Characterization of Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Peptides from Soft-Shelled Turtle Yolk Hydrolysate Using Orthogonal Bioassay-Guided Fractionations Coupled with In Vitro and In Silico Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effects of Different Proteases on Hydrolysates’ DPP-IV Activities
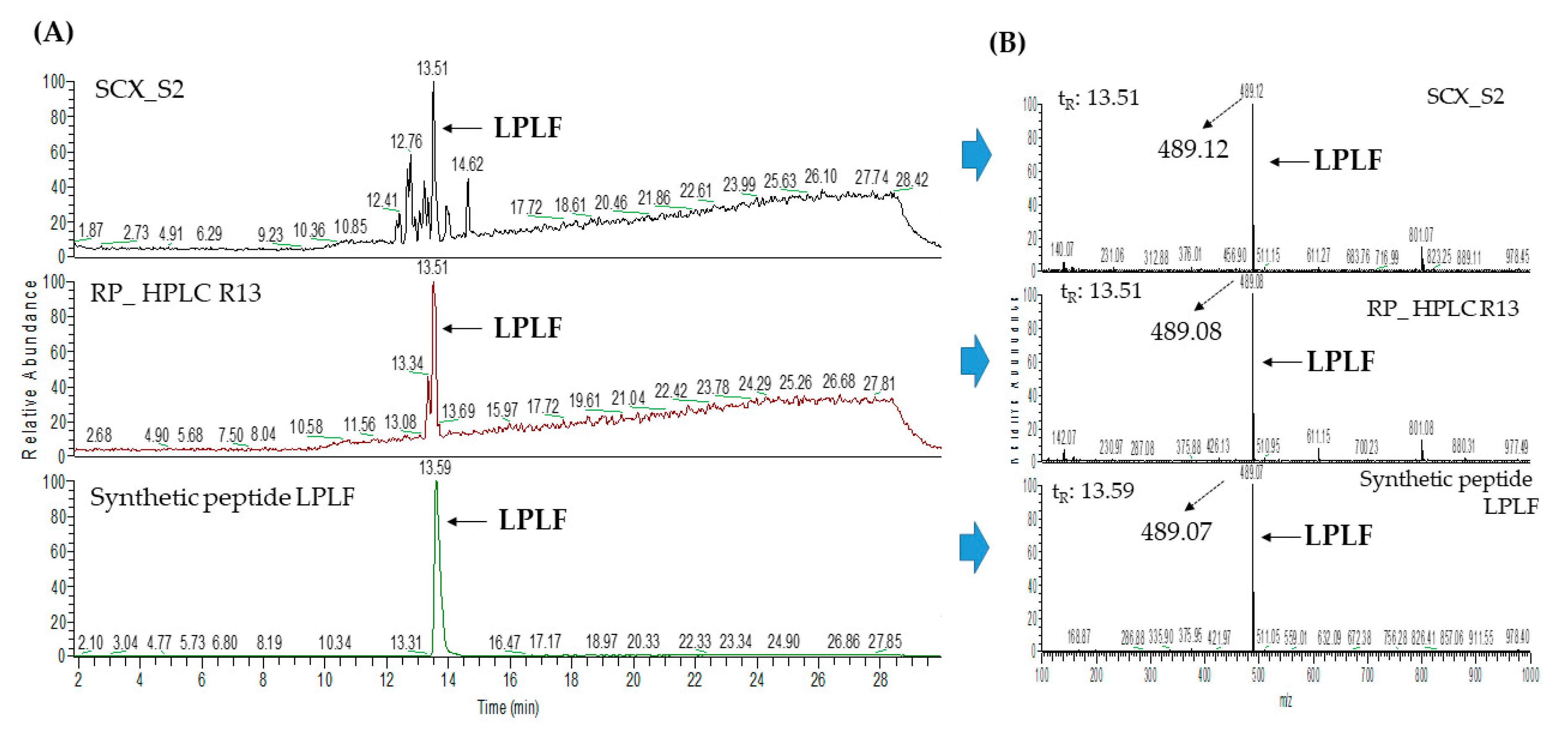
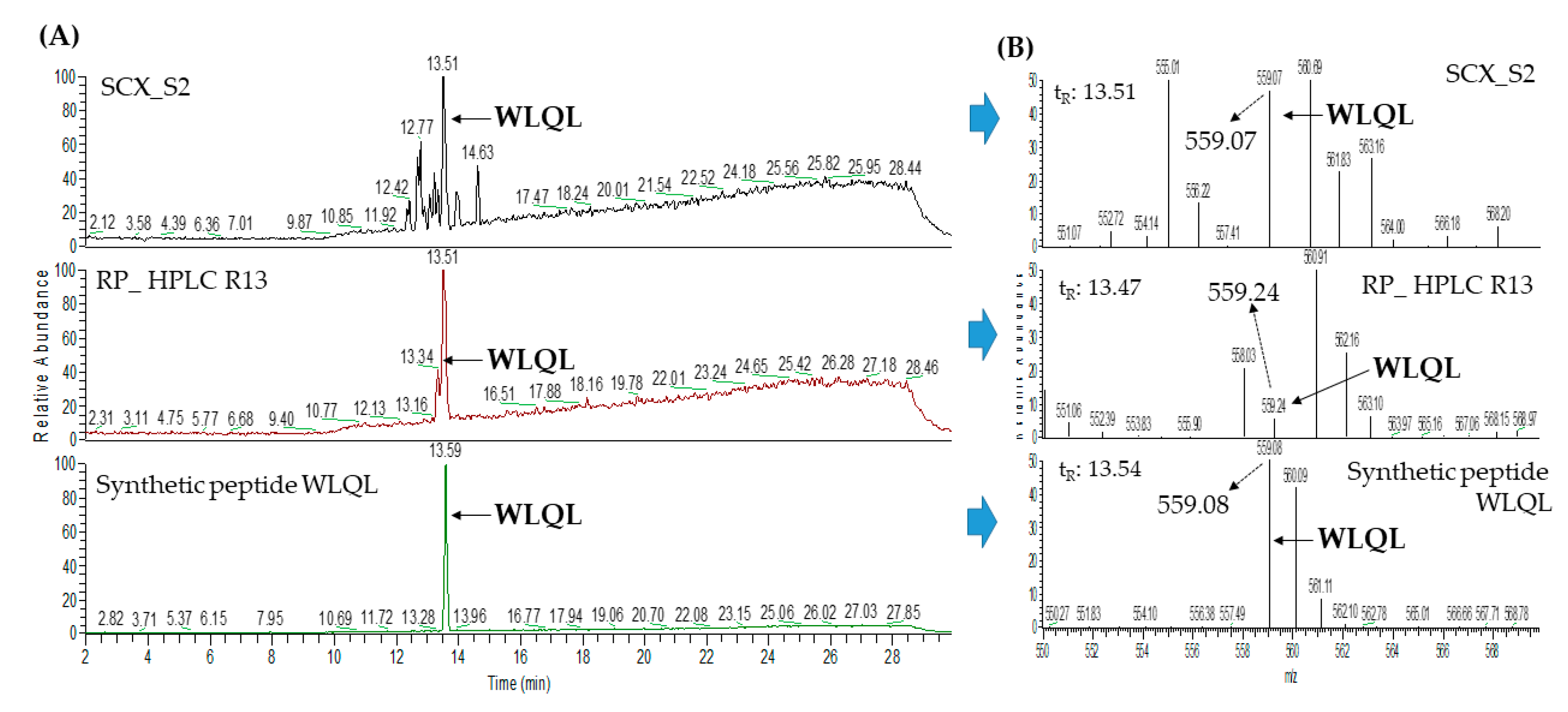
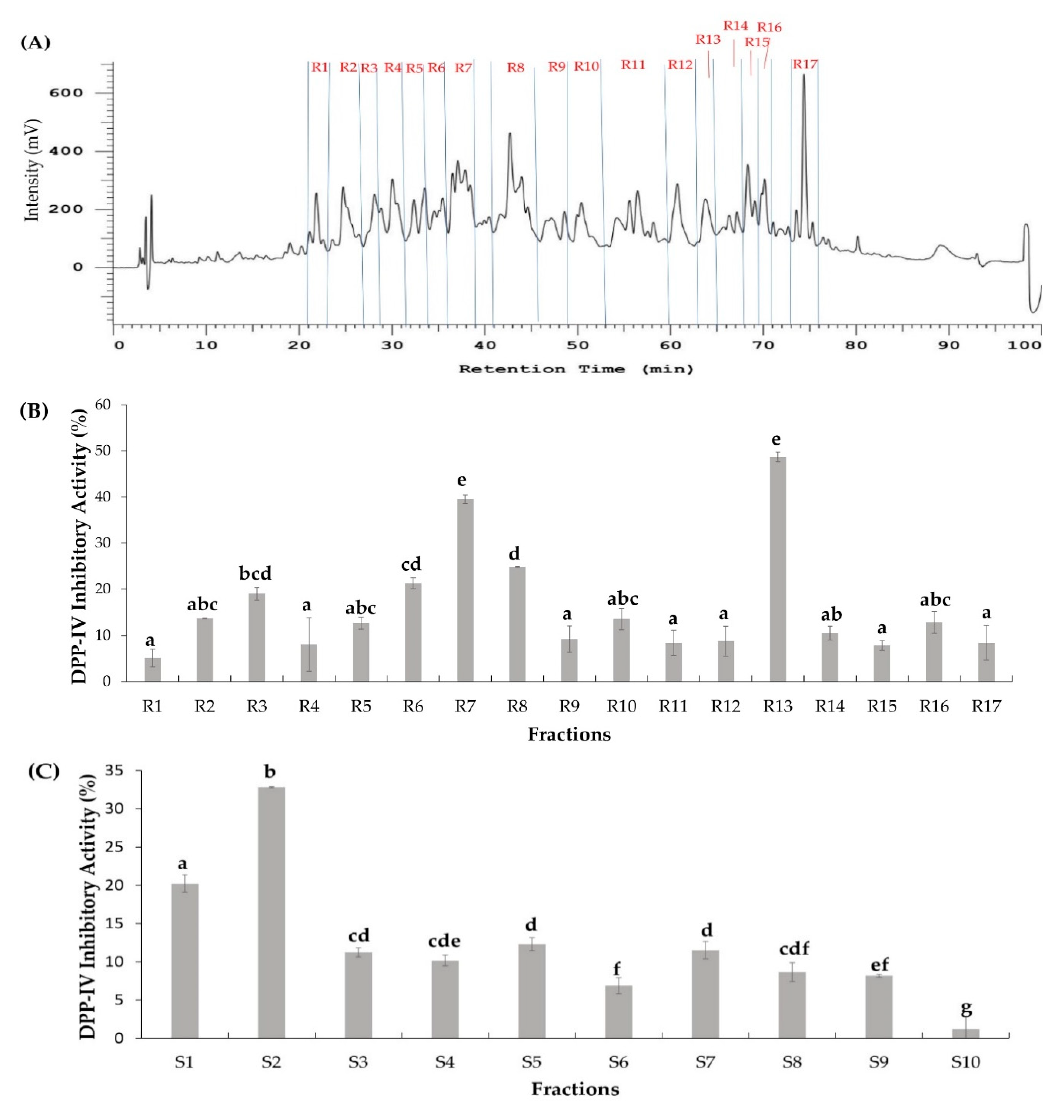
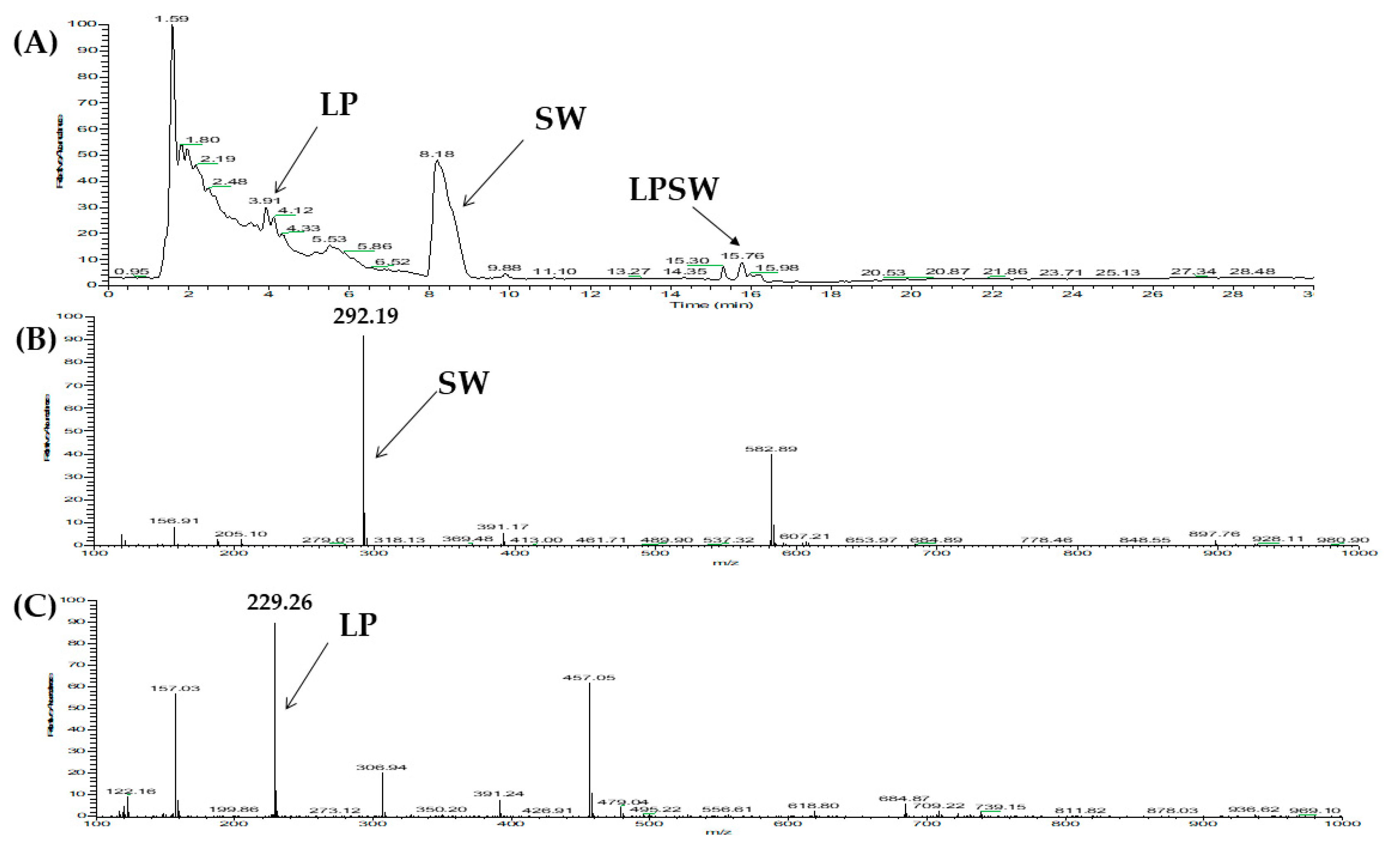
2.2. Two Orthogonal Bioassay-Guided Fractionations of SSTY Gastrointestinal Hydrolysate
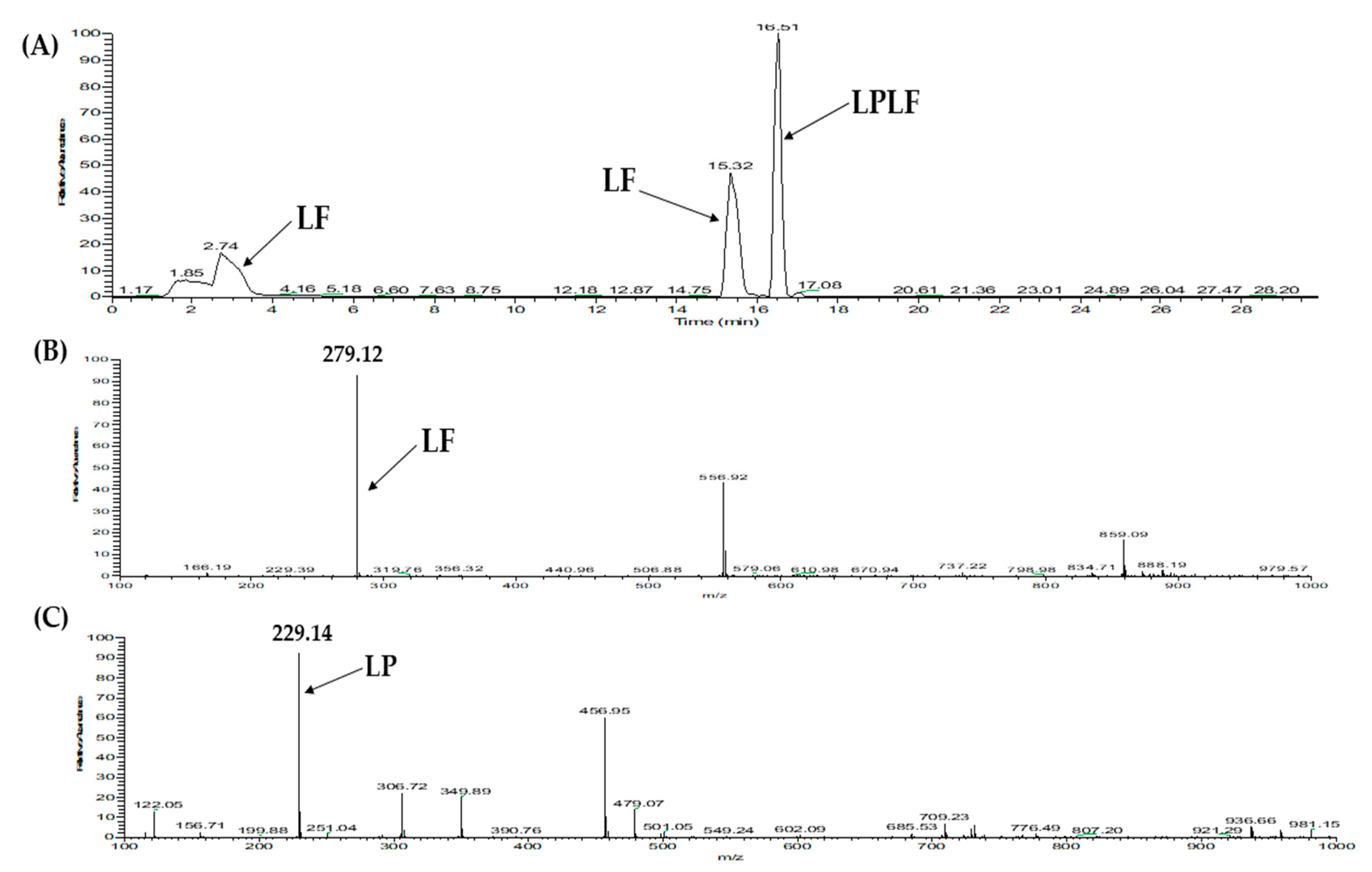
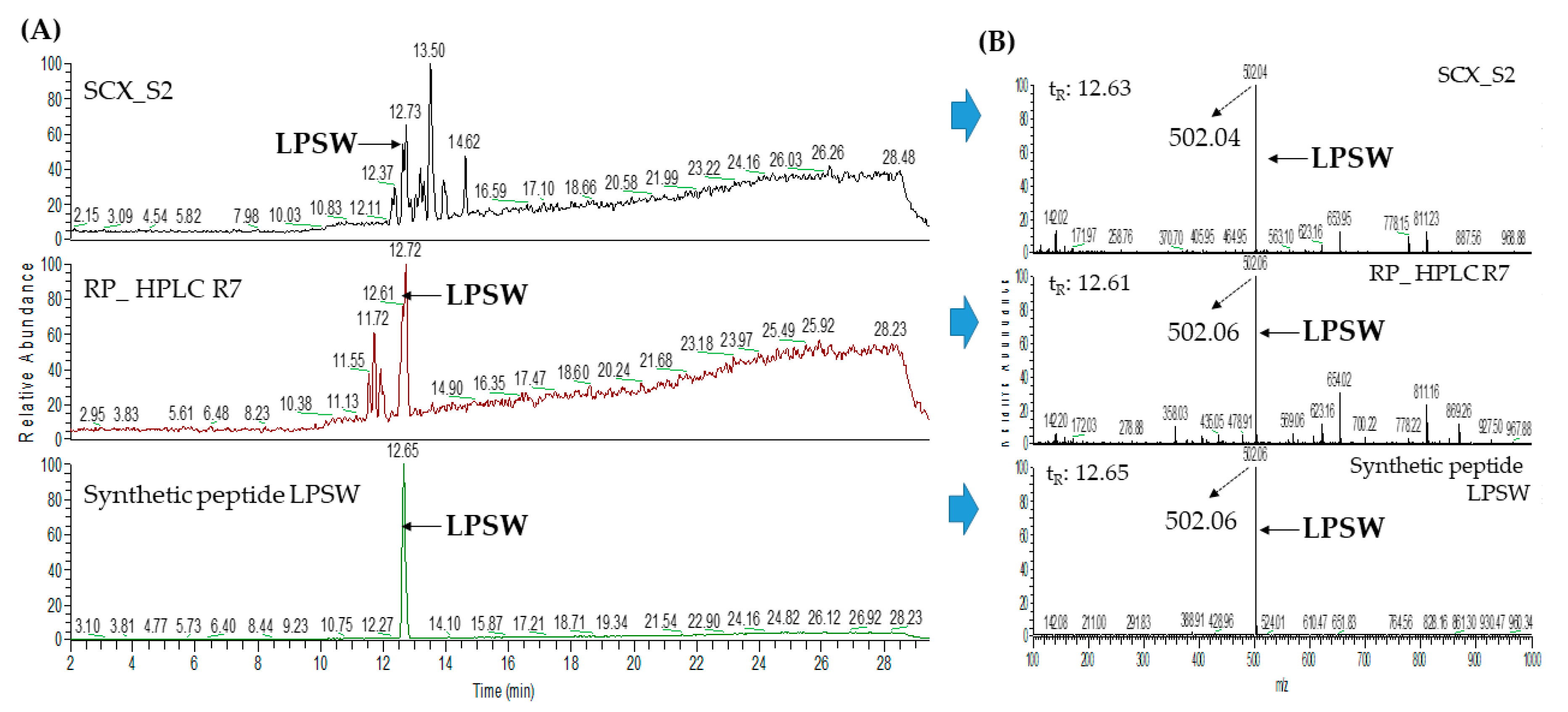
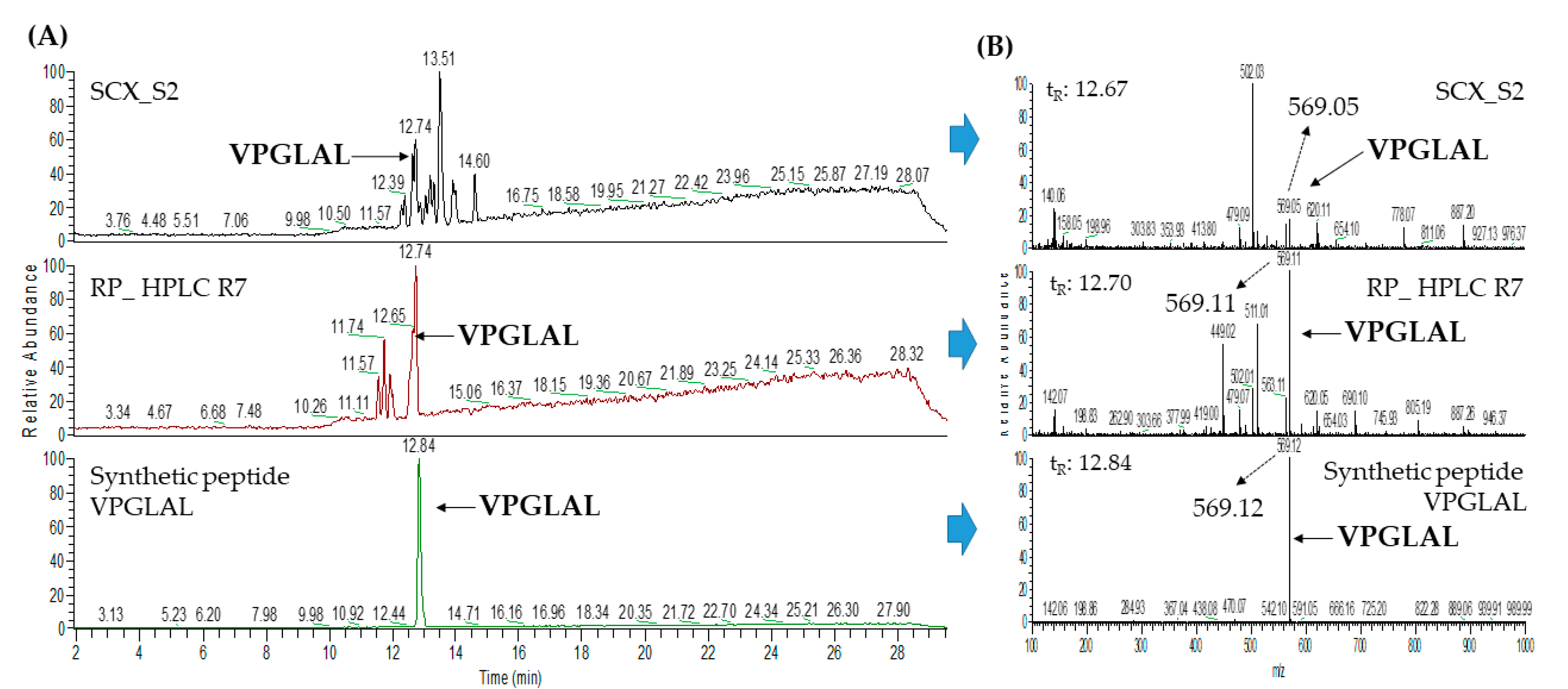
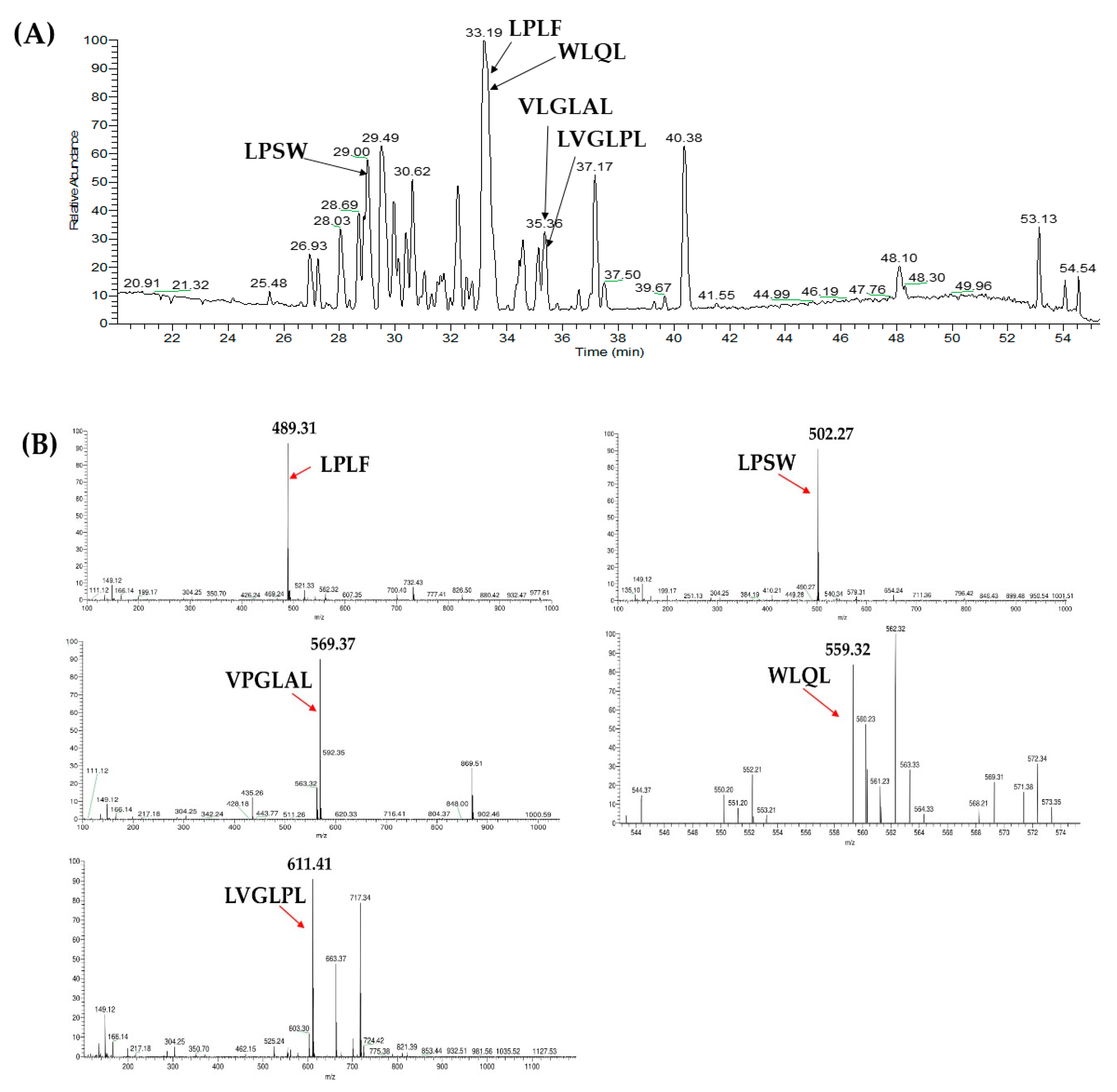
2.3. Database-Assisted Peptide Sequencing and In Silico Prediction of Potential DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides
2.4. Protein Profiling by SDS-PAGE
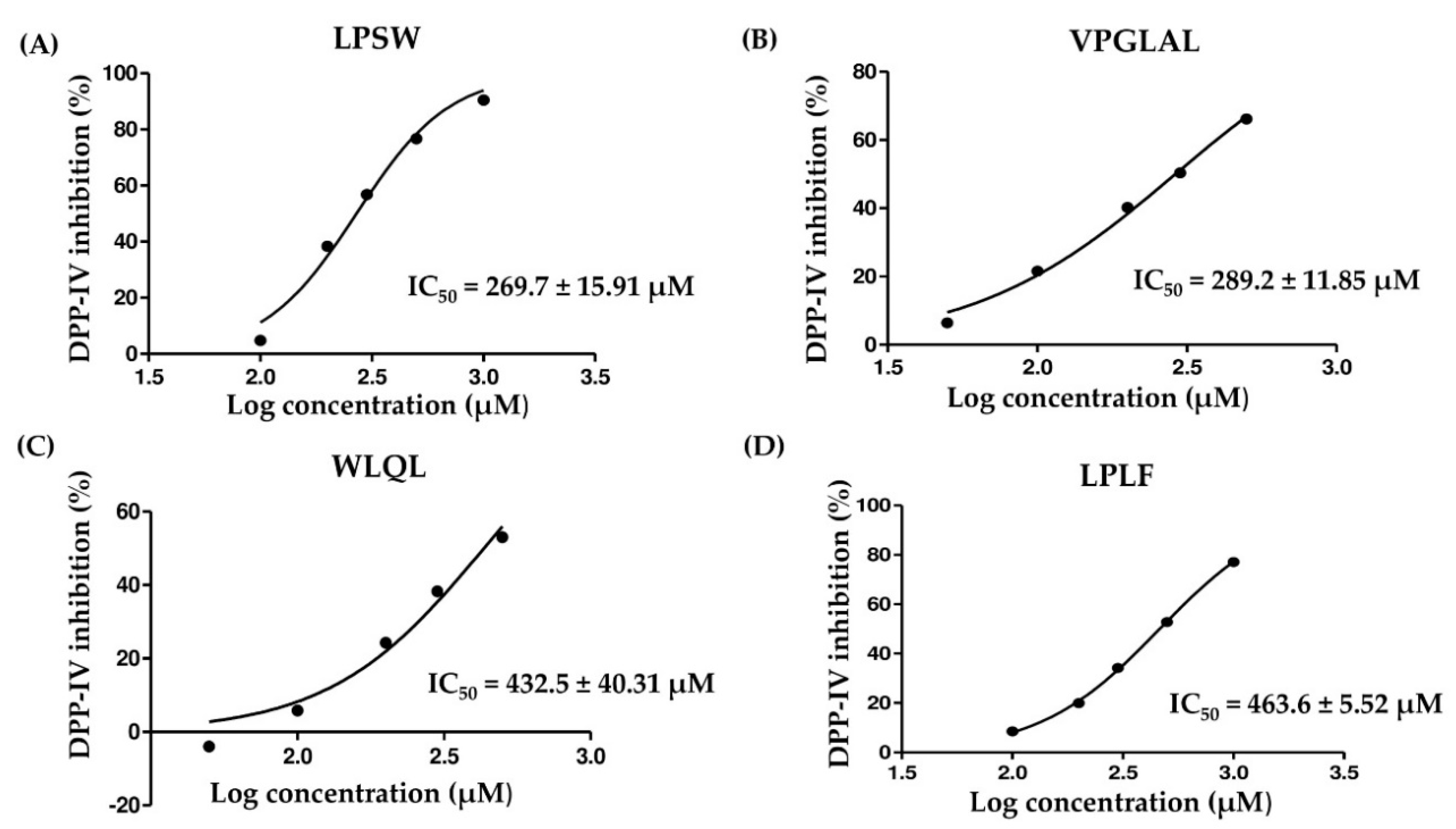
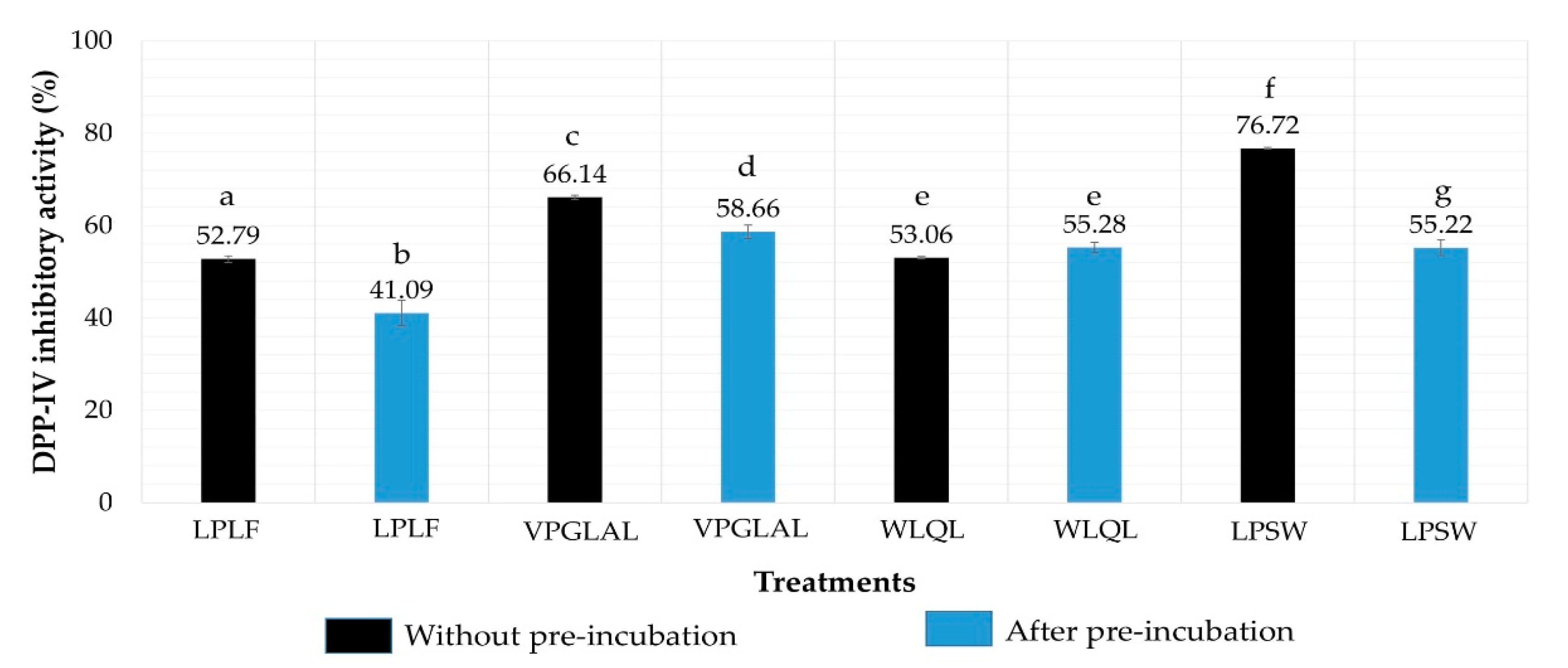
2.5. Determination of IC50 Value of Peptides against DPP-IV
2.6. Stability of Peptides against DPP-IV
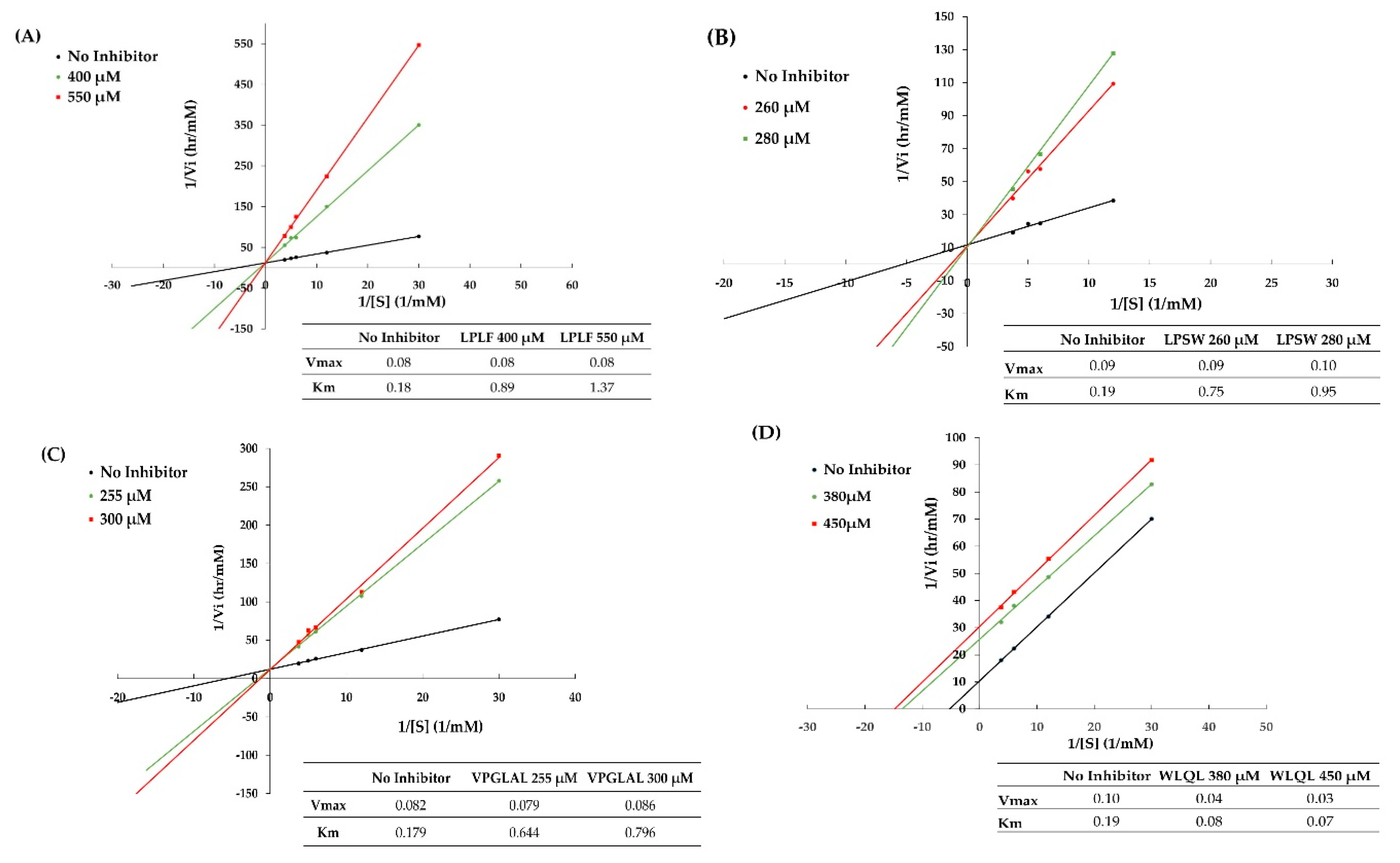
2.7. Inhibition Pattern of Synthetic Peptides
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Material and Chemical Reagents
3.2. Preparation of SSTY Protein Hydrolysate
3.3. Protein Profiling SSTY Protein Using SDS-PAGE
3.4. Two Independent Bioassay-Guided Fractionations
3.5. Peptide Identification with LC–MS/MS Analysis Coupled with Database-Assisted Matching
3.6. The Prediction of Potent DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides Using In Silico Software
3.7. Synthesis of SSTY Peptides
3.8. DPP-IV Inhibitory Assay
3.9. Determination of the Inhibition Modes of DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides
3.10. Stability of Synthesized DPP-IV Inhibitory Peptides
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- Chiu, L.H.; Hsu, G.S.W.; Lu, Y.F. Antihypertensive capacity of defatted soft-shelled turtle powder after hydrolysis by gastrointestinal enzymes. J. Food Biochem. 2006, 30, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, L.; Yan, W. Chinese soft-shelled turtle egg powder lowers serum cholesterol, increases faecal neutral steroids and bile acid excretion, and up-regulates liver cytochrome P450 mRNA level in rats. Br. J. Nutr. 2005, 94, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Lu, B.; Gong, L.