Abstract
The overexpression of gastrin-releasing peptide receptors (GRPRs) in frequently occurring human tumors has provided the opportunity to use bombesin (BBN) analogs as radionuclide carriers to cancer sites for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. We have been alternatively exploring human GRP motifs of higher GRPR selectivity compared to frog BBN sequences aiming to improve pharmacokinetic profiles. In the present study, we compared two differently truncated human endogenous GRP motifs: GRP(14–27) and GRP(18–27). An acyclic tetraamine was coupled at the N-terminus to allow for stable binding of the SPECT radionuclide 99mTc. Their biological profiles were compared in PC-3 cells and in mice without or with coinjection of phosphoramidon (PA) to induce transient neprilysin (NEP) inhibition in vivo. The two 99mTc-N4-GRP(14/18–27) radioligands displayed similar biological behavior in mice. Coinjection of PA exerted a profound effect on in vivo stability and translated into notably improved radiolabel localization in PC-3 experimental tumors. Hence, this study has shown that promising 99mTc-radiotracers for SPECT imaging may indeed derive from human GRP sequences. Radiotracer bioavailability was found to be of major significance. It could be improved during in situ NEP inhibition resulting in drastically enhanced uptake in GRPR-expressing lesions.
1. Introduction
Gastrin-releasing peptide receptors (GRPRs) are overexpressed in several human malignancies such as prostate cancer, mammary carcinoma, and lung cancer [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Consequently, they have attracted considerable attention as potential biomolecular targets for diagnosis and therapy with radionuclide carriers directed to GRPR-positive cancer lesions [11,12]. Originally, the frog tetradecapeptide bombesin (BBN, Pyr-Gln-Arg-Tyr-Gly-Asn-Gln-Trp-Ala-Val-Gly-His-Leu-Met-NH2) and its truncated C-terminal octapeptide fragment BBN(7–14) have served as motifs for the development of GRPR-targeting radioligands. However, BBN-like analogs bind with comparable affinity not only to GRPR (BB2R), but also to the neuromedin B (NMBR, BB1R), another member of the three mammalian bombesin receptor subtypes [1,2]. The above two subtypes are pharmacologically distinguished by their selectivity for different endogenous human homologs of amphibian BBN. Thus, the 27-mer GRP (H-Val-Pro-Leu-Pro-Ala-Gly-Gly-Gly-Thr- Val-Leu-Thr-Lys-Met-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Gly-Asn-His-Trp-Ala-Val-Gly-His-Leu-Met-NH2), the 14-mer GRP(14–27), and the C-terminal decapeptide GRP(18–27) fragments strongly bind to the GRPR, whereas neuromedin B (NMB, H-Gly-Asn-Leu-Trp-Ala-Thr-Gly-His-Phe-Met-NH2) exhibits high affinity for the NMBR [13]. The two GRPR and NMBR subtypes are physiologically expressed in the human brain and the gut, especially in stomach, pancreas, and gastrointestinal tract, and they are also implicated in cancer [14,15,16]. It is reasonable to assume, that radiolabeled BBN agonists of poor GRPR selectivity will show increased levels of background radioactivity by virtue of their binding to both GRPR and NMBR populations distributed in the body, especially in the abdomen. Furthermore, additive GRPR- and NMBR-mediated effects in the gastrointestinal tract, such as abdominal smooth muscle contraction and stimulation of gastrointestinal hormone secretion, are to be expected after intravenous injection of BBN-like agonist radioligands [17,18,19,20,21,22].
In contrast to amphibian BBN-like motifs, the respective human homologs have surprisingly remained unexploited as radionuclide carriers for targeting GRPR-positive cancer [13]. Motivated by this gap in the inventory of GRPR-directed radioligands we have expanded our research efforts to native human GRP sequences in order to explore their applicability in GRPR-targeted tumor diagnosis and therapy. First, we introduced a small library of tetraamine derivatized GRP(18–27) analogs labeled with the SPECT radionuclide 99mTc [23,24]. Compared to previously reported 99mTc-radiopeptides, which are based on the full-length BBN or its truncated BBN(7–14) octapeptide fragment [25], the 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) showed high GRPR selectivity and superior in vivo characteristics in tumor-bearing mice, such as faster renal clearance and improved tumor to background ratios. On the other hand, single or double amino acid substitutions in the decapeptide backbone exerted pronounced effects on several biological properties, eventually affecting tumor targeting capabilities and pharmacokinetics. In a following study, a series of differently truncated GRP sequences were coupled to the universal chelator DOTA (1,4,7,10- tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid) and labeled with 111In. Receptor affinity, internalization efficiency and tumor uptake of these analogs were favored both by longer peptide chain and by the presence of basic amino acids Lys13 and Arg17 in the native GRP sequence [26].
Following this line of research, we herein introduced 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and compared its biological profile in PC-3 cells and mice models with 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (Figure 1). It should be noted that basic positions Lys13 and Arg17 in the native GRP sequence are now occupied by the positively charged N4+x/[99mTc(O)2(N4)]+1-moiety and not by the negatively charged DOTA. This arrangement allows for comparisons with the DOTA-derivatized analogs and further studying the influence of positive/negative charges in 13 and 17 positions of the GRP chain [26]. Next, the selectivity of N4-GRP(14–27) for each of the three mammalian bombesin receptor subtypes was investigated applying receptor autoradiography in human excised biopsy samples, expressing one of the GRPR, NMBR, and bombesin subtype 3 (BB3R) receptors. Finally, the impact of in vivo stability of 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) on tumor targeting and pharmacokinetics was compared in mice. The role of neprilysin (NEP) [27] on the in vivo degradation of the two human GRP-based sequences was monitored by HPLC analysis of blood samples collected without or with coinjection of the NEP-inhibitor phosphoramidon (PA) [28,29], as previously described for BBN-like radioligands [30,31,32,33,34]. The enhancement of radiotracer localization in experimental GRPR-positive PC-3 tumors in mice during transient NEP inhibition induced by PA was assessed.
