Thin Layer-Protected Gold Nanoparticles for Targeted Multimodal Imaging with Photoacoustic and CT
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
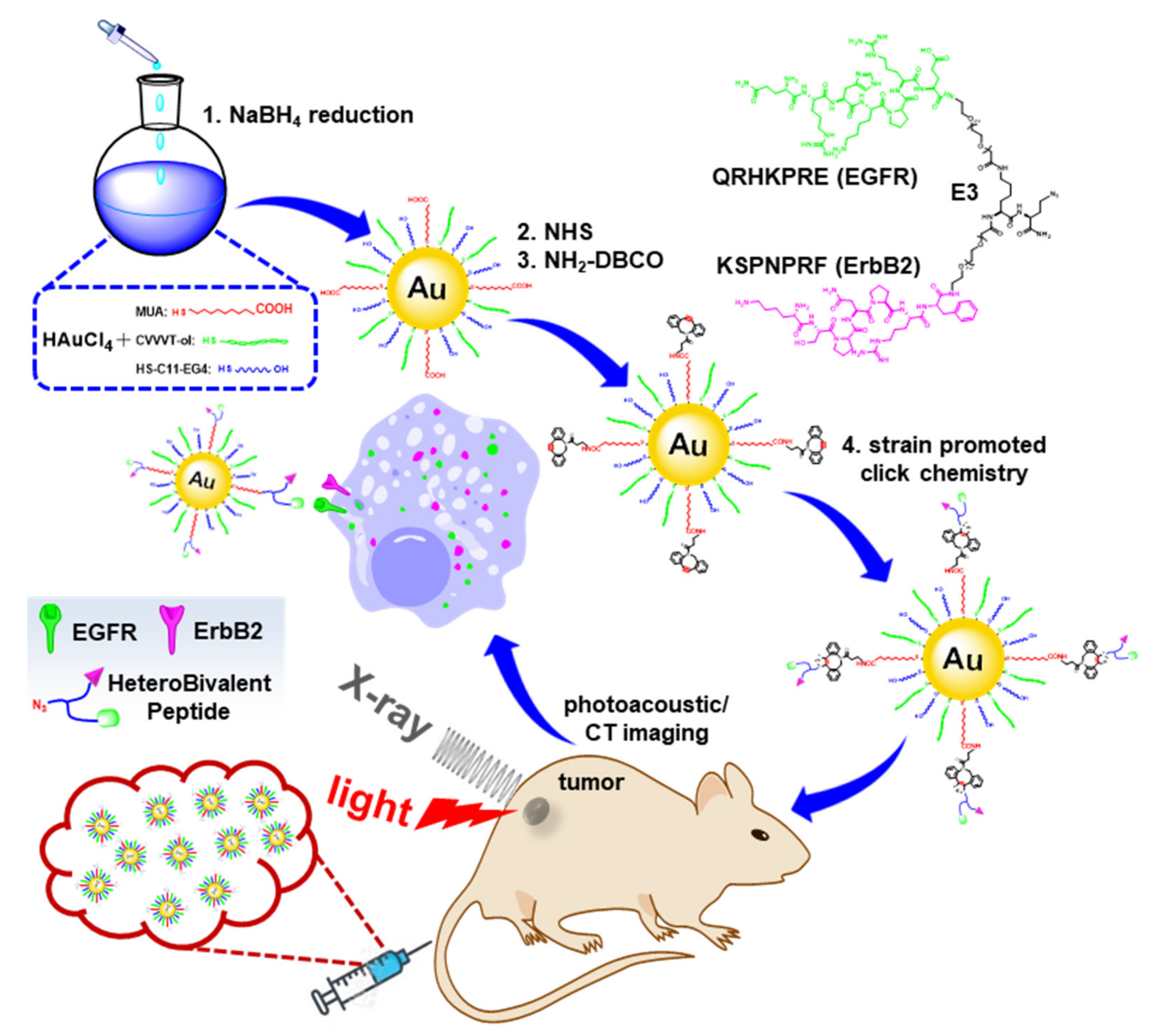
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of HB-Au-NPs
2.2. Nanoparticle Characterization
2.3. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
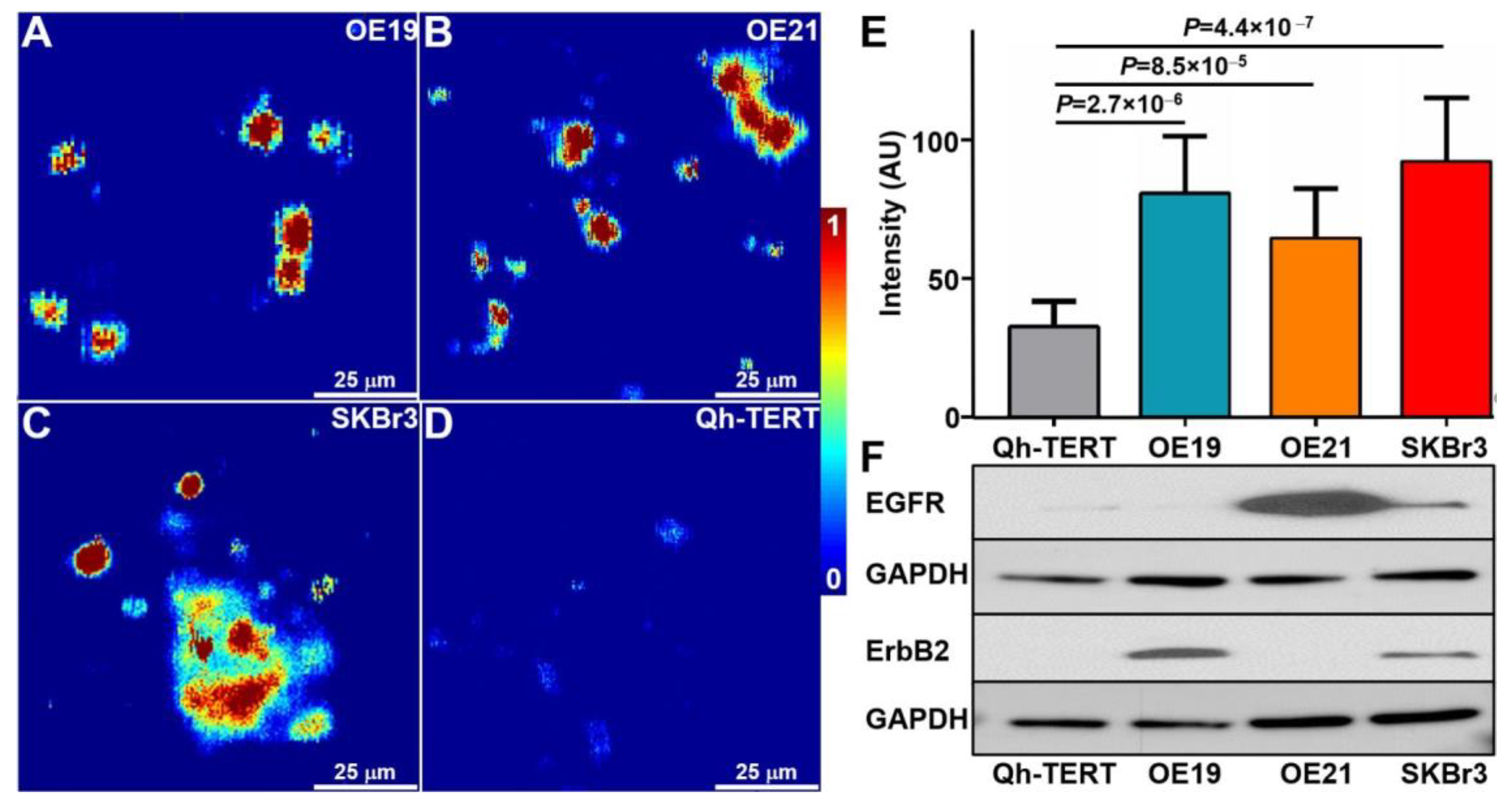
2.4. Photoacoustic Microscopy of Cells
2.5. Photoacoustic Imaging
2.6. CT Imaging
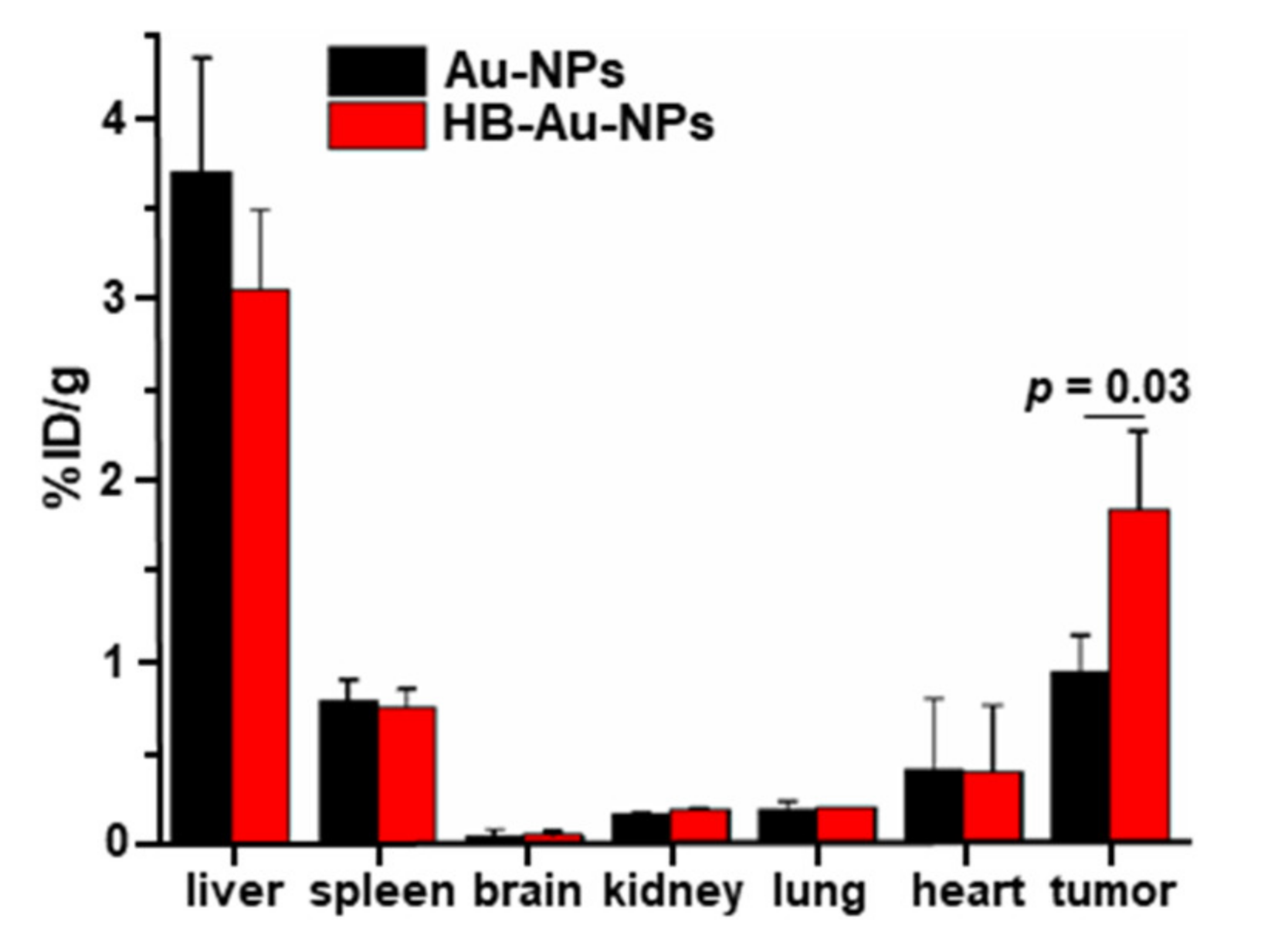
2.7. Nanoparticle Biodistribution
2.8. Animal Toxicity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation and Characterization of HB-Au-NPs
4.3. Nanoparticle Characterization
4.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
4.5. Photoacoustic Microscopy of Cells
4.6. Photoacoustic Imaging
4.7. CT Imaging
4.8. Animal Toxicity
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arnal, M.J.D.; Arenas, Á.F.; Arbeloa, Á.L. Esophageal cancer: Risk factors, screening and endoscopic treatment in Western and Eastern countries. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 7933–7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, J.; McAdam, E.; Danikas, A.; Tselepis, C.; Griffiths, P.; Baxter, J.; Thomas, L.; Manson, J.; Jenkins, G. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is overexpressed in high-grade dysplasia and adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and may represent a biomarker of histological progression in Barrett’s esophagus (BE). Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Bandla, S.; Godfrey, T.E.; Tan, D.; Luketich, J.D.; Pennathur, A.; Qiu, X.; Hicks, D.G.; Peters, J.H.; Zhou, Z. HER2 amplification, overexpression and score criteria in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dulak, A.M.; Schumacher, S.E.; van Lieshout, J.; Imamura, Y.; Fox, C.; Shim, B.; Ramos, A.H.; Saksena, G.; Baca, S.C.; Baselga, J.; et al. Gastrointestinal adenocarcinomas of the esophagus, stomach, and colon exhibit distinct patterns of genome instability and oncogenesis. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 4383–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dulak, A.M.; Stojanov, P.; Peng, S.; Lawrence, M.S.; Fox, C.; Stewart, C.; Bandla, S.; Imamura, Y.; Schumacher, S.E.; Shefler, E.; et al. Exome and whole-genome sequencing of esophageal adenocarcinoma identifies recurrent driver events and mutational complexity. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.T.; Moy, J.R.; Lin, L.; Schipper, M.; Normolle, D.; Brenner, D.E.; Iannettoni, M.D.; Orringer, M.B.; Beer, D.G. Gene amplification in esophageal adenocarcinomas and Barrett’s with high-grade dysplasia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 4819–4825. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.V.; Hu, S. Photoacoustic Tomography: In Vivo Imaging from Organelles to Organs. Science 2012, 335, 1458–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fu, Q.; Zhu, R.; Song, J.; Yang, H.; Chen, X. Photoacoustic Imaging: Contrast Agents and Their Biomedical Applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.; Beard, P.C.; Bohndiek, S.E. Contrast agents for molecular photoacoustic imaging. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Rao, J.; Pu, K. Recent progress on semiconducting polymer nanoparticles for molecular imaging and cancer phototherapy. Biomaterials 2018, 155, 217–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Choi, S.H.; Hyeon, T. Nano-Sized CT Contrast Agents. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2641–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, L.R. The Beatles, the Nobel Prize, and CT scanning of the chest. Radiol. Clin. North. Am. 2010, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusic, H.; Grinstaff, M.W. X-ray-Computed Tomography Contrast Agents. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1641–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.B.; Watson, A.D. Metal-Based X-ray Contrast Media. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2353–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallouard, F.; Anton, N.; Choquet, P.; Constantinesco, A.; Vandamme, T. Iodinated blood pool contrast media for preclinical X-ray imaging applications—A review. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6249–6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Daftary, A. Iodinated Contrast Media and Their Adverse Reactions. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2008, 36, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.L.; Cohan, R.H.; Ellis, J.H.; Adusumilli, S.; Dunnick, N.R. Frequency, Management, and Outcome of Extravasation of Nonionic Iodinated Contrast Medium in 69657 Intravenous Injections. Radiology 2007, 243, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, G.; Wang, T.D. Dual-modal in vivo fluorescence and photoacoustic imaging using a heterodimeric peptide. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 13196–13199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, F.; Duan, X.; Li, G.; Joshi, B.P.; Kuick, R.; Appelman, H.D.; et al. Multiplexed Targeting of Barrett’s Neoplasia with a Heterobivalent Ligand: Imaging Study on Mouse Xenograft in Vivo and Human Specimens ex Vivo. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 5323–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chang, T.S.; Joshi, B.; Zhou, J.; Rubenstein, J.H.; Wamsteker, E.J.; Kwon, R.S.; Appelman, H.; Beer, D.G.; et al. Multiplexed endoscopic imaging of Barrett’s neoplasia using targeted fluorescent heptapeptides in a phase 1 proof-of-concept study. Gut 2021, 70, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebtsov, N.; Dykman, L. Biodistribution and toxicity of engineered gold nanoparticles: A review of in vitro and in vivo studies. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1647–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Qoutah, W.W.; Free, P.; Hobley, J.; Fernig, D.G.; Paramelle, D. Features of Thiolated Ligands Promoting Resistance to Ligand Exchange in Self-Assembled Monolayers on Gold Nanoparticles. Aust. J. Chem. 2012, 65, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Huang, X. Nanoparticles Comprising a Mixed Monolayer for Specific Bindings with Biomolecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12047–12054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchesne, L.; Gentili, D.; Comes-Franchini, M.; Fernig, D.G. Robust Ligand Shells for Biological Applications of Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2008, 24, 13572–13580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Liu, Y.; Luo, M.; Xu, Q.; Ji, X.; He, Z. Peptide-Capped Gold Nanoparticle for Colorimetric Immunoassay of Conjugated Abscisic Acid. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 5010–5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leduc, C.; Si, S.; Gautier, J.; Soto-Ribeiro, M.; Wehrle-Haller, B.; Gautreau, A.; Giannone, G.; Cognet, L.; Lounis, B. A Highly Specific Gold Nanoprobe for Live-Cell Single-Molecule Imaging. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Lévy, R.; Fernig, D.G.; Brust, M. Kinase-Catalyzed Modification of Gold Nanoparticles: A New Approach to Colorimetric Kinase Activity Screening. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2214–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lévy, R.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Doty, R.C.; Hussain, I.; Nichols, R.J.; Schiffrin, D.J.; Brust, M.; Fernig, D.G. Rational and Combinatorial Design of Peptide Capping Ligands for Gold Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10076–10084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, X. Gold nanoparticles for photoacoustic imaging. Nanomedicine 2015, 10, 299–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Popovtzer, R.; Agrawal, A.; Kotov, N.A.; Popovtzer, A.; Balter, J.; Carey, T.E.; Kopelman, R. Targeted Gold Nanoparticles Enable Molecular CT Imaging of Cancer. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4593–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsvirkun, D.; Ben-Nun, Y.; Merquiol, E.; Zlotver, I.; Meir, K.; Weiss-Sadan, T.; Matok, I.; Popovtzer, R.; Blum, G. CT Imaging of Enzymatic Activity in Cancer Using Covalent Probes Reveal a Size-Dependent Pattern. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 12010–12020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, L.; Liang, X.; Deng, Z.; Feng, S.; Li, X.; Huang, M.; Li, C.; Dai, Z. Prussian blue coated gold nanoparticles for simultaneous photoacoustic/CT bimodal imaging and photothermal ablation of cancer. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 5814–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheheltani, R.; Ezzibdeh, R.M.; Chhour, P.; Pulaparthi, K.; Kim, J.; Jurcova, M.; Hsu, J.C.; Blundell, C.; Litt, H.I.; Ferrari, V.A.; et al. Tunable, biodegradable gold nanoparticles as contrast agents for computed tomography and photoacoustic imaging. Biomaterials 2016, 102, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foreman, K.W. A general model for predicting the binding affinity of reversibly and irreversibly dimerized ligands. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Fu, F.; Xiong, Z.; Shen, M.; Shi, X. Dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles modified with RGD peptide and alpha-tocopheryl succinate enable targeted theranostics of cancer cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 133, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, N.; Kattumuri, V.; Shukla, R.; Zambre, A.; Katti, K.; Upendran, A.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Kan, P.; Fent, G.M.; Casteel, S.W.; et al. Bombesin functionalized gold nanoparticles show in vitro and in vivo cancer receptor specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8760–8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, T.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, M.S. Multimodality Assessment of Esophageal Cancer: Preoperative Staging and Monitoring of Response to Therapy. Radiographics 2009, 29, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, C.; Tung, G.A.; Sun, S. Size and Concentration Effect of Gold Nanoparticles on X-ray Attenuation As Measured on Computed Tomography. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 4167–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Nguyen, V.P.; Jaiswal, S.; Kang, X.; Lee, M.; Paulus, Y.M.; Wang, T.D. Thin Layer-Protected Gold Nanoparticles for Targeted Multimodal Imaging with Photoacoustic and CT. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111075
Chen J, Nguyen VP, Jaiswal S, Kang X, Lee M, Paulus YM, Wang TD. Thin Layer-Protected Gold Nanoparticles for Targeted Multimodal Imaging with Photoacoustic and CT. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(11):1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111075
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jing, Van Phuc Nguyen, Sangeeta Jaiswal, Xiaoyu Kang, Miki Lee, Yannis M. Paulus, and Thomas D. Wang. 2021. "Thin Layer-Protected Gold Nanoparticles for Targeted Multimodal Imaging with Photoacoustic and CT" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 11: 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111075
APA StyleChen, J., Nguyen, V. P., Jaiswal, S., Kang, X., Lee, M., Paulus, Y. M., & Wang, T. D. (2021). Thin Layer-Protected Gold Nanoparticles for Targeted Multimodal Imaging with Photoacoustic and CT. Pharmaceuticals, 14(11), 1075. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14111075