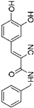The Link between Protein Kinase CK2 and Atypical Kinase Rio1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
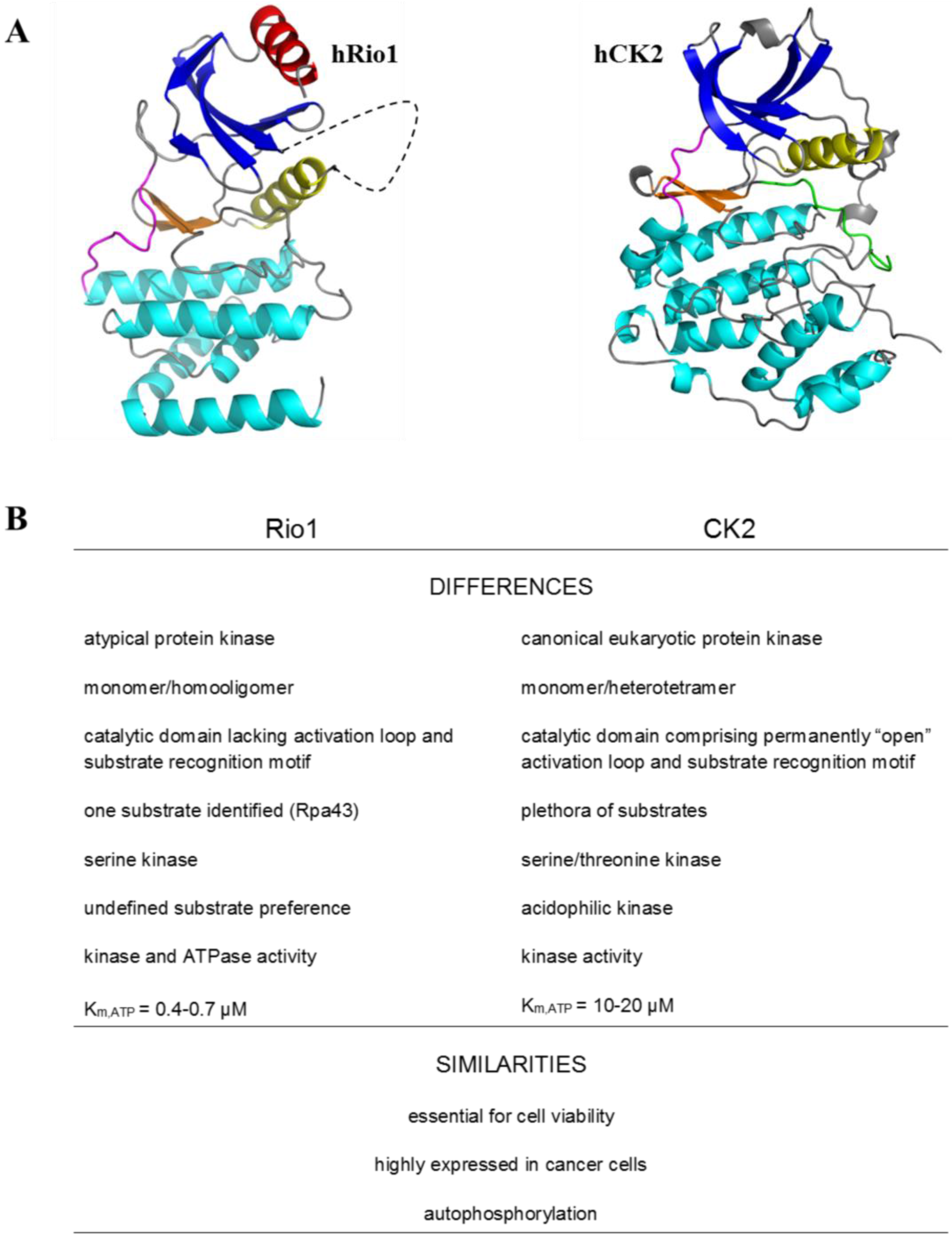
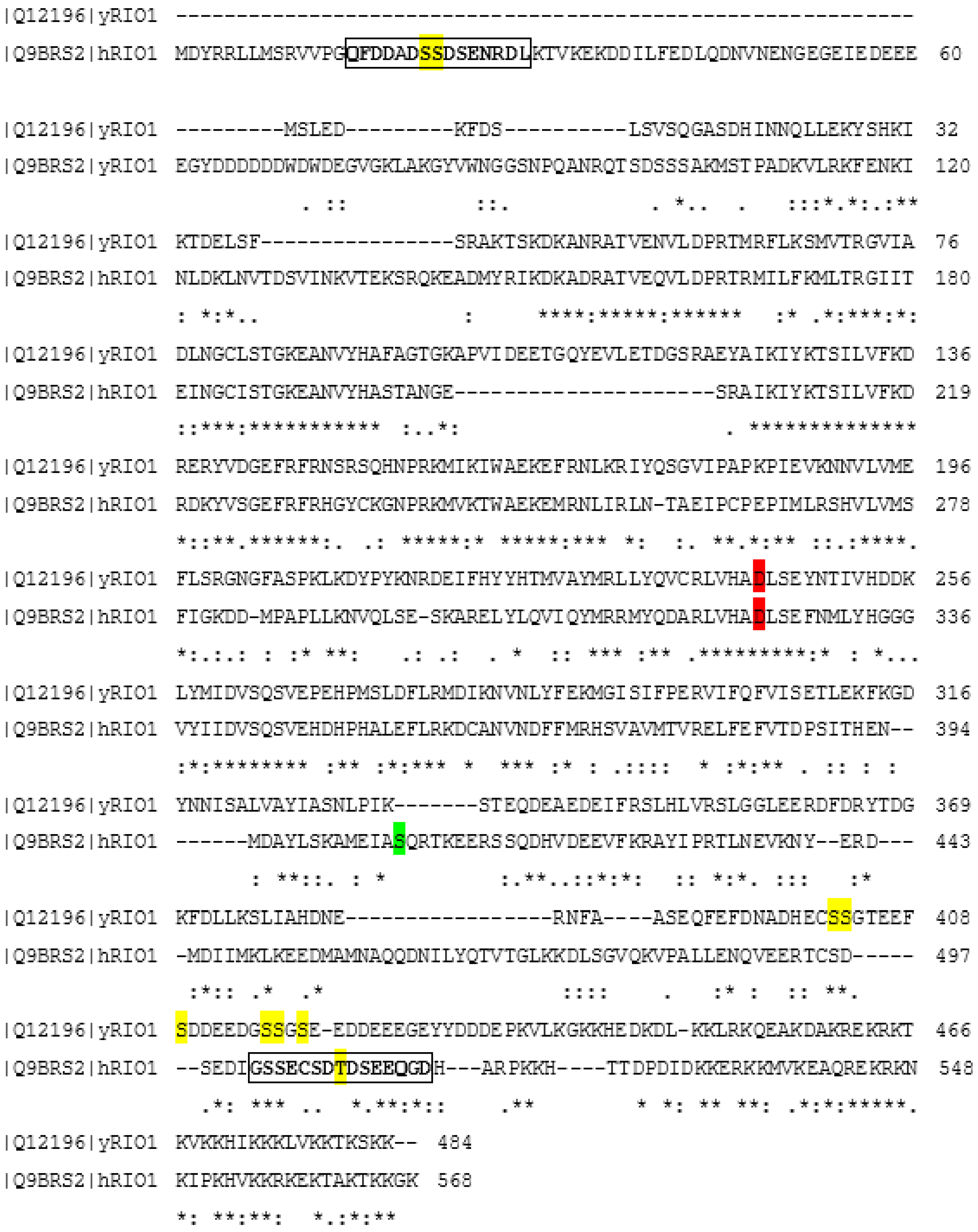
2. Protein Kinase Rio1
3. Rio1 as an Interacting Partner and Target for CK2
4. Regulation of Rio1 via CK2-Mediated Phosphorylation in Yeast
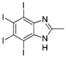
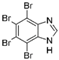
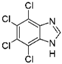
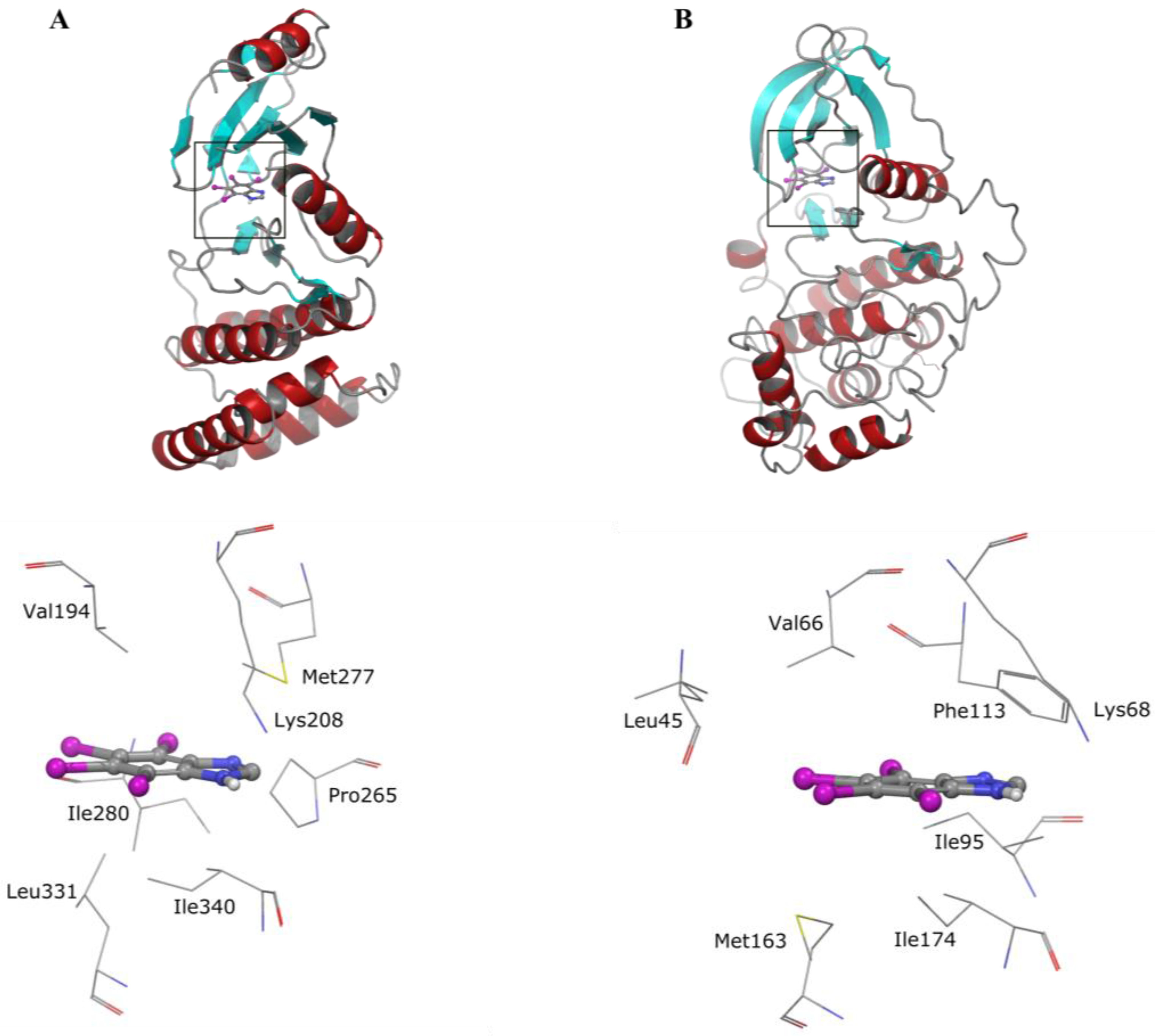
5. Collective Inhibition of CK2 and Rio1 by Benzimidazole Derivatives
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hafen, E. Kinases and phosphatases—A marriage is consummated. Science 1998, 280, 1212–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, P. The origins of protein phosphorylation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, E127–E130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.B.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blume-Jensen, P.; Hunter, T. Oncogenic kinase signalling. Nature 2001, 411, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brognard, J.; Hunter, T. Protein kinase signaling networks in cancer. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2011, 21, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angermayr, M.; Bandlow, W. Rio1, an extraordinary novel protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 2002, 524, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRonde-LeBlanc, N.; Wlodawer, A. A family portrait of the rio kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37297–37300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laronde-Leblanc, N.; Guszczynski, T.; Copeland, T.; Wlodawer, A. Structure and activity of the atypical serine kinase rio1. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 3698–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubiński, K.; Masłyk, M.; Orzeszko, A. Benzimidazole inhibitors of protein kinase CK2 potently inhibit the activity of atypical protein kinase rio1. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 426, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiburu, I.N.; LaRonde-LeBlanc, N. Interaction of rio1 kinase with toyocamycin reveals a conformational switch that controls oligomeric state and catalytic activity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meggio, F.; Pinna, L.A. One-thousand-and-one substrates of protein kinase CK2? FASEB J. 2003, 17, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira-Cerca, S.; Kiburu, I.; Thomson, E.; LaRonde, N.; Hurt, E. Dominant rio1 kinase/atpase catalytic mutant induces trapping of late pre-40s biogenesis factors in 80s-like ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 8635–8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacovella, M.G.; Golfieri, C.; Massari, L.F.; Busnelli, S.; Pagliuca, C.; Dal Maschio, M.; Infantino, V.; Visintin, R.; Mechtler, K.; Ferreira-Cerca, S.; et al. Rio1 promotes rdna stability and downregulates rna polymerase i to ensure rdna segregation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filhol, O.; Cochet, C. Protein kinase CK2 in health and disease: Cellular functions of protein kinase ck2: A dynamic affair. Cell. Mol. Life Sci 2009, 66, 1830–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litchfield, D.W. Protein kinase ck2: Structure, regulation and role in cellular decisions of life and death. Biochem. J. 2003, 369, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggero, D.; Pandolfi, P.P. Does the ribosome translate cancer? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esser, D.; Siebers, B. Atypical protein kinases of the rio family in archaea. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRonde, N.A. The ancient microbial rio kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 9488–9492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanks, S.K.; Quinn, A.M.; Hunter, T. The protein kinase family: Conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science 1988, 241, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanrobays, E.; Gleizes, P.E.; Bousquet-Antonelli, C.; Noaillac-Depeyre, J.; Caizergues-Ferrer, M.; Gélugne, J.P. Processing of 20s pre-RNA to 18s ribosomal RNA in yeast requires rrp10p, an essential non-ribosomal cytoplasmic protein. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 4204–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaRonde-LeBlanc, N.; Wlodawer, A. The rio kinases: An atypical protein kinase family required for ribosome biogenesis and cell cycle progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1754, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turowski, T.W.; Lebaron, S.; Zhang, E.; Peil, L.; Dudnakova, T.; Petfalski, E.; Granneman, S.; Rappsilber, J.; Tollervey, D. Rio1 mediates ATP-dependent final maturation of 40s ribosomal subunits. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 12189–12199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanrobays, E.; Gelugne, J.P.; Gleizes, P.E.; Caizergues-Ferrer, M. Late cytoplasmic maturation of the small ribosomal subunit requires rio proteins in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol 2003, 23, 2083–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widmann, B.; Wandrey, F.; Badertscher, L.; Wyler, E.; Pfannstiel, J.; Zemp, I.; Kutay, U. The kinase activity of human rio1 is required for final steps of cytoplasmic maturation of 40s subunits. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2012, 23, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshioka, K.; Matsushita, Y.; Kasahara, M.; Konagaya, K.; Nyunoya, H. Interaction of tomato mosaic virus movement protein with tobacco rio kinase. Mol. Cells 2004, 17, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayya, V.; Lundgren, D.H.; Hwang, S.I.; Rezaul, K.; Wu, L.; Eng, J.K.; Rodionov, V.; Han, D.K. Quantitative phosphoproteomic analysis of t cell receptor signaling reveals system-wide modulation of protein-protein interactions. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, ra46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnad, F.; Gunawardena, J.; Mann, M. Phosida 2011: The posttranslational modification database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D253–D260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angermayr, M.; Hochleitner, E.; Lottspeich, F.; Bandlow, W. Protein kinase CK2 activates the atypical rio1p kinase and promotes its cell-cycle phase-dependent degradation in yeast. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 4654–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, R.D.; Fenton, T.R.; Gomez, G.G.; Wykosky, J.; Vandenberg, S.R.; Babic, I.; Iwanami, A.; Yang, H.; Cavenee, W.K.; Mischel, P.S.; et al. A kinome-wide rnai screen in drosophila glia reveals that the rio kinases mediate cell proliferation and survival through TORC2-akt signaling in glioblastoma. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mielecki, M.; Krawiec, K.; Kiburu, I.; Grzelak, K.; Zagórski, W.; Kierdaszuk, B.; Kowa, K.; Fokt, I.; Szymanski, S.; Swierk, P.; et al. Development of novel molecular probes of the rio1 atypical protein kinase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, M.A.; Bain, J.; Kazimierczuk, Z.; Sarno, S.; Ruzzene, M.; Di Maira, G.; Elliott, M.; Orzeszko, A.; Cozza, G.; Meggio, F.; et al. The selectivity of inhibitors of protein kinase CK2: An update. Biochem. J. 2008, 415, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, M.A.; Andrzejewska, M.; Ruzzene, M.; Sarno, S.; Cesaro, L.; Bain, J.; Elliott, M.; Meggio, F.; Kazimierczuk, Z.; Pinna, L.A. Optimization of protein kinase CK2 inhibitors derived from 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzimidazole. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 6239–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Laronde-Leblanc, N.; Sternberg, P.W.; Gasser, R.B. Tv-rio1—An atypical protein kinase from the parasitic nematode trichostrongylus vitrinus. Parasit. Vectors 2008, 1, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianoncelli, A.; Cozza, G.; Orzeszko, A.; Meggio, F.; Kazimierczuk, Z.; Pinna, L.A. Tetraiodobenzimidazoles are potent inhibitors of protein kinase CK2. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 7281–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.C.; Kartarius, S.; Montenarh, M.; Orzeszko, A.; Kazimierczuk, Z. Modified tetrahalogenated benzimidazoles with CK2 inhibitory activity are active against human prostate cancer cells LNCaP in vitro. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 4390–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kubiński, K.; Masłyk, M. The Link between Protein Kinase CK2 and Atypical Kinase Rio1. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10010021
Kubiński K, Masłyk M. The Link between Protein Kinase CK2 and Atypical Kinase Rio1. Pharmaceuticals. 2017; 10(1):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10010021
Chicago/Turabian StyleKubiński, Konrad, and Maciej Masłyk. 2017. "The Link between Protein Kinase CK2 and Atypical Kinase Rio1" Pharmaceuticals 10, no. 1: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10010021
APA StyleKubiński, K., & Masłyk, M. (2017). The Link between Protein Kinase CK2 and Atypical Kinase Rio1. Pharmaceuticals, 10(1), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph10010021