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y. Studies on bioactive peptide from Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) with functionalities of ACE inhibition and antioxidation. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 6723–6729. [Google Scholar]
- Pujiastuti, D.Y.; Shih, Y.H.; Chen, W.L.; Hsu, J.L. Screening of angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from soft-shelled turtle yolk using two orthogonal bioassay-guided fractionations. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 28, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawendra, R.D.; Chang, C.I.; Chen, H.H.; Huang, T.C.; Hsu, J.L. A novel angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptide derived from proteolytic digest of Chinese soft-shelled turtle egg white proteins. J. Proteom. 2013, 94, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawendra, R.D.; Chen, S.H.; Chang, C.I.; Shih, W.L.; Huang, T.C.; Liao, M.H.; Hsu, J.L. Isolation and characterization of a novel angiotensin-converting enzyme-inhibitory tripeptide from enzymatic hydrolysis of soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) egg white: In vitro, in vivo, and in silico study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 12178–12185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, B.M.; Li, C. Diabetes and hypertension: Is there a common metabolic pathway? Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2012, 14, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, R.; Meisel, H. Food-derived peptides with biological activity: From research to food applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Chan, E.C. Bioactive peptides and protein hydrolysates: Research trends and challenges for application as nutraceuticals and functional food ingredients. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 1, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Bioactive properties of milk proteins in humans: A review. Peptides 2015, 73, 20–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhonen, H.; Pihlanto-Leppäla, A.; Rantamäki, P.; Tupasela, T. Impact of processing on bioactive proteins and peptides. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 9, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udenigwe, C.C. Bioinformatics approaches, prospects and challenges of food bioactive peptide research. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 36, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, E.S.; Deacon, C.F.; Holst, J.J. Do we know the true mechanism of action of the DPP-4 inhibitors? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deacon, C.F. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A comparative review. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagiannis, T.; Boura, P.; Tsapas, A. Safety of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors: A perspective review. Ther. Adv. Drug Saf. 2014, 5, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiStefano, J.K.; Watanabe, R.M. Pharmacogenetics of anti-diabetes drugs. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 2610–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, I.M.; Li-Chan, E.C. Food-derived dipeptidyl-peptidase IV inhibitors as a potential approach for glycemic regulation–Current knowledge and future research considerations. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 54, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jao, C.L.; Hung, C.C.; Tung, Y.S.; Lin, P.Y.; Chen, M.C.; Hsu, K.C. The development of bioactive peptides from dietary proteins as a dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the management of type 2 diabetes. Biomedicine 2015, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Structure activity relationship modelling of milk protein-derived peptides with dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory activity. Peptides 2016, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; Paolella, S.; Mudgil, P.; Maqsood, S.; FitzGerald, R.J. Identification of novel dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides in camel milk protein hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2018, 244, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrowicz, A.; Eckert, E.; Pokora, M.; Bobak, Ł.; Dąbrowska, A.; Szołtysik, M.; Trziszka, T.; Chrzanowska, J. Antioxidant