Complexes of Oligoribonucleotides with d-Mannitol Modulate the Innate Immune Response to Influenza A Virus H1N1 (A/FM/1/47) In Vivo
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
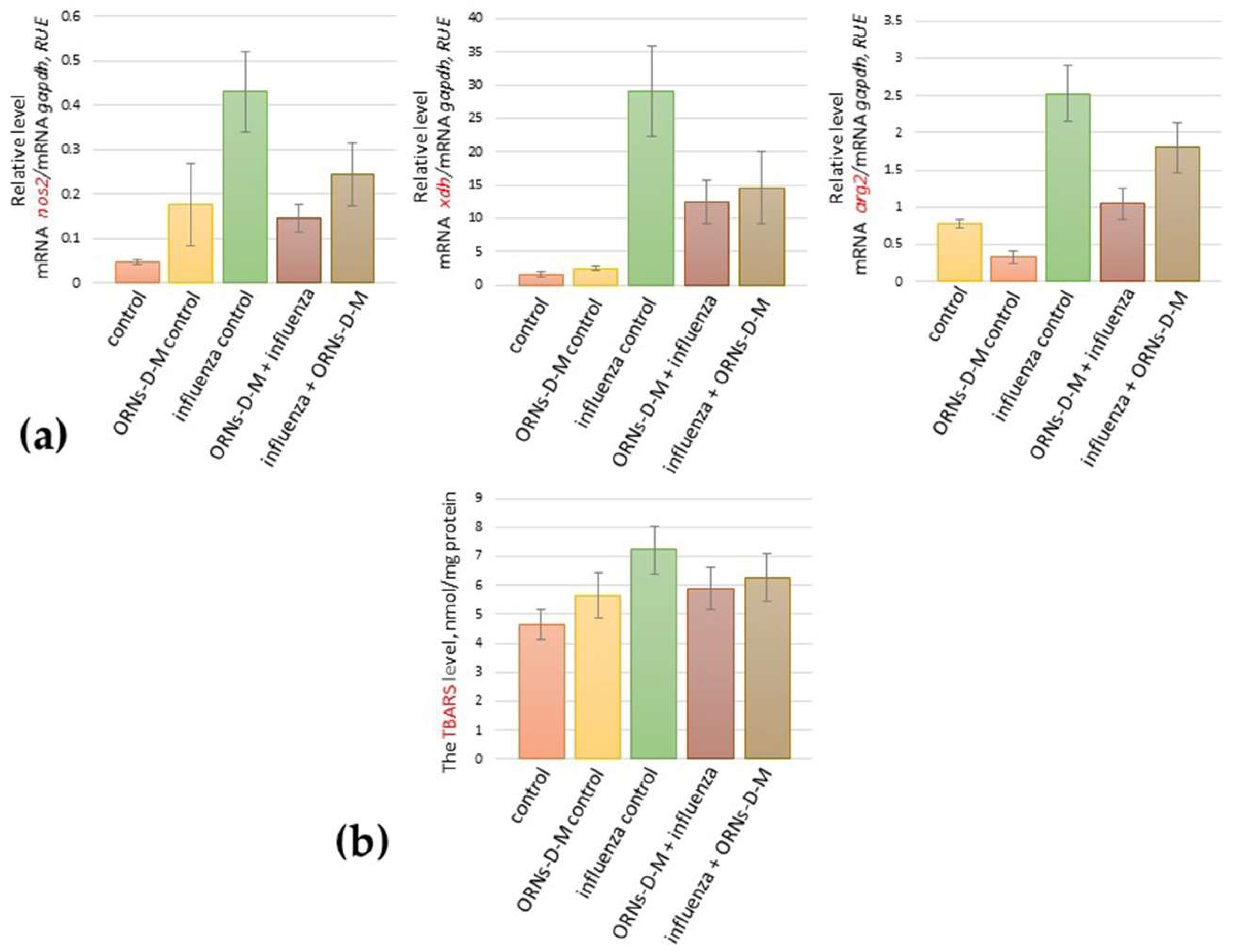
2.1. The ORNs-d-М Inhibit the Up-Expression of nos2, arg2, xdh Genes Induced by the Influenza Virus and Decrease the Level of Lipid Peroxidation Products in Lungs of Influenza-Infected Mice
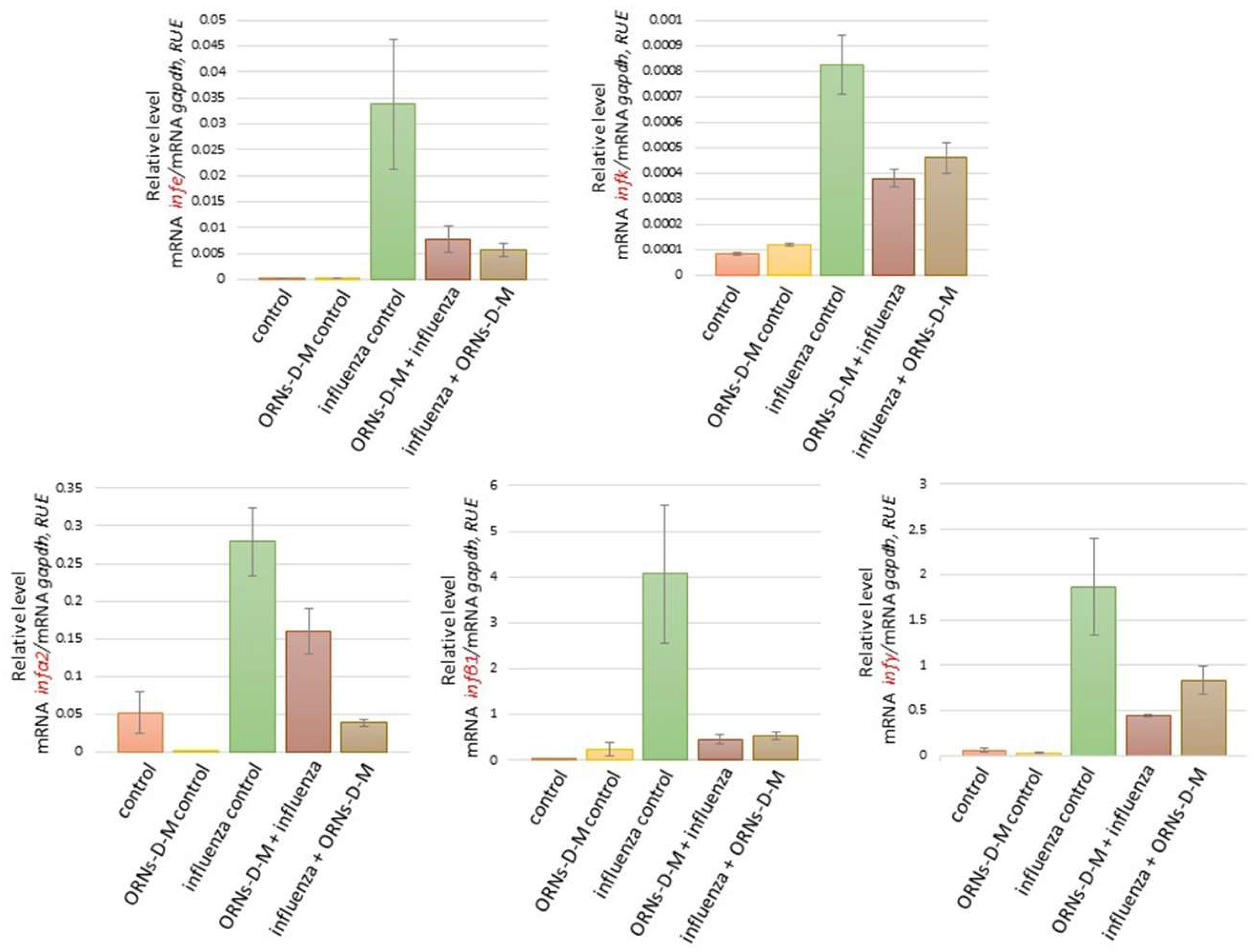
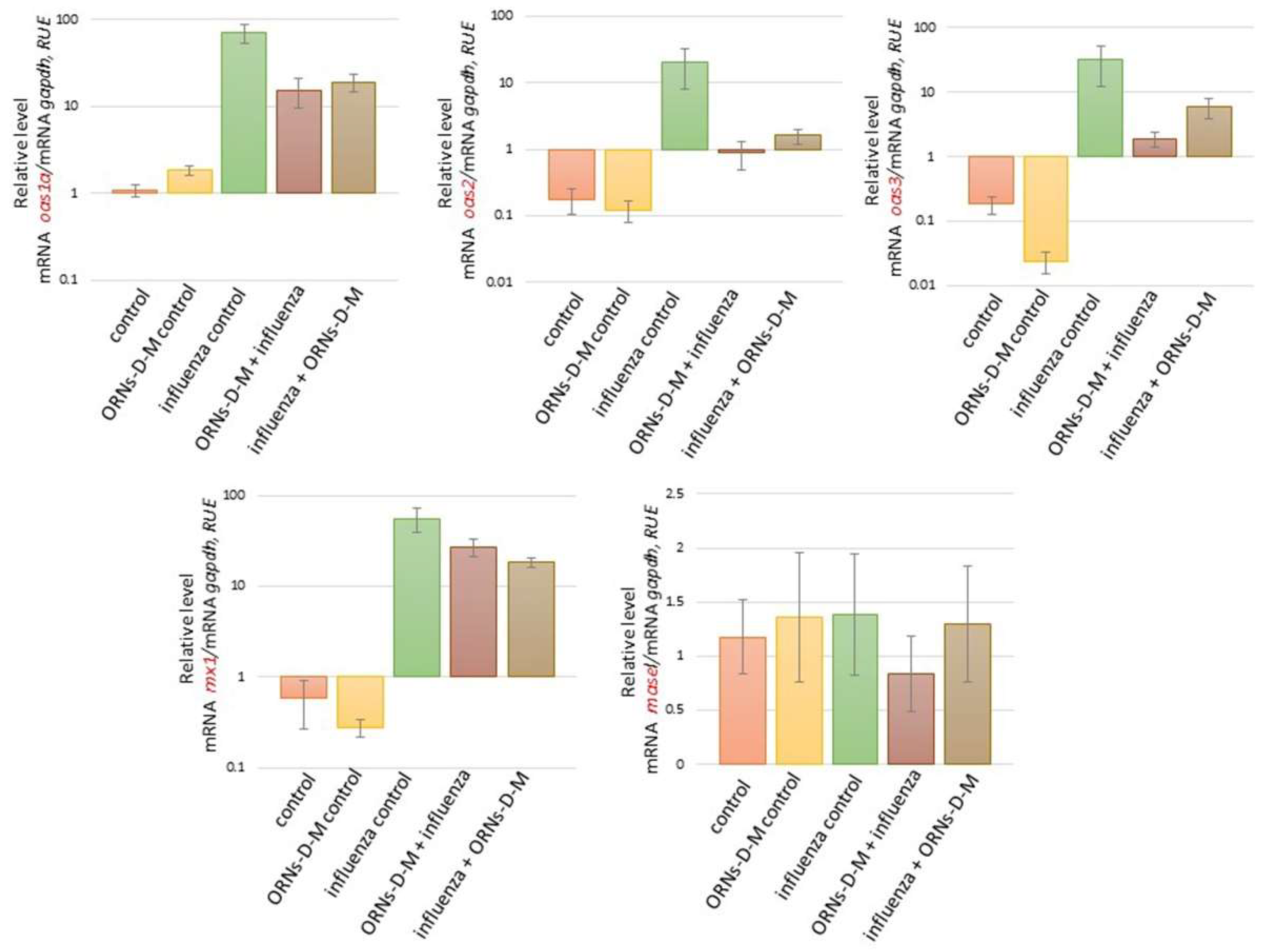
2.2. The ORNs-d-М Inhibit the Overexpression of Cytokines, Chemokines, and ISGs Induced by the Influenza Virus In Vivo
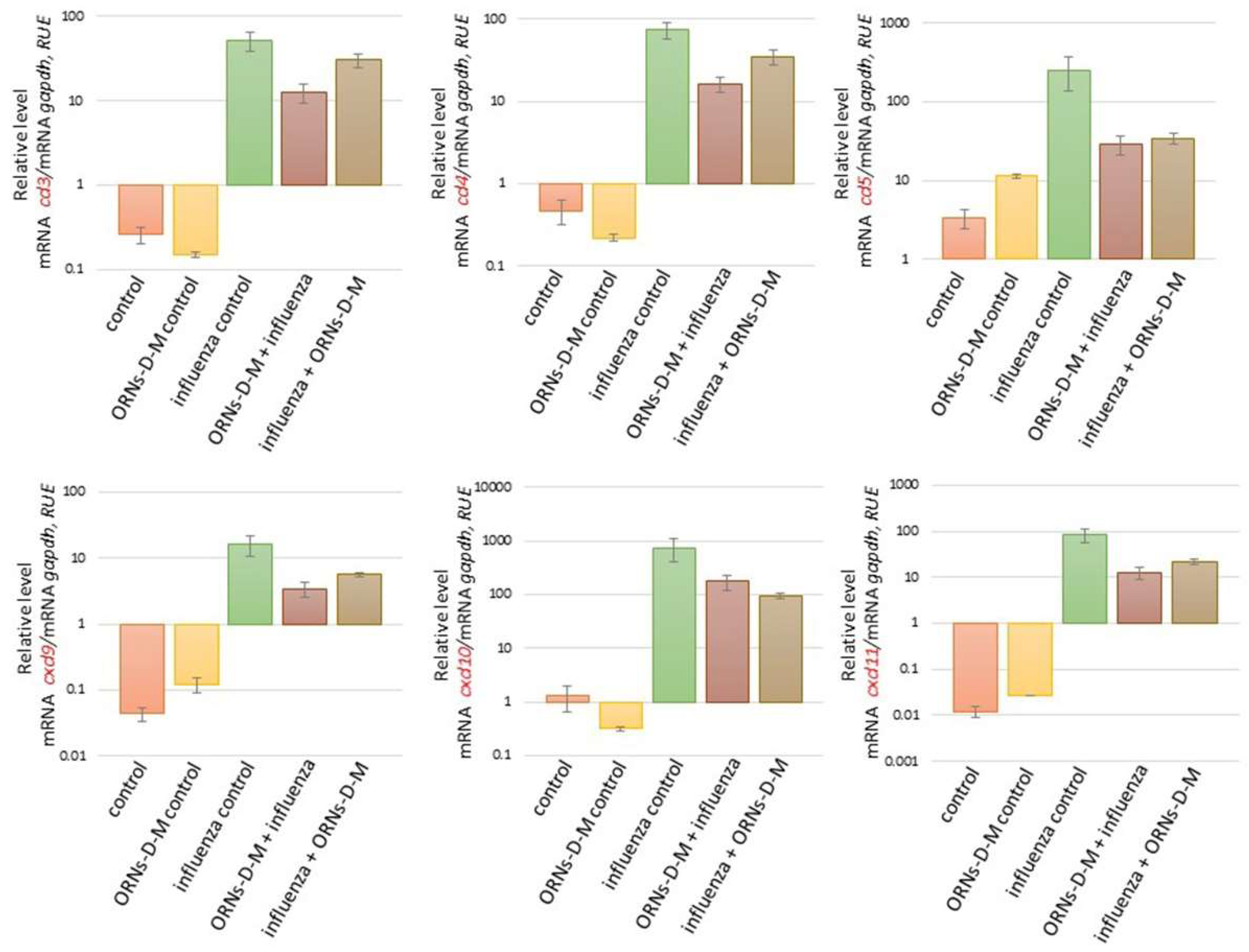
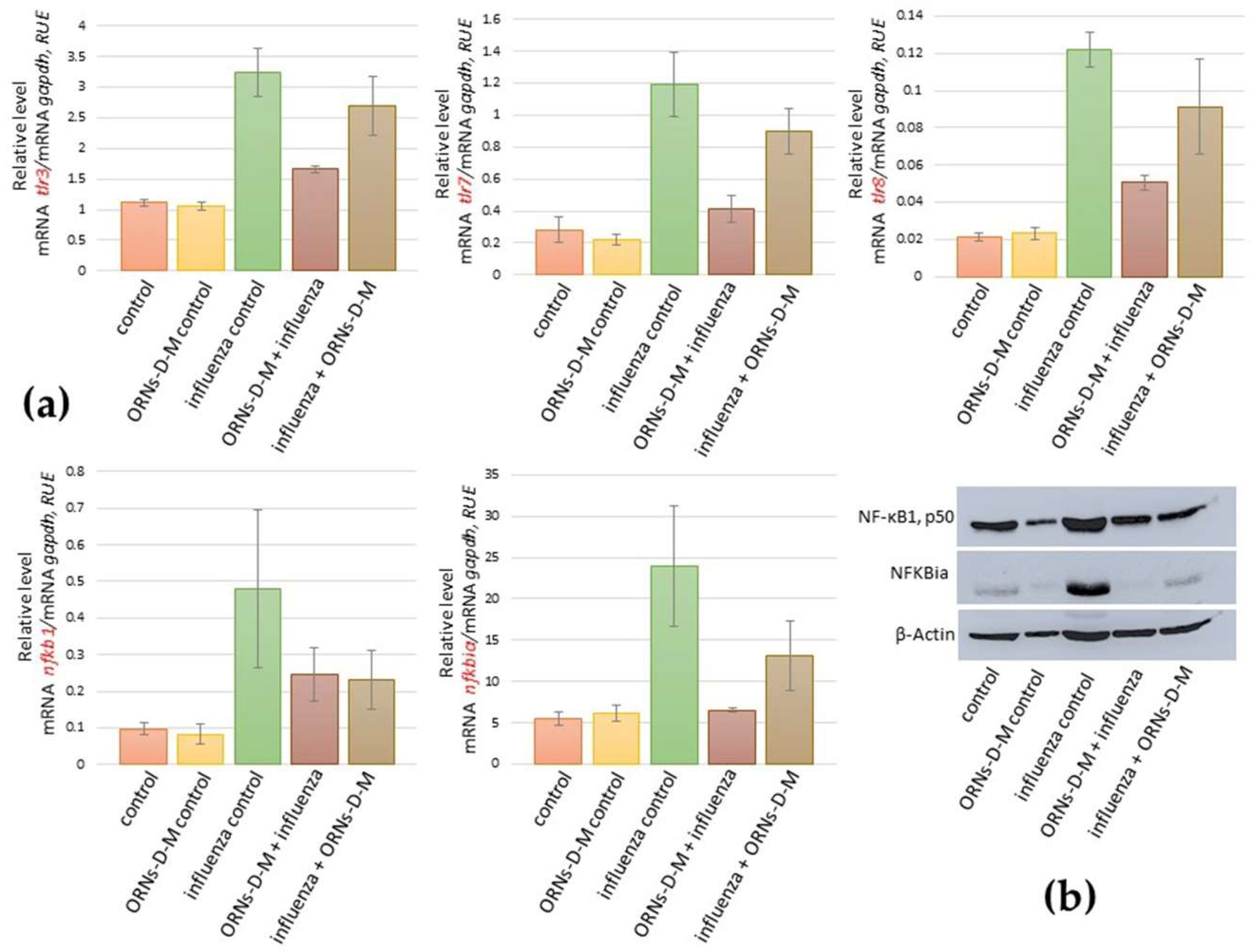
2.3. ORNs-d-М Inhibit the Overexpression of nfkb1, nfkbiα, tlr3, tlr7, and tlr8 Induced by the Influenza Virus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mouse In Vivo Experiment
4.2. TCID50 Assay
4.3. Real-Time qPCR Assay
4.4. Lipid Peroxidation Assay
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garten, R.J.; Davis, C.T.; Russell, C.A.; Shu, B.; Lindstrom, S.; Balish, A. Antigenic and genetic characteristics of swine-origin 2009 A(H1N1) influenza viruses circulating in humans. Science 2009, 325, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzberg, S. The contents of the syringe. Nature 2008, 454, 160–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davlin, S.L. Influenza activity—United States, 2015–2016 season and composition of the 2016–2017 influenza vaccine. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2016, 65, 567–575. Available online: cdc.gov/mmwr/volumes/65/wr/mm6522a3.htm (accessed on 18 July 2018). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensley, S.E. Challenges of selecting seasonal influenza vaccine strains for humans with diverse pre-exposure histories. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2014, 8, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houser, K.; Subbarao, K. Influenza vaccines: Challenges and solutions. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clercq, E. Antiviral agents active against influenza a viruses. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beigel, J.; Bray, M. Current and future antiviral therapy of severe seasonal and avian influenza. Antivir. Res. 2008, 78, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bright, R.A.; Shay, D.K.; Shu, B.; Cox, N.J.; Klimov, A.I. Adamantane resistance among influenza A viruses isolated early during the 2005–2006 influenza season in the United States. JAMA 2006, 295, 891–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscona, A. Global transmission of oseltamivir-resistant influenza. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, T.G. Dual resistance to adamantanes and oseltamivir among seasonal influenza A (H1N1) viruses: 2008–2010. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 203, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peasey, M.; Hall, R.J.; Sonnberg, S. Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 and Seasonal Influenza A (H1N1) Co-infection, New Zealand, 2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1618–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chertow, D.S.; Memoli, M.J. Bacterial coinfection in Influenza A. JAMA 2013, 309, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Duan, M.; Zhao, Y.; Ling, F.; Xiao, K.; Li, Q.; Li, B.; Lu, C.; Qi, W.; Zeng, Z. Saikosaponin a inhibits influenza a virus replication and lung immunopathology. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 42541–42556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, S.; Steinmueller, M.; vonWulffen, W.; Cakarova, L.; Pinto, R.; Pleschka, S.; Mack, M.; Kuziel, W.A.; Corazza, N.; Brunner, T.; et al. Lung epithelial apoptosis in influenza virus pneumonia: The role of macrophage-expressed tnf-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 3065–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, I.; Fernandez-Sesma, A. Modulating the innate immune response to influenza a virus: Potential therapeutic use of anti-inflammatory drugs. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Kao, W.C.; Wang, W.Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Yang, R.B.; Peck, K. Identification and characterization of oligonucleotides that inhibit Toll-like receptor 2-associated immune responses. FASEB 2009, 23, 3078–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Tu, K.; Tu, J. Selection of DNA aptamers that bind to four organophosphorus pesticides. Biotechnol. Lett. 2012, 34, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, T.; Kwon, Y.M.; Lu, H.; Jiao, P.; Liao, M.; Li, Y. Selection and characterization of DNA aptamers for use in detection of avian influenza virus H5N1. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 189, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Swiderski, P.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Neff, C.P.; Akkina, R.; Rossi, J.J. Selection, characterization and application of new RNA HIV gp 120 aptamers for facile delivery of Dicer substrate siRNAs into HIV infected cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 3094–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Beck, J.; Nassal, M.; Hu, K.H. A SELEXscreened aptamer of human hepatitis B virus RNA encapsidation signal suppresses viral replication. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levchenko, S.M.; Rebriev, A.V.; Tkachuk, V.V.; Dubey, L.V.; Dubey, I.Y.; Tkachuk, Z.Y. Studies on the interaction of oligoadenylates with proteins by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Biopolym. Cell 2013, 29, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorobogatov, O.Y.; Lozhko, D.N.; Zhukov, I.Y.; Kozlov, O.; Tkachuk, Z.Y. Study of dephosphorylated 2′-5′-linked oligoadenylates impact on apo-S100A1 protein conformation by heteronuclear NMR and circular dichroism. Biopolym. Cell 2014, 30, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorobogatov, O.Y.; Kukharenko, A.P.; Kozlov, O.V.; Dubey, I.Y.; Tkachuk, Z.Y. 2′-5′-Linked Triadenylates Act as Protein Kinase Activity Modulators. J. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachuk, Z. Multiantivirus Compound, Composition and Method for Treatment of Virus Diseases. U.S. Patent 20,120,232,129, 16 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Melnichuk, N.; Zarubaev, V.; Iosyk, I.; Andreychyn, M.; Semernikova, L.; Tkachuk, Z. Pre-Clinical and Clinical Efficiency of Complexes of Oligoribonucleotides with D-Mannitol against Respiratory Viruses. Pharmaceutics 2018, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkachuk, Z.Y.; Rybalko, S.L.; Zharkova, L.D.; Starostyla, D.B. Antiinfluenzal activity of drug Nuclex. Rep. Natl. Acad. Sci. Ukr. 2010, 9, 191–196. [Google Scholar]
- Melnichuk, N.S.; Semernikova, L.I.; Tkachuk, Z.Y. Complexes of Oligoribonucleotides with d-mannitol inhibit hemagglutinin–glycan interaction and suppress influenza A virus H1N1 (A/FM/1/47) infectivity In Vitro. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tkachuk, Z.Y.; Tkachuk, V.V.; Tkachuk, L.V. The study on membrane-stabilizing and anti-inflammatory actions of yeast RNA in vivo and in vitro. Biopolym. Cell 2006, 22, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachuk, Z.; Chercasova, V.; Frolov, V. Dynamics of indexes of interferon status of blood of patients with genital herpes at application of nuclex. Ukr. Morphol. Almanac. 2012, 10, 145–147. [Google Scholar]
- Tkachuk, Z.Y.; Frolov, V.M.; Sotska, Y.A.; Kruglova, O.V. Nuclex therapy for patients with chronic hepatitis C. Int. J. Immunol. Stud. 2012, 1, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelyoniy, I.I.; Tkachuk, Z.Y.; Afonin, D.N.; Tiutiunnyk, A.A. Influence of Preparation Nucleх on the Cytokine Profile of the Patients with Diabetes Type 2 and Neuropathic Form of Diabetic Foot. J. Diabetes Res. 2013, 2, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, T. Role of free radicals in viral pathogenesis and mutation. Rev. Med. Virol. 2001, 11, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, L.A.; Belser, J.A.; Wadford, D.A.; Katz, J.M.; Tumpey, T.M. Inducible Nitric Oxide Contributes to Viral Pathogenesis Following Highly Pathogenic Influenza Virus Infection in Mice. Infect. Diseases 2013, 207, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.; Chen, D.; Xiong, M.; Zhu, J.; Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; et al. Insights into the increasing virulence of the swine-origin pandemic H1N1/2009 influenza virus. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, T.C.; Beck, M.A.; Kuziel, W.A.; Henderson, F.; Maeda, M. Contrasting effects of CCR5 and CCR2 deficiency in the pulmonary inflammatory response to influenza A virus. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaike, T.; Ando, M.; Oda, T.; Doi, T.; Ijiri, S.; Araki, S.; Maeda, H. Dependence on O2 Generation by Xanthine Oxidase of Pathogenesis of Influenza Virus Infection in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 85, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, R.; Czikora, I.; Sridhar, S.; Zemskov, E.A.; Oseghale, A.; Circo, S. Arginase 1: An unexpected mediator of pulmonary capillary barrier dysfunction in models of acute lung injury. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikam, S.V.; Nikam, P.S.; Chandrashekar, M.R.; Kalsad, S.T.; Jnaneshwara, K.B. Role of lipid peroxidation, glutathione and antioxidant enzymes in H1N1 Influenza. Biomed. Res. 2010, 21, 457–560. [Google Scholar]
- Tkachuk, Z. Method of Protecting Erythricytes, in Particular for Improvement of Blood Cytopenia. U.S. Patent 6,737,271, 26 April 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, M.O.; Bohlander, S.; Allen, G. Nomenclature of the human interferon genes. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 1996, 16, 179–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, H.A. Regulation of interferon-γ gene expression. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 1996, 16, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, G.R.; Kerr, I.M.; Williams, B.R.; Silverman, R.H.; Schreiber, R.D. How cells respond to interferons. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 227–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestka, S.; Langer, J.A.; Zoon, K.C.; Samuel, C.E. Interferons and their actions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1987, 56, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, C.E. Mechanisms of the Antiviral Actions of IFN. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1988, 35, 27–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestka, S.; Krause, C.D.; Walter, M.R. Interferons, interferon-like cytokines, and their receptors. Immunol. Rev. 2004, 202, 8–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z.; Harper, R.; Anunciacion, J.; Yang, Z.; Gao, W.; Qu, B.; Guan, Y.; Cardona, C.J. Host immune and apoptotic responses to avian influenza virus H9N2 in human tracheobronchial epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 44, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, M.C.; Cheung, C.Y.; Chui, W.H.; Tsao, S.W.; Nicholls, J.M.; Chan, Y.O.; Chan, R.W.; Long, H.T.; Poon, L.L.; Guan, Y.; et al. Proinflammatory cytokine responses induced by influenza A (H5N1) viruses in primary human alveolar and bronchial epithelial cells. Respir. Res. 2005, 6, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haller, O.; Staeheli, P.; Kochs, G. Protective role of interferon-induced Mx GTPases against influenza viruses. Rev. Sci. Technol. 