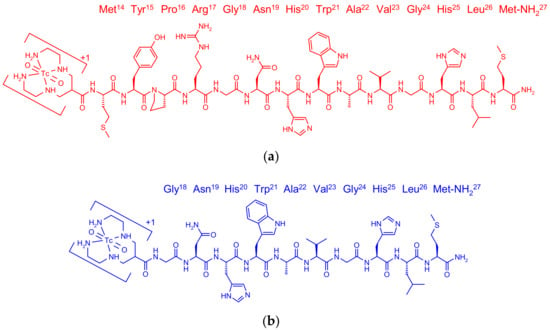
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of (a) 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) (red) and (b) 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (blue).
2. Results
2.1. Peptides and Radioligands
The bifunctional acyclic tetraamine chelator (6-(carboxy)-1,4,8,11-tetraazaundecane) was covalently coupled by its carboxy functionality at the N-terminal Met14 of GRP(14–27) or the Gly18 of GRP(18–27) via an amide bond [24], generating two different length GRP analogs amenable for labeling with the preeminent SPECT radionuclide 99mTc. Labeling was typically proceeded by a brief incubation with 99mTcO4− generator eluate, SnCl2 as reducing agent, and citrate anions as transfer ligand in alkaline pH at ambient temperature at molar activities of 20 to 40 MBq 99mTc/nmol peptide. Quality control of the radiolabeled products combined HPLC and ITLC analysis. The total radiochemical impurities, comprising 99mTcO4−, [99mTc] citrate, and 99mTcO2 × H2O, did not exceed 2%, while a single radiopeptide species was detected by RP-HPLC. In view of labeling yields >98% and >99% radiochemical purity of the resultant 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27), the radioligands were used without further purification in all subsequent experiments. Representative radiochromatograms of HPLC analysis of 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) are included in Figure 2a,b, respectively.
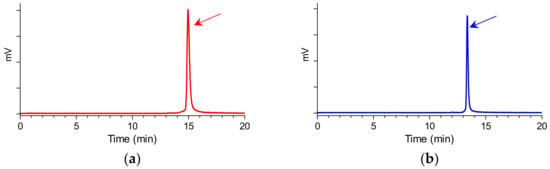
Figure 2.
Representative radiochromatograms of the radiolabeling reaction mixture of (a) 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) (red) and (b) 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (blue), confirming the quantitative formation of high purity radioligands at tR = 14.9 min and tR = 13.3 min, respectively (HPLC system 1).
2.2. In Vitro Assays
2.2.1. Receptor Autoradiography in Human Tumor Samples
The selective affinities of N4-GRP(14–27) for each of the three bombesin receptor subtypes found in mammals were studied during in vitro competition binding assays against the universal radioligand 125I-[DTyr6,βAla11,Phe13,Nle14]BBN(6–14) [6]. Receptor autoradiography was applied in cryostat sections of well characterized human cancers, preferentially expressing one of the subtypes. As summarized in Table 1, N4-GRP(14–27) showed high affinity for the GRPR expressed in resected prostate carcinoma specimens (IC50 = 4.2 ± 1.0 nM, n = 3, vs. IC50 = 2.4 ± 1.0 nM, n = 3 for N4-GRP(18–27) [23]), very low affinity for NMBR present in ileal carcinoid biopsy samples (IC50 = 72 ± 7.6 nM, n = 3, vs. IC50 = 106 ± 13 nM; n = 2 for N4-GRP(18–27) [23]), and no affinity for the BB3R expressed in bronchial carcinoid samples (IC50 > 1000 nM, n = 3, identical to N4-GRP(18–27) [23]). Thus, N4-GRP(14–27) similarly to N4-GRP(18–27), displayed good selectivity for the GRPR. Hence, the GRP-based analogs turned out to be more GRPR-preferring compared to BBN-based radioligands, like Demobesin 3 (N4-[Pro1,Tyr4]BBN) [25] or [DTyr6,βAla11,Phe13,Nle14]BBN(6–14) (Table 1).

Table 1.
Affinities for the three human bombesin receptor subtypes.
2.2.2. Binding Affinity for the Human GRPR
As shown in Figure 3a, N4-GRP(14–27) and N4-GRP(18–27) as well as the respective GRP(14–27) and GRP(18–27) parent peptide references displaced [125I-Tyr4]BBN from GRPR-sites on PC-3 cell membranes in a monophasic and dose-dependent manner. The respective half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values differed, yielding the following rank of decreasing receptor affinity: N4-GRP(14–27) (IC50 0.32 ± 0.03 nM) > GRP(14–27) (IC50 0.45 ± 0.02 nM) > N4-GRP(18–27) (IC50 0.63 ± 0.06 nM) > GRP(18–27) (IC50 1.66 ± 0.20 nM). We observe that the longer-chain peptides consistently showed higher binding affinity to GRPR than their shorter chain counterparts. Moreover, coupling of the positively charged acyclic tetraamine unit in the N-terminus of parent GRP(14/18–27) references improved the affinity of resulting analogs to the GRPR, as previously reported for similarly modified peptide analogs [35].
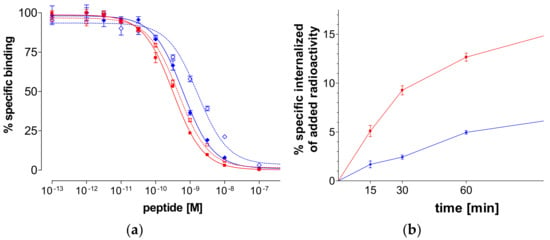
Figure 3.
