RETRACTED: Sanguinarine Inhibits Mono- and Dual-Species Biofilm Formation by Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus and Induces Mature Hypha Transition of C. albicans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Biofilm Inhibitory Concentration (MBIC90) of Sanguinarine Against C. albicans SC5314 and S. aureus CMCC26003
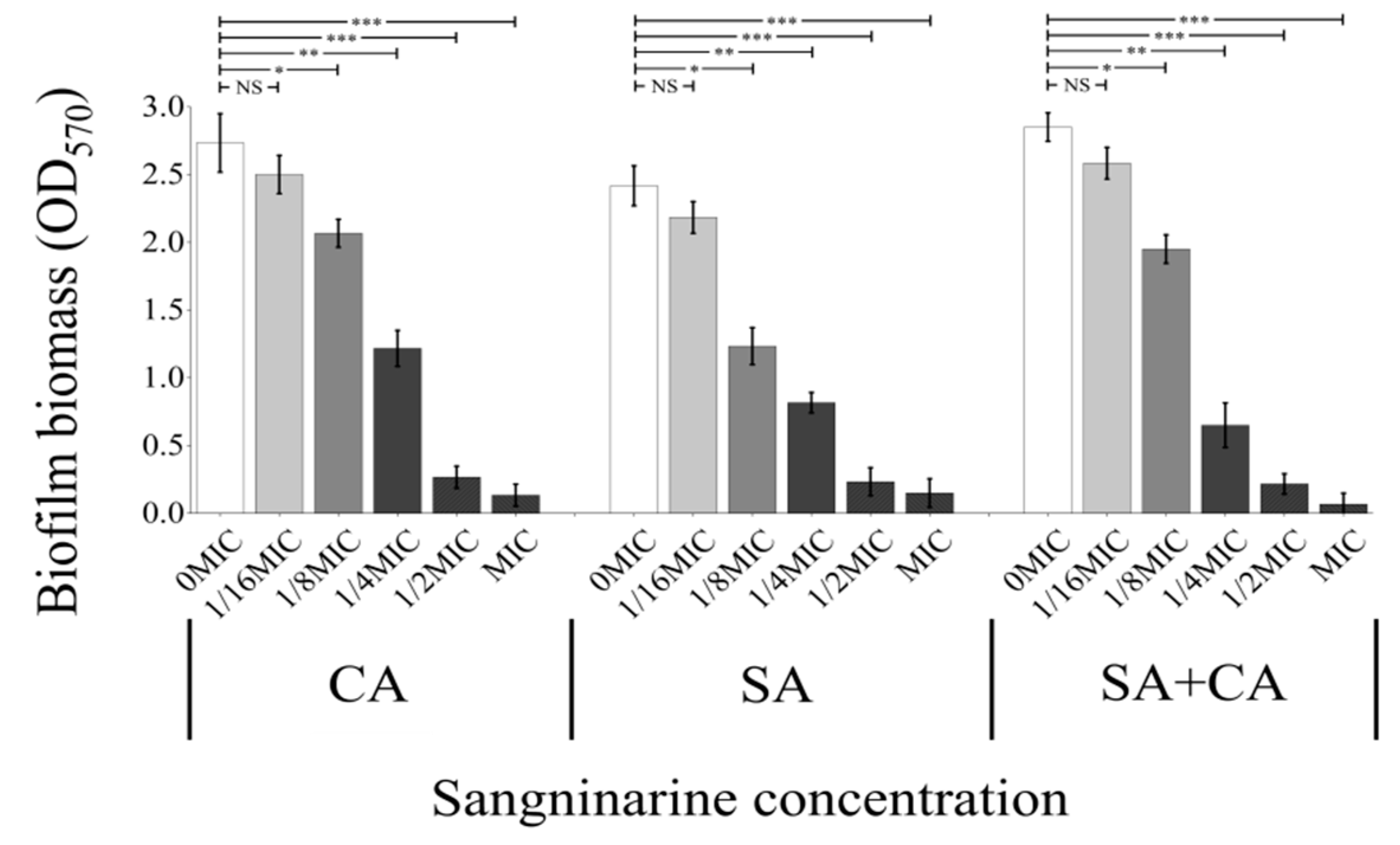
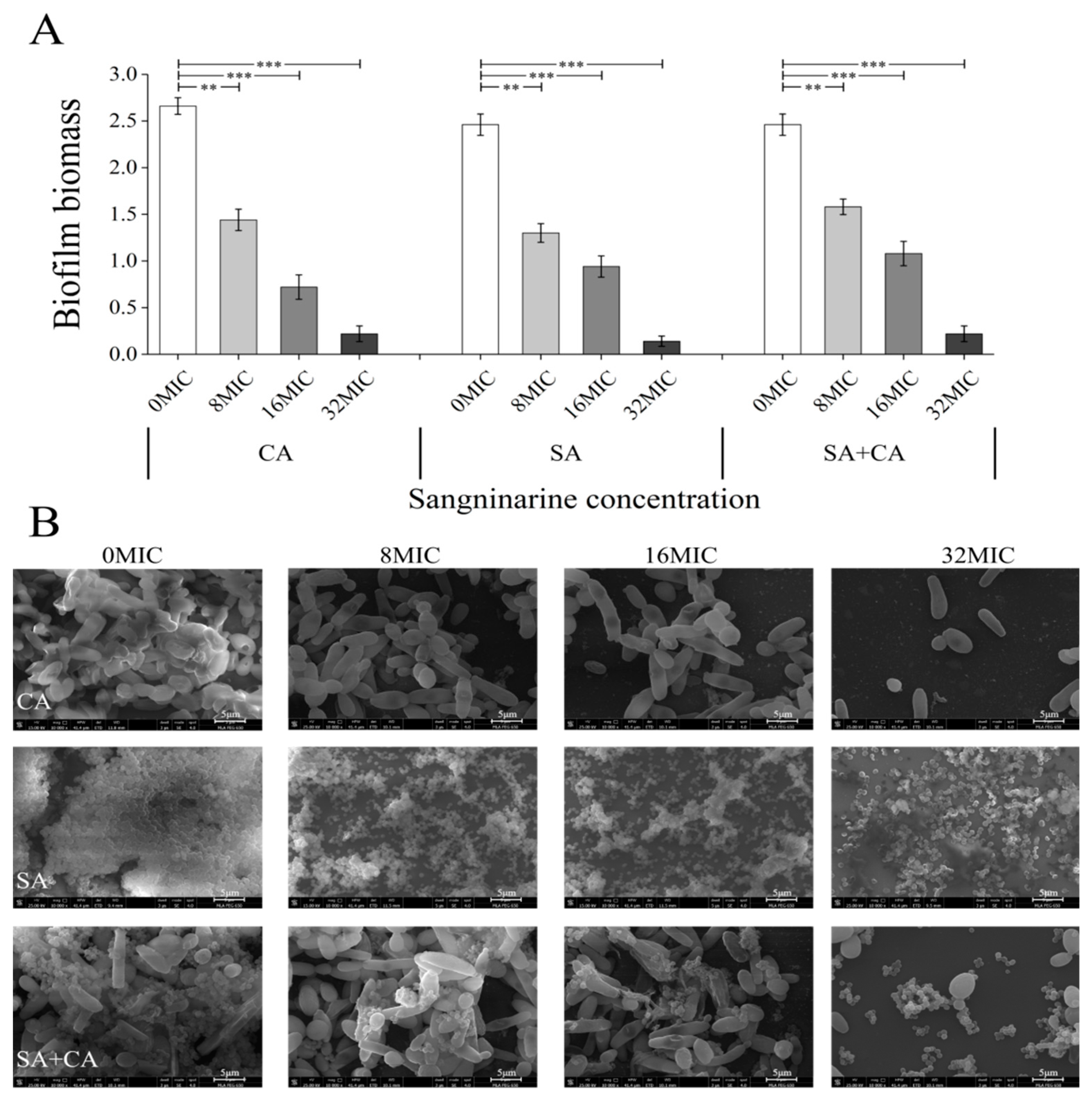
2.2. Sanguinarine Suppresses the Biofilm Formation of Mono- and Dual-Species
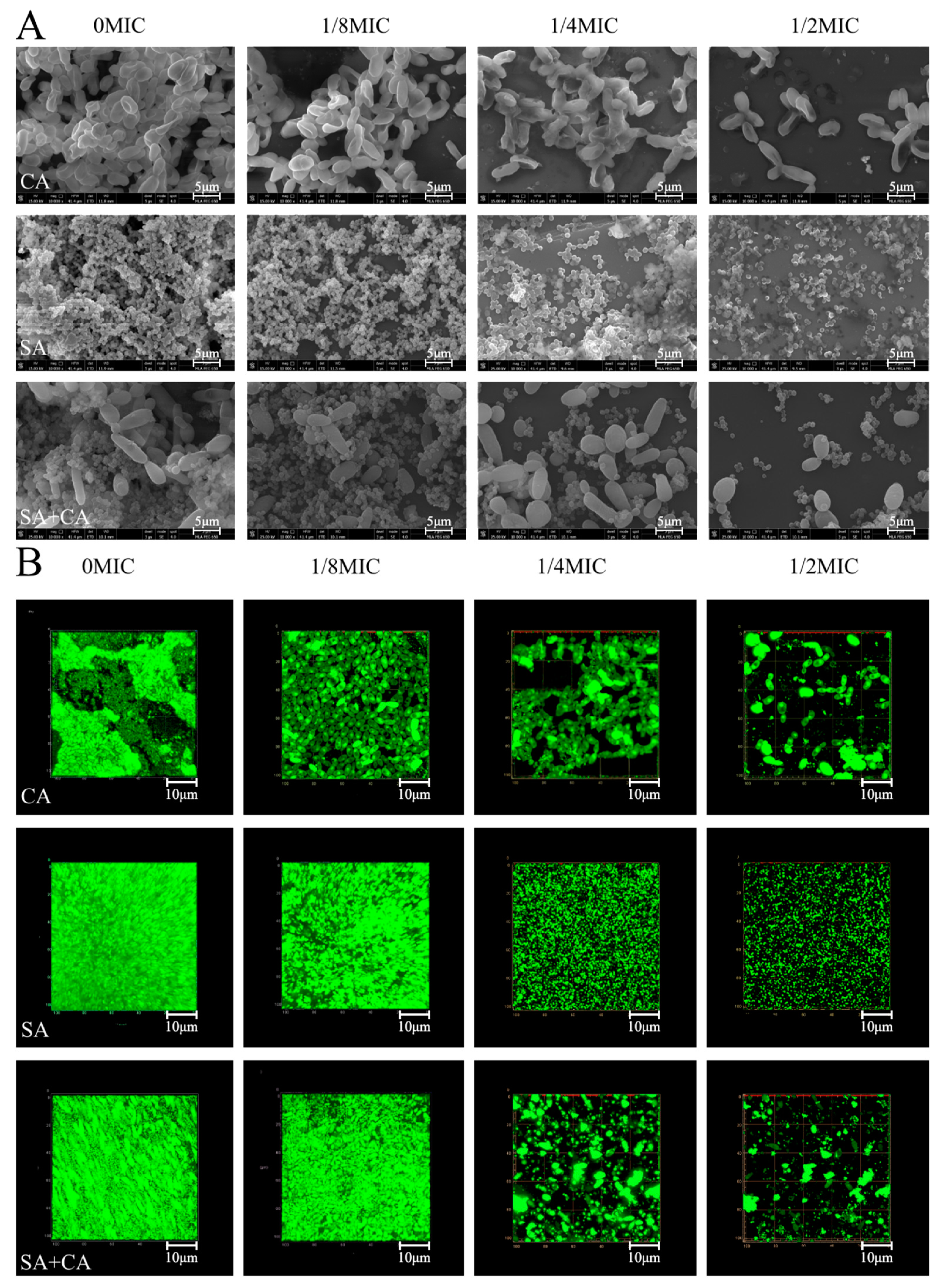
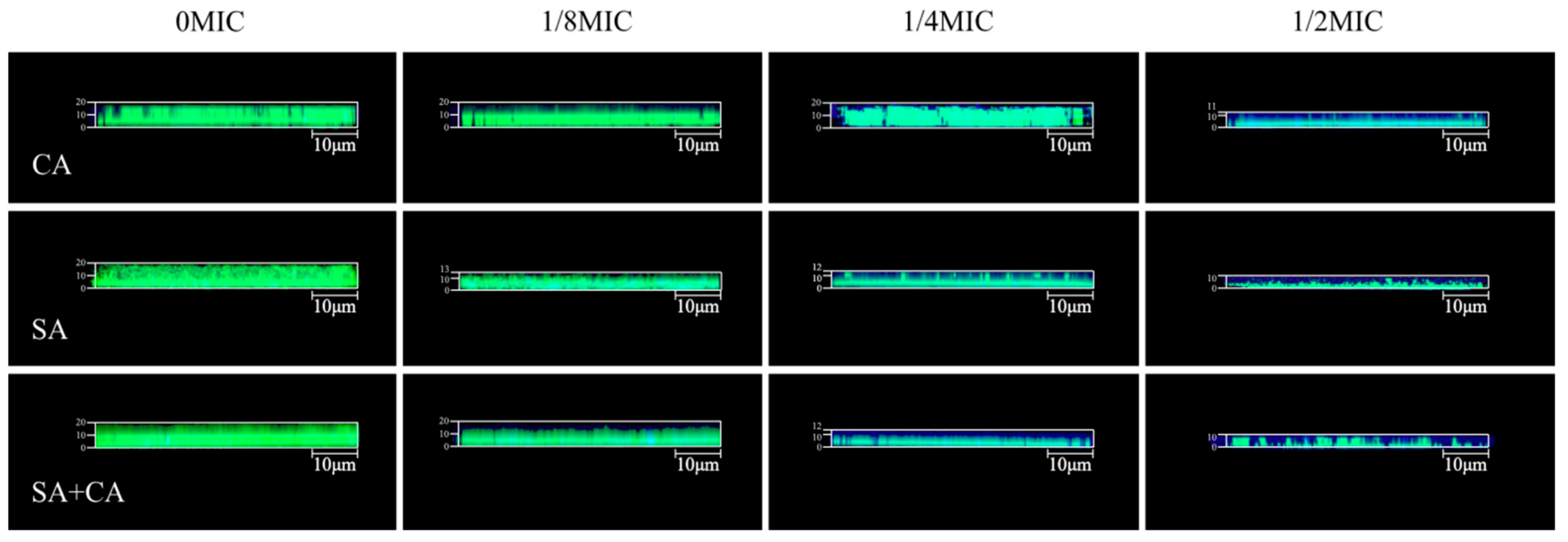
2.3. Sub-MIC Sanguinarine Changed the Biofilm Structure of Mono- and Dual-Species
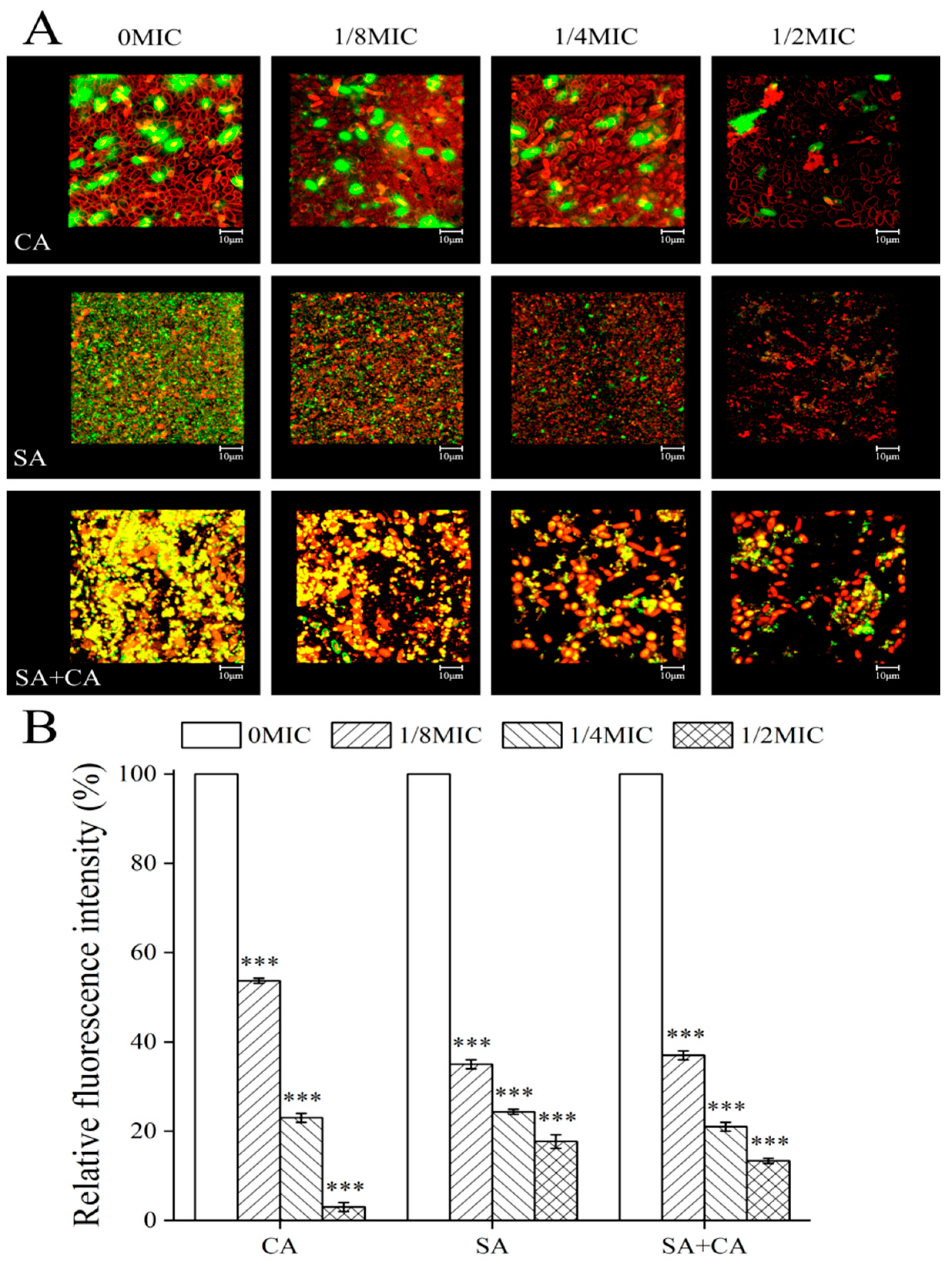
2.4. Sanguinarine Decreases the Biofilm Formation of C. albicans and S. aureus Mono- and Dual-Species by Mediating Extracellular Protein Levels in a Similar Manner
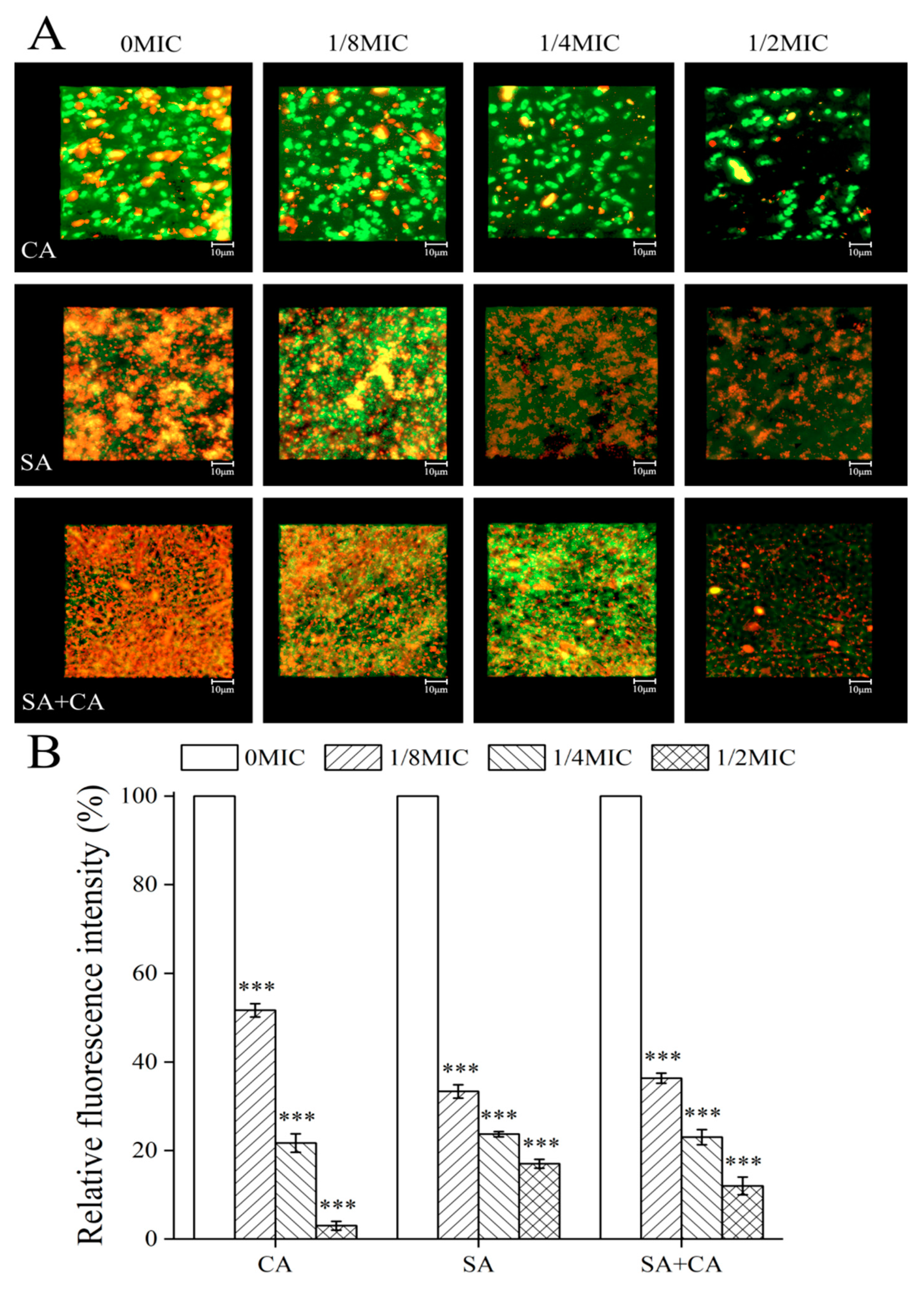
2.5. Sanguinarine Reduced the Biofilm Formation of S. aureus Mono-Species and Dual-Species by Mediating Extracellular Polysaccharide Levels
2.6. Sanguinarine Inhibits the Biofilm Formation of Dual Species by Reducing Extracellular DNA Levels
2.7. Sanguinarine Treatment Reduces Mono- and Dual-Species Biofilm Tolerance to Gatifloxacin
2.8. Sanguinarine Efficiently Eradicates Mature Biofilms of Mono- and Dual-Species
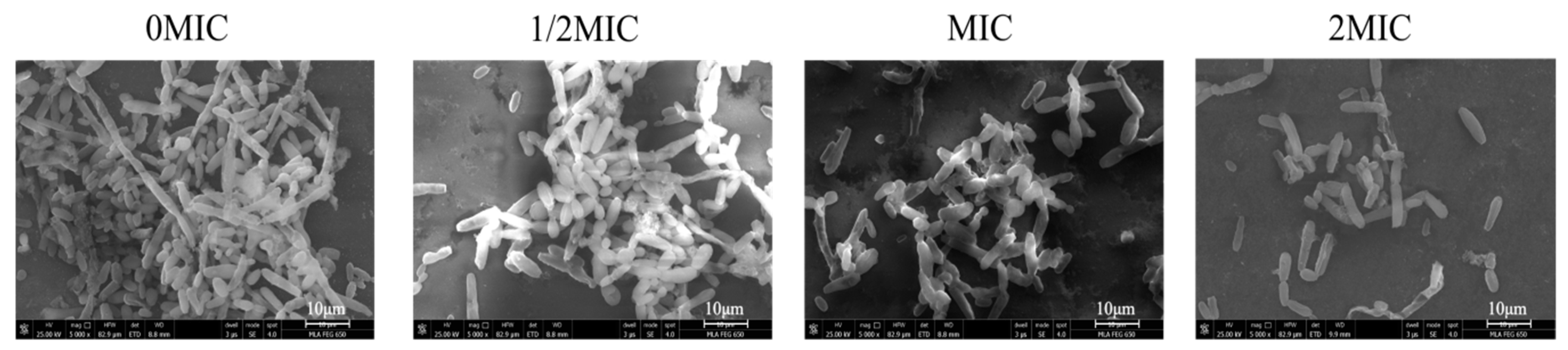
2.9. Sanguinarine Results in the Hypha-to-Yeast Transition in C. albicans
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Strains and Cultural Conditions
4.3. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
4.4. Minimum Biofilm Inhibitory Concentration (MBIC90)