and antidiabetic activities of peptides isolated from a hydrolysate of an egg-yolk protein by-product prepared with a proteinase from Asian pumpkin (Cucurbita ficifolia). RCS Adv. 2015, 5, 10460–10467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Z.; Ding, L.; Liu, J. Novel membrane peptidase inhibitory peptides with activity against angiotensin converting enzyme and dipeptidyl peptidase IV identified from hen eggs. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 64, 103649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, A.C.; Harnedy, P.A.; O’Keeffe, M.B.; Alashi, M.A.; Aluko, R.E.; FitzGerald, R.J. Peptide identification in a salmon gelatin hydrolysate with antihypertensive, dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory and antioxidant activities. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatanaka, T.; Inoue, Y.; Arima, J.; Kumagai, Y.; Usuki, H.; Kawakami, K.; Kimura, M.; Mukaihara, T. Production of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitory peptides from defatted rice bran. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Features of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides from dietary proteins. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e12451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnedy, P.A.; O’Keeffe, M.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Purification and identification of dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP) IV inhibitory peptides from the macroalga Palmaria palmata. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrowicz, A.; Pokora, M.; Setner, B.; Dąbrowska, A.; Szołtysik, M.; Babij, K.; Szewczuk, Z.; Trziszka, T.; Lubec, G.; Chrzanowska, J. Multifunctional peptides derived from an egg yolk protein hydrolysate: Isolation and characterization. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.H.; Chen, F.A.; Wang, L.F.; Hsu, J.L. Discovery and study of novel antihypertensive peptides derived from Cassia obtusifolia seeds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7810–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutopo, C.C.; Sutrisno, A.; Wang, L.F.; Hsu, J.L. Identification of a potent angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from black cumin seed hydrolysate using orthogonal bioassay-guided fractionations coupled with in silico screening. Process Biochem. 