(a) [125I-Tyr4]BBN displacement curves from gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRPR)-sites on PC-3 cells after 1-h incubation at 22 °C by N4-GRP(14–27) (red solid line—IC50 0.32±0.03 nM), GRP(14–27) (red dashed line—IC50 0.45 ± 0.02 nM), N4-GRP(18–27) (blue solid line—IC50 0.63±0.06 nM) and GRP(18–27) (blue dashed line—IC50 1.66 ± 0.20 nM). (b) GRPR-specific internalization of 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) (red solid line) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (blue solid line) in PC-3 cells during incubation at 37 °C at 15, 30, 60, and 120 min. Results represent average of cell internalized activity ± sd, n = 3; data is corrected for nonspecific internalization in the presence of 1 µM [Tyr4]BBN.
2.2.3. Internalization of 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) in PC-3 Cells
During incubation at 37 °C in PC-3 cells, both 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) were taken up by the cells via a GRPR-mediated process, as demonstrated by the lack of internalization observed in the presence of excess [Tyr4]BBN. In both cases the bulk of cell-associated radioactivity was found in the cells with 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) internalizing much faster in PC-3 cells compared to 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) at all time intervals (Figure 3b). For example, at 1 h, 12.7 ± 0.7% of total added 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) specifically internalized in the cells vs. 5.0 ± 0.3% of 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27), whereas at 2 h these values increased to 19.5 ± 1.4% and 6.9 ± 1.5%, respectively.
2.3. In Vivo Comparison of 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27)
2.3.1. Stability of 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) in Mice
The two 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) radiotracers exhibited distinct resistance to degrading proteases after injection in mice. As revealed by HPLC analysis of blood samples collected at 5 min postinjection (pi), 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) was found less stable (20.1 ± 4.5% intact, n = 3) than the shorter chain 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (31.0 ± 0.9% intact, n = 3). Representative radiochromatograms are shown in Figure 4a,b, respectively.
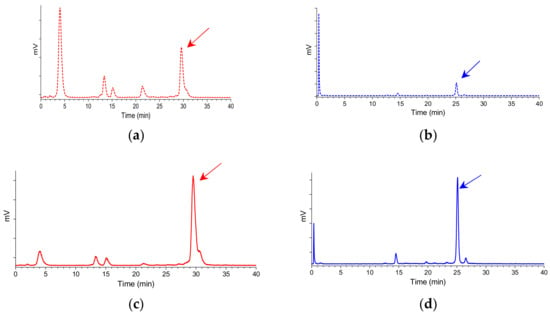
Figure 4.
Representative radiochromatograms of HPLC analysis of mouse blood samples collected 5 min pi of (a) 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) (25.2% intact radiotracer; red dashed line) or (b) 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (31.8% intact radiotracer; blue dashed line) without PA coinjection; the respective radiochromatograms of (c) 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) (63.1% intact radiotracer; tR = 29.6 min; red solid line) or (d) 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (68.1% intact radiotracer; tR = 25.1 min; blue solid line) with PA coinjection are also included; the tR of parent radiopeptide was determined by coinjection with the respective radioligand sample in the column (HPLC system 2) and is indicated here by the arrow.
It should be noted that coinjection of the NEP-inhibitor PA remarkably enhanced the in vivo stability of 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) (66.5 ± 4.8% intact, n = 3) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (70.8 ± 5.4% intact, n = 3) in the circulation, revealing NEP as a major degrading protease for both radiotracers in mice. Representative radiochromatograms are included in Figure 4c,d, respectively.
2.3.2. Biodistribution in PC-3 Xenograft-Bearing Mice
The biodistribution of 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) was studied in severe combined immune deficiency (SCID) mice bearing human PC-3 xenografts expressing the human GRPR. Subcutaneous tumors of suitable size developed in the flanks of mice about four weeks after inoculation of a suspension of prostate adenocarcinoma PC-3 cells and biodistribution was conducted.
Cumulative biodistribution results for 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) at the 1-, 4-, and 24-h pi intervals are summarized in Table 2, and are expressed as mean % injected dose per gram (%ID/g) values ± sd, n = 4. The radiotracer washed rapidly from the blood and the background tissues predominantly via the kidneys and the urinary system. High uptake was observed in the PC-3 tumor at 1-h pi (10.20 ± 0.72%ID/g) that remained at comparably high levels at 4-h pi (8.41 ± 4.16%ID/g; p > 0.05), declining by ~50% at 24-h pi (4.50 ± 0.69%ID/g). Tumor uptake at 4-h pi was significantly lower in the animals treated with excess [Tyr4]BBN (0.62 ± 0.24%ID/g; p < 0.001), suggestive of a GRPR-mediated process. Likewise, 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) highly localized in the GRPR-rich mouse pancreas via a GRPR-specific process, as demonstrated by the lack of pancreatic uptake during GRPR-blockade by coinjection of excess [Tyr4]BBN (35.24 ± 4.70%ID/g vs. 0.83 ± 0.24%ID/g in block; p < 0.001).

Table 2.
Biodistribution data for 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27), expressed as %ID/g mean ± sd, n = 4, in PC-3 xenograft-bearing SCID mice at 1-h, 4-h block, 4-h, and 24-h pi.
Comparative biodistribution results for 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) at the 4-h pi interval are included in Table 3. Data from additional 4-h pi animal groups coinjected with the NEP-inhibitor PA (300 µg) is also included in the Table. The radiotracers displayed similar tissue distribution patterns. The observed higher tumor and pancreatic uptake of 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) did not however differ significantly to that of 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (p > 0.05) [24]. Treatment with PA induced a drastic increase in tumor values for both radiotracers with 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) showing superior tumor values than the shorter chain 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (38.19 ± 4.79%ID/g vs. 28.37 ± 8.05%ID/g, respectively; p < 0.01). Pancreatic values increased by >3-fold for both radiotracers as well. Thus, in agreement with previous studies on BBN-based analogs [31,32,33,34], NEP inhibition likewise resulted in significant stabilization of GRP(14/18–27)-based radioligands in peripheral mouse blood and notable improvement of localization in GRPR-expressing lesions in mice.