4.5. Biofilm Inhibition Assay
4.6. Biofilm Composition by CLSM
4.7. Diffusion of Antibiotics within Biofilms
4.8. Biofilm Eradication Assay
4.9. Effect of Sanguinarine on C. albicans Mature Hypha
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lopes, J.P.; Stylianou, M.; Nilsson, G.; Urban, C.F. Opportunistic pathogen Candida albicans elicits a temporal response in primary human mast cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achkar, J.M.; Fries, B.C. Candida infections of the genitourinary tract. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 23, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeth Rimachi Hidalgo, K.; Cabrini Carmello, J.; Carolina Jordao, C.; Aboud Barbugli, P.; de Sousa Costa, C.A.; Mima, E.G.O.; Pavarina, A.C. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy in combination with nystatin in the treatment of experimental oral candidiasis induced by Candida albicans resistant to fluconazole. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harriott, M.M.; Noverr, M.C. Importance of Candida-bacterial polymicrobial biofilms in disease. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willems, H.M.; Xu, Z.; Peters, B.M. Polymicrobial biofilm studies: From basic science to biofilm control. Curr. Oral Health Rep. 2016, 3, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, S.A.; Chasin, B.S.; Powell, B.; Gaur, N.K.; Lipke, P.N. Polymicrobial bloodstream infections involving Candida species: Analysis of patients and review of the literature. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2007, 59, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, R.; Rajendran, R.; Haggarty, J.; Townsend, E.M.; Short, B.; Burgess, K.E.; Lang, S.; Millington, O.; Mackay, W.G.; Williams, C. Candida albicans mycofilms support Staphylococcus aureus colonization and enhances miconazole resistance in dual-Species interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiki, J.; Nakamura, T.; Furusawa, T.; Ohno, H.; Takahashi, H.; Kitana, J.; Usui, M.; Higuchi, H.; Tanji, Y.; Tamura, Y. Characterization of the lytic capability of a lysK-like endolysin, lys-phiSA012, derived from a polyvalent Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esher, S.K.; Fidel, P.L., Jr.; Noverr, M.C. Candida/Staphylococcal polymicrobial intra-abdominal infection: Pathogenesis and perspectives for a novel form of trained innate immunity. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, C.J.; Johnson, A.D. Candida albicans biofilms and human disease. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 69, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, B.; Baillie, G.S.; Douglas, L.J. Mixed species biofilms of Candida albicans and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2002, 51, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.K.; Drescher, K.; Pak, O.S.; Bassler, B.L.; Stone, H.A. Filaments in curved streamlines: Rapid formation of Staphylococcus aureus biofilm streamers. New J. Phys. 2014, 16, 065024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, L.R.; Reddinger, R.M.; Hakansson, A.P. Biofilm formation enhances fomite survival of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zago, C.E.; Silva, S.; Sanita, P.V.; Barbugli, P.A.; Dias, C.M.I.; Lordello, V.B.; Vergani, C.E. Dynamics of biofilm formation and the interaction between Candida albicans and methicillin-susceptible (MSSA) and -resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Z.; Yang, R.