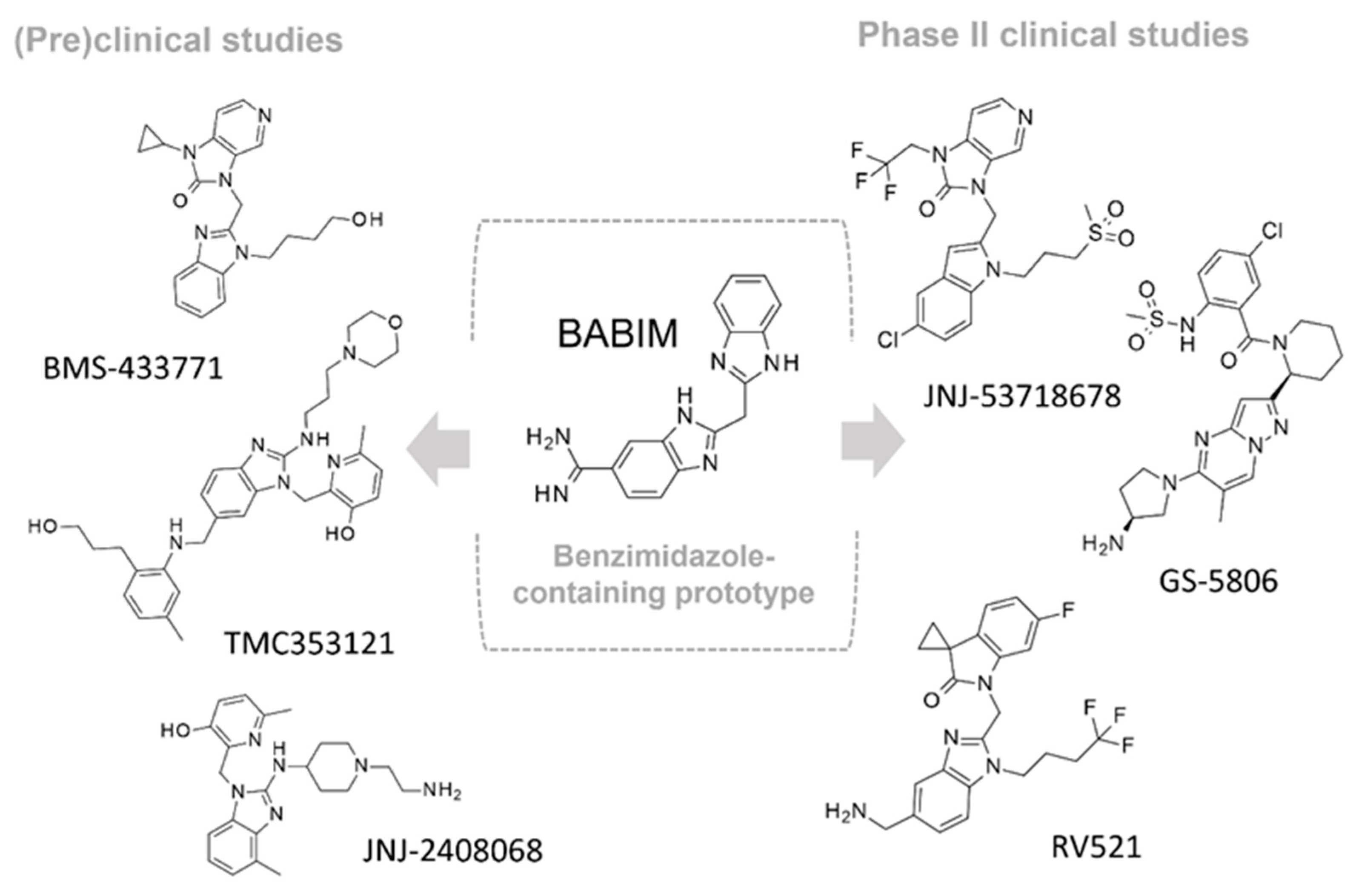
2.1. Exploring the X-ray Crystallographic Data of Known Preclinical Fusion Inhibitors
During the last years, a number of RSV glycoprotein inhibitors have been disclosed and experimentally investigated by means of X-ray crystallographic analysis, with most of them being endowed with a benzothiazole core or other heterocyclic rings, bioisosteres of the benzimidazole one, as shown in
Figure 1 [
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25].
Herein, we deemed it interesting to explore the structural information so far available concerning the RSV F protein in a complex with different inhibitors, in terms of X-ray crystallographic data, in order to highlight the main pharmacophore features turning in the related anti-RSV ability. In particular, collecting and exploring experimental data concerning the RSV F protein, in the presence of different chemotypes, besides the benzimidazole one, is expected to reveal more information about the target flexibility and behavior in the face of different putative drugs.
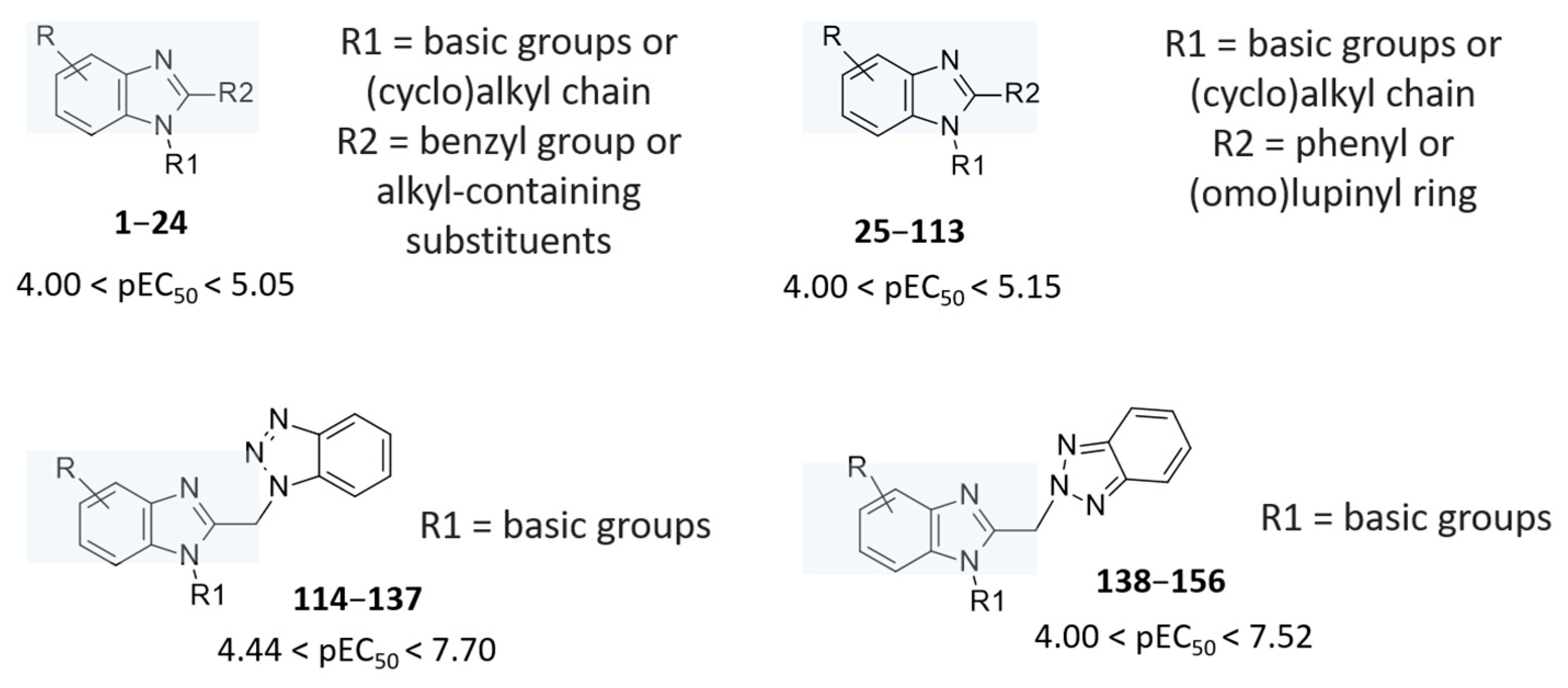
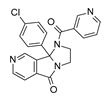
This piece of information allowed us to clarify the structure–activity relationship (SAR) of an in-house series of benzimidazoles
1–
156, endowed with RSV F protein inhibitory activity (see
Table S1 for chemical structure), bearing different substitutions especially at the position 1 and 2 of the main core (
Figure 2).
We started with a careful analysis by visual inspection of several X-ray data downloaded from the protein data bank [
26] of the RSV F protein in the presence of different inhibitors that have reached an advanced stage of development, as shown in
Table 1.
All of them have been explored by means of the Protein–Ligand Interaction Profiler website (PLIP) [
29], revealing a limited number of contacts with the exposed surface of the RSV F protein, mainly involving hydrophobic contacts and π-π stacking with F140 and F488 residues.
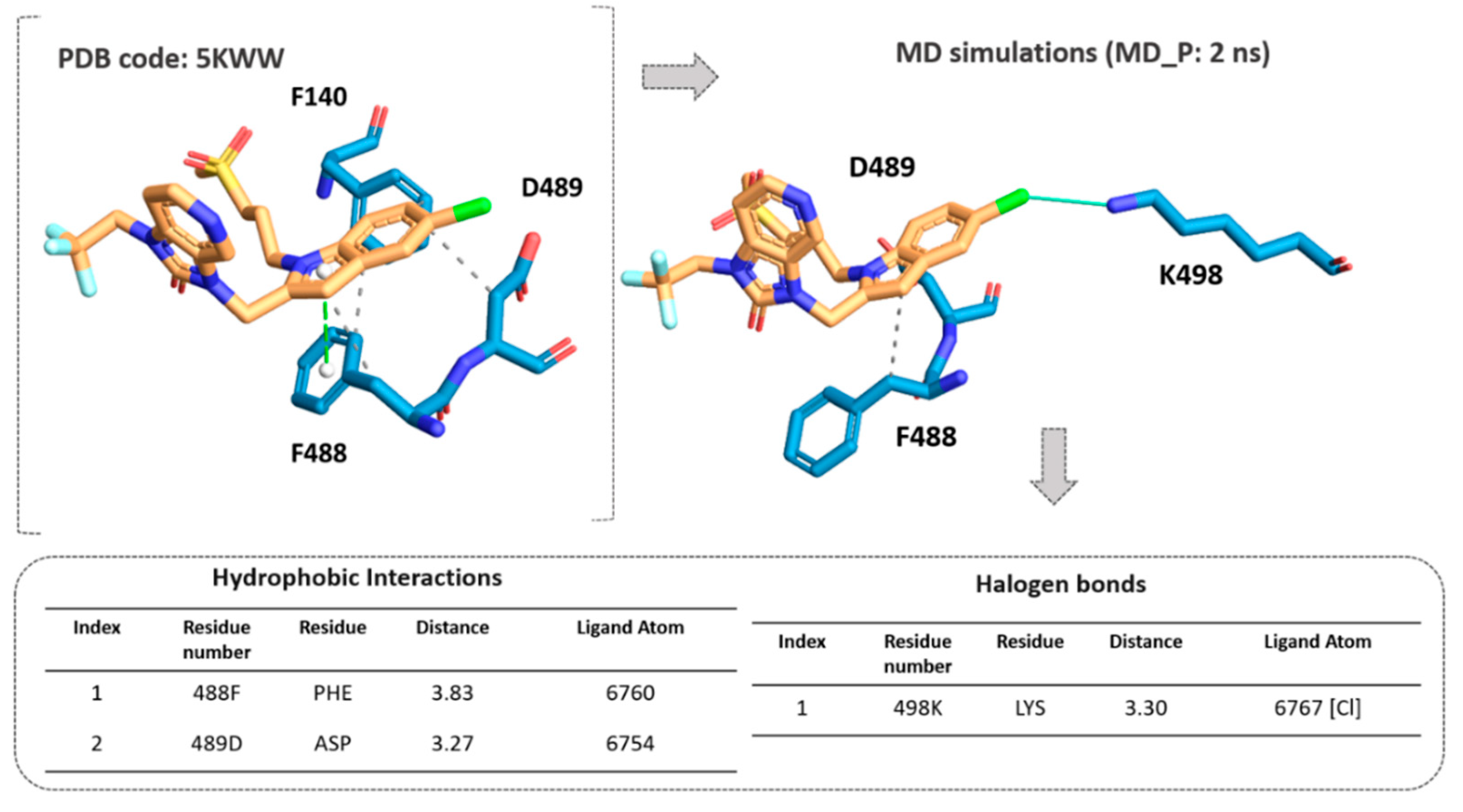
In particular, the clinical candidate JNJ-53718678, (pdb code = 5KWW) [
27], moved the indole ring in proximity of the D489 side chain and F140 aromatic ring, featuring Van der Waals interactions, also detecting π-π stacking with F488 (
Figure S2).
By contrast, the imidazopyridine ring as well as the sulphone moiety proved to be projected outside the protein surface lacking any contacts with the biological target. Indeed, previous computational studies revealed that the indole and benzimidazole-2-one were both involved in aromatic stacking interactions, the 5-chloro substituent was H-bonded to the backbone carbonyl of Thr397
A, and the sulfonyl oxygens formed water-mediated H bonds with Arg 339
A [
27].