Table 3.
Comparative biodistribution data for 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27), expressed as %ID/g mean ± sd, n = 4, in PC-3 xenograft-bearing SCID mice at 4-h pi (controls) and 4-h pi after coinjection of PA.
3. Discussion
A considerable number of radiolabeled analogs of frog BBN have been developed for potential application in the diagnosis and therapy of GRPR-expressing tumors in Homo sapiens [11,12]. This pursuit is based on the overexpression of GRPRs on the surface of malignant cells serving as easily accessible biomolecular targets on cancer lesions [3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]. Joining this effort, we have previously introduced a series of BBN-like analogs, generated by covalently coupling of an acyclic tetraamine at the N-terminus, Demobesin 3–6 [25]. Like native BBN, these peptide ligands displayed indistinguishable binding affinities for the human bombesin receptor subtypes GRPR and NMBR, but no affinity for the BB3R. The respective radiotracers [99mTc] Demobesin 3–6 specifically localized in GRPR-expressing human PC-3 xenografts in mice. Moreover, one of the analogs, [99mTc] Demobesin 4, was able to visualize malignant lesions in a small number of prostate cancer patients with SPECT/CT [36].
We have recently expanded our search toward radioligands based on human endogenous GRP sequences [23,24,26]. The latter are reported for higher GRPR selectivity compared to their frog homolog BBN [13]. This approach has surprisingly remained unexplored up to now, although it offers two major advantages. First, radioactivity levels in abdominal tissues physiologically expressing both GRPR and NMBR subtypes would favorably decrease when GRPR-selective radioligands are used [14,15,16]. Second, injection of GRPR-selective agonists will not activate the NMBR subtype populations in the gut and is hence associated with less adverse effects [17,18,19,20,21,22]. Promising GRPR-selective radioligands based on receptor antagonists have been developed and evaluated in animals and in human, showing excellent tumor targeting and pharmacokinetic profiles [37,38]. Yet, the suitability and efficacy of noninternalizing GRPR antagonists for therapy with low-range beta, alpha, or Auger emitters of high LET has not been established thus far [39,40]. Therefore, the study of radiolabeled GRPR-selective agonists is warranted and may provide an alternative platform for the development of radioligands exhibiting new combinations of biological features particularly suited for cancer theranostics.
As a part of this effort we herein introduced two analogs of endogenous truncated fragments of human GRP carrying an acyclic tetraamine at their terminus, one based on the tetradecapeptide GRP(14–27), and the other on a shorter decapeptide GRP(18–27) chain identical to human neuromedin C (NMC) (Figure 1). As revealed during receptor autoradiography studies in excised biopsy samples of well characterized human tumors expressing each of the GRPR, NMBR, and BB3R subtypes using the universal 125I-[DTyr6,βAla11,Phe13,Nle14]BBN(6–14) radioligand, both N4-GRP(14–27) and N4-GRP(18–27) analogs showed good selectivity for the GRPR subtype (Table 1). This finding is in agreement with previous reports documenting the preference of human GRP and its C-terminal native fragments for GRPR [13]. In contrast, the tetraamine derivatized BBN-like analogs Demobesin 3–6 do not distinguish between GRPR and NMBR, instead behaving like the native frog BBN [25]. The His20 of GRP corresponding to Gln7 of BBN seems to have significant impact on subtype selectivity, followed by the Met14-Tyr13-Pro12-Arg11-tetrapeptide in GRP(14–27) corresponding to the Pyr1-Gln2-Arg3-Leu4-counterpart in native BBN.
Both N4-GRP(14–27) and N4-GRP(18–27) analogs displayed sub-nM affinities for the GRPR during competition assays against [125I-Tyr4]BBN in PC-3 cell membranes, which were found to be increased compared to unmodified GRP(14/18–27) lead structures (Figure 3a). It is interesting to note that the presence of the positively charged N4+x-moiety at positions 13 and 17 of the native GRP chain occupy the two basic amino acids Lys13 and Arg17. When these positions were taken up by negatively charged DOTA instead, a drastic drop in binding affinity was observed (IC50 DOTA-GRP(14–27) = 6.6 ± 0.9 nM and IC50 DOTA-GRP(18–27) = 112 ± 16 nM) [26]. In all cases, longer chain GRP(14–27) analogs consistently displayed higher GRPR-affinity compared to their C-terminal decapeptide counterparts. In agreement with this observation, the internalization rate of 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) in PC-3 cells was clearly superior to that of 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (Figure 3b).
A crucial feature for efficient tumor targeting is metabolic stability that will ensure sufficient radioligand supply to tumor sites after injection in the living organism [31]. Recent studies have revealed the significance of in vivo stability assessment of BBN-like radiotracers vs. in vitro determinations in serum or tissue homogenate incubates to more accurately predict the actual protease(s) encountered by the radioligand after entering the circulation. These studies have demonstrated NEP as a major degrading protease of BBN and its radiolabeled analogs [41,42]. In a recently proposed approach, NEP-inhibitors, like PA [28,29], coinjected with the BBN-based radioligand drastically increased metabolic stability leading to notable enhancement of tumor uptake in animal models [31,32,33,34]. Following this rationale, we have tested the in vivo stability of the two 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) radiotracers in peripheral mouse blood collected 5 min pi by radioanalytical HPLC (Figure 4). The longer chain 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) displayed somewhat poorer stability (20.1 ± 4.5% intact, n = 3) compared to shorter chain 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (31.0 ± 0.9% intact, n = 3). Thus, the presence of additional amide bonds in the longer peptide chain offered further degradation sites for attacking proteases. It is interesting to note, that coinjection of PA drastically increased the stability of both analogs in the circulation, indicating NEP as a major protease in the catabolism of GRP sequences as well.