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.F.; Miao, F.; Yang, X.J.; Zhou, L. 2-(Substituted phenyl)-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-2-iums as novel antifungal lead compounds: Biological evaluation and structure-activity relationships. Molecules 2013, 18, 10413–10424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, H.; Reagan-Shaw, S.; Breur, J.; Ahmad, N. Sanguinarine induces apoptosis of human pancreatic carcinoma AsPC-1 and BxPC-3 cells via modulations in Bcl-2 family proteins. Cancer Lett. 2007, 249, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, F.; Yang, X.J.; Zhou, L.; Hu, H.J.; Zheng, F.; Ding, X.D.; Sun, D.M.; Zhou, C.D.; Sun, W. Structural modification of sanguinarine and chelerythrine and their antibacterial activity. Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 25, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obiang-Obounou, B.W.; Kang, O.H.; Choi, J.G.; Keum, J.H.; Kim, S.B.; Mun, S.H.; Shin, D.W.; Kim, K.W.; Park, C.B.; Kim, Y.G. The mechanism of action of sanguinarine against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 36, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Hu, D.D.; Hu, G.H.; Su, J.; Bi, S.; Zhang, Z.E.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.L.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, Y.Y. Activity of sanguinarine against Candida albicans biofilms. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02259-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Miao, F.; Yao, Y.; Cao, F.J.; Yang, R.; Ma, Y.N.; Qin, B.F.; Zhou, L. In vitro antifungal activity of sanguinarine and chelerythrine derivatives against phytopathogenic fungi. Molecules 2012, 17, 13026–13035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, C.G.; Vila, T.; Romo, J.A.; Montelongo-Jauregui, D.; Wall, G.; Ramasubramanian, A.; Lopez-Ribot, J.L. The Candida albicans biofilm matrix: Composition, structure and function. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulston, L.; Elsholz, A.K.W.; DeFrancesco, A.S.; Losick, R. The extracellular matrix of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms comprises cytoplasmic proteins that associate with the cell surface in response to decreasing pH. Mbio 2014, 5, e01667-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.A.; Cartmell, J.; Weisser, N.E.; Woods, R.J.; Bundle, D.R. Molecular recognition of Candida albicans, (1→2)-β-mannan oligosaccharides by a protective monoclonal antibody reveals the immunodominance of internal saccharide residues. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 18078–18090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, H.C.; Wingender, J. The biofilm matrix. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, K.; Yumoto, H.; Sapaar, B.; Matsuo, T.; Ichikawa, T.; Miyake, Y. Pathogenic factors in Candida biofilm-related infectious diseases. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, N.; Biswas, R.; Gotz, F.; Biswas, L. Impact of Staphylococcus aureus on pathogenesis in polymicrobial infections. Infect. Immun. 