The effective RSV inhibitor RV521 exhibited a comparable binding mode, folding the two heterocyclic rings to display π-π interaction and hydrophobic contacts with the aforementioned F140 and F488 (
Figure S3). Interestingly, the aminomethylene chain at position 5 of the benzimidazole ring highly mimicked the positioning of the 5-Cl atom on the indole ring of JNJ-53718678 [
28].
Exploring the mechanism of binding featured by the less flexible anti-RSV agent BTA-9881 at the X-ray crystallographic data of the RSV F protein (pdb code = 5EA6) [
13] definitively allowed us to substantiate the interactions with F488 as mandatory to achieve the F protein inhibitory ability (
Figure S4)
Indeed, the pyridine ring of BTA-9881 was engaged in π-π contacts with F488, moving the other functional groups outside the protein surface, as well as shown for BMS-433771 (pdb code = 5EA7) [
13]. Indeed, the BMS-433771 imidazopyridine-2-one unit preserved the same hydrophobic interactions, while its benzimidazole core, lacking any further (polar) substitution onto the positions 4, 5, or 6 of the benzene ring was solvent exposed.
The introduction at position 2 of the benzimidazole ring of flexible aliphatic chains bearing H-bonding features led to effective inhibitors when accompanied by aryl moieties at the position 1 and/or 6 of the main core, as shown for JNJ-2408068 (pdb code = 5EA3) and TMC-353121(pdb code = 5EA5), respectively. This allowed both the two anti-RSV agents to maintain the key contacts with F488 but also to benefit dipole–dipole interactions with the biological target. In particular, JNJ-2408068 exhibited a salt bridge involving the protonated nitrogen atom of the piperidine ring and D486, E487, while the N(3) atom of the benzimidazole core was H-bonded to E487 (
Figure S5). Then, the aromatic ring tethered to the position 1 of the main scaffold displayed π-π stacking with F488.
As regards TMC-353121, the presence of two hydrophobic pendants linked to the main benzimidazole ring guaranteed appropriate hydrophobic interactions with F140 and F488, as shown in
Figure S6, while the OH group of the pyridine ring and the 2-amino group of the benzimidazole were H-bonded to D486.
The oxygen atom of the morpholine was engaged in one H-bond with K498, while its protonated nitrogen atom stabilized the bioactive conformation of the molecule at the RSV F protein surface, driving the formation of additional salt bridges with D486 and E487.
2.2. Molecular Surface Analysis
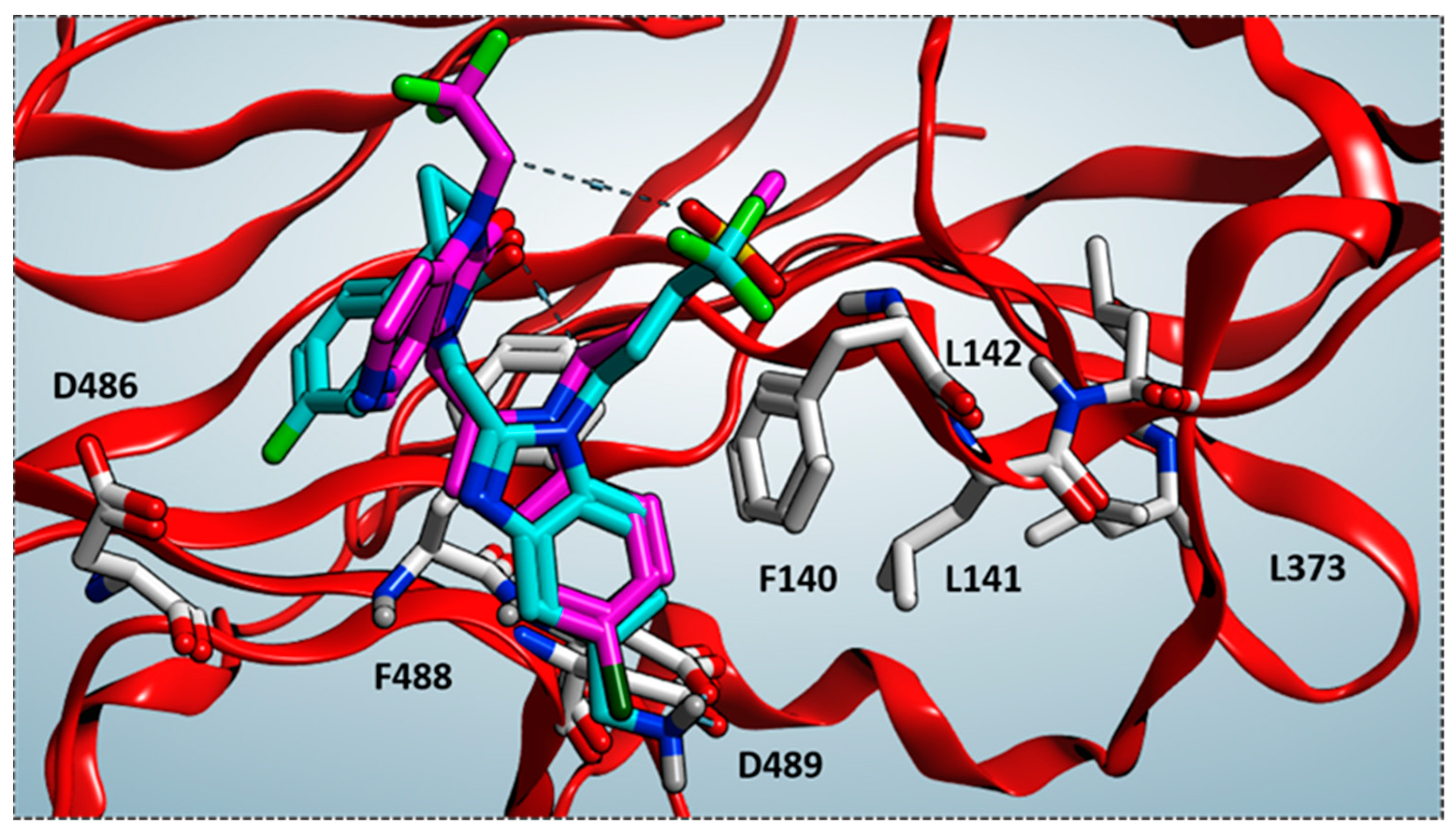
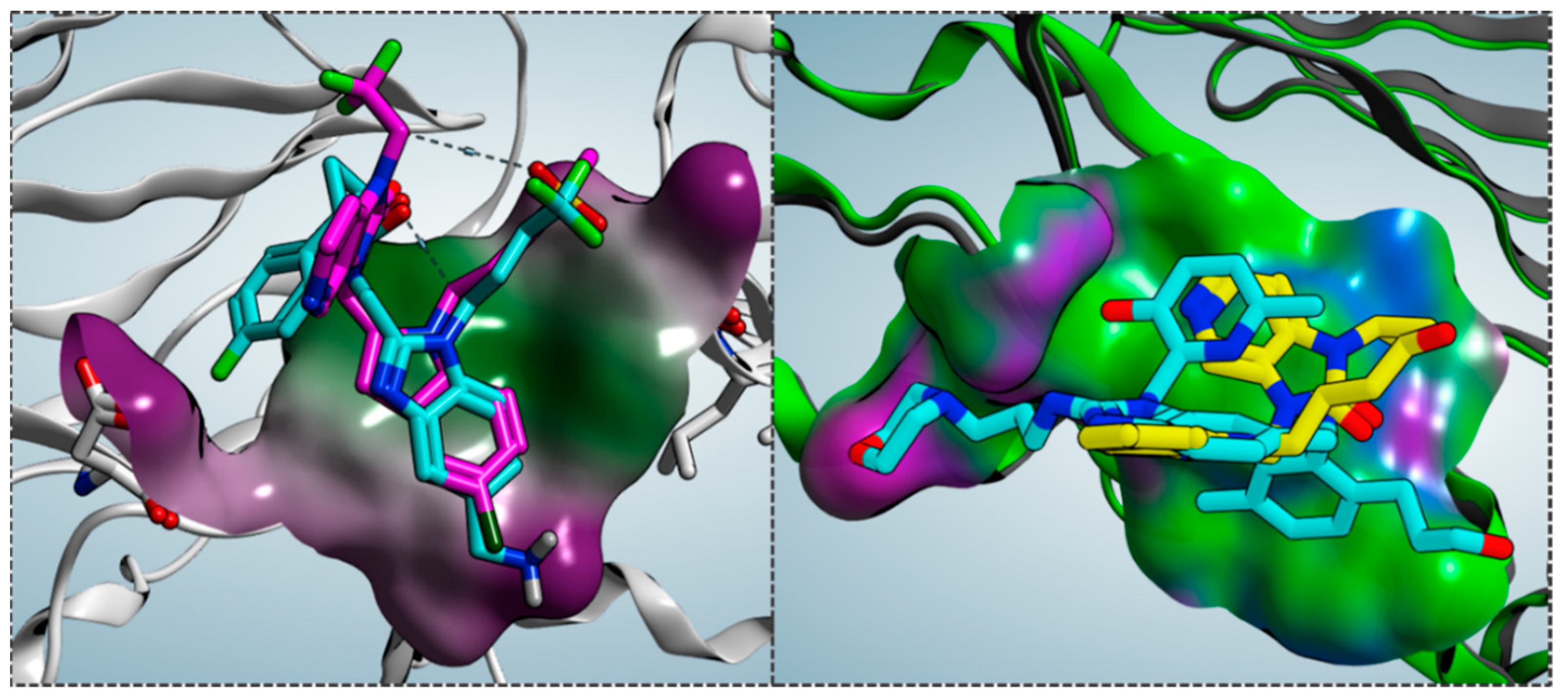
In order to obtain more in-depth information about the required pharmacophore features explaining the RSV F protein inhibitory ability experienced by these lead molecules, a comparison of the electrostatic properties at the RSV F protein surface anchoring the different anti-RSV agents was performed. This was performed by taking into account the aforementioned X-ray data: for (i) RV521 and JNJ-53718678 as inhibitors interacting with the target mostly via hydrophobic contacts and for (ii) TMC-353121 and BMS-433771 as anti-RSV agents decorated with H-bonding groups, given polar contacts with the protein.
As shown in
Figure 4, the bioactive conformation of RV521 (pdb code = 7KQD) [
28] and JNJ-53718678 (pdb code = 5KWW) [
27] is compared by the superimposition of the related X-ray crystallographic data within the RSV F protein, respectively.
Based on the superimposition of the two complexes (RMSD = 1.092 Å), both the two compounds share the same positioning for the indole (JNJ-53718678) and benzimidazole (RV521) main cores, projecting the Cl and aminomethyl substituents toward D489, in accordance with previous observation [
28]. The two hydrophobic and flexible chains bearing a sulphone and a trifluoromethyl group were oriented in proximity of F140 and of the cavity delimited by L141, L142, detecting Van der Waals contacts. As a consequence, the observed binding mode guarantees the proper π-π stacking with F140 and F488, thanks also to the heterocyclic moiety linked to position 2 of the indole or benzimidazole scaffold of the two analogues.
Thus, an efficient RSV fusion inhibitor should provide, as a mandatory prerequisite, adequate interactions with aromatic residues of the target as previously illustrated for the rigid anti-RSV agent BTA-9881 (pdb code = 5EA6) [
13], only exhibiting contacts with the key F488 residue.
The prominent hydrophobic properties of the RSV F protein surface occupied by JNJ-53718678 and RV521 are underlined by means of green areas, as shown in
Figure 5 (left side; polar and hydrophobic regions are shown in magenta and green, respectively).
On the other hand, comparing the X-ray data of the RSV F protein inhibitors TMC-353121 (pdb code = 5EA5) [
13] and BMS-433771 (pdb code = 5EA7) [
13] at the biological target surface led to lower values of RMSD (RMSD = 0.848 Å) in tandem with a more extended surface cavity interacting with the two compounds if compared with that previously discussed (
Figure 6).
While BMS-433771 experienced several hydrophobic contacts with the protein, TMC-353121, being endowed with an H-bonding substituent such as the morpholine ring, displayed several polar contacts with D486, E487, and K498. Indeed, the aforementioned morpholine ring was oriented toward K498 while the hydroxyl group of pyridine and the 2-amino group of the main benzimidazole core were projected in proximity to D486 and E487, respectively. Conversely, the aromatic rings were placed near the aromatic residues F137, F140, and F488 of the F protein, detecting π-π stacking. Notably, this kind of positioning agreed with the overall distribution of the polar and hydrophobic properties at the protein surface, revealing a proper electrostatic match between the most polar and lipophilic substituents of the TMC-353121 with respect to the corresponding areas at the F protein surface (see
Figure 5, right side).
Interestingly, the introduction at the main benzimidazole scaffold of a flexible alkyl chain bearing a terminal morpholine ring, as shown by TMC353121, allowed the better highlighting of those F protein features which cooperate to stabilize the most polar and/or basic inhibitors at the protein surface.