Aiming to explore the effects of peptide chain as well as NEP inhibition on the pharmacokinetics and tumor targeting capabilities of the two tracers, we have conducted biodistribution experiments in immunosuppressed mice bearing human GRPR-expressing xenografts. Interestingly, the biodistribution patterns of the two radiotracers did not clearly differ (Table 3). Compared to the previously reported 111In-DOTA analogs [26], 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) showed higher tumor uptake. Comparable in vivo tumor targeting was obtained only by 111In-DOTA-GRP(13–27), carrying basic Lys at position 13. However, kidney clearance was notably faster for the 99mTc-radiotracer (4.83 ± 2.12%/g at 4 h pi) than for the 111In-DOTA-Lys13-analog (46.02 ± 3.73%/g at 4 h pi) [26]. Treatment of mice with PA exerted a profound effect on the in vivo profile of both 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (Table 2), is in agreement with previous findings for other BBN-like radioligands. The longer chain 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) exhibited the highest uptake in the experimental tumor, as a combined result of higher internalization rate and pronounced in vivo stabilization induced by PA.
The present study has shown that GRP motifs of different chain length may provide new opportunities for the development of promising GRPR-selective radioligands. The latter may prove to be a useful asset in the arsenal of anti-GRPR radioactive drugs, by internalizing in cancer cells while evading binding to and activation of bombesin receptor subtypes other than the GRPR in the gut. Furthermore, it has shown the impact of in vivo metabolic stability in maximizing tumor localization. Structural modifications in peptide lead-structures to improve the stability of radiopeptides, such as amino acid replacements, cyclization, or changes of cleavable peptide bonds, may deteriorate other important biological features, as for example receptor affinity, cell uptake, tumor targeting, and overall pharmacokinetics. On the other hand, transient in situ inhibition of NEP represents a smart method to accomplish this goal and warrants further efforts for translation in the clinic. Despite challenges related to biosafety, regulatory and financial hurdles, once established in a proof-of-principal study, this strategy is expected to boost the development and clinical application of other NEP-catabolized radioligands, considerably saving costs and resources [31,32,33,34].
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptides and Reagents
The N4-GRP(14–27) and N4-GRP(18–27) peptide conjugates were synthesized on the solid support following a published method [24] and were provided by PiChem (Graz, Austria). The [Tyr4]BBN (Tyr4-bombesin, Pyr-Gln-Arg-Tyr-Gly-Asn-Gln-Trp-Ala-Val-Gly-His-Leu-Met-NH2) and GRP(14–27) (H-Met-Tyr-Pro-Arg-Gly-Asn-His-Trp-Ala-Val-Gly-His-Leu-Met-NH2) references were purchased from PSL GmbH (Heidelberg, Germany), whereas GRP(18–27) (H-Gly-Asn-His-Trp-Ala- Val-Gly-His-Leu-Met-NH2) was provided by PeptaNova GmbH (Sandhousen, Germany). Phosphoramidon disodium dehydrate (N-(α-rhamnopyranosyloxyhydro xyphosphinyl) -L-leucyl-L-tryptophan × 2Na × 2H2O; PA) was purchased from PeptaNova GmbH (Sandhousen, Germany).
Preparation and Quality Control of 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27)
Lyophilized N4-GRP(14–27) and N4-GRP(18–27) were dissolved in bidistilled water to a final 1 mM concentration and bulk solutions were distributed in 50 µL aliquots in Eppendorf vials (Protein LoBind Tube 1.5 mL; Eppendorf AG, Hamburg, Germany) and stored at −20 °C. For 99mTc labeling, the following solutions were added into an Eppendorf tube containing 0.5 M phosphate buffer pH 11.5 (25 µL): 0.1 M sodium citrate (3 µL), [99mTc]NaTcO4 (210 µL, 150–300 MBq) eluted from a commercial 99Mo/99mTc generator (Ultratechnekow, Tyco Healthcare, Petten, The Netherlands), N4-GRP(14–27) or N4-GRP(18–27) stock solution (7.5 µL, 7.5 nmol), and finally, fresh SnCl2 solution in EtOH (5 µg, 5 µL). After 30 min incubation at ambient temperature the reaction mixture was neutralized by addition of 1 M HCl (4 µL) and EtOH was added (25 µL).
Quality control of the radiolabeled products comprised radioanalytical HPLC and instant thin-layer chromatography (ITLC). HPLC analyses were performed on a Waters Chromatograph coupled to a 2998 photodiode array UV detector (Waters, Vienna, Austria) and a Gabi gamma detector (Raytest RSM Analytische Instrumente GmbH, Germany). For analysis, a Waters Symmetry Shield RP-18 cartridge column (5 μm, 3.9 mm × 20 mm) was eluted at a 1.0 mL/min flow rate with the following gradient, 0% B to 40% B in 20 min, where A = 0.1% aq. trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), B = MeCN (System 1). Under these conditions 99mTcO4− eluted at 1.8 min and 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) with a tR > 12 min. For the detection of reduced hydrolyzed technetium (99mTcO2·× H2O) ITLC was conducted on ITLC-SG strips (Pall Corporation, New York, NY, USA), as previously described. The resultant 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) radioligands were used without further purification in all subsequent experiments.
Radioiodination of [Tyr4]BBN was performed using 125I ([125I]NaI in 0.1 N NaOH (pH 12–14) provided by MDS Nordion, Ottawa, ON, Canada) according to the chloramine-T methodology, as previously described [34]. Methionine was added to the purified radioligand solution to prevent reoxidation of Met14 to the corresponding sulfoxide and the resulting stock solution in 0.1% BSA-PBS was kept at −20 °C; aliquots thereof were used in competition binding assays (molar activity of 81.4 GBq/μmol).