2020, 95, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dong, Y.; Cui, P. Vitellogenin is an immunocompetent molecule for mother and offspring in fish. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 46, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) by proline containing casein-derived peptides. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) by tryptophan containing dipeptides. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, V.T.T.; Ito, K.; Ohno, M.; Motoyama, T.; Ito, S.; Kawarasaki, Y. Analyzing a dipeptide library to identify human dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor. Food Chem. 2015, 175, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, V.T.T.; Ito, K.; Ito, S.; Kawarasaki, Y. Trp-Arg-Xaa tripeptides act as uncompetitive-type inhibitors of human dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Peptides 2014, 54, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaniak, A.; Minkiewicz, P.; Darewicz, M.; Sieniawski, K.; Starowicz, P. BIOPEP database of sensory peptides and amino acids. Food Res. Int. 2016, 85, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkiewicz, P.; Iwaniak, A.; Darewicz, M. BIOPEP-UWM Database of Bioactive Peptides: Current Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; FitzGerald, R.J. Susceptibility of milk protein-derived peptides to dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) hydrolysis. Food Chem. 2014, 145, 845–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongonierma, A.B.; Mooney, C.; Shields, D.C.; FitzGerald, R.J. In silico approaches to predict the potential of milk protein-derived peptides as dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitors. Peptides 2014, 57, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Yao, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, M.; Pan, M.; Ji, S.; Wu, J.; Jiang, D.; Ju, X.; Wang, L. Identification and Quantification of DPP-IV-Inhibitory Peptides from Hydrolyzed-Rapeseed-Protein-Derived Napin with Analysis of the Interactions between Key Residues and Protein Domains. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 3679–3690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, R.; Ma, H.; Chen, S. Isolation and identification of dipeptidyl peptidase IV-inhibitory peptides from trypsin/chymotrypsin-treated goat milk casein hydrolysates by 2D-TLC and LC–MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8819–8828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacroix, I.M.; Li-Chan, E.C. Isolation and characterization of peptides with dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activity from pepsin-treated bovine whey proteins. Peptides 2014, 54, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Kapoor, P.; Chaudhary, K.; Gautam, A.; Kumar, R.; Raghava, G.P.; Consortium, O.S.D.D. In silico approach for predicting toxicity of peptides and proteins. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroix, I.M.; Li-Chan, E.C. Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV inhibitory activity of dairy protein hydrolysates. Int. Dairy J. 2012, 25, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |

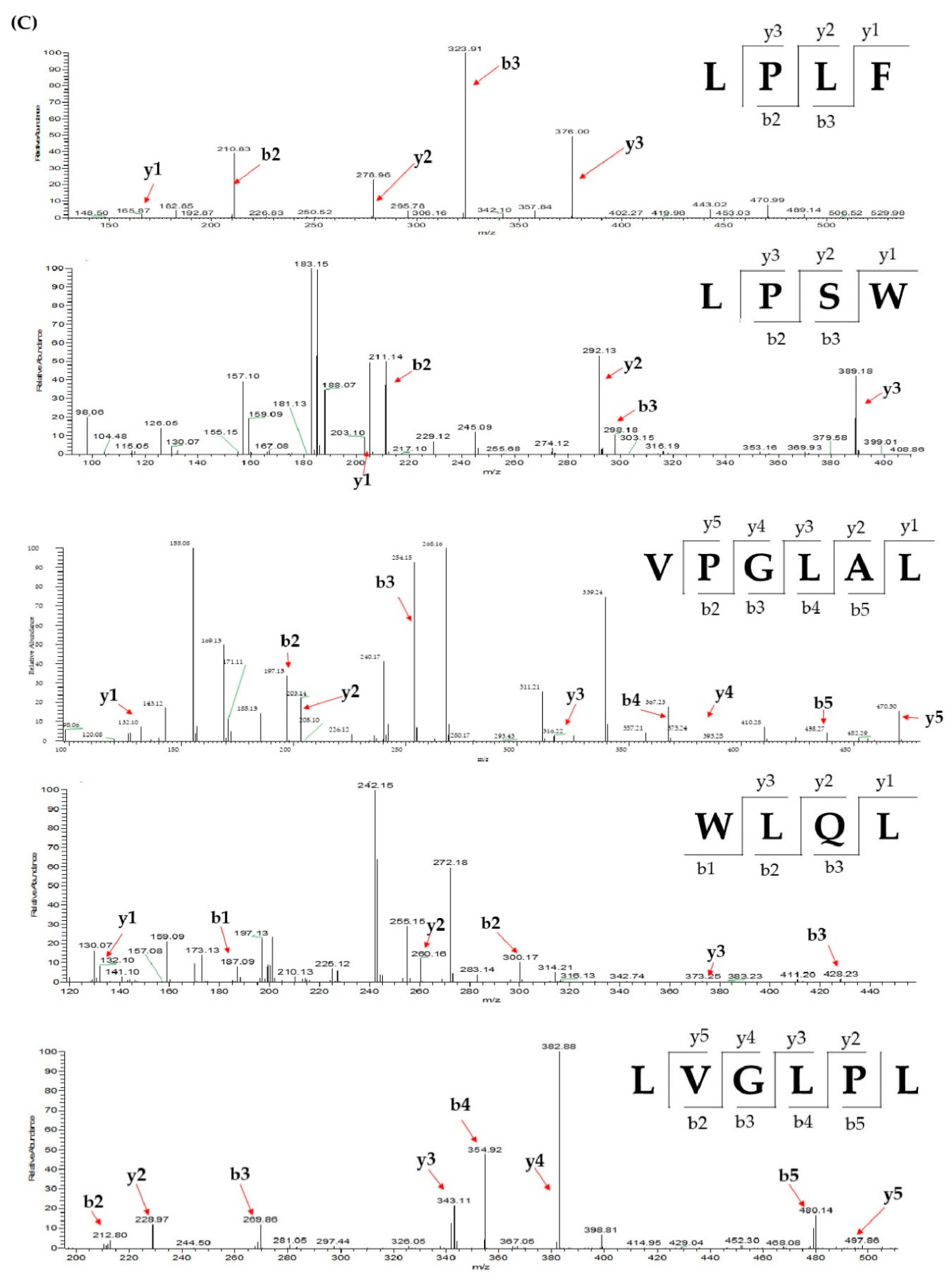
| No | Protein | Peptide | m/z | Retention Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identified peptides in fraction S2 from off-line SCX | ||||
| 1 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | VPGLAL | 569.36 | 30.31 |
| 2 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | LPSW | 502.27 | 29.00 |
| 3 | Vitellogenin-2-like (gi: 1394701588) | LPLF | 489.31 | 32.31 |
| 4 | Tesmin isoform X4 (gi: 1394748730) | LVGLPL | 611.41 | 35.30 |
| 5 | Low quality protein: M-phase phosphoprotein 9 (gi: 1394664164) | WLQL | 559.32 | 33.05 |
| 6 | Vitellogenin-2-like (gi: 1394701588) | VLPSENPVFK | 565.31 | 26.29 |
| 7 | Vitellogenin-2-like (gi: 1394701588) | YSLY | 542.26 | 28.84 |
| 8 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | LAAF | 421.24 | 24.73 |
| 9 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | NAPLY | 577.29 | 25.50 |
| 10 | Apolipoprotein B-100 (gi: 946679552) | LNEYLEDLR | 582.79 | 33.85 |
| 11 | Apolipoprotein B-100 (gi: 946679552) | LLLY | 521.33 | 32.25 |
| 12 | Apolipoprotein B-100 (gi: 946679552) | LGLL | 415.29 | 30.31 |
| 13 | Vitellogenin-2-like (gi: 1394701588) | PISLPVGPPVPESA | 680.38 | 36.08 |