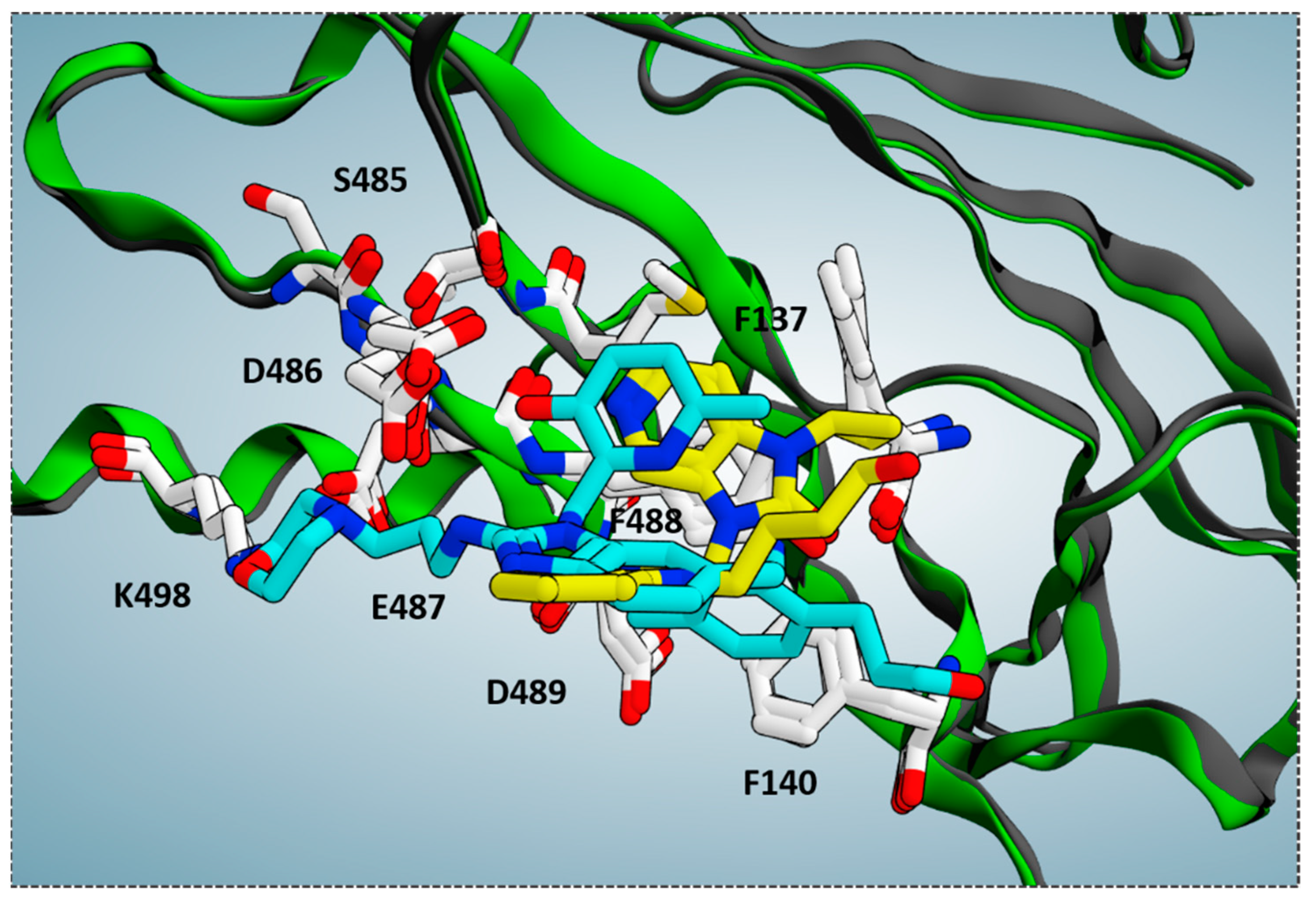
According to these data, further key residues can be described to achieve F protein inhibitor ability, such as D486, D489, E487, and K498, which are thought to guarantee a proper anchoring mode for the anti-RSV agents at the F protein surface, as well as the previously cited F140 and F488.
2.3. Molecular Dynamic Simulations of the Phase II Clinical Candidate JNJ-53718678
Based on the different positioning featured by the explored chemotypes as previously discussed, we proceeded with molecular dynamic simulation (MD) on the X-ray crystallographic data of the RSF F protein in presence of JNJ-53718678 (pdb code = 5KWW) [
27].
We deemed it interesting to better explore the putative mechanism of binding experienced by the clinical candidate JNJ-53718678 because of (i) its clinical effectiveness, (ii) its structural flexibility, (iii) the presence of hydrophobic groups tethered to two heterocyclic rings endowed with H-bonding moieties, and (iv) the related crystallographic information. Indeed, based on the 5KWW PDB code, this inhibitor experienced only lipophilic interactions with the biological target.
This approach would allow us to assess the stability of the aforementioned contacts as well as to underline the compound functional groups turning in the F protein targeting ability.
In this context, several publications confirmed the idea that running MD calculations represents a valuable tool to explore the protein–ligand complex flexibility [
30,
31].
Indeed, the contacts discussed previously could be not stable under dynamic conditions while other interactions could be disclosed as anchoring the inhibitors at the protein surface, thanks to dynamic perturbations.
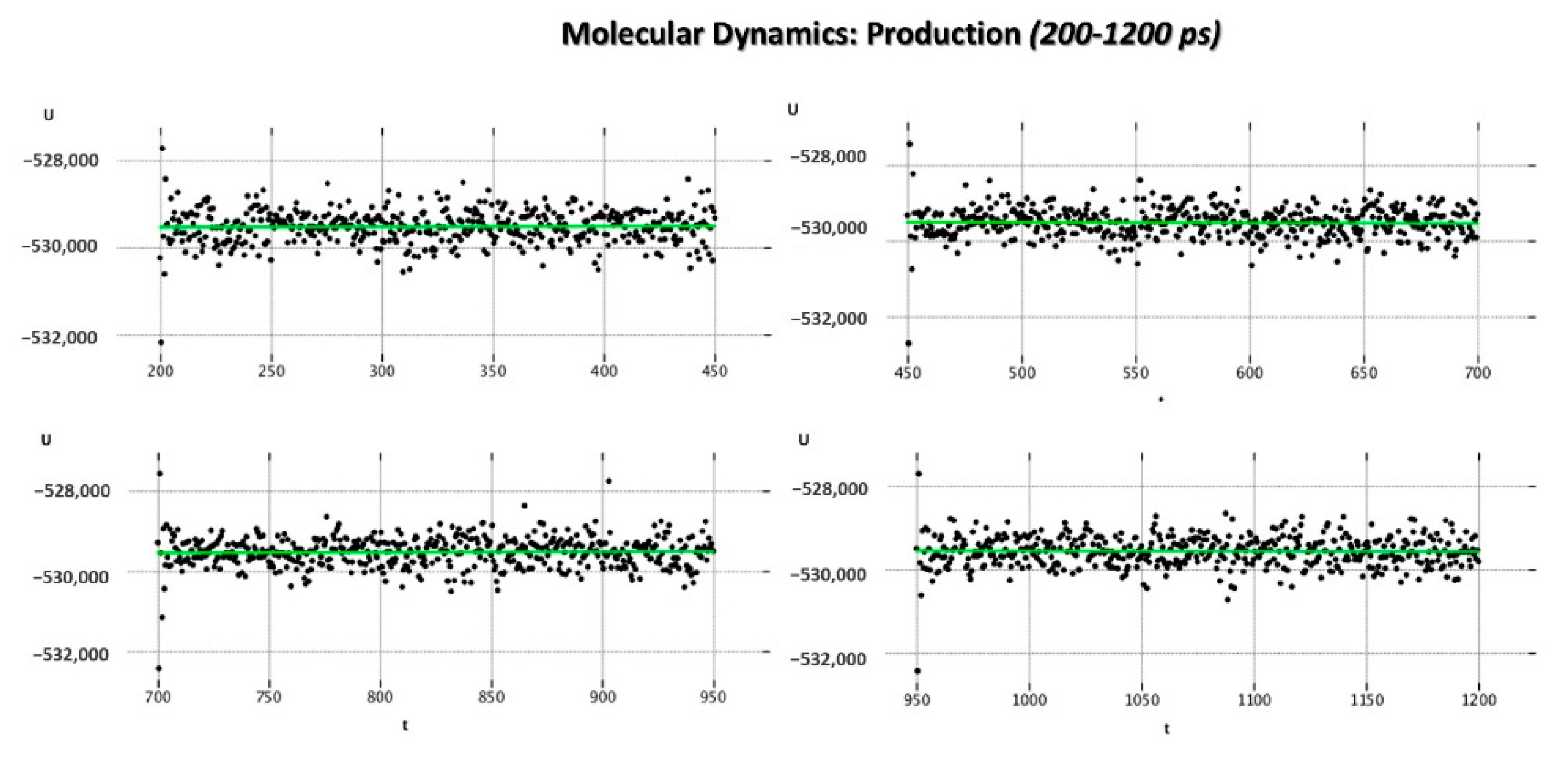
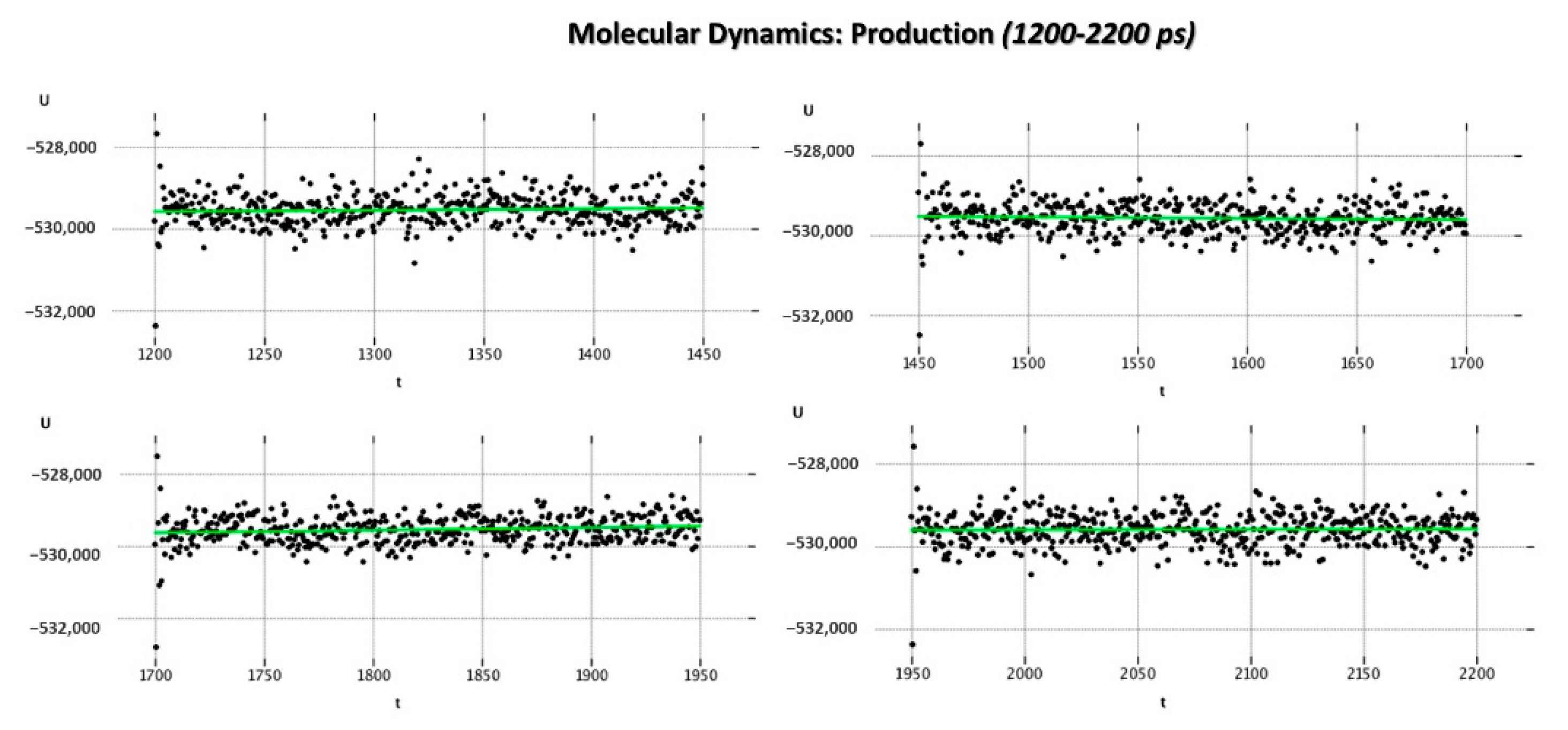
Thus, 2200 ps MD simulation was performed to analyze the X-ray data of JNJ-53718678 within the F protein (pdb code = 5KWW), heating (MD_H) the complex to 300 K for 100 ps, and followed by equilibration for 100 ps (MD_E) and production to 2200 ps (MD_P).
Evaluation of the potential energy (kcal/mol) and of the kinetic energy (kcal/mol) of the complex as a function of time during the MD_H and MD_E phases is shown in
Figure 7.
As regards the MD_P phase, the corresponding graphs reporting the evaluation of the potential energy (kcal/mol) and of the kinetic energy (kcal/mol) of the complex as a function of time are shown in
Figure 8 and
Figure 9.