4.2. In Vitro Assays
4.2.1. Cell Lines and Culture
Human androgen-independent prostate adenocarcinoma PC-3 cells endogenously expressing the human GRPR (LGC Promochem, Teddington, UK) were used in the present study [43]. Cells were cultured in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI)-1640 medium, supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 100 U/mL penicillin, and 100 µg/mL streptomycin, and kept in a controlled humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 at 37 °C. Passages were performed weekly using a trypsin/EDTA (0.05%/0.02% w/v) solution. All culture media were purchased from Gibco BRL, Life Technologies and supplements were provided by Biochrom KG Seromed.
4.2.2. Receptor Autoradiography
Binding affinities of N4-GRP(14–27) were determined by in vitro receptor autoradiography performed on cryostat sections of well characterized human tumor tissues, prostate carcinomas for GRPR, ileal carcinoids for NMBR and bronchial carcinoids for BB3R, as previously described [23]. The universal radioligand 125I-[DTyr6,βAla11,Phe13,Nle14]BBN(6–14) (2 Ci/mol; ANAWA, Wangen Switzerland) was used as tracer known to identify all three bombesin receptor subtypes [6]. IC50 values are given in nM ± SEM.
4.2.3. Competition Binding in PC-3 Cell-Membranes
Competition binding experiments against [125I-Tyr4] BBN were performed with N4-GRP(14–27) and N4-GRP(18–27), or with the unmodified parent peptide references GRP(14–27) and GRP(18–27) in PC-3 cell membranes. For the assay, triplicates per concentration point (concentration range: 10−13–10−6 M) of each test peptide were incubated together with the radioligand (~40,000 cpm per assay tube at a 50 pM concentration) in PC-3 cell-membrane homogenates in a total volume of 300 μL binding buffer (BB, 50 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 1% BSA, 5.5 mM MgCl2, 35 μM bacitracin) for 1 h at 22 °C in an Incubator-Orbital Shaker (MPM Instr. SrI, Bernareggio, Italy). Binding was interrupted by ice-cold washing buffer (WB, 10 mM HEPES pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl) and rapid filtration (Whatman GF/B filters presoaked in BB) on a Brandel Cell Harvester (Adi Hassel Ing. Büro, Munich, Germany). Filters were washed with ice-cold WB and counted in an automatic well-type gamma counter (NaI(Tl) 3′-crystal, Cobra Packard Auto-Gamma 5000 series instrument). The IC50 values were calculated using nonlinear regression according to a one-site model applying the PRISM 2 program (Graph Pad Software, San Diego, CA, USA).
4.2.4. Internalization Assay in PC-3 Cells
The internalization rates of 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) were compared in PC-3 cells. Briefly, PC-3 cells were seeded in six-well plates (~1 × 106 cells per well) 24 h before the experiment. Approximately 50,000 cpm of either 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) or 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) (corresponding to 250 fmol total peptide in 150 μL of 0.5% BSA/PBS) was added alone (total) or in the presence of 1 μM [Tyr4]BBN (nonspecific). Cells were incubated at 37 °C for 15, 30, 60, and 120 min and incubation was interrupted each time by placing the plates on ice, removing the supernatants and rapid rinsing with ice-cold 0.5% BSA/PBS. Cells were then treated 2 × 5 min with acid wash buffer (2 × 0.6 mL, 50 mM glycine buffer pH 2.8, 0.1 M NaCl) at room temperature and supernatants were collected (membrane-bound fraction). After rinsing with 1 mL chilled 0.5% BSA/PBS, cells were lysed by treatment with 1 N NaOH (2 × 0.6 mL) and lysates were collected (internalized fraction). Sample radioactivity was measured in the γ-counter and percent internalized radioactivity was determined vs. total added activity. Results represent the average values ± sd of three experiments performed in triplicate.
4.3. Animal Studies
4.3.1. In Vivo Stability Tests
For stability experiments, healthy male Swiss albino mice (30 ± 5 g, NCSR “Demokritos” Animal House Facility) were used. Test radioligand—99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) or 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27)—was injected as a 100 μL bolus (37–74 MBq, 3 nmol total peptide) in the tail vein together with injection solution (100 µL; control) or with a PA-solution (100 µL injection solution containing 300 µg PA). Animals were euthanized and blood (0.5–1 mL) was directly withdrawn from the heart in an ice-cold syringe and transferred in a prechilled EDTA and methionine-containing Eppendorf tube on ice. Blood samples were centrifuged for 10 min at 2000 g/4 °C and plasma was collected. After addition of an equal volume of ice-cold MeCN the mixture was centrifuged for 10 min at 15,000 g/4 °C. The supernatant was concentrated under a N2-flux at 60 °C to 0.05–0.1 mL, diluted with saline (0.4 mL), filtered through a 0.22 μm Millex GV filter (Millipore, Milford, CT, USA), and analyzed by RP-HPLC. The Symmetry Shield RP18 (5 μm, 3.9 mm × 20 mm) column was eluted at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min with the following linear gradient (system 2): 0% B at 0 min to 10% B in 10 min and then in 40 min to 30% B; A = 0.1% aq. TFA and B = MeCN. The tR of the intact radiopeptide was determined by coinjection with the 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) and 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) reference in the HPLC.
4.3.2. Induction of PC-3 Xenografts in SCID Mice
A suspension containing freshly harvested human PC-3 cells (≈150 μL of a ≈1.2 × 107 cells) was subcutaneously injected in the flanks of female SCID mice (15 ± 3 g, six weeks of age at the day of arrival, NCSR “Demokritos” Animal House Facility). The animals were kept under aseptic conditions and 4 weeks later developed well-palpable tumors (80–200 mg) at the inoculation sites.