2009, 28, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, C.E. Antiviral actions of interferons. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 778–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinchieri, G. Type I interferon: Friend or foe? J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsukura, S.; Kokubu, F.; Noda, H.; Tokunaga, H.; Adachi, M. Expression of IL6, IL-8, and RANTES on human bronchial epithelial cells, NCI-H292, induced by influenza virus A. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996, 98, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, M.; Matsukura, S.; Tokunaga, H.; Kokubu, F. Expression of cytokines on human bronchial epithelial cells induced by influenza virus A. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1997, 113, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nain, M.; Hinder, F.; Gong, J.H.; Schmidt, A.; Bender, A.; Sprenger, H.; Gemsa, D. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha production of influenza A virus-infected macrophages and potentiating effect of lipopolysaccharides. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Julkunen, I.; Melen, K.; Nyqvist, M.; Pirhonen, J.; Sareneva, T.; Matikainen, S. Inflammatory responses in influenza a virus infection. Vaccine 2000, 19, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julkunen, I.; Sareneva, T.; Pirhonen, J.; Ronni, T.; Melen, K.; Matikainen, S. Molecular pathogenesis of influenza A virus infection and virus-induced regulation of cytokine gene expression. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2001, 12, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.Y.; Yeung, A.C.; Chu, I.M.; Chan, P.K. Profiles of cytokine and chemokine gene expression in human pulmonary epithelial cells induced by human and avian influenza viruses. Virol. J. 2010, 7, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, W.Y.; Yeung, A.C.; Chan, P.K. Apoptosis, cytokine and chemokine induction by non-structural 1 (NS1) proteins encoded by different influenza subtypes. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Cui, X. Dynamic gene expression analysis in a H1N1 influenza virus mouse pneumonia model. Virus Genes 2017, 53, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, T.; Noguchi, Y.; Ijiri, S.; Setoguchi, K.; Suga, M.; Zheng, Y.M.; Dietzschold, B.; Maeda, H. Pathogenesis of influenza virusinduced pneumonia: Involvement of both nitric oxide and oxygen radicals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 2448–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, T.; Maeda, H. Nitric oxide and virus infection. Immunology 2000, 101, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, E.B.; Ghosh, S. NF-kappa B and rel proteins in innate immunity. Adv. Immunol. 1995, 58, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Baltimore, D. NF-kappa B: Ten years after. Cell 1996, 87, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeuerle, P.A.; Henkel, T. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994, 12, 141–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flory, E.; Kunz, M.; Scheller, C.; Jassoy, C.; Stauber, R.; Rapp, U.R.; Ludwig, S. Influenza virus-induced NF-kB-dependent gene expression is mediated by overexpression of viral proteins and involves oxidative radicals and activation of IkB kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 8307–8314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Dudziak, D.; Dirmeier, U.; Hobom, G.; Riedel, A.; Schlee, M.; Staudt, L.M.; Rosenwald, A.; Behrends, U.; Bornkamm, G.W.; et al. Active NF-kappaB signalling is a prerequisite for influenza virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2347–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Uematsu, S.; Takeuchi, O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell 2006, 124, 783–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Goffic, R.; Balloy, V.; Lagranderie, M.; Alexopoulou, L.; Escriou, N.; Flavell, R.; Chignard, M.; Si-Tahar, M. Detrimental contribution of the Toll-like receptor (TLR)3 to influenza A virus-induced acute pneumonia. PLoS Pathog. 2006, 2, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diebold, S.S.; Kaisho, T.; Hemmi, H.; Akira, S.; Reis e Sousa, C. Innate antiviral responses by means of TLR7-mediated recognition of single-stranded RNA. Science 2004, 303, 1529–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, I.K.; Iwasaki, A. Control of antiviral immunity by pattern recognition and the microbiome. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 245, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like Receptors and Their Crosstalk with Other Innate Receptors in Infection and Immunity. Immunity 2011, 34, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexopoulou, L.; Holt, A.C.; Medzhitov, R.; Flavell, R.A. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 2001, 413, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, L.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, L.; Chen, T.; Chen, Q.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Hu, P.; et al. Radix isatidis Polysaccharides Inhibit Influenza a Virus and Influenza A Virus-Induced Inflammation via Suppression of Host TLR3 Signaling In Vitro. Molecules 2017, 22, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivcharyk, M.; Iakhnenko, M.; Levchenko, S.; Chernykh, S.; Tkachuk, Z. Monitoring of Interferon-α (peg) conformational changes caused by yeast RNA. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference Physics of Liquid Matter: Modern Problems (PLM MP), Kyiv, Ukraine, 27–30 May 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asakawa, T.; Matsushita, S. Thiobarbituric acid test for detecting lipid peroxides. Lipids 1980, 14, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, G.; Amiraian, K.; Frey, H.; Stevens, R.W.; Berns, D.S. Densitometric analysis of Western blot (immunoblot) assays for human immunodeficiency virus antibodies and correlation with clinical status. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1987, 25, 1993–1998. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Group | Infectious Titer of Influenza, lgTCID50 | Weight loss, g |