According to our results, the MD_P phase was developed under stable values of potential and kinetic energies, leading to maintained interactions with the key residue F488 and revealing a further halogen contact between the Cl atom of JNJ-53718678 and the side chain of K498 (see
Figure 10). Interestingly, these preliminary data pave the way for the following design of new F protein targeting inhibitors and support the optimization of the in-house series of benzimidazoles as anti-RSV agents. Indeed, the most promising of them (see
Table S1) exhibited electron-rich atoms such as halogens at the same position of the benzimidazole ring.
2.4. Recross Docking Studies of (Pre)Clinical Candidates at the RSV F Protein
In order to evaluate the most predictive molecular docking protocol to be exploited for the following in-house benzimidazoles, we focused on the 5KWW complex (inhibitor JNJ-53718678/F protein), on the basis of: (i) the better resolution value than that of other PDBs (see the previous
Table 1), (ii) its drug-like behavior, being under clinical trial, and (iii) the presence of two (hetero)aromatic rings which mimic those of the in-house benzimidazoles
1–
158. In addition, the JNJ-53718678 chemical moieties tethered to the heteroaromatic rings quite resemble those displayed by
1–
158. Thus, in order to assess the most adequate docking protocol, deepening recross docking simulations taking into account the aforementioned six PDB codes and the related cocrystallized ligands were performed, following a procedure already applied in the literature [
32]. In particular, two series of docking calculations were performed by means of LeadIT (run A) [
33] and MOE (run B) Dock [
34].
Regarding run A, the top five best scored docking positioning for all the cited RSV F protein inhibitors docked within the aforementioned six different PDB codes are listed in
Table S2. Thus, a very different binding mode was calculated for all the compounds, turning in quite unreliable and poorly recurrent conformer clusters. In particular, most of them are endowed with very different predicted ΔG values spanning from −20 to +1 KJ/mol, for the related protein–ligand complex, as calculated by the Hyde tool implemented in LeadIT.
Molecular recross docking studies performed by MOE (run B) led to more comparable protein–ligand complexes for each series of inhibitor with respect to the six crystallized protein, also in terms of predicted ΔG mean values spanning from −5 to −3 KJ/mol (see
Table S3). In particular, we focused on the recross docking calculation results coming from the 5KWW, 5EA3, and 5EA6 PDB codes, including the inhibitors JNJ-53718678 (most related to the in-house benzimidazoles), JNJ-2408068 (featuring more flexible chains and H-bonding moieties than the previous one), and BTA-9881 (taken as rigid and poorly flexible inhibitor). The related scoring function obtained by run A (LeadIT software) and run B (MOE software) studies are reported in
Tables S4–S6 and Tables S7–S9, respectively (see
Section 3 for details).
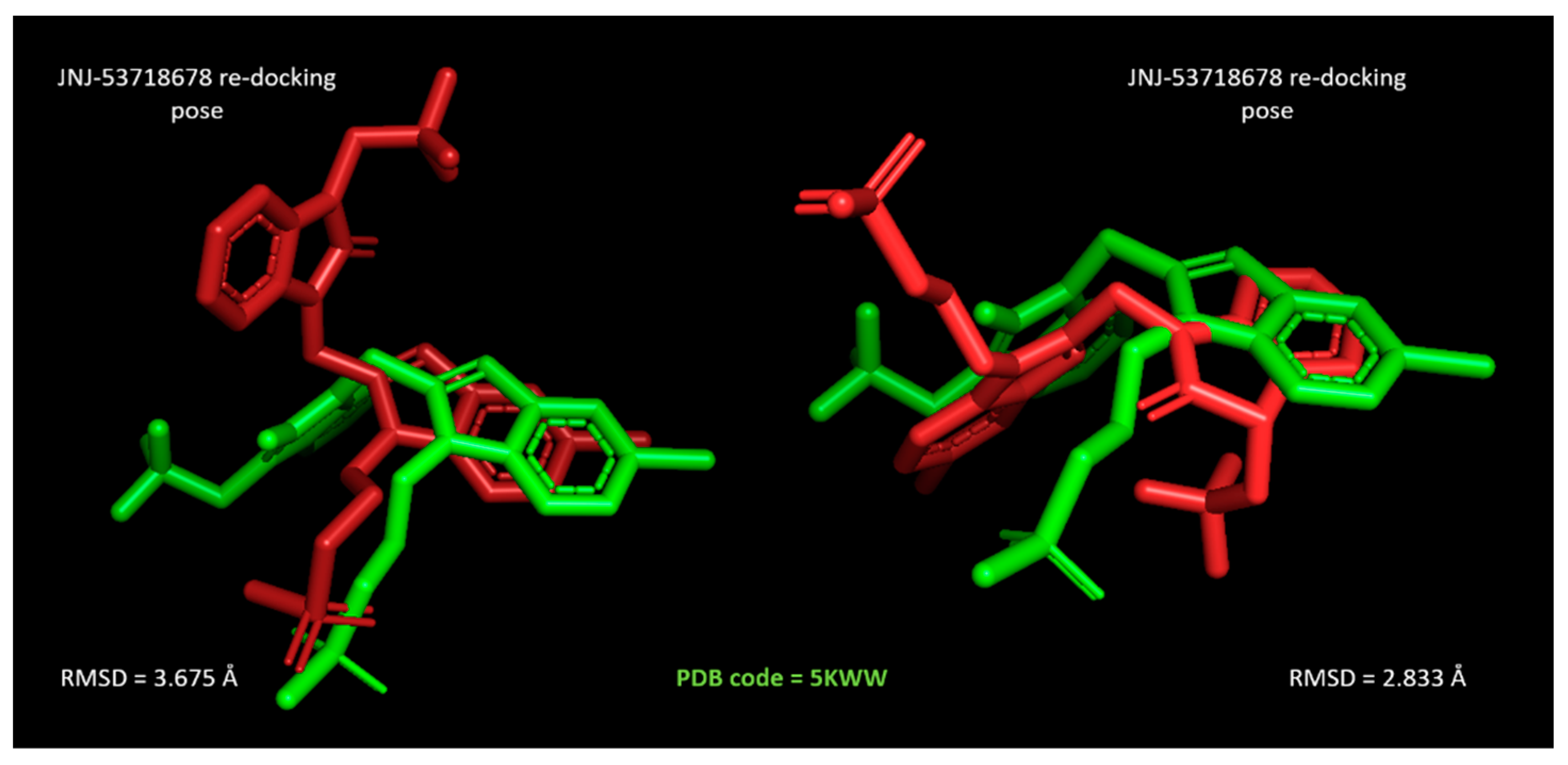
For all the three inhibitors, the MOE Dock module was able to suggest more comparable docking poses with respect to the related X-ray crystallographic data, than the LeadIT calculation. Indeed, run B led to lower RMSD values between the docked inhibitor and the reference compound than the corresponding ones by run A. As shown in
Figure 11, JNJ-53718678 taken as a reference inhibitor, as well as for the following docking studies about the in-house benzimidazoles
1–
158, was more efficiently predicted by MOE, featuring RMSD = 2.833 Å.
The same better predictive ability by run B was observed comparing the RMSD values for the docking poses and the corresponding X-ray data of the inhibitors, placed within the 5EA3 and 5EA6 PDB codes, JNJ-2408068, and BTA-9881 (see
Figures S7 and S8).
Nevertheless, RMSD values lower than 3 Å are known as preferred and desirable, in order to properly assess the docking protocol reliability. However, it should be noticed than this series of compounds binds at the outside protein surface, especially thanks to weak contacts, such as hydrophobic interactions, often featuring reversed bioactive positioning (see the previous
Figure 4). As a consequence, this could turn in quite produce higher RMSD values than those usually recommended in molecular docking calculations, with there being in any case quite plausible values.
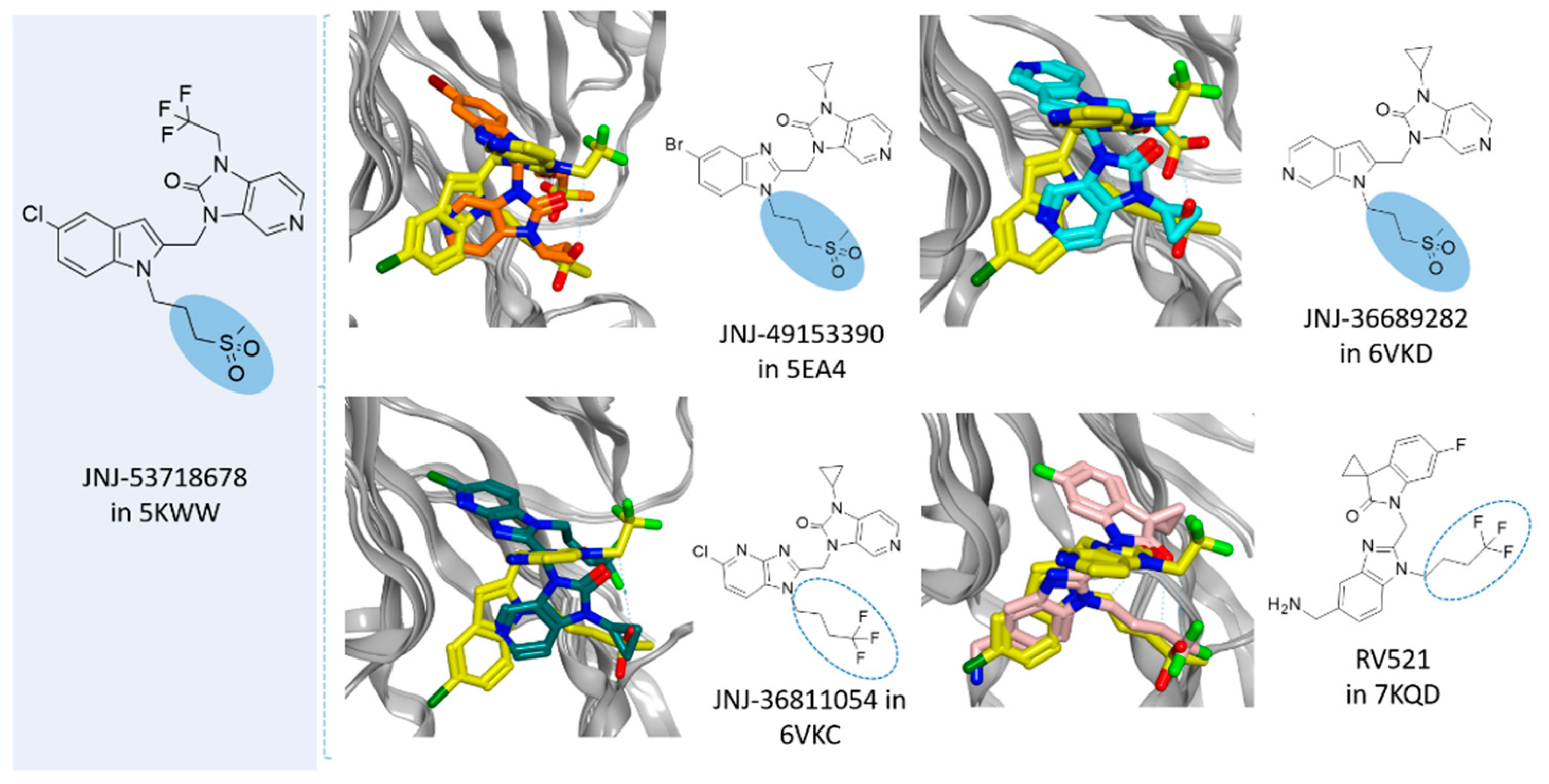
Along with this, we collected further experimental data on the bioactive conformation of a number of highly related JNJ-53718678 analogues. In particular, we considered not only the previously cited 7KQD PDB code including the RV521 anti-RSV agent but also 5EA4 [
13], 6VKD [
36], and 6VKC [
36]. The last three complexes were obtained in the presence of JNJ-49153390, JNJ-36689282, and JNJ-36811054, respectively. JNJ-36811054 maintained the same trifluoromethyl alkyl pendant of the previously cited RV521 at position 1 of the benzimidazole scaffold, and it was endowed with a basic chain at position 5 of the same bicyclic ring. The amine group replaced the halogen atom exhibited by RV521 as well as by JNJ-53718678. Conversely, JNJ-49153390 shared the same alkylsulphonyl group of JNJ-53718678 at the benzimidazole position 1, in tandem with a halogen atom in position 5, when JNJ-36689282 only featured the aforementioned alkylsulphonyl group. However, all of them displayed a pyrido imidazole ring, featured at the position 1 of the bicyclic ring a (spiro)alkyl portion as bioisostere of the trifluoromethyl group of JNJ-53718678. As shown in
Figure 12, all of them moved differently the pyrido-imidazolone ring if compared to the one of JNJ-53718678, with it often being the main benzimidazole or its bioisostere rings (the pirrolopyridine or imidazopyridine rings) projected on the opposite side than the indole ring of the reference JNJ-53718678, with the exception of RV521.
Indeed, the amine group at position 5 of the RV521 benzimidazole was properly superposed on the halogen atom at the corresponding position of the prototype indole core. This information suggests an overall quite variable but effective positioning exhibited by the RSV F protein inhibitors. Notably, all of the cited X-ray poses proved to guarantee the mandatory contacts with F140 and F488 through aromatic moieties.