4.3.3. Biodistribution in PC-3 Xenograft-Bearing SCID Mice
For the biodistribution study, animals in groups of 4 received via the tail vein a 100 μL bolus of 99mTc-N4-GRP(14–27) (180–370 kBq, corresponding to 10 pmol total peptide) coinjected either with injection solution (100 μL; control) or PA-solution (300 μg PA dissolved in 100 μL injection solution; 4 h + PA), or with excess [Tyr4]BBN (100 μL injection solution containing 50 μg [Tyr4]BBN for in vivo GRPR-blockade; 4 h block). Animals were euthanized at 1-, 4-, and 24-h pi; in the case of 99mTc-N4-GRP(18–27) two animal groups were included at the 4-h pi interval, namely the control and PA groups described above. Mice were dissected; samples of blood, tumors, and organs of interest were collected, weighed, and measured for radioactivity in the gamma counter. Intestines and stomach were not emptied of their contents. Data was calculated as percent injected dose per gram tissue (%ID/g) with the aid of standard solutions and represent mean values ± sd, n = 4. All animal experiments were performed in compliance with national and European guidelines and approved by national authorities (Prefecture of Athens, EL 25 BIO 021; #1609 and #1610).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.A.N.; Methodology, B.A.N., T.M.N. and J.C.R.; Investigation, A.K., E.L., P.K., B.W., B.A.N., T.M.N. and J.C.R.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, T.M.N.; Writing—Review and Editing, B.A.N., M.d.J., E.P.K. and J.C.R.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kroog, G.S.; Jensen, R.T.; Battey, J.F. Mammalian bombesin receptors. Med. Res. Rev. 1995, 15, 389–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.T.; Battey, J.F.; Spindel, E.R.; Benya, R.V. International union of pharmacology. LXVIII. Mammalian bombesin receptors: Nomenclature, distribution, pharmacology, signaling, and functions in normal and disease states. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwalder, R.; Reubi, J.C. Gastrin-releasing peptide receptors in the human prostate: Relation to neoplastic transformation. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Körner, M.; Waser, B.; Rehmann, R.; Reubi, J.C. Early over-expression of GRP receptors in prostatic carcinogenesis. Prostate 2014, 74, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, M.; Montani, M.; Gerhardt, J.; Wild, P.J.; Hany, T.F.; Hermanns, T.; Muntener, M.; Kristiansen, G. Profiling gastrin-releasing peptide receptor in prostate tissues: Clinical implications and molecular correlates. Prostate 2012, 72, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reubi, J.C.; Wenger, S.; Schmuckli-Maurer, J.; Schaer, J.C.; Gugger, M. Bombesin receptor subtypes in human cancers: Detection with the universal radioligand 125I-[d-Tyr6,beta-Ala11,Phe13,Nle14]bombesin(6-14). Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar]
- Halmos, G.; Wittliff, J.L.; Schally, A.V. Characterization of bombesin/gastrin-releasing peptide receptors in human breast cancer and their relationship to steroid receptor expression. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gugger, M.; Reubi, J.C. Gastrin-releasing peptide receptors in non-neoplastic and neoplastic human breast. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 2067–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, J.; Achcar, R.D.; Cano, C.H.; Macedo, B.R.; Meurer, L.; Batlle, B.S.; Groshong, S.D.; Kulczynski, J.M.; Roesler, R.; Dal Lago, L.; et al. Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor expression in lung cancer. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2014, 138, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinee, D.G., Jr.; Fishback, N.F.; Koss, M.N.; Abbondanzo, S.L.; Travis, W.D. The spectrum of immunohistochemical staining of small-cell lung carcinoma in specimens from transbronchial and open-lung biopsies. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1994, 102, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, P.; Ramos-Alvarez, I.; Moody, T.W.; Jensen, R.T. Bombesin related peptides/receptors and their promising therapeutic roles in cancer imaging, targeting and treatment. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 1055–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maina, T.; Nock, B.A. From bench to bed: New gastrin-releasing peptide receptor-directed radioligands and their use in prostate cancer. PET Clin. 2017, 12, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, H.; Gonzalez, N.; Sancho, V.; Mantey, S.A.; Nuche-Berenguer, B.; Pradhan, T.; Coy, D.H.; Jensen, R.T. Pharmacology and selectivity of various natural and synthetic bombesin related peptide agonists for human and rat bombesin receptors differs. Peptides 2011, 32, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigna, S.R.; Mantyh, C.R.; Giraud, A.S.; Soll, A.H.; Walsh, J.H.; Mantyh, P.W. Localization of specific binding sites for bombesin in the canine gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 1987, 93, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chave, H.S.; Gough, A.C.; Palmer, K.; Preston, S.R.; Primrose, J.N. Bombesin family receptor and ligand gene expression in human colorectal cancer and normal mucosa. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 82, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, A.; Laderach, U.; Friess, H.; Buechler, M.W.; Reubi, J.C. Bombesin receptors in distinct tissue compartments of human pancreatic diseases. Lab. Investig. 2000, 80, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delle Fave, G.; Annibale, B.; de Magistris, L.; Severi, C.; Bruzzone, R.; Puoti, M.; Melchiorri, P.; Torsoli, A.; Erspamer, V. Bombesin effects on human GI functions. Peptides 1985, 6 (Suppl. 3), 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzone, R.; Tamburrano, G.; Lala, A.; Mauceri, M.; Annibale, B.; Severi, C.; de Magistris, L.; Leonetti, F.; Delle Fave, G. Effect of bombesin on plasma insulin, pancreatic glucagon, and gut glucagon in man. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1983, 56, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Fave, G.; Kohn, A.; De Magistris, L.; Annibale, B.; Bruzzone, R.; Sparvoli, C.; Severi, C.; Torsoli, A. Effects of bombesin on gastrin and gastric acid secretion in patients with duodenal ulcer. Gut 1983, 24, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severi, C.; Jensen, R.T.; Erspamer, V.; D’Arpino, L.; Coy, D.H.; Torsoli, A.; Delle Fave, G. Different receptors mediate the action of bombesin-related peptides on gastric smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 260, G683–G690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, K.N.; Zhu, X.X. Expression of bombesin-receptor subtypes and their differential regulation of colonic smooth muscle contraction. Gastroenterology 1993, 105, 1672–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconieri Erspamer, G.; Severini, C.; Erspamer, V.; Melchiorri, P.; Delle Fave, G.; Nakajima, T. Parallel bioassay of 27 bombesin-like peptides on 9 smooth muscle preparations. Structure-activity relationships and bombesin receptor subtypes. Regul. Pept. 1988, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nock, B.A.; Cescato, R.; Ketani, E.; Waser, B.; Reubi, J.C.; Maina, T. [99mTc]Demomedin C, a radioligand based on human gastrin releasing peptide(18–27): Synthesis and preclinical evaluation in gastrin releasing peptide receptor-expressing models. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 8364–8374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsouvanidis, P.J.; Maina, T.; Sallegger, W.; Krenning, E.P.; de Jong, M.; Nock, B.A. 99mTc Radiotracers based on human GRP(18–27): Synthesis and comparative evaluation. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 1797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nock, B.A.; Nikolopoulou, A.; Galanis, A.; Cordopatis, P.; Waser, B.; Reubi, J.C.; Maina, T. Potent bombesin-like peptides for GRP-receptor targeting of tumors with 99mTc: A preclinical study. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsouvanidis, P.J.; Maina, T.; Sallegger, W.; Krenning, E.P.; de Jong, M.; Nock, B.A. Tumor diagnosis with new 111In-radioligands based on truncated human gastrin releasing peptide sequences: Synthesis and preclinical comparison. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 8579–8587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roques, B.P.; Noble, F.; Dauge, V.; Fournie-Zaluski, M.C.; Beaumont, A. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11: Structure, inhibition, and experimental and clinical pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 1993, 45, 87–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suda, H.; Aoyagi, T.; Takeuchi, T.; Umezawa, H. Letter: A thermolysin inhibitor produced by actinomycetes: Phosphoramidon. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1973, 26, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oefner, C.; D’Arcy, A.; Hennig, M.; Winkler, F.K.; Dale, G.E. Structure of human neutral endopeptidase (neprilysin) complexed with phosphoramidon. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 296, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsouvanidis, P.J.; Melis, M.; de Blois, E.; Breeman, W.A.; Krenning, E.P.; Maina, T.; Nock, B.A.; de Jong, M. In vivo enzyme inhibition improves the targeting of [177Lu]DOTA-GRP(13-27) in GRPR-positive tumors in mice. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2014, 29, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nock, B.A.; Maina, T.; Krenning, E.P.; de Jong, M. “To serve and protect”: Enzyme inhibitors as radiopeptide escorts promote tumor targeting. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatalic, K.L.; Konijnenberg, M.; Nonnekens, J.; de Blois, E.; Hoeben, S.; de Ridder, C.; Brunel, L.; Fehrentz, J.A.; Martinez, J.; van Gent, D.C.; et al. In vivo stabilization of a gastrin-releasing peptide receptor antagonist enhances pet imaging and radionuclide therapy of prostate cancer in preclinical studies. Theranostics 2016, 6, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maina, T.; Kaloudi, A.; Valverde, I.E.; Mindt, T.L.; Nock, B.A. Amide-to-triazole switch vs. In vivo NEP-inhibition approaches to promote radiopeptide targeting of GRPR-positive tumors. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2017, 52, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymperis, E.; Kaloudi, A.; Sallegger, W.; Bakker, I.L.; Krenning, E.P.; de Jong, M.; Maina, T.; Nock, B.A. Radiometal-dependent biological profile of the radiolabeled gastrin-releasing peptide receptor antagonist SB3 in cancer theranostics: Metabolic and biodistribution patterns defined by neprilysin. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nock, B.; Maina, T. Tetraamine-coupled peptides and resulting 99mTc-radioligands: An effective route for receptor-targeted diagnostic imaging of human tumors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2655–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mather, S.J.; Nock, B.A.; Maina, T.; Gibson, V.; Ellison, D.; Murray, I.; Sobnack, R.; Colebrook, S.; Wan, S.; Halberrt, G.; et al. GRP receptor imaging of prostate cancer using [99mTc]Demobesin 4: A first-in-man study. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2014, 16, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Castiglione, R.; Gozzini, L. Bombesin receptor antagonists. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 1996, 24, 117–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maina, T.; Nock, B.A.; Kulkarni, H.; Singh, A.; Baum, R.P. Theranostic prospects of gastrin-releasing peptide receptor-radioantagonists in oncology. PET Clin. 2017, 12, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassis, A.I. Therapeutic radionuclides: Biophysical and radiobiologic principles. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2008, 38, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, D.; Frischknecht, M.; Zhang, H.; Morgenstern, A.; Bruchertseifer, F.; Boisclair, J.; Provencher-Bolliger, A.; Reubi, J.C.; Maecke, H.R. Alpha- versus beta-particle radiopeptide therapy in a human prostate cancer model (213Bi-DOTA-Pesin and 213Bi-AMBA versus 177Lu-DOTA-Pesin). Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, K.E.; Metcalfe, E.; Arunachalam, T.; Chen, J.; Eaton, S.M.; Feng, W.; Fan, H.; Raju, N.; Cagnolini, A.; Lantry, L.E.; et al. In vitro and in vivo metabolism of Lu-AMBA, a GRP-receptor binding compound, and the synthesis and characterization of its metabolites. Bioconjug. Chem. 2009, 20, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shipp, M.A.; Tarr, G.E.; Chen, C.Y.; Switzer, S.N.; Hersh, L.B.; Stein, H.; Sunday, M.E.; Reinherz, E.L. CD10/neutral endopeptidase 24.11 hydrolyzes bombesin-like peptides and regulates the growth of small cell carcinomas of the lung. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 10662–10666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reile, H.; Armatis, P.E.; Schally, A.V. Characterization of high-affinity receptors for bombesin/gastrin releasing peptide on the human prostate cancer cell lines PC-3 and DU-145: Internalization of receptor bound 125I-(Tyr4)bombesin by tumor cells. Prostate 1994, 25, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).