Cell Adhesive Character of Phenylboronic Acid-Modified Insulin and Its Potential as Long-Acting Insulin
Abstract
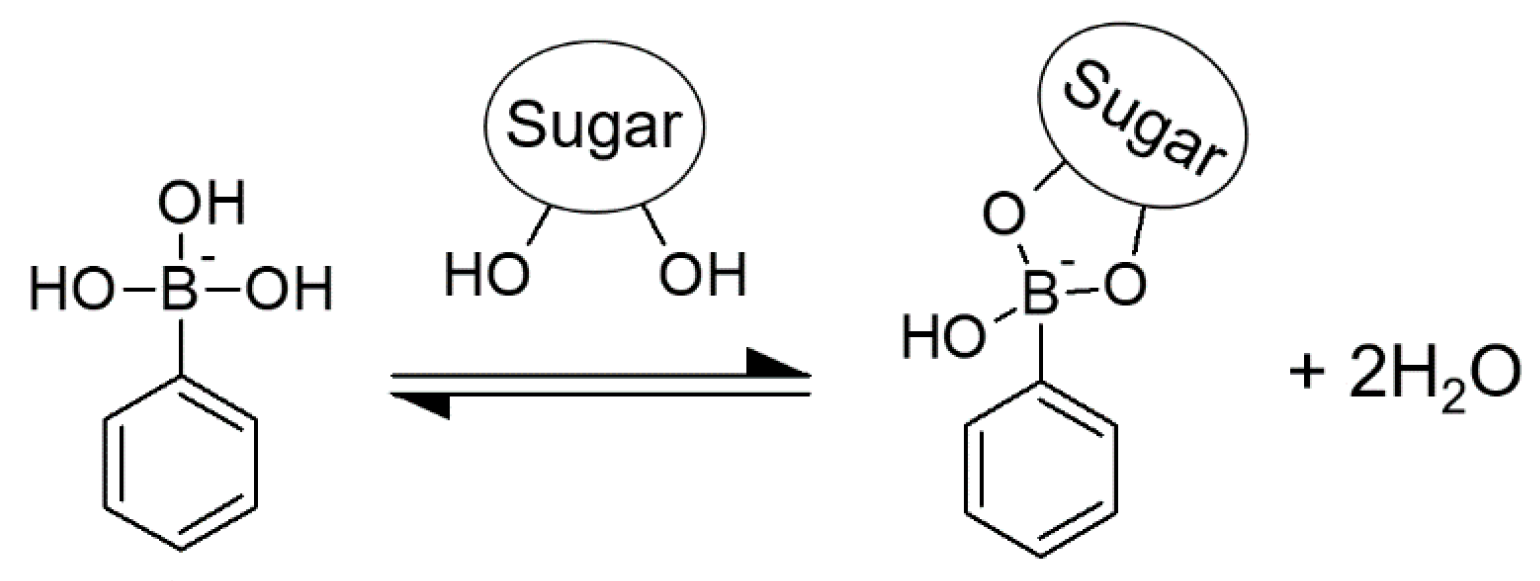
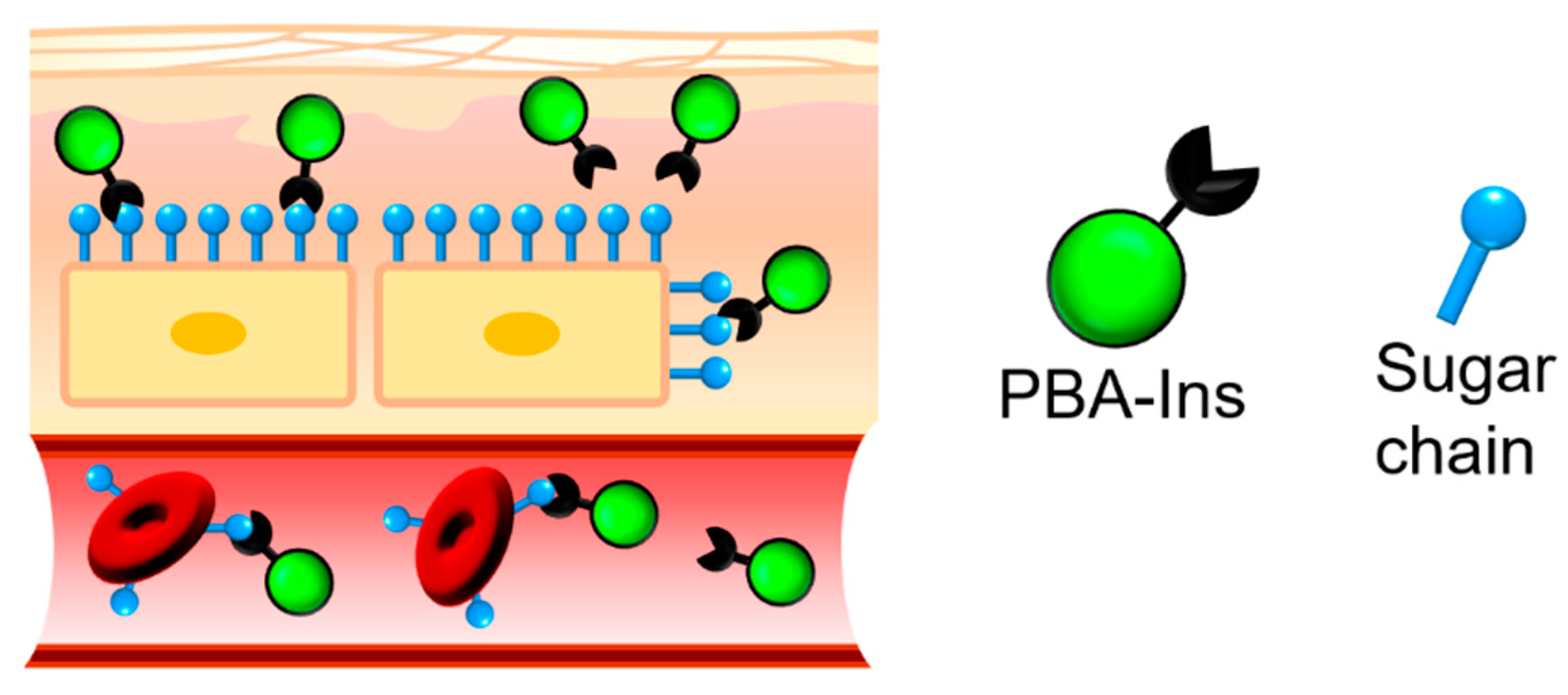
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PBA-Ins
2.3. Animal Test
2.4. RBC Agglutination
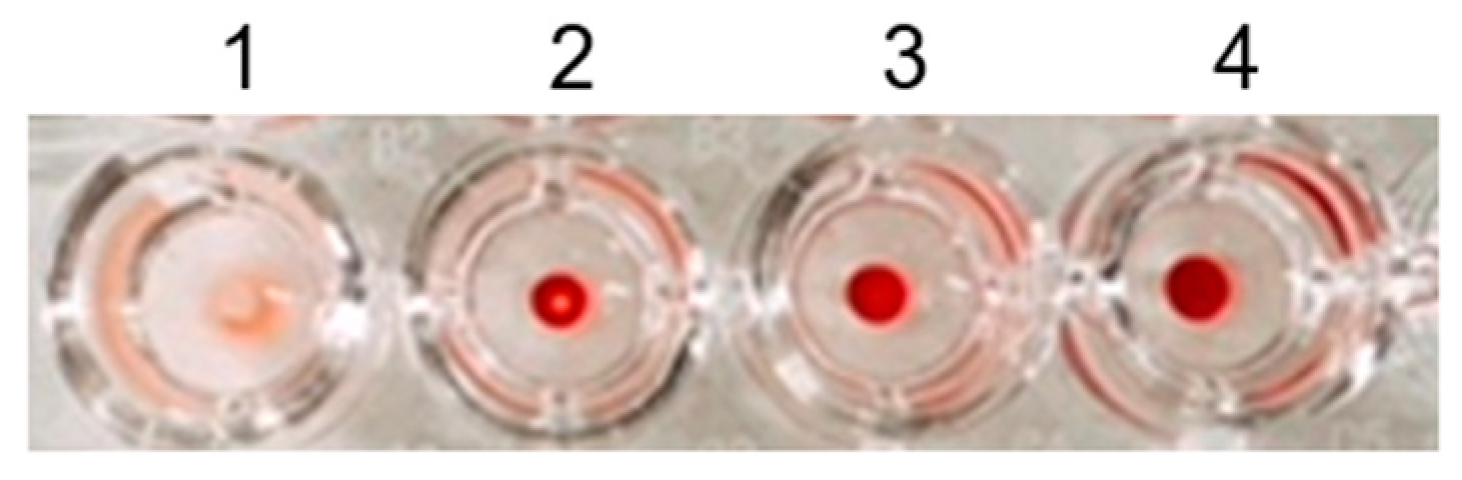
2.4.1. Investigation of an Appropriate Dilution Ratio of RBCs
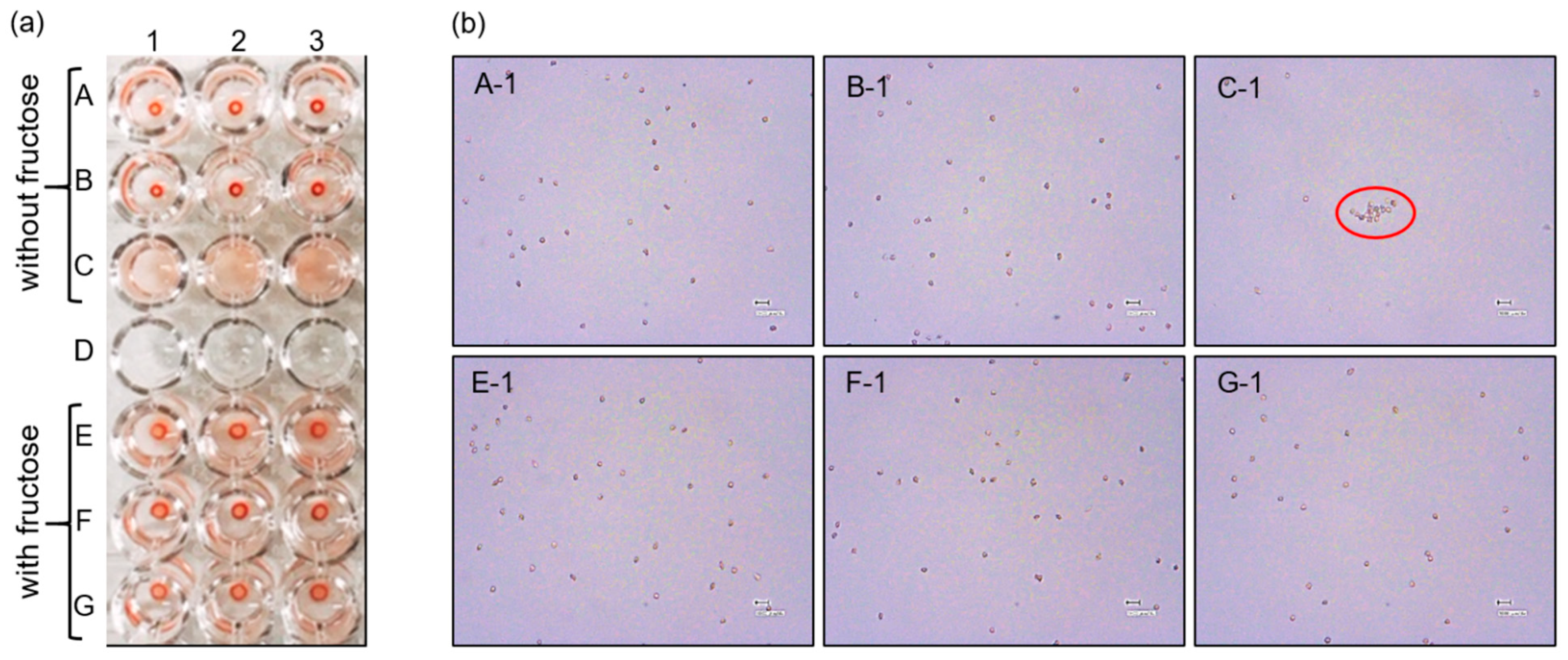
2.4.2. The Effect of Fructose on RBC Agglutination
3. Results and Discussion
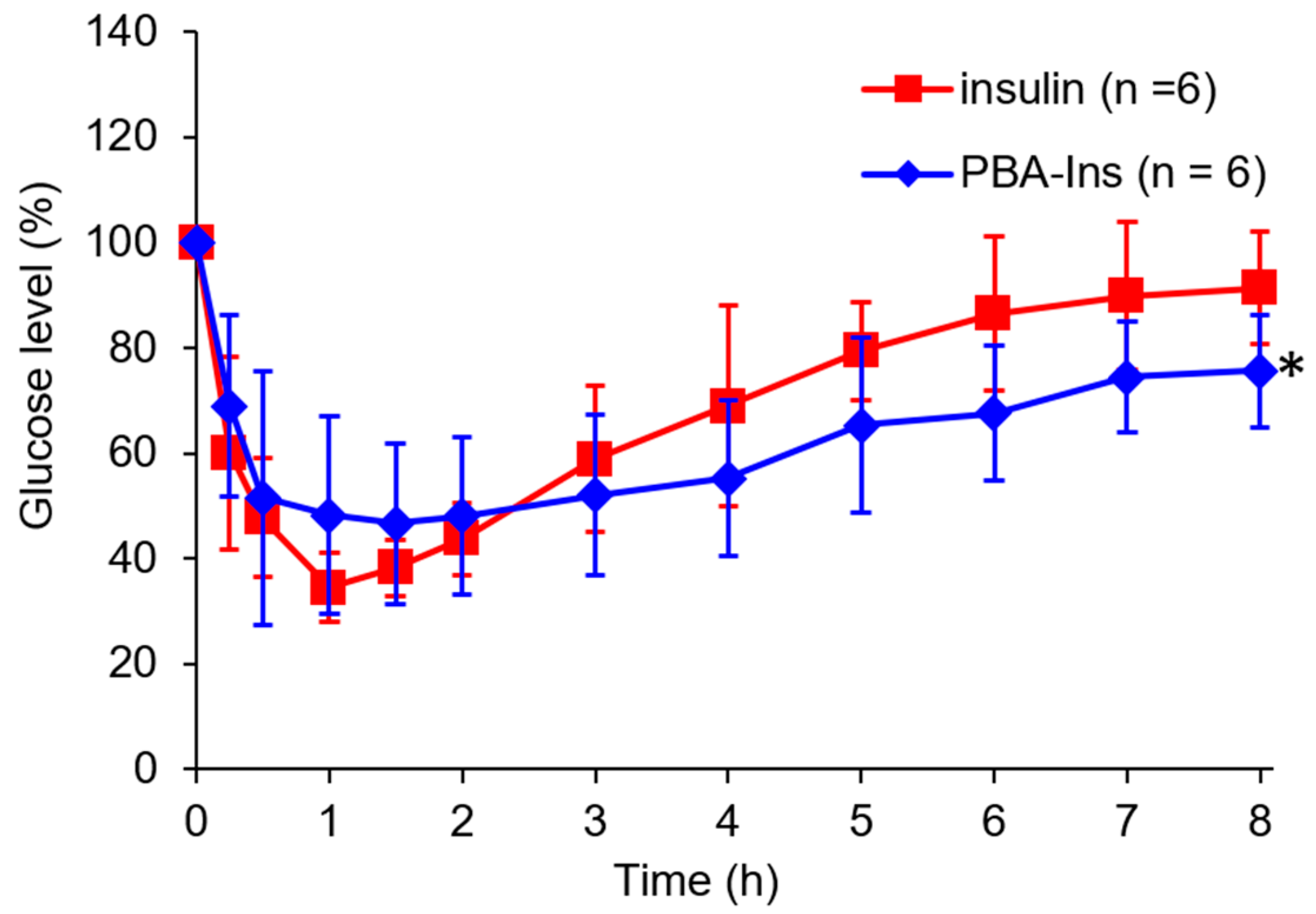
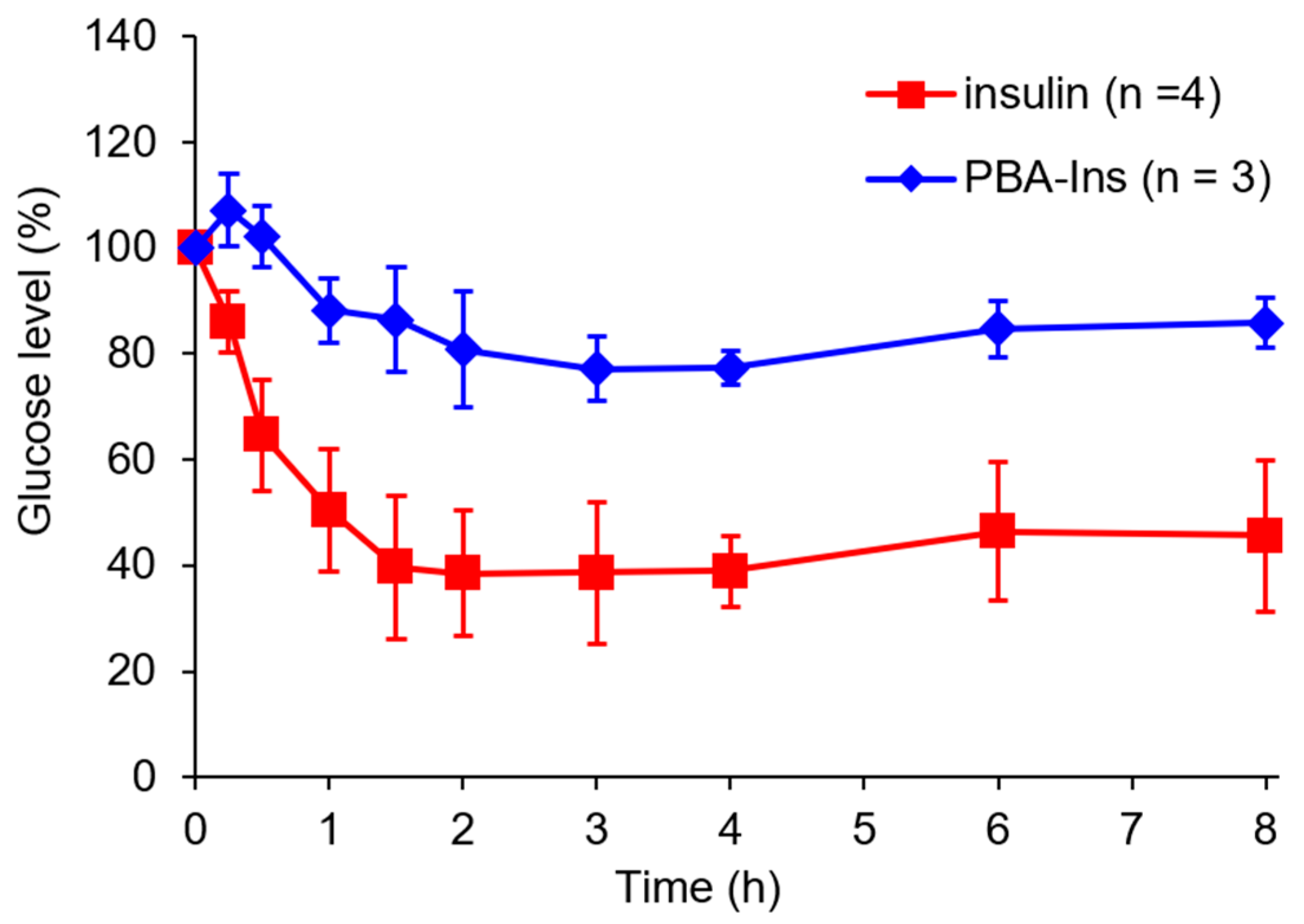
3.1. Glucose-Lowering Activity by Intravenous Injection
3.2. Agglutination of RBCs
3.2.1. Investigation of the Appropriate Dilution Ratio of RBCs
3.2.2. Investigating the Role of PBA in RBC Agglutination
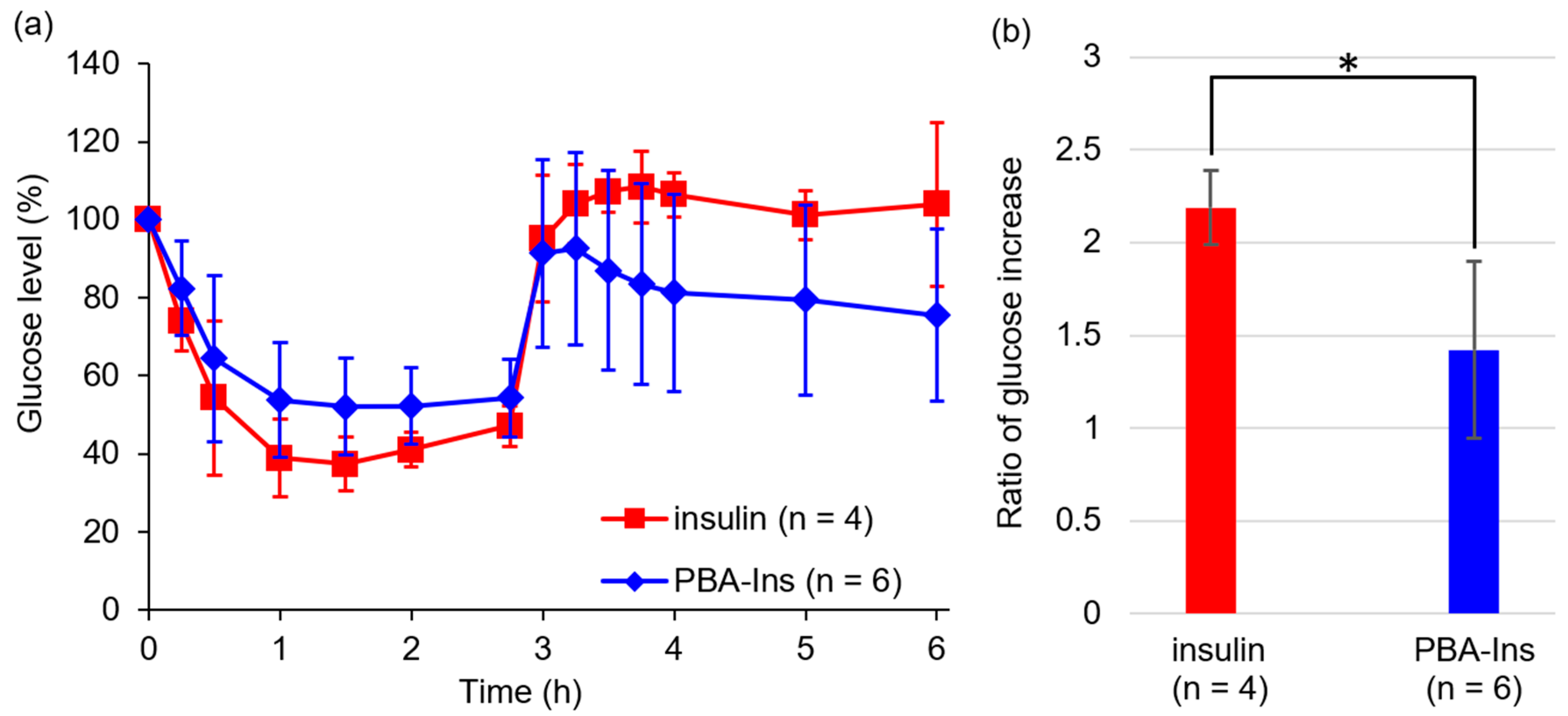
3.3. Glucose-Lowering Activity by Subcutaneous Injection
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishiyabu, R.; Kubo, Y.; James, T.D.; Fossey, J.S. Boronic acid building blocks: Tools for self assembly. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1124–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, S.D.; Davidson, M.G.; Van Den Elsen, J.M.H.; Fossey, J.S.; Jenkins, A.T.A.; Jiang, Y.B.; Kubo, Y.; Marken, F.; Sakurai, K.; Zhao, J.; et al. Exploiting the reversible covalent bonding of boronic acids: Recognition, sensing, and assembly. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, W.L.A.A.; Sumerlin, B.S. Synthesis and applications of boronic acid-containing polymers: From materials to medicine. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 1375–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Chen, X.-X.; Jiang, Y.-B. Recent advances in boronic acid-based optical chemosensors. Analyst 2017, 142, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, T.D.; Sandanayake, K.R.A.S.; Shinkai, S. Saccharide sensing with molecular receptors based on boronic acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1996, 35, 1910–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, Y.; Seki, T.; Takahashi, S.; Anzai, J. Electrochemical and optical sugar sensors based on phenylboronic acid and its derivatives. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2011, 31, 1257–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.S.; Christensen, J.B. Recent advances in fluorescent arylboronic acids for glucose sensing. Biosensors 2013, 3, 400–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.J.; Takeuchi, S. Towards smart tattoos: Implantable biosensors for continuous glucose monitoring. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Takahashi, S.; Du, X.; Anzai, J. Electrochemical biosensors based on ferroceneboronic acid and its derivatives: A review. Biosensors 2014, 4, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacina, K.; Skládal, P.; James, T.D. Boronic acids for sensing and other applications - a mini-review of papers published in 2013. Chem. Cent. J. 2014, 8, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, Y.; Miki, R.; Seki, T. Colorimetric sugar sensing using boronic acid-substituted azobenzenes. Materials 2014, 7, 1201–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzai, J. Recent progress in electrochemical biosensors based on phenylboronic acid and derivatives. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2016, 67, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zhou, S. Responsive materials for self-regulated insulin delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 1464–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Abe, K.; Egawa, Y.; Miki, R.; Juni, K.; Seki, T. A pseudopolyrotaxane for glucose-responsive insulin release: The effect of binding ability and spatial arrangement of phenylboronic acid group. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3807–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yoshida, K.; Sato, K.; Anzai, J. Phenylboronic acid-functionalized layer-by-layer assemblies for biomedical applications. Polymers 2017, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, Y.; Seki, T.; Miki, R.; Seki, T. Sugar-responsive smart materials based on phenylboronic acid and cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2019, 94, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springsteen, G.; Wang, B. A detailed examination of boronic acid-diol complexation. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 5291–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, H.; Uchimura, E.; Koshino, H.; Okano, T.; Kataoka, K. Anomalous binding profile of phenylboronic acid with N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac) in aqueous solution with varying pH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 3493–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes—2019 Abridged for primary care providers. Clin. Diabetes 2019, 37, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, A.J.R.; Pasparakis, G. Rapid formation of cell aggregates and spheroids induced by a “smart” boronic acid copolymer. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22930–22941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.E.; Kumar, A.; Nilsang, S.; Aguilar, M.R.; Mikhalovska, L.I.; Savina, I.N.; Nilsson, L.; Scheblykin, I.G.; Kuzimenkova, M.V.; Galaev, I.Y. Evaluation of boronate-containing polymer brushes and gels as substrates for carbohydrate-mediated adhesion and cultivation of animal cells. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 75, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Sun, K.; Fan, J.; Zhang, P.; Meng, J.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L. Dual-responsive surfaces modified with phenylboronic acid-containing polymer brush to reversibly capture and release cancer cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7603–7609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, F.; Collins, J.; Heath, D.E.; Connal, L.A. Dynamic covalent hydrogels for triggered cell capture and release. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 28, 2235–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Sato, N.; Kataoka, K.; Miyahara, Y. Noninvasive sialic acid detection at cell membrane by using phenylboronic acid modified self-assembled monolayer gold electrode. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 12022–12023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, C.; Ohno, Y.; Seki, T.; Miki, R.; Seki, T.; Egawa, Y. Sugar-responsive layer-by-layer film composed of phenylboronic acid-appended insulin and poly(vinyl alcohol). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 66, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, T.J.; Peebles, H.C.; Hageman, J.H. Synthesis of a fluorescent boronic acid which reversibly binds to cell walls and a diboronic acid which agglutinates erythrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1980, 96, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havelund, S.; Plum, A.; Ribel, U.; Jonassen, I.; Vølund, A.; Markussen, J.; Kurtzhals, P. The mechanism of protraction of insulin detemir, a long-acting, acylated analog of human insulin. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1498–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonassen, I.; Havelund, S.; Hoeg-Jensen, T.; Steensgaard, D.B.; Wahlund, P.O.; Ribel, U. Design of the novel protraction mechanism of insulin degludec, an ultra-long-acting basal insulin. Pharm. Res. 2012, 29, 2104–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgenfeld, R.; Seipke, G.; Berchtold, H.; Owens, D.R. The evolution of insulin glargine and its continuing contribution to diabetes care. Drugs 2014, 74, 911–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ohno, Y.; Kawakami, M.; Seki, T.; Miki, R.; Seki, T.; Egawa, Y. Cell Adhesive Character of Phenylboronic Acid-Modified Insulin and Its Potential as Long-Acting Insulin. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12030121
Ohno Y, Kawakami M, Seki T, Miki R, Seki T, Egawa Y. Cell Adhesive Character of Phenylboronic Acid-Modified Insulin and Its Potential as Long-Acting Insulin. Pharmaceuticals. 2019; 12(3):121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12030121
Chicago/Turabian StyleOhno, Yui, Momoko Kawakami, Tomohiro Seki, Ryotaro Miki, Toshinobu Seki, and Yuya Egawa. 2019. "Cell Adhesive Character of Phenylboronic Acid-Modified Insulin and Its Potential as Long-Acting Insulin" Pharmaceuticals 12, no. 3: 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12030121
APA StyleOhno, Y., Kawakami, M., Seki, T., Miki, R., Seki, T., & Egawa, Y. (2019). Cell Adhesive Character of Phenylboronic Acid-Modified Insulin and Its Potential as Long-Acting Insulin. Pharmaceuticals, 12(3), 121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph12030121