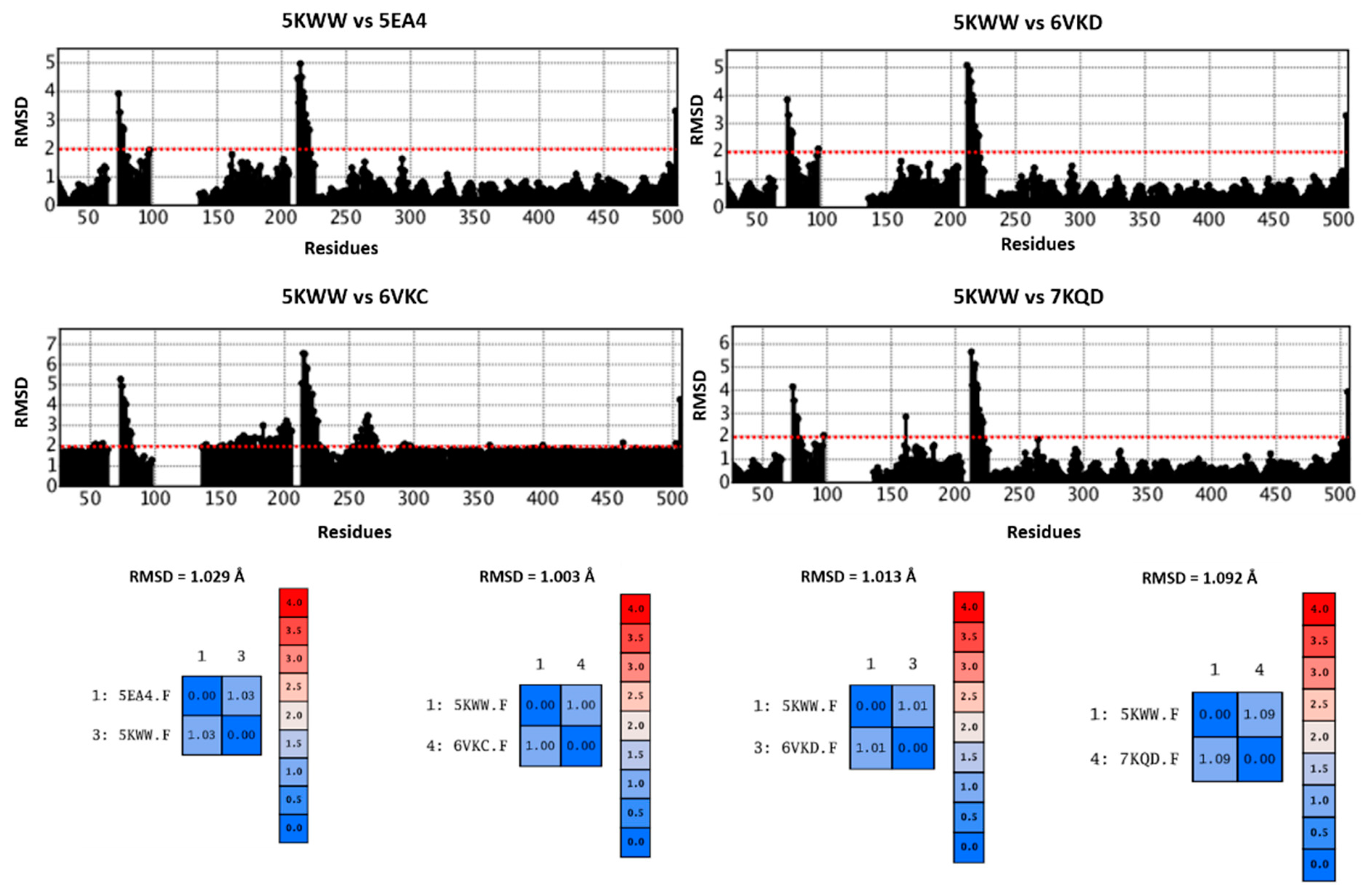
Comparing 5EA4, 6VKD, 6VKC, 7KQD, and the reference 5KWW in terms of protein flexibility, the corresponding RMSD values, calculated with respect to the alpha carbon atoms (CA atoms), revealed low structural differences spanning from 1.003 to 1.092 Å, thus supporting minimal discrepancies among the explored experimental data (see
Figure 13).
The alignment and superimposition of all the aforementioned five PDB codes led to an overall RMSD value of 0.667 Å, as reported in
Figure S9.
Interestingly, the use of all the atoms to calculate the superposition, thus including the evaluation of sidechain symmetries, led to an overall adequate RMSD value (overall RMSD = 1.717 Å) within the recommended limit of 2 Å, as reported in
Figure S10. In particular, despite the aforementioned discussed positioning of the specific co-crystallized inhibitors (see the previous
Figure 12), the 7KQD (RMSD = 1.37 Å) and the 6VKD (RMSD = 2.29 Å) proteins were, respectively, the most and least structurally similar to 5KWW. However, it should be noticed that the main flexible portion of the RSV F protein involves the 80–100 and 200–250 amino acids of the protein primary sequence (see
Figure S10) and not those involved in the inhibitor binding.
2.5. Molecular Docking Studies of the Benzimidazole-Based Derivatives 1–158 as Anti-RSV Agents
Based on the aforementioned preliminary studies, we proceeded our work with molecular docking calculations of the in-house series of anti-RSV agents (
1–
158; chemical structures are reported as SMILE format in
Table S10) exhibiting the benzimidazole main core, differently substituted mostly at positions 1, 2, and 5. This strategy allowed us to better explore those ligand-enzyme interactions supporting for the benzimidazole F protein inhibitory activity. For simplicity, only the scoring functions related to the inhibitors herein discussed are listed in
Table S11.
Among the whole in-house series of benzimidazoles, compounds
1–
24 were thought to be F protein inhibitors featuring basic flexible chains or more hydrophobic bulky groups, endowed with basic properties, at the position 1 of the main ring (R1 substituent; see
Figure 2). Most potent of them bear a
p-substituted-benzyl moiety in R2 in tandem with two halogens at positions 5 and 6 of the benzimidazole, as reported for
11 (pEC
50 = 5.30; R2 =
p-OCH
3-Ph) and
12 (pEC
50 = 5.30; R2 =
p-NH
2-Ph).
The introduction of a CF3 group at only position 5 of the benzimidazole was also effective when accompanied by (i) a p-substituted-benzyl moiety in R2 (see 20, 21; pEC50 = 4.60–4.82) or by (ii) a lupinyl group and a CF3 substituent in R1 and R2 (see 2; pEC50 = 4.66), respectively.
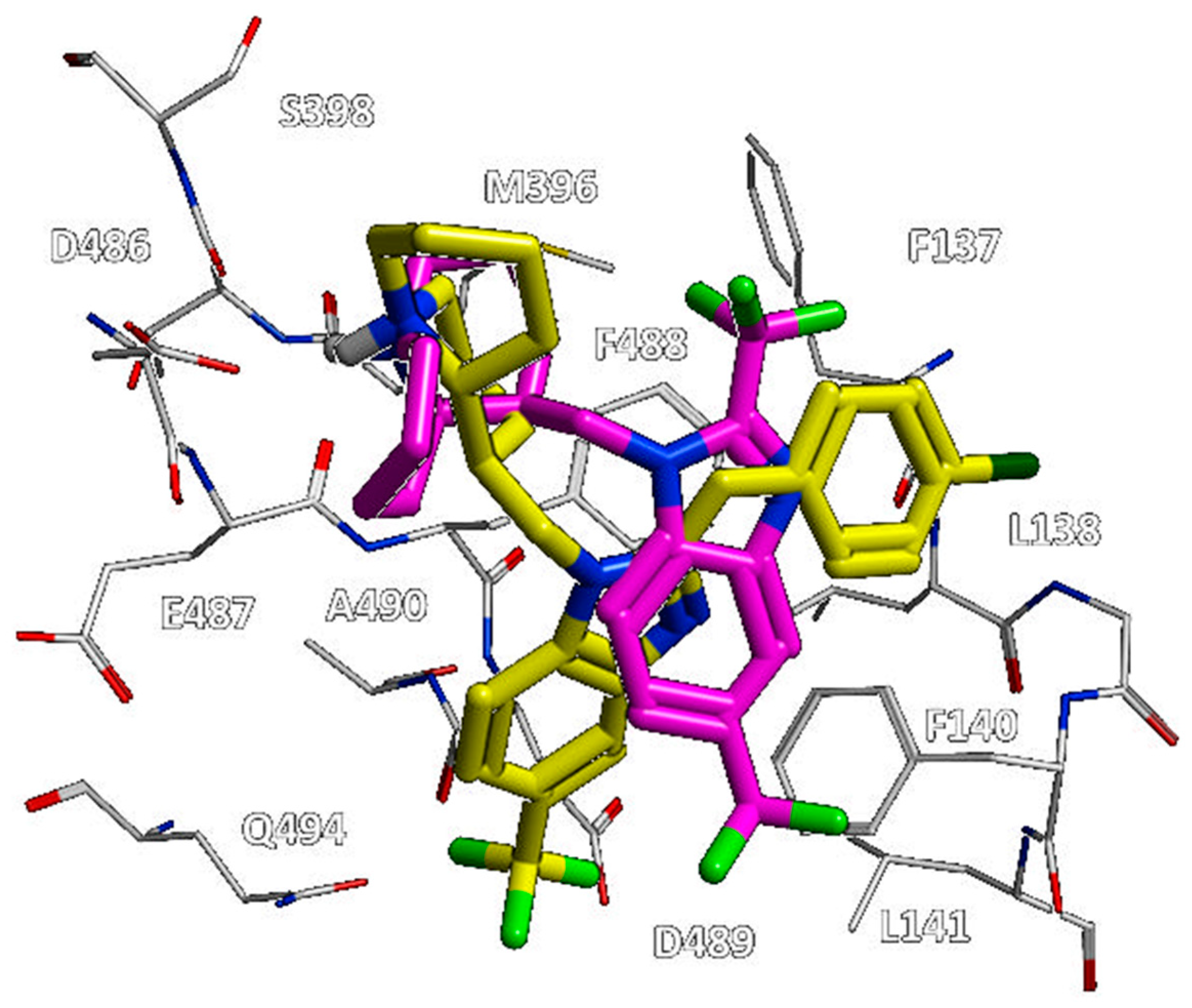
Accordingly, both F protein inhibitors
2 and
20 experienced comparable docking poses, featuring one salt bridge involving the protonated nitrogen atom of the lupinyl ring and D486 residue (
Figure 14).
In particular, the hydrophobic and bulky lupinyl properly occupied the protein cavity delimited by D486, E487, M396, F488, and A490, supporting the previously discussed pivotal role played by hydrophobic contacts between the F protein and the related inhibitors.
All the aromatic rings within the two inhibitors 2 and 20 were engaged in π-π stacking with F140 and F488, while the CF3 group in R2 for the inhibitor 2 and the p-Cl-benzyl substituent of 20 were projected toward F137.
Interestingly, the presence of hydrophobic and bulky groups endowed with basic moiety, such as the lupinyl ring, rather than extended and flexible aminoalkyl chains was preferred in R1. This information was supported by the higher potency of 24 (R1 = lupinyl, pEC50 = 5.05) if compared to 14 (R1 = diethylaminoethyl-, pEC50 = 4.12).
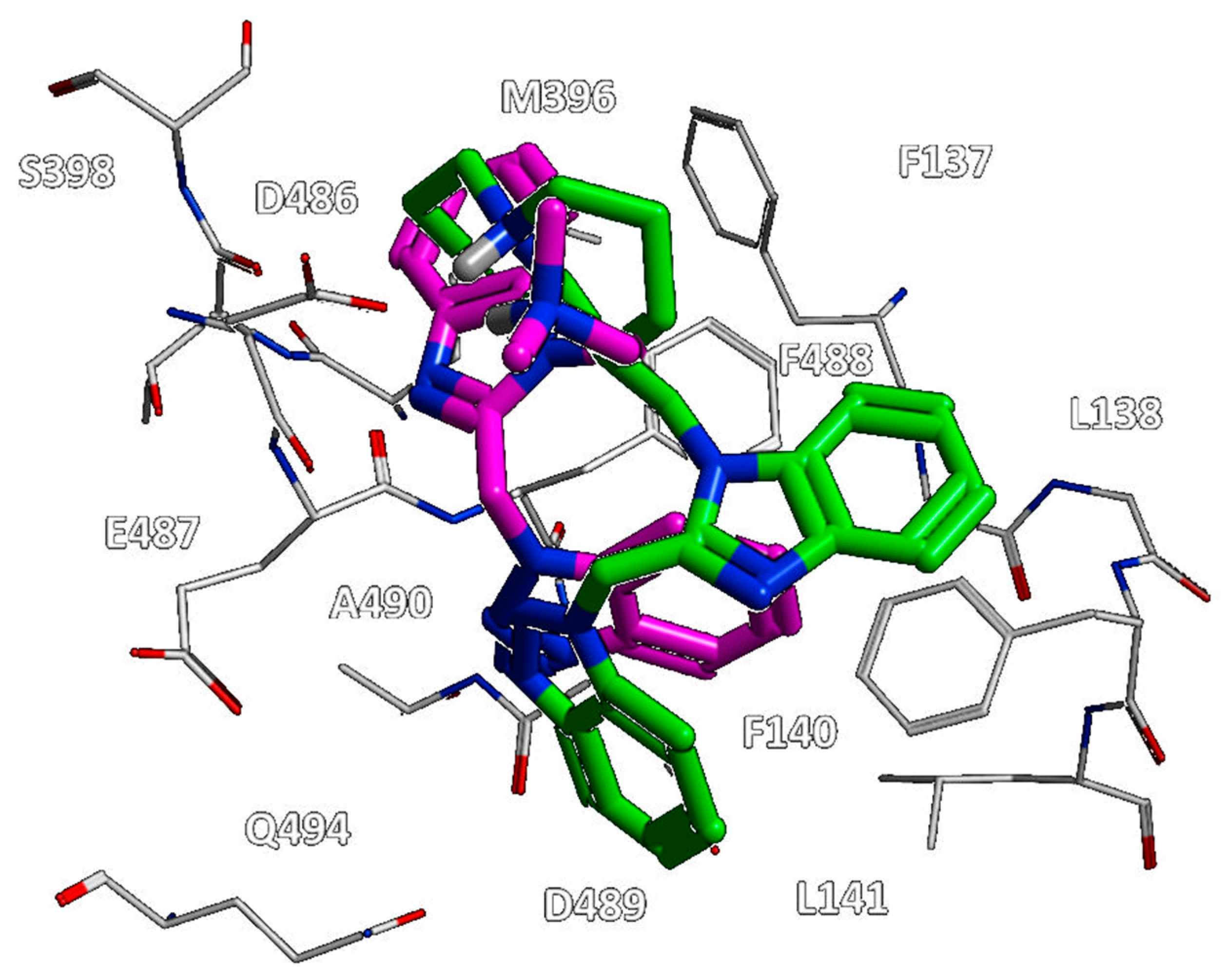
As shown in
Figure 15, analogues
23 and
24 displaying a halogen-substituted benzyl ring in R2 and the aforementioned lupinyl ring in R1 maintained the proper salt bridge with D486, as previously mentioned for
20.