2014, 82, 2162–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacioglu, M.; Haciosmanoglu, E.; Birteksoz-Tan, A.S.; Bozkurt-Guzel, C.; Savage, P.B. Effects of ceragenins and conventional antimicrobials on Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus mono and multispecies biofilms. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 95, 114863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.S.; Eom, Y.B. Efficacy of zerumbone against dual-species biofilms of Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tan, F.; Luo, Z.; Wu, Y. Antibiofilm efficacy of the gold compound auranofin on dual species biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus and Candida sp. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budzynska, A.; Rozalska, S.; Sadowska, B.; Rozalska, B. Candida albicans/Staphylococcus aureus dual-species biofilm as a target for the combination of essential oils and fluconazole or mupirocin. Mycopathologia 2017, 182, 989–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ribot, J.L. Large-scale biochemical profiling of the Candida albicans biofilm matrix: New compositional, structural, and functional insights. MBio 2014, 5, e01781-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, S.; Sato, F.; Miyakawa, R.; Chiba, A.; Onodera, S.; Hori, S.; Mizunoe, Y. Broad impact of extracellular DNA on biofilm formation by clinically isolated Methicillin-resistant and -sensitive strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciofu, O.; Rojo-Molinero, E.; Macia, M.D.; Oliver, A. Antibiotic treatment of biofilm infections. APMIS 2017, 125, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, D.; Misba, L.; Khan, A.U. Antibiotics versus biofilm: An emerging battleground in microbial communities. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allonsius, C.N.; Vandenheuvel, D.; Oerlemans, E.F.M.; Petrova, M.I.; Donders, G.G.G.; Cos, P.; Delputte, P.; Lebeer, S. Inhibition of Candida albicans morphogenesis by chitinase from Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaller, M.A.; Diekema, D.J. Progress in antifungal susceptibility testing of Candida spp. by use of clinical and laboratory standards institute broth microdilution methods, 2010 to 2012. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 2846–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkisian, S.A.; Janssen, M.J.; Matta, H.; Henry, G.E.; LaPlante, K.L.; Rowley, D.C. Inhibition of bacterial growth and biofilm production by constituents from Hypericum spp. Phytother. Res. 2012, 26, 1012–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Mittal, N. , Sharma, A. Multifunctional mesoporous carbon capsules and their robust coatings for encapsulation of actives: Antimicrobial and anti-bioadhesion functions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 19371–19379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, T.; Liu, M.; Yang, M.; Sun, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities of paeoniflorin against carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jegal, U.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.; Jeong, H.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, K.H. Ultrasound-assisted gatifloxacin delivery in mouse cornea, in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Strain | MICs (μg/mL) of Sanguinarine | MBIC90 (μg/mL) of Sanguinarine |
|---|---|---|
| C. albicans SC5314 | 4 | 2 |
| S. aureus CMCC26003 | 4 | 2 |
| Dual species | 8 | 4 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qian, W.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Fu, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Li, Y. RETRACTED: Sanguinarine Inhibits Mono- and Dual-Species Biofilm Formation by Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus and Induces Mature Hypha Transition of C. albicans. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13010013
Qian W, Wang W, Zhang J, Liu M, Fu Y, Li X, Wang T, Li Y. RETRACTED: Sanguinarine Inhibits Mono- and Dual-Species Biofilm Formation by Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus and Induces Mature Hypha Transition of C. albicans. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleQian, Weidong, Wenjing Wang, Jianing Zhang, Miao Liu, Yuting Fu, Xiang Li, Ting Wang, and Yongdong Li. 2020. "RETRACTED: Sanguinarine Inhibits Mono- and Dual-Species Biofilm Formation by Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus and Induces Mature Hypha Transition of C. albicans" Pharmaceuticals 13, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13010013
APA StyleQian, W., Wang, W., Zhang, J., Liu, M., Fu, Y., Li, X., Wang, T., & Li, Y. (2020). RETRACTED: Sanguinarine Inhibits Mono- and Dual-Species Biofilm Formation by Candida albicans and Staphylococcus aureus and Induces Mature Hypha Transition of C. albicans. Pharmaceuticals, 13(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13010013





