Safety of Repeated Administration of Parenteral Ketamine for Depression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
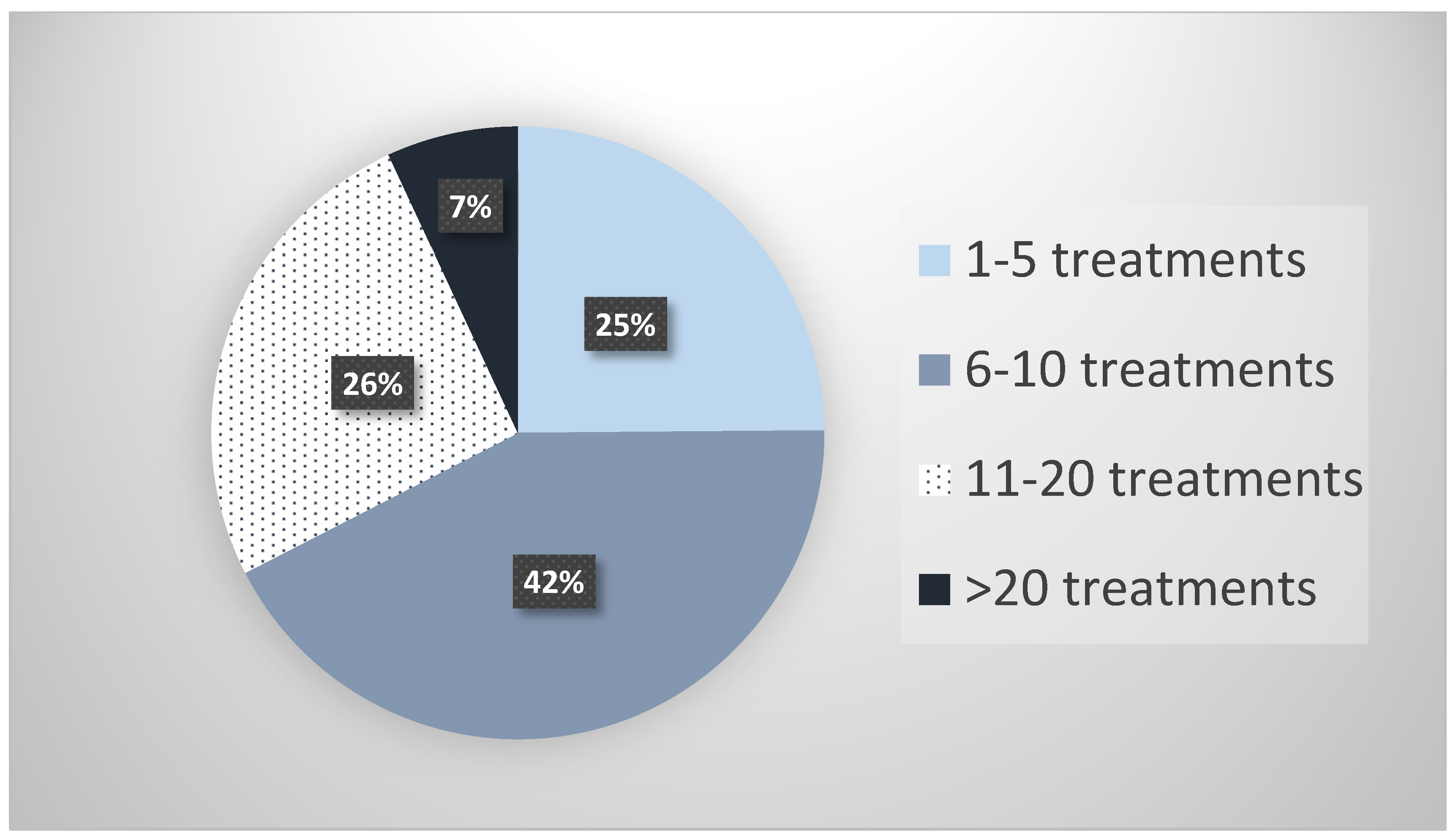
2.1. Survey
2.2. Literature Review
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Survey
4.2. Literature Review
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donisi, V.; Tedeschi, F.; Salazzari, D.; Amaddeo, F. Pre- and post-discharge factors influencing early readmission to acute psychiatric wards: Implications for quality-of-care indicators in psychiatry. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2016, 39, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, M.J. Depression Is the Leading Cause of Disability Around the World. JAMA 2017, 317, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, A.J.; Trivedi, M.H.; Wisniewski, S.R.; Nierenberg, A.A.; Stewart, J.W.; Warden, D.; Niederehe, G.; Thase, M.E.; Lavori, P.W.; Lebowitz, B.D.; et al. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: A STAR*D report. Am. J. Psychiatry 2006, 163, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazidou, E. The neurobiology of depression. Br. Med. Bull. 2012, 101, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketalar [Package Insert] Chestnut Rige, NY. PAR Pharmaceuticals. 2017. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/016812s043lbl.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Fond, G.; Loundou, A.; Rabu, C.; Macgregor, A.; Lancon, C.; Brittner, M.; Micoulaud-Franchi, J.A.; Richieri, R.; Courtet, P.; Abbar, M.; et al. Ketamine administration in depressive disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 3663–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spravato (esketamine) Nasal Spray Precribing Information. Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.: Titusville, NJ, USA, 2019. Available online: https://www.janssenlabels.com/package-insert/product-monograph/prescribing-information/SPRAVATO.-pi.pdf (accessed on 13 November 2019).
- Nemeroff, C.B. Ketamine: Quo Vadis? Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, D.; Wu, B.; Zhou, W. Ketamine abuse potential and use disorder. Brain Res. Bull. 2016, 126, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahani, R.; Streutker, C.; Dickson, B.; Stewart, R.J. Ketamine-associated ulcerative cystitis: A new clinical entity. Urology 2007, 69, 810–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahti, A.C.; Weiler, M.A.; Tamara Michaelidis, B.A.; Parwani, A.; Tamminga, C.A. Effects of ketamine in normal and schizophrenic volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 2001, 25, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, C.J.; Curran, H.V.; Independent Scientific Committee on Drugs (ISCD). Ketamine use: A review. Addiction 2012, 107, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsi, S.S.; Wood, D.M.; Dargan, P.I. The epidemiology and patterns of