Thus, 23 and 24 experienced a comparable positioning with respect to that of 20, with it being the main benzimidazole core of the three derivatives well overlapped.
Conversely, removing hydrophobic groups at the position 5 and 6 of the benzimidazole and inserting a flexible aminoalkyl chain in R1 instead of the lupinyl moiety led to the inactive analogue
13 (pEC
50 < 4.00), lacking any polar contacts with D486 (see
Figure S11).
In particular, the benzyl group of the F protein inhibitor 13 mimics the same positioning displayed by the benzimidazole of 20, while the main bicyclic core of 13 was overlapped onto the p-Cl-benzyl substituent of the most potent analogue 20. Despite a number of π-π stacking with F140, F488 and 13, this inhibitor was poorly stabilized at the protein surface lacking H-bonds with D486 and the R1 substituent.
The introduction of the rigid phenyl ring instead of the benzyl group in R2 led to most of the less potent analogues 25–113 (pEC50 = 4.00–5.15), also bearing a basic substituent in R1. Among them, 102–108 (pEC50 = 4.00–4.62) featured a modest anti-RSV ability, exhibiting the aforementioned groups in R1 and R2 while the main benzimidazole ring was substituted at position 5 or 6 with one hydrophobic moiety. The most effective 100 (pEC50 = 5.15) was characterized by reversed substitutions being a lupinyl ring in R2 and a phenyl one in R1, lacking any further substituents at the main bicyclic core.
As shown in
Figure S12, the benzimidazole core of
100 was bioisostere of the
p-Cl-benzyl group of the most potent
20, featuring π-π stacking with F140 and F488. The rigid phenyl group placed in R1 was projected toward F140, in order to mimic the same behavior experienced by compound
20. As a consequence, this kind of positioning allowed
100 to be H-bonded to D486, thanks to the lupinyl group in R2.
As regards compounds
114–
137 (4.44 < pEC
50 < 7.70), endowed by a N(1)-benzotriazolyl substituent in R2, they proved to be more potent than the previously cited analogues. This interesting RSV inhibitory ability was maintained, even in tandem with different pendants tethered to the main benzimidazole core. Among them, compounds
114 (pEC
50 = 6.15) and
118 (pEC
50 = 6.52) experienced comparable potency values and docking poses (
Figure 16).
Accordingly, both the two protonated nitrogen atoms of the 114 and 118 basic chains featured salt-bridges with D486, while the two N(1)-benzotriazolyl motifs were H-bonded to F488 and D489. Notably, this kind of positioning made the two analogues more effective than the previously cited benzimidazole series. In addition, 114 and 118 displayed hydrophobic contacts and π-π stacking with F140 and F488.
Applying the introduction of lipophilic and electron-withdrawing groups at positions 5 and/or 6 of the benzimidazole ring better stabilized the inhibitor at the protein surface, leading to more potent compounds such as 120–126 (pEC50 = 6.05–7.70). Indeed, the presence of a Cl atom at position 5 of the main bicyclic ring made these inhibitors more effective than the unsubstituted analogues 114–119 (pEC50 = 5.64–6.82).
Finally, most of the promising benzimidazole-containing derivatives, belonging to the in-house series of anti-RSV agents were decorated with the N(2)-benzotriazolyl group in R2, as reported for 138–156 (4.00 < pEC50 < 7.52). Among them, the most interesting analogues fear basic substituents, such as the lupinyl ring, at the position 1 of the main benzimidazole core, also accompanied by hydrophobic groups at the benzimidazole position 5 and/or 6.
This information was supported by the higher potency trend displayed by
146–
148 (pEC
50 = 6.00–7.52) if compared to
142–
145 (pEC
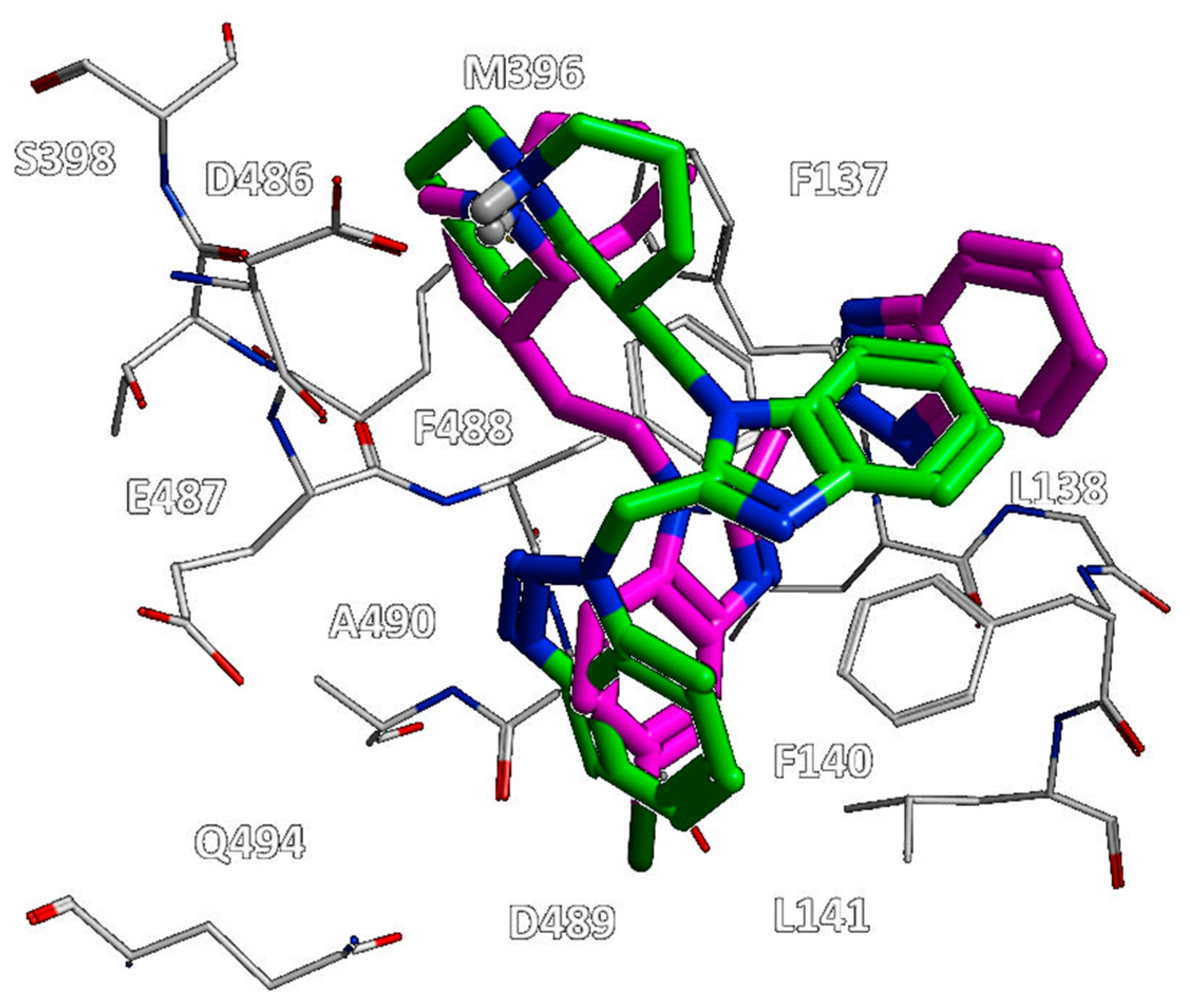
50 = 5.82–6.52). In particular, the docking mode observed for
148 resembled that of the previously cited effective analogue
118, maintaining the key interaction with D486, thanks to the basic ring, while the benzotriazolyl moiety was H-bonded to F137 (
Figure 17).
Notably, the presence of bulky groups linked to the position 1 of the benzimidazole, in tandem with the benzotriazolyl ring in R2, moved the anti-RSV agent 148 in proximity of F137, L138, F140, L141, M396, F488, and A490, increasing the number of hydrophobic and π-π stacking interactions with the biological target.
2.6. Structure-Based Pharmacophore Analysis
In order to gain more clear information about the specific requirements turning in RSV F protein binding ability, we deemed it interesting to proceed with a pharmacophore analysis focusing on the superimposition of the highly related JNJ-53718678 analogues on the basis of the previously discussed variable positioning (see
Figure S13). Thus, we relied on the X-ray data for the bioactive positioning of JNJ-53718678 (PDB code = 5KWW) [
27], RV521 (PDB code = 7KQD) [
28], JNJ-49153390 (PDB code = 5EA4) [
13], JNJ-36689282 (PDB code = 6VKD) [
36], and JNJ-36811054 (PDB code = 6VKC) [
36].
The overall pharmacophore model was generated thanks to the pharmacophore consensus module implemented into the MOE software. This tool is based on the identification and classification of the most recurrent pharmacophore moieties within the analyzed set of derivatives. Any pharmacophore feature is endowed by an identification code associated with the program (ID), the percentage by which this moiety appears among the compounds explored (SCORE), by a radius that stands for the maximum space within which this feature can be placed within the inhibitor (RADIUS) and by a symbol that is related to the interaction with the receptor (EXPRESSION).
As shown in
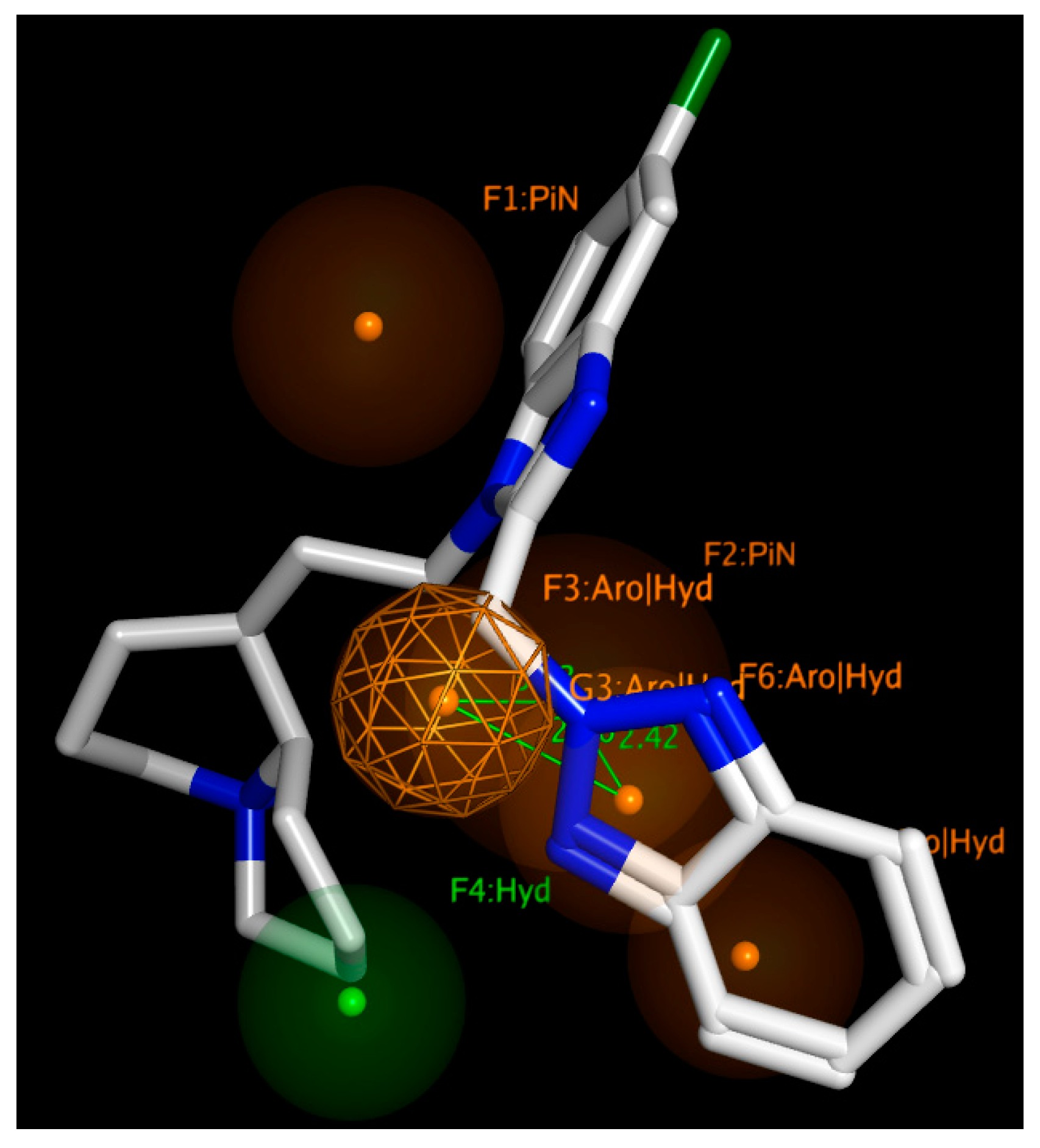
Table 2, based on the collected experimental data, the most important pharmacophore requirements (represented by at least 80% of the RSV F protein inhibitors under examination), to draw promising anti-RSV agents, include six features, especially electron-rich atoms tethered to (hetero)aromatic rings or hydrophobic groups.
