou, Y.-A., Chang, W.-C., Lin, C.-D., Chang, R.-L., Tsai, M.-H., Shih, L.-C., Staniczek, T., Wu, T.-F., Hsu, H.-Y., Chang, W.-D., Lai, C.-H., & Chen, C.-M. (2021). Metformin Increases Survival in Hypopharyngeal Cancer Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: Retrospective Cohort Study and Cell-Based Analysis. Pharmaceuticals, 14(3), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14030191