| 14 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | AQISPAPSSDF | 1119.53 | 27.69 |
| 15 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | ILDIMPAVSK | 543.81 | 30.05 |
| 16 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | MPGYAPSASDL | 1108 | 30.00 |
| 17 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | ISPAPSSDF | 920.43 | 26.41 |
| 18 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | SDDGLNF | 767.32 | 30.39 |
| 19 | Vitellogenin-2-like (gi: 1394701588) | YQIGAIE | 793.41 | 27.97 |
| 20 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | SGVGTQW | 734.35 | 25.17 |
| 21 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | ILDMPA | 772.42 | 34.53 |
| Identified peptides in fraction R7 from RP-HPLC | ||||
| 1 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | VPGLAL | 569.36 | 30.54 |
| 2 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | LPSW | 502.26 | 29.16 |
| 3 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | QELVQELHQF | 635.82 | 27.73 |
| 4 | Vitellogenin-2-like (gi: 1394701588) | SVPPELHL | 446.25 | 26.67 |
| 5 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | IRNAPLY | 423.74 | 20.08 |
| 6 | Apolipoprotein B-100 (gi: 946679552) | KIPEVTL | 400.25 | 26.05 |
| 7 | Vitellogenin-2-like (gi: 1394701588) | FADHPAIQ | 449.72 | 20.16 |
| Identified peptides in fraction R13 from RP-HPLC | ||||
| 1 | Vitellogenin-2-like (gi: 1394701588) | LPLF | 489.31 | 33.58 |
| 2 | Tesmin isoform X4 (gi:1394748730) | LVGLPL | 611.41 | 35.50 |
| 3 | Low quality protein: M-phase phosphoprotein 9 (gi:1394664164) | WLQL | 559.32 | 33.40 |
| 4 | Vitellogenin-2-like (gi: 1394701588) | LVGL | 401.27 | 34.82 |
| 5 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | PPGL | 383.23 | 30.30 |
| 6 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | QVESQLVENLR | 657.85 | 31.63 |
| 7 | Vitellogenin-1-like (gi: 558222264) | YLGDVLPGLPR | 600.34 | 34.18 |
| 8 | Pepsin A-like, partial (gi: 1394653157) | GLLGL | 472.31 | 34.34 |
| 9 | Apolipoprotein B-100 (gi: 946679552) | FLDLVIK | 424.26 | 32.17 |
| No | Co-Existing Peptides in RP-HPLC and SCX Fractionation | Length | BIOPEP | ToxinPred | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a A | b B | |||||
| 1 | RP R7 and SCX S2 | VPGLAL | 6 | 0.83 | 0.0004 | Non-toxic |