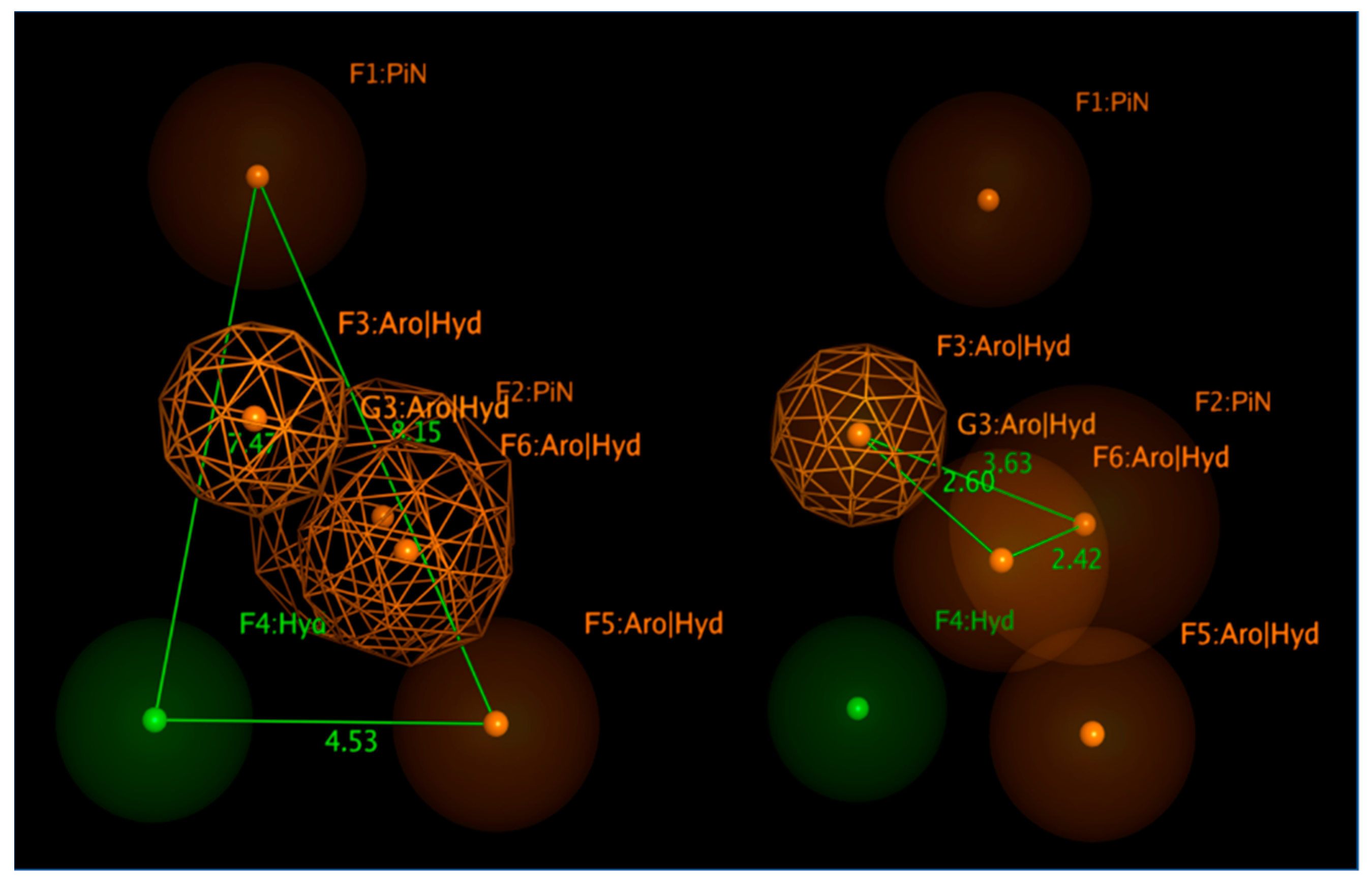
In particular,
Figure 18 shows bulky (hetero)aromatic rings including H-bonding function (namely F3, F5, F6:AroǀHyd) properly connected to a hydrophobic pendant (F4:Hyd), while the presence of further aromatic or aliphatic rings are reported by F1, F2:PiN.
The expected reciprocal distances between all the F1-F6 features shared by the collected RSV F protein inhibitors, exploited for the pharmacophore calculation, revealed useful information for the further evaluation of novel anti-RSV agents. Indeed, the aromatic or aliphatic core exemplified by F1:PiN should be at 8.15 and 7.47 Ǻ from a further (hetero)aromatic ring (F5:AroǀHyd) and a proper hydrophobic substituent (F4:Hyd). The last two features (F5:AroǀHyd and F4:Hyd) should be placed at 4.53 Ǻ to each other.
In addition, the F3: AroǀHyd group, shared by the 100% of the compounds, has to be tethered to F4:Hyd and F6:AroǀHyd, featuring in 2.60 and 3.63 Ǻ distances. On the other hand, the F4:Hyd and F6:AroǀHyd should be placed at 2.42 Ǻ to each other. Interestingly, this suggests once again a prominent role played by folded inhibitors displaying a methylene group as a flexible junction between two main (hetero)aromatic cores, which could alternatively interact with the key residues F140 and F488 of the biological target. This information appeared to be in good agreement with the previous information described for the highly related JNJ-53718678 analogues, beyond the specific positioning featured by the indole/benzimidazole ring or by the pyrido-imidazolone core.
Finally, the model allowed us to positively check the pharmacophore requirements to act as RSV F protein inhibitors also within the in-house series of benzimidazoles
1–
158. As shown in
Figure 19, compound
148, chosen as reference compounds for our benzimidazole library, properly fulfills the aforementioned features.
These data give further support to the well-known mechanism of action so far described in the literature for this kind of anti-RSV agents [
12].
2.7. In Silico Evaluation of ADME Properties
During the last years, efforts in the drug discovery process relied on the effectiveness of
in-silico evaluation of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion properties (ADME). Indeed, applying computational methods aimed at gaining information on the pharmacokinetic (PK) and toxicity behavior of compounds deeply accelerated the lead optimization process [
25,
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38]. On this basis, we performed a computational evaluation of the main PK properties related to the drug-like profile of the most promising in-house series of benzimidazoles, in comparison with the prediction obtained for the (pre)clinical TMC353121, BMS-433771, JNJ-2408068, and Phase II clinical candidates JNJ-53718678, GS-5806, and RV521, taken as reference compounds. In particular, we focused on the potent N(1)-benzotriazolyl-containing compounds
118,
120,
126,
157, and
158 (6.52 < pEC
50 < 7.70) and the N(2)-benzotriazolyl-based
141,
148 (7.00 < pEC
50 < 7.70).
Initially, in order to take into account putative violation of the well-known Lipinski’ rule [
39] and Veber’ rule [
40], we calculated the logarithmic ratio of the octanol–water partitioning coefficient (cLogP), the molecular weight (MW) of compounds, their number of H-bonding acceptor (HBA) and donor groups (HBD), the number of rotatable bonds (nRot_bond), and the topological polar surface area (TPSA) (see
Table 3).
While the first ones (Lipinski’s rule) are suggested for compounds featuring MW < 500, cLogP < 5, HBA < 10, and HBD < 5, the rule proposed by Veber relates drug bioavailability with ≤10 rotatable as nRot_bonds, total number of H-bonding atoms (as sum of HBA and HBD) < 12, and TPSA ≤ 140 Å2.
Based on the in silico evaluation, most of the in-house compounds fulfill all the Lipinski’s rule and Veber’s rule, with the exception of the suggested cLogP value which was quite > 5 for 126, 158 among the N(1)-benzotriazolyl-containing benzimidazoles, and for the explored N(1)-benzotriazolyl-containing benzimidazole 141, 148 analogues. On the other hand, all the reported benzimidazoles experienced adequate molecular weight values (MW < 500) and the number of H-bonding features (HBA + HBD < 12) if compared to the (pre)clinical and clinical candidates TMC-353121 and GS-5806 (MW > 500).
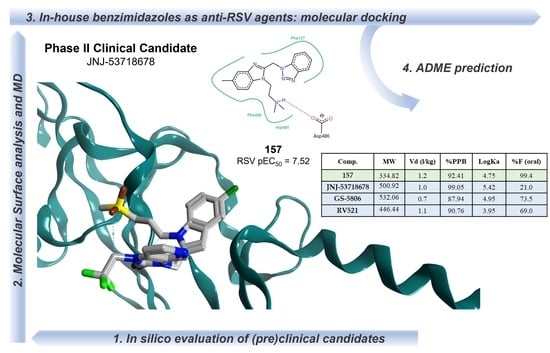
The prediction of ADME properties included human intestinal absorption (HIA), the volume of distribution (Vd), the role played by plasmatic protein binding (%PPB), and the ligand affinity toward human serum albumin (LogKa HSA) were all considered with the intent to determine the putative value of the oral bioavailability as a percentage (%F) (see
Table 4).
As shown in
Table 3, all the in-house anti-RSV agents were predicted as endowed with optimal absorption values (HIA = 100%) with respect to TMC-353121 (HIA = 3%), JNJ-2408068 (HIA = 71%), and also to GS-5806 (HIA = 93%). Even if they displayed comparable plasmatic protein binding values (%PPB = 92.41–99.27%) and affinity toward the human serum albumin (logKa HSA = 4.56–5.32) in comparison to the Phase II clinical candidates (%PPB = 87.94-99.05; logKa HSA = 3.95–5.42), all the benzimidazoles were characterized by higher bioavailability values (%F = 99.1–99.4%) than the aforementioned reference compounds (%F = 21.0–73.0%).
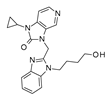
In addition, compound 157, designed as optimized analogue of 120, featured ameliorated %PPB, Log Ka HSA, and %F values compared to the prototype 120, giving a good validation of the previously applied rational design process.
In the search of putative new drugs, off-target adverse drug reactions (ADRs) are thought to be associated with significant morbidity and relevant costs for the healthcare system. While the desired drug action can be rationalized based on specific interactions between a molecule with its biological target, which leads to a specific biological event, side effects are often due to interaction of the drug molecule with further, unrelated proteins. In this context, the rapidly developing field of in silico modeling is expected to support, as useful predictive tool, the in vitro profiling, unraveling potential ADRs. Thus, current in silico profiling models or website, predicting the potential compound liabilities, are nowadays deeply applied in drug discovery, to sustain the drug development and optimization process [
41].
Herein, we deepened our study about the prediction of the in-house benzimidazole drug-like properties performing additional in silico evaluation of their PK features, thanks to SwissTarget and SwissADME website [
42,
43] and to the Molinspiration Property Calculation Service [
44].
The same tools have been exploited also for the search of further putative biological targets involving the same derivatives, which could turn in off-target effects.
This study was also applied to the (pre)clinical candidates JNJ-53718678, RV521, JNJ-2408068, BMS-433771, TMC353121, and GS-5806 (see
Figures S14–S19).
Regarding JNJ-2408068, both Molinspiration and SwissTarget databases suggested a prominent role as a kinase binding compound and then as a putative GPCR class ligand (see
Figure S14). While no violation of the bioavailability roles, such as the previously mentioned Veber’s and Lipinski’s ones, was detected, the inhibitory ability toward CYP1A2 was predicted by the SwissADME website.