acute and chronic toxicity associated with recreational ketamine use. Emerg. Health Threats J. 2011, 4, 7107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, B.; Fong, J.; Galvez, V.; Shelker, W.; Loo, C.K. Side-effects associated with ketamine use in depression: A systematic review. Lancet Psychiatry 2018, 5, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.T.; Toprak, M.; Turner, M.S.; Levine, S.P.; Katz, R.B.; Sanacora, G. A Survey of the Clinical, Off-Label Use of Ketamine as a Treatment for Psychiatric Disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2017, 174, 695–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaya, A.M.C.; Choi, J.K.; Lee, C.S.; Oh, E.; Kim, Y.; Moon, J.Y.; Lee, P.B.; Kim, Y.C. Ketamine infusion therapy for chronic pain management in South Korea: A national survey for pain physicians with a narrative review. Medicine 2018, 97, e11709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckland, D.M.; Crowe, R.P.; Cash, R.E.; Gondek, S.; Maluso, P.; Sirajuddin, S.; Smith, E.R.; Dangerfield, P.; Shapiro, G.; Wanka, C.; et al. Ketamine in the Prehospital Environment: A National Survey of Paramedics in the United States. Prehosp. Disaster Med. 2018, 33, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, M.M.; Umoren, R.A.; Harris, S.; Strandjord, T.P.; Sawyer, T. Use and perceived safety of stylets for neonatal endotracheal intubation: A national survey. J. Perinatol. 2018, 38, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- aan het Rot, M.; Collins, K.A.; Murrough, J.W.; Perez, A.M.; Reich, D.L.; Charney, D.S.; Mathew, S.J. Safety and efficacy of repeated-dose intravenous ketamine for treatment-resistant depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrough, J.W.; Perez, A.M.; Pillemer, S.; Stern, J.; Parides, M.K.; aan het Rot, M.; Collins, K.A.; Mathew, S.J.; Charney, D.S.; Iosifescu, D.V. Rapid and longer-term antidepressant effects of repeated ketamine infusions in treatment-resistant major depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zheng, W.; Liu, W.; Wang, C.; Zhan, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Li, M.; Ning, Y. Neurocognitive effects of six ketamine infusions and the association with antidepressant response in patients with unipolar and bipolar depression. J. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 32, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, S.; Chrenek, C.; Swainson, J. Maintenance Ketamine Therapy for Treatment-Resistant Depression. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2018, 38, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.T.; Katz, R.B.; Toprak, M.; Webler, R.; Ostroff, R.B.; Sanacora, G. Acute and Longer-Term Outcomes Using Ketamine as a Clinical Treatment at the Yale Psychiatric Hospital. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2018, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.L.; Norris, S.; Talbot, J.; Birmingham, M.; Hatchard, T.; Ortiz, A.; Owoeye, O.; Batten, L.A.; Blier, P. Single, Repeated, and Maintenance Ketamine Infusions for Treatment-Resistant Depression: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Psychiatry 2019, 176, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vande Voort, J.L.; Morgan, R.J.; Kung, S.; Rasmussen, K.G.; Rico, J.; Palmer, B.A.; Schak, K.M.; Tye, S.J.; Ritter, M.J.; Frye, M.A.; et al. Continuation phase intravenous ketamine in adults with treatment-resistant depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2016, 206, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ionescu, D.F.; Swee, M.B.; Pavone, K.J.; Taylor, N.; Akeju, O.; Baer, L.; Nyer, M.; Cassano, P.; Mischoulon, D.; Alpert, J.E.; et al. Rapid and Sustained Reductions in Current Suicidal Ideation Following Repeated Doses of Intravenous Ketamine: Secondary Analysis of an Open-Label Study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2016, 77, e719–e725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, D.F.; Bentley, K.H.; Eikermann, M.; Taylor, N.; Akeju, O.; Swee, M.B.; Pavone, K.J.; Petrie, S.R.; Dording, C.; Mischoulon, D.; et al. Repeat-dose ketamine augmentation for treatment-resistant depression with chronic suicidal ideation: A randomized, double blind, placebo controlled trial. J. Affect. Disord. 2019, 243, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.B.; Fedgchin, M.; Daly, E.J.; De Boer, P.; Cooper, K.; Lim, P.; Pinter, C.; Murrough, J.W.; Sanacora, G.; Shelton, R.C.; et al. A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Frequency Study of Intravenous Ketamine in Patients With Treatment-Resistant Depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2016, 173, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiroma, P.R.; Johns, B.; Kuskowski, M.; Wels, J.; Thuras, P.; Albott, C.S.; Lim, K.O. Augmentation of response and remission to serial intravenous subanesthetic ketamine in treatment resistant depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2014, 155, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, P.R.; Farmery, A.D.; Atkinson, S.; Haldar, J.; Williams, N.; Cowen, P.J.; Geddes, J.R.; McShane, R. Ketamine infusions for treatment resistant depression: A series of 28 patients treated weekly or twice weekly in an ECT clinic. J. Psychopharmacol. 2014, 28, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, K.A.; Altinay, M.; Finnegan, N.; Cromer, K.; Dale, R.M. Effects of Repeated Intravenous Ketamine in Treatment-Resistant Geriatric Depression: A Case Series. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 39, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.; Galvez, V.; Martin, D.; Kumar, D.; Leyden, J.; Hadzi-Pavlovic, D.; Harper, S.; Brodaty, H.; Glue, P.; Taylor, R.; et al. Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial of Titrated Subcutaneous Ketamine in Older Patients with Treatment-Resistant Depression. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2017, 25, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albott, C.S.; Lim, K.O.; Forbes, M.K.; Erbes, C.; Tye, S.J.; Grabowski, J.G.; Thuras, P.; Batres, Y.C.T.M.; Wels, J.; Shiroma, P.R. Efficacy, Safety, and Durability of Repeated Ketamine Infusions for Comorbid Posttraumatic Stress Disorder and Treatment-Resistant Depression. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2018, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segmiller, F.; Ruther, T.; Linhardt, A.; Padberg, F.; Berger, M.; Pogarell, O.; Moller, H.J.; Kohler, C.; Schule, C. Repeated S-ketamine infusions in therapy resistant depression: A case series. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 53, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymkowicz, S.M.; Finnegan, N.; Dale, R.M. A 12-month naturalistic observation of three patients receiving repeat intravenous ketamine infusions for their treatment-resistant depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 147, 416–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blier, P.; Zigman, D.; Blier, J. On the safety and benefits of repeated intravenous injections of ketamine for depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 72, e11–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Diaz, A.; Fernandez-Gonzalez, J.L.; Lujan-Jimenez, J.E.; Galiano-Rus, S.; Gutierrez-Rojas, L. Use of repeated intravenous ketamine therapy in treatment-resistant bipolar depression with suicidal behaviour: A case report from Spain. Ther. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 7, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, N.R.; Heifets, B.D.; Blasey, C.; Sudheimer, K.; Pannu, J.; Pankow, H.; Hawkins, J.; Birnbaum, J.; Lyons, D.M.; Rodriguez, C.I.; et al. Attenuation of Antidepressant Effects of Ketamine by Opioid Receptor Antagonism. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schak, K.M.; Vande Voort, J.L.; Johnson, E.K.; Kung, S.; Leung, J.G.; Rasmussen, K.G.; Palmer, B.A.; Frye, M.A. Potential Risks of Poorly Monitored Ketamine Use in Depression Treatment. Am. J. Psychiatry 2016, 173, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva-Posse, P.; Reiff, C.M.; Edwards, J.A.; Job, G.P.; Galendez, G.C.; Garlow, S.J.; Saah, T.C.; Dunlop, B.W.; McDonald, W.M. Blood pressure safety of subanesthetic ketamine for depression: A report on 684 infusions. J. Affect. Disord. 2018, 236, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KRIYA Ketamine Research Institute. Available online: https://www.kriyainstitute.com/ (accessed on 24 May 2019).
- Ketamine Advocacy Network. Available online: http://www.ketamineadvocacynetwork.org/mission-and-vision/ (accessed on 24 May 2019).
- SurveyMonkey Inc. San Mateo, California, USA. Available online: www.surveymonkey.com (accessed on 24 May 2019).