| 2 | LPSW | 4 | 0.75 | 0.0001 | Non-toxic | |
| 3 | RP R13 and SCX S2 | LVGLPL | 6 | 1.17 | 0.0008 | Non-toxic |
| 4 | WLQL | 4 | 0.50 | 0.0057 | Non-toxic | |
| 5 | LPLF | 4 | 0.75 | 0.0011 | Non-toxic | |
| Peptide Sequence | Molecular Mass (Da) | Peptide Size | DPP-IV IC50 (µM) | Mode of Inhibition | Peptide Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VPGLAL | 569 | 6 | 289.2 ± 11.85 | Competitive | Substrate |
| LPSW | 502 | 4 | 269.7 ± 15.91 | Competitive | Substrate |
| LPLF | 489 | 4 | 463.6 ± 5.52 | Competitive | Substrate |
| LVGLPL | 611 | 6 | >2000 | nd | nd |
| WLQL | 559 | 4 | 432.5 ± 40.31 | Uncompetitive | True inhibitor |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nong, N.T.P.; Chen, Y.-K.; Shih, W.-L.; Hsu, J.-L. Characterization of Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Peptides from Soft-Shelled Turtle Yolk Hydrolysate Using Orthogonal Bioassay-Guided Fractionations Coupled with In Vitro and In Silico Study. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100308
Nong NTP, Chen Y-K, Shih W-L, Hsu J-L. Characterization of Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Peptides from Soft-Shelled Turtle Yolk Hydrolysate Using Orthogonal Bioassay-Guided Fractionations Coupled with In Vitro and In Silico Study. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(10):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100308
Chicago/Turabian StyleNong, Nhung Thi Phuong, Yu-Kuo Chen, Wen-Ling Shih, and Jue-Liang Hsu. 2020. "Characterization of Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Peptides from Soft-Shelled Turtle Yolk Hydrolysate Using Orthogonal Bioassay-Guided Fractionations Coupled with In Vitro and In Silico Study" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 10: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100308
APA StyleNong, N. T. P., Chen, Y.-K., Shih, W.-L., & Hsu, J.-L. (2020). Characterization of Novel Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitory Peptides from Soft-Shelled Turtle Yolk Hydrolysate Using Orthogonal Bioassay-Guided Fractionations Coupled with In Vitro and In Silico Study. Pharmaceuticals, 13(10), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100308