TMC-353121 was once again identified as a putative GPCR binding derivative by both predictive tools, with them also being classified as kinase targeting compound or protease inhibitor, by SwissADME website and Molinspiration service (see
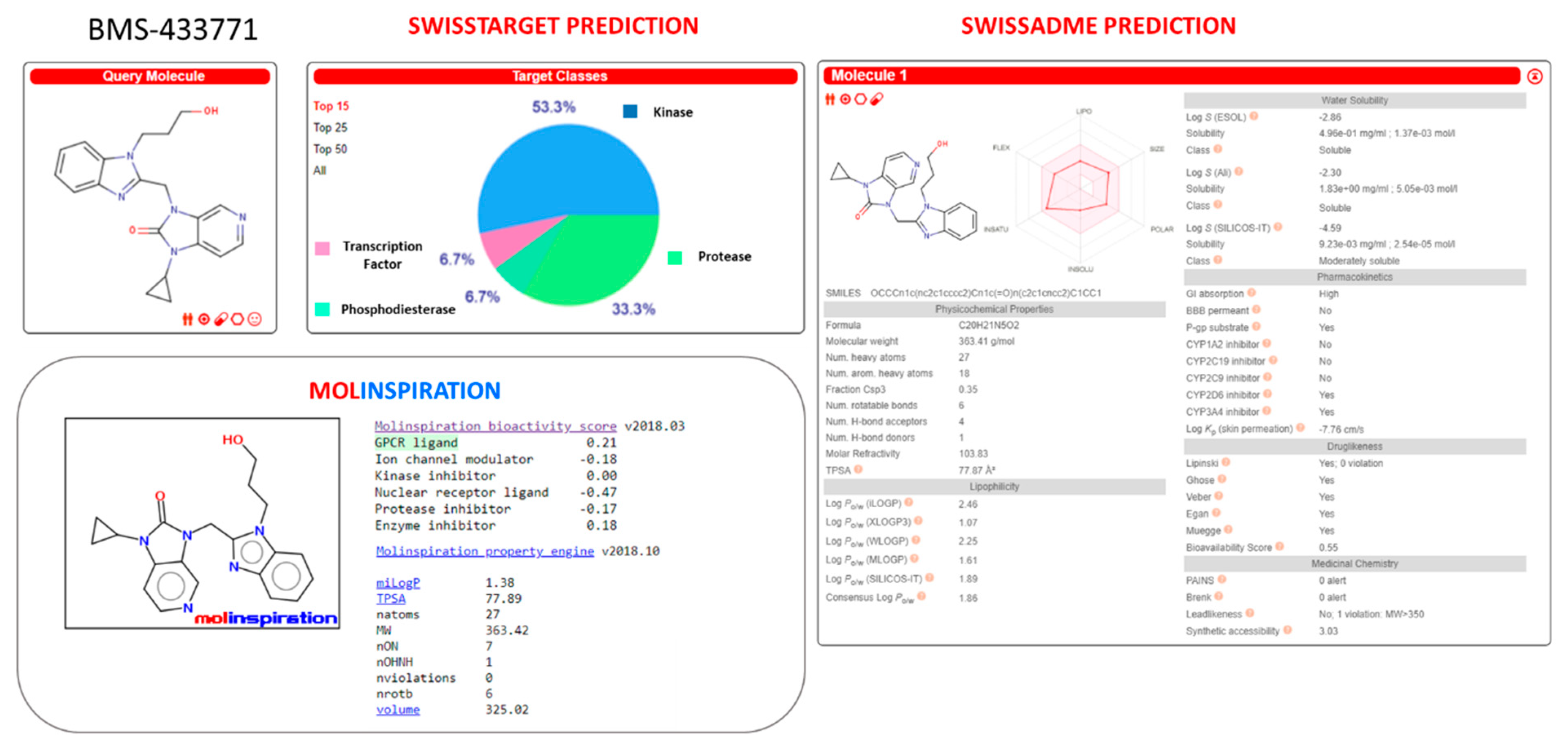
Figure S15). The violation in drug-like properties relied on the high molecular weight (MW = 575) and in the number of rotable bonds. BMS-433771 was predicted as kinase and GPCR targeting ligands by SwissTarget and Molinspiration, respectively. None of them pointed out drug-like properties violations, even if a sort of CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 inhibitory ability was suggested (see
Figure S16).
Among the Phase II clinical candidates, RV521 was also evaluated as kinase and GPCR targeting ligand by SwissTarget and Molinspiration, which was endowed with drug-like properties in terms of favorable Lipinski’s and Veber’s roles (see
Figure 20). On the other hand, it was predicted to inhibit a number of cytochromes such as CYP1A2, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4.
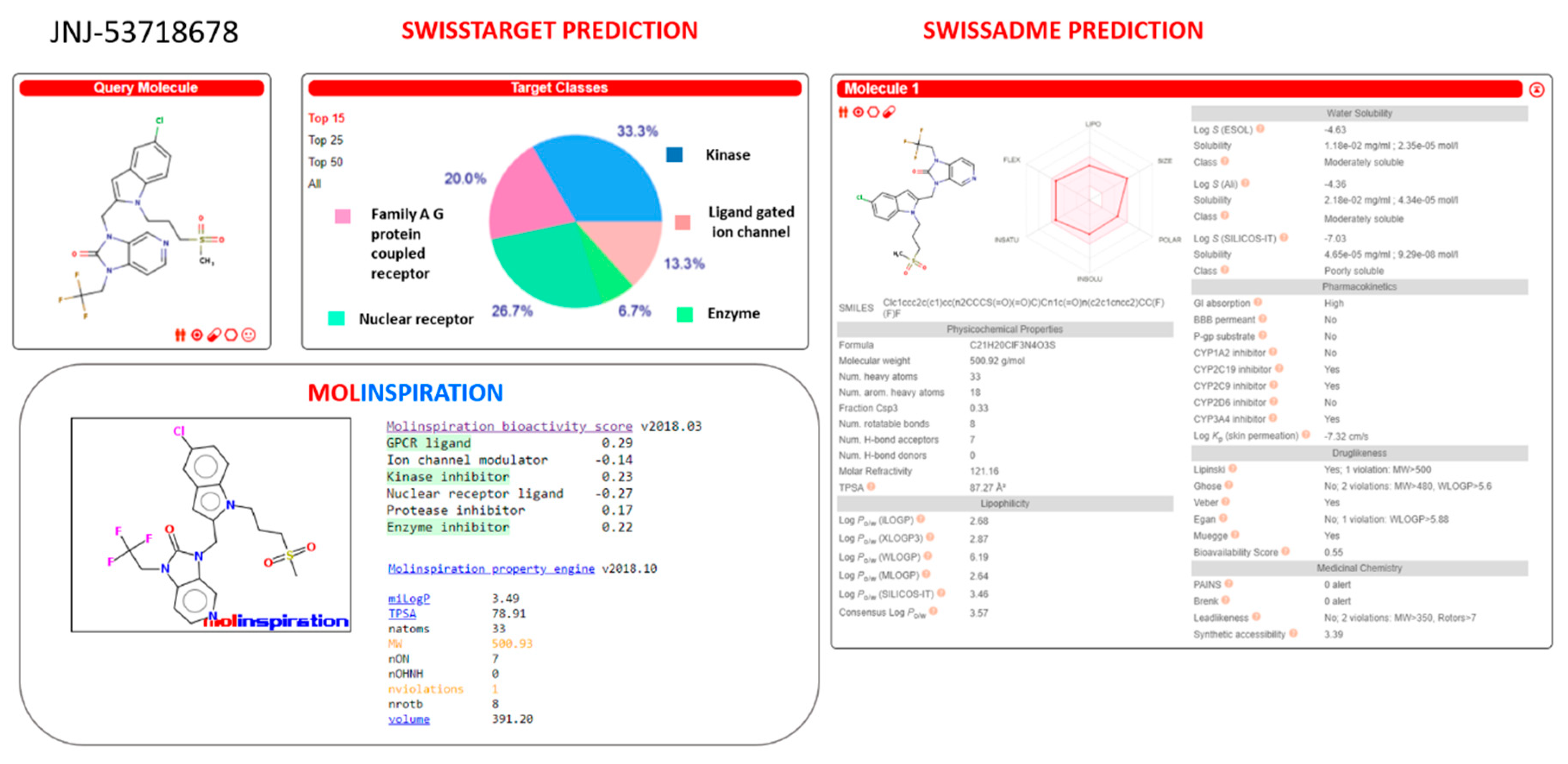
Similarly, JNJ-53718678 was identified as a putative CYP2C19, CYP2C9, and CYP3A4 inhibitor by SwissADME website, featuring a slightly high molecular weight value (MW > 500) with respect to the drug-likeness recommended guidelines (see
Figure 21). Then, the predictive putative off-targets events of JNJ-53718678 were attributed to the interactions with kinase and GPCR class A families, as reported by both Molinspiration and SwissTarget database.
The clinical candidate GS-5806 was classified as kinase and GPCR targeting ligand by SwissTarget and Molinspiration, respectively, featuring a limited number of drug-likeness violations based on the related TPSA and MW values (see
Figure S19). On the other hand, it was predicted as a putative CYP2D6 inhibitor.
Regarding the herein-discussed promising benzimidazoles
126,
157, and
158, all of them were classified by the aforementioned SwissTarget database as GPCR targeting compounds, while the Molinspiration service did not reveal a prominent putative off-target event (see
Figures S20–S22). The analogues
126 and
158 were predicted to fulfill the drug-likeness requirements except for the recommended MW value (MW > 500), also being putative cytochrome inhibitors. Indeed,
126 and
158 were classified as CYP1A2, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP3A4 and CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4 inhibitors, respectively.
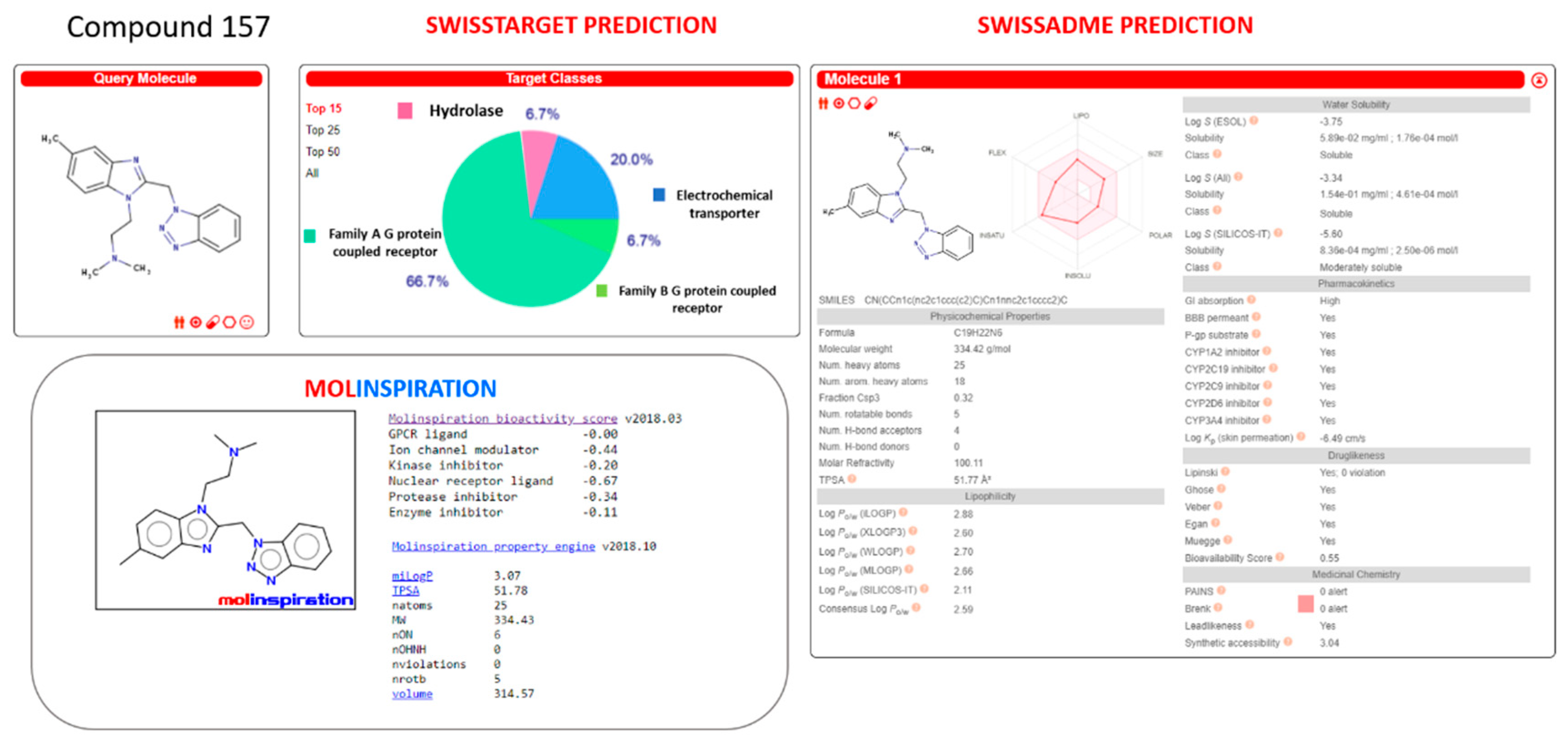
Similarly, the analogue
157 was scored as a possible CYP1A2, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4 inhibitor, with it being endowed with optimized oral bioavailability indices, fulfilling the suggested Veber’s and Lipinski’s roles (see
Figure 22).