| Specialty | N (%) |
| Psychiatry | 14 (51.9%) |
| Anesthesia | 7 (25.9%) |
| Emergency Medicine | 4 (14.8%) |
| Primary Care | 1 (3.7%) |
| Critical Care | 1 (3.7%) |
| Pain and Palliative Care | 0 (0%) |
| Practice Setting | N (%) |
| Private Practice | 25(92.6%) |
| Academic Medical Center | 0 (0%) |
| Non-Academic Medical Center | 2 (7.4%) |
| Adverse Effect | Cases Requiring Discontinuation * N (%) |
|---|---|
| Bladder Dysfunction | 3 (0.06%) |
| Addiction ** | 0 (NA) |
| Psychotic Symptoms | 1 (2%) |
| Cognitive Deficits | 0 (NA) |
| Psychological Distress | 33 (0.5%) |
| Hypomania | 2 (0.03%) |
| Hypertension | 0 (NA) |
| Nausea *** | 6 (0.09%) |
| Respiratory Distress *** | 1 (0.02%) |
| Seizure *** | 1(0.02%) |
| Total | 47 (0.7%) |
| Report | Number of Patients | Ketamine Dose and Rate | Route | Dis-Continuation Due to AE | Other Notable AEs | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aan het Rot et al. [19] | 10 | 0.5 mg/kg /40 min | IV | 0 | 0 | No significant AEs |
| Murrough et al. [20] | 24 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min | IV | 0 | 0 | No significant AEs |
| Zhou et al. [21] | 84 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min | 1 (1.1%) | 0 | One patient withdrew due to a manic switch | |
| Archer et al. [22] | 11 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min | IV | 0 | 0 | No significant AEs |
| Wilkinson et al. [23] | 14 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min | IV | 0 | 0 | No significant AEs |
| Phillips et al. [24] | 41 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min | IV | 0 | 0 | No serious AE and no evidence of craving or drug-seeking behavior during the infusions or follow-up |
| Vande Voort et al. [25] | 12 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min | IV | 0 | 2 (1.7%) | 1 subject developed behavioral outbursts and suicide threats during follow-up while hospitalized, and another died by suicide several weeks after the end of follow-up. Authors did not attribute events these AEs to ketamine treatments |
| Ionescu et al. [26] | 14 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min for first 3 infusions; 75 mg/kg/40 min for last three | IV | Not reported | Not reported | AEs not reported |
| Ionescu et al. [27] | 26 | 0.5 mg/kg/45 min | IV | 0 | 0 | |
| Singh et al. [28] | 21 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min | IV | 0 | 0 | 15–28% (twice weekly infusions) 6–41% (thrice weekly infusions) All symptoms resolved within 3 h of the infusions |
| Shiroma et al. [29] | 12 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min | IV | 0 | 2 (1.7%) | Single episode of vomiting effectively countered by IV labetalol and ondansetron |
| Diamond et al. [30] | 28 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min | IV | 2 (7.1%) | 5 (17.9%) | Two patients discontinued due to adverse reactions |
| Bryant et al. [31] | 6 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min | IV | 0 | 5 (83.3%) | panic attack (n = 1), rapid cycling of mood with a mild hypomanic episode (n = 1), emesis (n = 2) during treatment, symptomatic cystitis (n = 1), and a hypnogogic hallucination (n = 1) |
| George et al. [32] | 10 | 0.3–0.5 mg/kg | SC | 0 | 2 (20%) | One patient reported the urge to urinate slightly more often. One patient had elevated aspartate aminotransferase (42–60) and alanine aminotransferase (25–44) after 12 treatments of 0.5 mg/kg |
| Albott et al. [33] | 15 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min | IV | 0 | 0 | No significant AEs |
| Segmiller et al. [34] | 6 | 0.25 mg/kg/40 min | IV | 1 (16.7%) | 1 (16.7%) | One patient decided to discontinue before receiving all infusions due to the transient dissociative effects |
| Szymkowicz et al. [35] | 3 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min | IV | 0 | 2 (66.7%) | Transient hypomanic states over 12 months |
| Blier et al. [36] | 1 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min for most infusions | IV | 0 | 0 | No significant AEs |
| Lopez-Diaz et al. [37] | 1 | 0.5 mg/kg/40 min | IV | 0 | 1 (100%) | Transient sedation during infusion |
| TOTAL | 339 | 4 (1.2%) | 20 (5.9%) | Combined 24 (7.1%) | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feifel, D.; Dadiomov, D.; C. Lee, K. Safety of Repeated Administration of Parenteral Ketamine for Depression. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13070151
Feifel D, Dadiomov D, C. Lee K. Safety of Repeated Administration of Parenteral Ketamine for Depression. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(7):151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13070151
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeifel, David, David Dadiomov, and Kelly C. Lee. 2020. "Safety of Repeated Administration of Parenteral Ketamine for Depression" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 7: 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13070151
APA StyleFeifel, D., Dadiomov, D., & C. Lee, K. (2020). Safety of Repeated Administration of Parenteral Ketamine for Depression. Pharmaceuticals, 13(7), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13070151




