Immunogenicity of Multiple Doses of pDNA Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
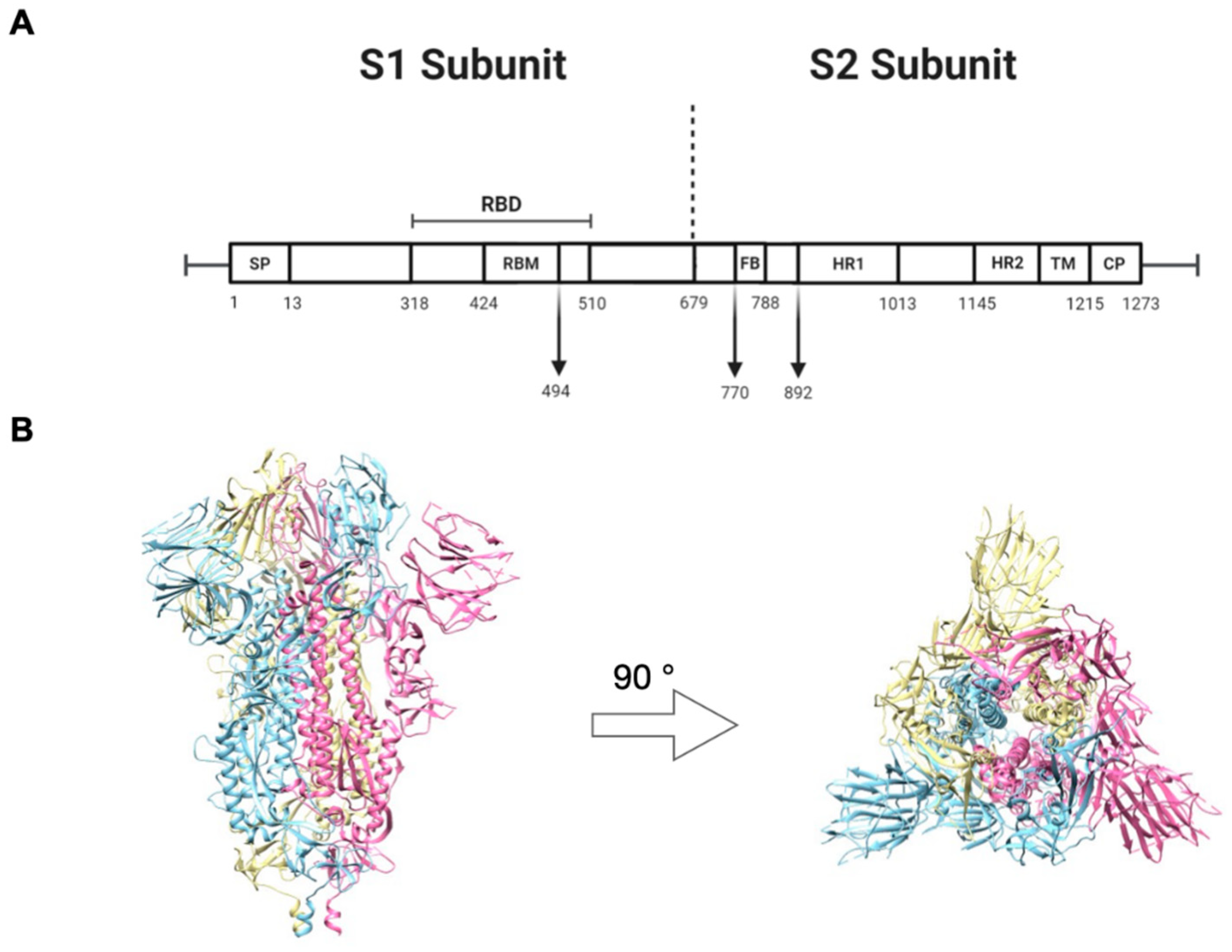
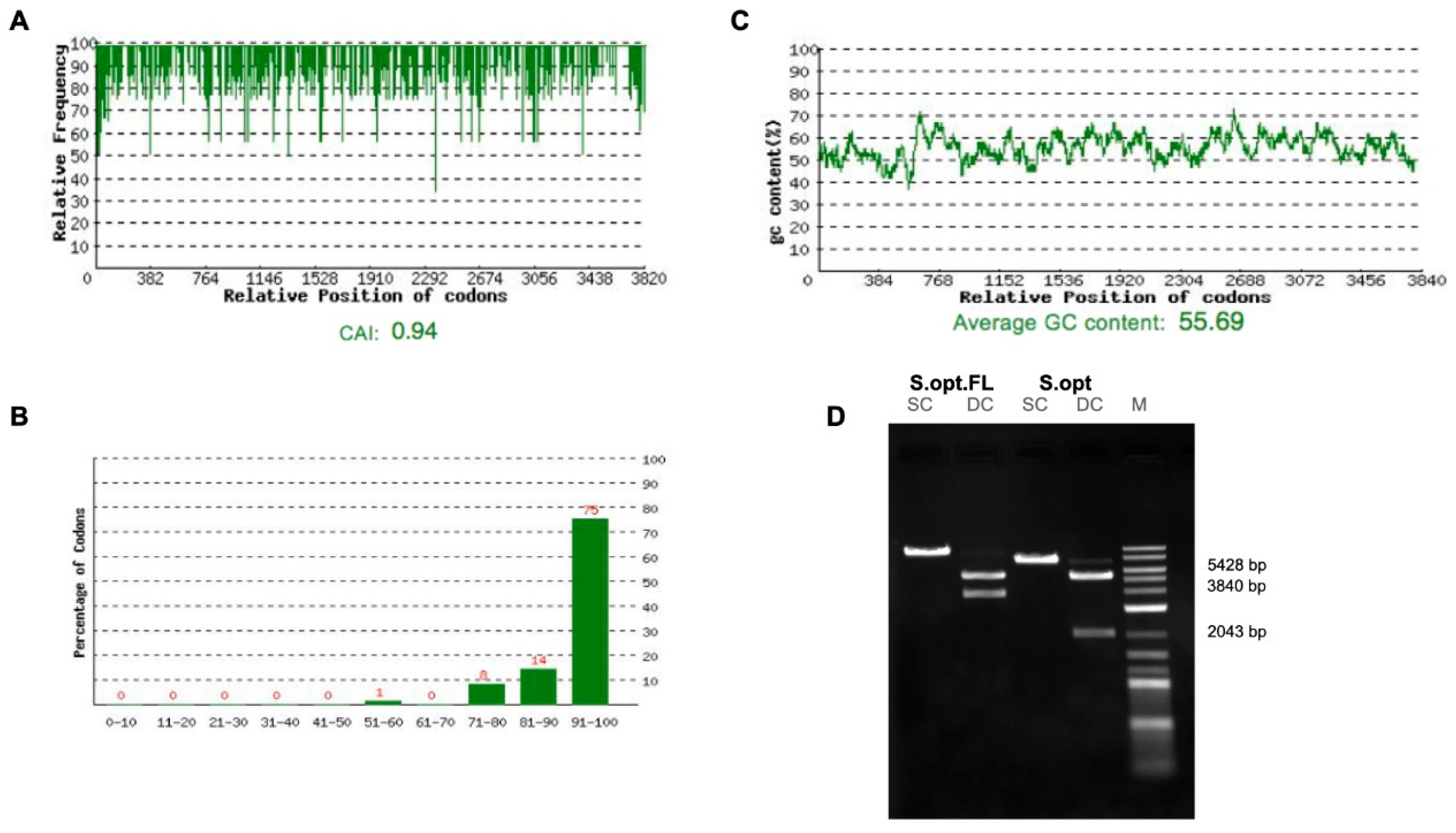
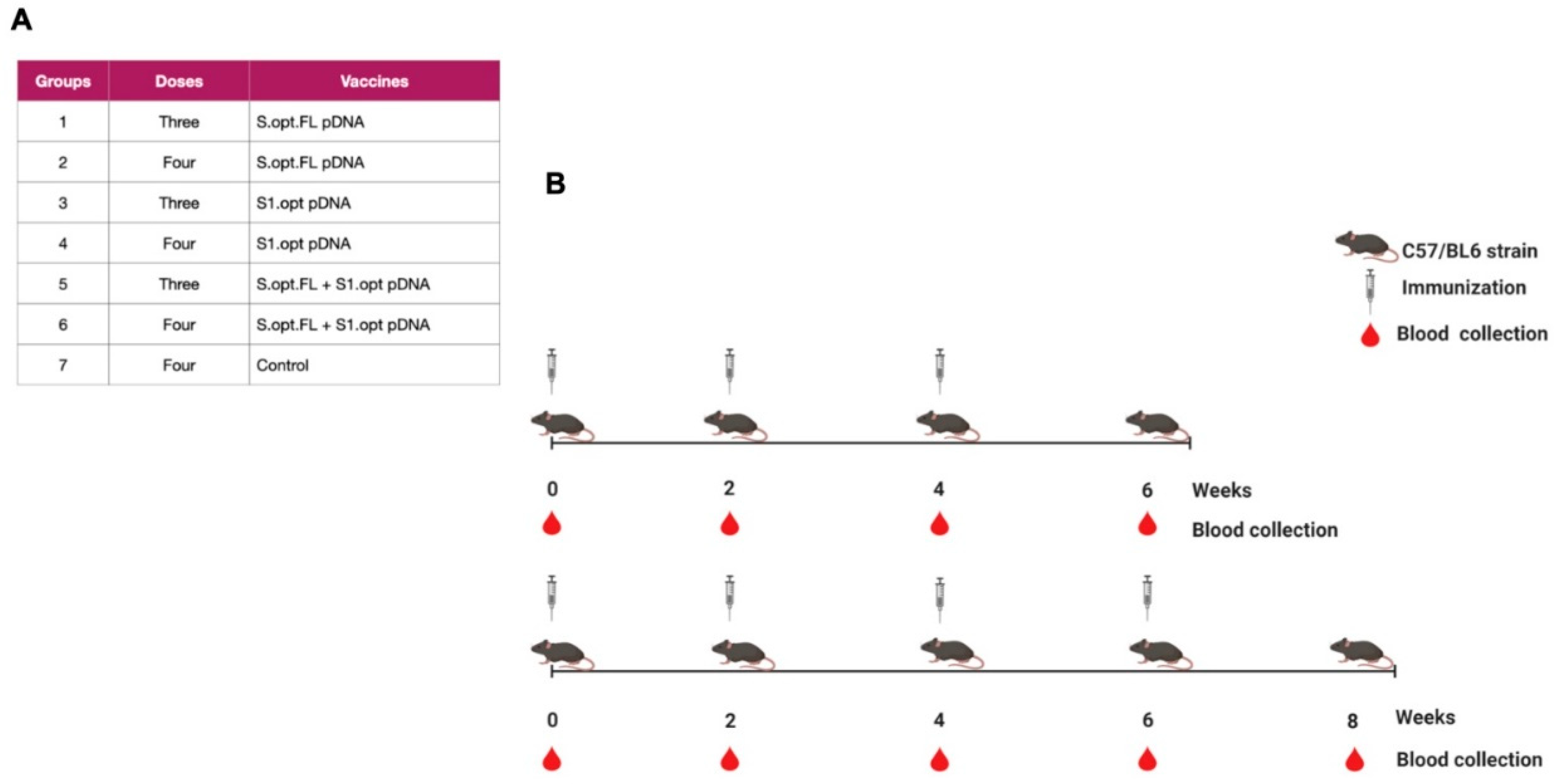
2.1. Construct Optimization and Vaccination Strategy
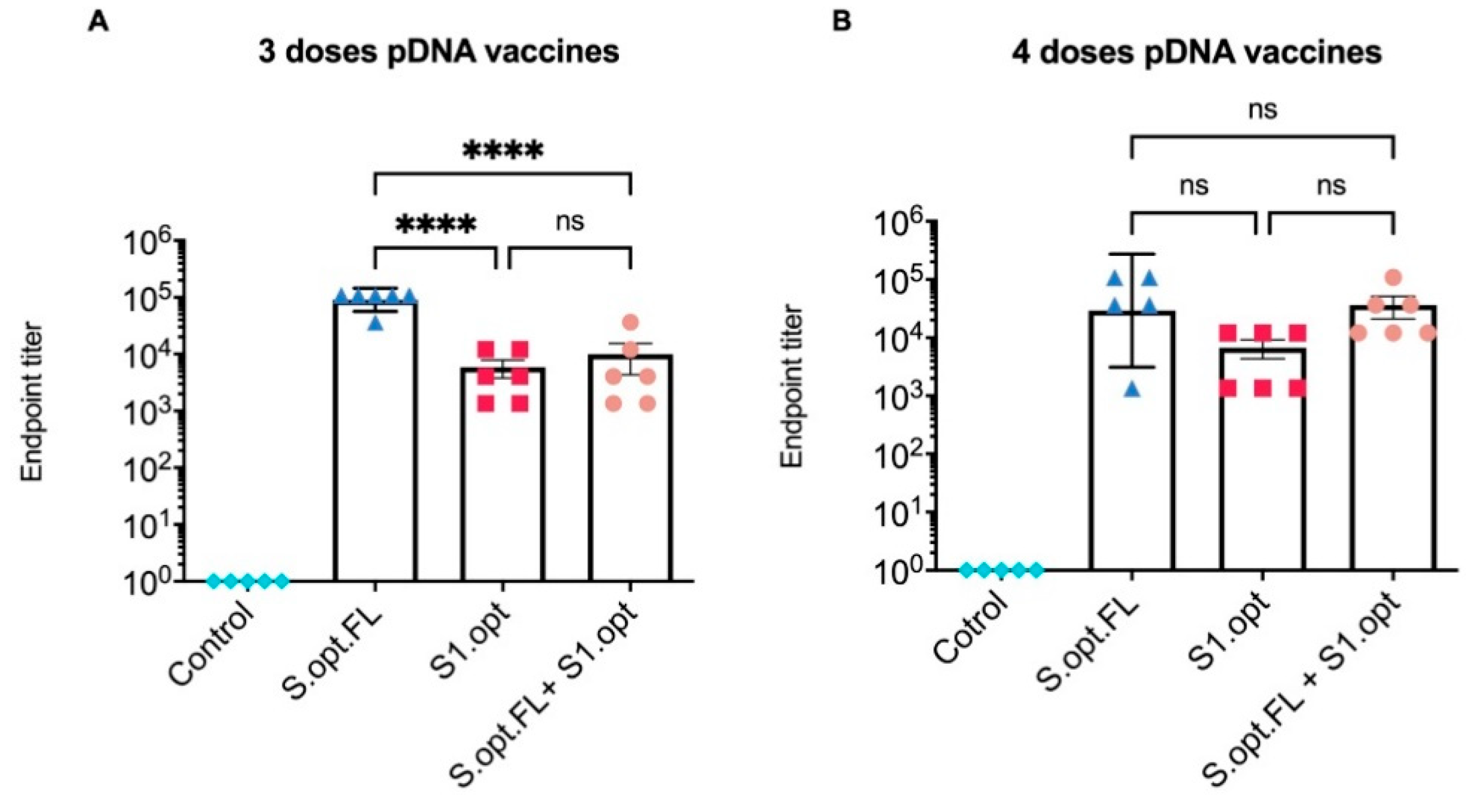
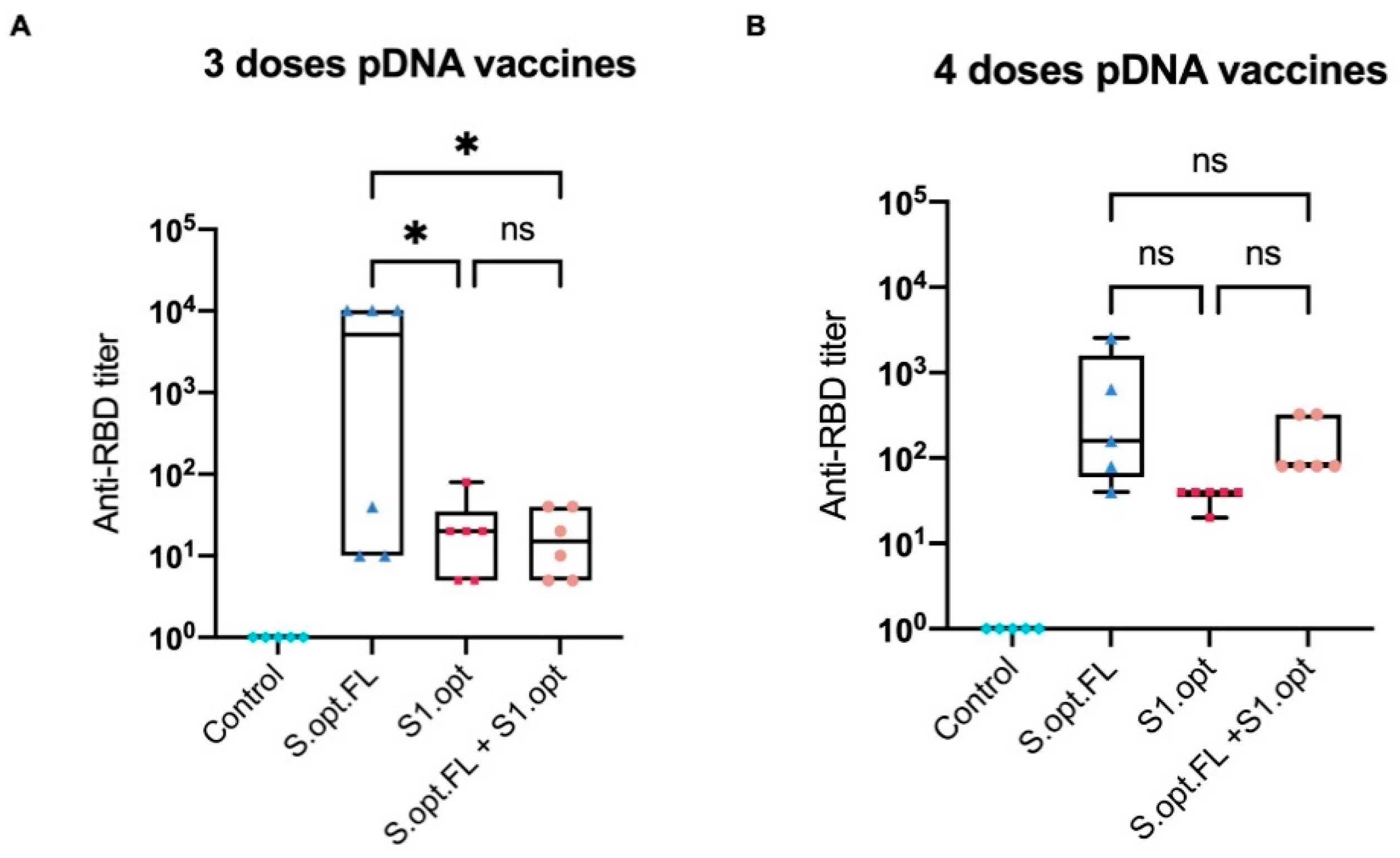
2.2. Immunogenicity in Mice: Production of Binding Antibodies
2.3. Immunogenicity in Mice: Production of Neutralizing Antibodies
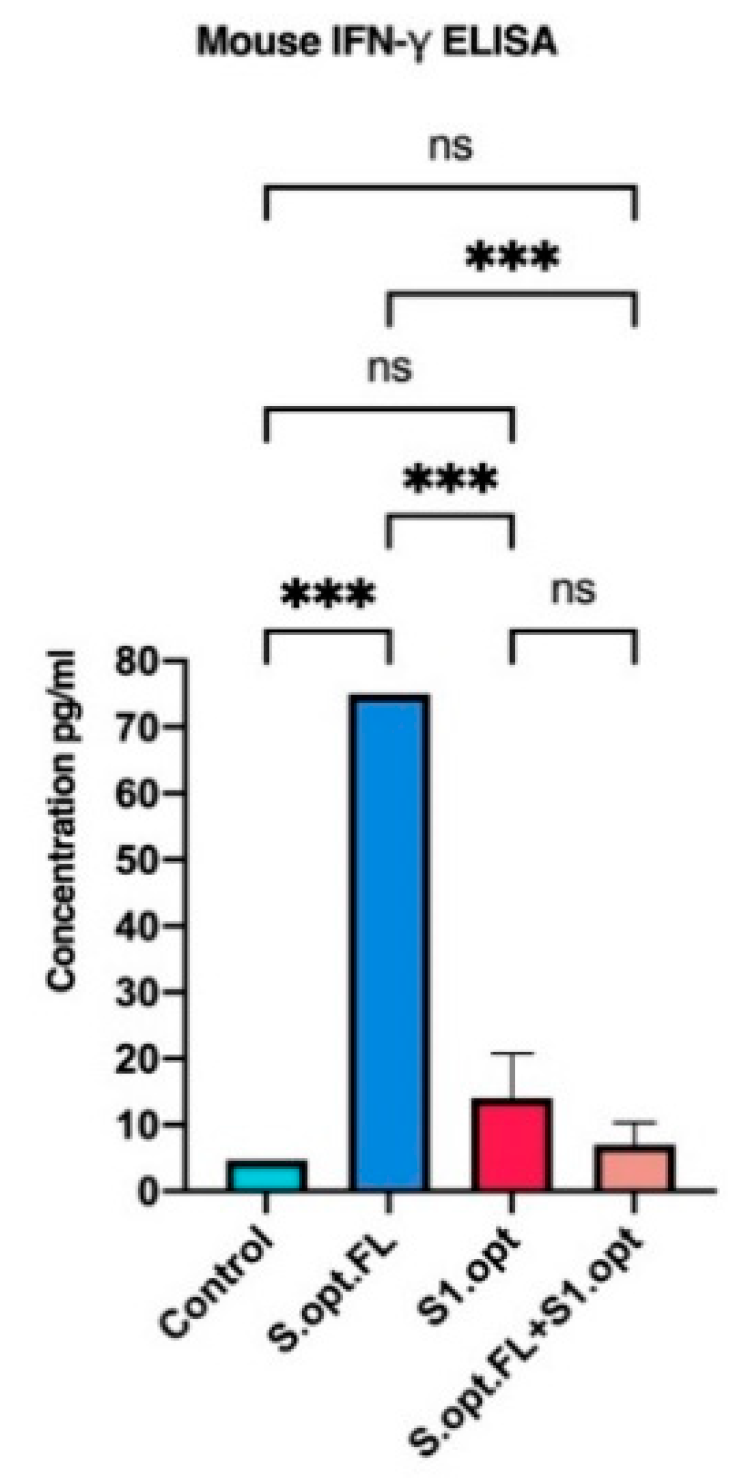
2.4. Immunogenicity in Mice: Production of IFN-γ
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. pDNA Vaccine Constructs
4.3. Immunizations
4.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.5. Neutralization Assay
4.6. IFN-γ