|---|---|---|
| control | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 13.0 ± 1.3 |
| ORNs-d-М control | 0.0 ± 0.0 | 13.2 ± 0.8 |
| influenza control | 6.8 ± 0.12 | 11.4 ± 1.4 |
| ORNs-d-М + influenza | 5.4 ± 0.35 | 12.0 ± 1.7 |
| Influenza + ORNs-d-М | 4.6 ± 0.62 | 12.5 ± 2.0 |
| Gene | Primers | Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|---|
| nitric oxide synthase 2, inducible (nos2) | Forward Reverse | 5′-TTT GTG CGA AGT GTC AGT GG-3′ 5′-TCC TTT GAG CCC TTT GTG C-3′ |
| arginase type II (arg2) | Forward Reverse | 5′-TGA TTG GCA AAA GGC AGA GG-3′ 5′-CTG ACA GCA ACC CTG TAT TAT GTA-3′ |
| xanthine dehydrogenase (xdh) | Forward Reverse | 5′-CCA AGA TGG TTC AGG TGG C-3′ 5′-TCT GAC AGG CTT CAT AAA TGG C-3′ |
| 2′-5′ oligoadenylate synthetase 1A (oas1a) | Forward Reverse | 5′-ACA GCT CAG AAA AGC CAG G-3′ 5′-CAG TTC TCT TCT ACC TGC TCA AA-3′ |
| 2′-5′ oligoadenylate synthetase 2 (oas2) | Forward Reverse | 5′-CTA TGA TGC ACT AGG TCA ACT GC-3′ 5′-TTC CTT TCA TAC TGT TTG TAC CAG T-3′ |
| 2′-5′ oligoadenylate synthetase 3 (oas3) | Forward Reverse | 5′-CAA AGC GTG GAC TTT GAC G-3′ 5′-ATG GTC TTG TTA CAC TGT TGG TA-3′ |
| MX dynamin-like GTPase 1 (mx1) | Forward Reverse | 5′-TGC TGT ACT GCT AAG TCC AAA-3′ 5′-GCA GTA GAC AAT CTG TTC CAT CTG-3′ |
| 2′,5′-oligoisoadenylate synthetase-dependent ribonuclease L (rnasel) | Forward Reverse | 5′-GGA CTT GGG AGA ACC GCT AT-3′ 5′-CAT TTT TGT CGA TCT TAG ATG TCC A-3′ |
| interferon epsilon (ifnε) | Forward Reverse | 5′-CTG GAA TAC GTG GAG TCA CTG-3′ 5′-GAA CCT GAA CAC AAA GAA CAT ACA-3′ |
| interferon kappa (ifnk) | Forward Reverse | 5′-GGA GTT GGG CAA GTA TTT CTT CA-3′ 5′-CTT GAA GGT GGG TGA TTC TGA TA-3′ |
| nterferon alpha 2 (ifna2) | Forward Reverse | 5′-CTT ACT CAG CAG ACC TTG AAC C-3′ 5′-CTG CTG CAT CAG ACA GGT TT-3′ |
| interferon beta 1 (ifnb1) | Forward Reverse | 5′-GAT GCT CCA GAA TGT CTT TCT TGT-3′ 5′-CGA ATG ATG AGA AAG TTC CTG AAG A-3′ |
| interferon gamma (ifnγ) | Forward Reverse | 5′-AAC TGG CAA AAG GAT GGT GA-3′ 5′-GTT GTT GAC CTC AAA CTT GGC-3′ |
| chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 3 (ccl3) | Forward Reverse | 5′-GCC ATA TGG AGC TGA CAC C-3′ 5′-TTC TCT TAG TCA GGA AAA TGA CAC C-3′ |
| chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 4 (ccl4) | Forward Reverse | 5′-AGG GTT CTC AGC ACC AAT G-3′ 5′-TCT TTT GGT CAG GAA TAC CAC AG-3′ |
| chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 (сcl5) | Forward Reverse | 5′-CTC ACC ATC ATC CTC ACT GC-3′ 5′-TGA CAA ACA CGA CTG CAA GA-3′ |
| chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 9 (cxcl9) | Forward Reverse | 5′-CAA AAC TGA AAT CAT TGC TAC ACT GAA-3′ 5′-GGC TGA TCT TCT TTT CCC ATT C-3′ |
| chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 10 (cxcl10) | Forward Reverse | 5′-TGT TGA GAT CAT TGC CAC GAT-3′ 5′-CCT TTT AGA CCT TTT TTG GCT AAA CG-3′ |
| chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 11 (cxcl11) | Forward Reverse | 5′-CTG CTC AAG GCT TCC TTA TGT T-3′ 5′-TTT TTC TAT TGC CTG CAT TAT GAG G-3′ |
| interleukin 6 (il6) | Forward Reverse | 5′-CTA CCA AAC TGG ATA TAA TCA GGA AAT-3′ 5′-TCT TTT ACC TCT TGG TTG AAG ATA TGA-3′ |
| interleukin 1 beta (il1b) | Forward Reverse | 5′-TTC ATC TTT GAA GAA GAG CCC AT-3′ 5′-TGG AGA ATA TCA CTT GTT GGT TGA-3′ |
| interleukin 12a (il12a) | Forward Reverse | 5′-GTG AAG ACG GCC AGA GAA AA-3′ 5′-ACA GGG TCA TCA TCA AAG ACG-3′ |
| tumor necrosis factor (tnf) | Forward Reverse | 5′-AAA GGG ATG AGA AGT TCC CAA AT-3′ 5′-ACT TGG TGG TTT GCT ACG AC-3′ |
| nuclear factor kappa B (nfkb1) | Forward Reverse | 5′-GGA CAT GGG ATT TCA GGA TAA CC-3′ 5′-AGA GGT GTC TGA TAC AGG TCA T-3′ |
| NFKB inhibitor alpha (nfkbiα) | Forward Reverse | 5′-GAG ACT CGT TCC TGC ACT TG-3′ 5′-AAG TGG AGT GGA GTC TGC TG-3′ |
| toll-like receptor 3 (tlr3) | Forward Reverse | 5′-CCT CTT GAA CAA CGC CCA AC-3′ 5′-AGA GAA AGT GCT CTC GCT GG-3′ |
| toll-like receptor 7 (tlr7) | Forward Reverse | 5′-ATC CTC TGA CCG CCA CAA TC-3′ 5′-TCA CAT GGG CCT CTG GGA TA-3′ |
| toll-like receptor 8 (tlr8) | Forward Reverse | 5′-GCC CCC TCA GTC ATG GAT TC-3′ 5′-GAG GGA AGT GCT ATA GTT TGG GG-3′ |
| glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gapdh) | Forward Reverse | 5′-TGT CGT GGA GTC TAC TGG TGT CTT C-3′ 5′-CGT GGT TCA CAC CCA TCA CAA-3′ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Melnichuk, N.; Kashuba, V.; Rybalko, S.; Tkachuk, Z. Complexes of Oligoribonucleotides with d-Mannitol Modulate the Innate Immune Response to Influenza A Virus H1N1 (A/FM/1/47) In Vivo. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030073
Melnichuk N, Kashuba V, Rybalko S, Tkachuk Z. Complexes of Oligoribonucleotides with d-Mannitol Modulate the Innate Immune Response to Influenza A Virus H1N1 (A/FM/1/47) In Vivo. Pharmaceuticals. 2018; 11(3):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030073
Chicago/Turabian StyleMelnichuk, Nataliia, Vladimir Kashuba, Svitlana Rybalko, and Zenoviy Tkachuk. 2018. "Complexes of Oligoribonucleotides with d-Mannitol Modulate the Innate Immune Response to Influenza A Virus H1N1 (A/FM/1/47) In Vivo" Pharmaceuticals 11, no. 3: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030073
APA StyleMelnichuk, N., Kashuba, V., Rybalko, S., & Tkachuk, Z. (2018). Complexes of Oligoribonucleotides with d-Mannitol Modulate the Innate Immune Response to Influenza A Virus H1N1 (A/FM/1/47) In Vivo. Pharmaceuticals, 11(3), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph11030073