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Drosten, C.; Günther, S.; Preiser, W.; van der Werf, S.; Brodt, H.; Becker, S.; Rabenau, H.; Panning, M.; Kolesnikova, L.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus in patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ksiazek, T.G.; Erdman, D.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Zaki, S.R.; Peret, T.; Emery, S.; Tong, S.; Urbani, C.; Comer, J.A.; Lim, W.; et al. A novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1953–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaki, A.M.; Van Boheemen, S.; Bestebroer, T.M.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1814–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.-L.; Wang, Y.-M.; Wu, Z.-Q.; Xiang, Z.-C.; Guo, L.; Xu, T.; Jiang, Y.-Z.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.-J.; Li, X.-W.; et al. Identification of a novel coronavirus causing severe pneumonia in human: A descriptive study. Chin. Med. J. 2020, 133, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Zhang, D.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Yang, B.; Song, J.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Shi, W.; Lu, R.; et al. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahase, E. Covid-19: UK approves Pfizer and BioNTech vaccine with rollout due to start next week. BMJ 2020, 371, m4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahase, E. Covid-19: Moderna applies for US and EU approval as vaccine trial reports 94.1% efficacy. BMJ Br. Med. J. 2020, 371, m4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Qian, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z. Single cell RNA sequencing of 13 human tissues identify cell types and receptors of human coronaviruses. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 526, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letko, M.; Marzi, A.; Munster, V. Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, X.; Liu, Y.; Lei, X.; Li, P.; Mi, D.; Ren, L.; Guo, L.; Guo, R.; Chen, T.; Hu, J.; et al. Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Hillyer, C.; Du, L. Neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and other human coronaviruses. Trends Immunol. 2020, 41, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, A.T.; Garcia-Carreras, B.; Hitchings, M.D.T.; Yang, B.; Katzelnick, L.C.; Rattigan, S.M.; Borgert, B.A.; Moreno, C.A.; Solomon, B.D.; Trimmer-Smith, L.; et al. A systematic review of antibody mediated immunity to coronaviruses: Kinetics, correlates of protection, and association with severity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callow, K.A.; Parry, H.F.; Sergeant, M.; Tyrrell, D.A.J. The time course of the immune response to experimental coronavirus infection of man. Epidemiol. Infect. 1990, 105, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Pan, Z.; Yue, S.; Yu, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Liu, B.; Yang, X.; Gao, L.; et al. Disease severity dictates SARS-CoV-2-specific neutralizing antibody responses in COVID-19. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Lu, S. DNA immunization. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2013, 31, 18.3.1–18.3.24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Song, L. Novel antibody epitopes dominate the antigenicity of spike glycoprotein in SARS-CoV-2 compared to SARS-CoV. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 536–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansour, I.; Alhagri, M. MMRdb: Measles, mumps, and rubella viruses database and analysis resource. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 75, 103982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansour, I.; Alfares, R.; Aljofi, H. Large-scale analysis of B-cell epitopes of envelope: Implications for Zika vaccine and immunotherapeutic development. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansour, I.; Alhagri, M.; Alfares, R.; Alshehri, M.; Bakhashwain, R.; Maarouf, A. IRAM: Virus capsid database and analysis resource. Database 2019, 2019, baz079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almansour, I.; Macadato, N.C.; Alshammari, T. Immunogenicity of Multiple Doses of pDNA Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14010039
Almansour I, Macadato NC, Alshammari T. Immunogenicity of Multiple Doses of pDNA Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. Pharmaceuticals. 2021; 14(1):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14010039
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmansour, Iman, Nabela Calamata Macadato, and Thamer Alshammari. 2021. "Immunogenicity of Multiple Doses of pDNA Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2" Pharmaceuticals 14, no. 1: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14010039
APA StyleAlmansour, I., Macadato, N. C., & Alshammari, T. (2021). Immunogenicity of Multiple Doses of pDNA Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2. Pharmaceuticals, 14(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14010039




